Fletcher Building Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fletcher Building Bundle
Fletcher Building faces intense competition, with significant threats from new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its complex market landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Fletcher Building’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fletcher Building's reliance on specific raw materials, such as cement, in New Zealand can be a concern. If there are only a few domestic suppliers for these critical inputs, those suppliers gain significant leverage, potentially driving up costs for Fletcher Building.
Conversely, for other materials like timber or steel, Fletcher Building likely benefits from a more diverse and competitive supplier market. This fragmentation means individual suppliers have less power to dictate terms, which is advantageous for the company's procurement strategy.
Fletcher Building's strategic move towards vertical integration, exemplified by its ownership of wood processing facilities, directly addresses this. By controlling more of its supply chain, the company reduces its dependence on external suppliers and strengthens its position against potential price hikes.
Fletcher Building faces considerable switching costs for critical building materials, particularly for specialized items or those with stringent certification requirements. These costs can manifest as financial outlays for new supplier qualification, potential production downtime during transitions, and the risk of quality inconsistencies, all of which bolster supplier leverage.
The complexity of integrating new suppliers into existing supply chains, especially for custom-engineered components, further entrenches Fletcher Building's reliance on established relationships. This dependence can translate into suppliers dictating terms, knowing that Fletcher Building's operational continuity is sensitive to supply disruptions.
However, recent government efforts in New Zealand to streamline the approval process for imported building products could gradually diminish these switching costs. By potentially expanding the range of approved overseas suppliers, these initiatives aim to foster greater competition and offer Fletcher Building more viable alternatives, thereby diluting supplier bargaining power in the long run.
The uniqueness of a supplier's offerings significantly impacts their bargaining power. If Fletcher Building relies on specialized components or advanced technologies from a limited number of providers, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, a supplier of a proprietary, high-performance concrete additive crucial for a specific infrastructure project could command higher prices.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while not prevalent in the heavy building materials industry, could significantly alter the competitive landscape for Fletcher Building. If a key supplier, such as a major aggregate provider, were to begin manufacturing and selling finished concrete products directly, it would represent a direct competitive challenge and bolster their leverage.
Such a move would increase their bargaining power by allowing them to capture more of the value chain. For example, if a large cement producer, which supplied Fletcher Building, decided to enter the pre-cast concrete manufacturing business, it could directly compete with Fletcher's own operations. This would likely necessitate significant capital investment and specialized expertise, acting as a considerable barrier to entry for most suppliers.
- Capital Intensity: Entering manufacturing or construction requires substantial investment, often in the billions for large-scale operations.
- Expertise Gap: Suppliers typically focus on raw material extraction or processing, lacking the intricate knowledge of construction processes or product development.
- Market Dynamics: The building materials sector is characterized by established players and complex distribution networks, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction quickly.
Importance of Fletcher Building to Suppliers
Fletcher Building's substantial presence in the New Zealand and Australian construction sectors positions it as a crucial client for numerous suppliers. This scale means that for many smaller suppliers, Fletcher Building can represent a significant portion of their annual revenue. For instance, if a supplier's revenue derived from Fletcher Building dropped by, say, 20% in 2024, it could severely impact their financial stability, thus diminishing their ability to negotiate favorable terms.
Conversely, the bargaining power dynamic shifts for larger, globally diversified suppliers. If Fletcher Building constitutes only a minor fraction of a multinational company's total sales – perhaps less than 1% of a global entity's turnover – then Fletcher Building's business is less critical to that supplier's overall performance. This disparity allows these larger suppliers to exert more influence in price negotiations and supply agreements.
- Fletcher Building's Market Dominance: As a key player in the construction industry across Australia and New Zealand, Fletcher Building's purchasing volume makes it a vital customer for many material and service providers.
- Impact on Smaller Suppliers: The loss of Fletcher Building as a client can disproportionately affect smaller suppliers, potentially leading to significant revenue shortfalls and consequently reducing their bargaining power in future dealings.
- Leverage of Global Suppliers: For large, international suppliers, Fletcher Building often represents a smaller segment of their diversified business, granting them greater leverage in price setting and contract negotiations.
- Revenue Dependency: In 2023, Fletcher Building reported revenue of NZ$8.7 billion, highlighting the substantial economic activity it generates and the dependency smaller suppliers might have on its contracts.
Fletcher Building's significant purchasing power, especially with smaller suppliers who depend heavily on its business for revenue, can reduce supplier leverage. For example, if a supplier's revenue from Fletcher Building constitutes a large percentage of their total sales, they are less likely to risk losing that business by demanding unfavorable terms. This dynamic was evident in 2023 when Fletcher Building's substantial revenue of NZ$8.7 billion underscored its importance to many in its supply chain.
Conversely, global, diversified suppliers often hold more power as Fletcher Building represents a smaller portion of their overall operations. For these entities, Fletcher Building's business might be less than 1% of their total turnover, allowing them to negotiate from a position of strength.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while not common, could significantly shift bargaining power. If a key supplier, like a cement producer, began offering finished concrete products, it would directly challenge Fletcher Building and enhance the supplier's leverage.
Fletcher Building's reliance on specialized or certified materials can increase switching costs, thereby strengthening supplier power. These costs include qualification processes and potential production disruptions, making it difficult to change suppliers for critical inputs.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Fletcher Building | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| High Dependency of Supplier on Fletcher Building | Reduced Supplier Bargaining Power | A small local aggregate supplier relies on Fletcher Building for 40% of its annual revenue in 2024. |
| Low Dependency of Supplier on Fletcher Building | Increased Supplier Bargaining Power | A global steel manufacturer's revenue from Fletcher Building is less than 0.5% of its total sales in 2024. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Increased Supplier Bargaining Power | A major cement producer begins manufacturing pre-cast concrete elements, directly competing with Fletcher Building. |
| High Switching Costs for Fletcher Building | Increased Supplier Bargaining Power | Fletcher Building requires specialized fire-rated insulation that needs extensive re-certification if sourced from a new supplier. |
What is included in the product
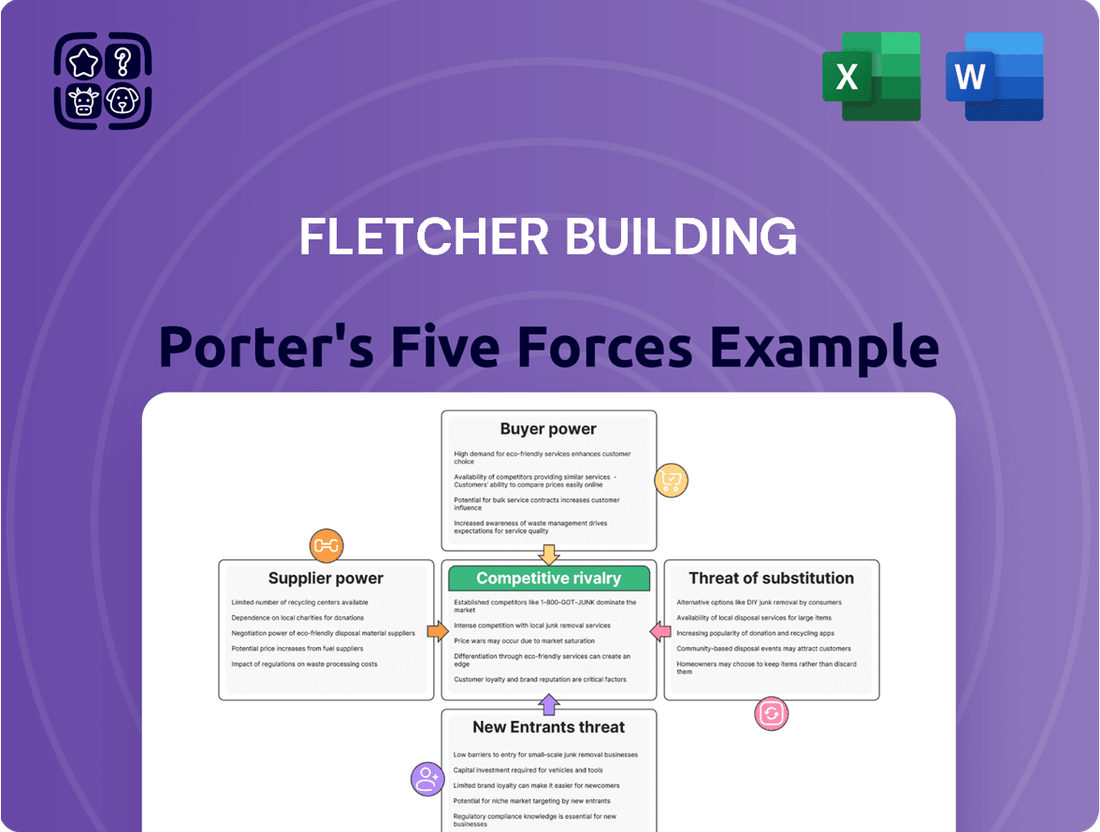
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Fletcher Building, detailing supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its diverse markets.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force for Fletcher Building.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fletcher Building caters to a broad spectrum of customers, from major commercial developers and government infrastructure initiatives to smaller construction firms and homeowners via its extensive distribution network. This diversity generally mitigates the bargaining power of any single customer segment.
However, the sheer volume of orders from large-scale construction projects or substantial residential developers can grant them a more significant individual bargaining leverage. For instance, securing a contract for a major infrastructure project in 2024 could represent a substantial portion of a specific division's revenue, giving that client more sway.
Customers in the construction sector, particularly for common materials, demonstrate significant price sensitivity. This is especially true when the market is competitive and subject to economic cycles.
During economic slowdowns, like the one experienced in New Zealand in 2024 and projected into early 2025, this price sensitivity becomes even more pronounced. Fletcher Building, like its peers, faces pressure to absorb rising costs rather than risk losing business by increasing prices.
Customers of Fletcher Building face a market where substitute products are readily available, significantly impacting the company's pricing power. For instance, government policies promoting imported building materials in key markets like Australia and New Zealand increase the competitive landscape. This means customers can often find comparable products from international suppliers or alternative domestic manufacturers, limiting Fletcher Building's ability to unilaterally set prices.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
Large construction firms or developers possess the potential to integrate backward by manufacturing some of their own basic building materials, like concrete or prefabricated components. This capability, though demanding substantial capital and specialized knowledge, grants them leverage when negotiating with suppliers such as Fletcher Building.
For instance, a major developer might invest in a precast concrete plant, reducing their reliance on external suppliers for structural elements. This strategic move directly impacts Fletcher Building's pricing power and market share in that specific segment.
Consider the 2024 construction landscape where rising material costs could incentivize such backward integration. If a significant portion of Fletcher Building's customer base begins producing key inputs internally, it directly erodes Fletcher's sales volume and bargaining strength.
- Potential for backward integration by large construction firms.
- Requirement of significant capital investment and expertise for integration.
- Impact on Fletcher Building's pricing power and market share.
- Influence of rising material costs in 2024 on integration decisions.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers today have unprecedented access to information regarding pricing and product details across the building materials sector. This transparency significantly reduces the historical information gap, enabling buyers to readily identify and compare offerings from Fletcher Building against its competitors.
This heightened awareness empowers customers to negotiate more effectively. For instance, readily available online price comparison tools and industry reports in 2024 allow consumers to pinpoint the most competitive rates for materials like cement or structural steel, directly impacting Fletcher Building's pricing power.
- Increased Online Price Comparison: In 2024, the proliferation of digital platforms offering real-time price comparisons for construction materials has made it simpler for customers to gauge market rates.
- Access to Product Specifications: Detailed product specifications are now widely available, allowing customers to make informed decisions based on quality and suitability, not just price.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: The ease of accessing information about alternative suppliers diminishes the advantage previously held by suppliers with proprietary market knowledge.
- Enhanced Negotiation Leverage: Armed with comprehensive data, customers can more confidently challenge prices and demand better terms from Fletcher Building and its rivals.
The bargaining power of Fletcher Building's customers is a significant force, driven by several factors. The availability of substitutes, price sensitivity, and the potential for backward integration by large clients all contribute to this pressure. In 2024, with increased market transparency and economic headwinds, this power is amplified.
Customers can easily compare prices for materials like cement and steel, especially with readily available online tools, directly impacting Fletcher Building's ability to dictate terms. For example, a major infrastructure project secured in 2024 could represent a substantial portion of revenue for a specific Fletcher division, granting that client significant leverage.
Furthermore, the possibility of large construction firms investing in their own production facilities, particularly for components like precast concrete, poses a direct threat to Fletcher's market share and pricing power. This trend is further incentivized by rising material costs observed in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Fletcher Building | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Substitute Availability | Limits pricing power; customers can switch suppliers. | Increased competition from imported materials. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are highly responsive to price changes. | Economic slowdown in NZ and Australia increases price pressure. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Reduces reliance on Fletcher for key materials. | Rising costs in 2024 may spur investment in internal production. |
| Information Transparency | Empowers customers with pricing and product data. | Online comparison tools make it easy to find competitive rates. |
What You See Is What You Get
Fletcher Building Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Fletcher Building Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing a comprehensive breakdown of industry competitiveness. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the construction sector. This detailed report is fully formatted and ready for your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Fletcher Building operates in markets with a significant number of competitors, ranging from large, established firms to many smaller, regional players. This diverse competitive landscape, particularly in Australia and New Zealand, means that in certain segments, like general construction or building material distribution, rivalry can be quite fierce.
For instance, in the Australian construction sector, companies like CIMIC Group and Lendlease are substantial competitors. In New Zealand, while Fletcher Building is a dominant force, it still faces competition from entities such as Downer Group and various specialized contractors. The presence of numerous smaller firms further intensifies this rivalry, especially in project bidding and market share battles.
The New Zealand construction industry is experiencing a challenging period, with forecasts suggesting a contraction in 2025. This downturn naturally intensifies competitive rivalry as businesses vie for a smaller pool of available projects. For companies like Fletcher Building, this means increased pressure on pricing and margins.
While large-scale infrastructure initiatives provide a degree of resilience, the broader market is being impacted by a decline in building consents. This trend, evident in recent data, signals a weaker near-term outlook for residential and commercial construction, further exacerbating the competitive landscape.
Fletcher Building faces intense competition, particularly in its commoditized product segments like standard concrete and timber, where pricing is the dominant factor. This means many of its offerings are viewed as interchangeable by customers, intensifying rivalry.
However, Fletcher Building does achieve some product differentiation through specialized or branded items, such as specific insulation materials or plasterboard systems. These differentiated products allow the company to move away from pure price competition, offering unique features or performance benefits that customers value, thereby reducing direct rivalry to a degree.
Exit Barriers
Fletcher Building faces substantial exit barriers due to the high fixed costs inherent in its operations. These include investments in manufacturing plants, specialized machinery, and a significant workforce.
These substantial sunk costs make it economically challenging for companies in the building materials and construction industry to cease operations. Consequently, firms often continue to compete even when market conditions are unfavorable, intensifying rivalry.
For example, in 2024, the building and construction sector in New Zealand, where Fletcher Building is a major player, continued to grapple with the high capital expenditure required for infrastructure projects and material production. This necessitates ongoing operational commitment, reinforcing the competitive landscape.
- High Capital Investment: Fletcher Building's extensive network of manufacturing facilities and specialized equipment represents a significant financial commitment that is difficult to recover upon exit.
- Operational Scale: The large employee base and complex supply chains also contribute to the difficulty and cost of winding down operations.
- Industry Norms: The industry's capital-intensive nature means that companies are accustomed to long-term investments, making premature exits less common and more costly.
Strategic Stakes
Fletcher Building's extensive operations spanning manufacturing, distribution, and construction create substantial strategic stakes across numerous market segments. This deep involvement necessitates a strong focus on preserving its competitive standing, driving intense rivalry.
The company’s considerable investments in production capacity and its strategy of vertical integration further fuel aggressive competition. These factors compel Fletcher Building to actively defend its market share and profitability against rivals.
- Strategic Stakes: Fletcher Building has significant interests in maintaining its market position across its diverse portfolio, including building materials, infrastructure, and construction services.
- Investment in Capacity: The company has made substantial capital expenditures, for instance, investing NZ$1.2 billion in its Wiri distribution centre and manufacturing facilities, highlighting its commitment to production scale.
- Vertical Integration: Fletcher Building’s vertical integration, from raw material supply to finished construction, means it has a vested interest in controlling every stage of the value chain, intensifying competition.
Fletcher Building operates in a highly competitive environment, particularly within the Australian and New Zealand construction and building materials sectors. The presence of numerous players, from large corporations like CIMIC Group to specialized local firms, intensifies rivalry, especially in bidding for projects and maintaining market share. This competition is further heightened by the commoditized nature of some of its products, where price is a primary differentiator.
The industry's high capital investment and operational scale create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to remain competitive even during downturns, such as the projected contraction in the New Zealand construction sector for 2025. This sustained competition puts pressure on pricing and margins, as seen with the decline in building consents impacting residential and commercial construction outlooks.
While Fletcher Building benefits from product differentiation in specialized offerings, its core business often faces direct price-based competition. For example, in 2024, the demand for basic building materials remained robust but highly contested, with numerous suppliers vying for contracts. This dynamic necessitates continuous strategic maneuvering to protect market share and profitability.
Fletcher Building's strategic stakes, reinforced by substantial investments like the NZ$1.2 billion Wiri distribution centre and its vertical integration strategy, mean it actively defends its market position across various segments, contributing to the overall intensity of competitive rivalry.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The construction sector is experiencing a growing adoption of alternative materials, like engineered timber, recycled plastics, and advanced composites, which can replace traditional concrete, steel, and asphalt used by Fletcher Building. For instance, the global green building materials market was valued at approximately USD 270 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, driven by sustainability mandates and technological advancements.
These emerging substitutes, while often niche, are gaining traction due to increasing environmental awareness and a push for reduced carbon footprints in construction projects. Innovations in straw-based construction and low-carbon concrete formulations are particularly noteworthy, offering performance characteristics that can rival conventional options. This trend signifies a potential long-term threat as these alternatives become more mainstream and cost-competitive.
The threat of substitutes for Fletcher Building's products hinges on whether alternative materials or methods offer a better price-performance ratio. For example, if off-site modular construction becomes substantially more cost-effective and quicker to implement without sacrificing quality, it could directly challenge traditional on-site building techniques and the materials Fletcher Building supplies.
Customers are increasingly considering substitutes for traditional building materials and methods. This shift is driven by growing awareness of sustainable building practices and regulatory mandates for enhanced energy efficiency. For instance, the New Zealand government's commitment to net-zero carbon buildings, as highlighted by initiatives like the Buildings for Climate Change framework, directly encourages the adoption of alternative, lower-impact solutions.
The desire for faster construction timelines also plays a significant role in customer propensity to substitute. Prefabricated and modular building systems, often utilizing advanced materials, offer a compelling alternative to conventional on-site construction. The adoption of standards like Passive House, which prioritizes airtightness and high insulation levels, further pushes demand for specialized materials and construction techniques that may not be core to traditional offerings.
Switching Costs for Buyers
While the New Zealand government is working to reduce barriers for imported building products, potentially lowering switching costs, the practical adoption of entirely new material systems still presents significant challenges. These include the need for re-education of the workforce, adaptation of existing construction methodologies, and navigating potential regulatory approvals, all of which can foster customer inertia towards familiar products.
For Fletcher Building, this means that even with policy shifts, the inherent complexities of integrating new materials can act as a substantial deterrent to switching. For instance, a large-scale shift to a novel insulation system might require extensive training for tradespeople, new installation tools, and potentially lengthy testing periods to ensure compliance with building codes, thereby maintaining a degree of customer loyalty to established, albeit potentially more expensive, options.
- Re-education Costs: Training staff on new materials and installation techniques can be a significant upfront investment for construction firms.
- Process Adaptation: Modifying established construction workflows to accommodate new products requires time and can introduce initial inefficiencies.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining approval for new building materials can be a lengthy and complex process, especially for innovative or untested systems.
- Inertia and Risk Aversion: Builders and developers often prefer to stick with proven materials to avoid potential project delays or performance issues associated with new technologies.
Innovation in Substitute Industries
The threat of substitutes for Fletcher Building is significantly influenced by ongoing innovation in related sectors. For instance, advancements in prefabrication techniques and the emergence of novel composite materials offer increasingly compelling alternatives to traditional construction products and methods. These innovations can directly challenge Fletcher Building's established market share by providing more efficient or cost-effective solutions.
Consider the rapid evolution of advanced manufacturing. Companies are developing highly specialized, prefabricated building modules that can be assembled on-site with greater speed and precision. This directly competes with Fletcher Building's core business in materials supply and traditional construction services. For example, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately USD 100 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift towards alternative building solutions.
Furthermore, the development of new composite materials, such as advanced polymers or engineered wood products, presents another layer of substitution threat. These materials often boast superior strength-to-weight ratios, enhanced durability, or improved sustainability profiles compared to traditional concrete, steel, or timber. Fletcher Building must remain vigilant and adapt its product portfolio to counter these disruptive innovations.
- Innovation in Prefabrication: Growing adoption of off-site construction methods offers faster project completion and potentially lower labor costs, directly challenging traditional on-site building.
- Advanced Material Development: New composite materials provide alternatives with enhanced properties like strength, durability, and sustainability, potentially displacing conventional building supplies.
- Digitalization in Construction: Technologies like BIM (Building Information Modeling) and AI-driven design are streamlining processes, creating more efficient alternatives to traditional workflows.
- Sustainability Focus: The increasing demand for green building solutions drives innovation in eco-friendly materials and construction techniques that may substitute existing offerings.
The threat of substitutes for Fletcher Building is growing as alternative materials and construction methods gain traction, driven by sustainability and efficiency demands. For instance, the global green building materials market reached approximately USD 270 billion in 2023, indicating a significant shift toward eco-friendly options that can replace traditional materials Fletcher Building supplies.
Innovations in areas like engineered timber, recycled plastics, and advanced composites are offering viable alternatives. Furthermore, the modular construction market, valued at around USD 100 billion in 2023, highlights a trend towards faster, more efficient building processes that can bypass conventional material supply chains.
While switching costs such as workforce re-education and regulatory hurdles can slow adoption, the increasing performance and cost-competitiveness of substitutes pose a continuous challenge. Fletcher Building must monitor these trends, as exemplified by New Zealand's net-zero building initiatives, which actively encourage lower-impact solutions.
| Substitute Area | Examples | Market Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Materials | Engineered timber, recycled plastics, advanced composites, low-carbon concrete | Global green building materials market valued at ~USD 270 billion (2023) |
| Construction Methods | Prefabrication, modular construction, off-site assembly | Global modular construction market valued at ~USD 100 billion (2023) |
| Sustainability Drivers | Net-zero building mandates, carbon footprint reduction | New Zealand's Buildings for Climate Change framework |
Entrants Threaten
The construction and building materials sectors, particularly for integrated firms like Fletcher Building that handle manufacturing and extensive projects, necessitate considerable capital outlays. These investments cover essential assets such as manufacturing plants, heavy machinery, and robust distribution channels.
This substantial financial barrier significantly deters potential new competitors from entering the market. For instance, establishing a new cement plant alone can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a sum that many aspiring companies cannot readily access.
Fletcher Building enjoys significant economies of scale in its manufacturing and distribution networks. This allows them to produce and deliver building materials at a lower per-unit cost compared to potential new competitors. For instance, their extensive operational footprint in Australia and New Zealand enables bulk purchasing and optimized logistics, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly or affordably.
Fletcher Building's established network of distribution channels and retail stores across New Zealand and Australia presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Building a comparable infrastructure and securing shelf space or direct relationships with key customers like builders and developers requires substantial investment and time, making market access a considerable hurdle.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
Fletcher Building benefits from strong brand loyalty and significant differentiation in the construction and building materials markets, particularly in New Zealand and Australia. Developing this level of customer trust and recognition is a lengthy and capital-intensive process, acting as a substantial barrier for potential new competitors.
The company’s established brands, such as Fletcher Insulation and Winstone Wallboards, have cultivated deep-rooted relationships with customers over many years. This customer loyalty means new entrants face an uphill battle to capture market share, as buyers often prefer the proven quality and reliability associated with Fletcher Building's offerings.
Consider the impact of brand equity: In 2024, the construction industry continues to see a premium placed on established reputations. New entrants must not only match product quality but also invest heavily in marketing and sales to even begin to erode Fletcher Building's ingrained customer preference.
- Established Brand Recognition: Fletcher Building's brands are well-known and trusted in its core markets.
- Long-Term Customer Relationships: Years of consistent service and quality have fostered strong customer loyalty.
- High Cost of Brand Building: New entrants face significant investment requirements to achieve comparable brand recognition.
- Differentiation in a Mature Market: Fletcher Building differentiates itself through product innovation and service, making it harder for new players to compete on these factors alone.
Government Policy and Regulations
While some government policies aim to streamline processes, the construction sector's regulatory landscape remains a significant hurdle. New entrants often face complex building codes, stringent environmental standards, and lengthy consent processes, increasing their initial operating costs and time to market. For instance, in 2024, the average time for obtaining building permits in major developed economies continued to be a point of contention, with some regions experiencing delays of several months, impacting project timelines and cash flow for new businesses.
These intricate regulations can act as a substantial barrier, particularly for foreign companies unfamiliar with local nuances and specific compliance requirements. Navigating these differences can be costly, requiring significant investment in legal counsel and local expertise. The ongoing evolution of environmental regulations, such as stricter embodied carbon limits in materials, further adds to the complexity and potential cost for new players entering the market in 2024.
- Regulatory Complexity: Building codes, environmental standards, and consent processes are intricate and costly for new entrants.
- Time and Cost Barriers: Navigating local regulations requires significant investment in legal and local expertise, increasing startup costs and timelines.
- Foreign Entrant Challenges: Companies unfamiliar with local nuances face amplified difficulties and expenses in compliance.
- Evolving Standards: Changes in regulations, like embodied carbon limits, add ongoing complexity and potential cost increases for new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Fletcher Building is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. However, regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive distribution networks also play a significant role in deterring new players.
In 2024, the construction sector continues to demand substantial upfront investment. For instance, setting up a new, modern concrete plant can easily cost upwards of $200 million, a figure that presents a formidable barrier for many aspiring competitors aiming to challenge established giants like Fletcher Building.
Fletcher Building's significant economies of scale in manufacturing and distribution further solidify its market position. Their ability to leverage bulk purchasing and optimized logistics across their extensive Australian and New Zealand operations provides a cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to match quickly or affordably.
The company’s strong brand equity, built over decades, is another key deterrent. In 2024, consumer trust in established brands like Fletcher Insulation remains high, requiring new entrants to invest heavily in marketing and product development to even begin to compete on quality and recognition.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Fletcher Building Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of manufacturing plants, machinery, and distribution networks. | Significant deterrent, requiring substantial funding. | Established infrastructure and financial capacity. |
| Brand Loyalty & Differentiation | Strong customer trust in established brands and product quality. | Difficult to overcome, requiring significant marketing investment. | Decades of brand building and customer relationships. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations and purchasing power. | New entrants face higher initial operating costs. | Optimized supply chains and bulk purchasing power. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating building codes, environmental standards, and consent processes. | Increases time to market and startup costs. | Established expertise in compliance and local market knowledge. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fletcher Building leverages a comprehensive suite of data sources, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial information providers.
