Exosens Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Exosens Bundle
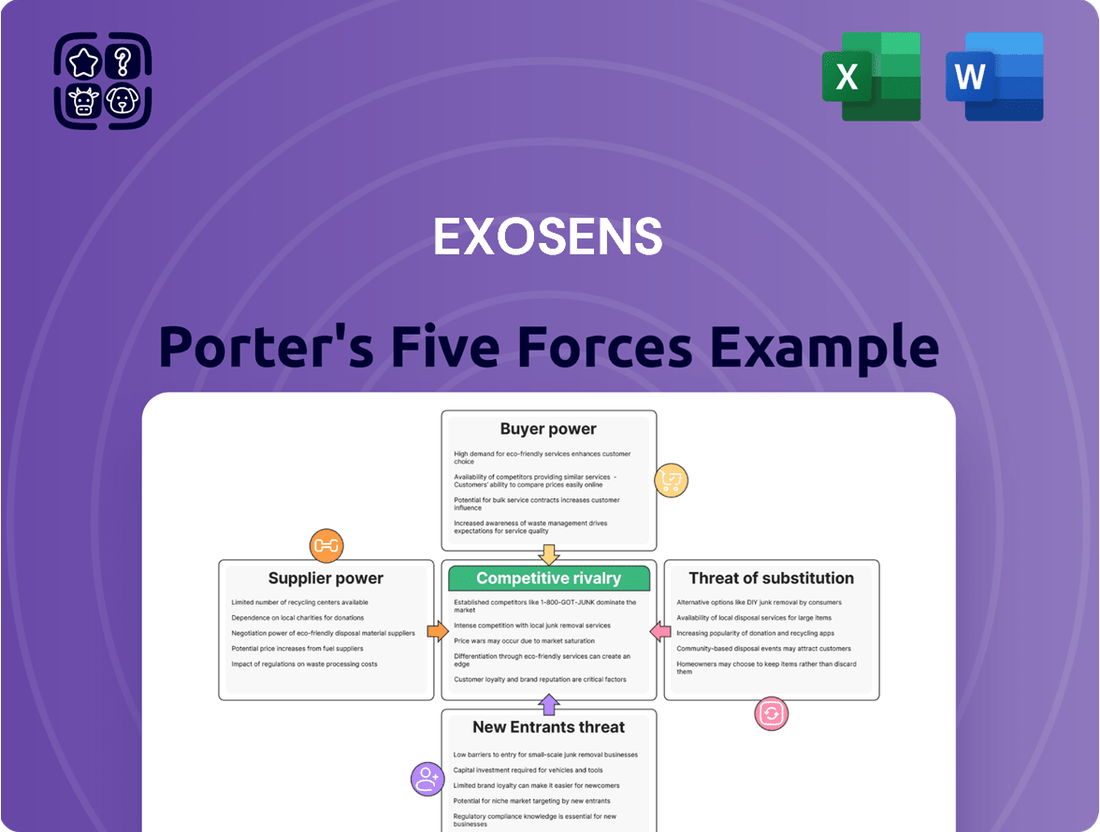
Exosens operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding the power of buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Exosens’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Exosens' reliance on highly specialized components and raw materials for its advanced detection and imaging technologies is a key factor in supplier bargaining power. If these critical inputs are only available from a select few suppliers possessing unique expertise or patented processes, their leverage grows substantially.
This dependency can translate into increased costs for Exosens, as suppliers can command higher prices for their specialized offerings. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a potential supplier of advanced components, faced ongoing supply chain constraints and increased demand, leading to price hikes for critical chips, a situation that could impact companies like Exosens if they face similar supplier dynamics.
The complexity and precision demanded by Exosens' advanced products significantly raise the stakes when considering a change in suppliers for crucial components. These specialized parts often require intricate integration and rigorous testing, making a switch a costly endeavor.
Switching suppliers for these critical components can involve substantial expenses for Exosens. Think about the re-qualification of new parts, the potential need for re-tooling manufacturing lines, and the extensive integration testing required to ensure compatibility and performance. These processes can easily add months to development cycles and incur millions in unexpected costs.
For instance, if a key supplier for Exosens' high-precision optical filters were to change its specifications, the cost for Exosens to re-qualify a new supplier could run into hundreds of thousands of dollars, not to mention the potential for production delays that impact revenue. These significant switching costs effectively enhance the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
Suppliers offering unique, proprietary technologies or rare materials essential for Exosens' specialized products wield significant bargaining power. For instance, if a supplier provides a critical component with unique performance characteristics that Exosens cannot easily source elsewhere, this supplier can dictate terms more effectively. This reliance on specialized inputs limits Exosens' ability to switch suppliers without compromising product quality or innovation.
Concentration of Suppliers
A market where a few large suppliers dominate the provision of essential inputs or technologies to Exosens signifies significant supplier power. This concentration inherently limits Exosens' negotiation leverage, as the few dominant suppliers face minimal competition for Exosens' business, allowing them to dictate terms more effectively.
For instance, consider the market for specialized rare earth elements crucial for certain advanced sensor technologies. If only a handful of global mining operations control the majority of these resources, Exosens would be highly dependent on these few suppliers. In 2024, geopolitical shifts and increased demand for these elements have further consolidated supply chains, potentially increasing the bargaining power of these few key players.
- Supplier Concentration: Markets dominated by a small number of suppliers grant those suppliers greater leverage.
- Reduced Negotiation Power: Exosens faces diminished ability to negotiate favorable terms when supplier options are limited.
- Dependency Risk: Reliance on a concentrated supplier base creates vulnerability to price hikes or supply disruptions.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, factors like resource scarcity and geopolitical events have amplified the concentration of power for certain input suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Exosens' business, while less prevalent in highly specialized component sectors, can significantly increase supplier bargaining power. If a supplier possesses the technical capacity and strategic drive to produce finished components or systems akin to Exosens' offerings, this capability grants them greater leverage in price and contract negotiations.
This potential for forward integration means suppliers can, in theory, become direct competitors. For instance, if a key material supplier for Exosens' advanced sensors also had the technology to assemble those sensors into a final product, they could choose to bypass Exosens altogether. This strategic option strengthens their hand when Exosens seeks to secure supply agreements or negotiate pricing, as the supplier can credibly threaten to capture more of the value chain.
- Increased Negotiation Leverage: Suppliers capable of forward integration can demand better terms from Exosens due to the risk of becoming a competitor.
- Potential for Disruption: If a supplier does integrate forward, it could directly disrupt Exosens' market position and supply chain stability.
- Strategic Consideration: Exosens must monitor suppliers' technological advancements and strategic intentions to anticipate and mitigate this threat.
Exosens faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to the specialized nature of its components and the limited number of capable providers. This reliance means suppliers can often dictate terms, leading to higher costs and potential disruptions for Exosens. For example, in 2024, the scarcity of advanced materials for high-performance sensors, exacerbated by geopolitical factors, allowed key suppliers to increase prices, impacting Exosens' cost structure.
| Factor | Impact on Exosens | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited negotiation options, higher prices | Key input markets saw consolidation |
| Switching Costs | High costs and delays to change suppliers | Integration complexity remains a barrier |
| Supplier Differentiation | Unique technologies give suppliers leverage | Proprietary processes are difficult to replicate |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within Exosens' markets by examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, eliminating the guesswork in strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Exosens operates in highly specialized sectors such as medical, scientific, industrial, and defense. In these niche markets, the customer base for its high-performance products can be concentrated, meaning a few key clients might represent a substantial portion of Exosens' revenue. For instance, if a single defense contractor or a major medical equipment manufacturer accounts for over 10% of sales, their bargaining power is amplified.
This concentration allows these significant customers to exert pressure on Exosens, potentially demanding lower prices, customized product specifications, or more favorable payment terms. Such leverage can directly impact Exosens' profitability and operational flexibility, as the company may feel compelled to meet these demands to retain its most important clients.
Customers in critical applications, such as aerospace or defense, often integrate Exosens' specialized components deeply into their existing systems. This integration necessitates significant investment in rigorous testing, precise calibration, and obtaining necessary regulatory approvals, making the process complex and time-consuming. For instance, a new sensor in an aircraft's navigation system requires extensive flight testing and airworthiness certification, which can cost millions and take years.
The substantial costs and inherent risks involved in switching to an alternative supplier significantly curtail customer bargaining power. The effort to re-qualify a new component, re-test integrated systems, and potentially re-certify the final product creates a formidable barrier. This complexity means that even if a competitor offers a slightly lower price, the total cost of ownership, including the switching expenses, often favors remaining with Exosens.
The bargaining power of customers for Exosens is significantly influenced by the critical nature of its product performance, particularly in high-stakes sectors like medical, defense, and scientific research. In these fields, the reliability and precision of detection and imaging solutions are not just desirable; they are essential for accurate diagnoses, mission success, and groundbreaking discoveries.
Customers in these demanding industries often exhibit lower price sensitivity because the cost of product failure or underperformance can be astronomically higher than the initial purchase price. For instance, a faulty medical imaging device could lead to misdiagnosis and adverse patient outcomes, while a defense system's malfunction could have severe strategic consequences. This inherent need for uncompromising quality empowers Exosens to command premium pricing, thereby diminishing the customers' leverage to negotiate lower prices based solely on cost.
Customer Knowledge and Specification
Exosens' customers are generally highly knowledgeable and demanding, often possessing intricate technical specifications for the components they require. This sophistication means they understand the value of Exosens' specialized offerings.
Despite their demanding nature, these customers often rely heavily on Exosens' unique research and development and manufacturing expertise for highly customized solutions. This dependency can significantly reduce their ability to readily switch to alternative suppliers, thereby moderating their bargaining power.
- Customer Sophistication: Clients often have deep technical knowledge and precise requirements, indicating a well-informed buyer base.
- Reliance on Customization: The need for Exosens' specialized R&D and manufacturing for bespoke solutions limits easy product substitution.
- Limited Switching Options: Customers may find it difficult and costly to find alternative suppliers capable of meeting their specific, advanced needs.
Backward Integration Potential of Customers
The backward integration potential for Exosens' customers is generally low. This is primarily due to the highly specialized nature of Exosens' core technologies, such as photomultiplier tubes and image intensifiers. Developing these capabilities in-house requires substantial research and development investment, specialized infrastructure, and significant intellectual property, which acts as a strong deterrent for most customers.
For instance, the barrier to entry for replicating Exosens' advanced sensor technologies is considerable. Companies typically lack the specific expertise and the capital outlay needed for such ventures. This lack of feasible backward integration significantly curtails the bargaining power customers can exert by threatening to produce these components themselves.
- Low Threat of In-House Production: Customers face high costs and technical hurdles in replicating Exosens' specialized technologies.
- Significant R&D and Infrastructure Needs: Developing advanced sensors requires substantial investment, deterring backward integration.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Exosens' proprietary technology further limits customers' ability to develop similar capabilities internally.
- Diminished Customer Bargaining Power: The difficulty in backward integration reduces customers' leverage in negotiations.
The bargaining power of Exosens' customers is generally low, primarily due to the critical nature and high specialization of its products. In sectors like medical, defense, and scientific research, the cost of product failure is extremely high, making customers less sensitive to price and more focused on reliability. For example, in 2024, the defense industry continued to prioritize proven, high-performance components for critical systems, where even minor deviations can have significant consequences.
Customers often integrate Exosens' components deeply into their complex systems, incurring substantial costs and time for testing and certification if they were to switch suppliers. This switching cost, coupled with the unique technical expertise Exosens possesses, significantly limits customers' ability to leverage alternative providers. The lack of viable backward integration options for customers further solidifies Exosens' position, as developing such specialized technologies in-house presents considerable financial and technical barriers.
What You See Is What You Get
Exosens Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use Exosens Porter's Five Forces Analysis. What you're previewing is precisely what you'll receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full immediate access to this professionally formatted strategic assessment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The advanced detection and imaging sector, where Exosens operates, thrives on high industry specialization. Companies here differentiate themselves through superior performance, pinpoint accuracy, and solutions tailored to very specific applications, rather than engaging in a race to the bottom on price. This focus on unique technological capabilities naturally moderates direct price competition among rivals.
The advanced detection and imaging sector thrives on relentless technological innovation, fueling fierce competition. Companies like Exosens are constantly pushing boundaries to deliver superior sensitivity, resolution, and seamless integration in their products. This dynamic environment means staying ahead requires significant and ongoing investment in research and development.
This rapid pace of innovation often results in accelerated product lifecycles. For instance, advancements in sensor technology can quickly render existing solutions less competitive, compelling firms to reinvest in R&D to maintain their market position. In 2024, the global market for advanced imaging technologies, including those relevant to Exosens' operations, is projected to see continued robust growth, underscoring the importance of innovation in capturing market share.
The competitive rivalry within Exosens' market segments, such as photomultiplier tubes and low-light imaging, is a significant factor. The intensity of this rivalry is directly tied to the number, size, and strategic actions of the companies operating in these specialized areas.
For instance, in the photomultiplier tube market, Exosens faces competition from established players like Hamamatsu Photonics and Photonis. These companies often compete on technological innovation, product quality, and customer service, creating a dynamic environment. In 2023, the global photomultiplier tube market was valued at approximately $600 million, indicating a substantial market where competition is keen.
The market structure, whether dominated by a few large entities or characterized by many smaller, specialized firms, dictates the level of competitive pressure. Exosens operates in niches where specialized expertise is paramount, meaning that while the overall market might seem fragmented, key segments can have a concentrated number of highly capable competitors.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The development and production of advanced components, such as those offered by Exosens, demand considerable initial investment. This includes substantial spending on research and development, specialized manufacturing equipment, and sophisticated cleanroom environments. For instance, the semiconductor industry, a sector where such high-performance components are crucial, saw global R&D spending reach an estimated $90 billion in 2023.
These substantial fixed costs and the specialized nature of assets create significant exit barriers. Companies are incentivized to stay operational and continue competing, even when market conditions are unfavorable, to recoup their investments. This persistence intensifies rivalry among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: Companies in this space must commit significant capital to R&D and specialized manufacturing facilities.
- Specialized Assets: The need for unique equipment and infrastructure makes it difficult and costly to reallocate resources.
- Exit Barriers: High sunk costs discourage firms from leaving the market, leading to sustained competitive pressure.
- Industry Persistence: Even during economic downturns, companies are compelled to remain active to avoid substantial losses on their investments.
Strategic Importance of Applications
The competitive rivalry for Exosens is intensified by the critical nature of its applications in defense, medical, and scientific research. In these sectors, performance and unwavering reliability are paramount, making product integrity the primary battleground. This strategic importance means competition is less about price wars and more about fostering deep customer relationships and securing long-term, high-stakes contracts.
Exosens' strategic importance is underscored by its role in supplying components for advanced technologies. For instance, in the defense sector, reliable imaging solutions are crucial for surveillance and targeting systems, where failure is not an option. Similarly, in medical imaging, the precision and clarity of Exosens' products directly impact diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. This focus on critical performance elevates the rivalry beyond simple feature comparisons to a contest of trust and proven capability.
- Critical Applications: Exosens' products are vital for defense, medical, and scientific research, demanding exceptional reliability.
- Strategic Contract Focus: Competition centers on securing long-term contracts and building strong customer trust, not just price.
- Product Integrity as Differentiator: Superior product performance and proven integrity are key competitive advantages.
- High Stakes in End Markets: The non-negotiable nature of performance in these sectors shapes the intense, strategic rivalry.
Competitive rivalry within Exosens' specialized detection and imaging markets is intense, driven by a few key players who compete on technological superiority rather than price. Significant capital investment in R&D and specialized manufacturing creates high barriers to entry, encouraging existing firms to persist. The critical nature of applications in defense and medical sectors further elevates the stakes, making product reliability and proven capability the primary differentiators.
| Competitor | Key Products/Technologies | 2023 Market Share (Est.) | 2024 R&D Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hamamatsu Photonics | Photomultiplier Tubes, Image Sensors | 15-20% | Higher sensitivity sensors, AI integration |
| Photonis | Image Intensifiers, Detectors | 10-15% | Low-light performance, ruggedized systems |
| Excelitas Technologies | Photodiodes, X-ray Detectors | 8-12% | Miniaturization, advanced material science |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary threat of substitutes for Exosens' core products, like photomultiplier tubes and image intensifiers, arises from alternative technologies aiming for similar detection capabilities. For instance, solid-state detectors such as silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs) and avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are increasingly encroaching on applications traditionally dominated by Exosens' offerings.
These solid-state alternatives often boast advantages like smaller size, lower power consumption, and greater robustness, making them attractive substitutes in various fields. While Exosens has historically held a strong position, the rapid evolution and adoption of these technologies represent a significant competitive pressure. The market for photon detection is dynamic, and the performance improvements in SiPMs and APDs continue to narrow the gap in certain performance metrics.
Substitutes often present a compelling value proposition through lower costs, but this frequently comes with inherent compromises. These trade-offs can manifest as reduced sensitivity, a narrower spectral range, or simply lower overall performance compared to Exosens' advanced solutions. For instance, a less sophisticated sensor might cost half as much but miss subtle anomalies that a higher-performing Exosens product would detect, impacting the quality of insights derived.
The real threat of these substitutes hinges directly on customer tolerance for these performance concessions. In applications where precision and detail are paramount, such as advanced medical diagnostics or critical industrial monitoring, the threat is minimal. Customers in these sectors understand that the reliability and accuracy provided by Exosens are non-negotiable, making the cost savings of a substitute insignificant compared to the potential for failure or misdiagnosis. In 2024, the demand for high-fidelity sensing in sectors like autonomous vehicles and advanced material inspection continued to grow, reinforcing the value of Exosens' specialized offerings.
Ongoing research and development in fields like advanced materials science and quantum sensing present a significant threat of substitutes for Exosens. Breakthroughs in these areas could yield entirely new ways to achieve detection and imaging, potentially bypassing Exosens' current technological foundations. For instance, advancements in metamaterials could offer superior performance in certain applications, impacting demand for existing solutions.
Customer Adoption of New Technologies
The willingness of Exosens' customers to adopt new substitute technologies hinges on several critical factors. These include how easily a new technology can be integrated into existing systems, its demonstrated reliability in real-world applications, and whether it has secured necessary regulatory approvals. The overall benefit-cost ratio is also paramount; customers will only switch if the advantages clearly outweigh the expenses and potential disruptions.
High switching costs for Exosens' customers play a significant role in mitigating the immediate threat posed by emerging substitute technologies. These costs can encompass the expense of new equipment, retraining personnel, and the potential for downtime during the transition period. For instance, if a customer has heavily invested in Exosens' specialized imaging solutions, the cost and effort to retool for a completely different technology might be prohibitively high, thus maintaining loyalty.
The market for advanced imaging and detection solutions, where Exosens operates, is characterized by a need for robust and proven performance. In 2024, industries such as aerospace, defense, and industrial inspection continue to prioritize reliability and safety, making rapid adoption of unproven substitutes unlikely. For example, a new sensor technology would need to demonstrate years of successful operation in demanding environments before widespread adoption, especially in critical applications where failure is not an option.
- Customer Adoption Factors: Ease of integration, proven reliability, regulatory approvals, and benefit-cost ratio are key drivers for customers adopting new technologies.
- Switching Costs Impact: High switching costs, including equipment investment and training, create a barrier for customers to adopt substitute technologies, thus protecting Exosens.
- Industry Prioritization: In 2024, sectors like aerospace and defense, major markets for Exosens, prioritize proven reliability and safety over rapid adoption of unproven substitute technologies.
- Demonstrated Performance: New technologies must exhibit a track record of success in demanding applications to overcome customer inertia and gain traction against established solutions.
Functional Equivalence and Application Specificity
The threat of substitutes for Exosens' products is significantly shaped by the specific application. A potential substitute might perform adequately in a general context but lack the critical functional equivalence, precise sensitivity, or robust performance demanded by Exosens' specialized defense or advanced scientific research sectors.
For instance, while a standard thermal imaging camera might suffice for basic surveillance, it cannot replace the high-resolution, multi-spectral capabilities required for identifying specific threats in complex battlefield environments. This application specificity acts as a strong barrier against direct substitution.
In 2024, the defense sector continued to invest heavily in advanced sensing technologies, with global military spending reaching an estimated $2.4 trillion. This sustained demand for cutting-edge solutions, where Exosens operates, underscores the limited viability of less sophisticated substitutes.
Key factors limiting substitutes include:
- Performance Requirements: Specialized applications demand highly specific technical capabilities that general-purpose substitutes often cannot meet.
- Reliability and Robustness: Exosens' target markets require equipment that functions flawlessly under extreme conditions, a benchmark difficult for substitutes to achieve.
- Integration and Compatibility: Existing systems in defense and research often require seamless integration, making it costly and complex to adopt non-standard substitute technologies.
- Regulatory and Certification Hurdles: Many of Exosens' markets have stringent certification processes that new or substitute technologies must pass, creating a significant barrier to entry.
The threat of substitutes for Exosens' specialized photon detection technologies is moderate, largely due to the demanding performance requirements of its core markets. While solid-state detectors like SiPMs and APDs are advancing, they often fall short in sensitivity, spectral range, or robustness for critical applications. For instance, in 2024, the defense sector, a key customer base, continued to prioritize proven reliability and advanced capabilities, with global military spending reaching approximately $2.4 trillion, limiting the appeal of less sophisticated substitutes.
Customer tolerance for performance compromises is a critical determinant. In high-stakes fields such as medical imaging or industrial inspection, where precision is paramount, substitutes offering lower cost but reduced accuracy are unlikely to gain significant traction. The high switching costs associated with integrating new equipment and retraining personnel further solidify Exosens' market position by acting as a deterrent to adopting unproven alternatives.
| Substitute Technology | Potential Advantages | Limitations vs. Exosens | Market Impact Likelihood | Example Application Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Photomultipliers (SiPMs) | Smaller size, lower power, lower cost | Lower sensitivity, narrower spectral range, less robust | Moderate in niche areas, low in core Exosens markets | General light sensing, less suitable for high-precision detection |
| Avalanche Photodiodes (APDs) | Faster response times, good sensitivity | Higher voltage requirements, can be sensitive to temperature | Moderate, potential for some overlap | Some scientific instrumentation, but less ideal for extreme environments |
| Advanced Materials (e.g., Metamaterials) | Potentially novel detection capabilities | Early-stage R&D, unproven reliability, high integration costs | Low in the short-to-medium term | Future disruptive potential, not a current threat |
Entrants Threaten
The high-performance detection and imaging component market demands significant capital for research and development, cutting-edge manufacturing, and specialized machinery. For instance, developing advanced sensor technologies often involves multi-year R&D cycles costing tens of millions of dollars. This substantial financial outlay acts as a formidable barrier, discouraging new companies from entering and providing a protective moat for established firms like Exosens.
Exosens' significant investment in proprietary technology and a robust patent portfolio acts as a formidable barrier to new entrants. For instance, in 2023, Exosens reported spending €124.5 million on research and development, a substantial portion of which fuels the creation and protection of its unique technological edge in areas like image intensifiers and thermal imaging.
This deep well of intellectual property, built over decades, makes it incredibly challenging and costly for newcomers to develop comparable products. Replicating Exosens' advanced capabilities would require not only immense R&D investment but also navigating complex patent landscapes, a hurdle that deters many potential competitors.
In critical sectors such as medical, scientific, and defense, brand reputation and customer trust are not just advantages, they are necessities. Exosens has cultivated a strong reputation over years of reliable performance, making it difficult for new players to gain traction. For instance, in the defense sector, long qualification processes and stringent performance requirements mean that a proven track record, which Exosens possesses, is invaluable.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
For Exosens, operating in sectors like medical devices and defense presents significant barriers to entry due to rigorous regulatory hurdles and the need for specialized certifications. These requirements demand substantial investment in time, capital, and technical expertise, making it difficult for new players to establish a foothold.
Navigating these complex approval processes, which can span years and involve multiple governmental agencies, acts as a powerful deterrent. For instance, obtaining CE marking for medical devices in Europe or ITAR compliance for defense-related products in the US are critical but resource-intensive steps.
- Stringent Approval Processes: Markets like medical technology and aerospace demand extensive testing and validation before products can be launched.
- High Compliance Costs: Meeting regulatory standards, such as FDA approval for medical devices, incurs significant expenses for documentation, legal review, and ongoing audits.
- Specialized Expertise Required: Companies need in-house or contracted expertise in regulatory affairs and quality management systems to successfully navigate these landscapes.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players in the thermal imaging sector, such as Exosens, leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs in production, raw material sourcing, and research and development. For instance, Exosens' integrated manufacturing capabilities contribute to cost efficiencies that new entrants would struggle to match immediately.
The experience curve plays a crucial role, with established companies possessing deep expertise in specialized manufacturing processes and application knowledge. This accumulated experience translates into higher operational efficiency and product quality, creating a substantial barrier for newcomers aiming to replicate these advantages swiftly.
- Economies of Scale: Exosens benefits from cost advantages in production, procurement, and R&D due to its established size.
- Experience Curve: Years of specialized manufacturing and application knowledge provide a competitive edge that is hard for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Cost Barrier: The scale and experience of incumbents like Exosens create a significant cost barrier for potential new competitors entering the market.
The threat of new entrants for Exosens is generally low, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements for research and development, sophisticated manufacturing, and the need for specialized expertise. These high entry costs, coupled with Exosens' established intellectual property and strong brand reputation, create significant barriers for potential competitors. Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments in key markets like defense and medical imaging demand extensive time and resources to navigate, further deterring new players.
| Factor | Impact on Exosens | Evidence/Example |
| Capital Requirements | High Barrier | R&D spending of €124.5 million in 2023 demonstrates significant investment needs. |
| Intellectual Property & Patents | High Barrier | Proprietary technology and patent portfolio make replication costly and difficult. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Moderate-High Barrier | Proven track record in defense and medical sectors builds customer loyalty. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | High Barrier | Complex approval processes (e.g., CE marking, ITAR compliance) require significant investment. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience Curve | High Barrier | Integrated manufacturing and years of specialized knowledge lower costs and increase efficiency. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Exosens Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial filings from publicly traded companies, and expert commentary from reputable trade publications.
