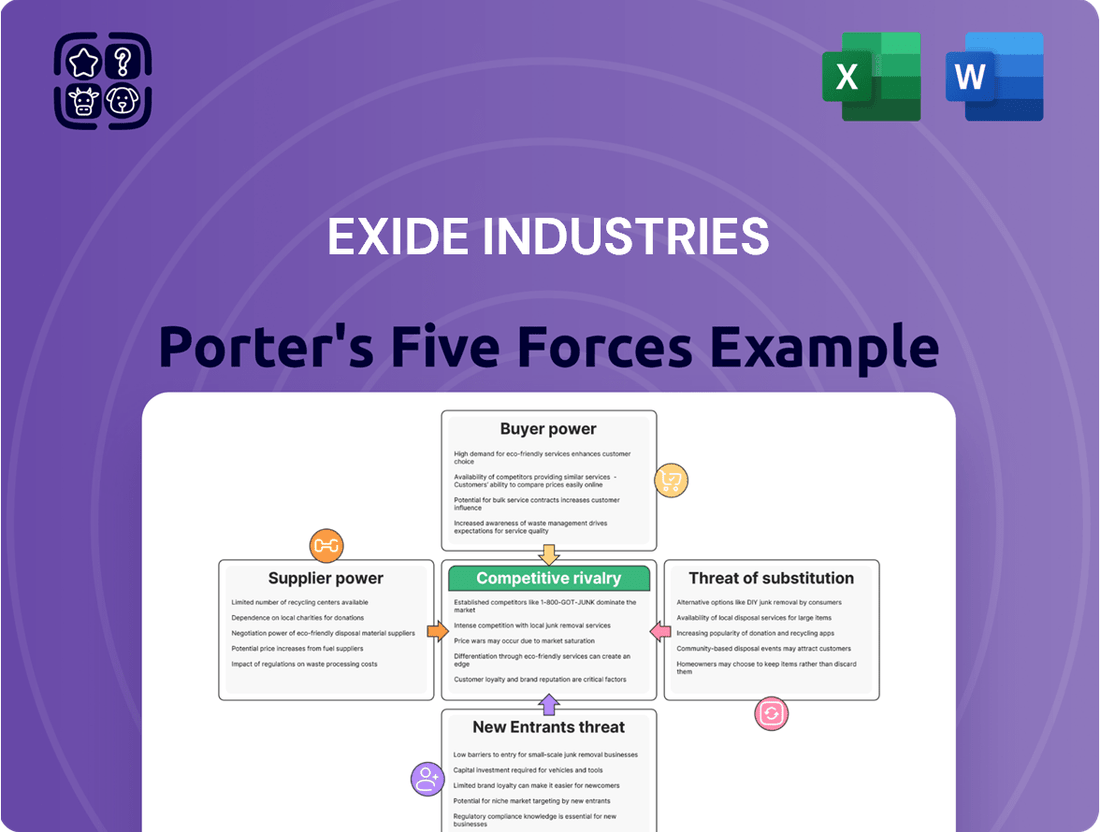
Exide Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Exide Industries Bundle
Exide Industries operates within a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry among established players and the constant threat of new entrants. Bargaining power of buyers can significantly influence pricing, while the availability of substitutes presents another challenge. The influence of suppliers, particularly for raw materials, also plays a crucial role in Exide's profitability and strategic decisions.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Exide Industries’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Exide Industries' dependence on critical raw materials like lead for its lead-acid batteries is a significant factor influencing its bargaining power with suppliers. The price of lead, a key component, is subject to global market volatility, directly affecting Exide's manufacturing expenses and overall profitability.
Despite efforts to mitigate this, such as securing long-term procurement agreements and sourcing approximately 40% of its lead from domestic markets, Exide remains exposed to international price swings. This reliance means suppliers of lead can exert considerable influence, particularly during periods of tight supply or increased demand, potentially leading to higher input costs for Exide.
Exide Industries faces significant supplier bargaining power due to India's heavy reliance on imported advanced battery components. For cutting-edge technologies like lithium-ion cells, the nation imports approximately 75-80% of the total battery material costs. This dependence stems from a lack of domestic lithium production and a nascent ecosystem for specialized battery inputs.
International suppliers of these critical materials, such as cathode and anode materials, electrolytes, and separators, hold considerable sway. Their ability to dictate terms, pricing, and supply availability directly impacts Exide's manufacturing costs and production timelines. In 2024, the global supply chain for these components remained concentrated among a few key players, further amplifying their leverage over Indian manufacturers like Exide.
Exide Industries faces a significant challenge due to India's limited domestic reserves of critical minerals essential for lithium-ion battery production. Key components like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are not readily available within India, forcing a heavy reliance on international suppliers.
This dependency grants considerable bargaining power to global mineral providers, as Exide and other domestic manufacturers must secure these materials from abroad. For instance, India's dependence on imports for lithium is substantial, with virtually all its lithium requirements being met through overseas sources, creating a bottleneck for domestic battery production growth.
Technological Expertise of Suppliers
Suppliers possessing advanced technological expertise and proprietary intellectual property in areas like battery chemistry or specialized manufacturing equipment can significantly enhance their bargaining power. This is particularly relevant for Exide as it ventures into new battery technologies. For instance, Exide's collaboration with companies like SVOLT Energy Technology for lithium-ion battery manufacturing highlights a reliance on external technological know-how, potentially giving these technology providers more leverage.
This reliance on specialized suppliers for cutting-edge battery components or manufacturing processes means Exide may face higher input costs or limited supplier options. The ability of these suppliers to differentiate their offerings through unique technological capabilities can translate into pricing power. The strategic importance of securing advanced battery technology for future growth in the EV market amplifies this supplier influence.
- Technological Dependence: Exide's strategic partnerships for lithium-ion battery technology underscore its reliance on specialized external expertise.
- Intellectual Property Advantage: Suppliers with unique patents or manufacturing processes in advanced battery materials hold significant leverage.
- Cost Implications: Accessing these advanced technologies may come with premium pricing, impacting Exide's cost structure.
- Market Dynamics: The growing demand for advanced batteries could further strengthen the bargaining power of key technology suppliers.
Government Initiatives to Mitigate Supplier Power
The Indian government is actively working to reduce the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly in critical sectors like battery manufacturing. Initiatives such as the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) battery storage are designed to boost domestic production capacity. This aims to create a more robust local supply chain, thereby lessening reliance on foreign suppliers. For instance, in 2023, the government announced PLI schemes that could potentially unlock significant investment in battery manufacturing, directly impacting the supplier landscape.
Furthermore, temporary import duty exemptions on essential raw materials are being implemented. These measures, evident in recent policy announcements throughout 2023 and early 2024, help to lower the cost of inputs for domestic manufacturers like Exide Industries. By making it easier and cheaper to acquire necessary components locally or through more diversified channels, these policies directly challenge the leverage held by concentrated foreign supplier groups.
- PLI Scheme for ACC Battery Storage: Aimed at encouraging domestic manufacturing and reducing import dependence.
- Temporary Import Duty Exemptions: Lowering the cost of critical raw materials for local producers.
- Fostering Domestic Supply Chains: Creating a more resilient and less supplier-dependent manufacturing ecosystem over the medium to long term.
- Reducing Reliance on Foreign Suppliers: Ultimately aiming to diminish the bargaining power of international entities by strengthening local alternatives.
Exide Industries faces considerable supplier bargaining power, particularly for lead and advanced battery components. Global lead price volatility and India's heavy reliance on imported lithium-ion battery materials, with approximately 75-80% of battery material costs imported, create significant leverage for international suppliers. This dependency, especially on cathode and anode materials, electrolytes, and separators, directly impacts Exide's production costs and timelines.
Suppliers with advanced technological expertise, such as those providing lithium-ion cell manufacturing know-how, also hold significant sway. Exide's collaborations, like the one with SVOLT Energy Technology, highlight this reliance, potentially leading to premium pricing for critical technologies. The concentration of key technology providers in 2024 further amplifies their market influence.
| Factor | Impact on Exide | Key Considerations |
| Lead Supply | High dependency on global prices; subject to volatility. | Exide sources ~40% domestically but remains exposed to international swings. |
| Lithium-ion Components | Significant reliance on imports (75-80% of costs). | Lack of domestic production for lithium, cobalt, nickel; concentrated global suppliers. |
| Technology Providers | Reliance on external expertise for advanced battery tech. | Partnerships can involve premium pricing and limited supplier options. |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the competitive landscape for Exide Industries by dissecting the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the battery sector.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic five forces dashboard, allowing Exide to quickly identify and address potential threats and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Exide Industries caters to a wide array of customers, from major automotive manufacturers (OEMs) to the vast aftermarket, and critical industrial sectors like power, solar, railways, and telecommunications. This broad customer base, which even extends to specialized defense applications like submarine batteries, significantly mitigates risk, as a downturn in one area can be balanced by growth in others.
Customers in the automotive aftermarket and the retail market for home UPS and inverter batteries are often very mindful of price. This means they can push Exide Industries to lower its prices, potentially squeezing profit margins. For instance, in the fiercely competitive aftermarket, battery replacement is a frequent need, and consumers actively compare prices across brands.
Despite this price sensitivity, Exide benefits from its established brand reputation. A strong brand like Exide can command a premium and foster customer loyalty, giving it some leverage against price-focused buyers. This brand strength is crucial in a market where performance and reliability are also key considerations for consumers.
Furthermore, Exide's widespread distribution network acts as another significant counter-balance. Having batteries readily available through numerous touchpoints, from authorized dealers to large retail chains, makes it convenient for customers to choose Exide. This accessibility reduces the customer's effort in finding alternatives, thus mitigating some of the power they might otherwise wield through price comparisons alone.
Exide Industries benefits from deep-rooted relationships with major automotive OEMs such as Tata Motors and Mahindra & Mahindra, often underpinned by exclusive, long-term supply agreements. These partnerships, critical for Exide's consistent demand, provide stability even as these large customers possess considerable bargaining leverage due to their substantial order volumes.
Evolving Customer Demand for Advanced Technologies
The accelerating global push towards electric vehicles and renewable energy storage is significantly amplifying customer expectations for cutting-edge battery technology. Customers are increasingly prioritizing lithium-ion batteries due to their superior energy density, faster charging capabilities, and longer lifespans compared to traditional lead-acid alternatives. This heightened demand for advanced performance places considerable power in the hands of consumers and businesses looking to adopt these greener technologies, compelling companies like Exide to innovate and adapt their product offerings swiftly to meet these evolving needs and maintain competitiveness.
This trend directly influences Exide's strategic direction, pushing the company to invest heavily in research and development for next-generation battery solutions. For instance, the global EV battery market was valued at approximately USD 50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. This growing market share for advanced batteries means customers have more choices and can therefore exert greater influence on pricing and product specifications.
- Increased EV Adoption: Global EV sales surpassed 10 million units in 2023, a significant jump from previous years, driving demand for high-performance batteries.
- Demand for Lithium-ion: Lithium-ion battery technology dominates the EV market, accounting for over 90% of all EV battery deployments.
- Customer Leverage: As more battery manufacturers enter the market, customers gain bargaining power, demanding better performance, faster charging, and improved safety features.
- Impact on R&D: Exide's investment in advanced battery chemistries and manufacturing processes is a direct response to this customer-driven demand for technological superiority.
Availability of Alternative Battery Options
Customers increasingly have a wider array of battery choices beyond Exide. This includes offerings from established competitors and newer players specializing in technologies like lithium-ion. For instance, by mid-2024, the Indian electric vehicle market saw significant growth, with multiple manufacturers offering diverse battery solutions, intensifying competition.
Government initiatives, such as subsidies for electric vehicle purchases and battery manufacturing, further bolster customer choice. These incentives make alternative battery technologies more financially attractive, empowering consumers to negotiate better terms or switch suppliers more readily. This trend is particularly evident in the burgeoning electric two-wheeler segment, where a variety of battery options are becoming standard.
- Customers benefit from a growing number of battery suppliers, including those offering advanced lithium-ion technology.
- Government incentives for electric vehicle adoption directly translate to increased customer bargaining power by subsidizing alternative options.
- The expanding EV market in India, for example, showcases this dynamic with numerous manufacturers providing competitive battery solutions.
The bargaining power of customers for Exide Industries is moderate but growing, particularly with the shift towards electric vehicles. While Exide's strong brand and extensive distribution network provide some leverage, customers in the aftermarket and industrial sectors remain price-sensitive. The increasing demand for advanced lithium-ion technology, driven by EV adoption and government incentives, empowers customers with more choices and greater influence over pricing and product specifications.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Exide |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Aftermarket/Retail | Price sensitivity, frequent need for replacement | Potential pressure on profit margins, focus on competitive pricing |
| Automotive OEMs | High order volumes, long-term contracts | Strong relationships offer stability, but OEMs possess significant leverage |
| Industrial/Specialized Sectors | Performance requirements, technological needs | Drives innovation, but specialized needs can create niche dependencies |
| EV/Renewable Energy Sector | Demand for advanced tech (Li-ion), increasing supplier options | Accelerated need for R&D, greater customer influence on specs and pricing |
Same Document Delivered
Exide Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You’re previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the competitive landscape of Exide Industries, meticulously examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the battery manufacturing sector. Understand the critical external factors shaping Exide's strategic decisions and market position. This in-depth analysis provides actionable insights essential for competitive strategy formulation.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian battery market is a battleground, with numerous established companies fiercely competing for dominance. Exide Industries faces significant rivalry from players like Amara Raja Energy & Mobility Limited, which has a strong presence in the automotive battery segment. Luminous Power Technologies is another major competitor, particularly in the home inverter and power backup solutions market. HBL Power Systems and TATA AutoComp GY Batteries also contribute to this competitive landscape, creating pressure on pricing and innovation.
Exide Industries enjoys a strong position in the Indian battery market, demonstrating significant competitive rivalry. It holds roughly 60% of the automotive battery market and around 40% of the industrial battery segment. This substantial market share indicates a high level of competition, as Exide must continually innovate and offer competitive pricing to maintain its dominance.
The company’s diversified product portfolio is a key factor in managing competitive rivalry. By offering batteries for automotive, industrial, and home UPS applications, Exide spreads its risk and caters to a broader customer base. This diversification makes it more resilient to fluctuations in any single market segment, allowing it to better withstand competitive pressures from specialized players.
Exide Industries contends with a significant unorganized sector, especially within the lead-acid battery replacement market. This segment often offers lower-priced alternatives, putting pressure on Exide's pricing strategies. The unorganized players, while smaller individually, collectively represent a considerable competitive force.
Furthermore, imports, particularly of lithium-ion cells and batteries, pose a growing threat. As of early 2024, India's push towards electric mobility is driving increased battery imports, creating a more complex competitive environment for established players like Exide. The cost-competitiveness of these imported components directly impacts the domestic market.
Strategic Investments in New Technologies
Competitive rivalry is intense as key players like Exide and Amara Raja pour significant capital into expanding production and venturing into advanced battery solutions, particularly lithium-ion. Exide's planned investment of close to ₹1,000 crore in its FY25 lithium-ion battery plant underscores the high capital expenditure required to maintain market position and embrace future technologies. This strategic investment highlights the industry's drive to innovate and capture emerging market share, intensifying the competitive landscape.
The race to dominate the burgeoning electric vehicle and energy storage markets fuels this rivalry. Companies are not just expanding existing capacities but are actively diversifying their product portfolios. This includes a strong focus on lithium-ion technology, which is poised to become a dominant force. The substantial financial commitments demonstrate a clear understanding that staying ahead requires significant upfront investment in cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities and research and development.
- Major Players: Exide Industries and Amara Raja Batteries are the primary competitors in the Indian battery market.
- Investment Focus: Both companies are heavily investing in capacity expansion and diversification into advanced battery technologies, especially lithium-ion.
- Capital Intensity: Exide's planned ₹1,000 crore investment in FY25 for its lithium-ion plant exemplifies the high capital requirements in this sector.
- Strategic Imperative: These investments are crucial for staying competitive and capturing future market growth, particularly in the electric mobility and energy storage segments.
Strong Brand Equity and Distribution Network
Exide Industries benefits from substantial competitive advantages stemming from its deeply ingrained brand equity and expansive distribution infrastructure. The company's long-standing reputation for reliability and quality translates into significant customer loyalty, a critical factor in the automotive and industrial battery sectors. This strong brand recognition allows Exide to command premium pricing and maintain market share even when faced with intense competition.
Furthermore, Exide's formidable distribution network, encompassing thousands of Exide Care locations and a vast network of dealers across India, ensures widespread product availability and accessibility. This extensive reach is a significant barrier to entry for new competitors and allows Exide to effectively serve diverse customer segments, from individual consumers to large industrial clients. Their established relationships with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) further solidify their market position, embedding Exide products into new vehicles and equipment from the outset.
- Brand Reputation: Exide has cultivated a brand image associated with durability and performance over decades.
- Distribution Network: The company operates over 2,000 Exide Care outlets and a vast dealer network, ensuring broad market penetration.
- OEM Relationships: Strong ties with major automotive manufacturers provide a consistent sales channel and brand endorsement.
- Market Share: These combined strengths help Exide maintain a leading position, particularly in the automotive battery segment, where they hold a significant market share in India. For instance, in FY23, Exide reported a consolidated revenue of INR 14,115 crore, underscoring its substantial market presence.
Competitive rivalry is a dominant force in the Indian battery market, with Exide Industries facing intense pressure from both organized and unorganized players. Key competitors like Amara Raja Energy & Mobility Limited are aggressively investing in capacity and new technologies, mirroring Exide's own strategic moves. This dynamic is characterized by significant capital expenditure, as evidenced by Exide's planned ₹1,000 crore investment in its FY25 lithium-ion battery plant, highlighting the industry's race for technological advancement and market share dominance in emerging sectors like electric mobility and energy storage.
| Competitor | Key Focus Areas | Recent Investments/Strategic Moves (as of early 2024/FY25 plans) |
|---|---|---|
| Amara Raja Energy & Mobility Limited | Automotive batteries, expanding into new energy solutions | Significant capacity expansion, focus on lithium-ion technology |
| Luminous Power Technologies | Home inverter and power backup solutions | Diversification and strengthening presence in energy storage |
| HBL Power Systems | Industrial batteries, defense applications | Focus on niche markets and technological upgrades |
| TATA AutoComp GY Batteries | Automotive batteries | Leveraging Tata Group's ecosystem for market penetration |
| Unorganized Sector | Lead-acid battery replacements | Price-based competition, leveraging lower overheads |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for Exide Industries stems from the widespread adoption of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. These batteries boast a higher energy density, meaning they can store more power in a smaller and lighter package, and generally offer longer lifespans and quicker charging times compared to Exide's traditional lead-acid offerings.
The global market for Li-ion batteries is expanding at an impressive rate, directly impacting Exide's established lead-acid battery segment. For instance, the global lithium-ion battery market size was valued at approximately $53.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $160 billion by 2030, highlighting the substantial shift in consumer and industry preference.
Government promotion of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional battery manufacturers. Initiatives like India's Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which offers subsidies for EV purchases, directly encourage consumers to adopt cleaner transportation, thereby reducing demand for internal combustion engine vehicles and their associated battery needs.
Furthermore, Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) battery storage, particularly favoring lithium-ion technology, are accelerating the transition away from conventional battery chemistries. For example, the PLI scheme for ACC Battery Storage aims to achieve manufacturing of 50 GWh of ACC and 5 GWh of niche ACC by 2025-26, directly impacting the market share of companies not aligned with these advanced technologies.
This strong government backing for EVs and renewable energy sources, coupled with targeted financial incentives, effectively lowers the switching costs for consumers and businesses towards technologies that utilize lithium-ion or other advanced battery solutions. This creates a powerful substitution effect, potentially eroding the market for older battery technologies.
Technological advancements are significantly impacting the threat of substitutes for traditional battery manufacturers like Exide Industries. Continuous improvements in lithium-ion battery technology, particularly in performance, safety, and cost, are making them increasingly viable alternatives. For instance, by late 2024, the average cost of lithium-ion battery packs for electric vehicles had fallen to around $130 per kilowatt-hour, a steep decline that makes them more competitive.
This evolution directly drives a preference for these alternatives, especially in emerging sectors like new energy storage and electric mobility. As lithium-ion batteries become more energy-dense and quicker to charge, they directly challenge lead-acid batteries in applications where power and convenience are paramount. This trend is evident in the rapid growth of the EV market, which is increasingly adopting advanced lithium-ion chemistries.
Lead-Acid Battery Resilience in Certain Segments
While lithium-ion batteries are gaining prominence, lead-acid batteries continue to hold their ground, especially in cost-sensitive sectors. Their affordability, proven dependability, and a well-developed recycling ecosystem ensure their continued utility in specific automotive segments like electric three-wheelers and various industrial uses. Exide Industries itself is actively enhancing its lead-acid offerings, developing advanced ABSORBED Glass Mat (AGM) batteries to further bolster their competitive edge.
The resilience of lead-acid technology is evident in its continued market share in certain applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lead-acid batteries are significantly cheaper to produce than lithium-ion alternatives, making them attractive for budget-conscious consumers and businesses.
- Established Infrastructure: A mature supply chain and recycling network for lead-acid batteries reduces operational costs and environmental concerns.
- Niche Market Strength: Applications such as backup power systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and certain types of electric vehicles still favor lead-acid due to a balance of performance and price.
- Technological Advancements: Exide's focus on AGM technology demonstrates an effort to improve lead-acid battery performance, extending their relevance against newer chemistries.
Consumer Preference for Sustainable Solutions
The increasing consumer and industrial demand for sustainable energy solutions directly impacts the threat of substitutes for traditional battery technologies. As environmental consciousness grows, there's a significant push towards greener alternatives, influencing purchasing decisions across various sectors. This trend is a powerful driver for innovation in battery technology.
This shift encourages companies like Exide Industries to explore and invest in advanced battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion, which offer higher energy density and a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. For instance, the global electric vehicle battery market, a key area for advanced battery adoption, was projected to reach over $300 billion by 2025, highlighting the substantial growth in demand for these alternative solutions. Exide's strategic investments in new battery technologies aim to address this evolving market preference and mitigate the threat posed by more sustainable substitutes.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by:
- Growing environmental regulations and incentives favoring cleaner energy storage.
- Technological advancements making alternative battery chemistries more cost-effective and efficient.
- Increasing availability and adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems, which rely heavily on advanced battery technologies.
- Consumer awareness campaigns promoting the benefits of sustainable products and practices.
The primary substitute threat to Exide Industries comes from lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, offering higher energy density, longer lifespans, and faster charging. The global Li-ion battery market was valued around $53.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to surpass $160 billion by 2030, demonstrating a significant shift in preferences.
Government policies, such as India's FAME scheme for EVs and PLI schemes for Advanced Chemistry Cells, actively promote Li-ion technology. These incentives reduce switching costs for consumers and businesses towards advanced battery solutions, directly impacting the market for traditional lead-acid batteries.
Technological progress in Li-ion batteries, particularly concerning performance, safety, and cost reduction, makes them increasingly competitive. By late 2024, the average cost of Li-ion battery packs for EVs dropped to approximately $130 per kWh, enhancing their appeal over older chemistries.
Despite the rise of Li-ion, lead-acid batteries remain relevant due to their cost-effectiveness and established infrastructure, especially in segments like electric three-wheelers and UPS systems. Exide is also innovating with AGM technology to maintain competitiveness.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantages | Market Growth Indicator (2023-2030 Est.) | Exide's Response |
| Lithium-ion (Li-ion) | Higher energy density, longer life, faster charging, lower weight | Global market projected to grow from ~$53.5 billion to over $160 billion | Investment in advanced battery technologies, focus on AGM |
| Advanced Lead-Acid (e.g., AGM) | Cost-effectiveness, established infrastructure, proven reliability in niche applications | Continued strong demand in specific automotive and industrial sectors | Enhancing existing product lines, developing improved lead-acid variants |
Entrants Threaten
The battery manufacturing sector, particularly for cutting-edge technologies such as lithium-ion, demands significant capital outlays. This includes the establishment of advanced production facilities and robust research and development initiatives.
Exide Industries' commitment to its lithium-ion cell manufacturing project, with an investment of approximately ₹3,602 crore slated for completion by April 2025, clearly highlights these substantial capital requirements as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants.
Exide Industries, a titan in the Indian battery market, has cultivated formidable brand loyalty over decades. This deep-rooted customer trust, built through consistent quality and service, acts as a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, Exide's brand recognition is a key factor in its market dominance, making it difficult for emerging players to capture even a small market share without substantial marketing efforts and proven product reliability.
Furthermore, Exide’s extensive and well-established distribution network, spanning across urban and rural India, presents another formidable hurdle. Replicating this reach, which includes thousands of dealers and service centers, would necessitate enormous capital investment and time. In 2024, this established infrastructure continues to be a critical competitive advantage, ensuring product availability and accessibility that new entrants would struggle to match quickly.
The threat of new entrants into the battery manufacturing sector, especially for advanced chemistries like lithium-ion, is significantly mitigated by high technological complexity and substantial R&D costs. Developing and refining battery technologies requires deep expertise and ongoing innovation, making it a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, Exide Industries, a key player, consistently invests in R&D to enhance battery performance and explore new materials. In FY23, Exide’s total R&D expenditure was ₹374 crore, underscoring the significant capital commitment required to stay competitive and develop next-generation battery solutions.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The battery sector faces significant regulatory challenges, particularly around environmental compliance for hazardous materials like lead. New companies entering the market must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these complex rules, which significantly raises the barrier to entry.
For instance, regulations such as the EU's Battery Directive and similar frameworks globally mandate specific recycling rates and prohibit certain hazardous substances, requiring substantial operational adjustments and financial outlay for compliance.
- High Capital Investment: Meeting environmental standards for battery manufacturing and disposal necessitates advanced technology and infrastructure, demanding substantial upfront capital.
- Complex Permitting Processes: Obtaining necessary environmental permits and licenses can be a lengthy and intricate process, delaying market entry.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Continuous monitoring, reporting, and waste management add to the operational expenses for established and new players alike.
- Recycling Infrastructure Demands: Establishing or partnering with robust recycling facilities, as mandated by law, is crucial but costly.
Government Support for Domestic Manufacturing
Government support for domestic manufacturing, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) battery sector, presents a nuanced threat of new entrants for companies like Exide Industries. Initiatives such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, designed to bolster local battery production, often favor significant capital investments and existing, established manufacturers. This structure can create a barrier for smaller, newer companies aiming to enter the market, as they may struggle to meet the scale and investment thresholds required to benefit from these programs.
However, this very push for localization can, over time, foster an environment where new players emerge, especially in specialized or niche segments of the battery market. The increased focus on domestic supply chains might encourage innovation and the development of unique technologies or materials, potentially creating opportunities for agile new entrants who can carve out specific market share. While the PLI scheme, for instance, has seen significant allocations, such as the approximately $3.2 billion designated for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) battery manufacturing under India's National Program, its benefits are more readily accessible to those with substantial existing infrastructure and financial capacity.
- PLI Scheme Focus: Government incentives like the PLI scheme for ACC battery manufacturing, totaling approximately $3.2 billion, primarily benefit large-scale investments and established players.
- Barrier for New Entrants: The stringent criteria for these schemes can create a significant hurdle for smaller, newer companies seeking to enter the domestic battery manufacturing landscape.
- Niche Opportunities: Despite the barriers, the overall drive for localization may eventually spur new entrants into specialized areas or advanced battery technologies.
- Competitive Landscape: While large players may leverage government support more easily, the evolving market dynamics could still allow for the emergence of focused competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Exide Industries is generally low, primarily due to the substantial capital required for setting up advanced battery manufacturing facilities, especially for technologies like lithium-ion. Exide's significant investments, such as the ₹3,602 crore for its lithium-ion cell project by April 2025, underscore this barrier.
Furthermore, Exide benefits from decades of built brand loyalty and an extensive distribution network across India, which would be costly and time-consuming for new players to replicate. The company’s FY23 R&D expenditure of ₹374 crore also signifies the ongoing investment needed to stay competitive technologically.
Regulatory complexities, particularly concerning environmental compliance and recycling mandates, add another layer of difficulty for potential entrants. While government incentives like the PLI scheme for ACC battery manufacturing, with its $3.2 billion allocation, aim to boost domestic production, they often favor large-scale, established players, further limiting new market entrants.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Exide Industries leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.
We incorporate insights from financial news outlets, competitor websites, and government trade data to assess the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.
