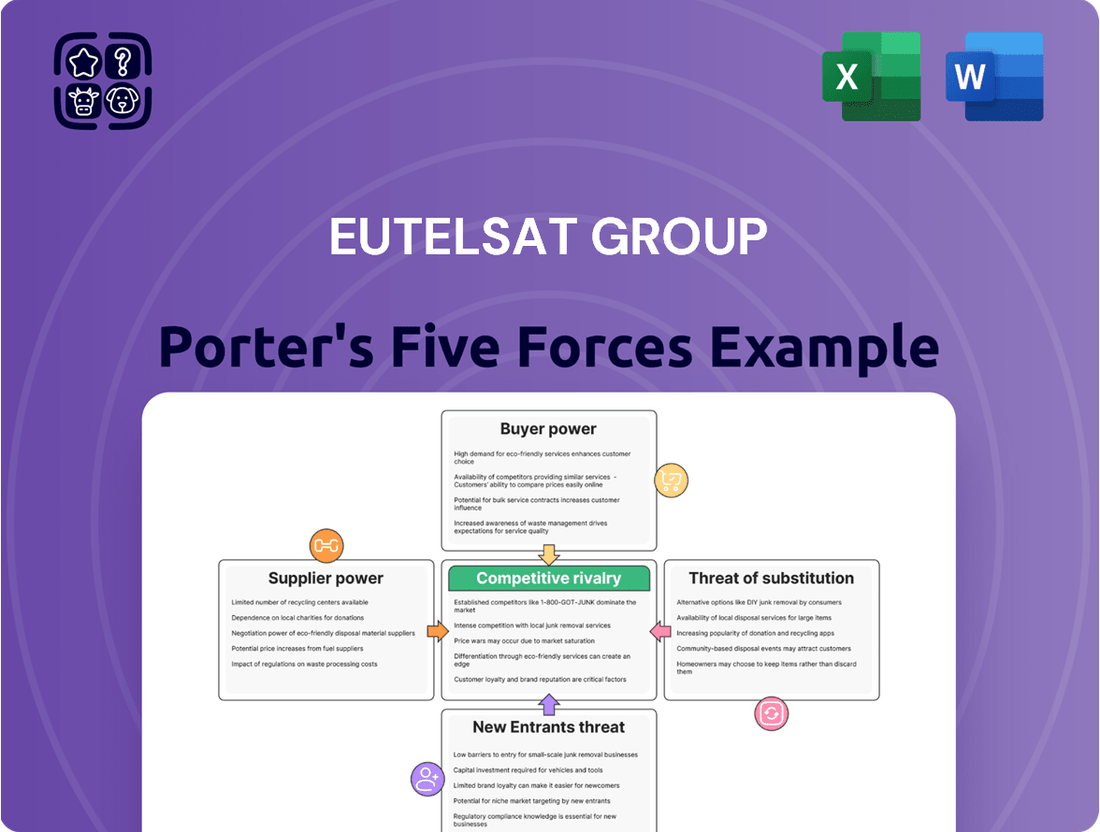
Eutelsat Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Eutelsat Group Bundle
Eutelsat Group navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, reflecting the industry's capital-intensive nature.
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by high entry barriers, including satellite development costs and regulatory hurdles.
Rivalry among existing competitors is intense, particularly in established satellite broadband and broadcast markets.
The threat of substitutes, such as terrestrial broadband and emerging wireless technologies, presents a persistent challenge to traditional satellite services.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Eutelsat Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The satellite manufacturing industry is highly concentrated, with a few dominant players like Airbus, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Thales Alenia Space. This limited number of suppliers gives them substantial bargaining power over satellite operators such as Eutelsat Group. For instance, in 2024, Eutelsat's significant capital expenditure for new satellites underscores its reliance on these specialized manufacturers. High barriers to entry, including the immense technological expertise and capital investment required, severely restrict new entrants. This scarcity of alternatives allows existing manufacturers to command premium pricing for critical components and complete satellite systems.
The bargaining power of satellite suppliers is significantly bolstered by high switching costs. Satellites, often built for lifespans exceeding 15 years, are intricately designed to integrate with specific ground infrastructure and operational systems, like Eutelsat's ground segment. For instance, replacing a geostationary satellite, which can cost upwards of $200 million for manufacturing and launch, necessitates substantial redesigns of ground control systems and procedures. This technological lock-in means that shifting to a new manufacturer for future satellite generations involves considerable capital expenditure, reinforcing the strong position of incumbent suppliers in 2024.
Eutelsat Group significantly relies on a limited number of launch service providers, including SpaceX and Arianespace, to place its satellites into orbit. This concentrated industry, with SpaceX alone completing 98 orbital launches in 2023, grants these suppliers substantial bargaining power. Any launch delays or failures, as seen with various missions, can incur significant financial penalties and operational disruptions for Eutelsat. The increasing demand for launch services, driven by new mega-constellations, further empowers these essential suppliers in 2024.
Specialized Technology and Components
Eutelsat Group relies heavily on highly specialized satellite components like advanced transponders, high-performance antennas, and efficient propulsion systems. These critical parts are sourced from a very limited global pool of qualified suppliers, such as Thales Alenia Space and Airbus Defence and Space. This scarcity, coupled with the high technological barrier to entry, grants these suppliers substantial bargaining power over Eutelsat. For example, a single geostationary communication satellite can cost upwards of €200 million, with a significant portion attributed to these specialized components.
- Satellite components are highly specialized, requiring unique expertise.
- A limited number of global suppliers dominate the market for critical parts like transponders.
- The high cost and complexity of these components increase supplier leverage.
- The long lead times for manufacturing further strengthen supplier positions.
Governmental and Regulatory Influence
Governmental and regulatory influence significantly shapes Eutelsat Group's supplier relationships. Satellite manufacturing and launch services are heavily regulated, with stringent government controls and export restrictions impacting the global supply chain. This environment limits Eutelsat's choice of suppliers, especially for sensitive technologies, concentrating power among a few approved vendors. For instance, in 2024, major satellite bus manufacturers like Airbus Defence and Space or Thales Alenia Space operate under strict national oversight, influencing their contracts. Governments also leverage industrial policy and national security concerns to influence supplier selection, further empowering established players in the space sector.
- Strict export controls on satellite components limit Eutelsat's supplier pool.
- Government industrial policies prioritize domestic or allied suppliers.
- National security considerations can mandate specific technology sources.
- Compliance costs for suppliers are high, reducing market entry.
The bargaining power of Eutelsat Group's suppliers is substantial, driven by the highly concentrated satellite manufacturing and launch industries. In 2024, Eutelsat's significant capital expenditure and high switching costs for satellite components, which can exceed €200 million per geostationary satellite, underscore its reliance. Additionally, a limited pool of specialized component providers and strict governmental regulations further empower these essential suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Key Players | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite Manufacturers | Airbus Defence & Space, Thales Alenia Space | High capital expenditure for new satellites |
| Launch Service Providers | SpaceX, Arianespace | SpaceX completed 98 orbital launches in 2023 |
| Specialized Components | Thales Alenia Space (transponders) | Geostationary satellite costs upwards of €200M |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the competitive forces shaping Eutelsat Group's satellite communications market, detailing buyer power, supplier leverage, new entrant barriers, substitute threats, and competitive rivalry.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures with a visual breakdown of Eutelsat's five forces, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic planning.
Effortlessly adapt the analysis to new market realities or competitive shifts by easily updating data points, ensuring your strategic insights remain current.
Customers Bargaining Power
Eutelsat Group serves a diverse customer base, including broadcasters, telecom operators, and government agencies, along with growing segments like maritime and in-flight connectivity. Despite this variety, a substantial portion of its revenue, particularly in the declining video segment, relies on a concentrated group of large broadcasting clients. For example, Eutelsat's video revenue, which accounted for approximately 60% of total revenues in fiscal year 2024, remains susceptible to the decisions of these key customers. The potential loss of even one major broadcasting client could significantly impact Eutelsat's financial performance and overall revenue streams.
Customers of Eutelsat Group, particularly in data connectivity, have a growing array of alternatives. Terrestrial fiber optic networks continue to expand globally, offering increasingly competitive solutions. Furthermore, the proliferation of new satellite operators, especially low Earth orbit (LEO) constellations like SpaceX’s Starlink, significantly enhances customer leverage. Starlink alone reported exceeding 3 million subscribers globally by mid-2024, intensifying competition for Eutelsat. This increased availability of diverse solutions grants customers substantial bargaining power, especially in regions with expanding terrestrial infrastructure.
The satellite communications market faces rising competition, intensifying price pressure on operators like Eutelsat. Customers can now easily compare service offerings and pricing from various providers, compelling Eutelsat to maintain highly competitive rates to attract and retain clients. This dynamic is particularly pronounced in the connectivity segment, where new low-Earth orbit (LEO) constellations entering service in 2024 are expanding options, and also impacts the broadcasting sector, albeit to a lesser degree. This increased customer leverage influences Eutelsat's revenue per user and contract negotiations.
Low Switching Costs for Some Services
While Eutelsat's long-term capacity leases offer some customer stickiness, the ability to switch providers for specific services, like data connectivity, is growing. As of 2024, advancements in ground equipment standardization and the rise of software-defined networks are significantly lowering the complexity and costs associated with migrating to alternative satellite networks. This shift empowers customers to actively seek more competitive pricing and flexible service terms, increasing their bargaining leverage.
- Satellite ground segment innovations, including multi-orbit terminals, are reducing vendor lock-in.
- The increasing adoption of open-standard interfaces facilitates easier integration with diverse satellite systems.
- For enterprise data services, customers can leverage a broader pool of providers beyond traditional geostationary operators.
- The proliferation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations by 2024 further diversifies options for certain connectivity needs.
Government and Enterprise Contract Negotiations
Government agencies and large enterprises frequently procure satellite capacity from Eutelsat Group through competitive tenders, resulting in substantial contracts. These entities wield significant bargaining power due to the sheer volume of their agreements and their sophisticated procurement processes. They can demand tailored solutions, favorable contractual terms, and often lower prices, as seen in the increasing competition for secure communication contracts. For instance, global government and defense satellite services market revenue is projected to reach approximately $13.5 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of these negotiations.
- Large-scale government contracts can represent 15-20% of a satellite operator's annual revenue.
- Enterprise customers often negotiate multi-year agreements, securing discounts for long-term commitments.
- The ability to switch providers or leverage in-house solutions strengthens customer leverage.
- Eutelsat's 2024 contracts with defense ministries reflect intense price and service negotiations.
Customers exert significant power due to diverse alternatives like expanding terrestrial fiber and new LEO constellations, such as Starlink exceeding 3 million subscribers by mid-2024. This intensifies price competition and allows customers to seek better terms. Large government and enterprise contracts, projected at $13.5 billion in 2024 for the global market, further amplify their leverage. Innovations like multi-orbit terminals also reduce switching costs.
| Customer Segment | Key Driver of Power | 2024 Impact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broadcasters | Revenue concentration | 60% of FY2024 revenue susceptible | ||
| Connectivity (Data) | Alternative solutions | Starlink 3M+ subscribers mid-2024 | ||
| Government/Enterprise | Contract volume/complexity | Global market $13.5B (2024 est.) |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Eutelsat Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the Eutelsat Group, detailing the competitive landscape within the satellite communications industry. You're viewing the exact document you'll receive, offering an in-depth examination of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This professionally written analysis is ready for immediate download and use upon purchase, providing actionable insights into Eutelsat's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Eutelsat faces intense competition from established geostationary (GEO) satellite operators like SES and Intelsat.
A significant and growing threat comes from Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations, notably SpaceX's Starlink, which exceeded 2.6 million subscribers by early 2024, and Amazon's Project Kuiper.
This rivalry impacts all of Eutelsat's core markets, from video broadcasting to critical data connectivity services.
Industry consolidation, such as the SES-Intelsat merger announced in 2024, reflects the intense competitive pressures within the satellite sector.
Low Earth Orbit LEO mega-constellations represent a significant disruptive force, offering lower latency and potentially lower-cost services highly appealing for data-intensive applications. Starlink, for instance, continues its aggressive expansion, reaching over 3 million subscribers globally by mid-2024, intensifying competition across consumer and enterprise markets. This rapid growth compels traditional satellite operators like Eutelsat to adapt their strategies, evidenced by the Eutelsat OneWeb merger completed in 2023, which aims to accelerate their own LEO deployment capabilities. The competitive landscape demands innovation and strategic partnerships to maintain market share against these agile newcomers.
The traditional video broadcasting market, a core revenue stream for Eutelsat, faces a significant secular decline due to the pervasive rise of over-the-top streaming services. This shift intensifies competitive rivalry, as evidenced by Eutelsat's video revenues decreasing by 6.4% in the first half of fiscal year 2024. The shrinking market size for satellite-based video distribution puts substantial pressure on pricing and reduces available contracts, forcing satellite operators to compete more aggressively for diminishing opportunities. This trend necessitates Eutelsat's strategic pivot towards connectivity services to offset the ongoing contraction in its legacy video segment.
High Capital Intensity and Exit Barriers
The satellite industry, where Eutelsat Group operates, demands substantial capital investment, evidenced by projected capital expenditures for Eutelsat of around €500-€520 million for fiscal year 2024. Building and launching advanced satellites, which can have operational lifespans exceeding 15 years, requires immense upfront costs. These specialized, long-lived assets create significant exit barriers, committing companies to the market for the long term. This high commitment fuels intense rivalry, as firms must compete aggressively for market share to amortize their massive investments, even if returns are constrained. Such conditions ensure sustained competitive pressure within the sector.
- Eutelsat's FY2024 capital expenditure is projected at approximately €500-€520 million.
- Satellite assets feature operational lifespans often exceeding 15 years.
- High initial investment and asset specialization create substantial exit barriers.
- Long-term market commitment intensifies rivalry for market share.
Government-Backed Competition and Strategic Interests
Competitive rivalry for Eutelsat Group is significantly shaped by government-backed entities and national strategic interests in the space sector. Governments globally view robust satellite communication as crucial infrastructure for national sovereignty and security, often leading to substantial support for domestic or regional satellite operators. For instance, the European Union's IRIS² secure connectivity program, where Eutelsat is a key partner, directly addresses the market dominance of non-European players like Starlink, aiming for operational readiness by 2024.
- IRIS² is projected to have an initial budget of €2.4 billion from the EU.
- Government contracts represented a significant portion of Eutelsat's revenue in 2024, emphasizing state reliance.
- National space policies increasingly prioritize secure, sovereign satellite capabilities over purely commercial considerations.
- This fosters a highly competitive environment where state backing can outweigh commercial efficiencies for strategic assets.
Eutelsat Group faces intense rivalry from established GEO players and disruptive LEO constellations like Starlink, which surpassed 3 million subscribers by mid-2024. The declining video market, with Eutelsat's video revenues down 6.4% in H1 FY2024, intensifies competition for diminishing opportunities. High capital expenditures, projected at €500-€520 million for FY2024, create significant exit barriers, fueling aggressive market share battles. Government-backed initiatives like EU's IRIS², operational by 2024, further shape this complex competitive landscape.
| Competitive Factor | Detail | 2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| LEO Rivalry | Starlink Subscribers | >3 million by mid-2024 |
| Video Market Decline | Eutelsat Video Revenue | -6.4% in H1 FY2024 |
| Capital Investment | Eutelsat FY2024 CapEx | €500-€520 million |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Terrestrial fiber optic networks present a significant substitute threat to Eutelsat Group, offering higher speeds and lower latency. The ongoing global expansion of fiber infrastructure, with Europe aiming for universal gigabit connectivity by 2025, directly erodes the market for satellite broadband. This widespread deployment, including into less densely populated regions, makes fiber the preferred solution for many fixed applications. As of 2024, fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) subscriptions continue their robust growth, impacting satellite demand. Consequently, Eutelsat faces increasing competition from these high-capacity, low-cost alternatives.
The widespread rollout of 5G and ongoing development of future terrestrial wireless technologies present a significant substitute for satellite connectivity, especially for mobile and some fixed wireless applications. While satellite can complement 5G for backhaul and coverage in remote areas, advancements in terrestrial networks are reducing reliance on satellite solutions. Global 5G subscriptions are projected to exceed 2 billion by late 2024, highlighting this market shift. Some satellite operators are actively pursuing direct-to-device services to integrate with, rather than be replaced by, mobile networks.
The proliferation of Over-the-Top (OTT) media services, such as Netflix, poses a major substitute for Eutelsat's video content delivery, as these platforms primarily use terrestrial broadband. This fundamental shift in consumer behavior away from traditional linear broadcasting directly impacts Eutelsat's financial performance. For the first nine months of fiscal year 2024, Eutelsat's Broadcast (Video) revenues were €442 million, representing a 9.4% like-for-like decline, largely driven by this market transition. Broadcasters themselves increasingly leverage terrestrial IP networks for content contribution and distribution, further reducing reliance on satellite for video. The trend indicates a continued migration to internet-based content consumption.
High-Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS)
High-Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS) represent an emerging, albeit still developing, substitute technology for satellite services like those offered by Eutelsat Group. These systems involve unmanned aerial vehicles or balloons operating in the stratosphere to deliver telecommunications services. While HAPS are not a widespread threat in 2024, they could evolve into a regional, lower-latency alternative to both geostationary (GEO) and low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites for specific applications in the future, particularly for localized connectivity needs. The HAPS market is projected to grow significantly, but its current operational scale remains limited compared to established satellite infrastructures.
- Airbus Zephyr platforms continue development, showcasing HAPS potential in 2024.
- Initial HAPS deployments are primarily focused on specialized use cases like disaster recovery.
- The HAPS market, though growing, is still in its early commercialization phase.
- Regulatory frameworks for HAPS are still evolving globally as of 2024.
Cable and Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT)
Cable and Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT) remain significant substitutes for Eutelsat Group's satellite broadcasting services in numerous markets. These platforms provide robust channel bundles, directly competing for consumer viewership. For instance, in 2024, DTT continues to be a primary TV reception method for millions across Europe, particularly in countries like France, where it is widely accessible. Consumer decisions often hinge on local infrastructure availability, specific content offerings, and the overall cost efficiency of these bundled services.
- DTT reaches over 250 million homes globally in 2024.
- Cable TV maintains strong penetration in markets like North America and parts of Europe.
- Content exclusivity often drives platform choice for consumers.
- Installation and subscription costs are key competitive factors.
Terrestrial fiber optics and 5G networks significantly substitute satellite services, offering higher speeds and lower latency, with global 5G subscriptions projected to exceed 2 billion by late 2024. The rise of OTT media, leveraging terrestrial broadband, directly led to Eutelsat's Broadcast revenues declining 9.4% to €442 million for 9M FY2024. Cable and Digital Terrestrial Television also remain strong competitors, with DTT reaching over 250 million homes globally in 2024. Emerging HAPS technology, though not widespread in 2024, represents a potential future localized alternative.
| Substitute Type | Key Metric (2024) | Impact on Eutelsat |
|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial Fiber | FTTH subscriptions robust growth | Erodes satellite broadband market |
| 5G Networks | >2 billion global subscriptions (projected) | Reduces reliance for mobile/fixed wireless |
| OTT Media | Eutelsat Broadcast revenue -9.4% (€442M 9M FY24) | Shifts video consumption from satellite |
| DTT | >250 million global homes reached | Maintains competition for TV viewership |
Entrants Threaten
The satellite industry demands enormous upfront capital investment, acting as a formidable barrier for new entrants. Designing, manufacturing, and launching a single geostationary satellite can cost well over $200 million, excluding ground infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the total expenditure for a new, advanced telecommunications satellite and its launch can exceed $350 million. This financial hurdle significantly limits the pool of potential competitors to only those with substantial backing, protecting established players like Eutelsat Group.
New entrants into the satellite communication sector, like those potentially challenging Eutelsat Group, confront substantial regulatory hurdles. Securing essential licenses for orbital slots and spectrum frequencies demands approval from international bodies, such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), and various national regulators. These orbital slots and valuable spectrum are inherently finite resources, making their acquisition a highly competitive and complex process. The intricate and often political nature of this licensing typically favors established operators, granting them a significant advantage in the 2024 landscape. This scarcity effectively deters new market participants, bolstering the position of incumbents like Eutelsat.
Established operators like Eutelsat Group benefit from decades of operational experience and advanced technological expertise, which creates a substantial barrier for new entrants. New competitors would need to invest heavily to acquire comparable satellite technology and build a robust customer base. Eutelsat's significant economies of scale, bolstered by its 2023 merger with OneWeb, enable efficient service delivery across its GEO and LEO fleets, making it challenging for smaller players to compete on cost. Furthermore, incumbents have deeply established relationships with critical suppliers, customers, and regulators globally. For instance, Eutelsat Group reported a backlog of €4.3 billion as of December 2023, showcasing strong customer commitment and long-term contracts.
Emergence of Well-Funded 'NewSpace' Companies
Despite high barriers, the threat to Eutelsat from new entrants is significant, driven by well-funded 'NewSpace' companies. Players like SpaceX, with its Starlink constellation reaching over 3 million subscribers by mid-2024, and Amazon's Project Kuiper, which secured 83 launches for its initial deployment, are rapidly disrupting the satellite communication market. These vertically integrated entities leverage cutting-edge innovations in launch technology and satellite manufacturing, substantially lowering operational costs and increasing deployment speed.
- Starlink's subscriber base exceeded 3 million in 2024, demonstrating rapid market penetration.
- Amazon's Project Kuiper secured 83 launch agreements for its initial satellite constellation.
- NewSpace companies benefit from vertically integrated models, controlling both manufacturing and launch.
- Innovations in reusable rockets and mass satellite production drive down entry costs.
Government-Sponsored and Sovereign Constellations
A significant new threat to Eutelsat Group emerges from government-sponsored and sovereign satellite constellations. Countries like China are rapidly developing their own Low Earth Orbit (LEO) networks, such as the Guowang project, driven by national security and data sovereignty concerns rather than purely commercial motives. These state-backed initiatives, with potentially vast government funding, could offer services at non-market rates, intensely pressuring commercial operators in 2024. Their strategic importance allows them to bypass traditional competitive hurdles, altering market dynamics.
- China's Guowang project aims for over 12,000 satellites.
- Government support can lead to significant infrastructure investment.
- National security priorities may override profitability.
- This creates an uneven competitive landscape for Eutelsat.
While substantial capital and regulatory barriers typically protect Eutelsat Group, the threat from new entrants is intensifying. Well-funded NewSpace companies like Starlink, exceeding 3 million subscribers by mid-2024, and government-backed initiatives such as China's Guowang project, are rapidly altering the competitive landscape. These players leverage vertical integration and significant funding to overcome traditional hurdles, introducing innovative, cost-effective services. This dynamic environment means Eutelsat faces increasing pressure from agile, well-resourced newcomers.
| New Entrant Type | Key Player Examples | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|---|
| NewSpace Commercial | SpaceX Starlink, Amazon Project Kuiper | Starlink: 3M+ subscribers (mid-2024); Kuiper: 83 secured launches |
| Government-Sponsored | China's Guowang, European Union's IRIS² | Guowang: Aims for 12,000+ satellites; Strategic national priorities |
| Traditional Barriers Overcome | Vertical integration, Reusable rockets, State funding | Reduced launch costs, Faster deployment, Non-market pricing potential |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Eutelsat Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, integrating information from Eutelsat's annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like Euroconsult and Northern Sky Research.
We also incorporate data from regulatory filings, financial news outlets, and competitor disclosures to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
