Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. Bundle
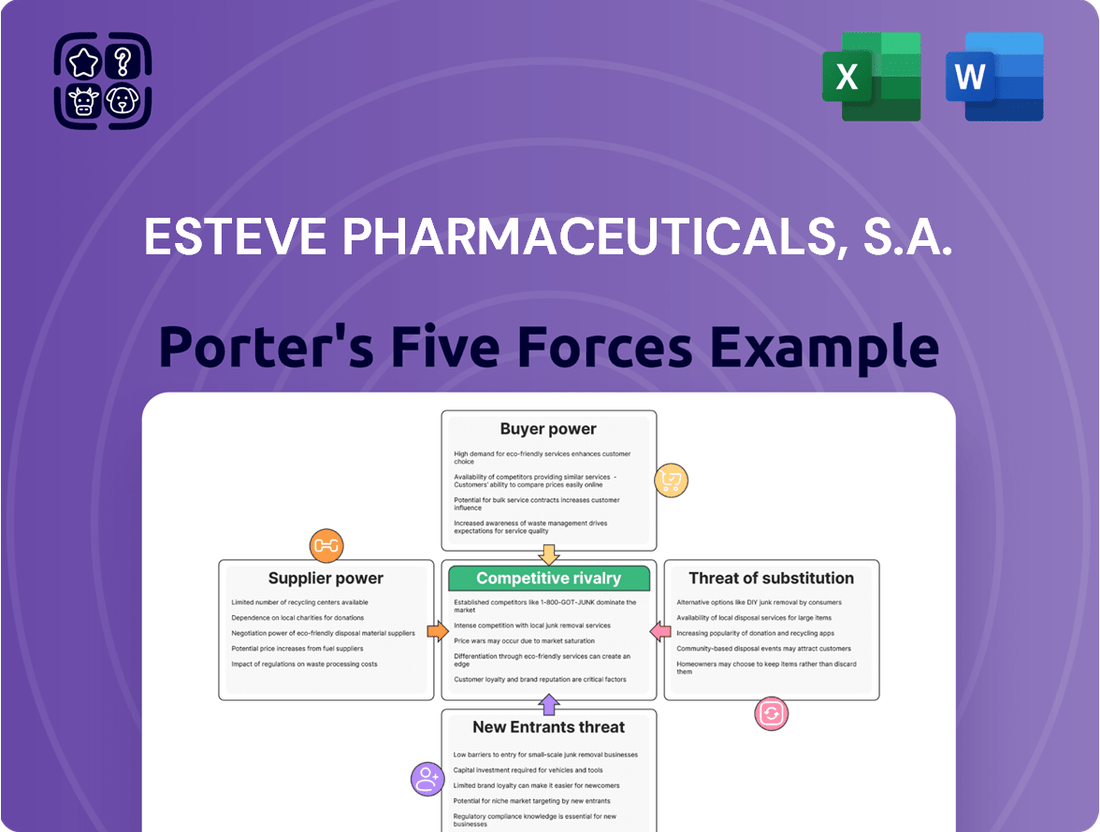
Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. faces moderate threats from new entrants due to high R&D costs and regulatory hurdles, while buyer power is significant, especially from large healthcare providers. The bargaining power of suppliers is also a key consideration in the pharmaceutical industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A.’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Esteve Pharmaceuticals, like its peers, depends on specialized API and raw material suppliers. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be significant when materials are patented, proprietary, or have few alternative sources, leading to high switching costs and regulatory complexities. For instance, in 2023, the global API market was valued at approximately $220 billion, with a substantial portion driven by patented compounds where supplier leverage is considerable.
Conversely, for more common chemical inputs, supplier power tends to be lower due to the availability of numerous chemical manufacturers. Esteve's strategic investments in its own manufacturing facilities across Spain, Mexico, and China, totaling over 3,000 employees in 2024, likely serve to bolster its supply chain security and reduce reliance on external, high-bargaining-power suppliers.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals' involvement as a Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) positions it uniquely within the supplier landscape. When Esteve procures specialized manufacturing or drug development services, the bargaining power of highly specialized CDMOs becomes a critical factor. These suppliers wield influence through their proprietary technologies, stringent quality adherence, and protected intellectual property.
The significant revenue Esteve's own CDMO operations generated, amounting to €456 million in 2024, underscores its dual capacity. This revenue stream highlights Esteve's ability to both demand services and provide them, directly impacting its position in negotiations with external CDMO partners.
Research and development service providers, including contract research organizations (CROs) and specialized technology firms, hold significant bargaining power in the pharmaceutical sector. Esteve Pharmaceuticals, like many in the industry, relies on these external partners for crucial aspects of drug discovery and development, such as clinical trials and advanced analytical services.
In 2024, Esteve allocated €46 million to innovation, underscoring its dependence on R&D capabilities, many of which are outsourced. The growing adoption of technologies like artificial intelligence in drug development further amplifies the influence of technology-focused R&D suppliers who possess unique, in-demand expertise.
Logistics and Distribution Partners
Logistics and distribution partners play a crucial role in Esteve Pharmaceuticals' ability to reach global markets. These specialized entities, particularly those managing temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, wield moderate bargaining power due to their essential infrastructure and regulatory expertise. Esteve's reliance on a robust distribution network means that any increase in their service costs or disruptions can directly affect Esteve's profitability and its capacity to serve patients internationally.
The bargaining power of these logistics suppliers is influenced by several factors:
- Specialized Infrastructure: Companies handling cold chain logistics or hazardous materials require significant investment in specialized vehicles, warehousing, and tracking systems, limiting the pool of qualified providers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex international pharmaceutical regulations for transport and storage is a significant barrier to entry, concentrating power among compliant partners.
- Network Reach: The ability of logistics firms to provide comprehensive global coverage is a key differentiator, making them indispensable for companies like Esteve with international ambitions.
Talent and Skilled Labor
The availability of highly skilled scientific, medical, and technical talent is paramount for Esteve Pharmaceuticals, directly impacting its research, development, and specialized manufacturing capabilities. A scarcity of such expertise can significantly enhance the bargaining power of these skilled professionals, potentially driving up labor costs and complicating recruitment efforts.
Esteve's commitment to its workforce is evident in its 2024 expansion, with a 6.6% increase in personnel. The company's strategic focus on achieving gender parity in management positions further underscores its investment in human capital. This emphasis is particularly critical given the specialized nature of Esteve's therapeutic areas, such as central nervous system disorders and rare diseases, which demand highly qualified and experienced professionals.
- Talent Availability: Pharmaceutical innovation relies heavily on specialized scientific and medical talent.
- Impact of Shortages: A deficit in skilled labor can lead to increased recruitment costs and higher salary demands, bolstering supplier (talent) bargaining power.
- Esteve's Workforce Growth: Esteve expanded its workforce by 6.6% in 2024, demonstrating a proactive approach to talent acquisition and retention.
- Specialized Needs: Esteve's focus on complex therapeutic areas like CNS disorders and rare diseases necessitates a deep pool of highly qualified personnel, increasing the bargaining power of those with relevant expertise.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals faces varying supplier bargaining power depending on the specificity of inputs. For patented Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or highly specialized contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), supplier leverage is high due to limited alternatives and proprietary technology. In contrast, suppliers of common chemicals or less specialized services generally have lower bargaining power.
Esteve's strategic investments in its own manufacturing capabilities, including facilities in Spain, Mexico, and China employing over 3,000 people in 2024, aim to mitigate reliance on powerful external suppliers. The company's €456 million revenue from its CDMO operations in 2024 also enhances its negotiation stance with potential CDMO partners.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Esteve's Mitigation Strategy | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized API Suppliers | Patented compounds, few alternatives | In-house R&D, strategic partnerships | Global API market ~$220 billion in 2023 |
| Specialized CDMOs | Proprietary technology, quality adherence | In-house CDMO services, careful partner selection | Esteve CDMO revenue: €456 million |
| R&D Service Providers (CROs) | Unique expertise (e.g., AI in drug discovery) | Internal R&D investment, technology adoption | Esteve innovation spend: €46 million |
| Logistics & Distribution | Specialized infrastructure, regulatory compliance | Diversified logistics partners, robust network | Global pharmaceutical logistics market growth |
| Skilled Talent | Scarcity in specialized fields (e.g., rare diseases) | Talent development, competitive compensation | Esteve workforce growth: 6.6% |
What is included in the product
This analysis for Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, revealing strategic levers for sustained profitability and market leadership.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals' Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of competitive pressures, perfect for quick decision-making regarding market entry and strategic positioning.
This analysis allows for the customization of pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends, offering a dynamic view of Esteve's competitive landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Government and institutional payers, such as national health systems and large insurance providers, wield considerable bargaining power in the pharmaceutical sector. These entities often represent a substantial portion of a company's revenue, enabling them to negotiate lower prices and dictate reimbursement terms. In the US, for instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 empowers Medicare to negotiate prices for certain high-cost drugs, a move that began impacting some medications in 2024 and will expand in subsequent years.
Esteve, as an international player, navigates a complex web of varying pricing regulations and reimbursement policies across different European countries and other global markets. The consolidation of healthcare providers further strengthens the negotiating leverage of these institutional buyers, as they can demand more favorable terms due to their increased market share and influence over drug formularies.
Large hospital networks and consolidated pharmacy chains wield considerable bargaining power. Their substantial purchasing volumes allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms with pharmaceutical manufacturers like Esteve. These entities can also influence which medications are prescribed and stocked, directly impacting a company's market access and revenue streams.
For Esteve, engaging effectively with these powerful institutional buyers is crucial. Their ability to dictate terms means that pharmaceutical companies must offer competitive pricing and demonstrate clear value to secure distribution and prescribing support. This dynamic is underscored by Esteve's reach to 8 million patients in 2024, a figure likely achieved through strong relationships with these key intermediaries.
In the generic and over-the-counter (OTC) markets, consumers wield considerable bargaining power due to their high price sensitivity and the abundance of readily available alternatives. Once a drug’s patent expires, patients can readily switch to more affordable generic versions, directly impacting the demand for branded products. Similarly, for OTC medications, consumers can easily choose from a wide array of competing brands, often driven by price promotions and perceived value.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals, with its substantial footprint in these segments, faces this dynamic head-on. The company must therefore employ aggressive pricing strategies to remain competitive. Building strong brand loyalty for its OTC offerings is also crucial to mitigate the impact of consumers easily switching to lower-cost options. For instance, the global generic drugs market was valued at approximately USD 450 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, highlighting the intense competition Esteve navigates.
Physicians and Healthcare Professionals (HCPs)
Physicians and healthcare professionals (HCPs) wield considerable influence over Esteve's product adoption, acting as key intermediaries between the company and the end consumer. Their prescribing decisions, while not directly paying for medications, are paramount to market penetration. In 2024, factors like demonstrated clinical efficacy, robust safety profiles, adherence to evolving clinical guidelines, and demonstrable cost-effectiveness are critical drivers for HCPs when selecting treatments. Esteve's strategy to engage these professionals hinges on clearly articulating the value proposition of its innovative therapies, emphasizing improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
The bargaining power of physicians and HCPs is shaped by several dynamics:
- Influence on Prescription: HCPs directly control which medications are prescribed, making their acceptance vital for Esteve's revenue.
- Information Dependency: Their prescribing habits are heavily influenced by clinical data, peer recommendations, and pharmaceutical marketing, creating an avenue for Esteve to communicate value.
- Cost-Consciousness: Increasingly, HCPs are mindful of healthcare system costs, making the economic benefits of Esteve's drugs a significant consideration.
Patient Advocacy Groups and Patient Influence
Patient advocacy groups, alongside increasingly informed patients, are a significant force impacting pharmaceutical companies like Esteve. These groups can lobby for better drug access, push for lower prices, and advocate for specific treatment options. While a single patient has limited direct power over pricing, the collective voice of patient communities can sway public opinion, influence regulatory bodies, and ultimately shape market demand for Esteve's products.
Esteve's commitment to improving lives, aiming to reach 8 million patients in 2024, highlights the critical role patient outcomes play in their strategy. This focus means that patient satisfaction and the perceived value of their treatments directly influence the company's success and its ability to maintain a strong market position.
- Patient Advocacy: Groups actively lobby for improved drug access and affordability.
- Collective Voice: Informed patient communities can influence public perception and regulatory decisions.
- Esteve's Goal: Aiming to reach 8 million patients in 2024 underscores the importance of patient-centricity.
Institutional buyers, including national health systems and large insurers, exert significant pricing power over pharmaceutical companies. Their substantial purchasing volumes and ability to influence drug formularies allow them to negotiate lower prices. For example, the US Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 began allowing Medicare to negotiate prices for certain high-cost drugs in 2024, a trend that consolidates buyer leverage.
Esteve's extensive reach, aiming for 8 million patients in 2024, necessitates strong relationships with these powerful entities. The company must demonstrate clear value and competitive pricing to secure market access and favorable reimbursement terms, especially as healthcare provider consolidation further amplifies buyer influence.
In the generic and OTC markets, consumers are highly price-sensitive, readily switching to more affordable alternatives once patents expire. This intense competition, with the global generic drugs market valued around USD 450 billion in 2023, forces companies like Esteve to adopt aggressive pricing and focus on brand loyalty for OTC products.
Physicians and healthcare professionals act as crucial intermediaries, with their prescription decisions heavily influencing Esteve's market penetration. Factors like clinical efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness, alongside peer recommendations, guide their choices in 2024. Esteve’s strategy focuses on clearly communicating the value and improved patient outcomes of its therapies to these key decision-makers.
Same Document Delivered
Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A., providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no hidden surprises or placeholder content. You're looking at the actual analysis, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning upon completing your transaction.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The pharmaceutical sector thrives on a fierce rivalry fueled by the constant demand for groundbreaking discoveries and significant research and development expenditures. Companies are locked in a race to develop and launch innovative therapies, particularly within niche medical fields.
Esteve's commitment to this competitive landscape is evident in its €46 million investment in innovation during 2024. This substantial allocation underscores the critical importance of staying ahead in the discovery and development of new treatments.
The ability to rapidly translate scientific advancements into commercially viable products is paramount for sustaining a competitive advantage. Speed to market directly impacts a company's ability to capture market share and recoup R&D costs.
The pharmaceutical industry is keenly aware of patent expirations, often referred to as patent cliffs. These events create significant openings for generic and biosimilar manufacturers, intensifying competition. For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical sector anticipates substantial sales being exposed to this competitive pressure as patents on blockbuster drugs expire.
When a drug's patent protection ends, generic versions can enter the market at substantially lower price points. This directly impacts the original innovator's market share and profitability. Esteve, with its involvement in the generic market, understands this dynamic firsthand, both as a participant and as a company whose own patented products will eventually face similar generic competition.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals navigates a highly competitive global and regional market, with its international sales representing a significant 75% of its total income. This broad exposure means Esteve contends with both established multinational pharmaceutical giants and nimble, specialized regional competitors across various therapeutic areas.
The intensity of rivalry is particularly pronounced in key markets where Esteve has a strong European presence, alongside its affiliates in Asia and America. This dynamic landscape requires continuous innovation and strategic positioning to maintain market share against a diverse set of players.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Strategic acquisitions and partnerships are a cornerstone of competition in the pharmaceutical sector, allowing companies to broaden their product offerings, increase market presence, and acquire novel technologies. Esteve is a prime example of this, having acquired HRA Pharma Rare Diseases in July 2024, a move that significantly bolstered its rare disease portfolio. This ongoing M&A trend, with further agreements anticipated in 2025, directly fuels competitive rivalry as firms strive to consolidate their market standing and diversify their research and development pipelines.
These strategic maneuvers, such as Esteve's acquisition of HRA Pharma Rare Diseases for an undisclosed sum in July 2024, represent a significant investment in future growth and competitive positioning. Such actions not only expand a company's therapeutic areas but also signal a proactive approach to market dynamics, forcing competitors to re-evaluate their own strategies for portfolio enhancement and innovation access. The pharmaceutical industry's high R&D costs and patent cliffs make these M&A activities critical for sustained competitiveness.
- Esteve's acquisition of HRA Pharma Rare Diseases in July 2024
- Focus on expanding rare disease portfolio
- M&A activity intensifies industry rivalry
- Drive to access new technologies and strengthen market position
Therapeutic Area Focus and Specialization
Esteve Pharmaceuticals' strategic focus on specialized therapeutic areas such as pain management, central nervous system (CNS) disorders, and respiratory conditions significantly influences its competitive landscape. This specialization allows Esteve to carve out niche markets, potentially reducing broad competition. However, it also means direct rivalry with other pharmaceutical firms concentrating on these same high-value, often complex, medical needs.
The competitive intensity within these specialized drug markets is often heightened due to the limited patient populations and the significant R&D investment required. For instance, in the CNS disorder segment, companies are vying for breakthroughs that address unmet medical needs, leading to fierce competition for market share and intellectual property. In 2023, the global CNS drug market was valued at approximately $130 billion, with significant growth projected, attracting numerous players.
- Specialized Therapeutic Areas: Esteve concentrates on pain, CNS disorders, and respiratory conditions.
- Niche Market Creation: Specialization can lead to less direct competition across the board.
- Intense Rivalry in Niches: Competition is fierce among companies targeting similar specialized patient groups.
- High R&D Investment: Developing specialized therapies requires substantial research and development expenditure, increasing barriers to entry but also the stakes for existing competitors.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals operates within a highly competitive pharmaceutical landscape, characterized by intense rivalry among global and regional players. This competition is driven by the continuous pursuit of innovation and the significant R&D investments required to bring new therapies to market. The company's international presence, with 75% of its income derived from global sales, means it contends with a broad spectrum of competitors across its key therapeutic areas, including pain management, CNS disorders, and respiratory conditions.
The pharmaceutical industry's dynamics, including patent expirations and the rise of generic and biosimilar alternatives, further intensify this rivalry. For example, in 2024, a significant portion of the pharmaceutical market experienced patent cliffs, creating opportunities for competitors and impacting innovator sales. Esteve's strategic acquisitions, such as the July 2024 purchase of HRA Pharma Rare Diseases, highlight the industry's trend towards consolidation and the acquisition of novel technologies to maintain a competitive edge.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Esteve |
|---|---|---|
| Global Pharma Giants | Extensive R&D budgets, broad product portfolios, established market access. | Significant competition across multiple therapeutic areas, requiring continuous innovation and strategic partnerships. |
| Specialized Biotechs | Focus on niche therapeutic areas, agile R&D, potential for disruptive innovation. | Direct competition in specialized segments like rare diseases and CNS disorders, necessitating strong IP protection and rapid market entry. |
| Generic/Biosimilar Manufacturers | Lower price points, rapid market entry post-patent expiry. | Pressure on pricing and market share for Esteve's products once their patents expire, underscoring the importance of a robust pipeline. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of generic and biosimilar drugs is a significant force in the pharmaceutical sector, directly impacting companies like Esteve. Once a branded drug's patent protection expires, generic versions can enter the market, offering substantially lower prices due to their lack of extensive R&D investment and regulatory pathways. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) estimates that generics have saved consumers and taxpayers over $2 trillion in the decade leading up to 2020, illustrating the scale of this cost-saving substitution.
This dynamic presents a dual challenge and opportunity for Esteve. While the availability of cheaper generics erodes the market share and pricing power of Esteve's own branded products post-patent, the company's strategic involvement in the generics and biosimilars market allows it to capture a portion of this demand. By offering its own affordable alternatives, Esteve can mitigate the negative impact of external generic competition and leverage its manufacturing and distribution capabilities.
Alternative therapies and natural medicines present a significant threat to Esteve Pharmaceuticals. Patients increasingly explore options like acupuncture, herbal remedies, or dietary changes, especially for chronic or less severe conditions, potentially reducing reliance on prescription drugs. For example, the global market for traditional and complementary medicine was valued at over $150 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a substantial and expanding substitute market.
These non-pharmaceutical approaches can directly compete with Esteve's product portfolio by offering perceived natural or holistic benefits. Furthermore, the growing acceptance and integration of these therapies into mainstream wellness practices can further erode the market share of conventional pharmaceuticals, impacting demand for certain drug classes.
The threat of substitutes for Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. is significantly influenced by the practice of off-label drug use and drug repurposing. Existing medications approved for one ailment might be prescribed for other conditions, offering patients and healthcare systems more economical options compared to novel treatments. In 2024, the global market for repurposed drugs was estimated to be worth billions, demonstrating its substantial impact.
This trend can directly affect the market penetration and pricing strategies of Esteve's newly developed pharmaceuticals. If older, less expensive drugs can effectively treat conditions for which Esteve is developing new therapies, it creates a powerful substitute. For instance, a study published in early 2025 highlighted that approximately 20% of all prescriptions in the US were for off-label uses, underscoring the prevalence of this substitute threat.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
The increasing emphasis on preventive medicine and healthier lifestyles acts as a significant substitute threat to pharmaceutical companies like Esteve. By reducing the incidence and severity of diseases through proactive measures, demand for certain medications can diminish.
Public health initiatives and widespread adoption of lifestyle changes such as improved diet and regular exercise are fundamentally addressing health at its root. This trend, while long-term, directly competes with the need for pharmaceutical interventions. For instance, the World Health Organization's 2024 report highlighted that an estimated 70% of premature deaths globally are linked to lifestyle factors, underscoring the potential impact of these substitutes.
Esteve's commitment to enhancing patient quality of life indirectly acknowledges this shift. The company's strategies must therefore consider how to integrate with or respond to these non-pharmacological approaches to health management.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Shift in healthcare focus: Growing investment in wellness programs and preventative care reduces reliance on reactive pharmaceutical treatments.
- Public health campaigns: Government-backed initiatives promoting healthy living directly impact the prevalence of conditions treatable by drugs.
- Patient empowerment: Increased access to health information encourages individuals to adopt lifestyle changes that may obviate the need for medication.
- Technological advancements: Wearable tech and health apps provide tools for self-monitoring and disease prevention, further eroding the market for certain pharmaceuticals.
Technological Advancements in Healthcare
Technological advancements in healthcare present a significant threat of substitutes for Esteve Pharmaceuticals. Innovations in medical devices, such as minimally invasive surgical tools or advanced diagnostic equipment, can directly replace the need for certain pharmaceutical interventions. For instance, a breakthrough in implantable drug delivery systems might reduce reliance on oral medications for chronic conditions.
Emerging technologies like gene therapy and personalized medicine are also potent substitutes. These approaches can offer curative solutions or significantly alter disease progression, potentially rendering traditional drug therapies obsolete. By 2024, the global gene therapy market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion, showcasing the rapid growth and disruptive potential of these alternatives.
- Disruptive Technologies: Gene therapies and advanced diagnostics offer alternative treatment paradigms.
- Market Impact: The gene therapy market reached an estimated $10.5 billion in 2024, indicating a strong substitute trend.
- Substitution Examples: New surgical techniques can replace chronic medication needs, and novel delivery systems might reduce oral drug reliance.
The threat of substitutes for Esteve Pharmaceuticals is multifaceted, encompassing generic and biosimilar drugs, alternative therapies, off-label drug use, preventive medicine, and technological advancements. These substitutes can significantly impact Esteve's market share and profitability by offering lower-cost alternatives or entirely different approaches to healthcare. For example, the U.S. FDA's estimate of over $2 trillion in savings from generics by 2020 highlights the cost-saving power of these substitutes.
The growing market for traditional and complementary medicine, valued at over $150 billion in 2023, illustrates another significant substitute threat, particularly for chronic conditions. Similarly, the billions generated by repurposed drugs in 2024 and the approximately 20% of prescriptions being off-label in the U.S. in early 2025 demonstrate how existing, cheaper medications can act as substitutes for new Esteve products.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on preventive medicine and healthier lifestyles, with an estimated 70% of premature deaths linked to lifestyle factors according to a 2024 WHO report, directly competes with the demand for pharmaceutical interventions. Technological innovations, such as the $10.5 billion gene therapy market in 2024, also present potent substitutes by offering alternative treatment paradigms that could render traditional drugs obsolete.
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical sector demands immense upfront capital for research and development (R&D) and sophisticated manufacturing. This substantial financial hurdle effectively deters new players from entering the market.
For instance, the cost of bringing a new drug to market can easily exceed billions of dollars, encompassing years of clinical trials and regulatory approvals. Esteve's own commitment to expanding its industrial footprint, evidenced by its investment in a new production site in Spain, underscores the significant capital outlays necessary to compete and grow within this industry.
The pharmaceutical industry, including companies like Esteve Pharmaceuticals, faces a significant threat from new entrants due to stringent regulatory requirements and lengthy approval processes. Agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandate rigorous clinical trials and extensive safety and efficacy evaluations for new drug submissions. For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market in 2023 was estimated to be over $2 billion, with development timelines often exceeding a decade, presenting a substantial financial and time commitment that deters many potential competitors.
The pharmaceutical industry, including companies like Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A., is heavily influenced by intellectual property (IP) and patent protection. Existing players leverage patents to safeguard their groundbreaking drugs, ensuring a period of market exclusivity. This exclusivity period, often lasting 20 years from the patent filing date, is crucial for recouping substantial R&D investments. For instance, in 2023, the global pharmaceutical R&D spending reached an estimated $240 billion, highlighting the high stakes involved.
New entrants face a significant hurdle: they must either discover novel drug compounds or wait for existing patents to expire. The lengthy patent lifecycle means that truly innovative new market entrants are scarce, and those that do emerge often face a long road to market. Esteve's strategic emphasis on developing innovative medicines and nurturing its R&D pipeline underscores the critical role IP plays in maintaining its competitive edge and market position.
Established Distribution Channels and Brand Loyalty
New entrants into the pharmaceutical market, like that of Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A., confront significant hurdles in replicating the established distribution channels and deep-rooted brand loyalty enjoyed by incumbent firms. These existing networks are crucial for reaching healthcare providers, pharmacies, and ultimately patients.
Esteve, along with its competitors, has cultivated decades-long relationships with key stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem. These relationships are not easily replicated by newcomers, who must invest heavily to build trust and secure access. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that it can take pharmaceutical companies an average of 5-7 years to fully establish a robust distribution network in a new major market.
- Established Relationships: Esteve leverages existing partnerships with hospitals, clinics, and retail pharmacies, making it difficult for new entrants to gain shelf space or physician recommendations.
- Brand Recognition: Patient familiarity and trust in Esteve's established brands act as a significant barrier, as switching to a less-known product often requires overcoming inertia and perceived risk.
- Distribution Costs: Building a comparable distribution infrastructure from scratch involves substantial capital expenditure and logistical complexities, adding to the cost of market entry.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Economies of scale significantly deter new entrants in the pharmaceutical industry. Established players like Esteve, with substantial global operations and revenue, can spread high fixed costs across a larger production volume, leading to lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, research and development (R&D), and marketing. For instance, in 2024, major pharmaceutical companies consistently reported R&D expenditures in the billions of dollars, a threshold nearly impossible for a new entrant to match initially.
This cost advantage, coupled with the experience curve effect where cumulative production leads to increased efficiency and reduced costs, creates a formidable barrier. New companies struggle to compete on price or investment capacity, as they lack the established infrastructure and market penetration to achieve similar cost efficiencies. Esteve's ability to invest heavily in novel drug discovery and clinical trials, supported by its scale, further solidifies its competitive position against potential newcomers.
- Economies of Scale: Large pharmaceutical firms benefit from lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, R&D, and marketing due to high production volumes.
- Experience Curve: Cumulative production experience allows established companies to refine processes and reduce costs over time.
- R&D Investment: In 2024, leading pharmaceutical companies continued to invest billions in R&D, a level difficult for new entrants to replicate.
- Competitive Disadvantage: New entrants face significant cost disadvantages and limited investment capacity compared to established players like Esteve.
The threat of new entrants for Esteve Pharmaceuticals is generally considered low, primarily due to the immense capital requirements and regulatory complexities inherent in the industry. The cost of bringing a single drug to market can exceed $2 billion, a figure that acts as a significant deterrent for potential new players. Esteve's own substantial investments in R&D and manufacturing infrastructure, such as its new Spanish production site, highlight the financial scale necessary to compete effectively.
Intellectual property protection, including patents that can last up to 20 years, further shields established companies like Esteve. This exclusivity allows them to recoup R&D investments, estimated at $240 billion globally in 2023, before competitors can enter with similar products. Newcomers must either innovate significantly or wait for patents to expire, a lengthy process that limits the immediate threat.
Established distribution networks and brand loyalty also present formidable barriers. Companies like Esteve have cultivated long-term relationships with healthcare providers, a process that can take 5-7 years to replicate in new markets, according to 2024 data. This deep integration into the healthcare ecosystem makes it challenging for new entrants to gain traction and market access.
Economies of scale enjoyed by established firms like Esteve provide a crucial cost advantage. Spreading high fixed costs across larger production volumes lowers per-unit expenses in R&D, manufacturing, and marketing. In 2024, leading pharmaceutical firms continued to report R&D budgets in the billions, a scale new entrants find exceedingly difficult to match, thus limiting their competitive capacity.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023/2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for R&D and manufacturing. | Significant financial hurdle. | Drug development costs > $2 billion. |
| Intellectual Property | Patent protection provides market exclusivity. | Limits competition for patented drugs. | Global R&D spending ~ $240 billion (2023). |
| Distribution & Relationships | Established networks and stakeholder trust. | Difficult to replicate access and market penetration. | Establishing distribution networks takes 5-7 years. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high volume. | Creates cost disadvantage for smaller players. | Major pharma R&D budgets in billions. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Esteve Pharmaceuticals, S.A. is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Esteve's annual reports and investor presentations, as well as industry-specific market research from firms like IQVIA and Evaluate Pharma.
