ENN Energy Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ENN Energy Holdings Bundle
ENN Energy Holdings operates within a dynamic energy sector where the bargaining power of buyers, particularly large industrial clients, significantly influences pricing and contract terms. The threat of new entrants, while potentially moderate due to capital requirements, remains a constant consideration as the industry evolves.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping ENN Energy Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of natural gas suppliers in China significantly impacts ENN Energy Holdings. Domestic production and imports are controlled by a few major state-owned enterprises and key international suppliers. PetroChina, for example, is a dominant force, producing and importing over 60% of China's natural gas supply, giving it considerable bargaining power.
Natural gas is the bedrock of ENN Energy's business, serving as the primary raw material for its extensive distribution network. The availability and cost of this crucial input directly dictate the company's operational efficiency and bottom line.
ENN Energy's 2024 financial reports highlighted the significant impact of international gas price volatility. These fluctuations directly influenced the profit attributable to the company's owners, underscoring the suppliers' considerable bargaining power.
Switching natural gas suppliers or altering existing supply contracts presents substantial logistical and financial hurdles for ENN Energy. These challenges often stem from long-term agreements already in place for pipeline gas and liquefied natural gas (LNG), making a swift changeover complex and costly.
China's ongoing investment in developing new pipeline infrastructure and expanding its LNG terminal capacity further solidifies commitment to specific supply channels. This strategic infrastructure development inherently raises the switching costs for distributors like ENN Energy, as it ties them to particular supply routes and sources.
Supplier Integration and Control
Major upstream natural gas suppliers in China, frequently state-owned entities, are increasingly integrating downstream and controlling critical pipeline infrastructure. This is exemplified by PipeChina, which introduced a new tariff system in early 2024. This vertical integration grants these suppliers enhanced control over the entire supply chain, potentially diminishing the bargaining power of downstream distributors like ENN Energy Holdings.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is also influenced by their market position and the essential nature of natural gas. For instance, in 2023, China's natural gas production reached approximately 230 billion cubic meters, with domestic supply playing a crucial role in meeting demand.
- Vertical Integration: State-owned suppliers controlling both upstream production and downstream distribution networks.
- Infrastructure Control: Dominance over pipeline networks, impacting access and costs for distributors.
- Market Dominance: Significant share in natural gas production limits alternative supplier options.
Geopolitical and Policy Influence on Supply
The Chinese government's focus on energy security significantly shapes natural gas supply, impacting ENN Energy's bargaining power with its suppliers. Geopolitical considerations and international relationships dictate terms for long-term Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) contracts and pipeline agreements, potentially consolidating the supplier base. This concentration can empower key national and international suppliers, as they become more critical to meeting China's energy demands.
For instance, in 2023, China's natural gas imports reached approximately 150 billion cubic meters, with a substantial portion secured through long-term contracts. The dominance of a few major suppliers in these agreements can translate to greater leverage for them when negotiating prices and terms with distributors like ENN Energy.
- Government Energy Security Goals: China's strategic objectives for energy independence and diversification directly influence the negotiation landscape for natural gas.
- Geopolitical Relationships: Alliances and trade agreements with gas-producing nations strengthen the position of suppliers involved in these partnerships.
- Consolidated Supplier Market: A less fragmented supplier market, often a result of government-backed deals, grants more power to the few dominant players.
- Long-Term Contract Dominance: The prevalence of multi-year LNG and pipeline deals means suppliers have secured demand, enhancing their bargaining strength.
Suppliers of natural gas hold significant sway over ENN Energy due to the concentrated nature of the market and the essential role of natural gas. China's reliance on a few major domestic producers and international LNG suppliers, like PetroChina, which accounts for over 60% of the market, means these entities can dictate terms. Furthermore, ENN Energy faces high switching costs due to long-term contracts and extensive pipeline infrastructure, reinforcing supplier leverage.
The vertical integration of key suppliers, such as PipeChina's new tariff system introduced in early 2024, further concentrates power. This integration allows suppliers to control both production and distribution channels, limiting ENN Energy's options and increasing its dependence. China's energy security goals and geopolitical relationships also consolidate the supplier base, empowering dominant national and international players in long-term contracts.
| Factor | Impact on ENN Energy | 2023/2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | High bargaining power for dominant suppliers | PetroChina supplies >60% of China's natural gas. |
| Switching Costs | High due to long-term contracts and infrastructure | Long-term LNG and pipeline agreements limit flexibility. |
| Vertical Integration | Reduced ENN Energy leverage as suppliers control more of the value chain | PipeChina's 2024 tariff system exemplifies this trend. |
| Government Policy | Energy security goals can consolidate supplier base | China's 2023 natural gas imports reached ~150 billion cubic meters, often via long-term deals. |
What is included in the product
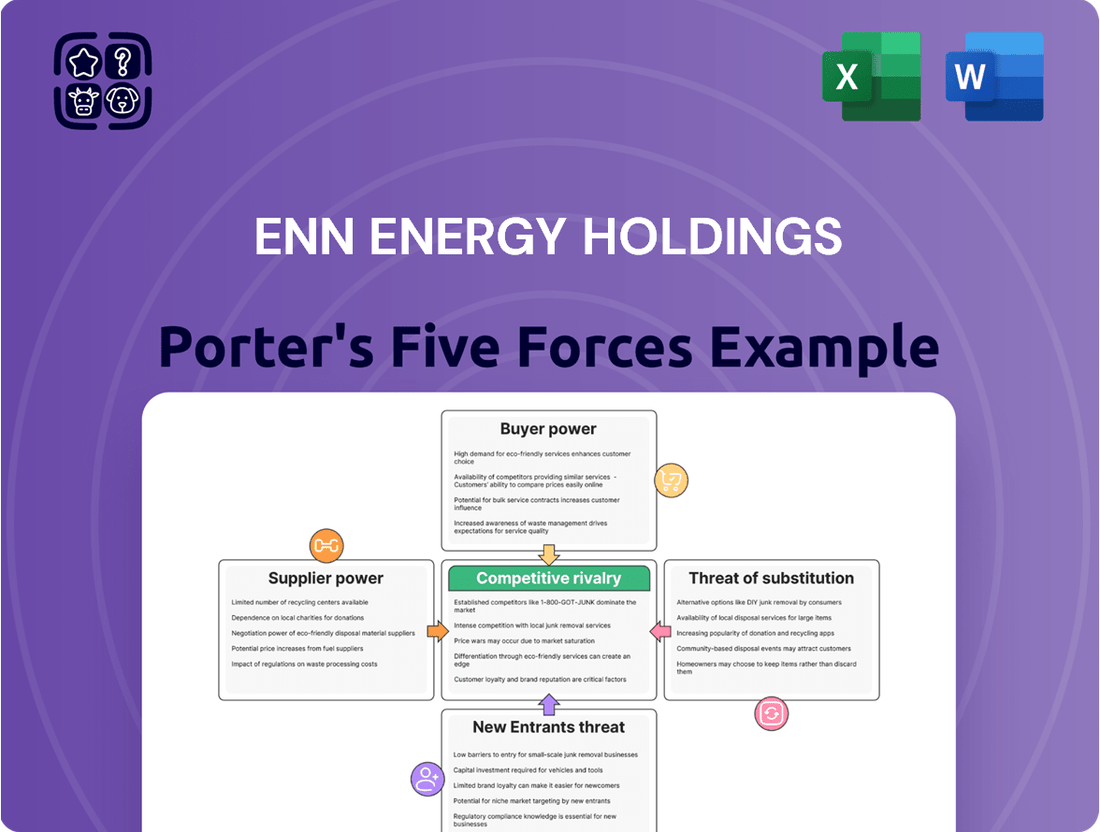
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping ENN Energy Holdings' market, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the energy sector.
Understand the competitive landscape of ENN Energy Holdings with a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
ENN Energy Holdings caters to a broad customer base, encompassing residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. As of December 31, 2024, the company served over 31 million residential households and more than 270,000 industrial and commercial clients.
This extensive diversification across different customer types means that no single segment holds significant sway over ENN Energy's operations. The sheer volume and variety of customers spread the bargaining power, making it less concentrated.
The bargaining power of customers within ENN Energy Holdings is influenced by price sensitivity across different user segments. Industrial and commercial clients often exhibit higher price sensitivity and possess greater flexibility to switch energy providers or negotiate terms, potentially impacting ENN's pricing power.
Conversely, residential customers typically face fewer immediate alternatives and are often subject to regulated pricing structures, which can limit their direct bargaining influence. However, the ongoing rationalization of residential gas pricing mechanisms in China is projected to positively affect gas companies' gross margins, with an expected improvement by 2025.
Customers, especially large industrial and commercial users, are finding more ways to power their operations beyond traditional ENN Energy offerings. The growing availability of alternative energy sources, like solar and wind, coupled with ENN Energy's own expansion into integrated energy services, means clients have more options. This increased choice directly translates to greater bargaining power for these customers.
Customer Switching Costs and Infrastructure
For residential and many commercial customers, switching natural gas providers for ENN Energy Holdings involves significant infrastructure changes and costs, creating a degree of lock-in. This makes it difficult for them to easily move to a competitor, giving ENN some leverage.
However, for large industrial users, the ability to invest in alternative energy systems or negotiate directly with multiple energy providers can lower their effective switching costs. This means ENN must remain competitive to retain these larger clients.
- Customer Lock-in: For residential users, the cost and complexity of changing gas infrastructure effectively tie them to their current provider.
- Industrial Flexibility: Large industrial consumers can more readily explore and adopt alternative energy sources or negotiate better terms, increasing their bargaining power.
- ENN's Competitive Imperative: To counter this, ENN must focus on service quality, pricing, and reliability, especially for its industrial segment.
Government Regulation of End-User Prices
Government regulation of end-user prices, particularly for residential natural gas, can significantly curb the direct bargaining power of individual customers. By implementing price ceilings or offering subsidies, regulatory bodies effectively shield consumers from the full impact of market fluctuations. This intervention limits the ability of customers to negotiate lower prices directly with ENN Energy.
However, China's ongoing market-based reforms are reshaping this dynamic. The focus on channeling civil gas procurement costs and fostering a more competitive environment aims to create a more transparent and potentially price-sensitive market. As of 2024, these reforms are gradually influencing how gas prices are determined, which could indirectly empower customers by creating more pricing visibility and options.
- Price Ceilings and Subsidies: Government-imposed price caps directly limit customer bargaining power.
- Market Reforms in China: Reforms are aimed at improving transparency in gas procurement costs.
- Competitive Landscape: Efforts to enhance competition may eventually offer customers more leverage.
- ENN Energy's Position: ENN Energy operates within this regulated and evolving market structure.
The bargaining power of customers for ENN Energy Holdings is a mixed bag, with significant differences between residential and industrial clients.
While residential customers are largely shielded by regulated pricing and infrastructure lock-in, industrial and commercial users possess greater leverage due to higher price sensitivity and the increasing availability of alternative energy solutions.
As of December 31, 2024, ENN served over 31 million residential households and more than 270,000 industrial and commercial clients, highlighting the broad customer base but also the concentrated power within the larger industrial segment.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on ENN Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | Regulated pricing, high switching costs (infrastructure) | Limited direct bargaining power |
| Industrial/Commercial | Price sensitivity, access to alternative energy, negotiation flexibility | Significant bargaining power, requires competitive pricing and service |
| Overall Customer Base (as of 2024) | 31M+ residential, 270K+ industrial/commercial | Diversified, but industrial segment's power is notable |
Same Document Delivered
ENN Energy Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details ENN Energy Holdings' competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive assessment provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning and future outlook of ENN Energy Holdings within the energy sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
ENN Energy Holdings operates within China's natural gas distribution sector, a market characterized by fragmentation despite ENN's leading position with 261 city-gas projects. This means while ENN is a significant player, it still contends with many other entities in the broader market.
However, a notable shift is occurring. The Chinese government's push for integrating urban pipeline gas infrastructure is driving consolidation. This trend suggests that the competitive landscape is likely to become less fragmented over time, with larger entities potentially absorbing smaller ones.
For ENN Energy, this consolidation presents both opportunities and challenges. It could lead to fewer, but larger, competitors, requiring strategic adaptation. By 2024, the emphasis on integrated energy systems and efficiency in China's energy sector is expected to accelerate this consolidation process.
ENN Energy Holdings operates in a sector where significant capital is tied up in essential infrastructure. Building and maintaining extensive natural gas pipeline networks, storage facilities, and distribution systems demands considerable upfront investment. For instance, in 2023, ENN Energy reported capital expenditures of RMB 17.6 billion, largely directed towards enhancing its integrated energy infrastructure.
These high fixed costs create a strong incentive for companies like ENN Energy to maximize their operational capacity. To achieve economies of scale and effectively recoup these substantial investments, there's a natural drive to capture and retain market share. This often leads to intense competition as players vie for customers and volume to spread their fixed cost burden over a larger base.
Historically, government licensing and regional concessions in China’s gas distribution sector fostered localized monopolies or oligopolies, effectively limiting direct competition within specific service territories. ENN Energy, like its peers, benefited from these structures, ensuring a stable customer base in its granted regions.
However, evolving government policies are reshaping this landscape. The introduction of market-based reforms and initiatives like infrastructure sharing, exemplified by PipeChina's new pipeline transmission tariff system, are gradually fostering greater inter-regional competition. This shift means ENN Energy can no longer solely rely on its established regional dominance, as access to national infrastructure opens doors for competitors.
Product and Service Differentiation
ENN Energy Holdings is actively differentiating its offerings beyond basic natural gas distribution. They are focusing on integrated energy solutions, digital low-carbon services, and developing value-added businesses. This strategic shift aims to move away from intense price competition by providing a more holistic and technologically advanced customer experience.
The company's emphasis on 'intelligence + low carbon' and customer-centric innovations is designed to reduce reliance on pure price-based rivalry. By offering comprehensive services that cater to evolving energy needs, ENN Energy seeks to build customer loyalty and command a premium for its differentiated value proposition. For example, in 2023, ENN Energy reported a 17.7% year-on-year increase in revenue from integrated energy projects, highlighting the growing demand for their advanced solutions.
- Integrated Energy Solutions: ENN Energy is expanding its portfolio to include services like distributed energy, energy storage, and smart grid management, moving beyond simple gas supply.
- Digital Low-Carbon Services: The company is investing in digital platforms and smart technologies to offer customers more efficient and environmentally friendly energy solutions.
- Value-Added Businesses: ENN Energy is developing businesses that complement its core operations, such as energy efficiency consulting and smart home energy management systems.
- Customer-Centric Innovation: A key strategy involves understanding and responding to customer needs with tailored energy solutions, thereby fostering stronger relationships and reducing price sensitivity.
Market Growth and Demand Dynamics
Competitive rivalry within ENN Energy Holdings' market is influenced by growth prospects. China's natural gas consumption is anticipated to expand by 6.5% in 2025, primarily fueled by urban and industrial demand. This robust growth can potentially moderate intense rivalry by ensuring ample opportunities for all market participants to expand their operations.
However, the competitive landscape is not without its challenges. A projected slight deceleration in growth compared to 2024, coupled with the increasing adoption of alternative energy sources, could heighten competition among existing players. This dynamic necessitates strategic maneuvering to maintain market share and capitalize on evolving energy demands.
- Projected Natural Gas Consumption Growth: 6.5% in China for 2025.
- Key Demand Drivers: Urbanization and industrial expansion.
- Competitive Pressure Factors: Slowdown in growth rate from 2024 levels and competition from alternative energy sources.
Competitive rivalry in China's natural gas sector, where ENN Energy Holdings operates, is characterized by a fragmented market with numerous players, though consolidation is underway. High capital intensity for infrastructure creates pressure to maximize capacity, driving competition for market share. Evolving government policies are also fostering greater inter-regional competition, moving away from historical regional monopolies.
ENN Energy is actively mitigating intense rivalry by focusing on integrated energy solutions and digital low-carbon services, aiming to differentiate beyond price. This strategy aims to build customer loyalty and reduce sensitivity to price-based competition. For instance, in 2023, ENN Energy reported a 17.7% year-on-year increase in revenue from integrated energy projects, demonstrating market acceptance of these advanced offerings.
The robust growth in China's natural gas consumption, projected at 6.5% for 2025, can moderate rivalry by providing ample opportunities for expansion. However, a potential slowdown in growth from 2024 levels and the rise of alternative energy sources could intensify competition, necessitating strategic adaptation.
| Metric | 2023 Value | Trend/Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| ENN Energy Capital Expenditure | RMB 17.6 billion | High investment fuels drive for market share to recoup costs, increasing rivalry. |
| Integrated Energy Revenue Growth | +17.7% (YoY) | Successful differentiation reduces reliance on price wars, potentially softening rivalry. |
| Projected China Natural Gas Consumption Growth (2025) | 6.5% | Strong growth can absorb competition, but a slowdown could intensify it. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
China's aggressive push into clean energy, aiming for non-fossil fuels to comprise 20% of its energy mix by 2025, directly impacts ENN Energy. The nation's renewable energy capacity already exceeded 40% of the global total in 2024, signaling a robust alternative to natural gas.
This burgeoning solar and wind power sector presents a substantial long-term threat by offering viable substitutes for natural gas across numerous industrial and residential uses, potentially eroding demand for ENN's core offerings.
Despite global decarbonization trends, coal's role in China's energy mix remains substantial. In late 2024, there was a notable surge in coal power generation, underscoring its continued importance. This resurgence, coupled with potential policy support in certain regions, positions coal as a potent substitute for natural gas, particularly in energy-intensive industries and power generation.
The accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the electrification of industrial operations pose a significant threat of substitution for ENN Energy Holdings. By 2025, new energy vehicle sales are projected to hit 20% of the market, directly impacting the demand for natural gas in transportation.
This trend extends to industrial sectors as well, where processes are increasingly powered by electricity, often sourced from renewables. This growing shift away from fossil fuels like natural gas towards cleaner electrical alternatives represents a substantial and escalating substitution threat for ENN Energy.
Other Fossil Fuels and LPG
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) and other traditional fossil fuels remain viable substitutes for natural gas, especially in regions with limited natural gas infrastructure. These alternatives can sway customer decisions based on their pricing and accessibility. In 2023, global LPG consumption reached approximately 300 million metric tons, highlighting its significant market presence as a substitute.
The cost-competitiveness of LPG and other fossil fuels directly impacts ENN Energy's customer retention and acquisition. For instance, fluctuations in crude oil prices, which influence LPG costs, can make these substitutes more or less attractive compared to natural gas. In early 2024, the average price of Brent crude oil hovered around $80 per barrel, providing a benchmark for the cost dynamics of these competing energy sources.
- LPG Availability: LPG is readily available in many markets, offering a direct alternative for heating and cooking where natural gas pipelines are absent.
- Price Sensitivity: Customer switching behavior is highly sensitive to the price differential between natural gas and its fossil fuel substitutes.
- Infrastructure Dependence: The threat is amplified in areas where the capital investment for natural gas infrastructure is high, making alternative fuels more appealing in the short term.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Measures
Energy efficiency and conservation measures present a significant threat of substitution for ENN Energy Holdings. China's 2024-2025 action plan for energy saving and carbon reduction targets a reduction in energy consumption and CO2 intensity, directly impacting demand for all energy sources, including natural gas. This focus on efficiency effectively acts as a 'negative substitute,' as it diminishes the overall need for energy services.
The drive towards greater energy efficiency means that less of any given energy source is required to achieve the same or better outcomes. For instance, advancements in building insulation, more efficient appliances, and smarter industrial processes all reduce the volume of natural gas needed for heating, cooling, and power generation. This trend can erode market share for traditional energy providers like ENN.
- Reduced Demand: Improved energy efficiency directly lowers the overall demand for natural gas.
- Policy Support: Government initiatives, like China's 2024-2025 action plan, actively promote these efficiency measures.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in energy-saving technologies make conservation increasingly viable and attractive.
- Cost Savings: Consumers and businesses adopting efficiency measures benefit from lower energy bills, making them less reliant on traditional supply.
The threat of substitutes for ENN Energy is significant, driven by China's aggressive clean energy push and the continued presence of coal. Renewables like solar and wind, which already accounted for over 40% of global capacity in 2024, offer a growing alternative to natural gas. Furthermore, the electrification trend, with EVs projected to reach 20% of new vehicle sales by 2025, directly impacts natural gas demand in transportation and industry.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) remains a competitive substitute, especially where natural gas infrastructure is lacking. Global LPG consumption in 2023 was around 300 million metric tons, demonstrating its market relevance. Price sensitivity to crude oil, which averaged around $80 per barrel for Brent in early 2024, directly influences the attractiveness of LPG versus natural gas.
Energy efficiency measures also act as a powerful substitute by reducing overall energy consumption. China's 2024-2025 action plan specifically targets energy saving, diminishing the need for all energy sources, including natural gas. This focus on efficiency, supported by technological advancements and policy, lowers demand and makes consumers less reliant on traditional supplies.
| Substitute | 2024/2025 Relevance | Impact on ENN Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy (Solar/Wind) | Exceeded 40% of global capacity in 2024; China targets 20% non-fossil fuels by 2025 | Erodes demand for natural gas in power generation and industrial uses. |
| Coal | Notable surge in coal power generation in late 2024 | Remains a potent substitute, particularly for energy-intensive industries. |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Projected 20% of new vehicle sales by 2025 | Reduces demand for natural gas in the transportation sector. |
| Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) | ~300 million metric tons global consumption in 2023; Brent crude ~$80/barrel (early 2024) | Offers direct competition based on price and infrastructure availability. |
| Energy Efficiency | China's 2024-2025 action plan for energy saving | Diminishes overall demand for natural gas by reducing energy needs. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a natural gas distribution business, like ENN Energy Holdings operates, requires immense capital for building extensive pipeline networks and related infrastructure. For instance, in 2023, ENN Energy's capital expenditure was approximately RMB 11.7 billion, highlighting the significant investment needed to expand and maintain such operations.
This substantial upfront cost acts as a significant barrier, deterring many potential new entrants who may lack the financial capacity to undertake such large-scale projects. The sheer scale of investment needed to compete effectively in this sector naturally limits the number of viable new players.
The natural gas distribution sector in China, where ENN Energy Holdings operates, is characterized by extensive regulatory and licensing hurdles. New companies entering this market must secure numerous permits and licenses, a process that is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Adherence to stringent safety and environmental standards, mandated by the government, further complicates market entry, acting as a significant barrier.
Existing network effects and a substantial customer base present a significant barrier to new entrants in the energy sector, particularly for companies like ENN Energy Holdings. ENN Energy boasts an extensive pipeline network and serves over 31 million household customers and 270,000 commercial and industrial clients. These established infrastructures and loyal customer relationships, built over years and often cemented by long-standing agreements with local authorities, make it incredibly difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate the same reach and market penetration.
Access to Natural Gas Resources and Supply Chains
Securing reliable and cost-effective access to natural gas, whether from domestic producers or international suppliers like LNG and pipeline gas, is a significant barrier for new entrants into ENN Energy Holdings' market. Existing players often benefit from established long-term contracts and deep-rooted supply chain relationships. This makes it challenging for newcomers to secure comparable supply terms and pricing, directly impacting their ability to compete effectively.
For instance, in 2024, the global LNG market saw continued volatility, with prices influenced by geopolitical events and demand fluctuations. New entrants would face the immediate hurdle of negotiating supply agreements in such an environment, potentially at less favorable rates than established companies like ENN Energy, which likely have secured supply through earlier, more stable contracts. This access disparity is a key component of the threat of new entrants.
- Established Supply Contracts: ENN Energy likely holds long-term agreements with major gas producers, providing price stability and volume security.
- LNG Infrastructure and Sourcing: Access to LNG regasification terminals and diversified international sourcing networks are crucial for new entrants, but often require substantial capital investment and existing relationships.
- Pipeline Access: Securing rights to utilize existing natural gas pipeline infrastructure can be a significant challenge for new market participants.
- Economies of Scale in Procurement: Larger, established players can leverage their scale to negotiate better prices for gas and transportation services.
Government Support for Established Players and Consolidation
While China actively supports clean energy, a key policy is to foster the consolidation and strengthening of existing large urban pipeline gas companies. This strategic direction inherently favors established players, making it more challenging for new entrants to penetrate the core distribution market.
This government stance can be seen in initiatives aimed at creating more robust, integrated energy networks. For instance, in 2023, the state continued to emphasize the importance of large-scale, efficient energy infrastructure, which often involves mergers and acquisitions among existing utility providers.
- Policy Focus on Consolidation: Chinese government policies often prioritize the integration of existing urban gas pipeline networks to improve efficiency and reliability, rather than encouraging a fragmented market with many new entrants.
- Support for Incumbents: This approach provides a degree of implicit support and a favorable operating environment for established companies, potentially limiting the attractiveness of the sector for new, smaller players.
- Barriers to Entry: The drive for consolidation, coupled with the capital-intensive nature of pipeline infrastructure, erects significant barriers to entry for potential new competitors in the core gas distribution business.
The threat of new entrants for ENN Energy Holdings is relatively low due to the substantial capital required for infrastructure development, with ENN Energy's 2023 capital expenditure reaching approximately RMB 11.7 billion. Stringent regulatory and licensing requirements, coupled with established network effects and a large customer base of over 31 million households, further deter new players. Securing reliable and cost-effective gas supply, often through long-term contracts, also presents a significant hurdle for potential competitors.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building extensive pipeline networks requires immense investment. ENN Energy's 2023 CAPEX was ~RMB 11.7 billion. | High financial barrier, limiting the number of capable entrants. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Numerous permits, licenses, and adherence to safety/environmental standards are necessary. | Time-consuming and resource-intensive market entry process. |
| Network Effects & Customer Base | ENN Energy serves over 31 million households and 270,000 commercial/industrial clients. | Difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate ENN's reach and customer loyalty. |
| Supply Chain Access | Securing stable, cost-effective gas supply is challenging, especially in volatile markets like 2024 LNG. | New entrants may face less favorable supply terms and pricing compared to established players. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for ENN Energy Holdings is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, including annual and interim statements, alongside industry-specific research from reputable energy sector publications and market intelligence providers.
We also leverage data from regulatory filings, government energy statistics, and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and external factors influencing ENN Energy Holdings.
