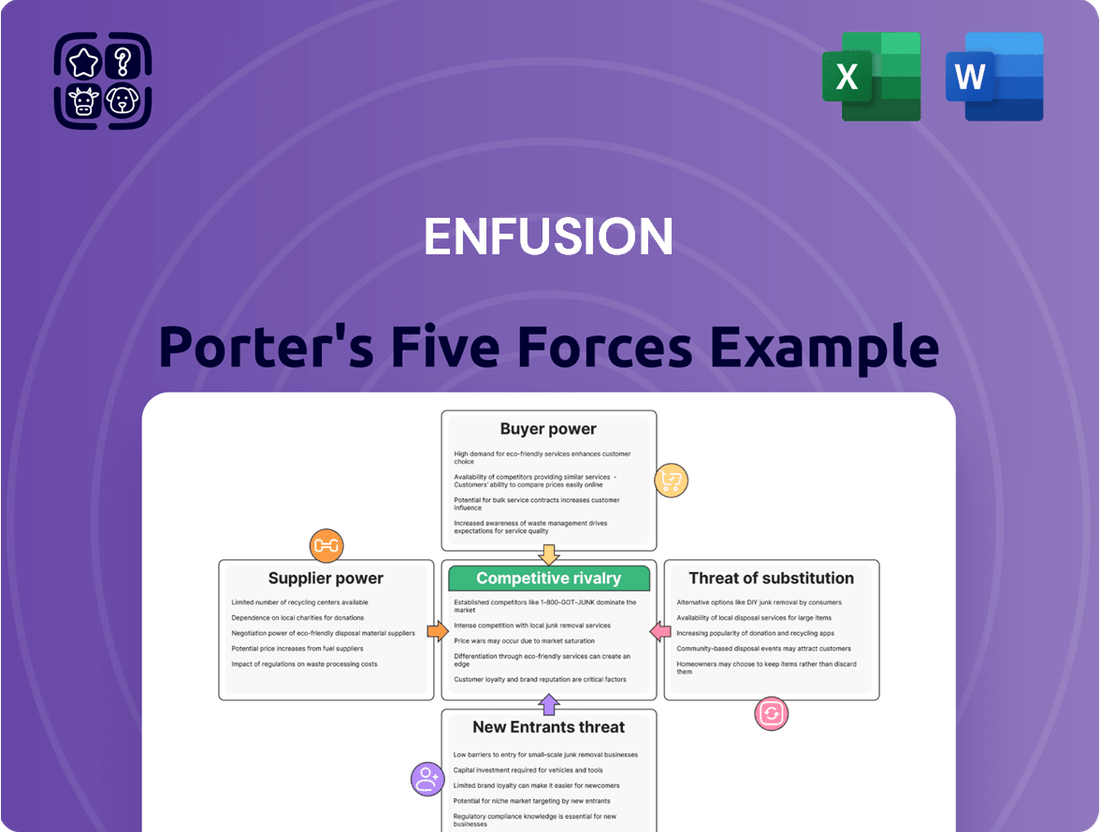
Enfusion Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enfusion Bundle
Our Enfusion Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intricate web of competitive forces shaping its market, from the power of its buyers to the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating Enfusion's landscape effectively.
The complete report goes far beyond this overview, offering a data-driven framework to dissect Enfusion's industry risks and opportunities. Gain actionable intelligence to inform your strategic decisions.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Enfusion’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of generic software and hardware, like those providing cloud infrastructure such as AWS, Azure, or GCP, and standard off-the-shelf components, generally possess limited bargaining power when dealing with a company like Enfusion. This is largely because these services and products are highly commoditized, meaning there are numerous providers offering similar solutions. For instance, the global cloud computing market, dominated by these major players, saw significant growth in 2024, offering ample choice for businesses.
The availability of multiple competitive providers means Enfusion can readily switch suppliers if pricing becomes unfavorable or if service terms are not met. This ease of switching significantly curbs the suppliers' ability to dictate terms. In 2024, the competitive landscape in cloud services continued to intensify, with providers actively competing on price and service offerings to attract and retain customers, further limiting individual supplier leverage.
Suppliers offering highly specialized technology, like niche APIs or critical data feeds for investment management, can exert moderate bargaining power. This is particularly true if their offerings are proprietary or involve significant costs to switch away from, potentially limiting Enfusion's negotiating leverage.
For instance, in 2024, the market for specialized financial data services saw continued consolidation, with fewer providers controlling unique datasets. This trend can increase the dependency on these suppliers. Building robust vendor relationships and securing long-term contracts are therefore strategic imperatives for Enfusion to mitigate this supplier influence.
For general administrative or non-specialized IT roles, the bargaining power of individual labor is typically low. This is because there's a vast pool of qualified candidates available, meaning Enfusion isn't reliant on any single employee. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported over 150 million employed individuals, highlighting the extensive labor market.
Enfusion can recruit from a wide range of candidates for these positions, which effectively mitigates the bargaining power of individual labor as a supplier. This broad talent availability allows Enfusion to maintain competitive compensation and benefits without facing undue pressure from individual employees seeking higher terms.
High Bargaining Power of Highly Skilled Talent
Enfusion faces significant supplier power from highly skilled talent, especially in specialized areas. Professionals like software engineers, quantitative analysts, and financial domain experts, particularly those with experience in cloud-native SaaS for investment management, are in high demand.
This scarcity means Enfusion must offer attractive compensation and benefits to secure and retain these critical employees. For instance, in 2024, the average base salary for a senior software engineer in major tech hubs often exceeded $150,000, with total compensation packages reaching $200,000 or more, significantly impacting labor costs.
- Talent Scarcity: The limited pool of individuals with niche skills in areas like AI-driven trading platforms or advanced data analytics directly translates to higher bargaining power for these professionals.
- Competitive Compensation: To attract top-tier talent, Enfusion is compelled to offer salaries and benefits that compete with other leading technology and financial services firms, driving up operational expenses.
- Retention Challenges: The ease with which highly skilled individuals can find alternative employment elsewhere necessitates continuous investment in retention strategies, further increasing the cost of acquiring and maintaining human capital.
- Impact on Margins: Increased labor costs due to strong supplier power can put pressure on Enfusion's profit margins, especially if these costs cannot be fully passed on to clients.
Dependence on Data Providers and Integrations
Enfusion's platform's extensive reliance on external data feeds and system integrations significantly influences supplier bargaining power. The company integrates with numerous market data providers and trading venues, making these suppliers crucial to its operational integrity.
Suppliers offering unique, real-time financial data or specialized integration services can wield considerable leverage. This is particularly true when their offerings are indispensable and lack readily available substitutes, as seen in the specialized derivatives data market where a few providers dominate.
- Critical Data Dependency: Enfusion's ability to provide clients with accurate, up-to-the-minute market insights hinges on the quality and availability of data from external sources.
- Integration Complexity: The technical effort and cost associated with integrating new data providers or replacing existing ones can be substantial, increasing switching costs for Enfusion.
- Market Data Costs: In 2024, the cost of premium financial data feeds continued to be a significant operational expense for financial technology firms, reflecting the value and exclusivity of the information provided.
Suppliers of generic software and hardware, like cloud infrastructure providers, generally have limited bargaining power due to the commoditized nature of their offerings and the abundance of competitors. This allows Enfusion to readily switch providers if terms are unfavorable, a dynamic reinforced by the intensifying competition in the cloud services market throughout 2024.
However, suppliers of highly specialized technology or critical, proprietary data, such as niche APIs for investment management, can exert moderate bargaining power. This is amplified when switching costs are high, as evidenced by the consolidation in specialized financial data services in 2024, which increased reliance on a few dominant providers.
The bargaining power of labor varies significantly. For general administrative roles, it's low due to a large talent pool, as seen in the U.S. labor market exceeding 150 million employed individuals in 2024. Conversely, highly skilled professionals in areas like AI or quantitative analysis face high bargaining power due to scarcity, driving up compensation and retention costs, with senior software engineers in tech hubs earning upwards of $150,000 base salary in 2024.
Enfusion's dependence on external data feeds and system integrations means suppliers of unique, real-time financial data or specialized integration services hold considerable leverage. The cost of premium financial data feeds remained a significant operational expense in 2024, underscoring the value and exclusivity of such indispensable offerings.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power | Key Factors | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure, GCP) | Low | High competition, commoditized services, ease of switching | Intensifying competition, price wars |
| Specialized Financial Data Providers | Moderate to High | Proprietary data, high switching costs, market consolidation | Consolidation in unique datasets |
| Highly Skilled Labor (Quant Analysts, AI Engineers) | High | Talent scarcity, high demand, competitive compensation | Senior SWE salaries >$150k base |
| General Labor (Admin roles) | Low | Large talent pool, abundant qualified candidates | Over 150 million employed in U.S. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Enfusion's position in the financial technology sector.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a streamlined, intuitive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large institutional investment managers, like BlackRock or Vanguard, represent substantial revenue streams for Enfusion, granting them significant leverage. These clients often have intricate needs, requiring bespoke software functionalities and can negotiate for preferential pricing or robust service level agreements due to the sheer volume of their business and the potential for enduring partnerships.
Mid-sized investment firms often possess moderate bargaining power with financial service providers. While they lack the sheer volume of business that mega-institutions bring, their collective demand and the presence of numerous competing solutions mean they can still negotiate favorable terms, especially on pricing and service customization.
Customers often face substantial switching costs when using a platform like Enfusion, which offers a comprehensive suite of financial solutions. These costs can include the significant effort involved in migrating vast amounts of data, the expense of retraining personnel on new systems, and the disruption caused by reconfiguring existing workflows. For instance, a study by Gartner in 2024 indicated that the average cost for an enterprise to switch financial software can range from 10% to 20% of their annual software budget, a figure that reflects the complexity and integration involved.
These high switching costs directly impact a customer's bargaining power. When the process of moving to a competitor is arduous and costly, customers are less likely to threaten to switch or to demand significant concessions. This integration deepens the customer's reliance on Enfusion's platform, thereby diminishing their leverage and strengthening Enfusion's position by reducing the immediate threat of customer churn.
Demand for Comprehensive, Integrated Solutions
Customers are increasingly looking for all-in-one solutions, often referred to as front-to-back office platforms. This trend helps to reduce the complexity of managing multiple vendors and streamlines operational workflows.
Enfusion's integrated platform directly addresses this demand. By offering a unified solution, the company enhances its value proposition, potentially lessening a customer's desire to negotiate aggressively on individual software components. Instead, the focus shifts to the overall efficiency and suitability of the complete Enfusion offering.
- Demand for Integrated Solutions: A 2024 survey indicated that 65% of financial institutions are prioritizing vendors offering comprehensive, integrated platforms to simplify IT infrastructure and reduce operational overhead.
- Vendor Sprawl Reduction: Companies adopting unified platforms reported an average 15% reduction in IT support costs related to vendor management in late 2023 and early 2024.
- Streamlined Operations: Clients utilizing Enfusion's integrated system have seen an average 20% improvement in trade processing efficiency, a key driver for adopting such solutions.
Customer Sophistication and Customization Needs
Institutional investment managers, Enfusion's target clientele, possess a high degree of financial acumen. This sophistication translates into a demand for highly specialized functionalities and tailored solutions to align with their distinct investment strategies and stringent regulatory frameworks.
This advanced understanding of their operational needs empowers these customers, increasing their bargaining power. They can effectively leverage their requirements for specific developments and adaptations from Enfusion, potentially influencing product roadmaps and pricing structures.
- Sophisticated Client Base: Enfusion primarily serves institutional investment managers, a group known for its deep understanding of financial markets and technology needs.
- Demand for Customization: These clients frequently require bespoke features and integrations to match their unique trading workflows and compliance mandates.
- Increased Bargaining Leverage: The ability to articulate precise functional requirements and the willingness to switch providers if needs aren't met grant these customers significant leverage in negotiations.
Enfusion's customers, particularly large institutional investors, wield considerable bargaining power due to their significant revenue contribution and sophisticated demands. These clients often require highly customized functionalities and can negotiate for favorable pricing or service agreements, as evidenced by the 2024 Gartner study showing enterprise software switching costs between 10-20% of annual budgets.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Enfusion |
| Large Institutional Investors | High volume, complex needs, demand for customization | Significant leverage on pricing and service level agreements. |
| Mid-sized Firms | Collective demand, numerous alternatives | Moderate leverage, can negotiate on pricing and customization. |
| All Clients | High switching costs (data migration, retraining) | Reduces likelihood of switching, strengthens Enfusion's position. |
What You See Is What You Get
Enfusion Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The preview you see is the exact Enfusion Porter's Five Forces Analysis document you will receive after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. This professionally formatted analysis details the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You'll gain immediate access to this complete, ready-to-use file upon completing your purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The investment management software market is a crowded space, with many established players holding significant sway. Firms like BlackRock’s Aladdin, SS&C Technologies, and FIS have built substantial client networks and offer comprehensive suites of services. This deep-rooted presence creates a formidable barrier for new entrants and intensifies the battle for market share among existing vendors.
Beyond the major software providers, Enfusion also contends with a landscape of niche and boutique firms. These smaller, specialized companies often focus on very specific functionalities within the broader financial technology space, such as advanced risk analytics, bespoke portfolio optimization, or highly targeted order management systems.
These niche players can be particularly disruptive because they offer deep expertise and tailored solutions that might resonate strongly with particular client segments. For instance, a boutique firm specializing in complex derivatives risk might attract clients who find Enfusion's broader platform less adept in that specific area.
While the overall market share of these boutique providers may be smaller, their ability to innovate rapidly and cater to unmet needs within specific niches intensifies competitive pressure on Enfusion. This dynamic was evident in 2024, where several specialized fintechs saw significant funding rounds, indicating investor confidence in their focused strategies.
Competitive rivalry in the financial technology sector, particularly for platforms like Enfusion, is intensely driven by continuous innovation and product differentiation. Companies must consistently upgrade their cloud-native infrastructure, roll out new functionalities, refine user interfaces, and maintain strict regulatory adherence to maintain a competitive edge. This dynamic necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in research and development, often resulting in aggressive feature development and what is commonly referred to as feature wars.
For instance, the global FinTech market size was valued at approximately $1.15 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, with compound annual growth rates expected to be robust through 2030. This expansion fuels the need for differentiation. Enfusion, as a provider of integrated front-to-back office solutions, faces rivals who are also investing heavily in AI-driven analytics, enhanced data visualization, and seamless integration capabilities. The pressure to offer superior performance, scalability, and security in a rapidly evolving digital landscape means that companies cannot afford to stand still. In 2024, we see continued focus on generative AI applications within financial workflows and the ongoing development of low-code/no-code customization options to attract a broader client base. The cost of staying competitive includes not just developing new features but also ensuring these innovations are robust, secure, and meet the stringent demands of institutional investors.
Pricing Pressure in a Maturing Market
As the investment management software market matures, particularly for established core features, Enfusion likely faces increasing pricing pressure. Competitors may resort to aggressive pricing tactics to capture market share or retain existing clients, potentially impacting Enfusion's profit margins. This necessitates a strong emphasis on Enfusion's unique value proposition to justify its pricing structure.
In 2024, the software-as-a-service (SaaS) market, where Enfusion operates, saw continued competition. For instance, reports indicated that average contract values for financial technology solutions remained competitive, with some vendors offering tiered pricing or discounts to attract new business. This environment means Enfusion must clearly articulate the advanced capabilities or superior service that differentiates it.
- Intensified Competition: The maturation of the investment management software market leads to increased rivalry among established players and emerging fintech firms.
- Aggressive Pricing Strategies: Competitors may employ lower pricing, bundled services, or promotional discounts to gain or maintain customer bases.
- Profitability Impact: Persistent price wars can erode profit margins for all market participants, including Enfusion.
- Value Proposition Necessity: Enfusion must effectively communicate its unique benefits and return on investment to command premium pricing.
Talent Acquisition and Retention as a Competitive Factor
The intense competition for skilled professionals, especially those adept in both finance and cutting-edge cloud technologies, significantly shapes competitive rivalry. Companies actively seek top-tier engineers, product managers, and sales experts, making talent acquisition a crucial battleground.
The demand for these specialized skills drives up compensation and necessitates robust retention strategies. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a cloud engineer in the financial sector saw an increase of approximately 15% compared to the previous year, reflecting this high demand.
- Talent Demand: High demand for individuals with combined finance and cloud expertise.
- Compensation Trends: Increasing salaries and benefits to attract and retain top talent.
- Retention Challenges: Firms invest heavily in employee development and work environment to prevent attrition.
- Competitive Edge: Companies with superior talent acquisition and retention capabilities gain a significant advantage.
The investment management software market is characterized by intense competition, with established giants like BlackRock's Aladdin and SS&C Technologies dominating. Smaller, specialized fintech firms also pose a threat by offering niche solutions, and this dynamic was underscored in 2024 by significant funding rounds for several specialized players. Enfusion must continually innovate its cloud-native infrastructure and functionalities, a trend evident in the market's substantial growth, projected to continue robustly through 2030. This necessitates substantial R&D investment, with a particular focus on AI-driven analytics and enhanced data visualization.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors | 2024 Trend Highlight |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Front-to-Back Office | BlackRock Aladdin, SS&C Technologies, FIS | Continued investment in AI and cloud infrastructure |
| Niche Solutions (e.g., Derivatives Risk) | Various Boutique Fintechs | Increased VC funding and product specialization |
| Overall FinTech Market | Broad spectrum of providers | Projected strong CAGR through 2030, driving differentiation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large investment management firms, particularly those with substantial IT budgets exceeding $50 million annually, might opt to build their own trading and portfolio management systems instead of subscribing to external SaaS providers. For instance, firms managing over $100 billion in assets often have the capital to invest in custom solutions, aiming for complete control over their technology stack. This internal development, while requiring significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance, can significantly reduce long-term operational costs and offer a competitive edge through tailored functionality, thereby posing a direct threat to vendors like Enfusion.
Manual processes and legacy systems present a threat of substitutes for modern SaaS platforms, especially for smaller or less technologically advanced firms. The perceived high cost and complexity of migrating from existing, albeit inefficient, systems can deter adoption. For instance, many small businesses still rely heavily on spreadsheets for financial management, a practice that, while functional, lacks the automation and real-time insights of cloud-based solutions.
Firms increasingly consider a best-of-breed strategy, integrating multiple specialized point solutions instead of a single, comprehensive platform. This approach allows for tailored functionality, potentially substituting for integrated solutions like Enfusion. For instance, a firm might use a leading portfolio management system alongside a separate best-in-class accounting software.
While this disaggregated model offers customization, it frequently creates significant integration challenges and can lead to higher overall costs. In 2024, the market for specialized financial technology solutions continued to grow, with many firms prioritizing flexibility over a single vendor. This trend directly challenges the value proposition of all-in-one platforms by offering specialized, often more advanced, capabilities in specific functional areas.
Consulting Services and Outsourcing
Firms may opt to outsource specific functions, such as back-office operations or risk analysis, to external consultants or service providers instead of implementing a software platform. These outsourced services, while not direct software substitutes, address similar client needs, offering an alternative approach to managing investment operations.
The global business process outsourcing (BPO) market, which includes many of these consulting services, was valued at approximately $260 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow. This indicates a significant market for outsourcing that competes for the same budget allocation as software solutions.
- Market Size: The BPO market represents a substantial alternative for firms seeking to manage investment operations.
- Service Overlap: Outsourcing firms often provide specialized services that directly mirror functionalities offered by investment management software.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Clients may find outsourcing more cost-effective or flexible for certain tasks compared to investing in and maintaining proprietary software.
- Strategic Fit: For some companies, outsourcing specific functions aligns better with their overall business strategy than adopting a new software platform.
Generic Business Software with Customizations
While specialized financial software is the norm, some firms might try to adapt generic business software like ERP or CRM systems with significant customizations to handle investment operations. This approach, though often inefficient for complex financial tasks, can represent a lower-cost alternative for companies hesitant to invest in dedicated industry solutions.
For instance, a small hedge fund might attempt to build out custom modules within a widely available CRM platform to track trades and client portfolios. This might seem like a cost-saving measure compared to a bespoke portfolio management system, but the ongoing maintenance and integration challenges can quickly outweigh initial savings.
- Limited Functionality: Generic software often lacks the deep, specialized functionalities required for sophisticated financial modeling, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
- High Customization Costs: While the base software might be cheaper, extensive customization to meet financial industry needs can become prohibitively expensive and time-consuming.
- Scalability Issues: As operations grow, these heavily customized generic systems may struggle to scale effectively, leading to performance bottlenecks.
- Security and Compliance Risks: Generic platforms may not inherently meet the stringent security and compliance standards demanded by financial regulators, posing significant risks.
The threat of substitutes for Enfusion arises from various alternatives that fulfill similar needs. Firms can build in-house systems, especially those with significant IT budgets like large investment management firms managing over $100 billion in assets. Many smaller or less tech-savvy firms continue using manual processes or legacy systems, finding the cost and complexity of migration prohibitive. Additionally, a growing trend involves adopting a best-of-breed strategy, integrating multiple specialized software solutions instead of a single, comprehensive platform.
Outsourcing specific functions, such as back-office operations, to external providers also serves as a substitute. The global business process outsourcing market, valued at approximately $260 billion in 2023, highlights the significant demand for these services. Furthermore, some companies attempt to adapt generic business software like ERP or CRM systems, though these often lack the specialized financial functionalities and can incur high customization costs.
| Substitute Type | Description | Key Considerations | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Development | Building proprietary trading and portfolio management systems. | High upfront investment, ongoing maintenance, full control. | A $150 billion AUM firm with a $75 million IT budget. |
| Manual/Legacy Systems | Continuing to use existing, often inefficient, systems. | Perceived high migration costs, resistance to change. | A small regional investment firm still relying on spreadsheets. |
| Best-of-Breed Strategy | Integrating multiple specialized software solutions. | Tailored functionality, potential integration challenges. | Using a top-tier PMS with a separate leading accounting package. |
| Outsourcing Services | Engaging external providers for specific operational functions. | Addresses similar needs as software, competes for budget. | A firm outsourcing its compliance reporting. |
| Customized Generic Software | Adapting ERP or CRM systems for financial operations. | Lower initial cost, limited functionality, high customization needs. | A startup fund using a modified CRM for client and portfolio tracking. |
Entrants Threaten
Developing a complete, cloud-native SaaS platform akin to Enfusion's demands substantial capital for research and development, infrastructure build-out, and skilled personnel acquisition. This considerable financial hurdle effectively deters many prospective competitors from attempting to create comparable, all-encompassing solutions, thereby mitigating the threat of new entrants.
Entering the investment management software arena requires a profound understanding of financial markets and intricate investment strategies. New players must navigate a complex web of regulations, demanding significant investment in specialized knowledge and compliance infrastructure.
For instance, in 2024, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) continued to emphasize robust compliance, particularly around areas like cybersecurity and data privacy, adding layers of complexity for software providers. This need for deep domain expertise and adherence to evolving regulatory landscapes, such as those governed by MiFID II in Europe, presents a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants.
Established players like Enfusion possess significant advantages due to their existing brand recognition and the deep client trust they've cultivated within the demanding financial sector. This trust is hard-won, built over years of reliable service and proven performance in managing complex financial operations.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in establishing credibility and convincing institutional clients to migrate from established, trusted providers. The financial industry places an immense premium on reliability and security, making clients hesitant to switch from solutions they know and depend on for safeguarding sensitive data and executing critical transactions.
Network Effects and Integration Challenges
Integrated platforms, like those in the investment management software space, often thrive on network effects. This means the more users and complementary services a platform has, the more valuable it becomes for everyone involved. For instance, a platform with extensive integrations to various data providers and trading venues becomes more attractive than a standalone solution.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating this. They must invest heavily to build a comprehensive ecosystem of integrations with essential financial infrastructure, such as market data vendors, custodians, and core banking systems. This process is not only costly but also takes considerable time, creating a substantial barrier to entry for newcomers aiming to compete with established, integrated players.
By mid-2024, the financial technology sector continued to see consolidation, with many firms prioritizing seamless integration. For example, major cloud providers expanded their financial services offerings, emphasizing the importance of interconnectedness. This trend highlights the difficulty for a new entrant to offer a compelling alternative without a pre-existing, robust network of partnerships and integrations.
- Network Effects: Value increases with user base and integrated services.
- Integration Costs: Building connections to data providers and custodians is resource-intensive.
- Ecosystem Development: New entrants must replicate existing integration networks.
- Market Trends: Mid-2024 saw continued emphasis on integrated financial technology solutions.
High Switching Costs for Customers
Customers deeply integrated with existing investment management platforms often face substantial switching costs. These costs can include data migration, retraining staff, and potential disruptions to ongoing operations. For instance, a study in 2024 found that the average cost for a financial institution to switch its core banking system could range from millions to tens of millions of dollars, a significant barrier for new entrants. This embeds loyalty and makes it challenging for newcomers to attract established client bases.
The perceived benefits of switching must therefore be exceptionally high to justify the considerable financial and operational investment. New entrants must offer not just competitive pricing but also demonstrably superior technology, functionality, or service levels to overcome this inertia. Without a compelling value proposition, the threat of new entrants remains muted due to these entrenched customer relationships.
- High Switching Costs: Customers are deeply embedded, making migration complex and expensive.
- Operational Disruption: Changing platforms can interrupt daily business activities.
- Data Migration Challenges: Transferring vast amounts of sensitive financial data is a significant hurdle.
- Training and Adaptation: New systems require staff retraining, adding to the overall cost and time investment.
The threat of new entrants for platforms like Enfusion is relatively low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for development and infrastructure, coupled with the need for deep financial market expertise and regulatory compliance, deter many potential competitors. For example, in 2024, the increasing complexity of financial regulations, such as those surrounding data privacy and cybersecurity, further elevated these entry costs.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Enfusion Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, leveraging annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
