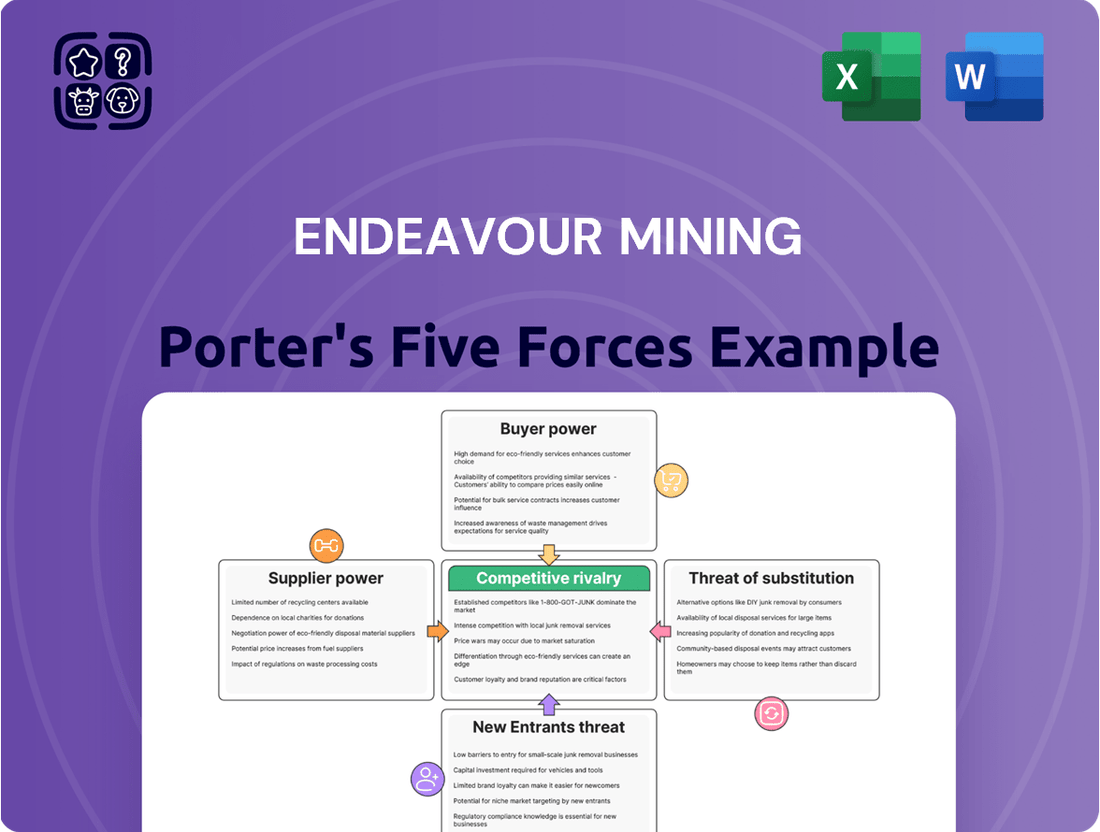
Endeavour Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Endeavour Mining Bundle
Endeavour Mining operates within a dynamic gold mining sector, facing significant pressures from powerful suppliers and intense rivalry among established players. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Endeavour Mining’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The gold mining sector, including companies like Endeavour Mining, is heavily dependent on specialized equipment, advanced technology, and essential services. This reliance creates a potential vulnerability if the supply market is concentrated.
A small number of global manufacturers for critical items such as heavy-duty excavators, sophisticated drilling rigs, and specialized processing chemicals hold considerable leverage. For instance, Caterpillar and Komatsu are dominant players in heavy machinery, and their pricing and availability directly impact mining operations.
These key suppliers often possess unique, patented technologies or benefit from significant economies of scale. This makes it challenging and costly for mining firms to switch to alternative suppliers, as doing so could lead to substantial upfront investment, integration issues, and potential disruptions to ongoing production schedules.
High switching costs for critical mining equipment and specialized services directly empower suppliers. Endeavour Mining faces substantial expenses and operational disruptions when changing vendors, including retooling machinery and retraining staff. For instance, a significant portion of mining operations relies on proprietary software for geological analysis and equipment maintenance, making a shift to a new provider incredibly complex and costly.
Certain raw materials, energy, and specialized technical expertise are absolutely crucial for Endeavour Mining's gold extraction and processing operations. Without them, production simply grinds to a halt. This reliance is a key factor in understanding their position.
Disruptions in the supply of these critical inputs, or significant price increases, can directly impact Endeavour Mining's production volumes and ultimately, their profitability. For instance, fluctuations in global energy prices, a major cost component for mining, directly affect their bottom line. In 2023, Endeavour Mining reported total operating costs of $1,249 million, with energy being a significant portion of that.
This dependence on a limited number of suppliers for specialized equipment or essential commodities gives those suppliers considerable leverage in negotiations. If a key supplier can't deliver or demands higher prices, Endeavour Mining has few immediate alternatives, impacting their ability to control costs and maintain consistent output.
Supplier Differentiation
Supplier differentiation significantly impacts bargaining power. When suppliers offer unique, specialized products or services, their influence grows. For Endeavour Mining, this could mean access to advanced exploration technology or innovative, eco-friendly processing solutions that are not readily available elsewhere.
These differentiated offerings allow suppliers to command better terms and pricing because Endeavour Mining may find it essential to secure them to maintain a competitive edge or comply with evolving environmental regulations. For instance, a supplier of a proprietary, low-emission cyanide leaching technology could hold considerable sway over Endeavour Mining's operational choices and costs.
- Supplier Differentiation: Endeavour Mining's reliance on suppliers with unique technologies, like advanced geophysical survey equipment or specialized chemical reagents for mineral processing, increases supplier bargaining power.
- Competitive Edge & Regulatory Compliance: Endeavour Mining's pursuit of cutting-edge exploration techniques or sustainable mining practices, often provided by specialized suppliers, grants these suppliers leverage in negotiations.
- Impact on Endeavour Mining: The need for these differentiated inputs can lead to higher costs or stricter contract terms for Endeavour Mining, influencing its operational efficiency and profitability.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration, while less prevalent in the mining industry, can significantly bolster their bargaining power. Should a major equipment manufacturer or a specialized technology provider decide to enter the gold mining space directly, it could create a scenario where existing mining operations face restricted access to essential goods or inflated prices for their products.
This hypothetical scenario, though rare, exerts a subtle but tangible influence on negotiations between mining companies like Endeavour Mining and their key suppliers. For instance, if a leading supplier of advanced autonomous mining vehicles were to establish its own mining ventures, it might prioritize its internal operations, potentially reducing availability or increasing costs for third-party buyers.
- Forward Integration by Suppliers: A theoretical risk where suppliers enter the mining business themselves.
- Impact on Endeavour Mining: Could lead to reduced supply or higher costs for essential equipment and technology.
- Negotiation Leverage: This potential threat can influence pricing and terms in supplier contracts.
Suppliers of specialized mining equipment, critical chemicals, and essential energy resources hold significant bargaining power over Endeavour Mining. This is due to the concentrated nature of some supplier markets and the high costs associated with switching vendors for vital operational inputs.
The dependence on a few key manufacturers for heavy machinery and advanced processing technology means Endeavour Mining has limited alternatives if these suppliers dictate terms. For example, Caterpillar and Komatsu dominate the heavy equipment sector, influencing pricing and availability for mining operations.
High switching costs, including retooling and retraining, further empower suppliers. Endeavour Mining's reliance on proprietary software for geological analysis and equipment maintenance exemplifies this, making transitions complex and expensive.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Endeavour Mining | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Market | Limited alternatives, increased supplier leverage | Few global manufacturers for specialized excavators and drilling rigs |
| High Switching Costs | Difficulty in changing suppliers, supplier pricing power | Proprietary software for geological analysis and equipment maintenance |
| Supplier Differentiation | Suppliers with unique technologies command better terms | Proprietary low-emission cyanide leaching technology |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for reduced supply or higher costs | Hypothetical scenario of equipment manufacturers entering mining |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Endeavour Mining, this Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the industry's competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes, providing strategic insights into Endeavour's market position.
Understand the competitive landscape at a glance, simplifying strategic planning for Endeavour Mining.
Easily identify and address key industry pressures, from supplier power to substitute threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
Endeavour Mining's primary customers, including global bullion dealers, central banks, and industrial users, represent a highly fragmented and diverse market. This diffusion of buyers means that no single entity possesses substantial leverage to influence the price of gold.
The inherent global nature of the gold market further amplifies this broad demand base. In 2024, the average gold price hovered around $2,300 per ounce, reflecting a robust global demand that prevents any individual customer from wielding significant price-setting power.
The bargaining power of customers in the gold market, and thus for Endeavour Mining, is exceptionally low. Gold is a globally traded commodity with a standardized price, meaning individual buyers cannot negotiate better terms for the raw material itself. For instance, in 2024, the price of gold remained a significant driver of revenue, fluctuating based on broader market forces rather than any single customer's purchasing power.
During periods of economic turbulence, such as those seen in 2024, investors often flock to gold as a secure store of value. This increased demand for safe-haven assets directly benefits gold producers like Endeavour Mining. For instance, in early 2024, gold prices saw significant upward movement, reaching record highs, which indicates a strong buyer appetite even with potential price increases.
Limited Product Differentiation
The bargaining power of customers for Endeavour Mining is significantly influenced by the limited product differentiation in the gold market. Gold, by its very nature, is a commodity where origin or brand loyalty plays a minimal role for most buyers. This means customers, whether they are jewelers, industrial users, or investors, focus primarily on the price and purity of the gold they purchase.
Consequently, Endeavour Mining faces a challenge in commanding premium pricing solely based on its brand reputation. The inherent fungibility of gold means that buyers can easily switch between suppliers if price or quality is not met, thereby strengthening their negotiating position. This dynamic limits Endeavour’s ability to exert significant influence over its customer base.
- Gold is a fungible commodity with minimal perceived differences between producers.
- Customers prioritize price and purity over brand when purchasing gold.
- Endeavour Mining struggles to differentiate its product to justify higher prices based on brand alone.
- This lack of differentiation grants customers considerable leverage in price negotiations.
Customer Information Asymmetry
Customer information asymmetry is a key factor in the gold market. Large institutional buyers, such as investment funds and central banks, possess sophisticated analytical capabilities and access to vast amounts of real-time data on global supply, demand, and price trends. This accessibility to comprehensive market intelligence significantly diminishes any information advantage Endeavour Mining might otherwise hold, thereby limiting the company's ability to leverage information gaps to its benefit.
For Endeavour Mining, this means that major customers are well-informed about production costs, inventory levels, and future market outlooks. For instance, by mid-2024, gold prices were influenced by factors like interest rate expectations and geopolitical stability, information readily available to all major market participants. This transparency directly impacts the bargaining power of these customers, as they can make informed decisions based on a clear understanding of market dynamics.
- Informed Buyers: Institutional buyers in the gold market have access to detailed global supply, demand, and price forecasts.
- Reduced Asymmetry: This extensive information reduces any potential information advantage Endeavour Mining might possess.
- Limited Leverage: The high level of customer knowledge keeps the bargaining power of these buyers relatively low.
The bargaining power of customers for Endeavour Mining is notably low due to the fungible nature of gold and a fragmented buyer base. In 2024, global gold prices, averaging around $2,300 per ounce, were dictated by macroeconomic factors and broad market sentiment rather than individual customer demands. This lack of product differentiation means buyers prioritize price and purity, limiting Endeavour's ability to command premium pricing based on brand alone.
| Factor | Impact on Endeavour Mining | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | No single customer dominates demand. | Low |
| Product Fungibility | Gold is a standardized commodity. | High |
| Price Sensitivity | Buyers focus on market price and purity. | High |
| Information Availability | Buyers possess extensive market data. | Low |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Endeavour Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Endeavour Mining delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. What you're previewing is the final, professionally formatted version you'll receive instantly after purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The gold mining sector, especially in West Africa, is populated by a number of significant companies. Endeavour Mining contends with established giants such as AngloGold Ashanti, Newmont Corporation, Gold Fields, and Barrick Gold, signaling a substantial level of competition.
These major players possess considerable resources and operational scale, intensifying the rivalry. For instance, in 2023, Newmont Corporation reported total gold sales of approximately 5.5 million ounces, demonstrating the sheer size of some competitors Endeavour faces.
While West Africa's gold production is expected to increase, the global gold mining sector is largely mature. This means companies often vie for existing market share rather than solely capitalizing on overall market growth, which can heighten competitive rivalry as firms aim to boost their reserves and output.
Gold, being a fundamental commodity, offers very little room for product differentiation among mining companies. This means that Endeavour Mining, like its peers, faces intense competition primarily based on operational efficiency and the quality of its mineral reserves.
The lack of product uniqueness forces companies to focus on cost leadership. For instance, in 2023, Endeavour Mining reported an all-in sustaining cost (AISC) of $967 per ounce, a figure that directly impacts its competitiveness against rivals who might achieve lower production costs.
Consequently, the drive for profitability hinges on continuous operational optimization, securing access to high-grade gold deposits, and managing production costs effectively. Companies that excel in these areas are better positioned to thrive in this highly competitive landscape.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The gold mining industry, including companies like Endeavour Mining, is characterized by exceptionally high fixed costs. These initial investments cover everything from extensive exploration and mine development to the construction of essential infrastructure like processing plants and transportation networks. For instance, developing a new gold mine can easily cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
These substantial upfront expenditures, combined with the long operational life of mines and the significant financial commitments for eventual environmental rehabilitation and closure, erect formidable exit barriers. Companies are essentially locked into their investments, making it difficult and costly to cease operations. This situation can fuel intense competition, as firms may feel compelled to maintain production and revenue streams even when market conditions are unfavorable, simply to cover ongoing operational expenses and avoid the penalties associated with early closure.
The impact of these high fixed costs and exit barriers on competitive rivalry is profound:
- Increased Pressure to Maintain Production: Companies are driven to keep mines operational to amortize their large capital outlays, leading to a more aggressive competitive stance.
- Slower Industry Consolidation: High exit barriers can make mergers and acquisitions more complex and less frequent, as acquiring companies must also assume these significant liabilities.
- Price Sensitivity: In periods of low gold prices, the need to cover fixed costs can make companies more sensitive to price fluctuations, potentially leading to price wars.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
The intensity of competition within the gold mining sector is significantly shaped by the strategic aims of rival companies. These objectives often involve ambitious expansion projects, strategic mergers and acquisitions, or a concentrated focus on lucrative geographical areas such as West Africa.
This dynamic is clearly illustrated by the substantial merger and acquisition activity observed in the West African mining landscape. In 2024 alone, deals in this region reached an estimated value of US$4 billion, underscoring a highly active and competitive marketplace.
- Aggressive Expansion: Competitors may pursue growth through developing new mines or increasing production at existing ones.
- Mergers & Acquisitions: Consolidation is a key strategy, with significant deal-making evident in regions like West Africa.
- Regional Focus: Companies often target specific geographic areas rich in mineral resources, like West Africa, to gain market share.
- Market Share Goals: Strategic objectives are frequently tied to increasing overall market share and establishing dominance.
The gold mining sector, particularly in West Africa where Endeavour operates, is characterized by robust competition from established global players. These companies, including AngloGold Ashanti, Newmont Corporation, Gold Fields, and Barrick Gold, possess significant resources and operational scale, creating an intense rivalry. For instance, in 2023, Newmont Corporation reported total gold sales of approximately 5.5 million ounces, highlighting the formidable size of Endeavour's competitors.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for gold as an investment is significant, especially when economic conditions favor other assets. During stable economic periods in 2024, investors often turn to fiat currencies, government bonds, and real estate, which can offer predictable income streams or capital appreciation. For instance, the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield fluctuated around 4.2% in early 2024, providing a competitive alternative to gold's non-yielding nature.
Furthermore, a diverse range of financial instruments, including stocks and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) tracking various sectors, present compelling alternatives. The S&P 500, for example, saw robust growth in 2023 and continued positive momentum into early 2024, attracting capital that might otherwise flow into gold. This broad availability of return-generating assets directly competes with gold's role as a safe-haven or inflation hedge.
Gold faces a moderate threat from substitutes in both its industrial and jewelry applications. In industrial uses like electronics and dentistry, advancements in less expensive metals or high-performance composites offer viable alternatives, potentially reducing gold's necessity in certain manufacturing processes.
The jewelry market, a significant driver of gold demand, is particularly susceptible to substitute materials and evolving consumer preferences. For example, the jewelry sector experienced a notable demand reduction of 10-20% in 2024-2025, largely attributed to elevated gold prices, highlighting the price sensitivity and the potential for consumers to shift towards more affordable or trend-driven alternatives.
The rise of digital currencies, like Bitcoin, and other alternative stores of value presents a potential, albeit nascent, threat to gold's long-standing position as a safe-haven asset. While still developing, these digital assets could eventually offer similar inflation-hedging properties. For instance, Bitcoin's market capitalization fluctuated significantly in 2024, reaching highs that rivaled smaller national economies, indicating growing investor interest in alternative digital stores of value.
However, gold's deep historical precedent and its physical tangibility offer a robust defense against these emerging substitutes. Unlike digital currencies, gold has been a recognized store of value for millennia, instilling a level of trust and familiarity that digital assets are still building. In 2024, global central bank gold reserves remained substantial, underscoring gold's continued perceived stability in financial planning.
Perceived Value and Cultural Significance
Gold's deep-rooted cultural significance and its long-standing perception as a store of value, especially during turbulent economic and geopolitical periods, significantly dampen the threat of substitutes for Endeavour Mining. This intrinsic appeal is hard for other assets to match, particularly when investors seek stability.
The enduring demand for gold as a safe-haven asset is evident in its price performance during periods of heightened global uncertainty. For instance, in 2024, as geopolitical tensions persisted and inflation concerns lingered, gold prices saw notable increases, demonstrating its continued relevance as a hedge against risk.
This inherent value proposition makes it challenging for alternative assets to fully replicate gold's role in investor portfolios. While other commodities or financial instruments might offer diversification, they often lack the same historical backing and widespread cultural acceptance that gold commands.
- Enduring Safe-Haven Status: Gold's historical role as a hedge against inflation and economic downturns limits the appeal of substitutes.
- Cultural Significance: Gold's widespread cultural and historical importance as a symbol of wealth and security is difficult for alternatives to replicate.
- Limited Substitutability in Crisis: During periods of geopolitical instability, investors often flock to gold, showcasing the limited substitutability of other assets in such scenarios.
- Price Resilience in 2024: Gold prices demonstrated resilience throughout 2024, reflecting continued investor confidence in its value as a safe asset amidst global uncertainties.
Inflationary Pressures and Geopolitical Risks
Persistent inflation and heightened geopolitical risks, particularly evident in 2024 and projected into 2025, tend to bolster gold's appeal as an investment. This environment diminishes the attractiveness of many potential substitutes for gold.
Gold's historical performance as a hedge against these specific economic and political uncertainties makes it a more desirable asset class. Consequently, the threat posed by substitutes is lessened as investors seek the perceived safety and stability of gold.
- Inflationary Environment: In 2024, inflation rates remained a significant concern globally, with many developed economies experiencing levels above central bank targets. For instance, the US CPI averaged around 3.4% in the first half of 2024, prompting a flight to assets like gold.
- Geopolitical Instability: Ongoing conflicts and trade tensions in various regions throughout 2024 have increased market volatility, driving demand for safe-haven assets.
- Gold as a Hedge: Historically, gold has shown a positive correlation with periods of high inflation and geopolitical uncertainty, outperforming many traditional financial instruments during such times.
- Reduced Substitute Attractiveness: Assets like cryptocurrencies or certain commodities, while sometimes considered alternatives, may not offer the same degree of perceived stability or historical track record as gold in these specific challenging conditions.
The threat of substitutes for gold is moderate, influenced by its dual role as an investment and a commodity. While fiat currencies and bonds offer yield, gold's safe-haven status during economic uncertainty, as seen in 2024 with persistent inflation concerns, provides a distinct advantage.
In industrial applications, advancements in materials science offer alternatives, but gold's unique properties limit widespread substitution. The jewelry market, however, is more susceptible to price sensitivity and alternative metals, with demand shifts observed in 2024 due to elevated prices.
Digital currencies like Bitcoin are emerging as potential substitutes for gold's store-of-value function, gaining traction in 2024. Yet, gold's millennia-old track record and physical tangibility offer a significant barrier to complete displacement.
The sustained demand for gold as a hedge against inflation and geopolitical risks, particularly prominent in 2024, underscores the limited substitutability of other assets in providing comparable perceived stability and historical precedent.
| Asset Class | 2024 Performance Indicator (Illustrative) | Substitute Threat Level to Gold | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiat Currencies (e.g., USD) | Interest Rates (e.g., Fed Funds Rate ~5.25-5.50%) | Moderate | Offer yield, but lack gold's inflation hedge in extreme scenarios. |
| Government Bonds (e.g., US Treasuries) | Yields (e.g., 10-Year Treasury ~4.2% in early 2024) | Moderate | Provide predictable income, but can lose value during high inflation. |
| Equities (e.g., S&P 500) | Growth (e.g., positive momentum into early 2024) | Moderate | Offer capital appreciation but are more volatile than gold. |
| Digital Currencies (e.g., Bitcoin) | Market Cap Volatility (e.g., significant fluctuations in 2024) | Emerging/Moderate | Potential store of value, but unproven long-term stability and regulatory uncertainty. |
| Alternative Jewelry Materials (e.g., Platinum, Silver) | Price Sensitivity (e.g., demand shifts in 2024 due to gold prices) | Moderate to High (Jewelry Segment) | Consumer preference and price elasticity can lead to substitution. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the large-scale gold mining sector presents formidable financial hurdles. Endeavour Mining's operations, for instance, necessitate substantial upfront capital for exploration, mine development, and the construction of essential infrastructure like processing plants and transportation networks. These high capital requirements act as a significant deterrent, effectively limiting the pool of potential new competitors.
The gold mining industry, especially in regions like West Africa where Endeavour Mining is active, faces substantial regulatory barriers. New companies must navigate a complex web of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) requirements. For instance, in 2024, the average time to secure mining permits in several West African nations exceeded 18 months, often involving significant upfront capital for environmental impact assessments and community engagement programs.
The threat of new entrants is significantly shaped by the difficulty of accessing scarce resources, particularly economically viable gold deposits. Identifying and securing these deposits, which must have sufficient scale and grade to be profitable, presents a substantial hurdle for any new player wanting to enter the gold mining industry.
Endeavour Mining's strategic advantage lies in its established portfolio of operating mines and development projects. These assets are concentrated in the highly prospective Birimian Greenstone Belt, a region known for its rich gold potential. This existing resource base and operational footprint create a significant barrier to entry, as new competitors would struggle to acquire comparable, high-quality gold reserves.
Need for Specialized Expertise and Technology
The threat of new entrants in the gold mining sector, particularly for companies like Endeavour Mining, is significantly mitigated by the substantial need for specialized expertise and advanced technology. Successful large-scale gold mining demands deep knowledge in geology, mining engineering, metallurgy, and intricate operational management. For instance, developing and operating a modern open-pit mine often involves multi-billion dollar capital expenditures and requires decades of experience to navigate efficiently and safely.
Furthermore, proficiency with cutting-edge mining technologies, such as advanced geological modeling software, automated drilling systems, and sophisticated processing plants, creates a considerable knowledge and skill barrier. New entrants must invest heavily not only in physical assets but also in acquiring and retaining highly skilled personnel. In 2024, the global mining technology market is projected to continue its growth, emphasizing the increasing importance of technological adoption as a competitive differentiator.
- Specialized Expertise: Geology, mining engineering, metallurgy, and operational management are critical skill sets.
- Technological Barriers: Advanced mining technologies require significant investment and expertise to implement and operate.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing new large-scale gold mining operations involves massive upfront capital requirements.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex environmental and mining regulations adds another layer of difficulty for potential new entrants.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
Established players like Endeavour Mining possess significant economies of scale in procurement, processing, and distribution, resulting in lower per-unit costs. New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies from the outset, creating a substantial competitive hurdle.
Endeavour Mining's operational efficiency, evidenced by its projected class-leading all-in sustaining costs for FY2025, underscores this inherent advantage. This cost leadership makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price without substantial upfront investment.
- Economies of Scale: Endeavour benefits from bulk purchasing power and optimized operational processes.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: New entrants lack the established infrastructure and volume to achieve similar cost structures.
- FY2025 Cost Projections: Endeavour's anticipated 'class-leading' all-in sustaining costs highlight its competitive cost position.
The threat of new entrants into the gold mining sector, particularly for a company like Endeavour Mining, is generally considered low. This is primarily due to the immense capital required to establish operations, with new large-scale mines often demanding billions of dollars for exploration, development, and infrastructure. For example, the average capital expenditure for a new gold mine development project in 2024 was estimated to be between $500 million and $2 billion, a significant barrier for most potential competitors.
Furthermore, navigating the complex and often lengthy regulatory landscape, which includes stringent environmental and social governance (ESG) compliance, presents another substantial hurdle. Securing the necessary permits can take years, as evidenced by the average of 18-24 months for full permitting in many West African jurisdictions in 2024. This, combined with the difficulty of acquiring economically viable gold deposits and the need for specialized expertise and advanced technology, significantly limits the number of viable new entrants capable of challenging established players.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for exploration, development, and infrastructure. | Significant deterrent; requires access to substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance and permitting processes. | Time-consuming and costly; delays market entry. |
| Resource Access | Difficulty in identifying and securing profitable gold deposits. | Limits the pool of viable projects for new companies. |
| Specialized Expertise & Technology | Need for deep knowledge in geology, engineering, metallurgy, and advanced mining tech. | Requires significant investment in human capital and technology adoption. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Endeavour Mining Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Endeavour's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific reports from reputable sources like Wood Mackenzie and S&P Global Market Intelligence.
