Emmi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Emmi Bundle
Emmi's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its suppliers to the constant threat of new companies entering the dairy market. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the industry effectively.
This snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Emmi’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration within the dairy sector, a key factor for Emmi, generally favors processors due to a fragmented farmer base. This means individual farmers typically have limited power to negotiate prices with large dairy companies.
However, this dynamic can shift. For instance, if Emmi sources from regions with a high concentration of specialized dairy farms, or if certain farms produce milk with unique qualities sought after by Emmi, those suppliers could gain more bargaining leverage.
In 2024, the global dairy market continued to see consolidation among processors, but the upstream supply of milk often remained diverse. For Emmi, managing relationships across its varied supplier network is crucial to mitigating risks associated with any localized supplier power imbalances.
Switching milk suppliers for Emmi presents moderate switching costs. These arise from the logistical complexities of establishing new delivery routes, ensuring consistent quality control across different farms, and the potential for temporary production disruptions during the transition. For instance, in 2023, Emmi's reliance on a stable supply chain was critical, as evidenced by their consistent milk procurement volumes to meet growing demand for their specialty cheese and dairy products.
Supplier product differentiation can significantly bolster their bargaining power. While basic commodities like raw milk might offer little differentiation, specialized offerings such as organic milk, A2 milk, or unique regional cheeses create distinct value propositions. This allows these specialized suppliers to command higher prices or more favorable terms, especially when a company like Emmi relies on these niche ingredients for its premium product lines.
Emmi's strategic emphasis on specialty and premium dairy products naturally increases its potential dependence on suppliers who can provide these differentiated inputs. For instance, if Emmi's success hinges on its organic yogurt range, it becomes more susceptible to the pricing and supply decisions of its organic milk producers. This reliance strengthens the suppliers' ability to negotiate.
Looking ahead, Emmi's objective for all milk suppliers to surpass average local standards by 2027 suggests a move towards cultivating deeper, more integrated relationships. By setting higher quality benchmarks and potentially fostering closer collaboration, Emmi might aim to reduce the leverage of suppliers who cannot meet these elevated expectations, while simultaneously strengthening its position with those who can.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, particularly individual dairy farmers, is generally low for a company like Emmi. The substantial capital investment needed for processing, packaging, and distribution, along with navigating complex regulatory environments and established distribution channels, makes it an unlikely strategy for most farmers to directly challenge Emmi's market position.
However, the landscape isn't entirely devoid of potential challenges. Farmer cooperatives, pooling resources and expertise, could represent a more credible, albeit still niche, threat. These cooperatives might explore forward integration to capture more value, potentially focusing on specialized or premium dairy products where they can differentiate themselves and gain a foothold.
For context, the Swiss dairy sector, Emmi's primary operating environment, is characterized by a high degree of farmer ownership in cooperatives. For instance, Emmi itself is majority-owned by the dairy cooperative Emmi AG, which comprises around 7,000 Swiss milk producers. This structure inherently limits the threat of external forward integration from individual suppliers, as the cooperative model already internalizes much of the supply chain.
- Low Likelihood of Individual Farmer Integration: The immense capital outlay and operational expertise required for dairy processing and distribution make it an impractical venture for most individual dairy farmers aiming to compete with established players like Emmi.
- Niche Threat from Cooperatives: Farmer cooperatives may present a limited threat by integrating forward into specific, value-added dairy product segments, leveraging collective resources and market access.
- Emmi's Cooperative Ownership Structure: Emmi's majority ownership by Emmi AG, a cooperative of Swiss milk producers, significantly mitigates the risk of forward integration by its primary suppliers, as the supply base is already intrinsically linked to the company's governance.
Importance of Emmi to Suppliers
Emmi's substantial revenue, reaching CHF 4.3 billion in 2024, positions it as a critical buyer for numerous dairy farmers. This scale means that many suppliers rely heavily on Emmi for a significant portion of their sales, inherently limiting their ability to demand higher prices or more favorable terms.
The dependence of smaller dairy farms on Emmi is particularly pronounced. For these operations, Emmi represents a primary, if not sole, market for their milk, which consequently diminishes their bargaining leverage.
- Emmi's 2024 Revenue: CHF 4.3 billion
- Supplier Dependence: Many dairy farmers rely on Emmi for a substantial share of their income.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: This reliance reduces suppliers' ability to negotiate favorable terms.
- Focus on Smaller Farms: Smaller operations experience a more significant reduction in bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Emmi is generally moderate, influenced by factors like supplier concentration, product differentiation, and switching costs. While a fragmented farmer base typically limits individual supplier leverage, specialized or differentiated milk products can empower certain suppliers.
Emmi's strong market position and significant revenue, CHF 4.3 billion in 2024, mean many suppliers depend on them, reducing their negotiating power. The threat of forward integration by suppliers is low, especially given Emmi's cooperative ownership structure, which ties many producers directly to the company.
| Factor | Impact on Emmi | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Generally low for individual farmers, moderate for cooperatives. | Fragmented farmer base in many regions, but potential for regional concentration. |
| Product Differentiation | Can increase supplier power for specialized inputs. | Emmi's focus on premium and specialty products increases reliance on differentiated milk sources. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate due to logistics and quality control. | Ensuring consistent quality and managing new delivery routes are key considerations. |
| Supplier Dependence | High for many farms, reducing their leverage. | Emmi's CHF 4.3 billion 2024 revenue highlights its importance as a buyer. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low for individual farmers, niche for cooperatives. | Emmi's majority ownership by Emmi AG (a cooperative) mitigates this risk. |
What is included in the product
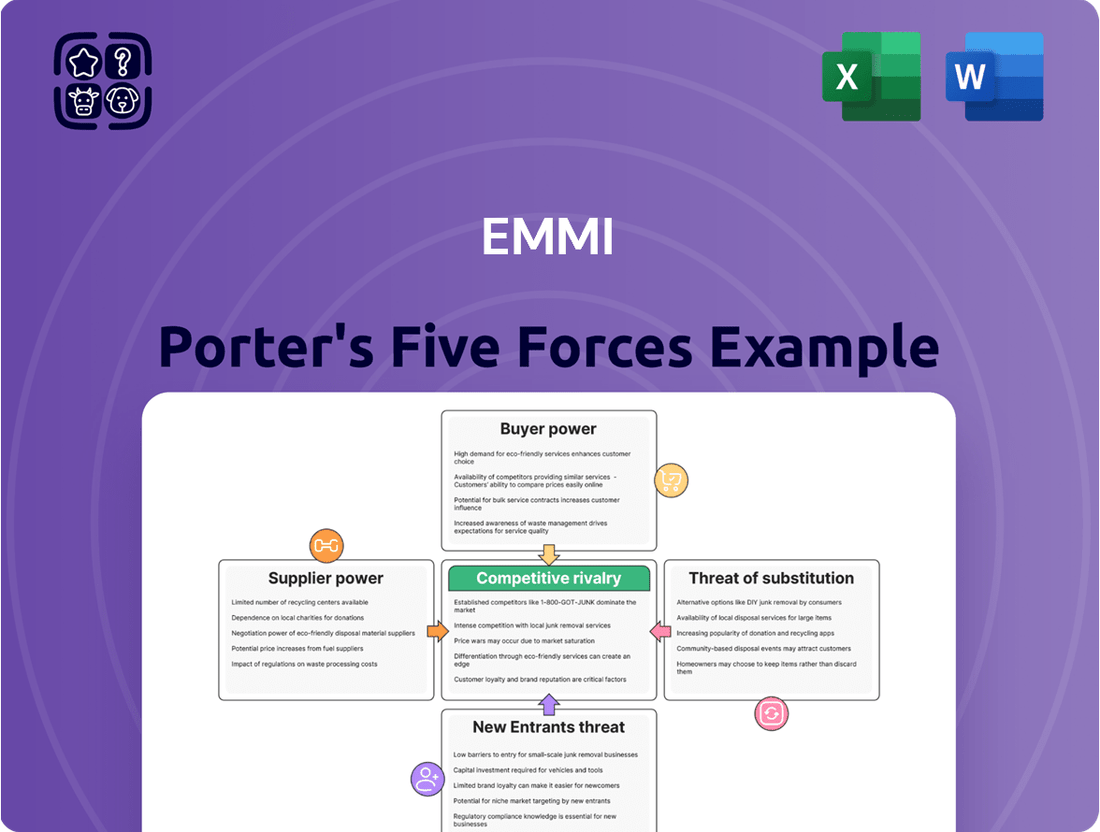
Emmi's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity and profitability of the dairy sector by examining threats from new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and existing rivalry.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Emmi's customer base is split between retail and food service. The retail segment, dominated by major supermarket chains, represents a significant source of bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volumes. These large retailers can indeed exert considerable pressure on Emmi regarding pricing, payment terms, and product assortment, impacting Emmi's profit margins.
For instance, in 2023, the top five supermarket chains in Switzerland, Emmi's primary market, accounted for approximately 70% of grocery retail sales. This high concentration means that these few large customers hold considerable sway over suppliers like Emmi, demanding favorable conditions to maintain shelf space and competitive pricing for consumers.
While the food service sector might appear more fragmented, large restaurant chains or institutional buyers within this segment can also consolidate their purchasing power. Their ability to negotiate bulk deals can similarly translate into significant leverage when dealing with dairy product suppliers, potentially influencing Emmi's sales strategies and profitability.
For Emmi's more generic dairy offerings, the cost for customers to switch to a competitor is quite low. Think about basic milk or yogurt; if Emmi's price increases slightly or availability dips, consumers can readily opt for another brand or a store's own private label without much hassle or expense. This ease of switching significantly weakens Emmi's bargaining power in these segments.
However, Emmi's specialized and branded products, such as Emmi Caffè Latte or their Kaltbach cheese, present a different picture. Here, factors like established brand loyalty, unique taste profiles, and the perception of higher quality can act as barriers to switching. Customers who have grown accustomed to these specific products may face a higher psychological or experiential cost in moving to alternatives, thereby increasing Emmi's leverage.
Customers now have unprecedented access to information about product ingredients, nutritional content, and a company's sustainability efforts. This readily available data empowers them to make more informed choices, directly impacting their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, consumer demand for transparent labeling regarding allergens and ethical sourcing continued to rise, with surveys indicating over 70% of shoppers checking ingredient lists before purchasing.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, while generally low for individual consumers, poses a significant concern for large retail buyers. These major retailers could potentially establish their own private label dairy production facilities, particularly for high-volume, standardized products. This strategic move would allow them to reduce their dependence on external suppliers like Emmi and gain greater control over their supply chain and product offerings.
For instance, in 2024, major supermarket chains in Europe, which are key customers for dairy companies, continued to expand their private label ranges. Data from NielsenIQ indicated that private label products accounted for over 30% of grocery sales in many European markets by the end of 2023, a trend that is expected to persist and even grow. This suggests a willingness and capability among large retailers to vertically integrate into production.
- Retailer Private Label Expansion: Large retailers are increasingly investing in their own brands, which can extend to private label dairy production.
- Commodity Product Focus: The threat is most pronounced for commodity dairy items where differentiation is low and price is a key driver.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Successful backward integration by a major customer directly diminishes the supplier's leverage and market share.
- Industry Trend: The ongoing growth of private label penetration across grocery sectors highlights the underlying capability and strategic intent of retailers to control more of the value chain.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers' price sensitivity for Emmi's products is not uniform. For staple items like basic milk and yogurt, consumers are generally more price-conscious. However, for premium offerings such as specialty cheeses or innovative desserts, perceived value often outweighs price, leading to lower sensitivity. For instance, while a 1% increase in price for a basic yogurt might significantly impact sales volume, a similar increase for a high-end Emmentaler cheese could have a more muted effect.
Economic conditions play a crucial role in shaping this sensitivity. During periods of economic downturn or high inflation, consumers tend to become more price-aware across all product categories. In 2023, for example, reports indicated that Swiss consumers, Emmi's primary market, were increasingly seeking value and promotions, suggesting a heightened price sensitivity for many food items. This trend is likely to continue into 2024 as economic uncertainties persist.
- Price Sensitivity Varies: Higher for basic products like milk and yogurt, lower for premium and specialty items.
- Perceived Value Matters: For specialty cheeses and desserts, higher perceived value can lessen price sensitivity.
- Economic Influence: Economic conditions, such as inflation and recession fears, increase overall customer price sensitivity.
- 2023-2024 Trends: Reports suggest a growing consumer focus on value and promotions in the Swiss market, indicating heightened price sensitivity.
Emmi faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly from large retail chains that dominate grocery sales. These powerful buyers can leverage their volume to negotiate lower prices and favorable payment terms, directly impacting Emmi's profitability. The ease with which customers can switch to competitor brands or private labels for generic dairy products further amplifies this power.
However, Emmi's differentiated and branded products, like Emmi Caffè Latte, benefit from brand loyalty and perceived quality, which can mitigate customer bargaining power. Consumers are increasingly informed, demanding transparency in ingredients and sourcing, which can also influence their purchasing decisions and negotiation leverage.
The threat of backward integration, where large retailers produce their own dairy products, is a growing concern. This trend, evidenced by the expanding private label ranges in European markets, allows retailers to reduce reliance on suppliers like Emmi and exert greater control.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Emmi's Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Large Retail Supermarkets | High purchase volume, price sensitivity for commodities, threat of private labels | Focus on branded, differentiated products; build strong relationships; emphasize quality and innovation |
| Food Service Chains | Bulk purchasing power, potential for contract negotiation | Offer tailored solutions, consistent supply, and competitive pricing for large contracts |
| Individual Consumers | Price sensitivity for basic items, informed purchasing decisions | Brand building, product innovation, clear communication of value proposition (quality, taste, convenience) |
What You See Is What You Get
Emmi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Emmi Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring a transparent and accurate transaction. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document, complete with all insights and ready for your strategic planning. There are no placeholders or altered content; what you see is precisely what you get, enabling immediate application of this valuable business tool.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global dairy market is a crowded space, featuring a dynamic interplay between massive multinational corporations and a vast array of regional and local dairy producers. This diverse competitive landscape means Emmi encounters a wide spectrum of rivals depending on the specific product category and geographical market it operates within. For instance, in 2023, the global dairy market was valued at an estimated $850 billion, with significant growth projected in the coming years, indicating ample room for competition across various segments.
While the overall dairy market might be mature in some areas, Emmi is strategically positioned by focusing on high-growth niches. They are actively pursuing segments like ready-to-drink coffee beverages, premium dessert products, and specialized cheese varieties. This targeted approach, combined with their international expansion efforts, helps them tap into markets with greater growth potential.
The plant-based dairy alternative sector is a significant growth driver, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 9-12% between 2025 and 2030. This rapid expansion in alternatives is likely to increase competitive pressures within this specific segment of the broader dairy industry.
Emmi actively cultivates product differentiation through its focus on branded goods and continuous innovation. Brands like Emmi Caffè Latte and Kaltbach cheeses are prime examples of how the company builds strong customer recognition and loyalty. This strategy effectively sets Emmi apart from less differentiated competitors, lessening the pressure of direct price wars.
Exit Barriers
The dairy sector, including companies like Emmi, faces substantial exit barriers due to the immense capital required for specialized processing facilities and sophisticated equipment. These high fixed costs, often running into millions of dollars for a single plant, make it economically unviable for many firms to simply shut down operations. For instance, a modern dairy processing plant can easily cost upwards of $50 million to build and equip.
Furthermore, established distribution networks, crucial for perishable goods like dairy products, represent another significant hurdle for exiting firms. Building and maintaining these logistics channels, which often involve refrigerated transport and extensive retail relationships, requires considerable time and investment. Companies that have spent years cultivating these networks are unlikely to abandon them easily, even when facing profitability challenges.
These high exit barriers can force companies to continue operating in the market, even when economic conditions are unfavorable, leading to intensified competitive rivalry. This persistence can manifest in price wars or aggressive market share battles as firms strive to cover their substantial fixed costs. In 2023, the global dairy market, while growing, experienced fluctuating commodity prices and increased operational costs, making the impact of these exit barriers even more pronounced for less efficient players.
- High Capital Investment: Dairy processing plants require significant upfront capital, often exceeding $50 million for modern facilities.
- Specialized Equipment: Investment in specialized machinery for pasteurization, homogenization, and packaging adds to the capital burden.
- Distribution Networks: Establishing and maintaining refrigerated supply chains and retail partnerships are costly and time-consuming.
- Forced Continuation: High exit costs compel companies to remain in the market, potentially increasing competitive pressure during downturns.
Acquisition Strategy
Emmi's competitive rivalry is intensified by its proactive acquisition strategy. By actively pursuing and completing acquisitions, Emmi aims to bolster its presence in key markets and specialized segments. This M&A activity directly influences the competitive dynamics, as it consolidates market share and introduces new capabilities or product lines into the existing landscape.
In 2024, Emmi's strategic acquisitions of Mademoiselle Desserts, Verde Campo, and Hochstrasser underscore this approach. These moves are not just about growth; they represent a deliberate effort to reshape the competitive environment. For instance, acquiring Mademoiselle Desserts, a significant player in the frozen pastry sector, immediately elevates Emmi's competitive standing in that particular food category.
- Acquisition of Mademoiselle Desserts: Strengthened Emmi's position in the European frozen pastry market.
- Acquisition of Verde Campo: Expanded Emmi's presence in the plant-based dairy alternatives sector in Switzerland.
- Acquisition of Hochstrasser: Enhanced Emmi's specialty cheese portfolio and market reach.
Competitive rivalry within Emmi's operating landscape is robust, fueled by a mix of large global players and numerous specialized regional firms. The sheer volume of competitors, especially in established markets, means Emmi must consistently innovate and differentiate to maintain its market position. For example, the global dairy market is projected to reach over $1 trillion by 2027, indicating continued intense competition for market share.
Emmi actively mitigates direct price competition through a strong emphasis on branded products and unique offerings, such as its premium cheese lines and ready-to-drink coffee beverages. This strategy aims to build customer loyalty and command higher margins, setting Emmi apart from competitors focused solely on volume or price. In 2023, Emmi reported a net profit margin of approximately 5.5%, demonstrating the effectiveness of its differentiation strategy.
The high capital investment required for dairy processing, often exceeding $50 million for a single modern plant, creates significant exit barriers. These barriers compel existing companies to remain in the market, even during economic downturns, thereby intensifying rivalry. This persistence can lead to aggressive pricing strategies or market share battles as firms attempt to cover their substantial fixed costs.
Emmi's strategic acquisitions, such as those of Mademoiselle Desserts and Verde Campo in 2024, directly impact competitive dynamics by consolidating market share and expanding its product portfolio. These moves not only strengthen Emmi's position but also alter the competitive landscape for rivals in those specific segments.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Emmi |
|---|---|---|
| Market Saturation | Many mature dairy markets have a high number of established players. | Requires strong differentiation and targeted niche strategies. |
| Product Differentiation | Emmi focuses on premium brands and innovation to stand out. | Reduces direct price competition and builds customer loyalty. |
| Exit Barriers | High capital investment in processing and distribution creates significant costs to leave. | Leads to sustained competition as firms are incentivized to stay operational. |
| Acquisition Strategy | Emmi actively acquires companies to gain market share and capabilities. | Intensifies rivalry by consolidating competitors and introducing new market dynamics. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The dairy industry, including companies like Emmi, faces a substantial threat from plant-based substitutes. Products such as almond milk, soy yogurt, and oat cheese are gaining significant traction with consumers. This shift is driven by growing awareness of health benefits, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations surrounding traditional dairy farming.
By the end of 2023, the global plant-based milk market was valued at approximately $16.9 billion and is projected to grow substantially. This increasing consumer preference for alternatives directly impacts demand for dairy products, forcing dairy companies to innovate and adapt to remain competitive.
Plant-based alternatives are increasingly competitive, offering better taste and texture at more attractive prices, directly challenging traditional dairy. This narrowing price-performance gap makes it easier for consumers to switch. For instance, the non-dairy milk market is expected to surge, reaching USD 56.2 billion by 2034, highlighting the growing appeal of substitutes.
Consumers are increasingly aware of lactose intolerance, dairy allergies, and the environmental footprint of traditional dairy farming. This growing consciousness directly fuels a higher propensity to switch to plant-based alternatives. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers are actively seeking out dairy-free options due to health or ethical concerns, significantly boosting the threat of substitutes for dairy products.
Innovation in Substitute Products
The threat of substitutes for traditional dairy is intensifying due to rapid innovation. Plant-based alternatives, like oat, almond, and soy milk, are continuously evolving with new flavors, textures, and enhanced nutritional content, making them increasingly attractive to consumers. For example, the global plant-based dairy market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $70 billion by 2030, indicating significant growth driven by these product improvements.
Further disrupting the market is the emergence of animal-free dairy produced through precision fermentation. Companies are developing milk proteins without the need for cows, offering a potentially more sustainable and ethically sourced alternative. This technological advancement allows for the creation of dairy products that mimic the taste and functionality of traditional dairy, posing a direct substitute threat.
- Plant-based dairy innovation: New product formats, flavors, and nutritional profiles enhance competitiveness.
- Animal-free dairy: Precision fermentation creates dairy proteins without cows, offering a novel substitute.
- Market growth: The plant-based dairy market is a significant and expanding substitute category.
Emmi's Response to Substitutes
Emmi, a prominent player in the dairy sector, recognizes the growing consumer interest in plant-based alternatives. This trend presents a significant threat of substitutes, as consumers increasingly opt for non-dairy options for various reasons, including health, environmental, and ethical concerns.
The company's strategic response involves actively investing in and innovating within the plant-based milk alternative market. This proactive approach aims to capture a share of this expanding niche and mitigate the impact of traditional dairy product substitution.
- Market Shift: The global plant-based milk market was valued at approximately USD 12.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 33.7 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 15.6%. This highlights the substantial and growing threat from substitutes.
- Emmi's Strategy: Emmi's long-term strategy explicitly includes developing and promoting its own range of plant-based products, such as oat and almond milk beverages, to cater to evolving consumer preferences.
- Innovation Focus: The company is prioritizing innovation in this space, aiming to differentiate its plant-based offerings through unique flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles, thereby directly addressing the substitute threat.
The threat of substitutes for Emmi's dairy products is significant and growing, primarily driven by the expanding plant-based alternatives market. These substitutes are becoming increasingly competitive in taste, texture, and price, making it easier for consumers to switch. For instance, the global plant-based milk market was valued at approximately $16.9 billion by the end of 2023, with projections indicating continued substantial growth.
| Substitute Category | Market Value (2023 Approx.) | Projected Growth Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Milk | $16.9 billion | Health, environmental, and ethical consumer concerns |
| Plant-Based Yogurt & Cheese | Significant portion of the broader plant-based market | Increasing product variety and improved taste profiles |
| Animal-Free Dairy (Precision Fermentation) | Emerging market segment | Technological advancements offering dairy-like functionality |
Entrants Threaten
The dairy industry demands significant upfront capital for establishing processing facilities, acquiring specialized equipment, and building robust distribution channels. For instance, Emmi, a major player, operates 72 production sites across 13 countries, illustrating the scale of investment required.
These high capital requirements act as a substantial deterrent for potential new entrants, making it challenging for them to compete with established companies that have already made these investments.
Established players in the dairy industry, like Emmi, leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can produce goods at a much lower cost per unit compared to a new company just starting out. For instance, Emmi's large-scale procurement of milk and other raw materials in 2024 likely secured better pricing than a smaller entrant could achieve.
This cost advantage is a major barrier. A new entrant would struggle to match Emmi's per-unit production costs, making it incredibly challenging to compete on price and attract customers. This inherent cost difference deters many potential new businesses from entering the market.
New companies entering the dairy market face significant hurdles in securing prime shelf space in major supermarkets and building efficient distribution networks. This often requires substantial upfront investment and existing ties with retailers, which new entrants typically lack.
Emmi benefits from its established presence, boasting a diverse product range that appeals to a broad consumer base. This strong market position, cultivated over years, provides a distinct advantage in negotiating favorable distribution terms.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Building strong brand recognition and customer loyalty in the dairy market, particularly for premium and specialty items, requires significant time and marketing expenditure. Emmi's established brands, such as Emmi Caffè Latte and Kaltbach, already possess substantial recognition, creating a barrier for potential new entrants aiming to capture market share through similar offerings.
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by the substantial investment needed to build brand identity and cultivate customer loyalty in the dairy sector. For instance, Emmi reported that its brand portfolio, including well-recognized names, contributes significantly to its market position. This loyalty is hard-won, making it challenging for newcomers to quickly establish a comparable presence.
- Brand Recognition: Emmi's established brands have high consumer awareness, making it difficult for new entrants to gain immediate traction.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customers are less likely to switch to unknown brands, especially for premium dairy products where trust and consistent quality are paramount.
- Marketing Investment: New companies need substantial capital for marketing to build brand awareness and loyalty comparable to Emmi's existing market presence.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The dairy industry faces significant barriers to entry due to rigorous food safety regulations, quality control mandates, and detailed labeling requirements. These compliance demands translate into substantial upfront costs and operational complexities for any new player looking to enter the market.
Emmi AG, for instance, operates under a framework of high quality and sustainability standards, which further elevates the investment and operational bar. For example, in 2023, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) continued to refine guidelines on hygiene and traceability, impacting all dairy processors.
- Stringent Regulations: Dairy processing is heavily regulated globally, requiring adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting these standards often necessitates significant investment in specialized equipment, testing facilities, and trained personnel, estimated to be millions of Swiss Francs for a new, large-scale dairy operation.
- Quality & Sustainability Focus: Companies like Emmi invest in certifications and sustainable sourcing practices, adding another layer of complexity and cost that new entrants must overcome to compete effectively.
The threat of new entrants in the dairy industry is generally low due to several formidable barriers. High capital requirements for processing facilities and distribution networks, coupled with significant economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like Emmi, make market entry financially challenging. Furthermore, established brand recognition and customer loyalty, cultivated through years of marketing and consistent quality, present a substantial hurdle for newcomers seeking to gain market share.
Regulatory compliance and the need for specialized knowledge in dairy processing add another layer of complexity and cost. For instance, adherence to stringent food safety standards, such as HACCP, requires considerable investment in infrastructure and personnel, deterring many potential entrants. Emmi's extensive network of 72 production sites across 13 countries underscores the scale of investment and operational expertise required to compete effectively.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing dairy processing plants, acquiring specialized machinery, and building distribution networks demand substantial upfront investment. | High; deters new players without significant funding. |
| Economies of Scale | Large producers like Emmi benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high-volume purchasing and production. | Significant cost disadvantage for new entrants; difficult to compete on price. |
| Brand Recognition & Loyalty | Established brands have strong consumer trust and repeat purchasing habits, especially for premium products. | Challenging for new brands to gain immediate market traction and capture share. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict food safety, quality control, and labeling regulations necessitate investment in compliance systems and expertise. | Increases operational complexity and upfront costs; requires specialized knowledge. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Emmi Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Emmi's annual reports, financial statements, and investor presentations. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and competitor analysis to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
