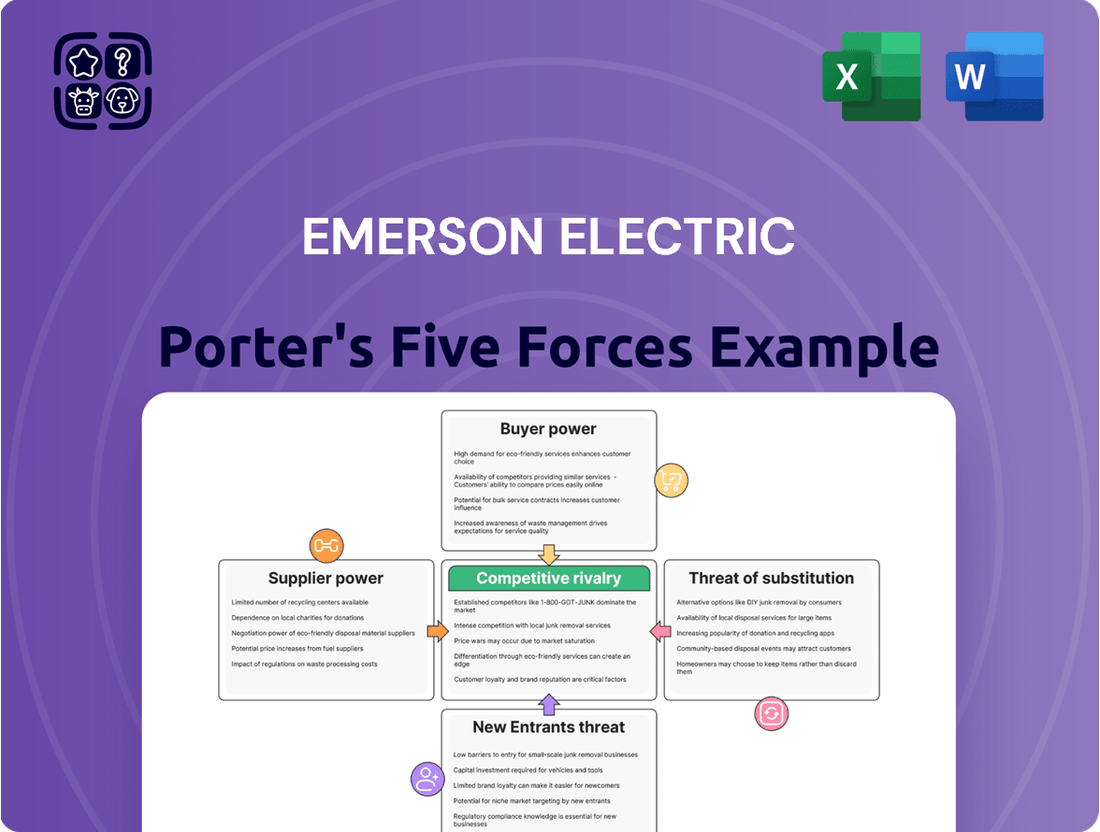
Emerson Electric Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Emerson Electric Bundle
Emerson Electric navigates a complex industrial landscape, where the threat of new entrants is moderate, tempered by significant capital requirements and established distribution channels. Similarly, the bargaining power of buyers is substantial, especially for large industrial clients, influencing pricing and product specifications.
The intensity of rivalry within Emerson's core markets is high, driven by a few dominant players vying for market share. Furthermore, the threat of substitute products, while not immediate, exists as technological advancements constantly offer alternative solutions for industrial automation and process control.
Supplier power, though present, is generally manageable for Emerson due to its scale and diverse supplier base. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Emerson Electric’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Emerson Electric's reliance on a select few suppliers for highly specialized components, like precision sensors and proprietary software vital for its automation systems, significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. This concentration limits Emerson's ability to easily switch suppliers, particularly given the integration complexities and stringent performance demands of its advanced control solutions.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier for many of Emerson's components, continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions and high demand, leading to increased lead times and component costs. For instance, lead times for certain advanced microcontrollers used in industrial automation could extend to 52 weeks, forcing companies like Emerson to commit to long-term orders and accept higher prices, thereby enhancing supplier leverage.
Emerson Electric operates in a market where certain specialized components for industrial automation and control systems are supplied by a limited number of manufacturers. This concentration among suppliers gives them significant leverage. For instance, if a crucial semiconductor or a specialized sensor is produced by only two or three dominant companies, Emerson has fewer options to turn to if those suppliers demand higher prices or dictate unfavorable contract terms.
This limited supplier choice can directly impact Emerson's cost of goods sold and its ability to maintain competitive pricing for its own products. In 2023, the industrial automation sector experienced ongoing supply chain challenges, with some component lead times extending, a trend that often benefits suppliers by increasing their pricing power.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the industrial sector, particularly for specialized components, can be significant. For a company like Emerson Electric, the costs and complexities involved in switching from one supplier to another for critical parts are substantial. These can include expenses related to re-tooling manufacturing processes, re-certifying new components to meet stringent quality standards, or the intricate task of re-integrating different parts into Emerson's existing, often complex, operational systems.
These high switching costs effectively translate into considerable leverage for Emerson's current suppliers. When it becomes difficult and expensive for a buyer like Emerson to simply shift its procurement to a competitor, the existing suppliers are in a stronger position to dictate terms, including pricing and supply agreements. This dynamic solidifies supplier power, making it challenging for Emerson to easily find alternative, more favorable sources for its essential components.
Forward Integration Potential
Suppliers with the capability to move into Emerson Electric's customer space, by developing their own end-products, significantly enhance their bargaining power. This forward integration threat means suppliers can potentially capture more of Emerson's value chain. For instance, a key component supplier could develop its own integrated system, directly competing with Emerson's offerings. This leverage allows them to demand better terms or risk Emerson losing business to them.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers may develop competing end-products, directly challenging Emerson's market position.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: This potential to become a competitor gives suppliers greater power to negotiate pricing and terms.
- Market Disruption: If a supplier successfully integrates forward, it could disrupt Emerson's established product lines and customer relationships.
- Strategic Consideration: Emerson must constantly assess suppliers' capabilities and intentions regarding forward integration to mitigate this risk.
Quality and Reliability are Key Supplier Differentiators
Emerson Electric's reliance on high-quality inputs means suppliers offering superior performance and unwavering reliability inherently gain leverage. Companies that consistently provide top-tier components reduce Emerson's incentive to explore alternative, potentially riskier, suppliers, thereby strengthening their bargaining position.
This dependence translates into tangible power for these suppliers. If Emerson's product lines, such as its automation solutions or climate technologies, rely on specific, high-performance components, a supplier of those critical parts can command better terms.
- Supplier Quality Impact: Emerson's 2023 annual report highlights investments in supply chain resilience, underscoring the critical nature of supplier quality for its diverse product portfolio.
- Reliability Premium: Suppliers with proven track records in delivering defect-free and consistently performing materials often secure longer-term contracts and potentially higher margins.
- Switching Costs: The cost and time involved in qualifying new suppliers for specialized or safety-critical components can be substantial, further empowering existing, reliable partners.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Emerson Electric is amplified when few suppliers can meet the exacting standards for critical components, such as specialized semiconductors for its automation division. This limited pool of qualified vendors means Emerson has fewer alternatives, granting these suppliers significant leverage in price negotiations and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of certain advanced microchips continued to inflate prices, forcing buyers to accept less favorable conditions.
When suppliers can easily integrate forward, potentially offering competing end-products or solutions, their bargaining power increases substantially. This threat means suppliers can capture more of the value chain, directly impacting Emerson's market share and forcing it to concede better terms to retain essential component supply. This dynamic was evident in 2023 as some component manufacturers explored offering integrated system solutions.
The significant costs and technical challenges associated with switching suppliers for highly integrated or proprietary components create substantial switching costs for Emerson. These costs, including re-tooling, re-certification, and system integration, empower existing suppliers by making it economically prohibitive for Emerson to seek alternatives, thus bolstering their negotiating strength.
Emerson Electric's reliance on suppliers who consistently deliver superior quality and reliability further enhances supplier bargaining power. When a supplier's components are critical for performance and defect-free operation, as seen with advanced sensors in 2024, Emerson has a reduced incentive to switch, even if prices increase, solidifying the supplier's advantageous position.
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Emerson Electric, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threats from new entrants and substitutes, and the company's strategic positioning.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with an intuitive spider chart, making complex market dynamics easily digestible.
Simplify strategic planning by providing a clear, actionable overview of each force, facilitating targeted improvements.
Customers Bargaining Power
Emerson Electric serves a broad range of industrial, commercial, and residential markets. Within these, particularly in industrial segments like oil and gas or power generation, there can be a few major clients who represent a substantial portion of Emerson's revenue. For example, in fiscal year 2023, Emerson's top 10 customers accounted for approximately 15% of total net sales, highlighting a degree of customer concentration.
These large industrial customers, due to their significant purchasing volumes, wield considerable bargaining power. Their ability to negotiate favorable terms and pricing is amplified by the sheer scale of their demand, potentially impacting Emerson's profit margins on large contracts.
Emerson Electric's products, while often specialized, face varying degrees of customer perception regarding standardization. If buyers see Emerson's solutions as interchangeable with those of competitors, their leverage grows.
This perception of standardization directly influences customer bargaining power. When switching to an alternative supplier is simple and inexpensive, customers can readily demand better pricing or terms from Emerson.
For instance, in segments where Emerson's automation solutions are perceived as less unique, customers might leverage competitive quotes to negotiate lower prices. This was evident in the industrial automation market, where in 2023, average price reductions of 2-5% were observed in more commoditized product categories due to intense competition and buyer consolidation.
Low switching costs, such as minimal integration effort or readily available alternative components, amplify this customer power. Emerson must therefore emphasize the unique value and integration benefits of its offerings to mitigate this pressure.
Customer price sensitivity is a key factor influencing Emerson Electric's bargaining power. During economic slowdowns or in markets with many alternatives, customers often prioritize lower prices. This can force Emerson to reduce its prices, impacting profitability, particularly for products that aren't highly unique.
For instance, in the highly competitive HVAC or industrial automation segments, if many suppliers offer similar solutions, buyers have more leverage to negotiate better deals. Emerson's revenue for the fiscal year ending September 30, 2023, was $15.2 billion, and any significant price concessions across its diverse product lines could have a material impact on its financial performance.
Backward Integration by Customers
Large industrial customers, particularly those with significant scale and technical expertise, can exert considerable bargaining power over suppliers like Emerson Electric. This power stems from their potential to integrate backward, meaning they could develop or manufacture certain components or solutions themselves.
For instance, a major manufacturing client of Emerson might have the in-house engineering and production capabilities to create a proprietary control system component that Emerson currently supplies. This credible threat to bypass Emerson and produce the item internally significantly strengthens the customer's negotiating position, potentially leading to lower prices or more favorable terms on other purchases.
- Backward Integration Threat: Customers may possess the technical and financial resources to produce Emerson's products internally.
- Increased Negotiation Leverage: The ability to self-manufacture allows customers to demand better pricing and terms from Emerson.
- Example Scenario: A large automotive manufacturer could develop its own automation sensors rather than buying from Emerson.
- Impact on Emerson: This threat forces Emerson to remain competitive on price and innovation to retain such key clients.
Availability of Alternative Solutions for Customers
The availability of alternative solutions significantly boosts customers' bargaining power with Emerson Electric. When customers have numerous choices from competing manufacturers, they can more readily switch if Emerson's pricing, product features, or service levels are not satisfactory. This competitive landscape allows buyers to demand better terms, as they have viable substitutes readily accessible.
For instance, in the industrial automation sector, customers often have a wide array of choices for components like sensors, drives, and control systems. If a customer requires a specific type of motor controller, they might find comparable products from Siemens, Rockwell Automation, or Schneider Electric, each offering slightly different price points and functionalities. This diffusion of options grants customers considerable leverage.
- Customer Choice: In 2024, the industrial automation market continues to be characterized by a substantial number of players offering a broad spectrum of solutions, making it easier for end-users to compare and select alternatives.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased competition among automation solution providers intensifies price sensitivity for buyers, enabling them to negotiate more aggressively with Emerson.
- Technological Parity: As technology matures in many segments, the differentiation between Emerson's offerings and those of competitors can diminish, further empowering customers to seek the best value proposition.
- Switching Costs: While switching costs can exist, the availability of standardized interfaces and open architectures in many Emerson products can lower these barriers for customers looking at alternative suppliers.
The bargaining power of customers for Emerson Electric is substantial, particularly among its large industrial clients. These customers, due to their significant purchasing volume and the availability of alternatives, can negotiate favorable terms. Emerson's ability to maintain strong customer relationships and highlight unique product value is crucial in mitigating this power.
In 2024, the industrial automation market, a key segment for Emerson, continues to offer a wide array of competing solutions. This intensifies buyer price sensitivity and makes switching between suppliers more feasible, directly impacting Emerson's pricing power.
Furthermore, the threat of backward integration by major customers, where they could produce components in-house, adds another layer to their leverage. For instance, a large energy company might possess the technical acumen to develop its own specialized control systems, reducing reliance on Emerson.
The table below illustrates key factors influencing customer bargaining power for Emerson Electric in 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Emerson | 2024 Data Point/Trend |
| Customer Concentration | A few large clients represent a significant portion of revenue. | Increased negotiation leverage for these clients. | Top 10 customers accounted for ~15% of FY2023 net sales. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous competitors offer similar products and solutions. | Customers can easily switch, demanding better terms. | Industrial automation market has many players with comparable offerings. |
| Switching Costs | Low integration effort or readily available alternative components. | Empowers customers to negotiate lower prices. | Standardized interfaces in many industrial products reduce switching barriers. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers prioritize lower prices, especially during economic downturns. | Forces Emerson to reduce prices, impacting margins. | Observed 2-5% price reductions in commoditized automation categories in 2023. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Customers' ability to produce Emerson's products internally. | Significant leverage to demand better pricing and terms. | Large clients possess in-house engineering capabilities for critical components. |
Same Document Delivered
Emerson Electric Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Emerson Electric Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The document details the competitive landscape for Emerson Electric, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning of Emerson Electric. You'll gain a thorough understanding of the forces shaping its market environment. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Emerson Electric faces robust competition in both its industrial automation and climate control segments. The global industrial automation market, valued at approximately $240 billion in 2023, features major players like Honeywell, Siemens, and Schneider Electric, all vying for market share. This intense rivalry means Emerson must continually innovate and maintain competitive pricing to retain its position.
Industry growth rate significantly shapes competitive rivalry. While segments like climate tech and industrial automation offer robust long-term growth prospects, slower expansion in certain sub-sectors, particularly during economic slowdowns, can amplify competition. This means companies are compelled to battle more fiercely for existing market share, rather than primarily benefiting from overall market expansion.
Emerson Electric actively pursues product and solution differentiation by focusing on advanced automation technologies and robust software capabilities, notably reinforced by its significant acquisition of AspenTech. This strategy aims to create unique value propositions that are difficult for rivals to easily match.
The intensity of competitive rivalry is directly influenced by how effectively competitors can replicate or offer comparable value. When Emerson's differentiators are unique and hard to imitate, it can lessen direct price-based competition.
However, if competitors develop similar advanced solutions or software, the market can move towards commoditization, thereby increasing price pressures and intensifying rivalry. For instance, in 2023, the industrial automation market saw increased competition as major players invested heavily in digital transformation and AI-driven solutions.
Emerson's integrated offerings, which combine hardware, software, and services, also serve as a point of differentiation. This holistic approach aims to provide end-to-end solutions for customers, making it harder for competitors to unbundle and undercut their value.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The industrial technology sector, where Emerson Electric operates, is characterized by substantial upfront investments. These include significant outlays for research and development, building and maintaining advanced manufacturing facilities, and establishing robust global distribution networks.
These considerable fixed costs, often tied to specialized and difficult-to-redeploy assets, create high exit barriers within the industry. Companies find it economically challenging to simply shut down operations and recover their initial investments.
Consequently, firms are incentivized to stay in the market and compete vigorously, even when facing downturns or reduced profitability, in an effort to amortize their fixed costs and eventually recoup their investments. This dynamic intensifies competitive rivalry.
- High R&D Investment: Emerson Electric invested approximately $850 million in research and development in fiscal year 2023, reflecting the substantial upfront costs in innovation.
- Capital Intensive Operations: The company's manufacturing footprint, including advanced automation and specialized machinery, represents billions in capital expenditures, contributing to high fixed costs.
- Specialized Assets: Many of Emerson's production lines and technological capabilities are highly specific to industrial applications, making them less transferable and thus increasing exit barriers.
- Market Persistence: The need to achieve economies of scale and spread fixed costs over a larger production volume encourages incumbent firms to maintain or increase market share, fueling competitive intensity.
Strategic Stakes and Market Leadership
Emerson Electric operates in a highly competitive environment where numerous players vie for market leadership. This intense rivalry fuels aggressive strategies, as companies prioritize gaining or defending substantial market share. For instance, in the industrial automation sector, companies frequently engage in price competition to attract customers, a dynamic clearly visible in the ongoing efforts by competitors to capture market share from established players. Innovation is also a key battleground, with companies like Rockwell Automation and Siemens investing heavily in new technologies to differentiate their offerings and secure a stronger market position.
This pursuit of market leadership often translates into rapid product development cycles and significant marketing expenditures. Companies are motivated to launch new products and upgrade existing ones swiftly to stay ahead of rivals. In 2023, for example, the industrial automation market saw a surge in new product introductions focused on digital transformation and sustainability. These efforts are crucial for building brand recognition and loyalty, especially in segments where Emerson Electric has a strong presence.
- Strategic Importance of Market Share: Many competitors in Emerson's markets consider significant market share to be paramount for long-term success and profitability.
- Aggressive Tactics: This strategic imperative drives intense competition through price adjustments, accelerated innovation, and heightened marketing campaigns.
- Innovation as a Differentiator: Companies are constantly introducing new technologies and solutions to capture and retain customers, particularly in areas like automation and software.
- Marketing Investment: Substantial resources are allocated to marketing and sales efforts to build brand visibility and customer relationships in a crowded marketplace.
Emerson Electric faces intense competition from established players and agile newcomers alike, particularly in its core industrial automation and climate technologies sectors. The sheer number of rivals, coupled with their aggressive strategies, necessitates continuous innovation and cost management. This dynamic is evident in the industrial automation market, which saw its value reach an estimated $245 billion in 2024, with significant investments in digital solutions by companies like Siemens and Rockwell Automation.
The rapid pace of technological advancement, especially in areas like AI and IoT integration, further fuels this rivalry. Companies must constantly invest in R&D, as Emerson did with approximately $870 million in fiscal year 2024, to develop differentiated offerings. Failure to keep pace can lead to commoditization and increased price pressure, making market share a critical battleground where aggressive pricing and marketing are common tactics.
High fixed costs associated with specialized manufacturing and distribution networks create substantial exit barriers, compelling companies to remain competitive even during economic downturns. This persistence intensifies rivalry as firms strive to cover their investments and achieve economies of scale. Consequently, Emerson must navigate a landscape where maintaining market leadership requires a constant strategic balancing act between innovation, pricing, and customer engagement.
| Rivalry Factor | Description | Impact on Emerson |
|---|---|---|
| Number and Balance of Competitors | Numerous global and regional players in industrial automation and climate control. | Requires constant effort to maintain market share and differentiate offerings. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Moderate to strong growth in key segments, but slower in mature sub-sectors. | Amplifies competition for market share during slower growth periods. |
| Product Differentiation | High degree of innovation and integration of software/services. | Emerson's AspenTech acquisition and integrated solutions are key differentiators. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to high due to integrated systems and long-term contracts. | Provides some customer stickiness but rivals actively seek to attract new clients. |
| Fixed Costs & Exit Barriers | Significant upfront investments in R&D and specialized assets. | Incentivizes incumbent firms to compete aggressively to recover costs. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
New and evolving technologies, such as advanced AI and machine learning, predictive maintenance, and IoT solutions, can pose a threat by offering alternative ways to solve customer problems traditionally addressed by Emerson's products. These innovations might provide similar functionalities with different underlying approaches, potentially disrupting Emerson's market share. For instance, the rise of cloud-based analytics platforms for industrial equipment could offer a substitute for Emerson's on-premise automation and control systems. Companies are increasingly looking at software-driven solutions that may reduce reliance on hardware-centric offerings.
Large industrial customers, especially those with substantial engineering expertise and financial backing, increasingly explore developing their own in-house automation and control systems. This trend presents a direct substitute for Emerson's commercial products, as these giants can tailor solutions precisely to their unique operational needs, potentially bypassing the need for third-party vendors. For instance, major oil and gas companies or automotive manufacturers often possess the internal talent to design and implement custom systems, reducing their reliance on external suppliers like Emerson.
The increasing availability of general-purpose software and hardware presents a significant threat of substitution for Emerson Electric. As more sophisticated and affordable open-source or lower-cost platforms emerge, they can increasingly serve as alternatives to Emerson's specialized industrial control systems. For instance, in 2024, the global market for open-source software in industrial automation saw continued growth, with many companies exploring these solutions for greater flexibility and reduced licensing costs.
Customers may opt to develop their own customized solutions using these broader, more accessible tools. This trend can lead to a reduced reliance on vendor-specific, often proprietary, systems like those offered by Emerson. By building bespoke applications with readily available components, businesses can potentially achieve cost savings and greater adaptability compared to investing in integrated, specialized platforms.
Shifting Industry Practices and Business Models
The threat of substitutes for Emerson Electric is amplified by evolving industry practices. For instance, the widespread adoption of lean manufacturing principles aims to minimize waste and optimize resource utilization, potentially reducing the demand for certain automation and process control equipment that Emerson specializes in. As of 2024, many manufacturers are investing heavily in process optimization, with reports indicating a significant increase in adoption rates for advanced lean methodologies across sectors like automotive and electronics.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on circular economy initiatives presents a substitution threat. Companies focused on reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling may require different types of equipment or integrated solutions than those traditionally supplied by Emerson. This shift could impact demand for new capital equipment as companies extend the lifecycle of existing assets. For example, the global circular economy market was projected to reach over $4.5 trillion by 2025, signaling a strong trend toward sustainable practices that could alter equipment replacement cycles.
- Lean Manufacturing Adoption: Increased focus on efficiency and waste reduction can decrease reliance on certain types of Emerson's process control and automation hardware.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: The drive towards reuse and remanufacturing of industrial assets may reduce the need for new equipment purchases, a core offering for Emerson.
- Energy Management Shifts: Changes in how industries manage energy, such as a greater reliance on distributed generation or energy efficiency software that integrates with existing systems rather than replacing them, could offer substitute solutions.
- Digitalization and Software Solutions: While Emerson offers digital solutions, standalone software platforms for asset management or predictive maintenance that integrate with a wider range of hardware could act as substitutes for Emerson's integrated hardware-software packages.
Third-Party Maintenance and Refurbished Components
The availability of third-party maintenance and refurbished components presents a significant threat of substitutes for Emerson Electric. For many of Emerson's industrial automation and climate technologies, customers can choose independent repair services or opt for pre-owned parts instead of engaging with Emerson's official support or purchasing new equipment. This can directly affect Emerson's aftermarket service revenue, which is a crucial component of its profitability.
For instance, in the industrial controls sector, while Emerson offers comprehensive service agreements and genuine replacement parts, a significant market exists for independent firms specializing in repairing and refurbishing older Emerson equipment. This can be particularly appealing to customers looking to reduce operational costs, especially for legacy systems where original parts might be costly or harder to source directly. The cost savings offered by these third-party options can be substantial, making them a compelling alternative.
- Cost Savings: Third-party services often provide maintenance and parts at a lower price point than OEM offerings, making them attractive to budget-conscious customers.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Refurbished components can extend the operational life of existing Emerson equipment, delaying the need for new capital expenditure.
- Market Availability: A robust secondary market for refurbished industrial parts and specialized repair shops provides accessible alternatives to Emerson's direct services.
- Impact on Aftermarket Revenue: The preference for these substitutes can directly erode Emerson's revenue from service contracts, spare parts sales, and remanufacturing programs.
The threat of substitutes for Emerson Electric is significant, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in customer preferences. For example, new AI and IoT solutions are offering alternative ways to manage industrial processes, potentially reducing reliance on Emerson's hardware-centric offerings. In 2024, the industrial automation software market continued to see substantial investment, with companies increasingly favoring flexible, cloud-based platforms over traditional integrated systems.
Entrants Threaten
High capital investment requirements pose a significant barrier to entry for new players in the industrial technology and automation market. Companies like Emerson Electric invest billions in research and development, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and robust global supply chains. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Emerson Electric reported significant capital expenditures supporting its growth initiatives, signaling the substantial financial commitment needed to compete effectively.
Emerson Electric's formidable brand recognition and deeply ingrained customer loyalty present a significant barrier to new entrants. The company's decades-long reputation for delivering reliable, high-quality products and integrated solutions fosters considerable trust among its clientele.
This established trust, built over years of consistent performance and customer service, makes it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to carve out market share. New companies must invest heavily in marketing to even begin to challenge Emerson's established relationships and perceived value.
For instance, Emerson's focus on innovation and its ability to provide end-to-end solutions, from automation to climate technologies, creates sticky customer relationships that are not easily replicated. This loyalty directly translates to a reduced threat of new entrants as potential competitors face a steep uphill battle in winning over Emerson's established customer base.
Emerson Electric's formidable array of patents and proprietary technologies in areas like process control, automation, and climate solutions presents a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants. This intellectual property creates a significant barrier, as newcomers would either need to navigate complex licensing agreements or undertake costly, time-consuming research and development to create truly novel solutions. For instance, Emerson's investment in advanced digital transformation technologies, often protected by patents, requires substantial upfront capital and expertise to replicate.
Complex Regulatory and Certification Hurdles
The industrial and commercial sectors where Emerson Electric operates are characterized by intricate regulatory frameworks and demanding certification processes. These often include safety standards, environmental compliance, and product-specific approvals, all of which are substantial hurdles for newcomers.
Successfully navigating these complex requirements is both a time-consuming and expensive undertaking. New entrants typically lack the established infrastructure, legal teams, and specialized personnel needed to efficiently manage compliance, making it a significant barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Landscape: Industries like aerospace, medical devices, and energy infrastructure, where Emerson has a presence, are heavily regulated, requiring adherence to standards like ISO 9001, UL certifications, and specific national safety codes.
- Cost of Compliance: For example, obtaining necessary certifications for a new industrial control system can cost tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars in testing and documentation, plus ongoing maintenance fees.
- Expertise Gap: New companies often struggle to recruit or develop the in-house expertise required to interpret and implement these complex regulations, which established players like Emerson have cultivated over years.
- Time to Market: The lengthy approval cycles for new products in regulated markets can delay market entry significantly, giving established companies a crucial advantage.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Economies of scale present a formidable barrier for new entrants in Emerson Electric's industry. Established players like Emerson leverage vast production volumes, global supply chains, and extensive distribution networks to drive down per-unit costs. For instance, in 2023, Emerson reported net sales of $15.2 billion, a testament to its operational scale. This allows them to invest more heavily in research and development and offer competitive pricing, making it difficult for newcomers to match their cost efficiency.
The ability to achieve economies of scope, offering a wide array of integrated products and services, further solidifies Emerson's competitive position. New entrants often find it challenging to replicate this comprehensive offering without significant upfront investment across multiple product lines and service capabilities. Emerson's broad portfolio, encompassing automation solutions, climate technologies, and professional tools, provides a one-stop shop for many customers, creating a sticky customer relationship that new, specialized entrants would struggle to penetrate.
- Economies of Scale: Emerson's significant production volume allows for lower per-unit manufacturing costs.
- Procurement Power: Large-scale purchasing grants Emerson better terms with suppliers.
- Global Reach: An established global footprint reduces logistical costs for widespread product delivery.
- Integrated Solutions: Offering a broad range of connected products and services enhances customer value and loyalty.
The threat of new entrants for Emerson Electric is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements, with the company making significant investments in R&D and advanced manufacturing. Emerson’s strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, built over decades, also create a formidable barrier, as new competitors would need extensive marketing to gain traction.
Emerson's extensive patent portfolio and proprietary technologies in automation and climate solutions necessitate significant investment and expertise for newcomers to replicate. Furthermore, stringent regulatory frameworks and certification processes across its operating sectors, from energy to medical, demand substantial time and resources for compliance, which established players like Emerson are well-equipped to handle.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Billions required for R&D, manufacturing, and supply chains. Emerson's fiscal 2023 capital expenditures highlight this. | High barrier; significant financial commitment needed. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Decades of trust and consistent performance foster deep customer relationships. | Difficult for newcomers to gain market share; requires substantial marketing investment. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patents and proprietary technologies in key areas. | Requires costly R&D or licensing to compete; costly to replicate. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex safety, environmental, and product certifications. | Time-consuming and expensive; requires specialized expertise and infrastructure. |
| Economies of Scale | Leverages vast production volumes and global supply chains for cost efficiency. Emerson's $15.2 billion net sales in 2023 demonstrate this scale. | New entrants struggle to match cost competitiveness and pricing. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Emerson Electric is built upon a foundation of diverse and credible data sources. We utilize Emerson's official annual reports and SEC filings for financial health and strategic direction. Additionally, industry-specific market research reports and publications provide insights into competitive landscapes and trends.
