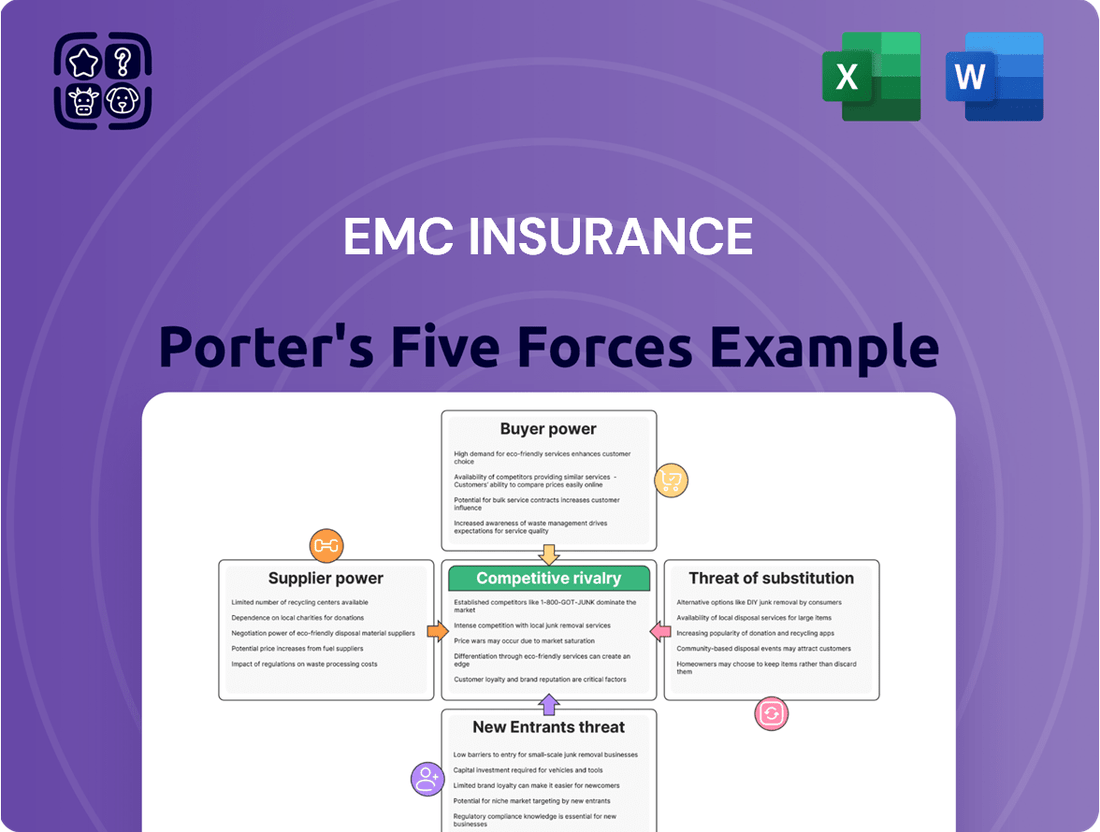
EMC Insurance Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
EMC Insurance Bundle
EMC Insurance operates within a dynamic insurance landscape, where factors like buyer bargaining power and the threat of new entrants significantly shape its competitive environment. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp EMC's market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping EMC Insurance’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Reinsurers, essential providers of risk capacity for primary insurers like EMC, currently wield significant bargaining power, especially in casualty insurance lines. This power stems from their ability to set terms and influence pricing.
Despite global reinsurance capital reaching a new high of $769 billion by the close of 2024, signaling robust capacity overall, the cost of casualty reinsurance has continued to escalate. Factors such as increasing social inflation and mounting litigation expenses are driving these price hikes, enabling reinsurers to secure more favorable contract terms.
This dynamic directly impacts EMC's operational costs and profitability, as reinsurers can dictate pricing and conditions, thereby affecting the primary insurer's ability to manage its own risk and pricing strategies.
EMC Insurance Companies' reliance on independent agents for distribution means these agents wield considerable influence. In 2024, independent agents commanded a substantial 61.5% of the property and casualty market share, a figure highlighting their collective power.
While individual agents might have varying sway over EMC, their capacity to direct business to numerous insurers provides them with significant leverage. EMC must actively cultivate its relationships with these agents to maintain access to a broad customer base.
The insurance sector's growing dependence on advanced technology, including AI and data analytics, significantly boosts the bargaining power of specialized tech and data providers. Insurtech innovations are crucial for improving underwriting, claims handling, and customer engagement, compelling insurers like EMC to adopt these advancements to stay competitive.
Capital and Investment Market Conditions
The availability and cost of capital from financial markets significantly influence insurers like EMC. In 2024, the U.S. property and casualty insurance industry generally enjoyed strong capital positions and healthy investment income. However, potential market volatility and ongoing geopolitical tensions in early 2025 could impact investment returns and how EMC deploys its capital, affecting its financial strength and growth potential.
- Capital Availability: Access to funding for underwriting and operations is crucial.
- Investment Income: Returns on invested premiums directly bolster insurer solvency and profitability.
- Market Volatility Impact: Fluctuations in financial markets can affect investment portfolios and capital levels.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Global events can introduce uncertainty, influencing investment strategies and risk appetite.
Specialized Service Providers
Beyond core insurance functions, EMC Insurance relies on specialized service providers like legal firms for claims litigation and loss control experts. The unique expertise these providers offer, particularly in complex claims or niche risk areas, can significantly influence their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized cybersecurity risk assessment services saw a notable increase, potentially strengthening the position of providers in this segment.
EMC's dedication to offering tailored coverage and risk management solutions often necessitates a strong dependence on these external specialists. This reliance means that providers with highly sought-after skills or proprietary technologies can command more favorable terms. The market for specialized legal services within the insurance sector, for example, saw average hourly rates increase by approximately 5% in the first half of 2024, reflecting this dynamic.
- Specialized Legal Services: Firms with proven track records in complex insurance litigation can leverage their expertise to negotiate higher fees.
- Loss Control & Risk Engineering: Providers offering advanced analytics or unique methodologies for risk mitigation gain leverage due to the scarcity of such skills.
- IT & Data Analytics: Companies providing specialized insurance software or data analysis tools are crucial for operational efficiency and can exert bargaining power.
- Reinsurance Brokers: While not direct service providers in the same vein, their role in accessing reinsurance capacity gives them significant influence.
Reinsurers continue to hold significant sway, particularly in casualty lines, as evidenced by the escalating cost of reinsurance. Despite a global reinsurance capital high of $769 billion by the end of 2024, factors like social inflation and increased litigation are allowing reinsurers to dictate more favorable terms, directly impacting EMC's pricing power.
Specialized technology and data providers are also gaining leverage. Insurers like EMC must adopt their innovations for competitive edge, making these providers essential. Furthermore, the market for specialized legal and risk assessment services saw rate increases in 2024, underscoring the power of niche expertise.
| Provider Type | 2024 Market Share/Trend | Impact on EMC |
|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Escalating costs in casualty lines | Dictate pricing and terms, affecting EMC's profitability |
| Independent Agents | 61.5% of P&C market share | Direct access to customers, influencing business flow |
| Tech/Data Providers | Growing dependence for competitive edge | Essential for operational efficiency, command higher prices |
| Specialized Legal/Risk Experts | Rate increases (e.g., ~5% for legal services H1 2024) | Unique expertise allows for negotiation of favorable terms |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting EMC Insurance, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the insurance sector.
Instantly assess competitive intensity and identify strategic vulnerabilities with a comprehensive, easy-to-understand breakdown of EMC Insurance's Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, especially small to medium-sized businesses and personal policyholders, are quite sensitive to price in the insurance sector. This is because there are so many different property and casualty insurers available. In 2024, the insurance market continued to see significant competition, with many companies vying for market share, putting pressure on pricing strategies.
The availability of numerous alternatives, easily accessible through independent agents or online comparison tools, empowers customers to switch insurers readily. This ease of comparison directly influences EMC's need to maintain competitive pricing to retain its customer base and ensure profitability, especially as market conditions evolve.
Independent agents, while a vital distribution channel for EMC Insurance, also function as powerful advocates for their policyholder clients. Their access to a broad spectrum of insurance products from numerous carriers grants them the leverage to steer business away from EMC if its pricing, coverage, or service falls short of market expectations.
EMC's unwavering dedication to this independent agent model underscores the collective influence these agents wield over both customer acquisition and retention. In 2024, the independent agent channel remained a cornerstone of the property and casualty insurance industry, with many insurers relying on these partnerships for a significant portion of their new business. This reliance amplifies the bargaining power of these agents, as they directly control access to a substantial customer base.
For many standard property and casualty insurance policies, the direct financial cost for a policyholder to switch insurers is minimal. This typically amounts to administrative effort rather than substantial fees, making it easier for customers to move to a competitor if they find better pricing or service.
This low switching cost significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers. They can readily explore alternatives if they are unhappy with EMC's pricing, claims processing, or overall customer experience, putting pressure on EMC to remain competitive and responsive.
EMC Insurance recognizes this dynamic and is actively working to counter it. Their emphasis on 'keeping insurance human' and continuously improving customer service is a strategic move to build loyalty and differentiate themselves, aiming to reduce the likelihood of customers switching solely based on price.
Information Transparency and Digital Tools
The rise of online comparison tools and digital platforms has dramatically increased customer access to insurance policy details and pricing. This heightened transparency levels the playing field, reducing information asymmetry and empowering customers to make more informed choices, thereby strengthening their bargaining power. EMC's strategic focus on technology, aiming to make transactions easier, faster, and more efficient, directly addresses this evolving customer expectation in the digital age.
This shift means customers can readily compare offerings from various insurers, putting pressure on companies like EMC to offer competitive pricing and superior value. For instance, in 2024, the online insurance comparison market continued its robust growth, with a significant percentage of consumers utilizing these platforms to research and purchase policies.
- Enhanced Information Access: Digital tools provide customers with unprecedented visibility into policy features, coverage levels, and pricing across multiple providers.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: This transparency diminishes the advantage insurers previously held due to proprietary information, leveling the playing field for consumers.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Customers can easily identify the most cost-effective options, leading to greater price sensitivity and a stronger negotiating position.
- EMC's Digital Strategy: EMC's commitment to technological advancement supports its ability to compete effectively in an environment where informed customers demand efficiency and competitive pricing.
Commercial Clients' Sophistication and Customization Demands
Commercial policyholders, especially large clients with intricate risk profiles, often exhibit a higher degree of financial literacy. This sophistication translates into a demand for bespoke insurance products, allowing them to negotiate for better terms and pricing. For instance, a significant portion of the commercial insurance market is dominated by large accounts that actively seek tailored coverage, leveraging their market power.
EMC Insurance's strategic initiative to launch new business units focused on large accounts and specialty business in 2025 directly addresses this dynamic. By offering more specialized and customized solutions, EMC aims to meet the evolving needs of these powerful customers and secure their continued loyalty in a competitive landscape.
- Sophisticated Commercial Clients: Large accounts and those with complex risks are more financially astute.
- Demand for Customization: These clients require tailored insurance solutions, not one-size-fits-all policies.
- Negotiating Power: Sophistication enables clients to negotiate favorable terms due to their ability to seek alternative providers.
- EMC's Strategic Response: The planned 2025 business units focus on catering to these high-value, demanding customers.
The bargaining power of customers for EMC Insurance is significant due to the highly competitive nature of the property and casualty insurance market. In 2024, numerous insurers competed for market share, driving price sensitivity among policyholders, particularly small to medium-sized businesses and personal lines customers. The ease with which customers can switch providers, facilitated by independent agents and online comparison tools, further amplifies their leverage. This dynamic necessitates that EMC maintains competitive pricing and superior service to retain its customer base.
Sophisticated commercial clients, in particular, possess considerable bargaining power. These entities often require customized insurance solutions and leverage their market knowledge to negotiate favorable terms. EMC's strategic expansion into specialized business units for large accounts, planned for 2025, directly addresses this by aiming to cater to the unique needs of these influential customers, thereby strengthening relationships and mitigating the risk of defection.
| Factor | Impact on EMC | 2024 Market Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity (Personal & SMB) | High | Intensified due to numerous competitors and easy comparison tools. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Customers can readily switch insurers, increasing pressure on EMC. |
| Independent Agent Influence | Moderate to High | Agents act as powerful intermediaries, influencing customer choice based on competitive offerings. |
| Low Switching Costs | High | Minimal administrative effort makes switching easy, enhancing customer leverage. |
| Digital Transparency | High | Online tools empower customers with pricing and policy information, increasing price sensitivity. |
| Commercial Client Sophistication | High | Large clients demand tailored solutions and negotiate aggressively for better terms. |
Preview Before You Purchase
EMC Insurance Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete EMC Insurance Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape within the insurance industry. You're viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be available for instant download upon purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of the forces shaping EMC's strategic environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. property and casualty insurance market is indeed a mature and fragmented space. This means there are many companies, both large and small, all competing for the same customers. EMC Insurance, while a significant player, finds itself among numerous established competitors, making it a challenging environment.
This maturity fuels intense rivalry. With the overall market not growing substantially, companies like EMC must focus on winning business from other insurers. In 2024, the property and casualty insurance sector is expected to continue this trend, with growth primarily driven by market share gains rather than an expansion of the customer base.
Many standard property and casualty insurance products, like auto and home coverage, are seen as quite similar by customers. This similarity often drives intense price competition among insurers. For instance, while EMC Insurance highlights its personalized service, the fundamental protection offered for common risks is available from numerous other companies, putting pressure on pricing strategies.
This focus on price can affect how profitable insurance companies are from their core underwriting activities. Despite this, the property and casualty insurance sector generally experienced improved underwriting performance in 2024, with some reports indicating a combined ratio below 95% for many carriers, a positive sign amidst the competitive landscape.
The insurance sector, including EMC Insurance, faces substantial exit barriers. These include immense capital commitments, the long-term nature of liabilities, and stringent regulatory oversight, all of which make a clean departure from the market exceedingly challenging for any insurer.
Consequently, even companies struggling financially often persist, thereby perpetuating competitive intensity. For EMC, maintaining its financial strength and its A.M. Best 'Excellent' rating is paramount for successfully navigating these industry-wide exit challenges.
Distribution Channel Competition
Competition in distribution channels is a significant factor for EMC Insurance, especially given its exclusive reliance on independent agents. Many other insurers also utilize this channel, creating a crowded marketplace where differentiation is key. For instance, in 2024, the independent agency channel continued to be a primary distribution method for a substantial portion of the property and casualty insurance market.
EMC's commitment to 100% independent agent distribution means it faces direct competition from insurers who may offer more aggressive commission structures or broader product portfolios through the same network. The rise of direct-to-consumer insurance models also presents an indirect competitive pressure, as some customers may opt for the perceived convenience and cost savings of online purchasing.
- Independent Agent Reliance: EMC's exclusive focus on independent agents places it in direct competition with numerous other insurers leveraging the same distribution strategy.
- Direct-to-Consumer Growth: The increasing popularity of direct-to-consumer insurance models creates an alternative channel that EMC must counter through superior agent support.
- Agent Loyalty and Support: To maintain its market position, EMC must continuously invest in enhancing its support, resources, and communication for its independent agents, ensuring they remain loyal and prioritize EMC business.
Impact of Catastrophe Losses and Social Inflation
The property and casualty (P&C) insurance sector, including companies like EMC Insurance, is grappling with a dual challenge: an increase in natural catastrophe losses and the rise of social inflation, especially impacting casualty lines. These combined forces are directly affecting underwriting outcomes and the overall cost of claims.
Insurers are compelled to adapt their pricing models and underwriting approaches to account for these escalating costs. For EMC, successfully navigating these risks is crucial for sustaining profitability and offering competitive rates in the market. Profitability trends, in turn, can dictate a company's willingness to compete aggressively for market share.
- Catastrophe losses: The Insurance Information Institute reported that insured losses from natural catastrophes in the U.S. reached an estimated $50 billion in 2023, a significant increase from previous years.
- Social inflation: This trend, characterized by rising litigation costs and larger jury awards, particularly in liability claims, adds further pressure to claims expenses.
- Impact on pricing: To counter these pressures, insurers are implementing rate increases. For instance, commercial property rates saw an average increase of 10-20% in 2023, according to industry analyses.
- Underwriting adjustments: Insurers are also tightening underwriting guidelines, focusing on risk selection and potentially reducing exposure in high-risk areas or lines of business.
Competitive rivalry within the property and casualty insurance market, where EMC Insurance operates, is exceptionally high. This is driven by market maturity, fragmentation, and the commoditized nature of many standard insurance products, leading to price-based competition.
In 2024, the sector's growth is largely dependent on insurers gaining market share rather than expanding the customer base, intensifying the battle for policyholders. Despite pressures, the industry saw improved underwriting in 2024, with combined ratios often below 95% for many carriers.
EMC's reliance on independent agents means it competes directly with many insurers using the same distribution channel, while also facing indirect pressure from direct-to-consumer models. This necessitates continuous investment in agent support to maintain loyalty.
The increasing frequency of natural catastrophes and the impact of social inflation are also key competitive factors, forcing insurers to adjust pricing and underwriting to manage rising claims costs, which can influence their ability to compete on price.
| Metric | 2023 (Estimate) | 2024 (Projection) | Impact on Rivalry |
| U.S. P&C Market Growth | Low single digits | Low single digits | Drives competition for market share |
| Combined Ratio (Industry Avg.) | ~97% | <95% | Improved profitability may fuel more aggressive competition |
| Insured Catastrophe Losses (U.S.) | ~$50 billion | Projected to remain elevated | Increases claims costs, impacting pricing competitiveness |
| Independent Agent Channel Share | Significant portion of P&C sales | Continued dominance | Intensifies rivalry among insurers relying on this channel |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For large commercial clients, self-insurance or establishing captive insurance programs presents a significant threat of substitution. These options allow businesses to manage their own risks and claims, potentially offering cost savings and enhanced control compared to traditional insurance policies.
In 2024, the trend towards risk retention continued, with many larger corporations exploring these alternatives to traditional insurance. For instance, the U.S. captive insurance market saw continued growth, with the number of domiciled captives in popular locations like Bermuda and the Cayman Islands remaining robust, indicating a persistent interest in self-funding risk management strategies.
EMC Insurance must therefore demonstrate clear advantages in its offerings, such as superior risk management expertise, efficient claims processing, or specialized coverage that captives may struggle to replicate cost-effectively. The ability to provide tailored solutions and a strong financial backing is crucial to retaining these sophisticated clients.
The threat of substitutes for risk management and loss prevention services is significant. Companies that effectively implement their own safety protocols, cybersecurity measures, and business continuity plans can reduce their reliance on external insurance providers or negotiate lower premiums. For instance, a company with a demonstrably strong cybersecurity posture might require less cyber insurance, thereby substituting a portion of EMC's offering with internal investment.
EMC Insurance itself acknowledges this dynamic by providing loss control insights and online resources. These tools empower clients to mitigate risks proactively, which can be viewed as a way to address the substitutive threat by partnering in risk reduction. By helping clients prevent losses, EMC can strengthen its client relationships and demonstrate value beyond just insurance coverage, even as these internal efforts act as a form of substitution.
Government programs and catastrophe bonds present a unique threat to P&C insurers like EMC Insurance. These alternatives can absorb or transfer certain risks, particularly large-scale natural catastrophes. For instance, FEMA's National Flood Insurance Program offers coverage for flood damage, a peril often insured by private P&C policies.
Catastrophe bonds, a form of alternative risk transfer, are also gaining traction in the reinsurance market. In 2023, the catastrophe bond market issuance reached a record $13.4 billion, demonstrating a growing appetite for these instruments. While not direct replacements for all P&C coverage, they can reduce the demand for traditional private market insurance for specific, high-severity events.
Non-Insurance Risk Transfer Mechanisms
Beyond traditional insurance, various non-insurance risk transfer mechanisms can act as substitutes for EMC Insurance. These include financial derivatives like futures and options, which allow parties to hedge against price fluctuations in commodities or interest rates. Indemnification clauses within contracts also shift liability from one party to another, often seen in construction or service agreements.
Specialized service agreements, where a third party assumes certain operational risks, can also reduce the need for traditional insurance coverage. For instance, outsourcing IT infrastructure management might transfer the risk of system failures to the service provider. While these are not direct replacements for all property and casualty insurance, they offer alternative solutions for specific, complex risk exposures that clients might otherwise insure.
For example, in 2024, the global market for financial derivatives was valued in the hundreds of trillions of dollars, indicating a significant volume of risk being managed outside of the insurance sector. This vast market demonstrates the willingness of businesses to employ financial instruments for risk mitigation.
- Financial Derivatives: Instruments like futures, options, and swaps allow for hedging against market volatility and specific financial risks.
- Indemnification Clauses: Contractual agreements where one party agrees to compensate another for specific losses or damages.
- Outsourcing and Service Agreements: Transferring operational or specialized risks to third-party service providers.
- Self-Insurance and Captives: While internal mechanisms, they represent a form of risk retention that can reduce reliance on external insurers for certain risks.
Digital Platforms and Embedded Insurance
The threat of substitutes for EMC Insurance is amplified by the rise of insurtech and digital platforms. These platforms simplify insurance purchasing, potentially bypassing traditional agents for less complex risks, thereby acting as a substitute for conventional advice and distribution models. For instance, by early 2024, a significant portion of consumers were exploring digital channels for insurance quotes, with some studies indicating over 60% of millennials prefer digital interactions for financial services.
Embedded insurance further intensifies this threat. By seamlessly integrating coverage into product or service purchases, it offers convenience that can substitute for a standalone insurance policy. This trend is growing, with projections suggesting the embedded insurance market could reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally in the coming years. EMC's strategic emphasis on human interaction and its brand update are direct responses to this evolving landscape, aiming to differentiate its value proposition against these increasingly prevalent digital substitutes.
- Digital platforms simplify insurance acquisition, potentially reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries for basic coverage.
- Embedded insurance offers convenience by bundling coverage with other purchases, acting as a direct substitute for standalone policies.
- EMC's brand strategy highlights human interaction to counter the appeal of purely digital, often substituted, insurance solutions.
The threat of substitutes for EMC Insurance is multifaceted, encompassing both direct alternatives to insurance products and methods of risk management that reduce the need for coverage. For instance, self-insurance and captive insurance programs offer large commercial clients greater control and potential cost savings, a trend that saw continued growth in the U.S. captive market in 2024. Similarly, financial derivatives and contractual indemnification clauses allow businesses to manage or transfer specific risks outside of traditional insurance frameworks, with the global derivatives market valued in the hundreds of trillions of dollars in 2024.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on EMC Insurance | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Retention | Self-insurance, Captive Insurance | Reduces demand for traditional policies, requires EMC to demonstrate superior value. | Continued growth in U.S. captive market, indicating persistent interest. |
| Alternative Risk Transfer | Catastrophe Bonds, Financial Derivatives | Can absorb or transfer specific, high-severity risks, lessening reliance on private market for certain perils. | Catastrophe bond market issuance reached a record $13.4 billion in 2023; global derivatives market valued in hundreds of trillions in 2024. |
| Internal Risk Mitigation | Enhanced safety protocols, Cybersecurity measures | Reduces the need for specific insurance coverage or allows for lower premiums. | Companies invest internally to mitigate risks, potentially substituting insurance for internal controls. |
| Digital & Embedded Insurance | Insurtech platforms, Bundled coverage | Simplifies acquisition and offers convenience, potentially bypassing traditional distribution. | Over 60% of millennials prefer digital financial service interactions; embedded insurance market projected for significant global growth. |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector, including companies like EMC Insurance, demands significant upfront capital. This is necessary to cover potential claims and adhere to stringent solvency regulations. For instance, in 2024, many states require insurers to maintain a minimum surplus of several million dollars, a substantial barrier for new players.
Navigating the complex web of state-specific licensing, compliance with evolving insurance laws, and continuous regulatory oversight presents another formidable challenge. Companies must also comply with guidelines from organizations like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC). EMC's consistent 'Excellent' AM Best rating highlights its robust financial stability, a key factor in overcoming these regulatory hurdles.
Existing insurers like EMC Insurance benefit significantly from deep-rooted brand loyalty and established relationships with both policyholders and independent agents. This trust, built over decades, is a formidable barrier for new entrants. For instance, EMC's century-plus legacy in the insurance market, coupled with its strong commitment to agent partnerships, has cultivated a loyal customer base that is less likely to switch to an unknown entity.
Securing access to established distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new insurance companies. EMC Insurance, like many established players, relies on a robust network of independent agents. Building and nurturing these relationships takes considerable time and resources, making it difficult for newcomers to gain immediate market penetration through this traditional avenue.
New entrants must therefore consider alternative strategies, such as developing their own direct-to-consumer digital platforms. However, this path is fraught with its own challenges, including substantial marketing costs and intense competition in the digital space. For instance, in 2024, the cost of acquiring a new customer online for insurance products continued to be a significant investment, with some channels exceeding $500 per policyholder.
Data and Technology Investment
While insurtech innovation can reduce some entry hurdles, it demands substantial investment in data analytics, AI, and advanced tech infrastructure to remain competitive. New players must gather extensive data for precise underwriting and claims processing, alongside developing sophisticated operational platforms.
This technological requirement acts as a significant barrier to entry, especially for those lacking substantial capital and expertise. For instance, in 2024, the global insurtech market continued its robust growth, with significant funding rounds directed towards companies leveraging AI for risk assessment and customer engagement, underscoring the capital intensity of this space.
- High Capital Outlay: Significant upfront investment is needed for data science teams, AI development, and scalable cloud infrastructure.
- Data Acquisition Costs: Acquiring and cleaning vast datasets for underwriting and actuarial modeling can be prohibitively expensive.
- Technological Expertise: Building and maintaining cutting-edge platforms requires specialized and often costly talent.
Expertise in Underwriting and Risk Assessment
The property and casualty insurance sector, including companies like EMC Insurance, demands significant expertise in underwriting and risk assessment. This involves a deep understanding of diverse and often complex risks across multiple industries and geographical locations. Acquiring this specialized knowledge, especially for niche markets or large commercial accounts, is a lengthy process that requires experienced and skilled personnel.
EMC Insurance's commitment to developing specialized underwriting units, planned for 2025, underscores the importance of this expertise as a substantial barrier to entry for potential new competitors. This deep-seated knowledge is not easily replicated, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively against established players with proven track records in risk evaluation and pricing.
- Deep Underwriting Expertise: Property and casualty insurance requires years of experience to master the nuances of risk assessment for varied industries and locations.
- Skilled Personnel: Developing and retaining individuals with this specialized underwriting knowledge is a significant investment and a barrier for new entrants.
- EMC's Strategic Focus: EMC's planned specialized underwriting units in 2025 demonstrate a proactive approach to reinforcing this critical competitive advantage.
The threat of new entrants in the insurance sector, impacting EMC Insurance, is considerably low due to substantial barriers. These include the immense capital required for solvency and regulatory compliance, with state minimum surplus requirements often in the millions of dollars as of 2024. Furthermore, navigating the complex and varied state-specific licensing and regulatory landscape, overseen by bodies like the NAIC, demands significant legal and operational resources that deter newcomers.
Established brand loyalty and deep agent relationships, cultivated over decades by companies like EMC Insurance, present another significant hurdle. For instance, EMC's century-plus legacy fosters trust, making it difficult for new, unproven entities to attract policyholders. Building a comparable network of trusted independent agents is a time-consuming and resource-intensive endeavor for any new entrant.
The need for specialized underwriting expertise and advanced technological infrastructure, including data analytics and AI, further elevates the barrier to entry. New players must invest heavily in acquiring vast datasets and specialized talent to compete effectively in risk assessment and pricing, a challenge underscored by the significant funding rounds in the insurtech space in 2024.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Meeting solvency ratios and regulatory capital needs. | High; requires substantial upfront investment. | Minimum surplus requirements often in the millions of USD. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating diverse state-specific licensing and laws. | High; demands significant legal and operational expertise. | Compliance with NAIC guidelines and evolving state insurance laws. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established customer trust and agent networks. | High; difficult to replicate long-term relationships. | EMC's legacy of over 100 years fostering agent partnerships. |
| Technological Investment | Data science, AI, and advanced tech infrastructure. | High; requires significant capital and specialized talent. | Insurtech funding rounds in 2024 focused on AI for risk assessment. |
| Underwriting Expertise | Deep knowledge of risk assessment and pricing. | High; requires years of experience and skilled personnel. | EMC's planned specialized underwriting units for 2025. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis of EMC Insurance's competitive landscape is built upon a foundation of industry-specific data, including financial reports from EMC and its competitors, market research from reputable firms, and insights from insurance trade publications. We also leverage publicly available information such as regulatory filings and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the forces shaping the industry.
