E-mart SWOT Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
E-mart Bundle
E-mart's strengths lie in its established brand and extensive store network, but it faces intense competition and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the retail landscape.
Want the full story behind E-mart's competitive edge, potential threats, and strategic opportunities? Purchase the complete SWOT analysis to gain access to a professionally written, fully editable report designed to support your market strategy and investment decisions.
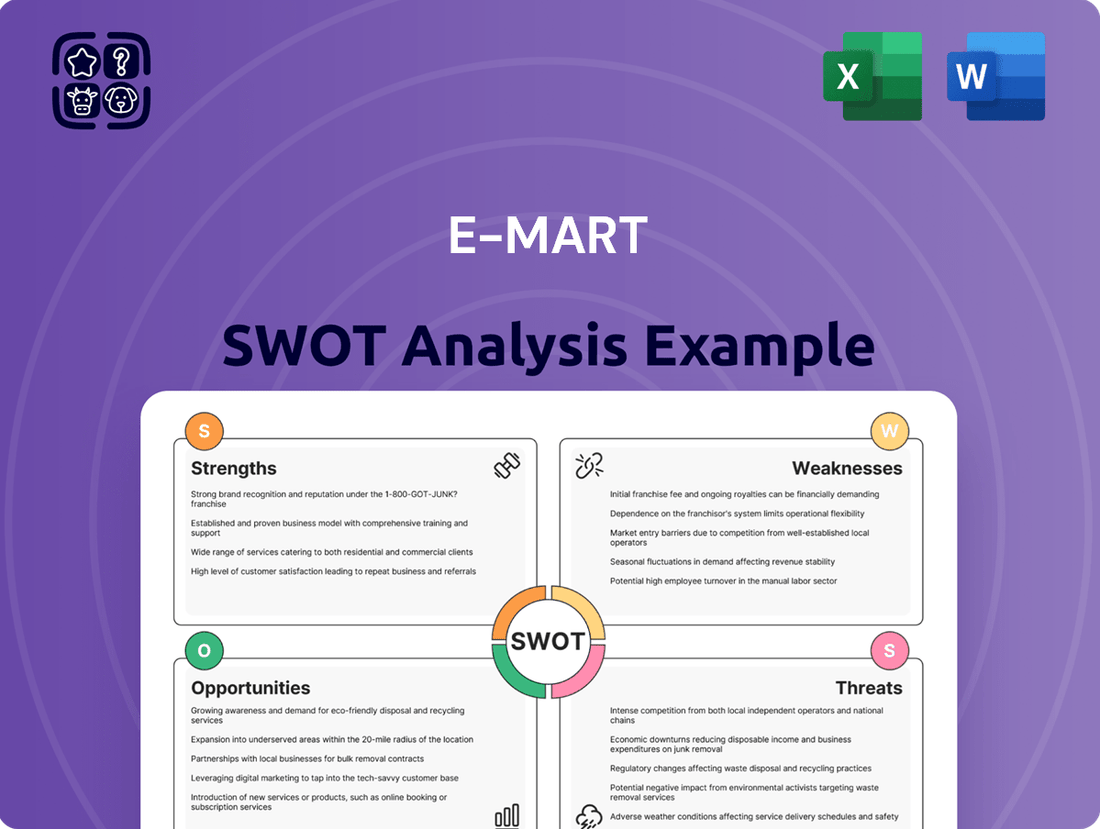
Strengths
E-Mart commands a dominant position in South Korea's retail landscape, operating a vast network of hypermarkets and various smaller store formats. This extensive physical presence ensures widespread accessibility for a diverse customer base, fostering robust brand recognition and deep-seated consumer trust.
As of early 2024, E-Mart operates over 150 hypermarkets nationwide, complemented by hundreds of smaller convenience stores and specialty outlets. This expansive footprint translates into significant economies of scale, particularly in sourcing and logistics, allowing for competitive pricing and efficient inventory management.
E-Mart's strength lies in its remarkably diversified product portfolio, spanning everything from essential groceries and everyday household items to fashion apparel and consumer electronics. This broad selection makes E-Mart a convenient, go-to destination for a wide array of consumer needs, simplifying shopping for its customers.
This comprehensive product range is a significant advantage, as it reduces E-Mart's dependence on any single market segment. For instance, in 2023, E-Mart's grocery segment continued to be a strong performer, while its electronics and apparel divisions also contributed significantly to overall revenue, demonstrating the resilience offered by this diversification.
E-Mart boasts strong omnichannel retail capabilities, seamlessly integrating its physical stores with well-developed online platforms. This allows customers to shop conveniently through various channels, whether browsing in-store or ordering online. In 2023, E-Mart's online sales continued to grow, contributing significantly to its overall revenue and demonstrating the effectiveness of its digital strategy in reaching a wider customer base.
Strong Supply Chain and Logistics Infrastructure
E-Mart's robust supply chain and logistics infrastructure are a significant strength, allowing for efficient inventory management and timely product delivery across its extensive network of stores. This operational efficiency is key to its ability to offer competitive pricing, a cornerstone of its discount store model.
The company's established logistics network, honed over years of operation, ensures that products reach shelves promptly, minimizing stockouts and enhancing customer satisfaction. For instance, E-Mart's investment in automated warehousing and advanced route optimization technologies contributes to reduced transportation costs and improved delivery speed, crucial in the fast-paced retail environment.
- Efficient Inventory Management: E-Mart's sophisticated systems likely reduce holding costs and waste by ensuring optimal stock levels.
- Cost Control: A streamlined logistics operation directly translates to lower operational expenses, enabling competitive pricing.
- Product Availability: A reliable supply chain ensures that popular items are consistently available to customers.
- Scalability: The existing infrastructure supports E-Mart's expansion plans and ability to handle increased demand.
Customer Loyalty and Market Share
E-Mart's enduring presence in the South Korean retail landscape has fostered a deeply loyal customer base, contributing to its substantial market share. This established position translates into a predictable revenue stream and a significant barrier to entry for competitors.
Customer loyalty initiatives, coupled with a consistent commitment to service excellence, further reinforce E-Mart's market standing. For instance, E-Mart's Shinsegae Point loyalty program boasts millions of active members, demonstrating the program's effectiveness in retaining customers.
- Strong Brand Recognition: E-Mart is a household name in South Korea, benefiting from decades of operation and extensive marketing efforts.
- High Customer Retention: Loyalty programs and consistent quality of goods and services contribute to a high rate of repeat business.
- Dominant Market Share: As of early 2024, E-Mart consistently holds one of the top positions in the South Korean discount store market, often exceeding 20% market share in key categories.
E-Mart's extensive store network, exceeding 150 hypermarkets and hundreds of smaller formats nationwide as of early 2024, provides unparalleled accessibility and strong brand recognition across South Korea.
This vast physical footprint enables significant economies of scale in sourcing and logistics, allowing for competitive pricing and efficient operations, a key advantage in the discount retail sector.
The company's diversified product range, from groceries to apparel and electronics, reduces reliance on any single market segment, as evidenced by strong performance across multiple divisions in 2023, enhancing its revenue resilience.
E-Mart's robust omnichannel strategy, integrating physical stores with growing online platforms, caters to evolving consumer preferences, with online sales showing continued growth in 2023.
| Strength Category | Key Aspect | Supporting Data/Fact |
|---|---|---|
| Market Presence | Extensive Store Network | Over 150 hypermarkets and hundreds of smaller formats nationwide (early 2024). |
| Operational Efficiency | Economies of Scale | Facilitates competitive pricing and efficient logistics due to large-scale operations. |
| Product Diversification | Broad Product Portfolio | Reduced dependence on single market segments; strong performance across groceries, apparel, and electronics in 2023. |
| Digital Integration | Omnichannel Capabilities | Growing online sales in 2023 demonstrate effectiveness of integrated physical and digital channels. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes E-mart’s competitive position through key internal and external factors, detailing its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Offers a clear breakdown of E-mart's competitive landscape, identifying opportunities to leverage strengths and mitigate weaknesses for improved market performance.
Weaknesses
E-Mart faces intense competition in South Korea's retail sector, a market saturated with both domestic giants like Lotte Mart and Coupang, and a growing number of specialized online and offline retailers. This crowded environment forces E-Mart into price wars, squeezing profit margins and necessitating significant investment in marketing to stand out. For instance, Coupang's aggressive expansion and same-day delivery model have significantly challenged traditional hypermarket players.
E-Mart's significant reliance on the traditional hypermarket format presents a notable weakness. This model is increasingly challenged by evolving consumer habits, with a growing preference for online shopping and smaller, more convenient retail spaces. For instance, in 2023, online grocery sales in South Korea continued their upward trajectory, capturing a larger share of the market, which directly impacts hypermarket foot traffic.
Adapting these large-format stores to meet changing consumer demands requires substantial investment and operational overhauls. This can include reconfiguring store layouts, integrating digital services, and managing inventory for a more omnichannel experience, all of which can strain resources and hinder agility in a rapidly shifting retail landscape.
E-mart's extensive network of physical hypermarkets and supermarkets comes with significant operating costs. These include substantial expenses for real estate leases, utilities, and staffing across numerous locations, which can be a considerable burden. For example, in 2023, E-mart's operating expenses were reported to be KRW 14.5 trillion, reflecting the ongoing costs associated with maintaining its vast physical footprint.
The sheer scale of E-mart's operations, coupled with a wide array of products, directly translates into high fixed and variable expenses. These costs, encompassing everything from energy consumption to employee wages and store upkeep, can put pressure on profit margins. This is particularly true during periods of economic uncertainty or rising inflation, as seen with the general increase in consumer prices impacting utility and labor costs throughout 2024.
These elevated operating costs can limit E-mart's agility in adjusting its pricing strategies to remain competitive. When a large portion of revenue is consumed by operational overheads, the company may have less room to maneuver on prices, potentially impacting its ability to attract price-sensitive customers or respond effectively to competitor pricing. This financial rigidity can be a significant weakness in a dynamic retail market.
Vulnerability to Economic Downturns
E-Mart, like many large retailers, faces significant vulnerability to economic downturns. Its broad product range means that a slowdown in consumer spending, particularly on non-essential items, directly impacts sales. For instance, during periods of high inflation or recessionary fears, consumers tend to cut back on discretionary purchases, which can lead to a noticeable drop in E-Mart's revenue.
Economic conditions directly influence consumer confidence and disposable income, key drivers for retail sales. A weakening economy often translates to job insecurity and reduced purchasing power, forcing consumers to prioritize essential goods over E-Mart's wider offerings. This sensitivity means E-Mart's financial performance is closely tied to macroeconomic stability.
- Economic Sensitivity: E-Mart's revenue streams are highly dependent on the overall health of the economy and consumer spending habits.
- Discretionary Spending Impact: Downturns typically see a reduction in spending on non-essential goods, directly affecting E-Mart's sales volume.
- Consumer Confidence Factor: Low consumer confidence, a hallmark of economic slowdowns, leads to decreased purchasing power and retail demand.
- Revenue Volatility: The company's financial results can exhibit significant volatility during periods of economic uncertainty.
Need for Continuous Digital Transformation and Innovation
E-Mart faces the ongoing challenge of maintaining its digital edge. Despite strong online capabilities, the company must continually invest in and adapt to rapidly evolving technologies and changing consumer digital habits. Staying ahead in areas like artificial intelligence for personalized recommendations or ensuring smooth integration between online and physical stores is crucial to avoid falling behind competitors.
The financial and operational demands of this continuous digital transformation are substantial. For instance, in 2024, global retail IT spending was projected to reach over $230 billion, highlighting the significant investment required to remain competitive in the digital space. E-Mart's ability to manage these costs and complexities effectively will be a key determinant of its future success.
- Constant Need for Technological Upgrades: E-Mart must consistently update its digital infrastructure to incorporate new technologies like advanced analytics and AI-driven personalization.
- Adapting to Shifting Consumer Behavior: The company needs to anticipate and respond to new digital shopping trends and expectations, such as hyper-personalization and seamless omnichannel experiences.
- High Investment in Innovation: Significant capital expenditure is required to fund research and development for new digital solutions and to implement them across the organization.
- Risk of Competitive Lag: Failure to innovate at the same pace as competitors could result in a loss of market share and customer loyalty in the increasingly digital retail landscape.
E-Mart's reliance on physical stores, particularly large hypermarkets, is a significant weakness as consumer preferences shift towards online shopping and smaller formats. This outdated model struggles to keep pace with evolving shopping habits, impacting foot traffic and sales. For example, in 2023, online grocery sales in South Korea continued to grow, directly challenging the traditional hypermarket experience.
The company's extensive physical footprint incurs substantial operating costs, including real estate, utilities, and staffing, which can strain profitability. In 2023, E-Mart's operating expenses reached KRW 14.5 trillion, underscoring the financial burden of maintaining its vast network of stores. These high overheads limit pricing flexibility, making it harder to compete effectively with more agile rivals.
E-Mart is vulnerable to economic downturns, as consumers tend to cut back on discretionary spending, directly impacting sales. During periods of inflation or recessionary fears, the company's broad product range means it's susceptible to reduced purchasing power. This economic sensitivity can lead to revenue volatility, as seen with rising consumer prices impacting utility and labor costs throughout 2024.
The company faces the challenge of continuous digital innovation to stay competitive. Keeping up with rapid technological advancements and evolving digital consumer behavior requires significant and ongoing investment. For instance, global retail IT spending in 2024 was projected to exceed $230 billion, highlighting the substantial capital needed to maintain a digital edge and avoid falling behind competitors.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
E-mart SWOT Analysis
This preview reflects the real document you'll receive—professional, structured, and ready to use. You're seeing the actual E-mart SWOT analysis, which will be fully accessible after your purchase. This ensures you know exactly what you're buying.
Opportunities
E-Mart can significantly boost its market presence by further integrating its online platforms with its physical stores. This omnichannel approach allows for a more cohesive customer journey, from browsing online to picking up in-store or receiving rapid home delivery.
Optimizing delivery services, a key component of online expansion, is crucial. For instance, by Q4 2024, E-Mart could aim to reduce its average online order delivery time by 15% through enhanced logistics and dark store utilization, directly addressing consumer demand for speed and convenience.
Leveraging data analytics to offer personalized recommendations and promotions on its digital platforms presents another strong opportunity. By analyzing purchasing patterns, E-Mart can increase customer engagement and average order value, potentially seeing a 5-10% uplift in sales from personalized campaigns in 2025.
Expanding its digital offerings, including a wider range of exclusive online products and services, will help E-Mart capture a larger share of the rapidly growing e-commerce market, which is projected to grow by over 10% annually in South Korea through 2025.
E-Mart has a significant opportunity to diversify into specialized retail segments, tapping into markets with potentially higher profit margins. For instance, the premium organic food market is projected to grow substantially. In 2024, the global organic food market was valued at approximately $250 billion and is expected to see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 9% through 2030, presenting a fertile ground for E-Mart to establish a strong presence.
Expanding into areas like high-end electronics or curated lifestyle products can attract affluent customer demographics seeking unique and quality offerings. This strategic move could create new revenue streams and reduce reliance on traditional discount retail, which often operates on thinner margins. For example, the global market for smart home devices, a specialized electronics segment, was estimated to reach over $100 billion in 2023 and is forecast to continue its upward trajectory.
E-mart can significantly boost customer engagement and sales by using its extensive customer data for highly personalized marketing and loyalty programs. For instance, in 2024, companies leveraging advanced customer data platforms saw up to a 20% increase in repeat purchase rates.
By analyzing purchasing behaviors, E-mart can offer tailored promotions and product recommendations, much like how Amazon's recommendation engine reportedly drives over 35% of its sales. This data-driven approach also improves inventory management, reducing waste and ensuring popular items are in stock.
Ultimately, this focus on data analytics can lead to a higher customer lifetime value and greater operational efficiency for E-mart.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Forming strategic alliances with technology firms, logistics providers, or even complementary retailers presents a significant opportunity for E-mart. These collaborations can unlock new growth avenues and foster innovation, for instance, by integrating advanced AI for personalized shopping experiences.
Such partnerships could accelerate the adoption of cutting-edge technologies, bolster delivery networks, and generate novel cross-promotional initiatives. E-mart's investment in AI and automation, aiming for a 15% increase in operational efficiency by 2025, can be further amplified through tech collaborations.
These collaborations will enable E-mart to enhance its service portfolio and tap into previously unreached customer demographics. For example, a partnership with a fintech company could streamline payment options, potentially attracting younger, digitally-native consumers, a segment that saw a 10% year-over-year growth in online grocery purchases in 2024.
- Technology Integration: Partnering with AI and data analytics firms to enhance customer personalization and optimize inventory management.
- Logistics Expansion: Collaborating with third-party logistics (3PL) providers to broaden delivery reach and improve delivery speed, especially in urban centers where E-mart aims to increase its same-day delivery coverage by 20% in 2025.
- Cross-Promotional Synergies: Aligning with complementary retail brands or service providers to offer bundled deals and expand customer acquisition channels.
Focus on Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
E-Mart has a significant opportunity to leverage the increasing consumer demand for sustainability and ethical sourcing. By highlighting its commitment to environmentally responsible practices and fair trade throughout its supply chain, E-Mart can strengthen its brand reputation. This strategic focus is projected to attract a growing segment of environmentally conscious shoppers, setting E-Mart apart from its rivals in the competitive retail landscape.
This emphasis on sustainability can translate into tangible benefits, including enhanced brand loyalty and potentially higher sales volumes from consumers who prioritize ethical consumption. For instance, in 2024, the global market for sustainable goods saw continued robust growth, with a significant percentage of consumers willing to pay a premium for products aligning with their values.
- Growing Consumer Preference: A significant portion of consumers, particularly younger demographics, actively seek out brands demonstrating strong environmental and social responsibility.
- Brand Differentiation: Highlighting ethical sourcing and sustainability can create a unique selling proposition, setting E-Mart apart from competitors who may not prioritize these aspects.
- Market Expansion: Catering to the demand for sustainable products can open up new market segments and attract customers who might otherwise choose alternative retailers.
- Operational Efficiencies: Implementing sustainable practices, such as waste reduction and energy efficiency, can lead to long-term cost savings and improved operational performance.
E-Mart can capitalize on the growing demand for specialized retail by expanding into premium segments like organic foods and high-end electronics. The global organic food market, valued around $250 billion in 2024, and the smart home device market, exceeding $100 billion in 2023, represent significant growth opportunities with potentially higher profit margins.
Leveraging its vast customer data for hyper-personalized marketing and loyalty programs offers another avenue for growth. Companies utilizing advanced data platforms in 2024 saw up to a 20% increase in repeat purchase rates, a trend E-Mart can emulate to boost customer lifetime value.
Strategic alliances with tech firms and logistics providers can accelerate innovation and expand reach. For example, partnerships can enhance AI-driven personalization, with E-Mart aiming for a 15% increase in operational efficiency by 2025 through such collaborations.
E-Mart has a substantial opportunity to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers by emphasizing sustainability and ethical sourcing. This focus can enhance brand loyalty and attract a growing market segment willing to pay a premium for responsible products.
Threats
The relentless expansion of e-commerce giants like Coupang and global players such as Amazon presents a formidable challenge to E-Mart. These platforms often leverage vast logistics networks and aggressive pricing strategies, making it difficult for traditional retailers to compete on cost and convenience. In 2024, the South Korean e-commerce market is projected to reach over $200 billion, with online channels capturing an increasing share of retail sales, directly impacting E-Mart's market share.
A prolonged economic downturn, marked by persistent inflation or rising interest rates in South Korea, poses a significant threat to E-mart by potentially curbing consumer discretionary spending. This directly impacts E-mart's sales volumes, especially for non-essential, higher-margin goods. For instance, as of Q1 2024, South Korea's consumer price index (CPI) remained elevated, and the Bank of Korea maintained its policy rate, signaling continued pressure on household budgets and a likely shift towards more essential purchases.
Emerging technologies like AI-powered personalization and augmented reality shopping are rapidly reshaping retail. E-Mart risks falling behind if competitors embrace these innovations faster, as seen with the accelerated adoption of e-commerce solutions globally. For instance, by the end of 2024, global retail e-commerce sales are projected to reach $7.7 trillion, highlighting the critical need for digital integration.
Failure to invest in and integrate advanced technologies such as automated logistics could erode E-Mart's competitive advantage. Companies that successfully leverage AI for inventory management and delivery optimization, potentially reducing operational costs by up to 20% according to industry estimates, will gain a significant edge.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Geopolitical Risks
E-Mart faces significant threats from global supply chain disruptions, amplified by ongoing geopolitical tensions and trade disputes. These external factors can directly impact procurement costs and the availability of goods, potentially leading to stockouts and increased prices for consumers. For instance, the ongoing conflicts in Eastern Europe and the Red Sea shipping disruptions in late 2023 and early 2024 have already demonstrated the fragility of global logistics, with shipping costs on key routes increasing by over 100% at times.
The company's reliance on international suppliers and intricate logistics networks makes it particularly vulnerable to these shocks. A disruption at a key port or a sudden imposition of tariffs could halt shipments, creating a ripple effect throughout E-Mart's operations. This exposure can translate into product shortages, forcing E-Mart to either absorb higher costs or pass them on, risking customer dissatisfaction and a loss of market share.
- Increased Procurement Costs: Fluctuations in global commodity prices and shipping rates, exacerbated by geopolitical instability, can lead to higher costs for E-Mart's inventory.
- Product Shortages: Disruptions in manufacturing or transportation can result in a lack of popular items, negatively impacting sales and customer loyalty.
- Logistical Bottlenecks: Congestion at ports or overland routes, driven by trade disputes or unforeseen events, can delay deliveries and increase operational expenses.
Changing Regulatory Environment and Labor Costs
E-Mart faces significant challenges from a shifting regulatory landscape. For instance, South Korea's minimum wage has seen consistent increases, with the 2024 minimum wage set at 9,860 KRW per hour, a 2.5% rise from 2023. This directly impacts labor costs, a substantial component of retail operations.
Furthermore, evolving environmental regulations and consumer protection policies necessitate ongoing investment in compliance and operational adjustments. Stricter rules on waste management or product labeling can add to overheads and potentially slow down expansion plans. E-Mart's ability to navigate these changes efficiently will be crucial for maintaining profitability.
- Increased Labor Costs: The 2024 minimum wage in South Korea stands at 9,860 KRW per hour, impacting E-Mart's operational expenses.
- Environmental Compliance: New regulations regarding sustainability and waste reduction require capital investment and process adaptation.
- Consumer Protection: Evolving consumer rights and safety standards demand continuous monitoring and adjustments to product and service offerings.
Intensified competition from e-commerce giants and evolving consumer preferences for digital engagement pose significant threats to E-Mart's market position. The ongoing digital transformation in retail, evidenced by the projected $7.7 trillion global e-commerce sales by the end of 2024, necessitates substantial investment in technology to remain competitive.
Economic headwinds, including persistent inflation as seen in South Korea's elevated CPI in Q1 2024, directly impact consumer spending power, potentially reducing demand for E-Mart's products. Furthermore, disruptions in global supply chains, highlighted by over 100% shipping cost increases on key routes in late 2023/early 2024, threaten inventory availability and increase procurement costs.
Regulatory changes, such as the 2.5% increase in South Korea's minimum wage to 9,860 KRW per hour for 2024, will escalate labor costs. Additionally, adapting to stricter environmental and consumer protection standards requires ongoing capital expenditure and operational adjustments, potentially impacting profitability.
| Threat Category | Specific Threat | Impact on E-Mart | Supporting Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Competition | E-commerce Giants (Coupang, Amazon) | Loss of market share, price pressure | South Korean e-commerce market projected over $200 billion in 2024 |
| Economic Conditions | Inflation & Reduced Consumer Spending | Lower sales volumes, shift to essentials | South Korea CPI elevated in Q1 2024; Bank of Korea maintained policy rate |
| Technological Advancements | AI Personalization, AR Shopping | Risk of falling behind competitors | Global retail e-commerce sales projected to reach $7.7 trillion by end of 2024 |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Geopolitical Tensions, Shipping Issues | Increased procurement costs, product shortages | Shipping costs on key routes increased over 100% in late 2023/early 2024 |
| Regulatory Environment | Minimum Wage Increases, Environmental Rules | Higher labor costs, compliance investment | South Korea minimum wage: 9,860 KRW/hour in 2024 (2.5% increase) |
SWOT Analysis Data Sources
This SWOT analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from the e-mart's official financial statements, comprehensive market research reports, and expert industry analyses to provide a well-rounded and actionable strategic overview.
