Elopak Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Elopak Bundle
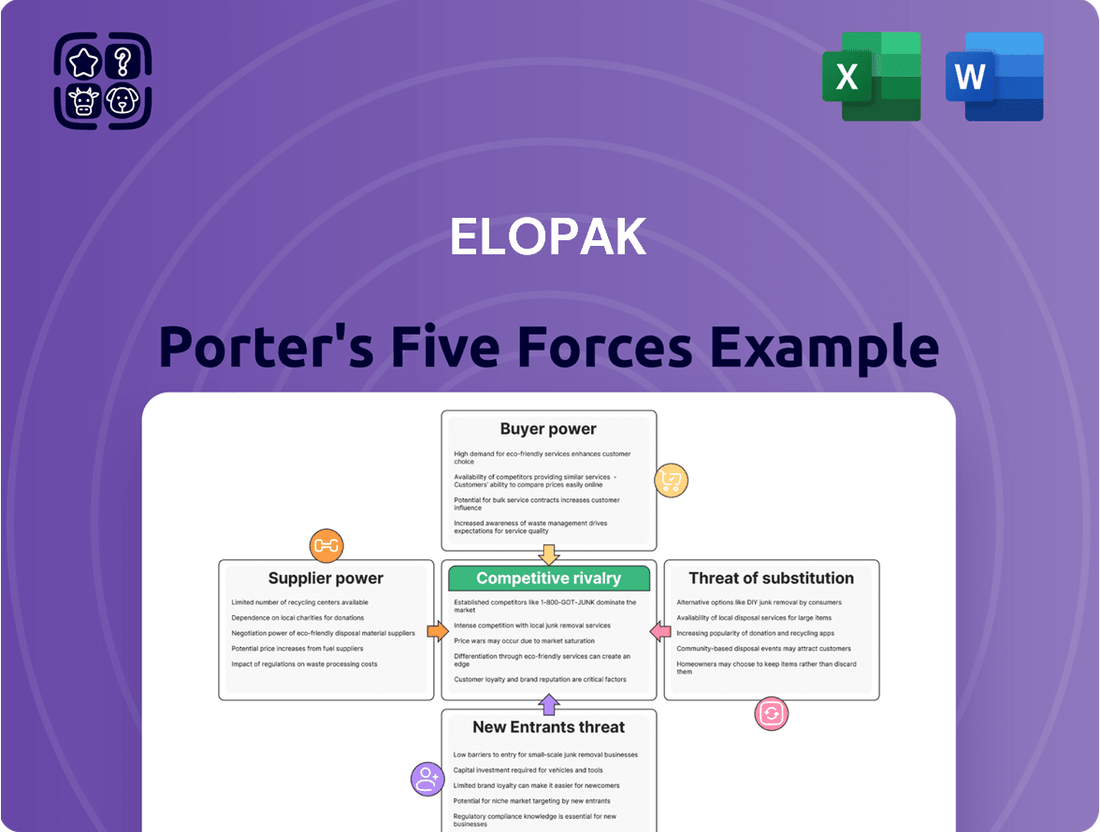
Elopak's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces, from the bargaining power of buyers to the threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating in or looking to enter the carton packaging sector. For instance, the intensity of rivalry among existing players significantly impacts pricing and profitability.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Elopak’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Elopak's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for paperboard significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. With only two key suppliers in Europe, Stora Enso Oyj and BillerudKorsnäs AB, and two in North America, Pactiv Evergreen Inc. and Nippon Paper Industries Co. Ltd., Elopak faces limited options if any of these suppliers experience disruptions or decide to increase prices.
This dependence is further underscored by the fact that paperboard represents a substantial 70-80% of Elopak's carton production costs. Such a high proportion of a critical input sourced from a small number of providers creates a notable vulnerability, giving these suppliers considerable leverage in price negotiations and supply terms.
Elopak faces considerable bargaining power from its paperboard suppliers, largely due to high switching costs. These costs can include the expense and time involved in re-certifying new paperboard materials to meet food-grade standards and performance requirements. Furthermore, adapting manufacturing lines to different paperboard specifications or thicknesses can incur significant capital expenditure and operational downtime. For instance, in 2023, Elopak reported that raw materials, primarily paperboard, constituted a substantial portion of its cost of sales. The need to maintain consistent product quality and operational efficiency makes abrupt supplier changes challenging and costly, thereby reinforcing the suppliers' leverage.
While the primary material, paperboard, is largely a commodity, Elopak's reliance on specialized inputs like bio-circular polymers and unique closures introduces a degree of differentiation. This can shift bargaining power towards suppliers of these niche components.
Elopak's commitment to renewable and sustainably sourced materials, a key differentiator for the company, narrows the available supplier base. Suppliers who can consistently meet these stringent environmental and ethical criteria may command greater leverage due to the limited number of alternatives.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Elopak's paperboard suppliers is generally considered low. The specialized nature of carton manufacturing and the sophisticated filling machinery required create significant barriers to entry for paper producers seeking to move downstream.
However, large, integrated paper and packaging conglomerates do possess the financial and technical capacity to potentially expand their operations into carton converting. Should these entities begin competing directly with Elopak's existing customer base by offering finished cartons, it could indeed shift the balance of power, amplifying supplier leverage.
While not an immediate concern for Elopak in the current market, this potential long-term shift warrants ongoing monitoring. For context, the global paper and packaging market was valued at approximately $1 trillion in 2024, with significant investments in advanced manufacturing technologies.
This potential for downstream expansion by major paper suppliers could lead to:
- Increased competition for Elopak's customers.
- Potential price pressures on Elopak's carton offerings.
- A need for Elopak to innovate and differentiate its value proposition.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Elopak's Cost Structure
Suppliers hold significant sway over Elopak due to the critical nature of raw materials, especially paperboard, which forms a large part of their production expenses. For instance, in 2023, paperboard costs were a primary driver of Elopak's cost of sales. This reliance means that any shifts in paperboard prices directly affect Elopak's bottom line, as evidenced by the inflationary pressures experienced throughout 2022 and into 2023.
While Elopak employs strategies like multi-year CPI-linked fixed-price contracts and regional revenue indexation to buffer against these price swings, the fundamental cost sensitivity remains. This inherent vulnerability to raw material price fluctuations grants suppliers considerable bargaining power. In 2024, continued volatility in global commodity markets could further amplify this supplier leverage.
- Paperboard as a Key Cost Component: Raw materials, predominantly paperboard, constitute a significant portion of Elopak's overall production expenditure, making the company susceptible to price changes.
- Impact of Price Fluctuations: Increases in paperboard prices, as observed during recent inflationary periods, can directly squeeze Elopak's profit margins.
- Mitigation Strategies: Elopak utilizes fixed-price contracts linked to the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and revenue indexation in certain markets to manage raw material cost volatility.
- Supplier Leverage: Despite mitigation efforts, the company's dependence on paperboard suppliers gives them substantial bargaining power, especially in a dynamic market environment.
Elopak's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly constrained by its heavy reliance on paperboard, which accounts for 70-80% of its carton production costs. With a limited number of major paperboard suppliers, including Stora Enso Oyj, BillerudKorsnäs AB, Pactiv Evergreen Inc., and Nippon Paper Industries Co. Ltd., these providers hold considerable leverage. High switching costs, stemming from the need for material re-certification and potential manufacturing line adjustments, further solidify supplier influence.
| Supplier Type | Key Players Identified | Cost Percentage (Approx.) | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paperboard | Stora Enso Oyj, BillerudKorsnäs AB, Pactiv Evergreen Inc., Nippon Paper Industries Co. Ltd. | 70-80% | High |
| Specialized Polymers/Closures | Various niche providers | Lower (but critical for differentiation) | Moderate to High |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Elopak's position in the aseptic packaging industry.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces on a single, intuitive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Elopak's customer base is quite varied, featuring major global Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) companies and robust regional players in the liquid food and beverage sector. They are also branching out into non-food areas like home care products.
While some of Elopak's clients are very large and purchase significant volumes, the company's strategy of serving customers in over 70 countries helps spread out the risk. This broad reach means Elopak isn't overly dependent on any single buyer, which strengthens its position.
For example, in 2023, Elopak reported that its top ten customers accounted for approximately 40% of its total net sales. This highlights that while concentration exists, the remaining 60% spread across many other customers provides a degree of resilience.
Elopak's business model centers on providing comprehensive packaging solutions, encompassing not just cartons but also the crucial filling machinery and associated systems. This integrated approach means customers are making significant, long-term investments in Elopak's technology. For example, a dairy producer investing millions in a fleet of Elopak filling machines faces substantial disruption and expense if they decide to switch to a competitor's equipment.
These considerable investments in proprietary filling machinery create high switching costs for Elopak's customers. The process of changing providers involves not only acquiring new machinery but also potentially retraining staff and reconfiguring production lines. Such complexity and financial outlay significantly deter customers from seeking alternative suppliers, thereby diminishing their bargaining power.
The inherent complexity and cost associated with replacing established filling systems solidify these long-term customer relationships. This lock-in effect means customers are less likely to leverage their purchasing power to negotiate lower prices or demand more favorable terms, as the effort and expense of switching outweigh the potential benefits.
Customers in the liquid food and beverage sectors are typically quite knowledgeable about packaging options and prevailing market prices. This awareness stems from the highly competitive environments they operate within, pushing them to constantly seek the best value. In 2024, the global liquid packaging market was valued at approximately USD 110 billion, highlighting the significant scale and competitive pressures faced by buyers.
While cost remains a crucial factor, a significant trend emerging in 2024 is the increasing demand for sustainable and innovative packaging solutions. Companies like Elopak, which focus on providing these differentiated offerings, can leverage this trend to mitigate pure price sensitivity, as customers may be willing to pay a premium for environmentally friendly or technologically advanced packaging.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers, particularly large beverage producers, integrating backward into Elopak's core business of producing beverage cartons is generally low. This is primarily due to the significant capital investment and specialized technical expertise needed for manufacturing carton packaging and the associated filling machinery. For instance, setting up a modern carton production facility requires hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier most customers find prohibitive.
Elopak's business model, which often includes providing integrated packaging and filling solutions, further deters backward integration. This comprehensive approach ensures seamless operation for their clients, making it more efficient and cost-effective to purchase complete systems rather than develop in-house capabilities. In 2024, the complexity of maintaining proprietary filling technologies alongside carton production represented a substantial operational hurdle for potential entrants.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing a carton manufacturing plant involves substantial upfront investment in specialized machinery and technology, often exceeding $100 million.
- Technical Expertise: The intricate processes of paperboard coating, printing, and die-cutting, as well as the development of aseptic filling technology, demand specialized knowledge.
- Integrated Solutions: Elopak's offering of combined packaging materials and filling equipment simplifies operations for customers, reducing the incentive to develop separate production lines.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale, dedicated carton manufacturers like Elopak benefit from economies of scale that are difficult for individual customers to replicate.
Importance of Elopak's Product to Customer's Business
Elopak's packaging plays a vital role in its customers' operations, directly impacting product integrity and market appeal. For instance, its aseptic carton solutions are essential for maintaining food safety and extending the shelf-life of beverages and liquid foods, a critical factor for major dairy and juice producers. This fundamental importance means customers cannot easily switch suppliers without risking product spoilage or compromising brand image.
The increasing consumer and regulatory focus on sustainability further amplifies the strategic significance of Elopak's packaging. Companies are actively seeking to reduce their environmental impact, and Elopak's commitment to renewable and recyclable materials, such as its 100% renewable carton introduced in 2023, directly supports these customer goals. This makes Elopak's offerings a key component in their customers' environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategies, thereby strengthening Elopak's position.
- Crucial for Product Integrity: Elopak's packaging ensures food safety and extends shelf-life, vital for customer product quality.
- Brand Presentation: The packaging contributes significantly to how a customer's product is perceived on the shelf.
- Sustainability Driver: Elopak's eco-friendly packaging options help customers meet growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
- Reduced Environmental Footprint: Customers rely on Elopak to achieve their own environmental targets and improve their ecological image.
Elopak's customers, particularly large beverage companies, have moderate bargaining power. While they represent significant volume, Elopak's global reach and integrated solutions create switching barriers. In 2023, the top ten customers accounted for about 40% of sales, indicating some concentration, but the remaining 60% is diversified. The high cost of switching filling machinery, often millions of dollars, significantly reduces customer leverage, as seen in the continued adoption of Elopak's integrated systems in 2024.
| Customer Type | Purchase Volume Impact | Switching Cost Factor | Bargaining Power Level |
| Large FMCG Companies | High | High (due to integrated machinery) | Moderate |
| Regional Players | Moderate | High (due to integrated machinery) | Moderate |
| New Entrants (Non-food) | Low to Moderate | Moderate (less entrenched) | Moderate to High |
Preview Before You Purchase
Elopak Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the comprehensive Elopak Porter's Five Forces analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase. The document is fully formatted and ready for your strategic planning needs. You are seeing the exact, professionally written analysis that will be delivered to you, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. This is the complete, ready-to-use file, giving you instant access to valuable market insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The liquid food packaging sector is highly competitive, featuring dominant global companies such as Tetra Pak, SIG Combibloc, Evergreen Packaging, and Nippon Paper Industries. Elopak navigates this moderately concentrated market, facing significant rivalry for customer contracts and market share.
In 2023, the global aseptic carton packaging market, a key segment for Elopak, was valued at approximately USD 20.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.2% through 2030. This growth indicates a dynamic environment where established players and emerging regional competitors vie for opportunities.
Elopak's competitive standing is shaped by these numerous global and regional players, each with their own innovations and market strategies. The presence of these diverse competitors means Elopak must continually adapt to maintain and expand its position in the market.
The liquid packaging market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a 5.1% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2025 to 2030. This expansion fuels competitive rivalry as companies strive to capture a larger piece of an increasingly valuable market.
Specifically, the aseptic paper packaging segment for liquid foods is expected to see even stronger growth, with a CAGR of 6% anticipated between 2025 and 2033. Such rapid expansion creates fertile ground for increased competition among established players and new entrants alike, intensifying the battle for market share and innovation.
Elopak distinguishes itself in the competitive landscape by emphasizing sustainable, paper-based packaging. Their offerings include innovative solutions like bio-circular polymers and natural brown board cartons, alongside comprehensive packaging systems. This focus on eco-friendly attributes is a key differentiator.
The company's commitment to continuous innovation is evident in its advancements in materials, design, and filling technology. For instance, the development of D-PAK™ cartons specifically for non-food items showcases their drive to create tailored solutions. This ongoing innovation is vital for staying ahead of competitors.
In 2024, the packaging industry saw a significant push towards sustainability, with Elopak's strategic focus aligning well with market demands. For example, the global sustainable packaging market was projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer preference for eco-conscious options. Elopak’s investments in areas like bio-circular polymers directly address this trend.
Exit Barriers
High capital investments in manufacturing facilities and specialized machinery represent a substantial hurdle for packaging companies looking to exit the market. For instance, the cost of setting up a modern packaging plant can run into tens of millions of dollars, making it difficult to recoup such an outlay if demand softens. This financial commitment effectively traps companies within the industry, even when economic conditions are unfavorable.
Long-term contracts for filling equipment further cement these exit barriers. Many packaging manufacturers provide specialized filling machines to their clients, often tied to multi-year supply agreements. These contracts create an ongoing obligation that makes it impractical to cease operations without incurring significant penalties or leaving customers without essential equipment.
These entrenched exit barriers can foster sustained competitive rivalry. Even if profitability shrinks, companies are compelled to remain operational to avoid substantial losses on their fixed assets and contractual obligations. This dynamic can lead to intense price competition and a struggle for market share as firms fight to cover their costs.
- High Capital Costs: The packaging industry requires significant upfront investment in plant and machinery, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars for large-scale operations.
- Specialized Equipment: Machinery is often tailored for specific packaging formats, limiting its resale value or adaptability to other industries.
- Long-Term Contracts: Agreements for filling machinery can extend for 5-10 years, creating a commitment that discourages early exit.
- Brand Reputation: Companies may fear damaging their reputation by withdrawing from supply agreements, further discouraging departure.
Competitive Strategies
Competitive rivalry within the aseptic carton packaging industry is intense. Key players, including Elopak, frequently employ strategies such as product innovation, mergers, acquisitions, and geographic expansion to gain market share. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous adaptation and strategic maneuvering.
Elopak's strategic focus, encapsulated by its 'Repackaging tomorrow' initiative, highlights its commitment to global expansion and reinforcing its leadership in established markets. A significant driver of this strategy is capitalizing on the ongoing shift away from plastic packaging, a trend that offers substantial growth opportunities for companies like Elopak.
- Product Innovation: Competitors invest in developing new packaging formats and materials to meet evolving consumer and regulatory demands, particularly regarding sustainability.
- Market Expansion: Companies actively pursue growth in emerging markets and seek to deepen penetration in existing ones through strategic partnerships or direct investment.
- Consolidation: The industry has seen a pattern of mergers and acquisitions as firms aim to achieve economies of scale, expand their product portfolios, and enhance their competitive positioning.
- Sustainability Focus: A major competitive battleground is the development of more environmentally friendly packaging solutions, including increased use of renewable materials and improved recyclability.
Competitive rivalry in the liquid packaging sector is intense, driven by major global players like Tetra Pak and SIG Combibloc, alongside regional competitors. Elopak operates within this dynamic market, characterized by a strong emphasis on innovation and sustainability as key differentiators. For instance, the global aseptic carton packaging market, valued at roughly USD 20.5 billion in 2023, is projected to grow at a CAGR of about 5.2% through 2030, fueling this rivalry.
The market's growth, with projections of a 5.1% CAGR for liquid packaging from 2025 to 2030, creates significant opportunities, intensifying competition. This is particularly true in the aseptic paper packaging segment, expected to grow at a 6% CAGR between 2025 and 2033, making it a crucial battleground for market share and technological advancement.
Companies like Elopak are investing heavily in sustainable solutions, such as bio-circular polymers and natural brown board cartons, to capture market share and meet evolving consumer demands. In 2024, the push for sustainable packaging was a dominant trend, with the global market for these solutions showing substantial projected growth, directly benefiting companies aligned with these eco-friendly initiatives.
High capital costs for manufacturing facilities, often in the tens of millions of dollars, coupled with long-term contracts for specialized filling equipment, create substantial exit barriers. These factors compel companies to remain operational, even during downturns, leading to sustained price competition and a constant struggle for market share as firms strive to cover their significant fixed costs.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Alternative packaging materials such as PET bottles, glass, and metal cans present a significant threat of substitutes for Elopak's paper-based cartons. These alternatives often compete on a price-performance trade-off, with plastic bottles frequently holding a cost advantage due to established production scales and widespread recycling infrastructure in certain markets.
While Elopak champions its cartons as a low-carbon, renewable, and recyclable option, the perceived value proposition of plastics, particularly concerning initial cost and convenience of disposal in some regions, directly challenges its market position. For instance, in 2023, the global PET bottle market was valued at approximately USD 100 billion, indicating a substantial installed base and consumer familiarity that Elopak must contend with.
Customer demand for sustainable packaging is a significant driver, pushing consumers towards paper-based alternatives like Elopak's cartons over traditional plastic bottles. This shift is amplified by evolving regulations; for instance, by 2024, many European nations have implemented or strengthened bans on single-use plastics, directly increasing the appeal and adoption of carton solutions. The global sustainable packaging market is projected to reach over $400 billion by 2027, with paper and paperboard holding a substantial share, indicating strong customer propensity to opt for these environmentally friendly substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Elopak's carton packaging is significant due to the wide availability of alternative packaging formats for liquid foods. These include rigid plastics like bottles, flexible pouches, glass containers, and metal cans. For instance, in 2023, the global plastic packaging market was valued at over $1 trillion, with a substantial portion serving liquid food applications, directly competing with Elopak's offerings.
These diverse packaging materials are not only readily available but are also widely adopted across various product categories that Elopak serves, such as milk, juices, and other beverages. Consumers and manufacturers often have established preferences or functional requirements that can be met by these substitutes, making it easier to switch away from carton packaging.
The competitive landscape in 2024 sees continued innovation in alternative packaging, with advancements in material science for plastics and flexible options offering improved barrier properties and sustainability claims. For example, the market for aseptic flexible packaging is projected for strong growth, indicating a direct challenge to carton dominance in certain segments.
Innovation in Substitute Materials
Innovations in substitute materials pose a significant threat to Elopak. For instance, ongoing advancements in plastic packaging, including lightweighting techniques and improved recyclability, are designed to mitigate environmental concerns. The development of bioplastics further strengthens this position, potentially eroding the perceived advantages of paper-based cartons. Elopak is actively responding by investing in its own innovations, such as bio-circular polymers and cartons with a lower carbon footprint, to maintain its competitive edge.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by material science advancements.
- Plastic packaging is seeing innovations like lightweighting and enhanced recyclability, making it a more appealing alternative.
- The rise of bioplastics offers a more sustainable perception for plastic packaging.
- Elopak is countering these trends with its own material innovations, including bio-circular polymers.
- The company is also focused on developing lower-carbon footprint cartons to remain competitive.
Switching Costs for End-Users and Brands
For end-users, the threat of substitutes is generally low. Switching between different beverage packaging types, like cartons, bottles, or cans, often involves minimal direct cost or effort. Consumer choices are more frequently influenced by factors such as portability, convenience, or a perceived alignment with environmental values, rather than substantial financial switching costs.
However, for brands, the switching costs associated with changing packaging formats are considerably higher. Implementing new packaging requires substantial capital expenditure for updated filling machinery and potential alterations to existing supply chain logistics. For instance, a dairy producer heavily invested in aseptic carton filling technology would face significant costs to retool for glass bottles or aluminum cans, making large-scale substitution a complex and expensive undertaking.
Consider the beverage industry in 2024. Companies like Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, with their vast global operations, have made significant investments in specific packaging technologies. For example, the widespread adoption of PET bottles for soft drinks represents billions of dollars in capital equipment and infrastructure. Shifting away from this established system to, say, aluminum cans for all their carbonated beverages would necessitate a complete overhaul of bottling plants and distribution networks, creating a substantial barrier.
- End-User Switching Costs: Typically low, influenced by convenience and environmental perceptions rather than direct financial outlay.
- Brand Switching Costs: High, involving significant investment in new filling lines and supply chain adjustments.
- Example: Beverage giants retooling from PET bottles to aluminum cans would incur billions in capital expenditure.
- Impact: These high brand switching costs limit the rapid and large-scale substitution of established packaging formats.
The threat of substitutes for Elopak's paperboard cartons is substantial, stemming from a wide array of alternative packaging materials like PET bottles, glass, and aluminum cans. These substitutes often present competitive pricing and established consumer familiarity, as seen with the global PET bottle market valued at approximately USD 100 billion in 2023. While Elopak emphasizes sustainability, the perceived convenience and cost-effectiveness of plastics, supported by extensive recycling infrastructure in some regions, directly challenges its market share.
Material science advancements are continuously improving substitutes, with innovations in plastic packaging, such as lightweighting and enhanced recyclability, making them more appealing. The emergence of bioplastics further bolsters the sustainability perception of plastic alternatives. Elopak is actively investing in its own material innovations, including bio-circular polymers and lower-carbon footprint cartons, to counteract these competitive pressures and maintain its market position.
While end-users face minimal switching costs, influenced more by convenience and environmental perceptions, brands encounter significant barriers. For instance, beverage giants like Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, with massive investments in PET bottle infrastructure, would incur billions in capital expenditure to transition to alternative formats like aluminum cans, limiting the speed of substitution.
| Substitute Material | Key Competitor Advantages | Elopak's Counter-Strategy |
| PET Bottles | Cost-effectiveness, established infrastructure, consumer familiarity | Focus on renewable materials, lower carbon footprint |
| Glass Bottles | Premium perception, perceived recyclability | Lightweight carton designs, improved recyclability |
| Aluminum Cans | High recyclability, lightweight | Development of advanced barrier coatings for cartons |
| Flexible Pouches | Lightweight, material efficiency | Innovations in carton design for reduced material usage |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the liquid paper-based packaging sector demands significant financial resources. This includes setting up advanced manufacturing plants, acquiring specialized machinery for carton production, and investing in filling equipment. Furthermore, research and development into sustainable packaging solutions adds to the initial capital burden.
For example, Elopak's recent investment in a new U.S. manufacturing facility highlights this. The construction and equipping of this plant alone represented a substantial capital outlay of USD 100 million.
This considerable upfront investment creates a formidable barrier for any new companies looking to enter the market. The sheer scale of capital required deters many potential competitors from even considering market entry.
Newcomers to the aseptic carton packaging market face a significant hurdle in accessing established distribution channels, a key advantage for incumbents like Elopak. Elopak, for instance, has cultivated deep, long-standing relationships with major global food and beverage manufacturers. These partnerships are crucial for securing consistent sales and market penetration.
Elopak's extensive global distribution network, spanning over 70 countries, is another formidable barrier. Replicating this reach and efficiency requires substantial investment and time, making it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively.
Securing contracts with key customers is a critical challenge for new entrants. These established relationships are built on trust, reliability, and often exclusive agreements, leaving little room for new players to gain a foothold.
In 2023, the global aseptic packaging market was valued at approximately USD 38.5 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This expanding market, however, is dominated by a few major players who control significant portions of the distribution infrastructure.
Elopak's considerable global manufacturing footprint and its massive annual production of 16 billion cartons create substantial economies of scale. This allows Elopak to spread its fixed costs over a vast number of units, driving down the per-unit production cost significantly.
For any new entrant to Elopak's market, achieving comparable cost efficiencies would necessitate an immediate and substantial investment in production capacity and volume. Without this, a new competitor would find it exceedingly difficult to match Elopak's pricing power, posing a significant barrier to entry.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
Elopak benefits from significant brand loyalty, especially for its iconic Pure-Pak® cartons, and a strong commitment to sustainability, which resonates with environmentally conscious consumers. This established reputation makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and consistently innovate to differentiate their products in a market already dominated by established brands like Elopak.
The threat of new entrants is thus moderated by the high cost and effort required to build comparable brand recognition and trust. For instance, the packaging industry, while not immune to disruption, often sees new players struggling to match the long-standing relationships and perceived quality associated with established names. Elopak’s focus on sustainable packaging solutions, a key differentiator, further raises the barrier to entry for those lacking similar eco-friendly credentials or the ability to communicate them effectively.
- Brand Loyalty: Elopak's Pure-Pak® cartons have cultivated a strong, enduring customer base.
- Sustainability Focus: Elopak's commitment to eco-friendly packaging serves as a significant differentiator.
- High Entry Costs: New entrants face substantial marketing and innovation expenses to compete with established brands.
- Differentiation Challenge: Replicating Elopak's brand reputation and product uniqueness requires considerable investment.
Regulatory and Environmental Hurdles
The threat of new entrants into the packaging industry, particularly for food and beverages, is significantly dampened by substantial regulatory and environmental hurdles. These existing players already contend with a complex web of compliance. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to enforce its ambitious Circular Economy Action Plan, placing increased pressure on packaging materials to be recyclable, reusable, or compostable. New companies entering this space must invest heavily to meet these evolving standards, including detailed testing and certification for food contact materials, which can easily add millions to initial setup costs.
Navigating these requirements is a considerable barrier. New entrants must understand and adhere to a multitude of regulations concerning product safety, labeling, and environmental impact. This includes securing approvals for materials that come into contact with food and ensuring that sourcing practices align with sustainable and ethical guidelines. The ongoing global focus on reducing plastic waste, exemplified by initiatives like the UN Environment Programme's efforts to establish a global plastics treaty, means that any new packaging solution must demonstrate clear environmental benefits and compliance from the outset.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting food safety and environmental regulations can cost new entrants millions in testing, certification, and process adaptation.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Establishing supply chains that meet stringent sustainability criteria is a complex and often expensive undertaking.
- Evolving Standards: Continuous updates to regulations, such as those driven by circular economy goals, require ongoing investment and agility from new players.
- Material Innovation: Developing and gaining approval for novel packaging materials that satisfy both performance and regulatory demands presents a significant challenge.
The threat of new entrants in the aseptic packaging market is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required for advanced manufacturing, specialized machinery, and R&D, exemplified by Elopak's $100 million U.S. plant investment. Furthermore, established players like Elopak have secured deep customer relationships and extensive global distribution networks spanning over 70 countries, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market access and achieve economies of scale necessary to compete on price, as demonstrated by Elopak's 16 billion carton annual production.
Brand loyalty, particularly for iconic products like Elopak's Pure-Pak® cartons, coupled with a strong sustainability focus, creates a substantial barrier. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and innovation to differentiate themselves, a challenge highlighted by the packaging industry's tendency for new players to struggle against established reputations and perceived quality. Regulatory compliance, including meeting stringent food safety and environmental standards, adds millions in costs for testing and certification, further deterring market entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for manufacturing and technology. | Elopak's USD 100 million U.S. plant investment. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to established networks and customer relationships. | Elopak's global distribution in over 70 countries; long-standing partnerships with major food/beverage manufacturers. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages derived from high production volumes. | Elopak's annual production of 16 billion cartons drives down per-unit costs. |
| Brand Loyalty & Differentiation | Customer preference for established brands and unique product features. | Strong loyalty to Elopak's Pure-Pak® cartons; focus on sustainability as a differentiator. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting food safety, environmental, and material standards. | EU Circular Economy Action Plan requirements; costs for testing and certification can reach millions. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Elopak Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse and credible data sources, including Elopak's official annual reports and sustainability disclosures, along with market research from firms specializing in the packaging industry.
We also leverage industry-specific trade publications, competitor financial filings, and data from reputable market intelligence platforms to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
