Elevance Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Elevance Health Bundle
Elevance Health navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, as revealed by our Porter's Five Forces analysis. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for grasping their strategic positioning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Elevance Health’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The healthcare sector, including companies like Elevance Health, often faces a concentrated supplier market for critical components such as pharmaceuticals and advanced medical devices. This means a few key players control a significant portion of the supply chain, giving them considerable bargaining power.
For instance, the pharmaceutical industry, a major supplier to health insurers, is characterized by patent protection for many blockbuster drugs, limiting competition and increasing supplier leverage. In 2024, the top 10 pharmaceutical companies by revenue held a substantial share of the global market, making it difficult for insurers to negotiate lower prices on essential medications.
Suppliers like hospitals and drug manufacturers are experiencing their own cost increases, which they pass on to insurers like Elevance Health through higher prices for services and medications. This dynamic, amplified by persistent medical inflation, directly affects Elevance Health's benefit expense ratio and overall profitability.
Elevance Health's comprehensive health plans rely heavily on a robust network of healthcare providers, including specialized physicians and advanced medical facilities. Suppliers offering unique or in-demand services, or those essential for meeting network adequacy requirements, wield significant leverage. Insurers like Elevance need these providers to attract and retain a broad membership base, giving these suppliers greater bargaining power.
Technological Dependence
Elevance Health's growing reliance on advanced technology and data analytics platforms significantly amplifies the bargaining power of its tech suppliers. These providers are crucial for optimizing operations, delivering personalized patient care, and managing financial risks effectively.
As these technological solutions become more deeply embedded and sophisticated, the switching costs for Elevance Health increase substantially. The specialized nature of these services, coupled with the critical role they play in Elevance's core functions, grants these tech providers considerable influence.
- Technological Integration: Elevance Health's investment in areas like AI-driven diagnostics and predictive analytics for population health management means deeper integration with specialized software and data providers.
- High Switching Costs: Migrating complex, data-intensive systems to new vendors can be prohibitively expensive and disruptive, locking Elevance into existing relationships.
- Critical Service Nature: The reliability and performance of these tech solutions directly impact patient care delivery and regulatory compliance, making suppliers indispensable.
Regulatory Influence
Government regulations significantly shape the bargaining power of suppliers in the healthcare industry. For instance, policies dictating pharmaceutical pricing or reimbursement models for providers directly influence how much leverage suppliers like drug manufacturers and healthcare systems have over insurers such as Elevance Health.
Changes in these regulatory landscapes can dramatically alter the power dynamics. For example, if the government mandates lower drug prices, the bargaining power of pharmaceutical suppliers would likely decrease. Conversely, regulations that increase reimbursement rates for healthcare providers could strengthen their negotiating position with insurers.
- Government Regulations: Policies on drug pricing and provider reimbursement directly impact supplier leverage.
- Impact on Insurers: Regulatory shifts can either enhance or diminish the negotiating power of healthcare providers and drug manufacturers against insurers like Elevance Health.
- Example: Stricter price controls on pharmaceuticals would likely weaken supplier power, while increased Medicare reimbursement rates could strengthen provider power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Elevance Health is a significant factor, particularly concerning pharmaceuticals and advanced medical technology. In 2024, the concentration within the pharmaceutical sector, driven by patent protections for key drugs, allows major suppliers to maintain considerable pricing leverage.
Suppliers like hospitals and specialized medical service providers also benefit from Elevance's need to maintain broad networks and offer comprehensive care. This is further compounded by Elevance's increasing reliance on sophisticated technology and data analytics, where high switching costs and critical service integration empower tech vendors.
Government regulations, such as those impacting drug pricing or provider reimbursement, directly influence the negotiating strength of these suppliers. For instance, shifts in Medicare reimbursement rates can bolster the bargaining power of healthcare providers against insurers like Elevance Health.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Elevance Health | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Patent protection, R&D costs, market concentration | Higher drug costs, reduced negotiation flexibility | Top 10 pharma companies' market share remains high |
| Medical Devices | Proprietary technology, regulatory approval, specialization | Increased costs for advanced equipment and services | Continued innovation drives demand for specialized devices |
| Healthcare Providers (Hospitals, Doctors) | Network adequacy needs, service specialization, reimbursement rates | Pressure on benefit expense ratios, need for strong provider relationships | Provider consolidation can increase their leverage |
| Technology & Data Analytics | System integration, switching costs, data security, critical functions | Higher IT expenditure, reliance on key tech partners | Growing demand for AI and analytics amplifies tech supplier power |
What is included in the product
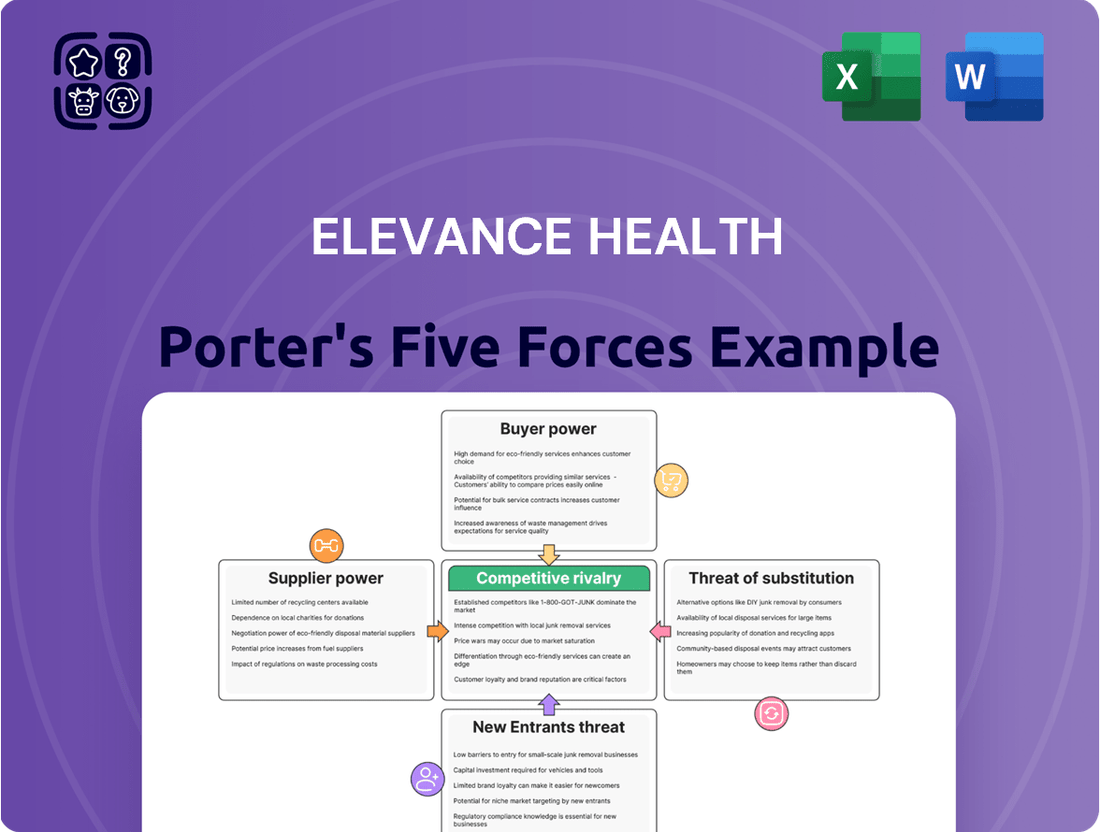
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Elevance Health dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within the health insurance industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting Elevance Health.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, including individuals and employers, are increasingly focused on price due to escalating healthcare expenses and higher deductibles. In 2024, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family health coverage reached approximately $24,000, a figure that significantly drives price sensitivity.
The proliferation of online platforms offering price comparisons and greater transparency in healthcare services empowers consumers to seek out more affordable options. This trend directly challenges Elevance Health, compelling it to maintain competitive premium pricing to retain its customer base.
For many individual and employer group clients, switching health insurance providers is relatively easy, especially with the prevalence of online marketplaces and brokers. This ease of switching significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, as they can readily move to competitors offering more favorable terms or benefits.
In 2024, the healthcare insurance landscape continues to be shaped by this accessibility. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reported that during the 2024 Open Enrollment Period for the Health Insurance Marketplace, 16.4 million Americans selected a plan, reflecting a robust market where consumers actively compare options.
Customers are increasingly seeking personalized healthcare experiences, wellness programs, and services that offer tangible value beyond standard medical coverage. This growing demand empowers them to seek out providers who can deliver tailored solutions. For instance, in 2024, many health insurance plans are expanding to include digital health tools and preventative care incentives, directly responding to this customer preference.
Influence of Large Employers and Brokers
Large employers and benefits consultants hold significant sway over Elevance Health due to the sheer volume of insured individuals they represent. This collective bargaining power allows them to negotiate for more favorable rates and tailored insurance plans, directly influencing Elevance Health's revenue streams within the employer group market. For instance, in 2024, large employer groups often account for a substantial percentage of a health insurer's total membership, making their demands difficult to ignore.
These powerful entities can leverage their size to demand competitive pricing and specific plan features that meet the needs of their workforce. This can lead to pressure on Elevance Health's profit margins as they strive to retain these valuable clients. The influence of these groups is a critical factor in how Elevance Health structures its offerings and pricing strategies.
- Volume-driven negotiations: Large employers and brokers can negotiate aggressively on behalf of their members.
- Customization demands: They often require customized plan designs to meet specific workforce needs.
- Profitability impact: Successful negotiation by these groups can reduce Elevance Health's per-member per-month revenue.
- Market concentration: A few large brokers or employers can control a significant portion of the market share for a health insurer.
Regulatory Protections and Mandates
Government regulations, like the Affordable Care Act (ACA), significantly shape the bargaining power of customers in the health insurance market. Mandates regarding essential health benefits and coverage requirements mean consumers have a baseline of services they expect, influencing plan selection and limiting insurers' ability to restrict offerings. For instance, the ACA’s requirement for coverage of pre-existing conditions directly enhances customer leverage by preventing insurers from denying coverage or charging exorbitant rates based on health status.
These regulatory protections empower consumers by standardizing plan features and increasing transparency. Changes in essential health benefits can broaden the scope of covered services, giving customers more options and thus more power to choose plans that best meet their needs. This regulatory environment can lead to increased competition among insurers to offer attractive plans within these mandated frameworks, further benefiting consumers.
Regulatory shifts can directly impact customer choices and bargaining leverage:
- Affordable Care Act (ACA) Provisions: Mandates on essential health benefits and coverage for pre-existing conditions empower consumers by ensuring a minimum standard of care and access, limiting insurer discretion.
- State-Level Regulations: Variations in state insurance laws can create different consumer protections and market dynamics, influencing the bargaining power of customers within specific geographic regions.
- Changes in Enrollment Periods: Regulations governing open enrollment periods can affect when consumers can switch plans, impacting their ability to leverage market competition at specific times.
The bargaining power of customers for Elevance Health is significant, driven by price sensitivity and the ease of switching providers. With average annual premiums for family coverage around $24,000 in 2024, individuals and employers are highly attuned to costs. The availability of online comparison tools and a robust marketplace, evidenced by 16.4 million selections during the 2024 Open Enrollment Period, further amplifies this power.
Large employers and benefits consultants wield considerable influence due to the volume of members they represent, enabling them to negotiate favorable rates and customized plans. This pressure on pricing can directly impact Elevance Health's profitability per member. Furthermore, government regulations, particularly the ACA, establish a baseline of expected services, limiting insurers' ability to restrict offerings and strengthening consumer leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Elevance Health | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Customers seek lower premiums and better value. | Average family premium ~ $24,000. |
| Ease of Switching | Customers can easily move to competitors. | 16.4 million Marketplace selections in 2024 Open Enrollment. |
| Large Employer Influence | Negotiate for lower rates and tailored plans. | Large groups represent substantial membership volume. |
| Regulatory Environment | ACA mandates enhance consumer protections. | Essential health benefits and pre-existing condition coverage are key. |
Full Version Awaits
Elevance Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Elevance Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces shaping the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning needs. This professionally formatted analysis is designed for immediate use, providing actionable insights into Elevance Health's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Elevance Health faces significant competitive rivalry from major players such as UnitedHealth Group, Cigna Group, and Humana. These entrenched competitors actively compete for market share across diverse healthcare segments, driving aggressive pricing strategies and a constant push for service and product innovation.
Competitors are increasingly broadening their reach beyond core health insurance. Many are integrating pharmacy benefits management (PBM), direct care delivery, and health technology solutions into their portfolios. This diversification means Elevance Health faces a wider array of rivals, pushing the company to enhance its own service breadth and technological capabilities to stay ahead.
Competitive rivalry in the health insurance sector is intensifying, with companies actively pursuing strategic partnerships and acquisitions to bolster their market position. This trend is driven by a desire to broaden service offerings, integrate new technologies, and achieve greater economies of scale. For instance, Elevance Health has strategically partnered with primary care providers, aiming to improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency, a move that underscores the critical role of collaboration in navigating this dynamic landscape.
Focus on Digital Transformation and AI
The healthcare industry, including companies like Elevance Health, is experiencing intense competitive rivalry driven by a significant focus on digital transformation and artificial intelligence (AI). Competitors are pouring resources into these areas to enhance customer engagement, streamline operations, and deliver more tailored healthcare solutions. For instance, in 2024, many health insurers announced substantial investments in AI-powered platforms, with some allocating upwards of $1 billion to digital initiatives aimed at improving member experience and administrative efficiency.
This technological arms race means Elevance Health must continually innovate and adapt to remain competitive. Failing to keep pace with advancements in AI, data analytics, and digital health tools could lead to a loss of market share as rivals offer superior, more personalized, and cost-effective services. The pressure to integrate these technologies is palpable, as consumers increasingly expect seamless digital interactions and personalized health insights.
- Digital Investment: Competitors are making significant capital outlays in 2024, with major health insurers reportedly earmarking 15-20% of their annual IT budgets for AI and digital transformation projects.
- AI Applications: Key areas of AI investment include predictive analytics for population health management, AI-driven chatbots for customer service, and machine learning for fraud detection and claims processing.
- Customer Experience Focus: The primary driver for these digital investments is to improve member satisfaction, offering personalized care plans and more intuitive digital platforms.
- Operational Efficiency Gains: Companies are leveraging AI to automate routine tasks, reduce administrative overhead, and improve the speed and accuracy of healthcare delivery.
Regulatory and Policy Landscape
Changes in healthcare regulations, including legislative acts and government programs like Medicare Advantage and Medicaid, profoundly shape the competitive landscape for insurers. For instance, in 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continued to refine reimbursement rates for Medicare Advantage plans, impacting profitability and strategic pricing for companies like Elevance Health. These evolving policies can either present new avenues for growth or introduce significant operational and financial hurdles, forcing companies to continuously adapt their business models to maintain market share and profitability.
The regulatory environment directly influences competitive rivalry by setting the rules of engagement and creating barriers to entry or expansion. For example, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, with its ongoing implementation in 2024, introduced measures that could affect drug pricing and, consequently, the cost of benefits offered by health insurers. Navigating these complex policy shifts requires substantial investment in compliance and strategic foresight, as missteps can lead to penalties or a loss of competitive advantage.
- Evolving Regulations: In 2024, insurers faced ongoing adjustments to regulations governing health insurance markets, impacting product design and pricing strategies.
- Government Program Influence: The financial performance of companies like Elevance Health is significantly tied to government programs such as Medicare Advantage and Medicaid, with policy changes in 2024 directly affecting revenue streams.
- Legislative Impact: New or amended legislation, such as provisions related to prescription drug costs, created both challenges and opportunities for insurers to differentiate their offerings and manage costs in 2024.
- Adaptation Imperative: The dynamic policy landscape necessitates continuous strategic adaptation by insurers to maintain profitability and competitive positioning amidst regulatory uncertainty.
The competitive rivalry within the health insurance sector remains exceptionally high, with major players like UnitedHealth Group, Cigna, and Humana consistently vying for market dominance. This intense competition forces companies to innovate rapidly, particularly in digital health and AI integration, as seen with significant investments in these areas throughout 2024.
Competitors are expanding their service offerings beyond traditional insurance, incorporating pharmacy benefits management and direct care delivery. This diversification intensifies rivalry by creating a broader competitive front, compelling Elevance Health to enhance its own integrated solutions and technological capabilities to maintain its market position.
Strategic partnerships and acquisitions are key tactics in this competitive environment, aiming for greater scale and broader service portfolios. For instance, Elevance Health's collaborations with primary care providers highlight the industry's move towards integrated care models, a trend driven by the need to improve outcomes and efficiency amidst fierce competition.
The digital transformation race is a defining characteristic of current competitive rivalry. In 2024, health insurers are channeling substantial resources, with some allocating 15-20% of their IT budgets to AI and digital initiatives, aiming to improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
| Key Competitor Actions (2024) | Focus Areas | Impact on Elevance Health |
| Increased investment in AI and digital platforms | Customer engagement, operational efficiency | Necessitates continuous innovation to avoid market share loss |
| Expansion into PBM and direct care delivery | Broader service offerings, integrated solutions | Requires enhancement of Elevance Health's own integrated capabilities |
| Strategic partnerships and acquisitions | Market consolidation, economies of scale | Pressures Elevance Health to secure similar strategic advantages |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Direct primary care and concierge medicine present a growing threat of substitutes for Elevance Health. These models, where patients pay a monthly fee directly to a physician for enhanced access and personalized care, bypass traditional insurance networks for primary services. For instance, the Direct Primary Care Coalition reported that by the end of 2023, over 1,000 direct primary care practices were operating in the United States, serving an estimated 300,000 to 500,000 patients.
The rising adoption of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) paired with High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance models. These plans empower individuals to manage their healthcare finances more directly, potentially reducing reliance on comprehensive insurance. In 2024, HSA assets under management reached an estimated $150 billion, reflecting this shift.
Government-provided healthcare, such as Medicare and Medicaid, acts as a significant substitute for private health insurance, particularly for eligible demographics. These programs offer a baseline of coverage, directly competing with the services provided by private insurers. For instance, in 2024, Medicare covers over 66 million Americans, while Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) provide coverage to more than 100 million people, underscoring their substantial market presence.
Self-Insured Employer Plans
Many large employers opt to self-insure their employee health benefits, meaning they take on the financial risk of healthcare expenses directly instead of paying premiums to an insurance provider like Elevance Health. This trend significantly impacts the traditional health insurance market by reducing the pool of potential customers for insurers.
For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of the U.S. workforce is covered by employer-sponsored health insurance, with self-insured plans being a dominant feature for many large organizations. This presents a direct substitute for fully insured products offered by companies such as Elevance Health.
- Self-Insured Employers Bypass Traditional Insurers: Large companies directly manage healthcare costs, reducing reliance on external insurance providers.
- Reduced Market for Insurers: This strategy shrinks the customer base for companies like Elevance Health that primarily offer fully insured plans.
- Financial Risk Assumption: Employers bear the direct financial burden of claims, acting as their own insurer.
- Growing Trend: The prevalence of self-insured plans continues to be a significant factor in the employer-sponsored health insurance landscape.
Wellness and Preventive Care Programs
The increasing emphasis on wellness and preventive care presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance. As individuals and employers invest more in proactive health management, they might reduce their perceived need for insurance to cover illnesses. This shift could impact Elevance Health's market by offering alternative pathways to health maintenance.
For instance, the U.S. corporate wellness market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow. This expansion reflects a trend where employers offer programs focused on nutrition, fitness, and mental well-being, aiming to lower long-term healthcare costs and improve employee health outcomes. Such initiatives can be seen as substitutes for comprehensive health coverage.
- Growing Corporate Wellness Investments: Employers are increasingly funding wellness programs, potentially reducing employee reliance on insurance for routine health needs.
- Individual Health Management Tools: Wearable technology and health apps empower individuals to monitor and manage their health proactively, acting as a substitute for traditional medical interventions.
- Preventive Care Focus: A societal shift towards preventing illness rather than just treating it can diminish the perceived value of insurance solely for managing sickness.
The threat of substitutes for Elevance Health is multifaceted, encompassing alternative healthcare delivery models and financing mechanisms. Direct primary care and concierge medicine offer personalized services outside traditional insurance frameworks. In 2023, over 1,000 direct primary care practices were operating in the US. Furthermore, the increasing popularity of High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) coupled with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) empowers consumers to manage healthcare spending directly, potentially reducing reliance on comprehensive insurance plans. HSA assets reached an estimated $150 billion in 2024.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Penetration/Growth Indicator (2023-2024) | Impact on Elevance Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Primary Care (DPC) | Monthly fee for enhanced physician access, bypassing insurance for primary care. | Over 1,000 practices in the US (2023), serving 300,000-500,000 patients. | Reduces demand for traditional insurance for primary care services. |
| Concierge Medicine | Premium membership for highly personalized and accessible healthcare. | Growing segment, though specific national numbers are less centralized than DPC. | Appeals to higher-income individuals seeking exclusive care, potentially diverting them from standard plans. |
| High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) with HSAs | Consumer-driven plans with tax-advantaged savings accounts for healthcare. | HSA assets under management reached an estimated $150 billion (2024). | Encourages self-management of healthcare costs, potentially lowering utilization of comprehensive insurance benefits. |
| Government Healthcare (Medicare/Medicaid) | Publicly funded health insurance programs. | Medicare covers over 66 million Americans; Medicaid/CHIP cover over 100 million (2024). | Directly competes for eligible populations, reducing the market for private insurers. |
| Self-Insured Employer Plans | Employers directly manage healthcare costs without purchasing traditional insurance. | Dominant feature for many large organizations in employer-sponsored health insurance. | Shrinks the customer base for fully insured products offered by companies like Elevance Health. |
| Wellness & Preventive Care Focus | Emphasis on proactive health management, potentially reducing need for illness-related insurance. | US corporate wellness market valued at ~ $50 billion (2023) and growing. | May decrease perceived need for insurance coverage if individuals and employers prioritize prevention. |
Entrants Threaten
The health insurance sector presents formidable barriers to entry, primarily due to the immense capital needed to operate. New companies must secure significant funding for state licensing, meeting stringent regulatory compliance, and developing robust provider networks. For instance, establishing the necessary administrative infrastructure and technology to manage claims and customer service also demands substantial upfront investment, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
The health insurance industry presents substantial regulatory barriers for potential new entrants. Navigating the intricate web of federal and state laws, including the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and various state-specific mandates, requires significant legal and compliance expertise. For instance, obtaining the necessary licenses to operate in multiple states can be a lengthy and costly process, demanding substantial upfront investment in legal counsel and administrative infrastructure.
Elevance Health, like other major health insurers, benefits significantly from deeply entrenched brand loyalty. Customers often stick with familiar providers due to the complexity of switching plans and the trust built over time. For instance, Elevance Health reported a membership of 115.3 million in the first quarter of 2024, demonstrating the scale of its established customer base.
Network effects further solidify this advantage. A large network of doctors, hospitals, and pharmacies makes a health plan more attractive to consumers. New entrants face a considerable hurdle in building a comparable network, which is crucial for offering competitive benefits and managing costs effectively.
Data and Technology Infrastructure
The threat of new entrants in the health insurance sector, particularly concerning data and technology infrastructure, is considerably low for companies like Elevance Health. Modern health insurance operations demand extensive investment in sophisticated data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and robust IT infrastructure. These capabilities are crucial for effective risk assessment, efficient claims processing, and delivering personalized member services.
Building or acquiring the necessary advanced technological capabilities presents a substantial barrier for any new company attempting to enter the market. For instance, in 2024, major health insurers are projected to spend billions on digital transformation initiatives. Elevance Health itself has been a significant investor in its digital platforms, aiming to enhance member experience and operational efficiency.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants require massive upfront capital to develop or license advanced data analytics and AI platforms, a cost that can run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Technological Expertise: Acquiring and retaining specialized talent in data science, AI, and cybersecurity is a significant challenge, creating an operational hurdle for newcomers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA, requires sophisticated IT systems designed for stringent data privacy and security, adding to the entry barrier.
- Established Data Sets: Incumbent players like Elevance Health benefit from years of accumulated data, which is vital for training AI models and improving predictive analytics, a resource new entrants lack.
Integration with Care Delivery
The increasing trend of integrated care delivery, where health insurers directly own or form close partnerships with healthcare providers, significantly raises the barrier for new entrants. These new players often lack the established networks and operational capabilities needed to compete in such a landscape. For instance, Elevance Health has been actively expanding its care delivery footprint, acquiring companies like CareMore Health and Aspire Health, which strengthens its integrated model. This integration demands substantial capital investment and complex strategic alliances to replicate, making it challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in matching the scale and scope of existing integrated care systems. Building a comparable network of providers, managing diverse patient populations, and navigating regulatory complexities requires extensive resources and time. By 2024, the healthcare industry continued to see a consolidation trend, with significant M&A activity focused on vertical integration. This environment makes it difficult for startups or smaller entities to challenge established players who benefit from economies of scale and established patient relationships.
- Integrated Care Models: Insurers increasingly own or partner with healthcare providers, creating a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Capital Investment: Establishing integrated care delivery requires substantial financial resources and strategic partnerships.
- Network Effects: Existing players benefit from established provider networks and patient bases, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate.
- Industry Consolidation: Ongoing mergers and acquisitions in healthcare further consolidate the market, making entry more challenging.
The threat of new entrants in the health insurance market remains low due to substantial capital requirements, stringent regulatory landscapes, and the need for extensive provider networks. Elevance Health benefits from significant economies of scale and established brand loyalty, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively. For example, as of the first quarter of 2024, Elevance Health served 115.3 million members, showcasing its vast reach.
Technological investment, particularly in data analytics and AI, presents another significant barrier. New entrants must invest heavily in advanced IT infrastructure and specialized talent to match the capabilities of incumbents like Elevance Health, which itself is investing billions in digital transformation initiatives in 2024. The increasing trend towards integrated care models further solidifies this barrier, requiring substantial capital and complex strategic alliances to replicate.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024/2025 Projections) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High upfront costs for licensing, infrastructure, and technology development. | Deters smaller, less-funded entities. | Billions projected for digital transformation in the health insurance sector. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex federal and state healthcare laws (e.g., ACA, HIPAA). | Requires significant legal and compliance expertise and infrastructure. | Lengthy and costly state licensing processes. |
| Brand Loyalty & Network Effects | Established customer base and extensive provider networks. | Difficult for new entrants to attract members and offer competitive benefits. | Elevance Health's 115.3 million members (Q1 2024). |
| Technology & Data | Need for advanced data analytics, AI, and robust IT systems. | Requires specialized talent and substantial investment in platforms. | Incumbents benefit from years of accumulated data for AI model training. |
| Integrated Care Models | Ownership or close partnerships with healthcare providers. | Demands significant capital and strategic alliances to replicate. | Consolidation trend with M&A activity focused on vertical integration. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Elevance Health Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of data from annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld and Statista.
