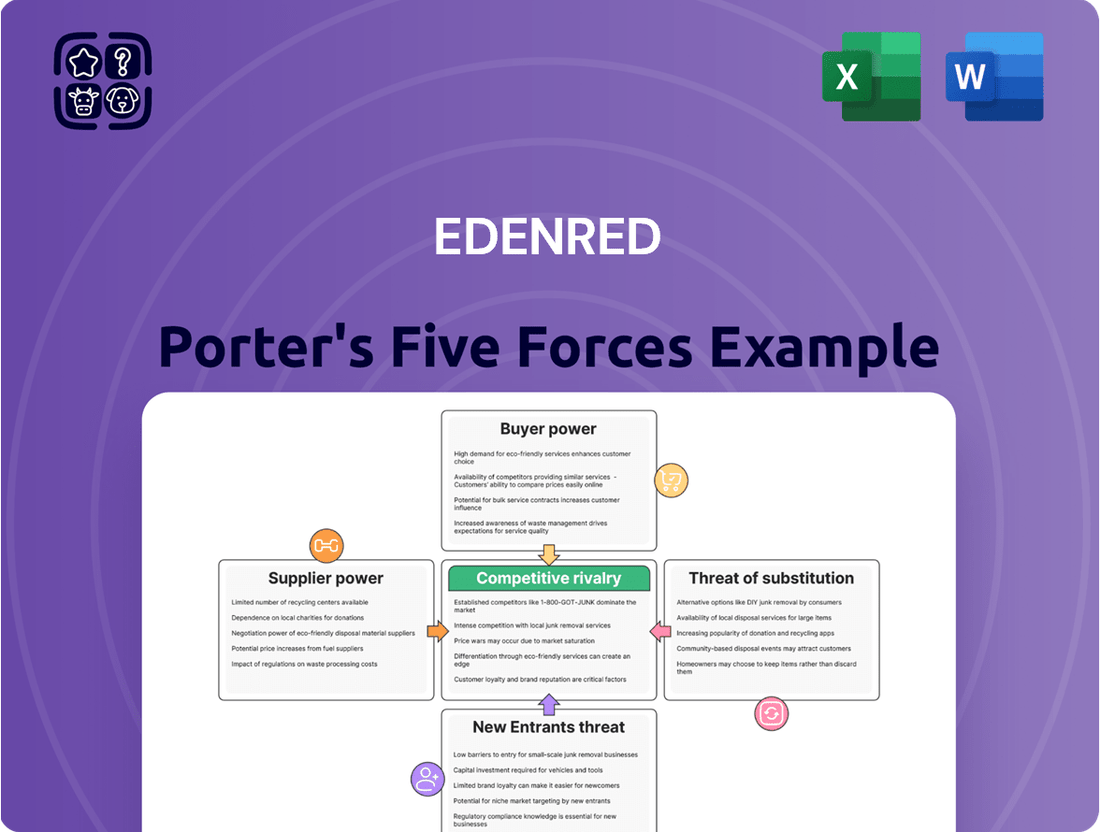
Edenred Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Edenred Bundle
Edenred operates in a dynamic market shaped by the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate its competitive landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Edenred’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Edenred's reliance on a concentrated group of specialized technology and payment infrastructure providers significantly influences supplier power. If only a few firms offer critical, unique services for their digital platforms, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the digital payments sector continued to consolidate, with major infrastructure providers like Stripe and Adyen handling a substantial portion of global online transactions. The cost and complexity for Edenred to migrate its core operations to alternative providers, should these key suppliers increase prices or alter terms, could be prohibitive, thus strengthening the suppliers' bargaining position.
The bargaining power of Edenred's suppliers is influenced by the uniqueness of their offerings. If suppliers provide highly specialized or proprietary technology, it becomes harder for Edenred to switch, thus increasing supplier leverage. For instance, a supplier with a unique digital platform for employee benefits management might command higher prices if integrating a new system would be costly and time-consuming for Edenred.
High switching costs are a significant factor. If Edenred's operations are deeply integrated with a particular supplier's system, the expense and disruption involved in changing providers can deter switching, thereby strengthening the supplier's position. This is particularly relevant for technology-dependent services where data migration and retraining can be substantial burdens.
Edenred's business model relies on a network of service providers, such as restaurants and retailers, who accept its payment solutions. The differentiation of these networks and the ease with which Edenred can onboard new partners versus the effort required to replace existing ones plays a role. In 2024, Edenred continued to expand its network, with over 2 million affiliated merchants across Europe, highlighting the importance of maintaining strong relationships with a diverse supplier base.
Edenred's suppliers generally have moderate bargaining power. The threat of forward integration by these suppliers, such as payment processors or technology providers, is somewhat limited by the significant capital investment and established infrastructure Edenred possesses in its core business of employee benefits and payment solutions. For instance, developing a comprehensive platform comparable to Edenred's requires substantial investment in technology, regulatory compliance, and a broad network of merchants and users.
While some technology suppliers might have the capability to offer similar services, the complexity of managing a large-scale benefits program, including employer relationships and employee satisfaction, presents a considerable barrier. Edenred's strong existing customer relationships and brand loyalty further solidify its market position, making it challenging for suppliers to replicate its service offering effectively. In 2023, Edenred reported revenue of €2,424 million, showcasing the scale of operations that a new entrant, even a supplier, would need to match.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of suppliers for Edenred is influenced by the proportion of their total costs tied to specific supplier inputs. A high dependency on a particular supplier, especially for services constituting a significant share of operational expenses, can empower that supplier to exert greater influence. This is particularly relevant if these suppliers offer specialized or unique solutions that are difficult for Edenred to substitute easily, potentially leading to increased costs if suppliers raise their prices.
For instance, consider the reliance on technology providers for platform development and maintenance, or on financial institutions for payment processing. If a substantial portion of Edenred's operating budget, say above 15-20% for a critical input, is directed towards a single, specialized provider, that provider gains leverage. This leverage can translate into demands for higher fees or less favorable contract terms, directly impacting Edenred's profitability.
- Cost Concentration: Assess the percentage of Edenred's total expenditures attributable to key supplier categories.
- Supplier Dependency: Evaluate the extent to which Edenred relies on a limited number of suppliers for essential services or components.
- Price Sensitivity: Analyze the potential impact of price hikes from critical suppliers on Edenred's overall cost structure and profit margins.
- Substitution Difficulty: Consider how easily Edenred can switch to alternative suppliers without incurring significant costs or operational disruptions.
Supplier Power 5
Edenred's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by its own size and the concentration of its supplier base. If Edenred represents a significant portion of a supplier's business, it can negotiate more favorable terms. For instance, in 2023, Edenred's global revenue reached €2.4 billion, indicating substantial purchasing power with its technology and service providers.
However, the power dynamic shifts if Edenred is a small customer for a particular supplier. In such cases, the supplier, especially if it serves a broad market or has unique offerings, can exert more influence on pricing and contract conditions. Edenred's reliance on specialized software and payment processing systems means some suppliers might hold considerable sway if they are key enablers of Edenred's core services.
- Edenred's substantial revenue of €2.4 billion in 2023 gives it considerable leverage with many suppliers.
- The strategic importance of Edenred to its suppliers is a key factor in determining bargaining power.
- A fragmented supplier market for essential services or technology would generally reduce supplier power.
- Conversely, reliance on a few specialized or dominant suppliers can increase supplier bargaining power.
Edenred's suppliers, particularly those providing specialized technology and payment infrastructure, possess moderate to significant bargaining power. This is driven by the concentration within certain tech sectors and the high costs Edenred would incur to switch providers, especially for critical digital platform services. For example, in 2024, major payment processors continued to consolidate their market share, making alternative solutions less readily available or more costly to integrate.
The uniqueness of supplier offerings, such as proprietary software for employee benefits management, further amplifies their leverage. High switching costs, stemming from data migration and system integration complexities, deter Edenred from easily changing providers, thereby strengthening the suppliers' negotiating position. This reliance on specialized inputs means suppliers can potentially dictate terms or increase prices, impacting Edenred's operational expenses.
Edenred's scale, evidenced by its €2.4 billion revenue in 2023, provides considerable purchasing power with many suppliers. However, this is counterbalanced when Edenred is a minor client for a dominant or highly specialized provider. The strategic importance of Edenred to its suppliers is a critical determinant of the power balance, with a fragmented supplier market generally reducing supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Edenred Context (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Digital payment infrastructure shows consolidation; key providers hold significant sway. |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Unique offerings increase power | Proprietary technology for benefits management is difficult to substitute. |
| Switching Costs | High costs increase power | Migrating core digital platforms is complex and expensive for Edenred. |
| Edenred's Size/Importance | Larger size/importance reduces power | €2.4 billion revenue in 2023 gives leverage, but dependence on niche providers can shift this. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Edenred's position in the employee benefits and payment solutions market.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a pre-populated Edenred Porter's Five Forces template, saving valuable time and resources.
Customers Bargaining Power
Edenred's large corporate clients, particularly those with extensive employee bases, hold significant bargaining power. For instance, a major client could represent a substantial portion of Edenred's revenue, allowing them to negotiate more favorable pricing and customized service terms. This concentration means that losing even one large account could have a noticeable impact, pushing Edenred to be more accommodating.
Buyer power for Edenred is influenced by the switching costs for its corporate clients. If it's easy for a company to move its employee benefits program to a competitor, perhaps due to straightforward data migration and minimal disruption to existing employee arrangements, then customers have more leverage. This ease of transition can be seen in the digital nature of many benefits platforms, where data portability is often a standard feature.
Conversely, if Edenred's platforms are deeply integrated into a client's HR systems, or if changing providers involves significant administrative hurdles and employee retraining, then buyer power is diminished. For instance, a complex rollout of a new benefits system can be costly and time-consuming for a business, making them less likely to switch. In 2024, many companies are focused on operational efficiency, so solutions that require extensive change management might be less attractive.
Corporate clients of Edenred face a moderate level of bargaining power due to the availability of numerous alternative solutions. These include other global and local employee benefits providers, traditional banking services for payroll and expense management, and even the option for companies to develop their own in-house systems.
The ease with which clients can compare offerings, often through detailed feature lists and pricing structures, further amplifies their leverage. For instance, in 2024, the digital payments and employee benefits sector saw continued innovation, with new entrants and established players like Sodexo and Up offering increasingly competitive packages, making switching costs for large corporate clients a significant consideration.
Buyer Power 4
Edenred's customers, especially large corporate clients, can exert significant bargaining power. This is particularly true when customers are price-sensitive, a common trait during economic downturns or in highly competitive sectors. These buyers can leverage their volume to negotiate better terms and pricing for employee benefits and corporate payment solutions.
The drive for cost savings among businesses means they will actively seek to reduce expenses, putting pressure on Edenred to offer competitive pricing. Customers evaluate the perceived value of Edenred's services against their cost, looking for solutions that deliver maximum benefit without excessive expenditure.
Several factors influence this buyer power:
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are highly attuned to pricing, especially for standardized services.
- Switching Costs: While switching costs can exist, if they are not prohibitively high, customers have more leverage.
- Information Availability: The availability of information about competitor offerings allows customers to compare prices and features effectively.
- Customer Concentration: A few large clients can hold substantial power over Edenred if they represent a significant portion of revenue.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers for Edenred, particularly in the employee benefits and corporate payments sectors, is influenced by information asymmetry. When customers are well-informed about market prices, competitor services, and industry benchmarks, they are in a stronger position to negotiate favorable terms.
Transparency in the employee benefits and corporate payment markets significantly empowers buyers. Understanding the true cost of services and available alternatives allows them to demand better pricing and service levels from providers like Edenred. For instance, in 2024, the increasing availability of online comparison tools for corporate services has made it easier for businesses to assess the competitive landscape.
- Information Asymmetry: Customers, especially large corporate clients, can reduce information gaps by conducting thorough market research.
- Informed Negotiation: Well-informed buyers leverage knowledge of competitor pricing and service quality to negotiate better contracts with Edenred.
- Market Transparency: Increased transparency in the benefits and payments sector allows customers to benchmark offerings and exert greater influence.
- Customer Concentration: While Edenred serves a broad base, large corporate clients represent a significant portion of revenue, giving them considerable leverage.
Edenred's customers, especially large corporate clients, wield considerable bargaining power. This is amplified by the availability of numerous alternative solutions, including competitors like Sodexo and Up, as well as in-house options. In 2024, many businesses are focused on cost optimization, making them highly price-sensitive and inclined to negotiate for better terms. The ease of comparing offerings, facilitated by increased market transparency and online tools, further empowers these buyers to demand competitive pricing and superior service from Edenred.
| Factor | Impact on Edenred | 2024 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for large clients | Major corporate clients can represent significant revenue streams, enabling strong negotiation. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to low for digital platforms | Ease of data migration in digital benefits platforms can reduce client inertia. |
| Information Availability | Empowers informed negotiation | Online comparison tools in 2024 allow clients to easily benchmark Edenred against competitors. |
| Price Sensitivity | Drives demand for competitive pricing | Economic pressures in 2024 encourage clients to seek cost-effective employee benefits solutions. |
What You See Is What You Get
Edenred Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Edenred Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You're looking at the actual, professionally written document, ready for your immediate download and use the moment you buy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive rivalry in the specific-purpose payment solutions market, where Edenred operates, is quite intense. There are numerous direct competitors, ranging from large global entities to smaller, specialized regional players. This fragmentation means companies are constantly vying for market share, which often translates into aggressive pricing strategies and a strong push for continuous innovation to differentiate their offerings.
The employee benefits and corporate payment solutions industry is experiencing robust growth, which generally tempers competitive rivalry. For instance, Edenred reported a 15.5% increase in revenue in 2023, reaching €2,315 million, driven by strong performance across its segments. This expansion allows companies to grow their market share organically without needing to aggressively poach customers from rivals.
However, even in a growing market, the intensity of competition can vary. In segments where growth is slower or more mature, companies might engage in price wars or increased marketing efforts to capture a larger slice of the existing pie. This dynamic is particularly relevant as new entrants or established players innovate their offerings, potentially disrupting established market positions.
Edenred operates in a market with varying levels of product differentiation. While some of its services, like employee benefits platforms, offer unique technological features and strong brand recognition, others, particularly in payment processing, can be more commoditized. This means that while Edenred can leverage its innovation and brand loyalty to mitigate direct price competition in certain segments, it faces more intense rivalry based on cost in others.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Companies in the employee benefits and payment solutions sector, like Edenred, often face significant exit barriers. High investments in technology infrastructure, proprietary platforms, and extensive distribution networks create substantial sunk costs. For instance, developing and maintaining secure payment processing systems requires continuous capital outlay, making it costly for firms to simply walk away. This can trap companies in a market even when returns are subpar, intensifying rivalry.
The presence of specialized assets, such as unique data analytics capabilities or established partnerships with merchants and issuers, further elevates exit barriers. These assets are not easily redeployed to other industries. Consequently, competitors may remain in the market, competing fiercely for market share, rather than incurring significant losses by divesting these specialized resources. This dynamic can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition.
Regulatory frameworks can also impact exit decisions. Compliance with financial regulations, data privacy laws, and consumer protection standards necessitates ongoing investment and adherence. The process of winding down operations and divesting assets in a compliant manner can be complex and expensive, acting as another deterrent to exiting the market. For example, in 2024, the ongoing evolution of digital payment regulations across Europe requires continuous adaptation, making a clean exit more challenging.
- High Sunk Costs: Significant investments in technology and infrastructure create substantial financial commitment, making withdrawal difficult.
- Specialized Assets: Unique platforms and partnerships are industry-specific, limiting redeployment options and increasing exit costs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with financial and data protection laws complicates and adds expense to exiting the market.
Competitive Rivalry 5
The competitive rivalry within Edenred's market is intense and multifaceted. Competitors range from established players with long histories and broad service offerings to nimble fintech startups focusing on niche solutions. For instance, Edenred's direct competitors include companies like Sodexo, which also offers employee benefits and services, and Up, a French competitor with a similar focus on meal and gift vouchers. The landscape also features newer entrants leveraging technology to offer digital payment solutions and employee engagement platforms, sometimes directly challenging traditional voucher systems.
This diversity in competitors means a variety of strategies are employed. Incumbents often rely on their established networks and brand recognition, while fintech startups might compete on technological innovation, user experience, and lower transaction fees. Traditional financial institutions are also increasingly entering the employee benefits space, offering integrated payroll and benefits management systems. This mix creates a dynamic environment where different business models, from physical voucher distribution to fully digital platforms, directly impact the nature and intensity of competition.
For example, in 2024, the digital transformation of employee benefits accelerated. Companies like Paycor and Rippling, while broader HR platforms, offer components that directly compete with Edenred's core offerings by integrating various employee perks and payment solutions. Edenred itself has been investing heavily in its digital capabilities, evidenced by its acquisition of services like Reward Gateway in 2022, aiming to bolster its digital employee engagement and benefits platform. This strategic move highlights the pressure from digital-native competitors.
- Diverse Competitors: Edenred faces competition from established players like Sodexo and Up, as well as agile fintech startups and traditional financial institutions.
- Varied Strategies: Incumbents leverage brand and networks, while startups focus on technology and user experience, creating a complex competitive dynamic.
- Business Model Impact: The rivalry is shaped by differing business models, from physical voucher systems to fully digital employee engagement platforms.
- Market Trends: The ongoing digital transformation in employee benefits, as seen with the growth of integrated HR platforms, intensifies rivalry and necessitates continuous innovation.
The competitive rivalry in Edenred's market is intense, driven by a mix of established global players and agile digital disruptors. Companies like Sodexo and Up, with their long-standing presence in employee benefits and voucher programs, directly challenge Edenred. Furthermore, the rise of fintech companies offering integrated HR and payment solutions, such as Paycor and Rippling, introduces new competitive pressures, particularly concerning digital engagement and streamlined employee perks.
Edenred's revenue growth, with a 15.5% increase in 2023 to €2,315 million, indicates its ability to navigate this competitive landscape. However, the market's dynamism demands continuous innovation. For instance, Edenred's 2022 acquisition of Reward Gateway underscores its strategy to bolster digital employee engagement, directly responding to the evolving competitive environment and the demand for more comprehensive digital solutions.
The intensity of rivalry is also influenced by varying degrees of product differentiation. While Edenred's innovative platforms and brand recognition offer a competitive edge in certain segments, other areas, like basic payment processing, can be more commoditized, leading to price-sensitive competition. This necessitates a strategic focus on value-added services and technological advancement to maintain market leadership.
| Competitor | Primary Offerings | Key Competitive Aspect |
|---|---|---|
| Sodexo | Employee benefits, food services, facility management | Established global network, broad service portfolio |
| Up | Meal vouchers, gift vouchers, employee savings plans | Strong presence in France, similar voucher solutions |
| Paycor | HR software, payroll, benefits administration | Integrated HR platform, digital employee engagement |
| Rippling | HR, IT, Finance platform | All-in-one business management, digital solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Edenred's employee benefits and payment solutions is moderate. While specialized platforms like Edenred's offer tailored benefits and streamlined administration, general-purpose payment methods like direct cash or standard credit/debit cards can fulfill the basic need of employees for compensation and purchasing power. The convenience and widespread acceptance of these traditional methods present a viable alternative for some employers and employees, especially for smaller businesses or those with simpler benefit structures.
The threat of substitutes for Edenred's services, particularly in employee benefits and payment solutions, is a key consideration. Substitutes can range from in-house managed programs to alternative digital payment platforms. For instance, if a company can offer similar meal voucher benefits through a simpler, less integrated system at a significantly lower administrative cost, that would represent a strong substitute. The relative price-performance trade-off is crucial here; if a substitute offers comparable convenience or value at a lower price point, Edenred's market position could be challenged.
Convenience and cost are the primary drivers for substitute adoption. If a competitor emerges offering a digital platform that streamlines expense management and employee perks with greater ease of use than Edenred's current offerings, and at a similar or lower price, it poses a direct threat. For example, a new fintech solution that integrates seamlessly with existing payroll systems and offers a wider range of customizable benefits could attract businesses looking for more flexibility than traditional voucher systems. The perceived value of Edenred's specialized, integrated solutions must consistently outweigh the appeal of these more generic, potentially cheaper alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Edenred is moderate, largely due to the relatively low switching costs for many of its clients. Companies can explore alternative employee benefit platforms or payment solutions with minimal administrative hassle or integration challenges. For instance, a business might opt for direct payroll additions for certain benefits or utilize simpler, less integrated payment systems if Edenred's specialized services are not deemed essential.
The ease with which employees can transition to alternative methods also plays a role. If Edenred's offerings, like meal vouchers or flexible spending accounts, can be easily replicated through direct employer payments or readily available third-party apps, the threat intensifies. This is particularly true for benefits that don't require complex infrastructure or unique technological capabilities, making the shift to a substitute solution straightforward for both employers and employees.
4
The threat of substitutes for Edenred's services is growing, particularly with advancements in financial technology. New digital platforms and mobile payment solutions are emerging that could allow companies to manage employee benefits and corporate expenses more directly, potentially bypassing traditional intermediaries. For instance, the rise of open banking and the increasing adoption of digital wallets present alternative avenues for payment and benefit distribution.
The speed of innovation in these substitute areas is a key concern. Fintech companies are rapidly developing user-friendly applications that simplify expense management and benefit allocation. This rapid evolution means that traditional players like Edenred must continually adapt to remain competitive and relevant in a landscape where digital alternatives are becoming increasingly accessible and efficient.
Consider these potential substitutes:
- Direct Digital Payment Platforms: Companies could leverage existing payroll systems or new fintech solutions to disburse funds directly to employees for specific benefit categories, reducing reliance on specialized voucher or card systems.
- Blockchain-based Solutions: Emerging blockchain technologies offer the potential for transparent and secure management of benefits and expenses, allowing for direct peer-to-peer transactions or smart contract-based distribution.
- Integrated HR and Finance Software: Comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are increasingly incorporating modules for benefits administration and expense management, offering a one-stop solution that could reduce the need for specialized third-party providers.
- Open Banking APIs: The increasing availability of open banking APIs allows for greater integration between financial institutions and third-party service providers, potentially enabling new ways for employees to access and manage their benefits through their primary banking applications.
5
The threat of substitutes for Edenred's offerings, such as meal vouchers or employee benefits platforms, is influenced by how employees and employers perceive value. If a company culture shifts towards simpler, cash-based bonuses or more flexible, direct financial incentives, the appeal of specialized, purpose-driven benefits might decrease. For instance, a growing preference for discretionary spending accounts over traditional meal vouchers could reduce demand for Edenred's core products.
Societal trends also play a significant role. A greater emphasis on work-life balance and holistic employee well-being could lead to demand for substitutes that offer broader lifestyle benefits, moving beyond just food or transportation. In 2024, companies are increasingly looking for integrated solutions that cater to diverse employee needs, potentially making single-purpose benefits less attractive.
The psychological aspect of perceived value is crucial. When employees view substitutes as more convenient, flexible, or directly aligned with their immediate financial needs, they are more likely to adopt them. This behavioral shift can erode the loyalty to established benefit providers like Edenred if they fail to adapt their value proposition.
- Behavioral Shift: Employees may prefer direct cash or flexible spending accounts over specific-purpose vouchers, viewing them as more valuable due to greater personal control.
- Cultural Impact: A corporate culture favoring simple, universal rewards over tailored benefits can diminish the perceived necessity of specialized solutions like those offered by Edenred.
- Societal Trends: Growing demand for comprehensive well-being programs and flexible work arrangements may drive employees and employers towards substitutes offering broader lifestyle support.
- Market Adaptation: In 2024, the market sees a trend towards integrated digital platforms that combine various benefits, posing a threat to standalone or less adaptable offerings.
The threat of substitutes for Edenred's specialized employee benefits and payment solutions is moderate but growing, driven by technological advancements and evolving employee preferences. While Edenred offers integrated platforms, direct digital payment methods and comprehensive HR software can serve as viable alternatives, especially if they offer lower costs or greater flexibility.
In 2024, companies are increasingly seeking holistic employee well-being solutions, which could diminish the appeal of single-purpose benefits. For instance, a shift towards flexible spending accounts or direct cash bonuses over traditional meal vouchers represents a significant substitute threat. This trend is amplified by the ease with which employees can adopt these alternatives, impacting Edenred's market position.
The key concern for Edenred lies in the rapid innovation of fintech solutions and integrated HR systems. These substitutes can offer comparable or superior convenience and cost-effectiveness, potentially bypassing traditional intermediaries. As such, Edenred must continuously adapt its value proposition to counter the growing appeal of these more adaptable and potentially cheaper alternatives.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Potential Impact on Edenred | 2024 Market Trend Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Digital Payments | Funds disbursed via payroll or fintech apps | Reduces reliance on specialized voucher/card systems | Increasing adoption for flexibility |
| Integrated HR/Finance Software | All-in-one benefits and expense management | Eliminates need for third-party providers | Growing demand for consolidated solutions |
| Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) | Employee-controlled accounts for various expenses | Shifts preference from purpose-specific benefits | Popularity driven by employee choice |
| Open Banking APIs | Enables integration with banking apps | Facilitates new benefit access methods | Enhances competitive landscape |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Edenred in the specific-purpose payment solutions market is moderate. Establishing a competitive presence requires substantial capital investment in developing robust technology platforms, building extensive networks of both corporate clients and merchant partners, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes. For instance, the European Commission's Digital Finance Strategy highlights the ongoing need for significant investment in digital infrastructure and cybersecurity to ensure secure and efficient payment systems, a cost barrier for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants for Edenred is moderately high, primarily due to the nature of the employee benefits and corporate payments industry. While the market offers significant opportunities, new players face substantial regulatory and legal barriers. These include stringent licensing requirements across various jurisdictions, complex data privacy regulations like GDPR, and intricate tax frameworks that demand significant investment in compliance expertise.
New companies entering this space must navigate a web of legal obligations, which can be a considerable hurdle. The compliance burden for handling sensitive employee data and processing financial transactions is immense. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing evolution of data protection laws and the increasing focus on financial crime prevention mean that any new entrant must allocate substantial resources to legal and compliance departments from day one, potentially delaying market entry and increasing initial operating costs.
The threat of new entrants for Edenred is relatively low, primarily due to significant network effects and economies of scale. The value of Edenred's platform, which connects employers, employees, and merchants, grows exponentially with each new participant. This creates a powerful barrier for newcomers trying to establish a comparable ecosystem.
For instance, as of late 2023, Edenred's Ticket Restaurant solution alone served over 50 million users and was accepted by 1.2 million merchants globally. This extensive network is incredibly difficult and time-consuming for a new entrant to replicate, as it requires substantial investment in sales, marketing, and partnership development to achieve critical mass.
New entrants would face immense challenges in building a sufficiently large base of both corporate clients and affiliated merchants to offer a compelling alternative. The time and capital required to reach a point where the network effects truly benefit users and merchants are considerable, making rapid market penetration highly improbable.
4
The threat of new entrants in the employee benefits and engagement solutions market, where Edenred operates, is moderate. Edenred benefits from strong brand loyalty and deeply entrenched relationships with its corporate clients and a vast network of merchant partners. These established connections, built on trust and long-term contracts, create significant barriers for newcomers aiming to gain traction, even with potentially innovative solutions.
The power of incumbency is substantial. For instance, in 2023, Edenred reported revenue of €1.85 billion, demonstrating its significant market presence and the established trust it commands. New entrants would find it challenging to replicate this scale and the loyalty Edenred has cultivated over years of service delivery.
- Brand Loyalty: Edenred's established reputation and consistent service delivery foster significant loyalty among its corporate clients, making switching costs high.
- Merchant Network: The extensive network of merchants accepting Edenred's solutions provides a strong competitive advantage that new players would struggle to match quickly.
- Client Relationships: Long-standing relationships with businesses, often solidified through multi-year contracts, create a sticky customer base.
- Incumbency Advantage: Edenred's years of experience and market penetration translate into operational efficiencies and a deeper understanding of client needs, which are difficult for new entrants to overcome.
5
The threat of new entrants into the employee benefits and engagement solutions market, where Edenred operates, is moderate. Established players like Edenred possess significant financial resources and extensive market experience, enabling them to respond effectively to new competition. For instance, in 2023, Edenred reported a revenue of €2,160 million, demonstrating its substantial market presence and capacity for investment in competitive strategies.
Incumbents can deploy aggressive tactics to deter newcomers. This might involve price reductions to make the market less attractive for startups, or increased marketing spend to reinforce brand loyalty and awareness. Edenred’s established network and brand recognition provide a strong defense against emerging players who lack similar reach and customer trust.
The potential for retaliation from existing players like Edenred is a key factor. They can leverage their scale to absorb initial competitive pressures and then respond with enhanced service offerings or strategic partnerships. For example, Edenred's ongoing investments in digital transformation and platform development aim to create a stickier ecosystem for its clients, making it harder for new entrants to gain a foothold.
- High barriers to entry exist due to significant capital requirements for technology development and regulatory compliance.
- Edenred's established brand reputation and extensive distribution networks create a competitive advantage.
- Existing players can engage in price wars or increased marketing to deter new entrants.
- Edenred's financial strength, evidenced by its 2023 revenue of €2,160 million, allows for robust defensive strategies.
The threat of new entrants for Edenred is moderate, primarily due to the significant capital investment required for technology development and navigating complex regulatory frameworks. For instance, the European Union's ongoing digital finance initiatives emphasize the need for robust cybersecurity and secure payment infrastructure, which new players must fund extensively.
Edenred's established brand loyalty and vast merchant network present substantial barriers. As of late 2023, Edenred's global network included over 1.2 million merchants, a scale that is incredibly challenging and costly for newcomers to replicate quickly, requiring significant investment in sales and partnership development.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Edenred's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (Technology, Regulation) | Established financial resources, economies of scale |
| Network Effects | Challenging to build critical mass | Over 50 million users and 1.2 million merchants (late 2023) |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Difficult to penetrate | Strong client trust, multi-year contracts |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex and costly | Existing expertise and infrastructure |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Edenred Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
