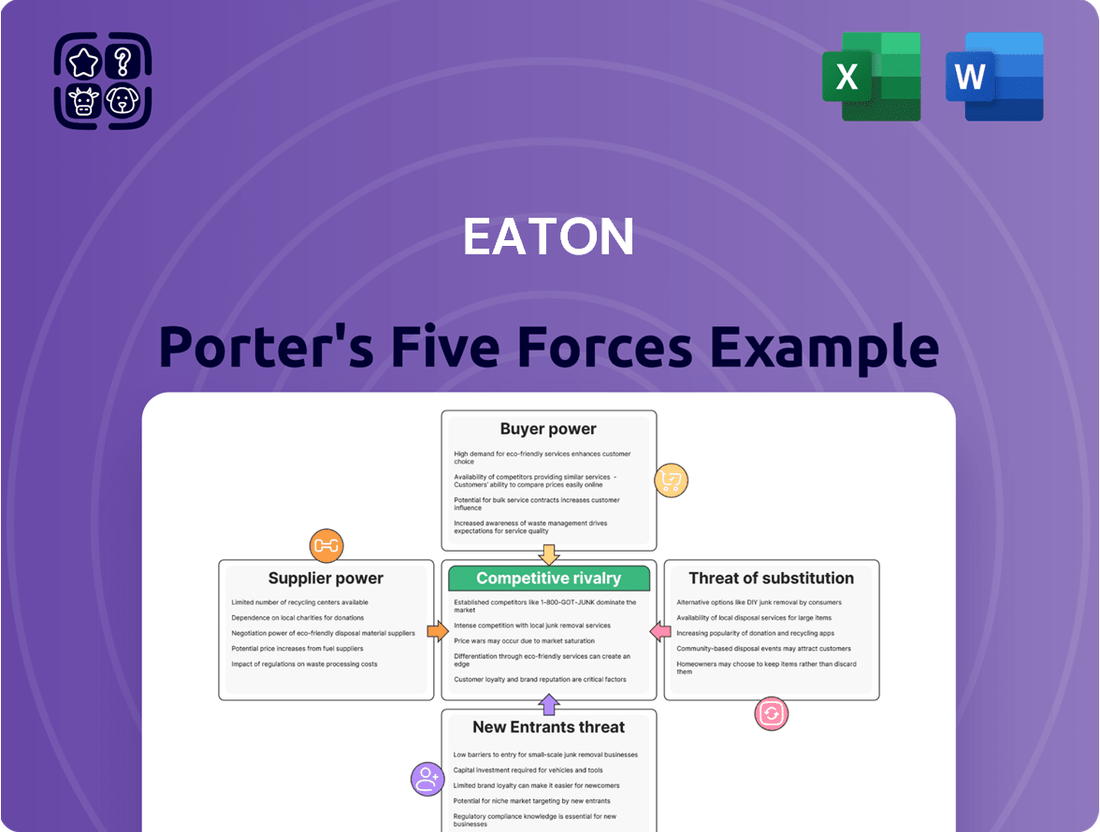
Eaton Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Eaton Bundle
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intense competitive landscape Eaton navigates, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any business operating within or adjacent to Eaton's markets.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Eaton’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Eaton's diverse operations, spanning electrical, aerospace, and hydraulic sectors, mean it relies on a vast range of specialized components and raw materials. The concentration of suppliers for critical, niche components can significantly amplify their bargaining power. For instance, if only a handful of companies can produce a highly specialized hydraulic valve essential for Eaton's systems, those suppliers can dictate terms, potentially driving up costs for Eaton and limiting negotiation leverage.
The cost and complexity Eaton faces when switching suppliers significantly impact supplier bargaining power. If Eaton has deeply integrated a supplier's unique technology or specialized processes into its own systems, the effort and expense to transition to a new provider can be substantial.
For instance, in the aerospace sector, where components often require rigorous certification and extensive testing, the time and financial investment to qualify a new supplier can be a major hurdle. This increases the leverage of existing suppliers who have already met these stringent requirements, especially for complex electrical systems or highly specialized components.
Suppliers offering unique technologies or intellectual property vital to Eaton's energy-efficient products possess significant bargaining power. This reliance can expose Eaton to potential price hikes or less favorable contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier for many of Eaton's power management solutions, experienced ongoing supply chain constraints and price volatility, directly impacting component costs for manufacturers like Eaton.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess the capability and motivation to integrate forward, meaning they could begin manufacturing the components Eaton currently sources, their bargaining power naturally escalates. This scenario allows them to capture more of the value chain.
For Eaton, a company heavily involved in complex and capital-intensive manufacturing, the threat of supplier forward integration is often mitigated. The high barriers to entry in producing sophisticated electrical components and systems make it challenging for many suppliers to effectively transition into Eaton's operational space.
- Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers could move into producing Eaton's finished goods, increasing their leverage.
- Eaton's Industry Context: The capital-intensive and technically demanding nature of Eaton's product lines makes this threat less prevalent for many suppliers.
- Mitigating Factors: High R&D investment and established manufacturing processes create significant hurdles for suppliers attempting forward integration.
Importance of Eaton to Supplier Revenue
The significance of Eaton as a customer directly impacts a supplier's willingness to concede on terms. For suppliers where Eaton constitutes a substantial portion of their sales, there's a greater incentive to offer favorable pricing and conditions to retain this crucial business. For instance, if a key component supplier derives over 15% of its annual revenue from Eaton, they are likely to be more accommodating during negotiations.
Conversely, if Eaton represents a minor fraction of a supplier's total revenue, the supplier holds more leverage. In such scenarios, the supplier is less dependent on Eaton's business and can therefore dictate terms more assertively, knowing that losing Eaton as a client would have a minimal impact on their overall financial performance. This imbalance of dependency is a critical factor in assessing supplier bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: The percentage of a supplier's revenue derived from Eaton is a key determinant of bargaining power.
- Negotiating Leverage: High dependence on Eaton grants suppliers more leverage, while low dependence empowers Eaton.
- Strategic Importance: For suppliers with significant Eaton business, maintaining the relationship often outweighs short-term profit maximization on individual deals.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Eaton is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, and the uniqueness of their offerings. When few suppliers can provide critical, specialized components, their leverage increases, potentially driving up costs for Eaton. For example, in 2024, ongoing semiconductor shortages meant suppliers of advanced chips for Eaton's power management systems could command higher prices due to limited availability and high demand.
High switching costs, often due to deeply integrated technologies or extensive certification requirements, further empower suppliers. In the aerospace sector, qualifying new suppliers for complex electrical systems can take years and significant investment, solidifying the position of established providers.
Suppliers offering proprietary technologies or intellectual property crucial for Eaton's innovative products also hold considerable sway. This reliance can lead to less favorable contract terms for Eaton, especially when market conditions, like those seen in the specialized materials sector in early 2024, favor suppliers.
The relative importance of Eaton as a customer to its suppliers plays a critical role; if Eaton represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier is more likely to offer favorable terms to retain the business.
| Factor | Impact on Eaton | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized components | Limited suppliers for advanced aerospace hydraulics |
| Switching Costs | High for integrated technologies | Aerospace component certification delays |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Significant for proprietary tech | Semiconductor price volatility impacting power solutions |
| Customer Dependence (Supplier's View) | Low dependence = High supplier leverage | Suppliers with <5% Eaton revenue |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the five competitive forces impacting Eaton, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and their collective influence on Eaton's profitability and strategic positioning.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual, actionable breakdown of industry forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Eaton's customer base is quite diverse, spanning critical sectors like data centers, utilities, industrial, commercial, aerospace, and mobility. This broad reach generally dilutes the power of any single customer or small group of customers.
However, the situation can shift if a few exceptionally large clients exist within specific segments. For instance, major data center operators or significant original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in the aerospace or mobility sectors could wield considerable influence over pricing and contract terms, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by switching costs. For Eaton, if customers find it difficult and expensive to transition to a competitor's offerings, their ability to demand lower prices or better terms diminishes. This is particularly true for complex solutions where integration is key.
Eaton's strategy of providing end-to-end solutions and intelligent power management is designed to increase these switching costs. For instance, if a customer's entire electrical infrastructure is built around Eaton's integrated systems, the effort and expense to reconfigure or replace these components with a competitor's products would be substantial, thereby reducing customer leverage.
Customer price sensitivity significantly influences their bargaining power. In markets where products are largely undifferentiated and easily substitutable, like many commodity electrical components, customers will naturally gravitate towards the lowest price. This heightened sensitivity grants them considerable leverage to negotiate better terms or switch suppliers, putting pressure on manufacturers like Eaton.
However, this sensitivity isn't universal. For Eaton's specialized offerings, particularly those in critical infrastructure, data centers, or industrial automation, customers often prioritize reliability, energy efficiency, and long-term operational savings over upfront cost. For instance, a data center operator might be willing to pay a premium for Eaton's uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems if they guarantee uptime and reduce energy consumption, as downtime can cost millions. In 2024, the increasing focus on sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors further reduces price sensitivity for products that demonstrably improve environmental performance.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers can significantly shift bargaining power. If Eaton's major clients, particularly those with substantial financial and technical capabilities, could realistically produce the electrical components and systems they currently purchase in-house, their leverage over Eaton would undoubtedly increase. This scenario allows them to dictate terms more forcefully or even withdraw their business entirely.
However, the inherent complexity and specialized nature of Eaton's product portfolio often present a considerable barrier to entry for such in-house production. For instance, developing and manufacturing advanced power management solutions, like sophisticated circuit breakers or intelligent power distribution units, requires significant capital investment in research and development, specialized manufacturing equipment, and a highly skilled workforce. This complexity generally mitigates the immediate threat of widespread backward integration, especially for customers who may not possess the core competencies in electrical engineering and manufacturing that Eaton has cultivated over decades.
Consider the automotive sector, a key market for Eaton. While large automotive manufacturers possess considerable resources, the intricate design and manufacturing processes for advanced electrical distribution systems and vehicle electrification components are highly specialized. In 2024, the ongoing global push for vehicle electrification means automotive OEMs are increasingly focused on battery technology and software integration, rather than replicating the complex power electronics and distribution systems that Eaton specializes in. This focus allows Eaton to maintain its competitive edge and leverage its expertise.
- Customer Capability: Large, resource-rich customers with technical expertise are more likely to consider backward integration.
- Eaton's Barriers: The complexity and specialization of Eaton's product offerings create significant hurdles for customer in-house production.
- Industry Trends: In sectors like automotive electrification, customers are prioritizing core competencies, reducing the immediate threat of backward integration for specialized component suppliers like Eaton.
Customer Information and Transparency
The increasing availability of detailed product specifications, competitive pricing, and comprehensive information on alternative suppliers significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. In markets where transparency is high, customers can readily compare options and negotiate more favorable terms. Eaton's strong reputation for innovation and quality helps it stand out, allowing it to command premium pricing and reduce the direct impact of price-based competition.
In 2023, Eaton reported revenue of $23.2 billion, underscoring its significant market presence. This scale allows for considerable negotiation leverage with suppliers, but also means customers, particularly large industrial clients, have significant purchasing power. For instance, a major data center operator can compare Eaton's power distribution units against those from Schneider Electric or Siemens, demanding competitive pricing and service level agreements.
- Information Accessibility: Customers can easily access detailed product specifications and pricing online, facilitating comparisons across numerous suppliers.
- Price Sensitivity: In segments where product differentiation is less pronounced, customers may prioritize price, increasing their leverage.
- Eaton's Differentiation: Eaton's focus on energy transition solutions and advanced technologies, as highlighted in its 2024 strategic outlook, provides a basis for value beyond price.
- Customer Concentration: The presence of large, sophisticated buyers in sectors like aerospace and data centers means these customers can exert substantial influence on terms and conditions.
The bargaining power of customers hinges on their ability to influence pricing and terms, often driven by switching costs and price sensitivity. For Eaton, high switching costs associated with integrated systems reduce customer leverage, as seen in their complex power management solutions. However, in segments with more commoditized products, customers can exert greater pressure by easily comparing prices and specifications from various suppliers. For example, in 2024, the emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability means customers might prioritize long-term value over initial cost, thereby lessening price sensitivity for specialized solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Eaton's Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Lowers power if high | Complex integrated systems increase costs for customers to switch. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases power if high | Commoditized components are subject to price negotiation. |
| Information Availability | Increases power | Easy access to competitor pricing and specs empowers buyers. |
| Customer Concentration | Increases power if concentrated | Large clients in data centers or aerospace can negotiate significant terms. |
Full Version Awaits
Eaton Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Eaton Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate utility. You're looking at the actual, professionally crafted analysis, ready for download and application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Eaton navigates a competitive landscape populated by both colossal multinational corporations, such as Schneider Electric and Siemens, and a multitude of smaller, specialized firms. This dual-edged competition presents a complex challenge, as Eaton must contend with the scale and resources of global giants while also addressing the agility and focused expertise of niche players.
The sheer diversity of industries Eaton serves, spanning electrical, hydraulic, aerospace, and vehicle sectors, means its competitive environment is far from uniform. For instance, in the electrical sector, Eaton faces rivals like ABB and General Electric, while in hydraulics, Parker Hannifin and Danfoss are key competitors, each with distinct market dynamics and strategic priorities.
In 2024, the electrical components market alone was valued at over $270 billion globally, a segment where Eaton's diverse product portfolio directly confronts a wide array of competitors. This broad market participation necessitates a nuanced understanding of varied competitive pressures across each of its operational segments, demanding tailored strategies to maintain market share and drive growth.
The power management industry is on a strong growth trajectory, fueled by major shifts like electrification, digitalization, and the global energy transition. Markets such as data centers and electric vehicles are particularly driving this expansion, creating a dynamic environment for companies.
While robust industry growth typically softens direct competition as firms can grow by capturing new demand, the sheer size of these emerging opportunities means rivalry remains sharp. Companies are vying intensely to secure leadership positions in these high-potential sectors.
For example, the global data center power market was projected to reach over $30 billion by 2024, and the electric vehicle charging infrastructure market is expected to see compound annual growth rates exceeding 25% in the coming years, highlighting the lucrative nature of these segments and the competition they attract.
Eaton's product differentiation, particularly in intelligent power management and aerospace, is a key strength. For instance, their focus on energy efficiency and digital solutions in electrical products allows them to command premium pricing. In 2023, Eaton reported significant growth in its Electrical Americas segment, driven by demand for these advanced offerings.
Switching Costs for Customers
High switching costs for customers, as detailed in the bargaining power of customers section, directly dampen competitive rivalry. When it is difficult or costly for clients to move to a competitor's offerings, the pressure to aggressively compete for existing business diminishes.
For Eaton, this translates into a more stable customer base, reducing the need for constant price wars or extensive promotional campaigns to retain market share. For instance, in the electrical components sector, integrating Eaton's sophisticated control systems often requires significant re-engineering and retraining, creating substantial barriers to switching.
- Reduced Customer Churn: High switching costs mean fewer customers are likely to defect to rivals.
- Less Price Sensitivity: Customers less willing to switch may tolerate current pricing structures more readily.
- Focus on Innovation: Companies with high switching costs can allocate more resources to product development rather than customer acquisition.
- Market Stability: This dynamic contributes to a more predictable and less volatile competitive landscape for Eaton.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the power management sector, stemming from specialized manufacturing equipment and substantial investments in research and development, can trap even underperforming companies within the industry. This situation often leads to prolonged competitive battles, as firms strive to retain their market positions despite unfavorable economic conditions.
For instance, in 2024, companies heavily invested in advanced semiconductor fabrication facilities for power management integrated circuits face significant capital depreciation and resale challenges, effectively raising their exit barriers. Similarly, long-term supply agreements with major industrial clients can lock manufacturers into ongoing operations, even if profitability wanes.
- Specialized Assets: The power management industry often requires highly specific machinery, making it difficult and costly to repurpose or sell these assets if a company decides to exit.
- R&D Investments: Continuous and substantial investment in new product development and technological innovation creates a knowledge and capital barrier to leaving the market.
- Long-Term Contracts: Binding agreements with customers can obligate companies to continue production and service, even when operations are no longer economically viable.
- Brand Reputation: Established brands in the power management space have significant goodwill that is difficult to divest, encouraging continued operation to preserve value.
Eaton faces intense rivalry from large, established players like Schneider Electric and Siemens, as well as agile, specialized competitors. This dynamic intensifies across its diverse sectors, from electrical to aerospace, with significant market value in areas like the global electrical components market exceeding $270 billion in 2024.
The rapid growth in sectors like data centers and electric vehicles, projected to reach over $30 billion and show over 25% CAGR respectively by 2024, attracts fierce competition as companies vie for dominance in these high-potential markets.
Despite strong industry growth, competition remains sharp as companies aggressively seek leadership in expanding segments. Eaton's differentiation, especially in intelligent power management and aerospace, helps mitigate direct price wars, though market share battles persist.
High customer switching costs and significant exit barriers, due to specialized assets and R&D, can lead to prolonged competition as firms are incentivized to stay in the market, even in challenging conditions.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Eaton's offerings is a dynamic factor that shifts across its diverse business segments. In certain areas, alternative technologies or entirely different solutions can effectively address the same customer needs. For example, traditional electrical distribution equipment might face substitution from more integrated, smart grid technologies or even localized, renewable energy sources that reduce reliance on centralized power infrastructure.
Eaton's electrical sector, in particular, sees this threat. While its circuit breakers and power distribution units are critical, advancements in building automation and distributed energy resources (like rooftop solar coupled with battery storage) offer alternatives that can perform similar functions, potentially at a lower lifecycle cost or with greater energy efficiency. For instance, the increasing adoption of microgrids, which can operate independently or connected to the main grid, presents a substitute for traditional utility-dependent power solutions.
The attractiveness of substitute products for Eaton's offerings hinges significantly on their price-performance trade-off. If alternatives emerge that deliver comparable or even better functionality at a reduced price point, the competitive pressure on Eaton intensifies.
For instance, if a competitor's energy-efficient power distribution unit offers similar reliability and features but at a 15% lower cost, this directly impacts Eaton's market share. Eaton's strategic focus on research and development, aiming for enhanced product performance and a lower total cost of ownership, directly counters this threat by making their solutions more appealing despite potentially higher upfront costs.
Customers' willingness to switch to alternatives hinges on how aware they are of those options, how risky they perceive the change to be, and how simple it is to start using a new product. For instance, if a competitor offers a slightly cheaper, yet functionally similar, electrical component, customers might consider switching if the perceived risk of using an unknown brand is low and the installation process is straightforward.
Eaton's formidable brand recognition, built over decades, and its deep-rooted relationships with clients serve as significant deterrents to substitution. In 2024, Eaton reported a robust customer retention rate of over 90% across its key industrial segments, underscoring the loyalty that makes switching less appealing for many.
Technological Advancements
Rapid technological advancements are a significant force shaping the threat of substitutes for traditional power management solutions. Innovations in renewable energy sources, advanced battery storage systems, and intelligent smart grid technologies continuously emerge, offering alternative ways to generate, store, and distribute power. These new technologies can directly compete with and potentially displace established power management offerings.
Eaton is proactively addressing this threat by actively investing in and acquiring companies that are at the forefront of these technological shifts. For instance, in 2023, Eaton announced significant investments in its power distribution and electrical systems businesses, including those focused on grid modernization and energy transition technologies. This strategic approach allows Eaton to not only mitigate the risk of being disrupted by substitutes but also to capture opportunities within these evolving markets.
The pace of innovation means that what is considered a substitute today could become a mainstream solution tomorrow. Consider the growth in distributed energy resources (DERs); by the end of 2024, the global DER market is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, showcasing the rapid adoption of these alternatives. Eaton's commitment to R&D and strategic acquisitions in areas like microgrids and advanced energy management software positions it to adapt and remain competitive.
- Technological Disruption: New technologies like advanced battery chemistries and AI-driven grid optimization are constantly emerging, presenting viable alternatives to traditional power management.
- Eaton's Mitigation Strategy: Eaton's participation in and acquisition of companies in renewable energy and smart grid sectors directly addresses the threat of substitutes.
- Market Dynamics: The increasing adoption of distributed energy resources, with market growth expected to continue robustly through 2024 and beyond, highlights the growing influence of substitute technologies.
Regulatory and Environmental Shifts
Changes in regulations and a growing emphasis on environmental sustainability present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional energy infrastructure. For instance, stricter emissions standards or mandates for renewable energy adoption can accelerate the shift towards alternative technologies, potentially impacting demand for products and services tied to fossil fuels. This trend is evident as global renewable energy capacity saw significant growth in 2024, with solar and wind power leading the expansion.
Eaton's strategic focus on sustainability and its ambitious net-zero targets are crucial in navigating this evolving landscape. By aligning its offerings with these macro-level shifts, Eaton is positioning itself to capitalize on the increasing demand for greener solutions. For example, Eaton's investments in energy storage and smart grid technologies are designed to support the integration of renewables, a market segment projected for substantial growth through 2025.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Governments worldwide are increasingly implementing policies favoring decarbonization, such as carbon pricing mechanisms and renewable portfolio standards, which directly encourage the adoption of substitute technologies.
- Consumer and Investor Demand: A heightened awareness of climate change is driving both consumer preferences and investor sentiment towards sustainable businesses and products, creating a market pull for alternative solutions.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in renewable energy generation, energy efficiency, and energy storage are continuously improving the cost-effectiveness and performance of substitute technologies, making them more competitive.
- Eaton's Strategic Alignment: Eaton's commitment to providing solutions that enable energy transition, including its extensive portfolio of power management technologies and services, directly addresses the threat by offering viable alternatives to less sustainable options.
The threat of substitutes for Eaton's products is multifaceted, driven by technological innovation and evolving market demands. For instance, advancements in distributed energy resources (DERs) like solar panels and battery storage offer alternatives to traditional grid-tied power solutions. By the end of 2024, the global DER market is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating strong customer adoption of these substitutes.
Eaton actively counters this by investing in and acquiring companies at the forefront of these shifts, such as its 2023 investments in grid modernization. This strategy allows Eaton to not only adapt but also to lead in emerging markets, ensuring its offerings remain competitive against disruptive alternatives.
The increasing adoption of microgrids, which can operate independently or connected to the main grid, presents a substitute for traditional utility-dependent power solutions. This trend is supported by regulatory shifts favoring decarbonization, which directly encourage the adoption of alternative technologies.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the power management industry, particularly in specialized areas like aerospace or advanced hydraulics, demands immense upfront capital. Eaton, for instance, operates in sectors where building state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, investing heavily in research and development for cutting-edge technologies, and establishing robust global distribution channels can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This high barrier to entry significantly deters potential new competitors.
Economies of scale present a significant barrier for new entrants. Eaton, with its substantial global presence and nearly $25 billion in sales in 2024, leverages these scale advantages across production, procurement, and research and development.
New companies entering the market would find it extremely difficult to match Eaton's cost efficiencies, particularly in areas like bulk purchasing of raw materials and spreading R&D investments over a larger output.
This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete effectively on price, thereby deterring their entry into the market.
Eaton's deep well of proprietary technology, bolstered by over a century of innovation in power management, creates a significant barrier for newcomers. The company holds numerous patents, safeguarding its advanced solutions.
The sheer investment and time required to replicate Eaton's technological sophistication and secure critical industry certifications, particularly in demanding sectors like aerospace, present a formidable hurdle for potential entrants. For instance, obtaining FAA certification for aerospace components is a lengthy and expensive process.
Access to Distribution Channels
New competitors entering Eaton's markets would struggle to establish effective distribution channels. Eaton boasts a vast network, serving customers in over 160 countries, a testament to its deep-rooted customer relationships. Building similar reach requires substantial investment and time, creating a significant barrier.
For instance, in the electrical sector, securing shelf space and strong relationships with distributors and installers is paramount. Eaton's established presence means new entrants face an uphill battle to gain comparable access. By 2024, the global electrical equipment market was valued at hundreds of billions, highlighting the scale of distribution required.
- Established Distribution Networks: Eaton's extensive global reach and long-standing partnerships with distributors and end-users present a formidable hurdle for new entrants.
- High Setup Costs: Replicating Eaton's distribution infrastructure and customer loyalty would necessitate significant capital expenditure and years of effort.
- Customer Relationships: Eaton's deep customer loyalty, built over decades, makes it difficult for new players to attract and retain clients through distribution channels alone.
- Market Access: Gaining access to key markets and customer segments is challenging without pre-existing, reliable distribution channels, which Eaton already commands.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation act as a significant deterrent to new entrants in many industries, including those where Eaton Corporation operates. Strict regulations, industry standards, and mandatory certifications, especially prevalent in sectors like aerospace and utilities, necessitate substantial upfront investment and a considerable time commitment for compliance. For instance, obtaining FAA certification for aerospace components can take years and millions of dollars, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
These regulatory hurdles mean that potential competitors must not only develop competitive products but also navigate complex legal and bureaucratic landscapes. Failure to meet these stringent requirements can result in severe penalties or outright exclusion from the market. In 2024, the global aerospace market, a key area for Eaton, continued to see robust regulatory oversight, with ongoing updates to safety and environmental standards impacting manufacturing processes and requiring continuous adaptation.
- High Capital Requirements: Compliance with safety and environmental regulations often demands significant capital expenditure for specialized equipment, testing facilities, and skilled personnel.
- Lengthy Approval Processes: Obtaining necessary certifications and approvals from regulatory bodies can be a protracted process, delaying market entry and increasing initial costs.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Beyond initial setup, companies must invest continuously in maintaining compliance, including audits, training, and process updates, adding to operational expenses.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Sectors like aerospace and energy have particularly rigorous standards, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and national aviation authorities, which are costly to meet.
The threat of new entrants in Eaton's power management sectors is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, estimated in the hundreds of millions to billions of dollars, deter many potential competitors. Eaton's established economies of scale, evident in its 2024 sales exceeding $25 billion, provide significant cost advantages, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Eaton's Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building advanced manufacturing and R&D facilities requires immense upfront investment. | High deterrent for new players. | Leverages vast existing infrastructure. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs achieved through high production volumes. | New entrants face cost disadvantages. | Significant cost efficiencies from global operations and high sales volume. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | Unique innovations and intellectual property protect market share. | Replication is time-consuming and expensive. | Extensive patent portfolio and over a century of innovation. |
| Distribution Networks | Established channels for reaching customers globally. | Difficult and costly to build comparable reach. | Extensive network serving over 160 countries. |
| Government Regulations & Certifications | Strict industry standards and lengthy approval processes. | Adds significant time and cost to market entry. | Expertise in navigating complex regulatory environments, e.g., FAA certification. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from reputable sources such as industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and government economic data to provide a comprehensive competitive landscape.
