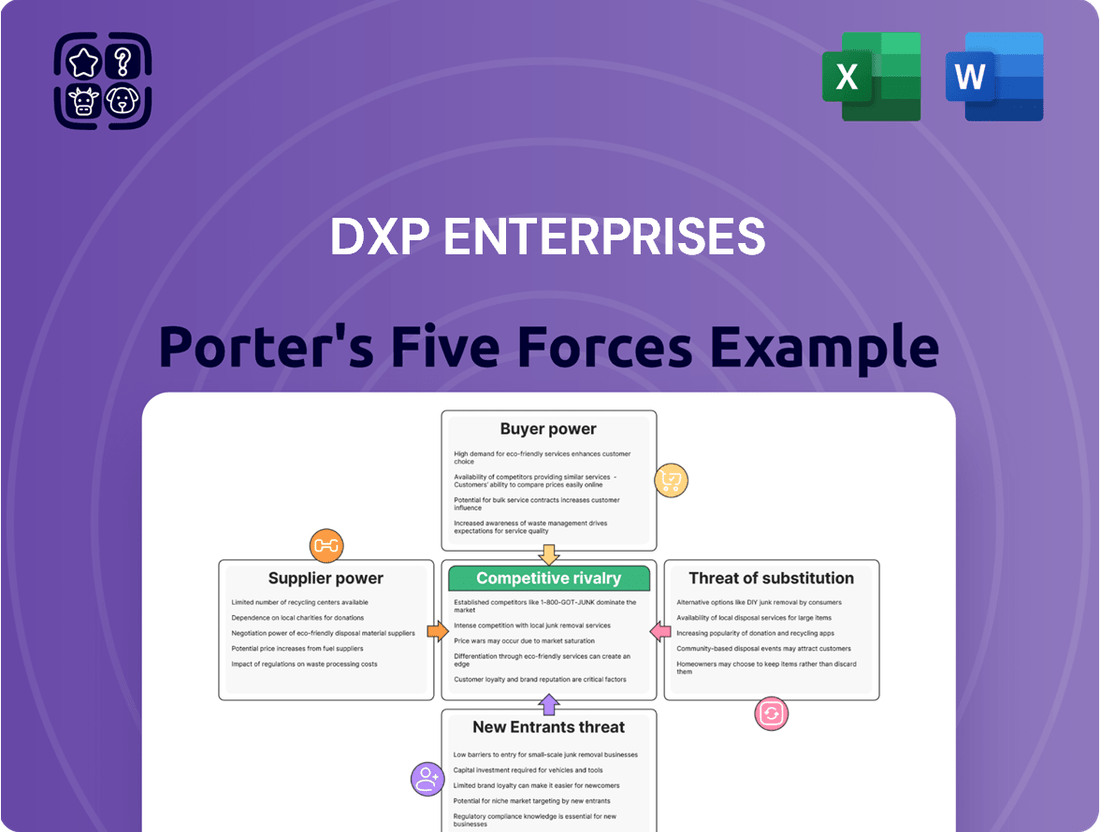
DXP Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DXP Enterprises Bundle
DXP Enterprises navigates a competitive landscape shaped by powerful forces. Understanding the threat of new entrants and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for success. Bargaining power of suppliers and buyers also significantly influences profitability.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore DXP Enterprises’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly impacts DXP Enterprises' bargaining power. If a few key suppliers dominate the market for specialized Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) products or critical industrial equipment, their ability to dictate terms, including pricing and delivery schedules, becomes considerable.
For instance, if DXP relies heavily on a limited number of manufacturers for specific rotating equipment or advanced instrumentation, these suppliers can leverage their market position. This situation could lead to higher input costs for DXP, potentially squeezing profit margins.
DXP actively mitigates this supplier power by diversifying its vendor base. By sourcing similar products from multiple suppliers, DXP can foster competition and avoid over-reliance on any single provider. This strategy is crucial for maintaining cost-effectiveness and ensuring supply chain resilience.
Suppliers gain significant leverage when the Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) products or components they offer are highly unique, proprietary, or lack readily available alternatives. This uniqueness can stem from specialized manufacturing processes, patented technologies, or exclusive material sourcing. For a company like DXP Enterprises, which deals with a vast array of MRO items across different sectors, the bargaining power of suppliers can fluctuate considerably based on the specific input.
DXP's extensive product catalog, encompassing power transmission, pumps, and fluid power systems, inherently involves a spectrum of supplier relationships. While many components might be standardized or commoditized, allowing DXP to negotiate favorable terms due to competition, there are likely specialized or highly engineered solutions where supplier power is more pronounced. For instance, if a supplier provides a critical, custom-engineered pump component for a specific industrial application, DXP's ability to switch suppliers without incurring substantial costs or production disruptions is limited.
The impact of supplier uniqueness on DXP Enterprises' profitability is directly tied to the proportion of its procurement that relies on these less substitutable inputs. In 2023, DXP reported cost of goods sold of $3.2 billion, highlighting the significant scale of its purchasing power. However, within this vast spend, the concentration of purchases from suppliers offering highly differentiated or proprietary products could exert upward pressure on DXP's input costs, potentially impacting its gross margins if these increases cannot be passed on to customers.
The cost and complexity DXP Enterprises faces when changing suppliers significantly influence supplier leverage. If DXP must invest heavily in retooling machinery, requalifying product specifications, or unwinding complex, long-term agreements, suppliers gain considerable bargaining power. This means suppliers can often dictate terms more forcefully when such hurdles exist.
DXP's strategic emphasis on providing integrated solutions often necessitates deeper collaborations with specific manufacturers. This integration can create dependencies, making it more expensive and time-consuming to switch suppliers. For instance, if a supplier's components are deeply embedded in DXP's custom-engineered systems, the effort to find and implement alternatives rises substantially.
Consider DXP's recent performance in 2023, where they reported revenue of $1.4 billion. The efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their supply chain directly impact this revenue. A significant increase in switching costs due to specialized product integration could lead to higher input prices, potentially squeezing DXP's profit margins if they cannot pass these costs onto their customers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers represents a significant concern for DXP Enterprises. If suppliers decide to bypass distributors like DXP and sell their products directly to end customers, it would directly impact DXP's business model and market share. This move could intensify competition and potentially erode DXP's margins.
While DXP has cultivated robust relationships with its manufacturing partners, the possibility remains that larger component manufacturers could establish their own direct sales channels. This is especially relevant in the market for high-volume, standardized MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) items, where direct sales can be more cost-effective for suppliers.
- Suppliers' Forward Integration: The potential for suppliers to move into direct distribution and compete head-on with DXP is a notable threat.
- Impact on DXP's Business Model: Direct sales by suppliers could diminish DXP's role as an intermediary, affecting its revenue streams and customer relationships.
- Focus on MRO Items: The risk is heightened for standardized MRO products, where suppliers have a strong incentive to capture the full value chain.
- Leveraging Existing Relationships: DXP's established supplier relationships are a key asset, but they don't entirely negate the risk of suppliers pursuing direct market access.
Importance of DXP to Suppliers
The significance of DXP Enterprises as a distribution channel for its suppliers directly impacts the bargaining power they hold. If a supplier heavily relies on DXP for a substantial portion of their sales, their leverage is naturally reduced, as they are more dependent on DXP’s business. For example, if DXP accounts for over 20% of a particular component manufacturer's revenue, that manufacturer would likely be less inclined to push for unfavorable terms.
Conversely, for very large, diversified manufacturers, DXP may represent only a small fraction of their overall sales. In such scenarios, DXP's bargaining power is diminished because these suppliers have numerous other distribution avenues and customers. This dynamic means DXP must be strategic in its supplier relationships, particularly with dominant players in niche markets.
- Supplier Dependence: The greater a supplier's reliance on DXP for sales volume, the weaker their bargaining position becomes.
- DXP's Market Share for Suppliers: If DXP constitutes a significant portion of a supplier's total sales, DXP gains leverage.
- Supplier Diversification: Highly diversified suppliers, for whom DXP is just one of many channels, retain stronger bargaining power.
- Industry Concentration: In industries where DXP is a primary distributor for specialized components, its bargaining power is enhanced.
The bargaining power of suppliers for DXP Enterprises is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, product uniqueness, switching costs, the threat of forward integration, and DXP's importance as a distribution channel. High supplier concentration and unique, proprietary products give suppliers more leverage, potentially increasing DXP's input costs.
Conversely, high switching costs for DXP and the potential for suppliers to engage in forward integration pose significant threats to DXP's business model and profitability. The extent to which suppliers depend on DXP for their sales volume directly correlates with DXP's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
In 2023, DXP Enterprises reported a cost of goods sold totaling $3.2 billion, underscoring the critical nature of managing supplier relationships and costs effectively. The company's strategy of diversifying its vendor base aims to mitigate the inherent power held by suppliers, particularly for specialized MRO products.
| Factor | Impact on DXP's Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier power | Reliance on few suppliers for specialized equipment |
| Product Uniqueness | Increases supplier power | Proprietary components with limited alternatives |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier power | High costs for retooling or requalifying components |
| Forward Integration Threat | Decreases DXP's role | Suppliers selling directly to end customers |
| DXP's Importance to Suppliers | Decreases supplier power | DXP representing a significant portion of supplier revenue |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to DXP Enterprises' position in the industrial distribution market.
Effortlessly visualize DXP Enterprises' competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing for rapid identification of key strategic pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
DXP Enterprises' customer concentration is a key factor in assessing customer bargaining power. Large industrial clients, especially those demanding complex, integrated solutions, can wield considerable influence due to the sheer volume of their business. This concentration means that losing even one major customer could have a noticeable impact on revenue.
However, DXP's strategy of serving a wide array of industries, from oil and gas to general manufacturing and water treatment, helps to mitigate this risk. This diversification spreads the customer base, lessening the dependence on any single entity and thereby diluting the bargaining power of individual large customers.
Customers face switching costs when moving from DXP Enterprises to another MRO provider. These costs can arise from integrating DXP's supply chain, learning new specialized equipment, or simply the ease of using DXP's all-in-one solutions. For example, a customer heavily reliant on DXP's custom inventory management software would incur significant costs to migrate to a new system.
Conversely, low switching costs allow customers to easily jump to competitors offering lower prices or superior service. This puts pressure on DXP to maintain its value proposition. In 2023, the industrial distribution market saw a general trend of customers seeking cost efficiencies, making switching costs a critical factor.
DXP actively works to increase these customer switching costs by fostering deep, collaborative relationships. They aim to become an indispensable partner by offering tailored solutions rather than just products, making it more complex and costly for clients to disengage.
DXP Enterprises can effectively mitigate customer bargaining power by focusing on product and service differentiation. By offering value-added services, leveraging deep technical expertise, and providing integrated supply solutions, DXP creates a unique proposition that goes beyond simple product distribution.
When DXP delivers distinct benefits like demonstrable cost reductions and tangible productivity improvements for its clients, customers are significantly less inclined to switch to competitors based solely on price. This strategic differentiation strengthens DXP's market position.
For instance, DXP's commitment to providing comprehensive support and customized solutions can foster customer loyalty. In 2024, the industrial distribution market saw increased demand for integrated services, with companies like DXP seeing success by bundling product supply with technical consultation and maintenance, thereby reducing price sensitivity among buyers.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers' price sensitivity is a key driver of their bargaining power. For DXP Enterprises, this is particularly true for Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) products, which often function as commodities where switching costs are low and numerous alternatives exist. Industries that are themselves under pressure due to thin profit margins or fierce competition are more inclined to push DXP for price reductions, directly impacting DXP's revenue streams.
DXP Enterprises actively works to mitigate this by focusing on total cost savings solutions. This approach highlights the value they bring beyond the initial unit price, demonstrating how their services and product bundles can lead to greater overall efficiency and cost reduction for their clients. For example, in 2024, many industrial sectors continued to experience inflationary pressures, making cost optimization a paramount concern for buyers, thus increasing their leverage in price negotiations.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: High price sensitivity among customers, especially for MRO items, directly amplifies their bargaining power.
- Competitive Pressure: Industries with tight margins or intense competition tend to exert greater downward pressure on pricing from suppliers like DXP.
- DXP's Value Proposition: DXP counters this by offering total cost savings, proving value that extends beyond mere product price.
- 2024 Market Context: Inflationary pressures in 2024 heightened customer focus on cost reduction, increasing their negotiating leverage.
Availability of Alternative Distributors
The availability of alternative distributors significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. For DXP Enterprises, this means that customers can easily switch to competitors if DXP’s pricing, product selection, or service levels are not satisfactory. Major national distributors such as Grainger and MSC Industrial, alongside growing e-commerce platforms, offer a wide array of industrial supplies, providing ample choices for buyers. This competitive landscape compels DXP to maintain aggressive pricing and superior service to retain its customer base.
In 2024, the industrial distribution market continues to see robust competition. E-commerce penetration in industrial MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) procurement is on the rise, with some estimates suggesting it could reach over 30% of total sales in the coming years. This trend empowers customers by simplifying the comparison of prices and product availability across multiple vendors. DXP's strategy to combat this involves leveraging its broad product portfolio and established market presence to offer value beyond just price.
- Increased Competition: The presence of numerous MRO distributors, including large national firms and online marketplaces, gives customers more options.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can easily compare prices, putting pressure on DXP to remain competitive.
- Service Differentiation: Beyond price, customers can choose distributors offering better service, faster delivery, or specialized support.
- E-commerce Growth: The expanding role of online platforms further amplifies customer choice and bargaining power in the industrial supply sector.
DXP Enterprises' customers possess significant bargaining power, particularly when they are large, concentrated clients or operate in price-sensitive industries. The availability of numerous alternative suppliers and the increasing influence of e-commerce further empower buyers. DXP counteracts this by focusing on product differentiation, value-added services, and fostering strong customer relationships to increase switching costs and reduce price sensitivity.
| Factor | Impact on DXP | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High potential leverage for large clients. | Industry diversification to reduce dependence. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs enable easy customer movement. | Building integrated solutions and collaborative relationships. |
| Price Sensitivity | High for commodity MRO products. | Focusing on total cost savings and value-added services. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Empowers customers with choice. | Offering broad product portfolios and superior service. |
| 2024 Market Trend | Inflation increased buyer negotiating leverage. | Highlighting cost optimization benefits. |
Preview Before You Purchase
DXP Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for DXP Enterprises, offering a thorough examination of industry competition. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, detailing threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector. This comprehensive report is ready for your immediate strategic use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial MRO distribution market is indeed quite crowded. DXP Enterprises finds itself competing with giants like Grainger and MSC Industrial Supply, which boast extensive national reach and deep product catalogs. Fastenal is another significant player, known for its strong presence in industrial and construction markets. This competitive intensity means DXP needs to constantly prove its value.
Beyond these national titans, DXP also contends with a multitude of smaller, regional distributors. These companies often have strong local relationships and can be very agile. Furthermore, there are specialized distributors focusing on specific product categories or industries, adding another layer of competition that requires DXP to maintain distinct offerings.
The MRO distribution market is expected to see a compound annual growth rate of 2.77% between 2024 and 2032. This signals a market that is expanding, but at a measured pace.
In markets with more modest growth, the struggle for existing customers and market share tends to intensify among competitors. This means companies need to be particularly strategic in how they attract and retain business.
However, DXP Enterprises demonstrates a capacity to grow both internally and through strategic acquisitions at a pace that outstrips the overall market. For instance, the company reported a notable 15.5% year-over-year sales increase in the first quarter of 2025.
This superior growth rate for DXP suggests it is not just participating in the market's expansion but is actively gaining market share from rivals, indicating a strong competitive position.
DXP Enterprises distinguishes itself by offering an extensive product portfolio complemented by value-added services and integrated supply chain solutions. Their technical expertise, particularly in rotating equipment and pumping solutions, allows them to provide comprehensive problem-solving capabilities rather than just individual products. This approach aims to lessen direct competition based solely on price.
While DXP focuses on differentiation, rivals also actively pursue similar strategies, offering specialized services and technical support to capture market share. This ongoing effort by competitors to provide unique value means that rivalry in this segment remains robust, even with DXP's strong differentiation efforts.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers are a significant factor in the industrial distribution sector, including for companies like DXP Enterprises. These barriers, such as specialized assets and extensive supply chain investments, can trap companies in the market even when they are not profitable. This dynamic often leads to sustained, intense rivalry because competitors are hesitant to exit due to the costs and difficulties involved.
DXP's own substantial infrastructure, a hallmark of the industrial distribution business, suggests it faces similar challenges. The significant capital tied up in facilities, technology, and logistics means that exiting the market is not a simple or inexpensive decision. This can prolong competition, as firms may continue to operate at reduced profitability rather than incur substantial exit costs.
- Specialized Assets: Industrial distributors often invest in highly specific equipment and facilities tailored to their product lines and customer needs, making them difficult to repurpose or sell.
- Long-Term Customer Contracts: Binding agreements with key clients can obligate distributors to continue service, even if the business segment is underperforming, hindering a swift exit.
- Supply Chain Infrastructure: The extensive networks of warehouses, transportation fleets, and inventory management systems represent massive investments that are costly to dismantle or abandon.
- Employee Expertise: Skilled workforces with specialized knowledge of industrial products and customer relationships are not easily transferable, adding to the cost of exiting.
Pricing Strategies and Intensity
The MRO distribution sector, where DXP Enterprises operates, frequently sees intense price competition, particularly for standard, easily sourced items. This aggressive pricing can pressure margins for all participants. DXP aims to counter this by emphasizing its integrated solutions, which offer customers broader value beyond just the product price, focusing on total cost savings through efficiency and expertise.
Despite DXP's value-added approach, the market remains highly sensitive to price. This means that competitive pricing will continue to be a critical factor in customer acquisition and retention. For instance, in 2024, many distributors reported that while customers are increasingly looking for supply chain solutions, price remains a primary consideration in at least 60% of purchasing decisions for many MRO categories.
- Price sensitivity remains high in the MRO market.
- DXP's strategy focuses on total value to mitigate direct price competition.
- Aggressive pricing is common for commoditized MRO products.
- Customer purchasing decisions are often heavily influenced by price, even with value-added offerings.
Competitive rivalry within the industrial MRO distribution market is fierce, with DXP Enterprises facing off against national giants like Grainger and MSC Industrial Supply, alongside agile regional players and specialized distributors. This crowded landscape necessitates continuous value demonstration. Despite a market growth rate of 2.77% between 2024 and 2032, DXP's reported 15.5% year-over-year sales increase in Q1 2025 signifies its success in gaining market share through differentiated offerings and integrated solutions, rather than solely competing on price.
| Key Competitors | Market Presence | DXP's Competitive Edge |
| Grainger, MSC Industrial Supply | Extensive National Reach, Deep Product Catalogs | Value-added services, technical expertise, integrated supply chain solutions |
| Fastenal | Strong presence in industrial & construction | Problem-solving capabilities beyond product sales |
| Regional & Specialized Distributors | Local relationships, agility, niche focus | Comprehensive solutions, total cost savings emphasis |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers might bypass distributors like DXP Enterprises and buy maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) products directly from manufacturers, particularly for significant orders or specialized items. This is a persistent threat in the MRO sector, where direct relationships can sometimes offer cost advantages or better access to technical expertise.
However, DXP counters this by providing consolidated procurement services, streamlining the purchasing process for clients who would otherwise manage multiple manufacturer relationships. This consolidation is a significant value-add, especially when considering the complexity of sourcing diverse MRO needs.
Furthermore, DXP’s logistical efficiency in delivering products across various locations is a key differentiator that many individual manufacturers struggle to match. Their ability to manage inventory and ensure timely delivery directly impacts operational uptime for their customers.
The local support and technical assistance DXP offers are crucial in mitigating the threat of direct purchasing. For instance, DXP's extensive branch network provides on-the-ground expertise and immediate problem-solving, which is often lacking when dealing solely with a remote manufacturer.
Large industrial firms possess the capability to handle their Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) needs internally. This involves maintaining their own stock of spare parts and utilizing in-house personnel for repair services, thereby lessening their dependence on external suppliers like DXP Enterprises. This internal approach aims to control costs and streamline operations.
DXP Enterprises directly addresses this threat by showcasing substantial cost reductions and enhanced operational efficiency stemming from its integrated supply chain solutions. By consolidating MRO procurement and services, DXP offers a compelling alternative to in-house management, often proving more economical and effective for its clientele.
For instance, in 2024, many manufacturing sectors faced inflationary pressures on spare parts and labor, making in-house MRO management more costly. Companies that shifted to DXP's integrated supply chain reported an average of 15% reduction in MRO spend, highlighting the tangible benefits over self-management.
The ability of large corporations to maintain their own MRO operations represents a significant competitive force. However, DXP's proven track record in delivering measurable savings, as evidenced by client testimonials and financial performance data, effectively mitigates this threat by offering superior value and expertise.
Emerging technologies like predictive maintenance, IoT sensors, and AI analytics present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) products. These advancements can preemptively address equipment issues, thereby reducing the reliance on reactive MRO solutions. For instance, companies are increasingly investing in IoT platforms; in 2024, the global IoT market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, indicating a strong trend towards data-driven asset management.
While DXP Enterprises is actively integrating these advanced technologies into its own service offerings, the broader market adoption of these solutions could fundamentally shift demand away from DXP's traditional product lines. This shift represents a long-term substitute threat where proactive, technology-driven maintenance replaces the need for many conventional MRO components. The increasing efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these technological substitutes are key drivers of this potential substitution.
Alternative Service Models
Customers increasingly explore alternative service models that bypass traditional purchase and repair cycles. Options like equipment leasing with built-in maintenance from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or subscription-based access to specific components represent significant substitutes. These arrangements directly challenge DXP Enterprises' core business, which often relies on the sale and subsequent servicing of industrial equipment.
For instance, the rise of Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS) models, where customers pay for usage rather than ownership, is a growing trend. Companies are looking at how to integrate their offerings into these flexible service structures. DXP's competitive standing is directly impacted as these evolving models offer convenience and predictable costs, potentially drawing customers away from DXP’s traditional service offerings.
- Equipment Leasing with OEM Maintenance: Customers can lease equipment and have all maintenance handled by the manufacturer, reducing their reliance on third-party service providers.
- Subscription-Based Services: For certain components or software, subscription models offer continuous access and updates, substituting the need for outright purchase and separate maintenance contracts.
- Managed Services: Outsourcing the entire lifecycle management of industrial equipment to specialized providers can also serve as a substitute for DXP's traditional service model.
- Digitalization and Predictive Maintenance: Advanced digital platforms offering predictive maintenance can reduce the frequency and need for reactive repairs, impacting the volume of traditional service work.
General Purpose Retailers/E-commerce
The burgeoning presence of large general-purpose retailers and e-commerce giants poses a significant substitute threat to DXP Enterprises. These platforms, like Amazon Business or Grainger’s online marketplace, can offer a vast array of maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) supplies, often at highly competitive price points. For less specialized or commodity MRO items, the convenience and cost savings of these broad-reach online channels can divert customers. In 2023, the B2B e-commerce market continued its robust growth, with platforms capturing an increasing share of industrial supply sales, underscoring the competitive pressure.
DXP's strategy to counter this threat hinges on its value proposition beyond mere product availability. By focusing on specialized product knowledge, the ability to engineer and provide complex solutions, and cultivating deep, personalized customer relationships, DXP aims to retain clients who require more than just a transactional purchase. This differentiation is crucial as generalist platforms excel at high-volume, low-touch sales of standardized items.
- Substitute Threat: General retailers and e-commerce platforms offer broad MRO selection at competitive prices.
- Customer Impact: Convenience and lower costs on non-specialized items can attract customers away from DXP.
- DXP's Differentiation: Focus on specialized knowledge, complex solutions, and strong customer relationships.
- Market Context: B2B e-commerce growth in 2023 highlights the increasing reach of substitute channels.
Emerging digital platforms and technological advancements present a significant threat of substitutes for DXP Enterprises' traditional MRO offerings. Solutions like predictive maintenance, leveraging IoT sensors and AI, can preemptively identify and address equipment issues, thereby reducing the need for reactive repairs and spare parts. The global IoT market, projected to exceed $1.1 trillion in 2024, signifies a strong shift towards data-driven asset management.
These technological substitutes offer increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness, potentially diverting demand from DXP's core product lines. Furthermore, alternative service models, such as equipment leasing with integrated maintenance from OEMs or subscription-based access to components, directly challenge DXP’s business. The growing adoption of Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS) models, focusing on usage over ownership, provides predictable costs and convenience, drawing customers away from traditional purchase and service cycles.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on DXP | Market Trend Example (2024) |
| Predictive Maintenance & IoT | Proactive equipment monitoring and repair scheduling | Reduces demand for reactive spare parts and services | IoT market projected over $1.1 trillion |
| Equipment Leasing (EaaS) | Pay-per-use models with included maintenance | Shifts revenue from product sales to service subscriptions | Growing customer preference for flexible asset management |
| Direct OEM Service Agreements | Customers bypass distributors for manufacturer-provided maintenance | Undermines DXP's role in the service lifecycle | Manufacturers increasingly offer bundled service packages |
Entrants Threaten
The industrial MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) distribution sector, where DXP Enterprises operates, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes significant outlays for maintaining a diverse and extensive inventory, establishing and operating warehousing facilities, building out a robust logistics network, and acquiring specialized handling and delivery equipment. These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, deterring potential new competitors from entering the market.
For context, in 2023, DXP Enterprises reported total inventory of $877.4 million, underscoring the scale of capital tied up in goods. The company's strategic approach, often involving acquisitions to expand its reach and capabilities, further emphasizes the substantial investment needed to achieve a competitive footprint in this industry.
Established players like DXP Enterprises enjoy significant advantages due to economies of scale. This means they can produce and distribute goods at a lower per-unit cost compared to smaller competitors. For instance, DXP's large-volume purchasing power likely secures better pricing from suppliers, directly impacting their cost of goods sold and enabling more competitive market pricing.
New entrants would find it challenging to replicate these cost efficiencies. Building the infrastructure and customer base necessary to achieve similar economies of scale is a substantial barrier. Without this scale, new companies would face higher operating costs, making it difficult to match the pricing strategies of incumbents like DXP, which can offer more attractive terms to customers.
DXP's ability to leverage its scale in inventory management also plays a crucial role. Larger operations can optimize stock levels, reducing holding costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence. This efficiency translates into better financial performance and a stronger competitive position, further deterring new market entrants who lack this operational maturity.
Newcomers face significant hurdles in establishing robust distribution networks and forging dependable supplier partnerships within the industrial products sector. DXP Enterprises benefits from a deeply entrenched and extensive network cultivated over years, making it difficult for new players to gain comparable market access and product sourcing capabilities.
Securing prime shelf space or digital visibility for industrial products often requires substantial upfront investment and proven track records, areas where established firms like DXP have a clear advantage. For instance, in 2024, the average time for a new industrial supplier to secure a contract with a major distributor was reported to be upwards of 18 months, highlighting the entrenched nature of existing relationships.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Switching Costs
DXP Enterprises cultivates strong customer relationships by offering comprehensive, solution-oriented services, fostering significant brand loyalty. This deep engagement makes it challenging for new competitors to attract DXP’s established clientele.
The switching costs for customers to move from DXP to a new Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) provider are substantial. These costs include not only financial outlays but also the disruption of established workflows and the loss of specialized technical support.
DXP’s integrated solutions, which combine product offerings with expert services, further solidify customer ties. This holistic approach creates a sticky customer base that is less susceptible to competitive overtures.
- Brand Loyalty: DXP’s focus on building deep, solution-oriented relationships fosters strong customer loyalty.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with changing MRO providers present a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Integrated Solutions: DXP's combined product and service offerings further entrench its customer base.
- Technical Expertise: The company’s specialized knowledge adds another layer of stickiness for its clients.
Regulatory Barriers and Technical Expertise
While not as heavily regulated as some sectors, the distribution of industrial equipment and maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) products often requires specific certifications and adherence to stringent safety standards. New companies entering this space would need substantial investment to develop the necessary technical expertise and ensure compliance.
DXP Enterprises benefits from its team of seasoned professionals who possess extensive technical knowledge, a significant competitive edge. This deep understanding allows DXP to navigate complex product requirements and provide specialized solutions that new entrants may struggle to replicate quickly.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining necessary certifications for handling specialized industrial components can be time-consuming and costly for new market entrants.
- Technical Know-How: The need for in-depth product knowledge and application expertise presents a barrier, requiring significant training and experience.
- Investment in Compliance: New entrants must allocate capital to meet safety regulations and quality assurance standards prevalent in the industrial distribution sector.
- DXP's Advantage: DXP's established workforce with deep technical acumen and industry experience provides a differentiated service offering, deterring potential competitors.
The threat of new entrants for DXP Enterprises is relatively low. High capital requirements for inventory and logistics, coupled with established economies of scale, make market entry costly. Furthermore, strong customer loyalty and high switching costs, bolstered by DXP's integrated solutions and technical expertise, create significant barriers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for DXP Enterprises is built upon a robust foundation of industry research reports, financial filings, and market intelligence platforms. We leverage data from sources like IBISWorld, S&P Capital IQ, and company investor relations materials to thoroughly assess competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
