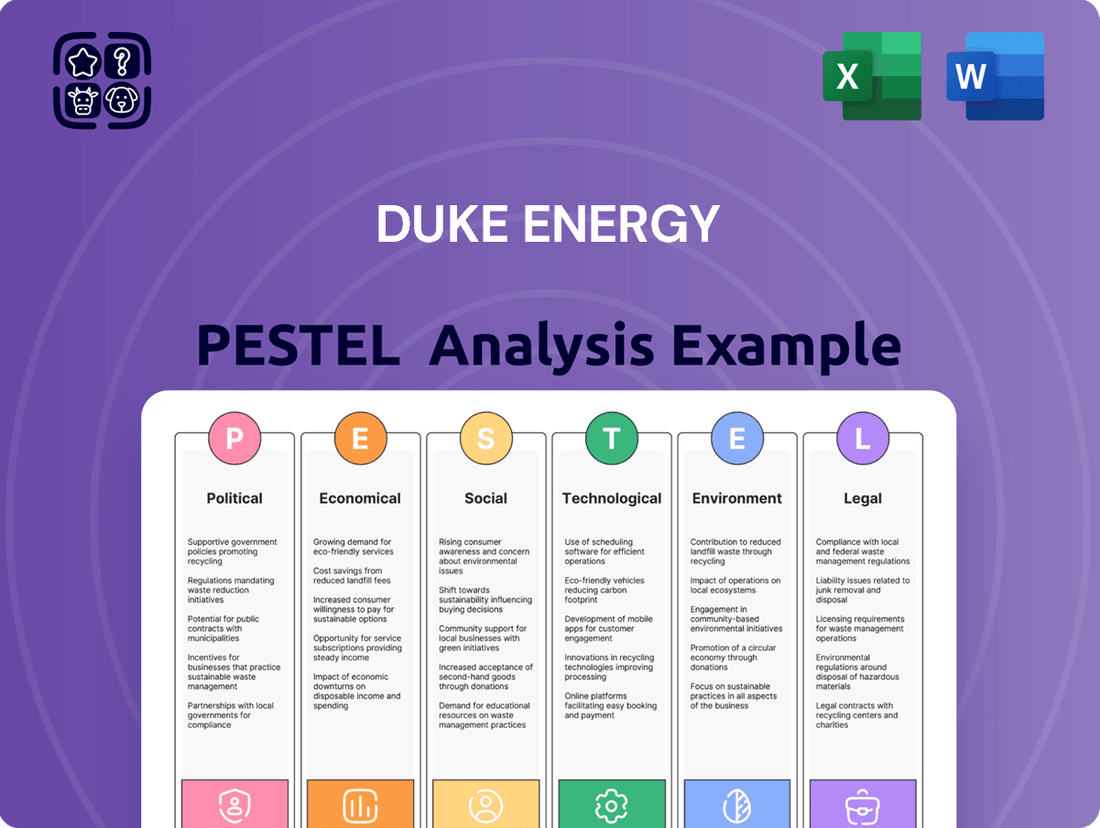
Duke Energy PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Duke Energy Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Duke Energy's future with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that create both challenges and opportunities for the company. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to inform your strategic decisions and gain a competitive edge.
Unlock a deeper understanding of Duke Energy's operating environment. Our expertly crafted PESTLE analysis provides critical insights into the trends that matter most, from evolving regulations to technological advancements. Purchase the full version now to access the detailed breakdown and empower your business planning.
Political factors
Governmental energy policy shifts significantly influence Duke Energy's strategic direction. For instance, the Biden administration's Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 provides substantial tax credits for renewable energy, potentially boosting Duke's investments in solar and wind power. Several states where Duke operates, like North Carolina, have also enacted or are considering clean energy mandates, such as the state's Clean Energy Act, which aims for significant carbon reductions, directly impacting Duke's generation mix and infrastructure plans.
Utility commissions and regulatory bodies across Duke Energy's operating states, such as the North Carolina Utilities Commission and the Public Service Commission of South Carolina, wield significant influence. These bodies approve rate cases, which directly impact Duke Energy's revenue stability and profitability by setting the prices customers pay for electricity and gas. For example, in 2023, Duke Energy sought rate increases in several jurisdictions, highlighting the ongoing negotiation between operational costs and customer affordability.
The recovery of capital expenditures, particularly for grid modernization and renewable energy projects, is a critical function of these regulators. Mechanisms like performance-based ratemaking can incentivize efficiency and investment, but their structure heavily influences Duke Energy's ability to fund its ambitious energy transition plans. In 2024, the company continued to invest billions in grid upgrades and clean energy, with regulatory approvals being paramount for recouping these investments.
Political stability in the United States is crucial for Duke Energy, as shifts in domestic policy can significantly impact the energy sector. For instance, changes in environmental regulations or energy infrastructure funding can alter operational costs and investment strategies. Geopolitical events, such as international conflicts, also play a vital role by influencing global energy prices and supply chain reliability, directly affecting fuel costs for Duke Energy.
Trade policies enacted by the U.S. government can have a ripple effect on Duke Energy's fuel supply chains, particularly for natural gas and coal. Tariffs or trade disputes can increase the cost of imported fuels or equipment, impacting operational expenditures. Conversely, favorable trade agreements can stabilize or reduce these costs, benefiting the company's bottom line.
Global geopolitical events, including conflicts in energy-producing regions, can lead to price volatility in the energy markets. For example, disruptions in the Middle East or Eastern Europe have historically caused spikes in oil and natural gas prices, which can affect Duke Energy's fuel procurement costs and, consequently, consumer electricity rates.
Lobbying and Political Influence
Duke Energy actively engages in the political arena, employing lobbying and advocacy to shape policies that align with its business interests. This includes influencing legislation concerning large-scale infrastructure investments, such as transmission lines and renewable energy projects, which are crucial for its long-term growth strategy.
The company's political influence extends to environmental regulations, where it advocates for approaches that balance ecological protection with the economic realities of energy production. For instance, Duke Energy has been a proponent of market-based solutions for emissions reduction, seeking flexibility in compliance with evolving climate change policies.
Furthermore, Duke Energy works to shape energy market structures, advocating for regulatory frameworks that support its existing asset base while also facilitating the transition to cleaner energy sources. This strategic engagement aims to secure a stable operating environment and predictable revenue streams, particularly as the energy sector undergoes significant transformation.
- Lobbying Expenditures: In 2023, Duke Energy reported spending approximately $17.5 million on federal lobbying efforts, reflecting a significant investment in influencing policy decisions.
- Policy Focus: Key legislative areas of focus for Duke Energy include infrastructure modernization, carbon pricing mechanisms, and the regulatory treatment of new energy technologies.
- State-Level Influence: Beyond federal efforts, the company maintains substantial lobbying operations in the states where it operates, engaging with state legislatures and regulatory bodies on issues like rate cases and renewable portfolio standards.
Public-Private Partnerships and Infrastructure Funding
Government support through public-private partnerships is crucial for funding Duke Energy's extensive infrastructure upgrades. Federal initiatives, such as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, are injecting significant capital into modernizing the grid and expanding clean energy. For instance, the law allocated $65 billion for grid modernization, which directly benefits utilities like Duke Energy in their efforts to enhance reliability and integrate renewables.
These partnerships accelerate investments in key areas like grid resilience against extreme weather and the integration of variable renewable sources. Furthermore, federal loan programs and grants, coupled with state and local government collaborations, can de-risk and expedite the development of vital infrastructure, including widespread electric vehicle charging networks. This collaborative approach is essential for Duke Energy to meet its ambitious clean energy transition goals.
Key government funding mechanisms impacting Duke Energy include:
- Federal Grants: Direct funding for specific projects like renewable energy deployment and grid modernization initiatives.
- Loan Programs: Government-backed loans offering favorable terms for large-scale infrastructure investments.
- State and Local Initiatives: Partnerships with regional governments to co-fund projects and streamline permitting processes.
Governmental policies and regulatory frameworks are paramount to Duke Energy's operations and strategic planning. The company's engagement with these political factors is extensive, aiming to shape legislation and regulations that support its business objectives, particularly concerning infrastructure investment and the energy transition.
Duke Energy's lobbying efforts in 2023 alone amounted to approximately $17.5 million at the federal level, highlighting its commitment to influencing policy decisions on critical issues such as infrastructure modernization and carbon pricing. This political engagement extends to state-level advocacy, where the company actively interacts with legislatures and regulatory bodies on matters like rate cases and renewable portfolio standards.
The company's strategy involves advocating for regulatory approaches that balance environmental goals with economic realities, often favoring market-based solutions for emissions reduction. Furthermore, Duke Energy actively seeks to influence energy market structures to ensure a stable operating environment and predictable revenue streams amidst the evolving energy landscape.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors influencing Duke Energy, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
It offers actionable insights for strategic decision-making by detailing how these forces present both challenges and opportunities for the company's operations and future growth.
A concise PESTLE analysis for Duke Energy offers a readily digestible overview of external factors, streamlining strategic discussions and reducing the time spent deciphering complex market dynamics.
Economic factors
Duke Energy's revenue is intrinsically linked to economic growth within its service territories, particularly in the Carolinas and Florida. As the economy expands, industrial output and commercial activity increase, directly driving higher electricity consumption. For instance, in 2023, Duke Energy reported that residential customer growth and economic development in its Carolinas region contributed to a 1.5% increase in retail electricity deliveries compared to the previous year.
Conversely, economic slowdowns or recessions typically lead to reduced industrial and commercial demand, impacting Duke Energy's top line. A significant economic downturn could see a dip in electricity sales, potentially pressuring earnings and necessitating adjustments to capital expenditure plans. The company's financial forecasts often account for projected GDP growth rates in its key states to anticipate future energy demand.
Fuel price volatility, particularly for natural gas and coal, directly impacts Duke Energy's operational expenses. For instance, in 2023, natural gas prices experienced significant fluctuations, with Henry Hub spot prices ranging from below $2.00 per MMBtu to over $3.00 per MMBtu at various points, affecting generation costs.
Duke Energy employs hedging strategies and diversifies its energy portfolio to mitigate these price swings. By securing fuel contracts in advance and increasing reliance on renewables, the company aims to stabilize costs. Regulatory mechanisms also allow for fuel cost recovery, helping to ensure that unexpected price increases don't disproportionately burden the company or customers.
Interest rates significantly influence Duke Energy's cost of capital, impacting its ability to fund large-scale infrastructure projects like new power plants and grid modernization. For instance, if the Federal Reserve raises its benchmark interest rate, Duke Energy's borrowing costs for new debt issuance will likely increase, making projects more expensive. This could potentially lead to higher electricity rates for customers or a reduction in planned capital expenditures.
In 2024 and projected into 2025, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy, particularly regarding interest rates, remains a critical factor. If rates remain elevated, the cost of financing Duke Energy's substantial investments in renewable energy, such as solar and wind farms, and critical grid upgrades will be higher. This directly affects the projected return on investment for these projects and could necessitate adjustments to consumer pricing structures to maintain financial viability.
Inflationary Pressures
Inflationary pressures significantly impact Duke Energy's operational costs. Rising prices for labor, essential equipment, and ongoing maintenance directly increase expenditures. For instance, the U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) saw a notable increase, with annual inflation rates fluctuating throughout 2024 and into early 2025, impacting the cost of materials and services Duke Energy relies on.
These rising costs can squeeze profit margins if Duke Energy cannot pass them on to consumers through approved rate adjustments. Without effective strategies like efficiency improvements or securing favorable long-term contracts for materials, the company's financial performance could be negatively affected. This dynamic is crucial for understanding Duke Energy's ability to maintain profitability in a changing economic climate.
- Increased Operational Expenses: Higher costs for fuel, materials, and labor directly impact Duke Energy's bottom line. For example, the average hourly earnings in the utilities sector have seen upward trends, reflecting broader labor market inflation.
- Erosion of Profit Margins: If rate increases lag behind cost inflation, Duke Energy's profit margins can shrink, affecting shareholder returns and reinvestment capacity.
- Impact on Capital Projects: Inflation can also drive up the costs of large-scale infrastructure projects, such as grid modernization or renewable energy installations, potentially delaying or altering project scopes.
- Regulatory Lag: The process of seeking and receiving approval for rate adjustments from regulatory bodies can create a time lag, during which Duke Energy absorbs higher costs, further impacting profitability.
Customer Affordability and Rate Design
Customer affordability is a critical economic factor for Duke Energy, directly impacting their ability to collect revenue and influencing regulatory decisions on rate design. As of early 2024, inflation and persistent cost-of-living pressures continue to strain household budgets across Duke Energy's service territories. This economic reality makes it harder for many customers to absorb rising energy bills.
Regulators face the complex task of balancing Duke Energy's need to recover investments in infrastructure and clean energy with the imperative to keep electricity affordable. For instance, in North Carolina, Duke Energy filed for a rate increase in late 2023 that sought to recover costs associated with grid modernization and renewable energy projects. The North Carolina Utilities Commission ultimately approved a lower increase than requested, reflecting concerns about customer affordability.
The economic sensitivity of different customer segments also plays a role. Lower-income households and small businesses are often disproportionately affected by energy price volatility. This necessitates careful consideration in rate design, potentially including tiered pricing structures or assistance programs to mitigate the economic burden.
- Inflationary Pressures: Persistent inflation in 2023 and early 2024 has reduced the discretionary income available for energy expenses for many households and businesses served by Duke Energy.
- Regulatory Balancing Act: Regulators must weigh Duke Energy's revenue requirements against the economic capacity of customers to pay, as seen in rate case decisions where approved increases are often moderated.
- Impact on Rate Design: The economic conditions of customers influence the structure of approved rates, with a focus on maintaining affordability, especially for vulnerable populations.
- Customer Assistance Programs: Duke Energy's service territories often feature customer assistance programs, such as the Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP), which become even more critical during periods of economic strain.
Economic growth directly fuels Duke Energy's revenue through increased electricity demand, with a 1.5% rise in retail electricity deliveries in its Carolinas region in 2023 attributed to customer growth and economic development. Conversely, economic downturns reduce demand, impacting sales and potentially capital expenditures. Fuel price volatility, particularly for natural gas, directly affects operational costs, with Henry Hub prices fluctuating significantly in 2023.
Elevated interest rates in 2024-2025 increase Duke Energy's cost of capital, making significant investments in renewables and grid modernization more expensive. Inflation also drives up operational expenses for labor and materials, with the CPI showing notable increases throughout 2024, potentially squeezing profit margins if not offset by rate adjustments.
Customer affordability remains a key concern, as persistent inflation strains household budgets, complicating regulatory decisions on rate increases. Regulators balance Duke Energy's investment needs with customer capacity, often moderating requested rate hikes, as seen in North Carolina's late 2023 rate case.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Duke Energy PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Duke Energy delves into Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic landscape Duke Energy navigates.
Sociological factors
Public perception significantly shapes Duke Energy's ability to operate, especially as societal views on energy sources and climate change evolve. Growing concern over climate change, for instance, puts pressure on utilities to transition away from fossil fuels, impacting Duke Energy's strategic planning and investment in renewables. In 2024, surveys indicated a majority of Americans favor increased investment in renewable energy, a trend Duke Energy must address to maintain public trust and its social license to operate.
Maintaining strong community relations is crucial for Duke Energy, particularly when undertaking infrastructure projects or responding to environmental issues. Transparent communication and a proactive approach to addressing local concerns, such as those related to new transmission lines or potential impacts from severe weather events, are vital. For example, in 2024, Duke Energy faced local opposition to a proposed transmission line project in North Carolina, highlighting the need for robust community engagement to mitigate negative sentiment.
Demographic shifts significantly influence Duke Energy's energy demand. For instance, in North Carolina, a key service area, the population is projected to grow, with an increasing urbanization trend concentrating demand in metropolitan areas. This growth, coupled with changing household compositions, means more housing units requiring electricity.
Evolving lifestyles are also reshaping energy consumption. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a prime example; by the end of 2024, EV registrations in the US are expected to surpass 3 million, directly increasing electricity demand for charging. Similarly, the proliferation of smart home devices and increased reliance on technology for work and leisure further contribute to higher and potentially more varied energy needs.
Duke Energy faces the sociological challenge of attracting and retaining skilled talent in the evolving energy sector, particularly with the increasing demand for expertise in areas like renewable energy and grid modernization. Employee satisfaction and robust labor relations are crucial for operational continuity, especially as an aging workforce necessitates effective knowledge transfer. In 2024, Duke Energy reported a significant focus on diversity and inclusion, aiming to build a workforce that reflects the communities it serves, which is a key sociological driver for long-term success and employee engagement.
Customer Expectations for Sustainability and Reliability
Customers increasingly expect Duke Energy to provide sustainable energy solutions and ensure highly reliable power delivery. This societal shift is pushing the company to prioritize investments in renewable energy sources and grid modernization.
Duke Energy is responding to these heightened expectations by expanding its clean energy portfolio. For instance, by the end of 2024, the company plans to have more than 10,000 megawatts of regulated renewable energy projects in service or under development, reflecting a commitment to cleaner energy options.
Furthermore, customers demand greater grid resilience, especially in the face of more frequent and severe weather events. Duke Energy is investing in infrastructure upgrades to enhance reliability, such as hardening power lines and implementing advanced grid technologies. In 2023 alone, the company invested $1.7 billion in grid improvements.
- Growing Demand for Renewables: Duke Energy aims to achieve net-zero carbon emissions from its operations by 2050, with interim goals to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 50% from 2005 levels by 2030.
- Grid Modernization Investments: The company is implementing smart meter technology across its service territories, with over 5 million smart meters installed by early 2024, enabling better outage detection and customer energy management.
- Customer Engagement Tools: Duke Energy is enhancing its digital platforms to offer customers more personalized energy management tools and real-time usage data, fostering greater control and transparency.
Social Equity and Energy Access
Societal implications of energy access and affordability are critical for Duke Energy, particularly for vulnerable populations. The company plays a role in addressing energy poverty through various initiatives, aiming to ensure equitable distribution of energy transition benefits.
Duke Energy's commitment to low-income assistance programs is a key aspect of its social equity strategy. For instance, in 2023, the company provided over $200 million in energy assistance to customers, helping to alleviate the burden of high energy costs.
- Energy Assistance: Duke Energy's customer assistance programs, such as Energy Neighbor and Share the Light, provided support to hundreds of thousands of low-income households in 2023.
- Equitable Transition: The company is investing in renewable energy projects and grid modernization, with a focus on ensuring these advancements benefit all communities, including those historically underserved.
- Affordability Concerns: Rising energy prices present ongoing challenges, making Duke Energy's efforts to maintain affordable rates and provide robust assistance programs more vital than ever for its customer base.
Duke Energy's social license to operate is increasingly tied to public perception of its environmental stewardship and commitment to community well-being. Growing societal pressure for climate action, evidenced by a majority favoring renewable energy investment in 2024 polls, directly influences Duke Energy's strategic direction and capital allocation towards cleaner energy sources.
Maintaining strong community relations is paramount for Duke Energy, especially when developing new infrastructure or addressing environmental concerns. Proactive engagement and transparent communication are vital, as seen in 2024 when local opposition arose for a North Carolina transmission line project, underscoring the need for robust community outreach.
Demographic shifts, such as population growth and urbanization in key service areas like North Carolina, are driving increased electricity demand. Evolving lifestyles, including the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, with over 3 million expected registrations by the end of 2024, also contribute to higher and more complex energy consumption patterns.
Duke Energy faces the sociological challenge of attracting and retaining skilled talent, particularly in renewable energy and grid modernization. Employee satisfaction and effective knowledge transfer are crucial, with the company emphasizing diversity and inclusion in 2024 to build a workforce reflective of its communities.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on Duke Energy | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Public Opinion on Climate Change | Drives demand for renewables and decarbonization efforts. | Majority of Americans favor increased renewable energy investment (2024). |
| Community Relations | Crucial for infrastructure project approval and operational continuity. | Local opposition to projects highlights need for enhanced engagement (e.g., NC transmission line, 2024). |
| Demographic Shifts | Influences energy demand patterns and infrastructure needs. | Projected population growth and urbanization in NC increase demand. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Impacts energy consumption through new technologies. | EV registrations expected to surpass 3 million by end of 2024, increasing electricity demand. |
| Workforce Development | Essential for innovation and operational efficiency. | Focus on diversity and inclusion to attract and retain talent (2024). |
Technological factors
Duke Energy is actively benefiting from the rapid evolution of renewable energy technologies. The increasing efficiency and decreasing costs of solar and wind power, coupled with advancements in battery storage, allow the company to integrate more clean energy into its generation mix. For instance, by the end of 2023, Duke Energy had committed to adding approximately 11,000 megawatts of regulated renewable energy projects to its portfolio by 2030, a significant step towards decarbonization.
Duke Energy is actively investing in grid modernization, rolling out smart meter technology across its service territories. This initiative, part of a broader smart grid strategy, aims to improve operational efficiency and customer service. For instance, by the end of 2023, Duke Energy had installed over 6 million smart meters in North Carolina alone, a significant step towards a more responsive and automated energy infrastructure.
These smart grid technologies, including advanced metering infrastructure and distribution automation, are crucial for enhancing grid reliability. They allow for faster detection and restoration of outages, optimizing energy flow, and enabling dynamic pricing and demand-side management programs. This technological upgrade also facilitates the seamless integration of distributed energy resources like solar and battery storage, a growing trend in the energy sector.
Technological advancements in energy storage, especially utility-scale batteries, are rapidly transforming the energy landscape. These solutions are crucial for enhancing grid stability by smoothing out the variability of renewable sources like solar and wind. For Duke Energy, improved storage capabilities mean greater operational flexibility, enabling better management of peak demand periods and a more seamless integration of cleaner energy sources.
By 2024, the global energy storage market, particularly for batteries, is projected to see significant growth, with investments in grid-scale projects accelerating. Duke Energy itself has been actively investing in and deploying battery storage projects, such as its Hyde County Energy Storage project in North Carolina, which came online in 2024 with a capacity of 100 MW. This type of deployment directly addresses the need for peak shaving and improved grid reliability, especially as the company increases its renewable energy portfolio.
Cybersecurity and Digital Infrastructure
Cybersecurity is paramount for Duke Energy, safeguarding its operational technology and vast information systems against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Robust digital infrastructure and advanced cybersecurity measures are not just best practices but necessities for maintaining grid reliability and protecting sensitive customer data.
Investments in these areas are crucial for preventing disruptions and ensuring the secure flow of energy. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy allocated $25 million to enhance the cybersecurity of the nation's electric grid, a testament to the growing focus on this critical infrastructure vulnerability. Duke Energy, like its peers, must continuously adapt its defenses to counter evolving threats, ensuring the resilience of its services.
- Cybersecurity Investments: Duke Energy's commitment to cybersecurity is reflected in ongoing investments to fortify its digital defenses against cyberattacks.
- Grid Reliability: Enhanced cybersecurity directly supports the reliable operation of the power grid, minimizing the risk of outages caused by malicious actors.
- Data Protection: Protecting customer information and operational data is a core tenet of Duke Energy's digital infrastructure strategy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to evolving cybersecurity regulations and standards is a key driver for technological advancements within the company.
Carbon Capture and Advanced Nuclear Technologies
Emerging technologies like carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) present a significant technological factor for Duke Energy. Innovations in CCUS could allow for the decarbonization of existing natural gas power plants, extending their operational life while meeting environmental goals. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy has been actively funding CCUS projects, with significant investments expected through 2024 and beyond to drive down costs and improve efficiency.
Advanced nuclear technologies, including small modular reactors (SMRs) and next-generation fission designs, offer another crucial technological pathway. These reactors promise enhanced safety, reduced waste, and greater flexibility, potentially providing reliable, carbon-free baseload power. Duke Energy, like other utilities, is closely monitoring the development and commercialization of SMRs, which are anticipated to become more widely deployable in the late 2020s and early 2030s.
- CCUS advancements: Potential to reduce emissions from existing fossil fuel assets.
- Advanced nuclear potential: Offers reliable, carbon-free dispatchable power.
- Government support: Significant U.S. DOE funding for CCUS development and deployment.
- SMR deployment timeline: Expected commercial availability in the late 2020s/early 2030s.
Technological advancements are reshaping Duke Energy’s operational landscape, particularly in renewable energy integration and grid modernization. The company is actively embracing innovations in solar, wind, and battery storage to expand its clean energy portfolio. For example, Duke Energy has committed to adding approximately 11,000 megawatts of regulated renewable energy projects by 2030, underscoring its strategic technological pivot.
Legal factors
Federal and state environmental laws like the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act significantly shape Duke Energy's operational landscape. These regulations mandate compliance, influencing everything from emissions control to water discharge permits.
Increasingly stringent emissions standards for power plants, coupled with robust waste disposal and site remediation requirements, compel substantial capital expenditures. For instance, in 2023, Duke Energy reported investing billions in grid modernization and cleaner energy solutions, partly driven by these environmental mandates.
Duke Energy operates within a stringent legal framework heavily influenced by state public utility commissions, which are responsible for setting electricity and gas rates. These commissions, such as the Public Service Commission of South Carolina and the North Carolina Utilities Commission, must approve any changes to Duke's pricing structure. For instance, in 2023, Duke Energy filed for a rate increase in North Carolina, seeking to recover investments in grid modernization and clean energy, a process that involves extensive legal review and public hearings.
Legal challenges and the need for regulatory approvals directly impact Duke Energy's financial performance and strategic initiatives. Failure to gain commission approval for rate increases can hinder cost recovery and limit the company's ability to earn a reasonable return on its substantial infrastructure investments, which exceeded $15 billion in capital expenditures in 2023 alone. Compliance with commission orders is paramount, as deviations can lead to penalties and further regulatory scrutiny, affecting the company's operational flexibility and future growth plans.
Duke Energy must navigate a complex web of consumer protection and privacy laws, ensuring fair billing practices and robust data security for its millions of customers. Regulations like the North Carolina's Consumer Financial Protection Act and similar state-level statutes mandate transparency in pricing and prohibit deceptive marketing. For instance, in 2023, Duke Energy reported spending millions on regulatory compliance and customer service initiatives aimed at meeting these evolving legal standards, particularly concerning data breach prevention and customer data handling.
Antitrust and Competition Laws
Antitrust and competition laws are critical for the energy sector, impacting how companies like Duke Energy operate and grow. These regulations aim to prevent monopolies and ensure a level playing field for all participants. For instance, regulatory bodies scrutinize mergers and acquisitions to ensure they don't stifle competition. In 2024, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) continued its focus on market concentration across various industries, including utilities, with potential implications for any future consolidation Duke Energy might consider.
These laws directly influence Duke Energy's strategic decisions regarding market expansion and partnerships. By preventing monopolistic practices, regulators ensure that consumers benefit from competitive pricing and a wider range of energy choices. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and operational restrictions, making adherence to antitrust guidelines a cornerstone of Duke Energy's business strategy.
Key aspects of antitrust enforcement relevant to Duke Energy include:
- Merger Review: Scrutiny of proposed mergers and acquisitions to prevent undue market concentration.
- Market Dominance: Oversight to prevent dominant firms from abusing their position to harm competitors or consumers.
- Anti-competitive Practices: Prohibition of practices like price-fixing or predatory pricing that distort market competition.
Land Use and Permitting Laws
Duke Energy navigates a complex web of land use and permitting laws, crucial for its extensive infrastructure development. Local, state, and federal regulations dictate everything from where power plants can be sited to the routing of new transmission lines. This often involves lengthy legal reviews and public comment periods, impacting project timelines and costs.
For instance, the permitting process for a new natural gas plant or a large-scale solar farm can span years, requiring adherence to environmental impact assessments and zoning ordinances. In 2024, Duke Energy's ongoing investments in grid modernization and renewable energy projects, such as its planned expansion of solar capacity in North Carolina, are subject to these evolving legal frameworks. The company must secure numerous permits, often facing challenges related to land acquisition and environmental compliance.
- Federal Regulations: The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and the Clean Water Act are key federal laws influencing project approvals for Duke Energy's infrastructure.
- State-Level Oversight: State public utility commissions and environmental agencies, like the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality, play a significant role in permitting and siting decisions for Duke Energy's operations.
- Local Zoning and Land Use: Municipal and county zoning laws directly affect the feasibility of constructing new facilities or expanding existing ones, often requiring specific land use permits.
- Public Hearings and Stakeholder Engagement: Many permitting processes mandate public hearings, providing opportunities for community input and potential legal challenges to Duke Energy's projects.
Duke Energy's operations are significantly shaped by environmental regulations, requiring substantial investments in compliance and cleaner technologies. The company's capital expenditures in 2023, exceeding $15 billion, were partly allocated to meet these mandates, including grid modernization and cleaner energy solutions.
Rate setting by state public utility commissions, such as the North Carolina Utilities Commission, directly impacts Duke Energy's revenue and investment recovery. For instance, a 2023 rate increase filing in North Carolina highlighted the extensive legal review and public hearings involved in approving pricing adjustments.
Navigating consumer protection laws and antitrust regulations is crucial for Duke Energy's market operations and customer relations. Compliance with these laws, including data security and fair billing practices, involves ongoing investment, with millions spent in 2023 on regulatory compliance initiatives.
Land use and permitting laws significantly influence Duke Energy's infrastructure development, often leading to lengthy legal processes and cost impacts. Projects like solar farm expansions in 2024 face scrutiny under federal and state environmental laws, requiring numerous permits and stakeholder engagement.
Environmental factors
The escalating urgency of climate change and global decarbonization mandates are fundamentally reshaping the energy sector, directly impacting Duke Energy's operational and strategic landscape. The company is actively pursuing a significant transition, aiming to reduce its carbon footprint and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. This strategic pivot is not only a response to scientific consensus on global warming but also a critical element in meeting evolving stakeholder expectations and regulatory pressures.
Duke Energy's commitment involves substantial investments in cleaner energy sources, with plans to retire a significant portion of its coal-fired generation capacity. For instance, by the end of 2024, the company expects to have retired approximately 70% of its coal fleet. This transition is geared towards increasing renewable energy generation, such as solar and wind power, and exploring advancements in energy storage and grid modernization to support a low-carbon future.
Duke Energy is navigating the environmental imperative to integrate more renewable energy, a significant shift from its historical fossil fuel reliance. This transition aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, a key environmental benefit. For instance, by the end of 2023, Duke Energy had already retired approximately 70% of its coal-fired generation capacity.
However, managing the intermittency of sources like solar and wind presents environmental challenges, requiring grid modernization and energy storage solutions. The environmental footprint of new renewable infrastructure, including land use for solar farms and manufacturing impacts for wind turbines, also requires careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
Water is a critical resource for Duke Energy, especially for cooling its thermal power plants. In 2023, the company reported using approximately 250 billion gallons of water, with a significant portion being recycled or returned to its source after use. This highlights the substantial environmental consideration of water usage in power generation.
Duke Energy is actively engaged in water conservation and responsible water management. The company has invested in technologies and strategies to reduce its water footprint, including increasing water recycling rates and employing more efficient cooling systems. For instance, their advanced cooling technologies aim to minimize water withdrawal and consumption.
Compliance with stringent water quality regulations is paramount for Duke Energy. The company adheres to regulations set by agencies like the EPA, ensuring that discharged water meets specific quality standards to protect aquatic ecosystems. This commitment to responsible water management is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and ensuring the long-term sustainability of water resources.
Waste Management and Pollution Control
Duke Energy faces significant environmental challenges stemming from waste streams generated by its power generation activities, particularly coal ash from its coal-fired plants. Managing these byproducts safely and effectively is crucial for regulatory compliance and environmental stewardship. In 2023, Duke Energy continued its efforts to safely close coal ash sites, with a significant portion of its ash basins undergoing closure processes, aiming to prevent potential groundwater contamination.
The company employs a multi-faceted approach to waste management and pollution control. This includes investing in advanced technologies for wastewater treatment and air emission scrubbing to minimize pollutants released into the environment. Duke Energy's strategies also focus on recycling and beneficial reuse of materials where feasible, reducing the volume of waste requiring disposal.
- Coal Ash Management: Duke Energy is actively managing legacy coal ash, with substantial progress made in closing or dewatering ash basins across its service territories as of late 2024.
- Pollution Control Investments: The company has invested billions in pollution control equipment, such as scrubbers and selective catalytic reduction systems, to meet stringent air quality standards.
- Water Quality Protection: Measures are in place to monitor and protect water quality around its facilities, addressing concerns related to industrial wastewater discharge and potential runoff.
Biodiversity and Land Conservation
Duke Energy actively manages its landholdings and operational sites to mitigate impacts on biodiversity and promote land conservation. The company focuses on responsible land management for its extensive transmission and distribution corridors, aiming to preserve natural habitats and minimize fragmentation. In 2024, Duke Energy continued its commitment to ecological restoration, investing in projects designed to enhance local ecosystems and support wildlife populations adjacent to its infrastructure.
Key initiatives include:
- Habitat Restoration: Implementing projects to restore native plant communities and improve habitat quality at former industrial sites and along rights-of-way.
- Sustainable Land Management: Employing practices that reduce invasive species and promote ecological diversity within its operational areas.
- Conservation Partnerships: Collaborating with environmental organizations on land conservation efforts and ecological research to inform best practices.
- Biodiversity Monitoring: Conducting assessments to understand and track the impact of operations on local flora and fauna, guiding conservation strategies.
The increasing focus on environmental sustainability and climate change mitigation directly impacts Duke Energy's operational strategies and investments. The company is committed to reducing its carbon footprint, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050, which necessitates significant shifts in its energy generation portfolio.
Duke Energy is actively retiring coal-fired power plants, with plans to phase out a substantial portion of its coal fleet by the end of 2024. This transition involves substantial investments in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, alongside advancements in energy storage and grid modernization.
Managing water resources is critical, as Duke Energy utilizes significant amounts for cooling thermal plants. The company is investing in water conservation and advanced cooling technologies to minimize consumption and adhere to stringent water quality regulations.
Waste management, particularly coal ash, remains a key environmental consideration. Duke Energy is actively working on safely closing coal ash sites, implementing advanced wastewater treatment, and air emission controls to minimize environmental impact.
| Environmental Focus Area | Key Initiatives & Data (as of late 2024/early 2025) | Impact & Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Decarbonization | Net-zero emissions target by 2050. | Requires substantial investment in renewables and grid modernization. |
| Coal Fleet Retirement | ~70% of coal fleet retired by end of 2024. | Shifts generation mix towards cleaner sources. |
| Water Management | ~250 billion gallons water used in 2023; increased water recycling. | Focus on efficient cooling and regulatory compliance. |
| Waste Management | Ongoing closure of coal ash sites. | Mitigating potential groundwater contamination and ensuring safe disposal. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Duke Energy is constructed using a comprehensive blend of data from government regulatory bodies, economic forecasting agencies, and reputable industry publications. This ensures a thorough understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors influencing the energy sector.
