D.R. Horton Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
D.R. Horton Bundle
D.R. Horton, a titan in the homebuilding industry, faces a complex web of competitive forces. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for navigating this dynamic market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping D.R. Horton’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a key factor in the homebuilding industry, with D.R. Horton depending on numerous suppliers for essential materials like lumber, concrete, and appliances, as well as for labor. When a small number of suppliers control a significant portion of a specific input, they gain considerable leverage. This allows them to dictate pricing and terms, potentially increasing costs for D.R. Horton.
For instance, in 2024, lumber prices experienced volatility, with futures contracts for framing lumber showing fluctuations influenced by supply chain dynamics and demand. A highly concentrated lumber market could have allowed a few major producers to command higher prices, directly impacting D.R. Horton's cost of goods sold. Conversely, a fragmented supplier base offers D.R. Horton more options and strengthens its negotiating position.
The criticality of certain inputs, like lumber and skilled labor, significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for D.R. Horton. If these essential components have limited substitutes, suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, fluctuations in lumber prices, a key component in home construction, directly impact D.R. Horton's cost structure.
In 2024, the U.S. housing market continued to grapple with supply chain challenges. While specific data for D.R. Horton's reliance on individual inputs isn't readily available, the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) reported persistent elevated costs for materials like lumber and concrete throughout much of the year. This indicates a continued strong position for suppliers of these essential goods.
D.R. Horton's ability to manage its supply chain effectively is paramount, especially in light of potential economic headwinds. The company's scale allows for some negotiation power, but reliance on specialized labor and fluctuating material costs means supplier influence remains a key factor in its operational costs and profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for D.R. Horton is influenced by switching costs. If suppliers can impose high costs for D.R. Horton to switch to alternative materials or components, their power increases. This could involve retraining labor or re-engineering designs, which are significant undertakings in home construction.
However, D.R. Horton's considerable scale and standardized construction processes offer a degree of leverage. By purchasing in bulk and establishing long-term contracts, the company can negotiate more favorable terms, thereby mitigating the impact of high switching costs and reducing supplier power. For instance, in 2023, D.R. Horton reported revenues of $32.2 billion, reflecting its substantial purchasing volume.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the homebuilding market, essentially becoming competitors, is generally considered low for companies like D.R. Horton. The construction industry, particularly at the builder level, is highly fragmented, making it difficult for a single supplier to gain significant market share. However, large material manufacturers, possessing substantial capital and established supply chains, could theoretically partner with or acquire smaller, existing homebuilders to enter the market.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers entering the homebuilding sector themselves.
- Industry Fragmentation: The homebuilding market is highly fragmented, limiting supplier integration impact.
- Potential for Large Manufacturers: Major material suppliers could acquire or partner with smaller builders.
- Limited Impact on D.R. Horton: D.R. Horton's scale and established operations make it less vulnerable to this specific threat.
D.R. Horton's Ability to Backward Integrate
D.R. Horton's strategic move to backward integrate, primarily through its majority-owned subsidiary Forestar Group, directly tackles the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly land developers. By controlling a significant portion of its land acquisition and development pipeline, D.R. Horton can secure land inventory at more favorable terms, reducing its reliance on external suppliers and their pricing power.
This vertical integration extends beyond land. D.R. Horton also offers mortgage financing and title services, creating a more comprehensive and controlled ecosystem. This not only captures additional revenue streams but also insulates the company from the potential price increases or service disruptions from third-party providers in these crucial areas.
- Forestar Group's Role: Forestar Group, in which D.R. Horton held approximately 62% ownership as of late 2023, is instrumental in developing and managing a substantial land portfolio, directly impacting D.R. Horton's land supply costs and availability.
- Mitigating Supplier Power: By controlling a significant portion of its land through Forestar, D.R. Horton reduces its exposure to the fluctuating prices and availability dictated by independent land developers, thereby lessening their bargaining power.
- Expanded Integration: The company's in-house mortgage and title services further solidify its control over the homebuilding process, minimizing reliance on external suppliers and enhancing operational efficiency and cost management.
The bargaining power of suppliers for D.R. Horton is moderate, influenced by industry concentration and input criticality. While D.R. Horton’s scale provides some leverage, the reliance on specialized labor and volatile material costs, like lumber, means suppliers can still exert significant influence. The company's efforts in backward integration, particularly through Forestar Group for land acquisition, aim to directly counter this power by securing essential inputs at more favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on D.R. Horton | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Higher concentration increases supplier leverage. | Lumber prices showed volatility, indicating potential supplier pricing power. |
| Input Criticality | Essential inputs with few substitutes strengthen supplier position. | Lumber and skilled labor remain critical, impacting D.R. Horton's costs. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs empower suppliers. | Significant costs to change materials or labor processes favor existing suppliers. |
| Backward Integration | Reduces reliance on external suppliers. | Forestar Group's land development mitigates land supplier power. |
What is included in the product
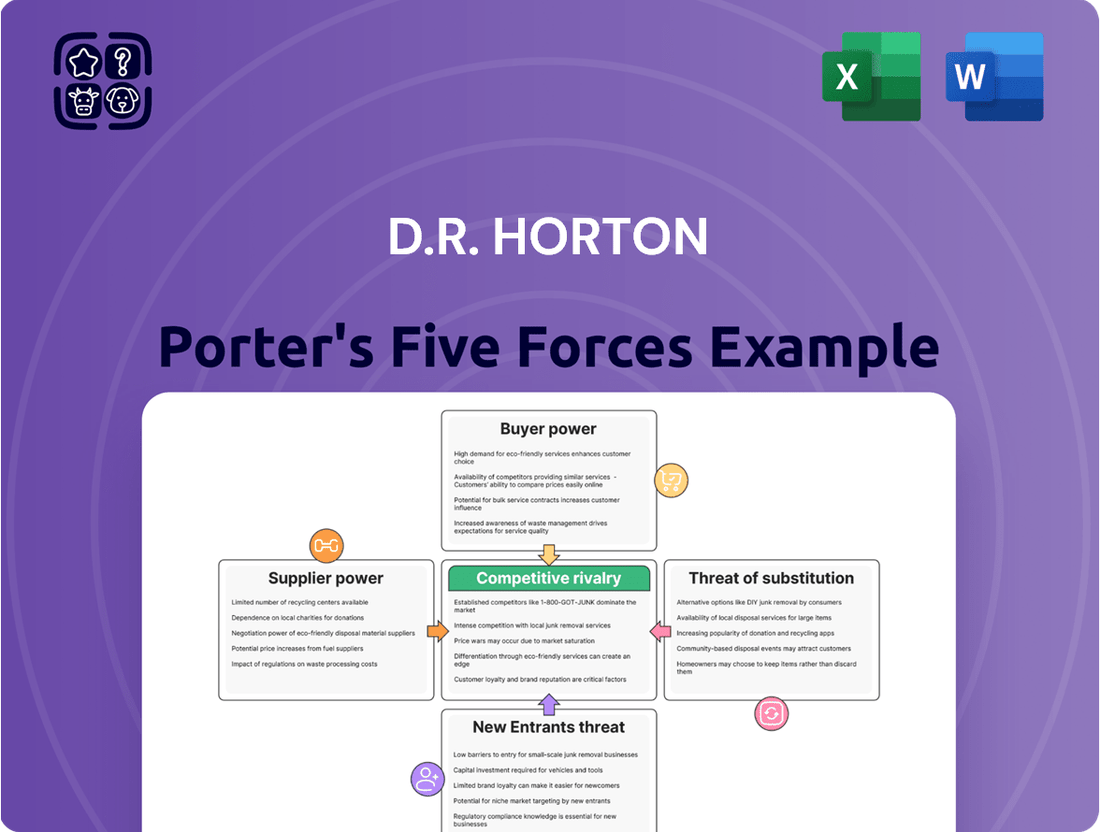
This analysis dissects D.R. Horton's competitive environment by examining the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for D.R. Horton, empowering strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Homebuyers' price sensitivity is a major force impacting D.R. Horton. In 2024, with ongoing affordability concerns and a generally cautious consumer sentiment, buyers are keenly aware of price points. This sensitivity directly influences D.R. Horton's pricing strategies and the average price of the homes they build and sell.
The availability of substitute homes significantly boosts customer bargaining power for D.R. Horton. Buyers can easily compare D.R. Horton's offerings with existing homes on the resale market, new construction from competitors like Lennar or PulteGroup, and even rental options. This abundance of alternatives means customers aren't locked into a single builder and can readily demand better pricing or incentives. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Census Bureau reported a substantial inventory of existing homes for sale, providing a direct comparison point for new builds.
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, which significantly boosts their bargaining power when it comes to home purchases. With the internet, they can easily compare prices, examine home features, and research builder reputations. This wealth of readily available data empowers buyers to make much more informed decisions, putting them in a stronger negotiating position.
Switching Costs for Customers
For potential homebuyers, the initial bargaining power is significant because switching costs are quite low before a purchase agreement is finalized. They can readily compare D.R. Horton's offerings against competitors or opt for pre-owned homes without incurring substantial financial penalties. This ease of comparison empowers customers to negotiate terms or walk away if they find a better deal elsewhere.
However, once a buyer commits to D.R. Horton by signing a contract, the switching costs begin to rise. These costs can include earnest money deposits, which are forfeited if the buyer defaults, as well as potential legal fees associated with breaking the agreement. Beyond the financial aspect, buyers also invest emotionally in the home selection process, making a change at this stage more difficult.
In 2024, the housing market saw varied demand across regions, influencing D.R. Horton's ability to command prices and terms. For instance, while national housing starts showed some fluctuations, specific markets might have experienced tighter inventory, giving builders like D.R. Horton more leverage. Conversely, areas with abundant supply would see customers retaining greater bargaining power due to the readily available alternatives.
- Low initial switching costs: Buyers can easily compare D.R. Horton with other builders or existing homes before signing a contract.
- Increasing costs post-contract: Deposits, legal fees, and emotional investment make switching more difficult once an agreement is in place.
- Market conditions impact leverage: Regional housing market dynamics in 2024 influenced customer bargaining power based on supply and demand.
Concentration of Customers
The customer base for D.R. Horton is overwhelmingly fragmented, comprising millions of individual homebuyers. This diffuse structure inherently weakens the collective bargaining power of customers, as there isn't a concentrated group of large buyers capable of dictating terms. While individual negotiations on specific homes occur, the sheer volume of buyers means D.R. Horton can often absorb the impact of any single buyer's demands.
In 2023, D.R. Horton reported closing on 87,547 homes. This massive volume underscores the dispersed nature of its customer base, making it difficult for any small subset of buyers to exert significant influence over the company's pricing or sales practices. The company's ability to sell such a high volume of homes across diverse markets further dilutes any potential for concentrated customer pressure.
- Fragmented Customer Base: D.R. Horton's customers are primarily individual homebuyers, not large institutional entities.
- Limited Collective Power: The wide distribution of buyers prevents them from forming a unified front to negotiate terms.
- High Sales Volume: With 87,547 homes closed in 2023, the company serves a vast and diverse market.
- Individual Negotiation: While collective power is low, individual buyers may still negotiate on specific property deals.
The bargaining power of D.R. Horton's customers is moderate, influenced by market conditions and buyer information levels. While individual buyers have limited collective power due to a fragmented customer base, their ability to compare options and their price sensitivity in 2024, especially with available resale inventory, can lead to negotiation leverage. The sheer volume of homes D.R. Horton sells, such as the 87,547 homes closed in 2023, indicates a broad market reach that diffuses individual buyer influence.
| Factor | Impact on D.R. Horton | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High | Buyers are keenly aware of affordability and compare prices closely. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate | Resale homes and competitors offer alternatives, increasing buyer options. |
| Customer Information Level | Moderate to High | Easy access to online data empowers buyers to research and negotiate. |
| Switching Costs (Pre-Contract) | Low | Buyers can easily compare and walk away before signing. |
| Customer Base Fragmentation | Lowers Bargaining Power | Millions of individual buyers lack collective negotiation strength. |
Same Document Delivered
D.R. Horton Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact D.R. Horton Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces impacting the homebuilder. You'll gain immediate access to this professionally formatted document, allowing you to understand the industry's landscape without any surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. homebuilding landscape is characterized by a robust competitive environment. While D.R. Horton stands as the largest builder by volume, it operates alongside a multitude of national and regional competitors, creating a dynamic market.
In 2024, the top ten homebuilders in the United States collectively accounted for a significant 44.7% of all new single-family home closings. D.R. Horton alone secured a substantial 13.6% of this market share. This data highlights a growing concentration among the leading entities, yet it also underscores the persistent presence of numerous other builders vying for market position.
The pace at which the home construction market grows significantly influences how fiercely companies compete. When growth is sluggish, like the modest projections for single-family housing in 2025, builders often find themselves fighting harder for each sale. This can lead to more aggressive pricing and marketing efforts.
In 2024, the industry experienced a mixed growth environment, with some segments showing resilience while others faced headwinds. For 2025, analysts are forecasting a more measured expansion for single-family homes. This scenario naturally amplifies competitive rivalry as companies like D.R. Horton must work harder to capture market share in a less dynamic demand environment.
While D.R. Horton boasts a broad range of home types, from starter homes to active adult communities, the actual product differentiation in the single-family housing market can be quite subtle. Many builders, including D.R. Horton, find themselves competing more on factors like price, available incentives, prime locations, and specific, often standard, features rather than truly unique product offerings.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the homebuilding industry, like the considerable capital tied up in land inventory and construction equipment, can trap even struggling companies in the market. This persistence by unprofitable builders intensifies competition for everyone. D.R. Horton, with its vast asset base and extensive land holdings, exemplifies these significant exit barriers.
For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, D.R. Horton reported total assets of approximately $37.5 billion, a substantial portion of which is allocated to land and inventory. This massive investment makes it economically challenging for them, or any similarly situated builder, to simply walk away from operations, even during downturns.
- High Capital Investment: D.R. Horton's significant investment in land inventory and construction equipment creates substantial financial commitments.
- Asset Specificity: These assets are highly specialized for home construction, limiting their resale value or alternative uses.
- Market Saturation: The presence of builders unable to exit due to these barriers can lead to oversupply and depressed pricing, especially in certain regional markets.
Strategic Commitments and Incentives
D.R. Horton, like its major competitors, has been actively employing substantial incentives, such as mortgage rate buydowns, to sustain sales momentum in a demanding market environment. This aggressive use of incentives highlights the fierce competition and the resulting pressure on profit margins within the homebuilding sector.
The need for such incentives underscores the intense rivalry among leading builders. For instance, during the first quarter of 2024, many builders reported increased use of these sales tools to attract buyers. This strategy, while boosting volume, directly impacts the profitability of each sale.
- Aggressive Incentive Spending: Homebuilders are offering significant concessions, including interest rate buy-downs, to stimulate demand.
- Margin Pressure: The cost of these incentives directly reduces the profit margin on each home sold.
- Market Share Defense: These strategies are often employed to protect or gain market share in a competitive landscape.
- Impact on Profitability: While sales volume may be maintained, the reduced margin per unit can negatively affect overall earnings.
The competitive rivalry in the U.S. homebuilding sector is intense, with D.R. Horton, the largest builder by volume, facing numerous national and regional players. In 2024, the top ten builders captured 44.7% of single-family home closings, with D.R. Horton holding 13.6% of that share, indicating both concentration and persistent competition from many others. This rivalry is amplified in slower growth markets, such as the projected modest expansion for single-family housing in 2025, forcing companies to compete more aggressively on price and incentives.
| Builder | 2024 Market Share (Single-Family Closings) | 2024 Total Revenue (Billions USD) |
|---|---|---|
| D.R. Horton | 13.6% | 32.0 |
| PulteGroup | 7.1% | 16.0 |
| Lennar | 6.9% | 25.0 |
| NVR | 5.0% | 10.0 |
| Taylor Morrison | 3.5% | 7.5 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for D.R. Horton's new single-family homes is the existing home market. Many buyers, especially first-time purchasers, consider pre-owned properties as a viable alternative. In 2023, existing home sales in the U.S. reached approximately 4.1 million units, according to the National Association of Realtors.
However, factors like elevated interest rates and the homeowner 'lock-in effect' can influence the availability of existing homes. When current homeowners have secured mortgages at much lower rates, they become less inclined to sell, thereby reducing the supply of resale properties and potentially increasing demand for new construction.
Multi-family housing, such as apartments and condos, presents a significant substitute threat to D.R. Horton's single-family home business, particularly for individuals prioritizing urban accessibility or seeking more budget-friendly living arrangements.
The emerging build-to-rent sector also offers an alternative, although D.R. Horton experienced a decrease in single-family build-to-rent completions in 2024. This trend suggests potential shifts in how consumers access housing, moving beyond traditional ownership models.
Manufactured homes present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional housing. These homes offer a much lower price point, with the median price for a new manufactured home in 2024 around $130,000, compared to the median price of a new site-built home exceeding $400,000. This affordability makes them an attractive alternative for budget-conscious buyers, especially in regions with high housing costs.
The speed of construction also contributes to their substitutability. Manufactured homes can be produced in factories and assembled on-site in a matter of weeks, drastically reducing the timeline compared to the months often required for traditional home building. This efficiency appeals to buyers seeking quicker occupancy, further intensifying the substitute threat, particularly in fast-growing or transient markets.
Home Renovations and Additions
For existing homeowners, the option to renovate or add onto their current property presents a significant substitute to buying a new home. This is particularly relevant given the substantial homeowner equity accumulated, with many homeowners having significant capital tied up in their existing homes. This equity can be leveraged for substantial renovations, making it a financially attractive alternative to the costs and complexities of a new home purchase.
Deferred remodeling demand, exacerbated by supply chain issues and labor shortages in previous years, is now being addressed by many homeowners. This pent-up demand, combined with the desire to customize and improve living spaces, fuels the renovation market. For instance, the U.S. Census Bureau reported that in 2023, spending on residential improvements and repairs reached an estimated $485 billion, demonstrating a strong preference for enhancing existing homes.
- Renovation as an Alternative: Homeowners can upgrade kitchens, bathrooms, or add extensions, effectively creating a "new" home without the transaction costs of a sale and purchase.
- Leveraging Home Equity: Record-high homeowner equity provides the financial means for significant renovation projects, making it a viable substitute for buying a new property.
- Deferred Demand Release: A backlog of desired home improvements, delayed by past economic conditions, is now being fulfilled, diverting spending away from new home purchases.
- Market Data Support: The substantial figures in residential improvement spending underscore the strength of renovations as a substitute for new home acquisition.
Economic Conditions and Affordability
Broad economic conditions, such as rising interest rates and inflation, directly impact the affordability of new homes, potentially pushing buyers toward substitute housing options. For instance, in early 2024, mortgage rates hovered around 6.5% to 7%, a significant increase from previous years, making new construction less accessible for many.
When economic conditions tighten, consumers may consider alternatives like renting, purchasing existing homes, or even delaying homeownership altogether. This shift in buyer behavior directly affects the threat of substitutes for homebuilders like D.R. Horton.
- Interest Rate Impact: Higher mortgage rates in 2024 increased monthly payments, making new homes less affordable compared to rentals or older, less expensive properties.
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising inflation in 2023 and early 2024 increased the cost of building materials and labor, which can translate to higher home prices, further incentivizing substitutes.
- Consumer Confidence: Fluctuations in consumer confidence, often tied to economic outlook, can lead potential buyers to postpone large purchases like a new home, opting for more flexible rental arrangements.
- Affordability Constraints: When affordability is a major concern, buyers actively seek out lower-cost housing solutions, including fixer-uppers, smaller homes, or even multi-generational living arrangements, all of which serve as substitutes for new builds.
The threat of substitutes for D.R. Horton's new homes is substantial, encompassing existing homes, multi-family rentals, manufactured housing, and even home renovations. Buyers often weigh the cost, location, and lifestyle offered by these alternatives against new construction. In 2023, existing home sales were around 4.1 million units, highlighting a significant market segment that directly competes with new builds.
The affordability of manufactured homes, with a median price around $130,000 in 2024, presents a strong substitute for those priced out of traditional new homes, which often exceed $400,000. Furthermore, homeowners leveraging significant equity for renovations, a market that saw an estimated $485 billion in spending in 2023, are effectively upgrading their existing properties rather than purchasing new ones.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on D.R. Horton |
|---|---|---|---|
| Existing Homes | Resale market, potentially lower price points | 4.1 million units sold (2023) | Direct competition, influenced by homeowner lock-in effect |
| Multi-Family Housing | Apartments, condos; urban accessibility, lower cost | N/A (Sector-specific data varies) | Appeals to renters and those seeking urban living |
| Manufactured Homes | Affordability, rapid construction | Median price ~$130,000 (2024) | Strong alternative for budget-conscious buyers |
| Home Renovations | Upgrading existing properties, leveraging equity | ~$485 billion spent on improvements (2023) | Reduces demand for new homes by enhancing current residences |
Entrants Threaten
The sheer amount of money needed to even start in homebuilding acts as a significant hurdle. Companies need vast sums for buying land, covering construction costs, and setting up all the necessary operational bits. D.R. Horton’s considerable land holdings and strong financial backing clearly demonstrate how this capital requirement deters newcomers.
Established homebuilders like D.R. Horton leverage substantial economies of scale, particularly in bulk purchasing of lumber, drywall, and labor, which significantly lowers their per-unit costs. For instance, in 2023, D.R. Horton reported revenues of $32.1 billion, indicating the sheer volume of their operations and the associated purchasing power.
New entrants face a steep uphill battle to achieve comparable cost efficiencies. Without the established network and massive order volumes of a company like D.R. Horton, smaller builders would likely pay higher prices for materials and struggle to secure favorable labor rates, creating an immediate competitive disadvantage.
New companies entering the homebuilding market often struggle to secure prime land parcels, a critical component for development. They also find it difficult to build the necessary infrastructure for efficient supply chains and robust sales networks, which are essential for competing with established players.
D.R. Horton, for instance, has a significant advantage due to its integrated business model. This includes its own lot development capabilities, which streamline the process from land acquisition to finished homes, giving them better control over costs and timelines compared to rivals who might rely more on external lot developers.
In 2024, the housing market continued to see high demand for buildable lots, making access to these resources a significant barrier to entry. D.R. Horton's substantial land inventory, strategically acquired over time, positions them favorably against nascent competitors who must navigate a more challenging land acquisition landscape.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation
Brand loyalty and reputation are significant barriers to entry in the homebuilding sector. It takes considerable time and a proven track record of quality and reliability to build trust with homebuyers. New companies struggle to replicate the established goodwill that market leaders possess.
D.R. Horton, a consistent leader in the U.S. homebuilding market for over twenty years, benefits immensely from its strong brand recognition. This established reputation means customers often choose D.R. Horton over less-known competitors, even when pricing is comparable. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, D.R. Horton reported revenues of $32.4 billion, underscoring its market dominance and the customer trust that drives these sales.
New entrants face the daunting task of building a comparable level of trust and brand equity. Without this, they often have to compete aggressively on price, which can erode profit margins. This makes it difficult for them to gain significant market share against a well-established player like D.R. Horton.
- Established Brand Equity: D.R. Horton's long-standing presence as the largest U.S. homebuilder provides a significant advantage.
- Customer Trust: Years of consistent delivery and service have cultivated strong customer loyalty.
- Barriers to Entry: New competitors must invest heavily in marketing and time to build a similar reputation.
- Market Share Impact: Brand loyalty directly translates to market share, making it challenging for new entrants to disrupt D.R. Horton's position.
Government Regulations and Permitting
The homebuilding sector faces a significant barrier to entry due to extensive government regulations. Navigating complex zoning laws, environmental impact studies, and lengthy permitting processes requires specialized knowledge and substantial time investment, often proving prohibitive for new companies. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain building permits in major U.S. metropolitan areas continued to be a significant factor, with some regions experiencing delays of several months, impacting project timelines and initial capital outlay for aspiring builders.
These regulatory hurdles translate into considerable upfront costs and operational complexities. New entrants must invest in legal counsel, consultants, and dedicated staff to ensure compliance with federal, state, and local building codes, land-use restrictions, and safety standards. This can divert crucial resources away from core business functions like land acquisition and construction, especially in a market where D.R. Horton, as a leading builder, has established streamlined processes and relationships with regulatory bodies.
- Regulatory Complexity: Homebuilding is subject to a dense web of federal, state, and local regulations, including zoning, environmental, and building codes.
- Permitting Delays: Obtaining necessary permits can be a lengthy and unpredictable process, impacting project timelines and cash flow for new entrants.
- Compliance Costs: New companies must invest in expertise and resources to ensure adherence to these regulations, increasing initial overhead.
- Established Players' Advantage: Incumbents like D.R. Horton have developed expertise and relationships that mitigate these regulatory burdens, creating a competitive advantage.
The homebuilding industry presents a formidable barrier to entry for new companies due to the immense capital required. Securing land, managing construction expenses, and establishing operational infrastructure demand substantial financial resources, which often deter nascent competitors. D.R. Horton's robust financial standing and extensive land portfolio underscore this significant hurdle.
Economies of scale also play a crucial role, with established builders like D.R. Horton benefiting from bulk purchasing power for materials and labor, leading to lower per-unit costs. In 2023, D.R. Horton's revenue of $32.1 billion illustrates the scale of their operations and their significant purchasing leverage, making it difficult for smaller entrants to compete on cost.
Access to prime land and the development of efficient supply chains and sales networks are critical challenges for new entrants. D.R. Horton's integrated business model, including lot development, provides greater control over costs and timelines, a distinct advantage over less established firms. In 2024, the continued high demand for buildable lots further amplified this barrier, with D.R. Horton's strategic land acquisition positioning them favorably.
Brand reputation and customer trust are vital, requiring years of consistent quality and service to build. D.R. Horton, a consistent market leader for over two decades, benefits from strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share without significant investment in marketing and time.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | D.R. Horton's Advantage | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for land, construction, and operations. | Significant financial hurdle, potentially prohibitive. | Strong financial backing and extensive land holdings. | D.R. Horton's 2023 revenue: $32.1 billion. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs through bulk purchasing and operational efficiency. | Inability to match cost efficiencies of established players. | Massive purchasing power and optimized supply chains. | D.R. Horton's market leadership for over 20 years. |
| Land Access & Infrastructure | Difficulty securing prime lots and building robust networks. | Challenges in establishing efficient operations and distribution. | Integrated business model including lot development. | High demand for buildable lots in 2024. |
| Brand Equity & Trust | Building customer loyalty and reputation takes time and consistent performance. | Struggle to attract customers without established goodwill. | Long-standing reputation and proven track record. | D.R. Horton's consistent market leadership. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our D.R. Horton Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from D.R. Horton's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry reports from sources like IBISWorld and housing market data from the National Association of Home Builders.
