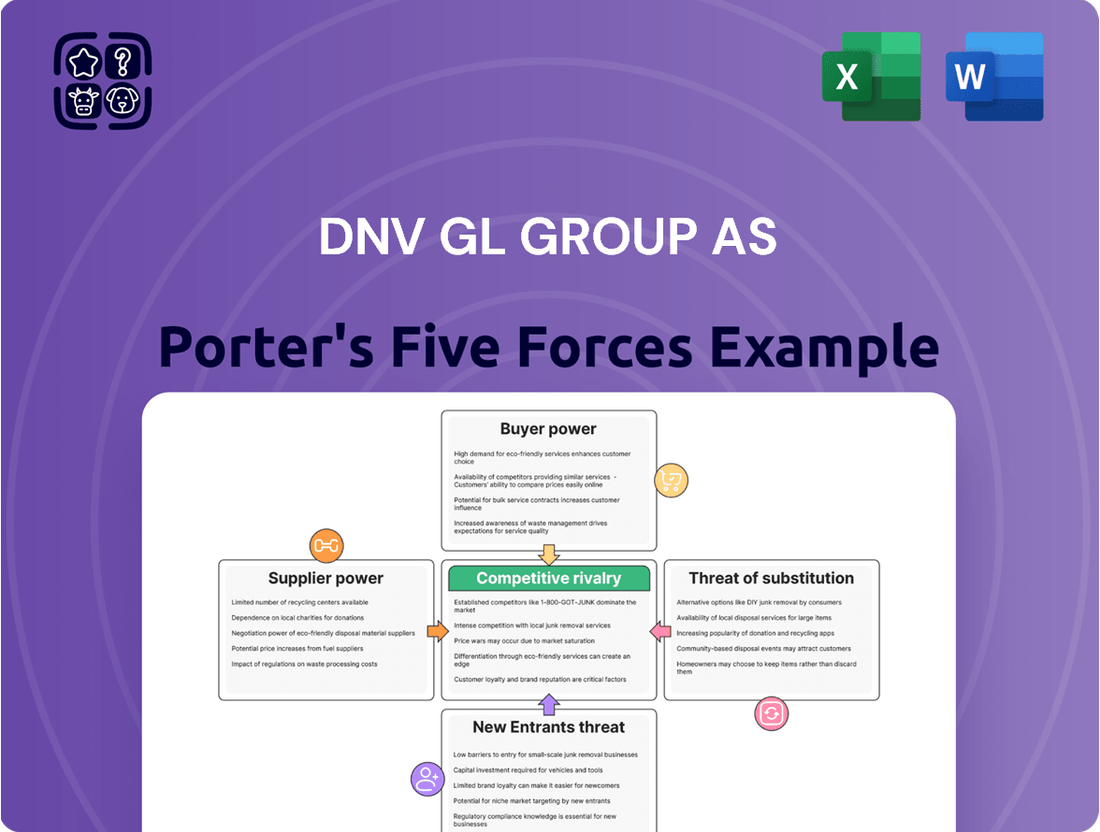
DNV GL Group AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DNV GL Group AS Bundle
DNV GL Group AS operates in a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the looming threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping DNV GL Group AS’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
DNV GL Group AS relies heavily on a workforce possessing highly specialized expertise. This includes engineers, scientists, and seasoned industry professionals crucial for their classification, assurance, and advisory services. The availability of these niche skills directly impacts DNV GL's operational capabilities.
The scarcity of such specialized talent, especially in rapidly evolving fields like cybersecurity for operational technology or the development of advanced maritime fuels, significantly bolsters the bargaining power of these human capital suppliers. For instance, the demand for cybersecurity experts in the maritime sector outstrips supply, allowing these professionals to command higher compensation and better terms.
Suppliers offering proprietary software or advanced testing equipment crucial for DNV GL's operations can wield considerable influence. For instance, if a software vendor holds a patent on a critical simulation tool, DNV GL’s ability to switch to an alternative is severely limited, increasing supplier power.
The high switching costs associated with integrating new, specialized technologies into DNV GL's established workflows further solidify the bargaining power of these key technology providers. This reliance on unique, difficult-to-replicate solutions means suppliers can command premium pricing or favorable terms.
Data and Information Providers can hold significant sway over DNV GL, especially as the company relies heavily on specialized datasets for its advisory and risk management functions. In 2024, the demand for granular market intelligence and industry benchmarks continued to surge, making providers of unique or comprehensive data particularly influential. These suppliers can leverage their position through licensing terms and by controlling access to proprietary information, directly impacting DNV GL's operational capabilities.
Limited Number of Accredited Subcontractors
The DNV GL Group AS faces potential supplier bargaining power stemming from a limited number of accredited subcontractors for specialized services. In highly regulated sectors like maritime classification or energy project certification, DNV GL may depend on a select group of subcontractors holding specific accreditations or enjoying regional exclusivity.
This scarcity can empower these subcontractors, allowing them to command higher prices or dictate terms, thereby impacting DNV GL's operational costs and flexibility. For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized drone inspection services for offshore wind turbines, requiring specific certifications, saw a notable increase in subcontractor rates by an estimated 10-15% due to the limited availability of qualified providers.
- Limited Pool of Specialized Subcontractors: Reliance on a small number of accredited entities for critical services.
- Accreditation and Regional Monopolies: Subcontractors with unique certifications or exclusive regional presence gain leverage.
- Impact on DNV GL: Increased operational costs and reduced flexibility due to supplier power.
- Market Trends (2024): Rising demand for specialized services like drone inspections leading to higher subcontractor fees.
Regulatory and Standard-Setting Bodies
Regulatory and standard-setting bodies, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, wield significant influence over DNV GL's operations by providing the foundational frameworks for its services. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) sets global standards for shipping, impacting DNV GL's classification and certification activities. In 2023, the IMO continued its work on decarbonization, with member states discussing further emissions reduction targets, directly influencing DNV GL's advisory services.
The introduction of new or revised regulations, such as those concerning the use of artificial intelligence in maritime or energy sectors, can compel DNV GL to invest heavily in new expertise and service development. This capacity to mandate changes effectively grants these bodies indirect bargaining power, as DNV GL must adapt to remain compliant and competitive. For example, the European Union's ongoing development of AI regulations in 2024 will likely create new compliance requirements for businesses DNV GL serves.
- IMO's 2023 GHG Strategy: Updated targets for greenhouse gas reduction in shipping directly shape DNV GL's decarbonization consulting services.
- EU AI Act Progress: Advancements in AI regulation during 2024 will necessitate DNV GL's adaptation in its assurance and advisory offerings for AI systems.
- Industry Standards Evolution: The continuous evolution of standards in sectors like renewable energy requires DNV GL to maintain cutting-edge knowledge and service offerings.
DNV GL Group AS faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly those providing highly specialized human capital and proprietary technology. The scarcity of niche expertise, such as maritime cybersecurity professionals, allows these individuals to negotiate favorable terms, as seen in 2024 with increased compensation demands. Similarly, vendors of critical, patented simulation software or advanced testing equipment hold significant leverage due to the high switching costs involved in integrating new solutions into DNV GL's established workflows.
Furthermore, data and information providers wield influence, especially concerning granular market intelligence and industry benchmarks, which saw increased demand in 2024. Limited pools of accredited subcontractors for specialized services, like drone inspections for offshore wind turbines, also exert power. In 2024, these specialized subcontractors saw rate increases of an estimated 10-15% due to high demand and limited availability, impacting DNV GL's operational costs and flexibility.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on DNV GL | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Human Capital | Scarcity of niche skills (e.g., maritime cybersecurity) | Higher labor costs, negotiation leverage for talent | Increased compensation demands for cybersecurity experts |
| Proprietary Technology Providers | Patented/unique software, high switching costs | Premium pricing, limited alternative options | Continued reliance on specialized simulation tools |
| Data & Information Providers | Unique/comprehensive datasets, industry benchmarks | Control over access, licensing terms impact operations | Surging demand for granular market intelligence |
| Accredited Subcontractors | Limited number, specific accreditations, regional exclusivity | Increased operational costs, reduced flexibility | 10-15% rate increase for specialized drone inspections |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for DNV GL Group AS dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within its diverse service markets, focusing on the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, substitutes, and rivalry.
Quickly identify and mitigate threats with a visual breakdown of competitive intensity—ideal for proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
DNV GL's customer base is concentrated within major industries like maritime, oil & gas, energy, and healthcare. This means many of its clients are substantial organizations, such as leading shipping lines or national energy providers, which represent significant business volume.
When these large customers are also consolidated, their collective purchasing power intensifies. For example, a merger of several major shipping companies would create an even larger entity with greater leverage to negotiate pricing and service agreements with DNV GL.
This considerable leverage allows these significant clients to demand favorable terms, impacting DNV GL's pricing power and profitability. The strategic importance of their business to DNV GL further bolsters their bargaining position.
While customers might face substantial switching costs once deeply integrated with DNV GL's classification or software systems, the initial decision to select a provider still presents a significant opportunity for bargaining. For instance, in 2024, the maritime industry saw ongoing investments in digital transformation, making the upfront selection of classification and management software a critical, high-stakes decision for shipowners.
Long-term contracts and the embedded nature of DNV GL's services, such as ship classification or management system certification, can effectively diminish customer power once an agreement is in place. However, the negotiation phase before commitment remains a period where customers can exert considerable influence on pricing and service terms.
In industries like maritime and oil & gas, where prices are closely tied to global commodity markets and economic cycles, customers often have considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the volatility in oil prices directly impacted the demand for offshore services, giving clients more room to negotiate on pricing for essential certifications and surveys.
When services are perceived as largely standardized, such as routine safety inspections or basic classification work, customers are more likely to shop around for the best deal. This price sensitivity can force DNV GL to offer more competitive rates, especially when clients can easily switch to another provider for similar, undifferentiated offerings.
Customer Demand for Integrated and Digital Solutions
Customers are increasingly seeking integrated solutions that blend physical and digital services, especially in areas like decarbonization and cybersecurity. This trend empowers them, as they can leverage their demand for these complex offerings to negotiate for more tailored and potentially cost-effective packages from providers like DNV GL. For instance, a large shipping company looking for comprehensive emissions monitoring and compliance software might have significant leverage to ask for specific features or pricing structures.
DNV GL's ability to provide these advanced, digital-first solutions is a key differentiator, but it also means that sophisticated clients can exert considerable bargaining power. They understand the value of these integrated platforms and can shop around for the best combination of features, service, and price. This is particularly true as digital transformation accelerates across industries, making integrated solutions a necessity rather than a luxury.
- Customer Demand for Integrated Solutions: Clients are actively seeking bundled services that address complex challenges, driving demand for digital platforms and comprehensive support.
- Digitalization and Decarbonization Focus: The growing emphasis on digital transformation and environmental sustainability fuels customer requirements for advanced, integrated solutions in these critical areas.
- Leverage for Tailored Packages: Customers with specific, advanced needs can use their demand for integrated and digital offerings to negotiate for customized and potentially more economical service packages.
- DNV GL's Role as a Differentiator: The group's capacity to deliver cutting-edge, integrated solutions positions it favorably, but also highlights the potential for strong customer negotiation in this specialized market.
Access to Multiple Reputable Providers
Customers of DNV GL Group AS benefit from a competitive landscape where multiple reputable global assurance and risk management providers exist. Companies like Bureau Veritas, SGS, and Lloyd's Register offer comparable services, giving clients significant leverage.
This availability of strong alternatives empowers customers to compare pricing, service quality, and expertise across different providers. For instance, in 2024, the global market for business assurance services, which includes many of DNV GL's offerings, was valued at over $60 billion, indicating a substantial number of players competing for market share.
- Increased Customer Choice: The presence of major competitors like Bureau Veritas, SGS, and Lloyd's Register provides customers with a wide array of options, preventing any single provider from dominating.
- Price Sensitivity: With readily available alternatives, customers can more easily negotiate pricing and seek the best value, putting pressure on DNV GL to remain competitive.
- Service Quality Benchmarking: Clients can benchmark DNV GL's performance against its peers, demanding high standards and potentially switching if service levels are not met.
- Flexibility in Provider Selection: Customers are not locked into a single provider, allowing them to switch based on evolving needs, project requirements, or dissatisfaction with current terms.
DNV GL's customers, particularly large corporations in sectors like maritime and energy, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial business volume and the availability of credible alternatives. This leverage is amplified when customers seek integrated digital and decarbonization solutions, allowing them to negotiate tailored packages. For example, in 2024, the maritime industry's focus on sustainability drove demand for advanced compliance software, giving major shipping lines more influence in pricing and feature discussions.
| Factor | Impact on DNV GL | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration & Volume | High reliance on key clients | Clients can demand better terms due to significant business contribution |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increased competition | Customers can switch providers, forcing DNV GL to be competitive on price and service |
| Switching Costs | Can reduce power post-contract | Initial selection phase offers significant bargaining opportunity |
| Demand for Integrated Solutions | Opportunity for differentiation | Customers can negotiate for customized, cost-effective bundled services |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
DNV GL Group AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of DNV GL Group AS, detailing competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into DNV GL's strategic position within the maritime and energy industries.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The assurance and risk management sector features formidable global competitors like Bureau Veritas and SGS, which offer a broad spectrum of services mirroring DNV GL's core offerings. This creates a highly competitive landscape where market share is fiercely contested across DNV GL's key operational industries.
In 2024, the global assurance market, encompassing inspection, verification, and certification services, was valued at approximately $180 billion, with these established players holding significant portions. For instance, SGS reported revenues of CHF 6.6 billion (approximately $7.3 billion USD) for 2023, showcasing its substantial market presence and competitive heft.
Competitive rivalry within the maritime classification and assurance sector, including players like DNV GL, is increasingly defined by differentiation through specialized expertise and digital innovation. Companies are focusing on niche areas such as offshore wind energy and the burgeoning hydrogen sector, offering highly specialized knowledge and services that set them apart.
Significant investment in research and development is a key battleground, with companies pouring resources into creating new services, advanced software, and integrated digital platforms. DNV GL's Veracity platform, for example, exemplifies this trend by providing a digital ecosystem for data sharing and collaboration, aiming to enhance efficiency and offer unique value propositions to clients.
In 2024, the demand for specialized maritime expertise, particularly in decarbonization technologies and digital transformation, continued to surge. DNV GL reported a strong performance, with its maritime segment revenue growing, reflecting the market's recognition of its specialized digital offerings and deep industry knowledge. This focus on innovation and niche specialization allows companies to command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty in a competitive landscape.
For highly standardized services like ISO 9001 certifications, DNV GL Group AS faces intense price competition. This pressure compels the company to prioritize operational efficiency and cost control to maintain its market position. In 2024, the global market for management system certifications, a significant portion of DNV's business, continued to see aggressive pricing from numerous accredited certification bodies.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
The maritime and energy services industry, where DNV GL operates, has experienced significant merger and acquisition (M&A) activity. Companies are actively consolidating to broaden their service offerings, extend their global footprint, and acquire advanced technological expertise. This trend is particularly noticeable as firms aim to integrate digital solutions and sustainability services into their portfolios.
These strategic consolidations can lead to a more concentrated competitive landscape. For instance, the 2013 merger forming DNV GL itself, combining Det Norske Veritas and Germanischer Lloyd, created a larger, more comprehensive entity. More recently, in 2024, we've seen ongoing M&A in adjacent sectors, such as the acquisition of specialized maritime software firms by larger classification societies, aiming to bolster their digital service capabilities and gain a competitive edge.
- Industry Consolidation: M&A activity is a key driver of industry structure, leading to fewer, larger players.
- Service Portfolio Expansion: Companies acquire others to gain new services, such as advanced digital analytics or decarbonization consulting.
- Geographical Reach: Acquisitions allow companies to enter new markets or strengthen their presence in existing ones.
- Technological Advancement: M&A is crucial for acquiring cutting-edge technologies, especially in digitalization and sustainable solutions.
Focus on Sustainability and ESG Services
The drive for sustainability and ESG services intensifies competitive rivalry within the industry. Companies are vying to be the go-to providers for businesses seeking to enhance their environmental, social, and governance credentials and reporting. This competition is fueled by the growing demand for assurance and advisory services that help clients navigate complex sustainability transformations.
DNV GL, for instance, is actively expanding its ESG and sustainability offerings. In 2024, the company reported significant growth in its assurance and advisory services related to climate and sustainability, reflecting this market trend. This focus means that competitors are not just offering traditional services but are increasingly judged on their ability to deliver credible and impactful ESG solutions.
- Growing Demand: The global ESG reporting market is projected to reach over $2.5 billion by 2025, indicating a substantial opportunity and driving intense competition among service providers.
- Service Differentiation: Companies are differentiating themselves by offering specialized services, such as supply chain sustainability assessments and green finance advisory.
- Regulatory Push: Evolving regulations, like the EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), are compelling more companies to seek expert guidance, thereby intensifying the competitive landscape for ESG service providers.
- Reputation and Trust: Building a reputation for expertise and trustworthiness in ESG assurance is a key competitive advantage, as clients seek reliable partners for their sustainability journeys.
The competitive rivalry within DNV GL Group AS's operating sectors remains intense, driven by a mix of established global players and emerging specialists. Differentiation through digital innovation and specialized expertise, particularly in areas like maritime decarbonization and burgeoning energy sectors, is a key battleground. Companies are heavily investing in R&D, exemplified by DNV GL's Veracity platform, to offer unique digital ecosystems and data-driven solutions.
While highly standardized services like ISO certifications face significant price competition, leading to a focus on operational efficiency, the broader assurance and risk management market is shaped by consolidation and portfolio expansion. The increasing demand for sustainability and ESG services further intensifies rivalry, with companies differentiating themselves through specialized ESG solutions and building trust in this rapidly evolving domain.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx. USD) | Key Service Areas |
|---|---|---|
| SGS | $7.3 billion | Inspection, Verification, Certification, Testing |
| Bureau Veritas | $6.2 billion | Certification, Inspection, Testing, Auditing |
| Intertek | $3.9 billion | Testing, Inspection, Certification, Assurance |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large organizations within DNV GL's core sectors, such as maritime, oil & gas, and energy, may bolster their internal capabilities. For instance, a major shipping company could expand its in-house technical expertise to handle routine surveys and certifications, directly substituting some of DNV GL's traditional service offerings.
This trend is amplified as companies invest more in digital transformation and data analytics, enabling them to manage compliance and risk more autonomously. In 2024, many energy firms increased spending on internal HSE (Health, Safety, and Environment) departments, potentially reducing reliance on external assurance providers for certain functions.
While DNV GL is a significant force, clients seeking certification and verification services can turn to a variety of other accredited bodies. The presence of numerous reputable alternatives, even those focusing on niche markets or specific standards, directly challenges DNV GL's market position.
This availability of choice means clients aren't solely reliant on DNV GL, creating a tangible substitute threat. For instance, in 2024, the global market for third-party certification services, which includes bodies competing with DNV GL, was estimated to be worth billions of dollars, indicating a robust competitive landscape.
Emerging technologies like AI-driven analytics and advanced sensor systems pose a significant threat by potentially automating DNV GL's core inspection and assurance services. For instance, the increasing sophistication of drone technology for remote inspections could reduce the demand for traditional on-site personnel. The global market for industrial automation, including AI and IoT solutions, was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in 2024, indicating a substantial shift towards technologically driven alternatives.
Consulting Firms and Niche Advisory Services
DNV GL Group AS faces a threat from consulting firms and niche advisory services that can offer similar strategic risk management and advisory solutions. Generalist management consulting firms often have broader reach and can bundle services, while highly specialized niche consultancies can provide deep expertise in areas like energy transition or digital risk, potentially at a lower cost or with greater focus.
For instance, the global management consulting market was valued at approximately $300 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a competitive landscape where specialized firms can carve out significant market share. These specialized firms can offer agile and targeted solutions that might appeal to clients seeking very specific expertise.
- Specialized Expertise: Niche firms can offer deeper, more focused knowledge in areas critical to DNV GL's clients, such as renewable energy integration or advanced cybersecurity protocols.
- Cost Competitiveness: Smaller, specialized consultancies may operate with lower overheads, allowing them to offer more competitive pricing for specific project scopes.
- Agility and Focus: Boutique firms can often be more agile and responsive to rapidly evolving market needs within their specialized domains compared to larger, more diversified organizations.
Self-Regulation or Industry Associations
The threat of substitutes for DNV GL Group AS, particularly concerning self-regulation and industry associations, is a nuanced consideration. While DNV GL provides crucial third-party assurance, some sectors are increasingly developing their own robust standards and best practices. This internal governance can reduce the perceived need for external verification for certain services.
Industry associations are actively shaping standards, which can act as substitutes for traditional assurance services. For instance, in the maritime sector, organizations like the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS) set stringent rules and standards that member societies, including DNV GL, adhere to. The effectiveness and widespread adoption of these self-imposed rules can influence the demand for DNV GL's independent verification services.
The increasing sophistication of industry-led initiatives presents a potential substitute. For example, the growing focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting is seeing industry groups develop their own frameworks and guidelines. In 2024, many industries are investing heavily in internal ESG expertise and reporting mechanisms, which could lessen the reliance on external assurance providers for compliance with these evolving standards.
- Industry Associations as Standard Setters: Organizations like IACS set critical standards, influencing the need for external assurance.
- Self-Regulation in ESG: Industries are developing their own ESG reporting frameworks, potentially reducing reliance on third-party verification.
- Internal Expertise Growth: Companies are building internal capabilities for compliance and assurance, a direct substitute for external services.
- Focus on Best Practices: Proactive industry adoption of best practices can preempt the need for external validation in certain areas.
The threat of substitutes for DNV GL is significant, encompassing a range of alternatives that can fulfill similar client needs. These substitutes range from in-house capabilities developed by large corporations to specialized consulting firms and even industry self-regulation. The growing trend of digital transformation and investment in internal expertise by clients directly diminishes the need for some of DNV GL's traditional assurance and verification services.
Emerging technologies, such as AI and drone-based inspections, are also creating powerful substitutes by automating processes previously handled by DNV GL personnel. The global market for industrial automation, projected to reach hundreds of billions in 2024, underscores this technological shift. Furthermore, niche consulting firms can offer focused expertise, sometimes at a more competitive price point, challenging DNV GL's market share.
Industry associations, by setting their own standards and best practices, also act as a form of substitution, particularly in areas like ESG reporting where internal frameworks are increasingly being developed. This internal governance and the availability of numerous accredited third-party bodies mean clients have a broad choice, reducing their sole reliance on DNV GL.
| Substitute Type | Example | Impact on DNV GL | Market Trend (2024 Data/Projections) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Capabilities | Major shipping company expanding technical survey teams | Reduced demand for external certification | Increased corporate investment in HSE departments |
| Emerging Technologies | AI-driven analytics for risk assessment | Automation of core DNV GL services | Global industrial automation market projected in hundreds of billions |
| Specialized Consulting Firms | Boutique energy transition advisors | Competition on niche expertise and pricing | Global management consulting market valued at ~$300 billion |
| Industry Associations/Self-Regulation | Industry-developed ESG reporting frameworks | Potential decrease in need for third-party ESG assurance | Growing industry focus on internal ESG expertise |
Entrants Threaten
The maritime, oil & gas, energy, and healthcare sectors, where DNV GL Group AS operates, are characterized by stringent regulations and substantial capital needs. For instance, establishing a classification society or a major energy consultancy requires billions in investment for infrastructure, technology, and skilled personnel, presenting a formidable hurdle for newcomers.
Furthermore, the deep technical expertise and specialized industry knowledge essential for providing services like risk assessment, certification, and digital solutions are not easily acquired. New entrants would need to invest heavily in training and development to match the established capabilities of firms like DNV GL, making the threat of new entrants relatively low.
DNV GL Group AS benefits immensely from its established reputation and the trust it has cultivated over many years. This long-standing history, particularly within the maritime and energy sectors, translates into a significant barrier for any potential new entrants seeking to disrupt the market. Newcomers would face the daunting task of replicating DNV GL's hard-won credibility and the deep-seated client confidence it enjoys.
Building a reputation for independence, trustworthiness, and technical excellence, as DNV GL has, is not something that can be quickly achieved. It requires consistent delivery of high-quality services and unwavering integrity. For instance, DNV GL's extensive accreditations and certifications, crucial for operating in many of its core markets, represent substantial investments in time and resources that new companies would need to match, a process that typically takes years, if not decades.
New entrants venturing into the maritime, oil and gas, and renewable energy sectors, where DNV GL operates, would encounter significant regulatory hurdles and substantial compliance costs. For instance, in the maritime industry, classification societies like DNV GL must adhere to stringent International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations and flag state requirements, demanding extensive expertise and rigorous certification processes.
Economies of Scale and Scope
New entrants face substantial hurdles due to DNV GL's established economies of scale and scope. The sheer breadth of services offered across its global operations allows DNV GL to spread fixed costs over a larger output, resulting in lower per-unit costs. For instance, their extensive network of laboratories and testing facilities, built over years, represents a massive capital investment that a newcomer would find difficult and expensive to replicate.
Achieving comparable cost efficiencies and offering a similarly comprehensive portfolio of services, from maritime classification to digital solutions and energy advisory, would require immense upfront capital and considerable time for a new entrant. This comprehensive service offering also creates significant switching costs for existing clients who benefit from integrated solutions and established relationships.
Consider the digital transformation efforts in the maritime sector. DNV GL's investment in platforms like Veracity, which connects stakeholders in the maritime ecosystem, creates a network effect. New entrants would need to build a comparable digital infrastructure and attract a critical mass of users to compete effectively, a task that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. In 2024, DNV GL continued to invest heavily in digital solutions, aiming to enhance efficiency and data-driven decision-making for its clients.
- Global Reach and Integrated Services: DNV GL's worldwide presence and ability to offer a vast array of interconnected services create a significant barrier to entry.
- Capital Investment Requirements: Replicating DNV GL's extensive infrastructure, including advanced testing facilities and digital platforms, demands substantial financial resources.
- Cost Efficiencies: Established economies of scale allow DNV GL to operate at a lower cost per service unit than potential new competitors.
- Network Effects: Digital platforms like Veracity foster customer loyalty and create a competitive advantage through user engagement and data aggregation.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Data
DNV GL Group AS's significant intellectual property, encompassing proprietary methodologies, specialized software like Synergi Life, and a wealth of historical operational data, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. This deep reservoir of knowledge and unique data sets is exceptionally challenging and time-consuming for potential competitors to replicate, thereby solidifying DNV GL's competitive edge in the market.
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by DNV GL's substantial investment in research and development, which continuously expands its intellectual property portfolio. For instance, in 2023, DNV GL reported a strong focus on digital solutions and sustainability research, further enhancing its unique knowledge base. This ongoing innovation makes it increasingly difficult for newcomers to match the depth and breadth of DNV GL's expertise and data-driven insights.
- Proprietary Software: DNV GL's Synergi Life platform, used extensively for risk management and safety, represents a significant technological barrier.
- Extensive Data Archives: Decades of operational data across various industries provide DNV GL with unparalleled analytical capabilities.
- Methodological Expertise: Unique methodologies for risk assessment, certification, and assurance are deeply embedded and difficult to reverse-engineer.
- R&D Investment: Continued investment in innovation ensures that DNV GL's intellectual property remains cutting-edge and difficult for new entrants to match.
The threat of new entrants for DNV GL Group AS is generally low due to significant barriers like high capital requirements for infrastructure and technology, and the necessity of deep, specialized industry expertise that takes years to develop. For example, establishing a fully accredited maritime classification society requires immense investment in personnel, global offices, and regulatory compliance, a cost easily running into hundreds of millions of dollars. DNV GL's established reputation, built over decades of reliable service and integrity, further deters newcomers, as replicating this trust and client loyalty is a long and arduous process.
Economies of scale and scope also play a crucial role, allowing DNV GL to offer a broad range of services at competitive prices, a feat difficult for smaller, newer firms to match. Their significant investment in digital platforms, like Veracity, creates network effects and customer stickiness, demanding substantial technological and user-acquisition investment from potential entrants. In 2024, DNV GL continued its strategic investments in digital transformation and sustainable solutions, further solidifying its market position and increasing the barriers for new competitors.
| Barrier Type | Description | DNV GL Example | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment needed for infrastructure, technology, and skilled personnel. | Establishing global network of testing facilities and R&D centers. | Formidable financial hurdle; requires substantial funding. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Long-standing history of reliability and integrity builds strong client loyalty. | Decades of experience in maritime classification and energy advisory. | Difficult and time-consuming to replicate; clients prefer proven track records. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Ability to spread fixed costs over a larger output and offer diverse services. | Offering integrated solutions across maritime, energy, and digital sectors. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies and comprehensive service portfolios. |
| Intellectual Property & Data | Proprietary software, methodologies, and extensive historical data. | Synergi Life software for risk management; vast operational data archives. | Challenging and time-consuming for competitors to develop comparable assets. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our DNV GL Group AS Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, incorporating information from DNV GL's annual reports, investor presentations, and official press releases. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial databases to provide a comprehensive competitive landscape.
