Diebold Nixdorf Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Diebold Nixdorf Bundle
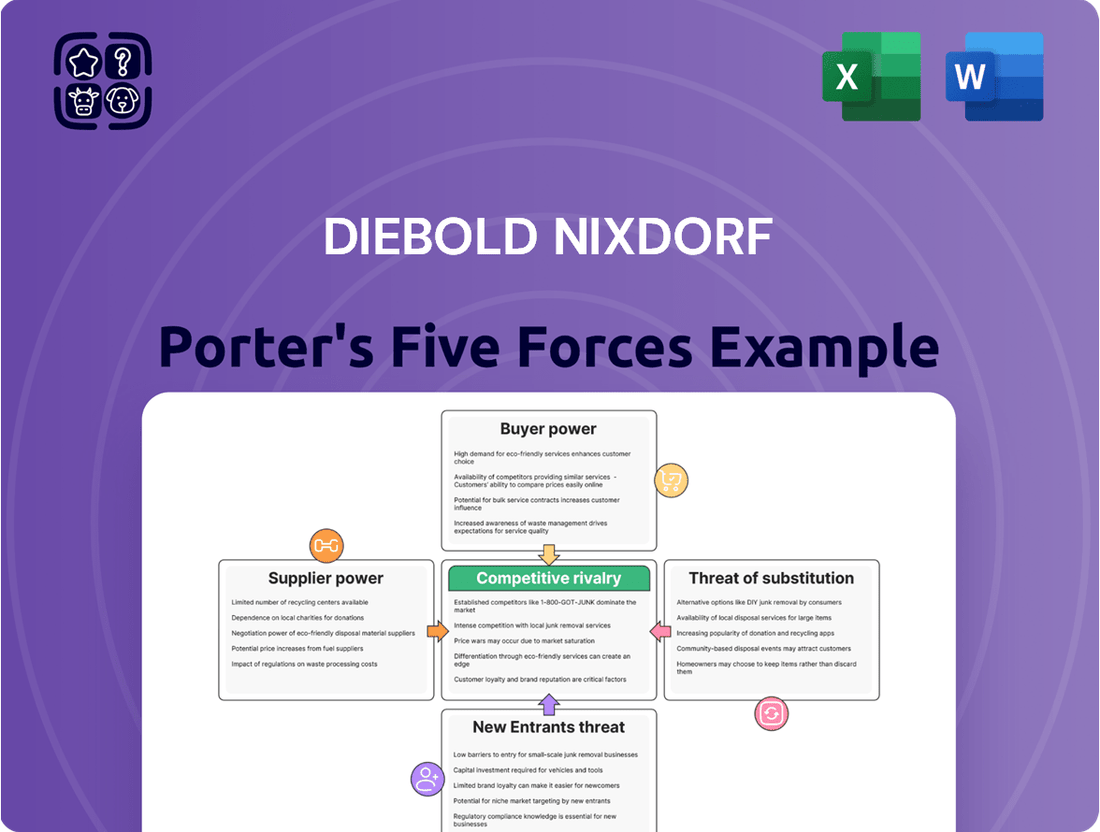
Understanding the competitive landscape for Diebold Nixdorf requires a deep dive into the forces shaping its market. From the bargaining power of its customers to the ever-present threat of new entrants, each factor plays a crucial role in its strategic positioning. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Diebold Nixdorf’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Diebold Nixdorf's reliance on specialized components for its ATMs and point-of-sale (POS) systems means that a limited number of suppliers for critical hardware or software can wield considerable power. This concentration allows these few suppliers to dictate pricing and terms, potentially increasing Diebold Nixdorf's input costs.
For instance, if a single supplier dominates the market for a unique microchip essential to Diebold Nixdorf's advanced ATM functionalities, that supplier holds significant leverage. This can directly impact Diebold Nixdorf's profit margins and operational efficiency, especially if supply chain disruptions occur. In 2024, the global semiconductor shortage, while easing, still highlighted the vulnerability of companies dependent on a narrow supplier base for advanced electronics.
Suppliers offering highly specialized or proprietary components, like advanced security modules or unique sensor technologies, possess significant bargaining power. Diebold Nixdorf's reliance on such inputs makes finding viable alternatives difficult, increasing its dependence and limiting negotiation leverage on pricing and innovation.
Diebold Nixdorf faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers, encompassing expenses related to product redesign, rigorous retesting for compatibility, and the complex process of re-certifying solutions. These substantial costs limit Diebold Nixdorf's ability to easily move between vendors.
The high switching costs effectively bolster the bargaining power of Diebold Nixdorf's existing suppliers. Suppliers are aware that the financial and operational burden for Diebold Nixdorf to transition to a new provider is considerable, giving them leverage in negotiations.
Threat of Supplier Forward Integration
The threat of supplier forward integration can significantly boost a supplier's bargaining power against Diebold Nixdorf. If suppliers possess the resources and motivation to start producing ATMs, POS terminals, or offering their own integrated services, they can directly compete. This potential forces Diebold Nixdorf to cultivate strong supplier relationships and negotiate favorable terms to avoid losing business to its own suppliers.
For instance, a key component manufacturer for Diebold Nixdorf could leverage its expertise to produce finished terminals. In 2024, the global market for self-service terminals, including ATMs and POS systems, continued to see innovation, with companies exploring integrated software and hardware solutions. This trend means suppliers who can offer end-to-end solutions rather than just components gain leverage.
- Increased Leverage: Suppliers capable of forward integration can dictate terms more effectively, as they can threaten to enter Diebold Nixdorf's market directly.
- Competitive Pressure: Diebold Nixdorf must offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain suppliers who might otherwise transition into direct competitors.
- Market Dynamics: The ongoing evolution of payment and self-service technologies, with a growing emphasis on integrated solutions, amplifies the risk of supplier forward integration in 2024 and beyond.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Product Cost/Quality
The significance of a supplier's contribution to Diebold Nixdorf's product cost and quality directly influences their bargaining power. When a supplier's component is critical for the performance, reliability, or security of Diebold Nixdorf's ATMs, that supplier gains considerable leverage. For example, if a unique, high-performance processing unit is essential for the advanced features of a new ATM model, its supplier can negotiate more favorable terms due to the component's indispensable nature.
This dependence means suppliers of specialized or proprietary components for Diebold Nixdorf's technology can exert greater influence. For instance, if Diebold Nixdorf relies on a single supplier for a patented security module that differentiates its ATMs, that supplier's input cost and quality control directly impact Diebold Nixdorf's competitive edge and profitability. In 2023, Diebold Nixdorf reported cost of goods sold was approximately $1.9 billion, highlighting the substantial impact of supplier inputs on their overall financial performance.
- Critical Components: Suppliers providing unique or essential parts for Diebold Nixdorf's ATMs, such as advanced biometric scanners or secure payment processors, possess higher bargaining power.
- Quality Impact: The degree to which a supplier's component affects the perceived quality, durability, and customer satisfaction of Diebold Nixdorf's end products amplifies the supplier's leverage.
- Cost Contribution: If a supplier's material or part represents a significant portion of the total manufacturing cost for Diebold Nixdorf, their ability to influence pricing increases.
- Technological Dependence: Diebold Nixdorf's reliance on specific technological innovations or intellectual property from a supplier strengthens that supplier's bargaining position.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Diebold Nixdorf is significant due to the specialized nature of components required for ATMs and POS systems. A limited supplier base for critical hardware or software allows these entities to dictate pricing and terms, potentially increasing Diebold Nixdorf's input costs and impacting profit margins.
Suppliers offering proprietary or highly specialized components, such as advanced security modules or unique sensor technologies, hold considerable leverage. Diebold Nixdorf's dependence on these inputs makes finding alternatives challenging, thus limiting its negotiation power and increasing reliance.
High switching costs for Diebold Nixdorf, encompassing redesign, retesting, and recertification, further bolster existing suppliers' bargaining power. This financial and operational burden discourages Diebold Nixdorf from easily transitioning between vendors, giving suppliers an advantage in negotiations.
The threat of supplier forward integration also amplifies their bargaining power. Suppliers with the capability to produce finished terminals or offer integrated services can directly compete with Diebold Nixdorf, compelling the company to offer favorable terms to retain these critical relationships.
| Factor | Impact on Diebold Nixdorf | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased pricing power for suppliers | A single supplier for a critical ATM microchip |
| Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility for Diebold Nixdorf | Expenses for redesign and recertification of new components |
| Forward Integration Threat | Leverage for suppliers to enter Diebold Nixdorf's market | Component manufacturers developing their own POS systems |
| Component Criticality | Higher influence for suppliers of essential parts | Suppliers of patented security modules for ATMs |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Diebold Nixdorf's competitive environment, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the financial technology and retail automation sectors.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments for Diebold Nixdorf.
Customers Bargaining Power
Diebold Nixdorf's customer base is notably concentrated, with a significant portion of the world's top 100 financial institutions and top 25 global retailers relying on its services. This concentration means that a few large clients represent a substantial portion of Diebold Nixdorf's revenue.
These major clients, due to their sheer size and purchasing volume, possess considerable bargaining power. They can effectively leverage their substantial orders to negotiate more favorable pricing, demand stringent service level agreements, and push for customized solutions, directly impacting Diebold Nixdorf's profitability and operational flexibility.
Customers hold significant bargaining power when switching costs are low. While implementing new systems for businesses like retail or banking can be disruptive, customers will weigh this against potential long-term benefits from alternative providers. If Diebold Nixdorf's offerings are not seen as uniquely valuable or if competitors like NCR Atleos provide easier migration options, customer leverage grows.
Financial institutions and retailers are indeed quite sensitive to price. This is largely because they are constantly looking for ways to cut costs and stay competitive in their own industries. For instance, in 2023, many retail businesses faced shrinking profit margins, leading them to scrutinize every expense, including the cost of point-of-sale systems and related services.
When certain hardware elements become more like commodities, or when pricing becomes more open and understandable, customers naturally start pushing for lower prices from companies like Diebold Nixdorf. This increased transparency means buyers can more easily compare offerings and negotiate better deals, directly impacting the supplier's pricing power.
Threat of Customer Backward Integration
The threat of customer backward integration, particularly for software and service components, can significantly influence Diebold Nixdorf's bargaining power. Large clients, such as major banks or retail conglomerates, possess the financial clout and technical expertise to potentially develop proprietary solutions in-house.
While the complete in-house development of complex hardware remains challenging, the capacity for clients to create their own software or service layers is a growing concern. For instance, many financial institutions are investing heavily in their digital banking platforms, which could reduce reliance on third-party providers for certain customer-facing technologies.
- Customer Integration Capability: Major financial institutions and large retail chains often have substantial IT budgets and skilled workforces, enabling them to explore in-house development of critical software and service components.
- Software and Service Focus: The threat is more pronounced in the software and service segments of Diebold Nixdorf's offerings, where customization and integration with existing client systems are key.
- Reduced Reliance: Successful backward integration by customers can lead to a reduced need for Diebold Nixdorf's specific software solutions or managed services, thereby diminishing customer dependence.
Availability of Substitute Products and Services
The availability of substitute products and services significantly impacts Diebold Nixdorf's customer bargaining power. Customers can easily shift their spending to alternative solutions or technologies, diminishing their dependence on traditional ATMs and point-of-sale (POS) systems. This trend is fueled by the rapid growth of digital banking, mobile payment platforms, and the expansion of e-commerce, all of which offer viable alternatives to Diebold Nixdorf's physical hardware. Consequently, customers' need for Diebold Nixdorf's specific offerings is reduced, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations.
For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at approximately $2.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This expansion means more consumers and businesses are adopting non-traditional payment methods, reducing the necessity for physical POS terminals. Similarly, the increasing adoption of contactless payment technologies and QR code systems further erodes the demand for traditional card-swiping machines. This shift directly strengthens the bargaining power of customers who can now demand more competitive pricing or integrated digital solutions from Diebold Nixdorf.
- Shift to Digital: The increasing preference for digital banking and mobile payments reduces reliance on physical ATM and POS hardware.
- E-commerce Growth: The rise of online transactions provides alternatives to in-person purchases requiring traditional POS systems.
- Technological Advancements: Contactless payments and QR code systems offer convenient substitutes for traditional card readers.
- Increased Negotiation Power: These alternatives empower customers to negotiate better terms or seek providers offering more integrated digital solutions.
Diebold Nixdorf's customers, particularly large financial institutions and retailers, wield significant bargaining power due to their concentrated purchasing volume and price sensitivity. The increasing availability of digital payment alternatives and the potential for customers to develop in-house software solutions further amplify this leverage, forcing Diebold Nixdorf to compete on price and integrated digital offerings.
| Factor | Impact on Diebold Nixdorf | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High revenue dependence on a few large clients | Clients can negotiate favorable terms due to volume |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers actively seek cost reductions | Pressure on Diebold Nixdorf's pricing and margins |
| Switching Costs | Moderate, but influenced by competitor ease-of-migration | Customers may switch if alternatives offer better value or simpler integration |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for clients to develop own software/services | Reduced reliance on Diebold Nixdorf's offerings, especially in software |
| Availability of Substitutes | Digital payments and e-commerce offer alternatives | Diminished need for traditional hardware, increasing customer negotiation power |
Full Version Awaits
Diebold Nixdorf Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Diebold Nixdorf Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. You are looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file. This comprehensive analysis will equip you with a thorough understanding of the market landscape, enabling informed strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking and retail technology market is highly competitive, featuring formidable global players like NCR Voyix, Glory, and Hitachi Channel Solutions. This intense rivalry means Diebold Nixdorf faces constant pressure to innovate and secure lucrative contracts, as each competitor actively seeks to expand its market share.
While the markets for next-generation ATMs and point-of-sale (POS) systems are experiencing growth, the traditional hardware segments for these devices are relatively mature. This maturity often translates into intensified rivalry as companies fight harder for existing market share rather than solely pursuing new opportunities. For instance, in 2024, Diebold Nixdorf, a key player, continues to navigate these mature markets while investing in its DN Series™ portfolio for future growth.
The slower growth in these established segments can naturally fuel more aggressive competition, often leading to price-based strategies and increased promotional activities. Companies may resort to discounts or special offers to attract and retain customers in a market where expansion is less pronounced. This dynamic puts pressure on profit margins and necessitates efficient operations.
While Diebold Nixdorf provides integrated solutions, the differentiation in its core ATM and POS hardware can be relatively low, as rivals like NCR Atleos offer similarly comprehensive ATM and managed services. This limited differentiation in hardware means that competition often shifts towards price, impacting profit margins.
To truly stand out and mitigate direct price wars, Diebold Nixdorf must focus on enhancing differentiation through advanced software capabilities, the integration of artificial intelligence into its offerings, and the development of truly unique service packages that go beyond standard support.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The competitive landscape for Diebold Nixdorf is intensified by substantial fixed costs. Significant investments are necessary for research and development, advanced manufacturing facilities, and maintaining a widespread global service infrastructure. These capital-intensive requirements mean that companies entering or operating within this sector face a high barrier to entry and, crucially, high exit barriers.
These substantial fixed costs and the specialized nature of assets within the industry make it difficult and costly for companies to divest or exit the market, even when facing financial challenges. This situation often results in companies continuing to operate and compete aggressively to utilize their existing capacity, even in less favorable market conditions. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense price competition and market share battles as firms strive to maintain profitability.
- High R&D and Capital Expenditures: Companies in this sector typically allocate a significant portion of their revenue to R&D, with reported figures often exceeding 10% for leading players. For example, in 2023, major competitors in the ATM and retail technology space continued to invest heavily in software development and hardware innovation.
- Extensive Global Service Networks: Maintaining a global presence for installation, maintenance, and support requires substantial investment in personnel, logistics, and infrastructure. This creates a cost disadvantage for smaller or newer entrants without an established network.
- Asset Specificity and Exit Costs: Specialized manufacturing equipment and the global nature of service operations mean that assets are not easily repurposed, leading to significant write-offs or losses upon exiting the market. This discourages premature exits, prolonging competitive pressures.
Strategic Stakes and Market Leadership
For companies like Diebold Nixdorf, maintaining a leading market position is paramount. This drive to lead means significant investment in new technologies, aggressive marketing campaigns, and competitive pricing to secure market share. The stakes are incredibly high, especially when bidding for lucrative contracts with major banks and large retail chains.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a constant battle for dominance, where firms are willing to expend considerable resources to either capture or defend their market standing. This intense rivalry is evident in the fierce competition for large-scale deals that can significantly shape a company's revenue and future growth trajectory.
- Strategic Importance of Market Share: Maintaining a significant market share is a key objective for industry leaders, influencing their investment decisions and competitive strategies.
- Investment in Innovation and Marketing: Companies allocate substantial funds to research and development, marketing, and sales efforts to stay ahead of competitors.
- Competition for Major Contracts: The pursuit of large contracts with top-tier financial institutions and retailers is a primary driver of intense rivalry within the sector.
- Impact on Financial Performance: Success in securing these major contracts directly translates to substantial revenue streams and enhanced market influence for the winning firms.
Diebold Nixdorf faces intense rivalry from global competitors like NCR Voyix and Glory, particularly in mature ATM and POS hardware markets where differentiation is often low. This leads to price-based competition and aggressive pursuit of market share, fueled by high fixed costs in R&D and global service networks, making market exit costly and prolonging competitive pressures.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Product Areas |
|---|---|---|
| NCR Voyix | ~7.0 | ATM, POS, Digital Banking Solutions |
| Glory | ~1.7 | Cash Handling, Payment Solutions |
| Hitachi Channel Solutions | N/A (Part of Hitachi) | Financial Kiosks, Self-Service Terminals |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of digital banking platforms and mobile applications significantly reduces the need for traditional ATM transactions and physical bank branch visits. Customers can perform a wide range of financial activities, such as fund transfers, bill payments, and account inquiries, directly from their smartphones, diminishing their reliance on Diebold Nixdorf's physical self-service systems.
By early 2024, over 80% of banking customers in developed markets were actively using mobile banking apps, a trend that continued to grow. This shift means fewer in-person interactions at ATMs and branches, directly impacting the demand for the hardware and related services Diebold Nixdorf provides.
The relentless expansion of e-commerce presents a significant threat of substitution for Diebold Nixdorf's traditional point-of-sale (POS) hardware and software. As more consumer transactions migrate online, the demand for in-store POS systems diminishes, directly impacting revenue streams that rely on physical retail environments.
In 2024, global e-commerce sales were projected to reach over $6.3 trillion, a substantial figure that highlights the growing preference for online shopping. This shift means fewer in-person purchases, thereby reducing the necessity for Diebold Nixdorf's core offerings in physical retail locations and favoring online payment solutions instead.
The rise of contactless and biometric payment solutions presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional point-of-sale (POS) hardware. Technologies like NFC-enabled mobile wallets and fingerprint scanners offer consumers faster, more secure, and often more convenient transaction methods, bypassing the need for physical card insertion or PIN entry at terminals. This shift diminishes the perceived necessity of older POS hardware.
By 2024, the global contactless payment market is projected to reach substantial figures, with mobile contactless payments alone expected to see significant growth. For instance, projections indicate that by the end of 2024, a large percentage of all card transactions will be contactless. This increasing adoption directly challenges the installed base of traditional POS systems, as consumers and merchants alike gravitate towards these newer, more integrated payment experiences.
Growth of Embedded Finance
The growth of embedded finance presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional financial transaction providers. As non-financial platforms increasingly offer integrated payment and lending solutions, the reliance on standalone financial infrastructure diminishes. For instance, a consumer buying a car through an automotive dealership's app might secure financing directly within that app, bypassing traditional banking channels and the need for separate point-of-sale systems.
This trend means that companies like Diebold Nixdorf, which historically provided hardware and software for financial transactions, face competition from technology companies embedding financial services into their existing ecosystems. The market for embedded finance is projected to reach substantial figures, with some estimates suggesting it could grow to trillions of dollars in transaction volume globally by the end of the decade.
- Embedded finance allows financial services to be integrated directly into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce sites or social media apps.
- This integration can reduce customer demand for traditional banking interfaces and payment terminals.
- The global market for embedded finance is experiencing rapid expansion, with significant growth projected in the coming years.
- This shift could lead to decreased reliance on specialized financial technology providers for transaction processing.
Shift towards Cashless Societies
The global move towards cashless societies presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional ATM providers like Diebold Nixdorf. As digital payment methods become more prevalent, the need for physical cash withdrawal decreases.
This trend is accelerating, with many countries actively promoting digital transactions. For instance, in 2024, the global digital payments market was valued at over $10.5 trillion, with projections indicating continued strong growth. This shift directly impacts the demand for ATMs, which are essentially a substitute for digital payment infrastructure.
Consider these points:
- Declining Cash Usage: Many consumers now prefer contactless payments, mobile wallets, and online transfers for everyday transactions, reducing their reliance on ATMs.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of peer-to-peer payment apps and integrated digital banking services offers convenient alternatives to cash.
- Government Initiatives: Several governments are encouraging or mandating digital payments to improve efficiency and reduce the costs associated with handling physical currency.
- Impact on ATM Footprint: As cash transactions diminish, financial institutions may reduce their ATM networks, impacting the market for new ATM hardware and maintenance services.
The increasing prevalence of digital and mobile payment solutions offers a strong substitute for Diebold Nixdorf's traditional self-service terminals. Consumers are increasingly comfortable managing their finances and conducting transactions via smartphone apps, reducing the need for physical interactions with ATMs or bank branches.
By early 2024, mobile banking adoption rates in major economies surpassed 80%, demonstrating a clear shift away from traditional banking channels. This trend directly diminishes the demand for Diebold Nixdorf's hardware and associated service contracts.
The rapid growth of e-commerce and online payment gateways poses a significant substitute threat to Diebold Nixdorf's in-store point-of-sale (POS) hardware. As more transactions move online, the need for physical retail transaction hardware declines.
Global e-commerce sales were projected to exceed $6.3 trillion in 2024, underscoring the substantial migration of consumer spending to online platforms. This shift directly reduces the market for Diebold Nixdorf's physical POS systems.
Emerging payment technologies like contactless cards, wearables, and biometric authentication provide faster and more convenient alternatives to traditional PIN-based transactions at POS terminals. These innovations reduce the necessity for consumers and merchants to rely on older POS hardware.
The contactless payment market is experiencing exponential growth, with projections indicating a significant portion of all card transactions will be contactless by the end of 2024. This adoption directly challenges the installed base of traditional POS systems.
Embedded finance, where financial services are integrated into non-financial platforms, acts as a substitute for traditional financial transaction infrastructure. This allows for seamless transactions within existing user experiences, bypassing dedicated financial hardware.
The embedded finance market is expected to grow substantially, with transaction volumes potentially reaching trillions of dollars globally by the end of the decade. This growth signifies a reduced reliance on standalone financial technology providers.
The global trend towards cashless societies directly substitutes the need for ATMs. As digital payment methods become dominant, the demand for cash withdrawals decreases significantly.
In 2024, the global digital payments market was valued at over $10.5 trillion, reflecting a strong preference for digital transactions. This trend directly impacts the demand for ATM hardware and services.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Diebold Nixdorf | 2024 Market Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Banking & Digital Wallets | Reduces demand for ATM transactions and physical branch services. | Over 80% mobile banking adoption in developed markets by early 2024. |
| E-commerce & Online Payments | Decreases need for in-store POS hardware. | Global e-commerce sales projected over $6.3 trillion in 2024. |
| Contactless & Biometric Payments | Lowers reliance on traditional card-swiping POS terminals. | Significant growth in contactless payment market; a large percentage of card transactions expected to be contactless by end of 2024. |
| Embedded Finance | Bypasses traditional financial transaction infrastructure. | Market projected to reach trillions in transaction volume globally. |
| Cashless Society Trend | Diminishes demand for ATMs. | Global digital payments market valued at over $10.5 trillion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the competitive landscape of financial and retail transaction systems, such as those offered by Diebold Nixdorf, necessitates a considerable outlay of capital. This includes significant investment in cutting-edge research and development to innovate new technologies, establishing robust manufacturing facilities capable of producing complex hardware, and creating a widespread global sales and support network. For instance, companies in this sector often spend hundreds of millions of dollars annually on R&D alone.
These substantial initial financial commitments serve as a formidable barrier to entry. Smaller firms or those with limited financial backing find it exceedingly difficult to match the scale and scope of established players like Diebold Nixdorf. Consequently, the high capital requirements effectively deter many potential new competitors from entering the market, thereby protecting the market share of existing, well-funded companies.
Diebold Nixdorf enjoys significant advantages due to its strong brand recognition and deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with major global financial institutions and retailers. Newcomers would find it extremely difficult to replicate this level of trust and access, which is crucial in a sector demanding reliability and integrated service offerings.
Diebold Nixdorf's substantial investment in research and development, spanning decades, has resulted in a robust portfolio of proprietary technologies and intellectual property. This includes patents for secure transaction processing, advanced self-service kiosk designs, and integrated software platforms that manage complex financial ecosystems. For instance, their focus on embedded security features in their ATM and retail solutions represents a significant technological moat.
This deep well of intellectual property acts as a formidable barrier to entry for potential new competitors. Developing comparable, innovative solutions from scratch requires considerable time, financial resources, and specialized expertise, making it challenging for newcomers to match Diebold Nixdorf's established technological capabilities. In 2023, Diebold Nixdorf reported R&D expenses of approximately $350 million, highlighting their ongoing commitment to innovation and IP creation.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The threat of new entrants in the ATM and retail technology sector, particularly for companies like Diebold Nixdorf, is significantly dampened by substantial regulatory and compliance hurdles. The financial and retail industries operate under a dense web of regulations concerning data security, transaction integrity, and customer privacy. For instance, compliance with standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is non-negotiable for any entity handling payment card information, a core function for many ATM and POS systems.
New players must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these complex, often country-specific, regulatory frameworks. This includes obtaining certifications for hardware and software, which can be a lengthy and costly undertaking. In 2024, the increasing focus on data protection, exemplified by regulations such as GDPR and its global counterparts, adds another layer of complexity, requiring robust data handling protocols and significant legal and technical expertise to implement and maintain.
The capital expenditure required to meet these stringent requirements, coupled with the need for specialized legal and compliance teams, acts as a significant barrier. This makes it challenging for smaller, less capitalized entrants to compete effectively against established players who have already built the necessary infrastructure and expertise.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating global financial and retail regulations, including data privacy laws like GDPR, presents a significant challenge for newcomers.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining essential certifications, such as PCI DSS for payment processing, requires substantial investment in time and resources.
- Security Standards: Meeting stringent industry standards for transaction security and data protection demands advanced technological capabilities and ongoing vigilance.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Effects
Established players like Diebold Nixdorf leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, Diebold Nixdorf's extensive global supply chain likely allowed for bulk purchasing discounts on components for their self-service terminals and retail solutions, a feat difficult for a new entrant to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, Diebold Nixdorf benefits from an experience curve advantage, having honed its operational processes and customer service over decades. This accumulated knowledge translates into greater efficiency and potentially higher quality, making it challenging for newcomers to match their established cost structures and service delivery standards without substantial upfront investment.
- Economies of Scale: Diebold Nixdorf's large-scale production lowers per-unit costs.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational refinement yield efficiency gains.
- Cost Disadvantage for Entrants: New companies struggle to match existing cost efficiencies.
- Barriers to Entry: These factors create a significant hurdle for new competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Diebold Nixdorf is considerably low due to the immense capital required for research, development, and establishing a global support network. For example, companies in this sector often invest hundreds of millions annually in R&D alone, a prohibitive cost for most potential newcomers. This high barrier effectively deters smaller or less-funded entities from entering the market, thereby safeguarding the positions of established players.
New entrants face significant challenges in replicating Diebold Nixdorf's established brand loyalty and deep customer relationships, especially with major financial institutions and retailers. The trust and access built over years are critical in this industry, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold. Furthermore, Diebold Nixdorf's extensive patent portfolio and proprietary technologies, developed through decades of R&D, create a substantial technological moat, requiring considerable time and investment for competitors to match.
Regulatory and compliance burdens represent another major hurdle. Navigating stringent data security, transaction integrity, and customer privacy laws, such as PCI DSS and GDPR, demands significant investment in expertise and certification. In 2024, the increasing complexity of data protection regulations further elevates these barriers, making it difficult for new firms to achieve compliance without substantial resources.
Diebold Nixdorf also benefits from economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, as well as an experience curve advantage. In 2024, their global supply chain likely facilitated bulk purchasing discounts, a cost advantage that new entrants cannot easily replicate. This operational efficiency and accumulated knowledge make it challenging for newcomers to compete on cost and service delivery standards.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024 Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, and sales networks. | Deters smaller, less-funded companies. | Annual R&D spending in the sector often exceeds $300 million. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established trust with major financial and retail clients. | Difficult for newcomers to gain market access and credibility. | Long-term contracts with global banks and retailers. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patents and proprietary technologies. | Requires significant investment to develop comparable solutions. | Patents covering secure transaction processing and kiosk design. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to data security and privacy laws (PCI DSS, GDPR). | Demands substantial legal, technical expertise, and certification costs. | Ongoing compliance costs for data protection regulations. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs and operational efficiencies. | New entrants face a cost disadvantage. | Bulk purchasing discounts on components for terminals. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Diebold Nixdorf Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Diebold Nixdorf's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and IDC. We also incorporate macroeconomic data and competitor financial disclosures to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
