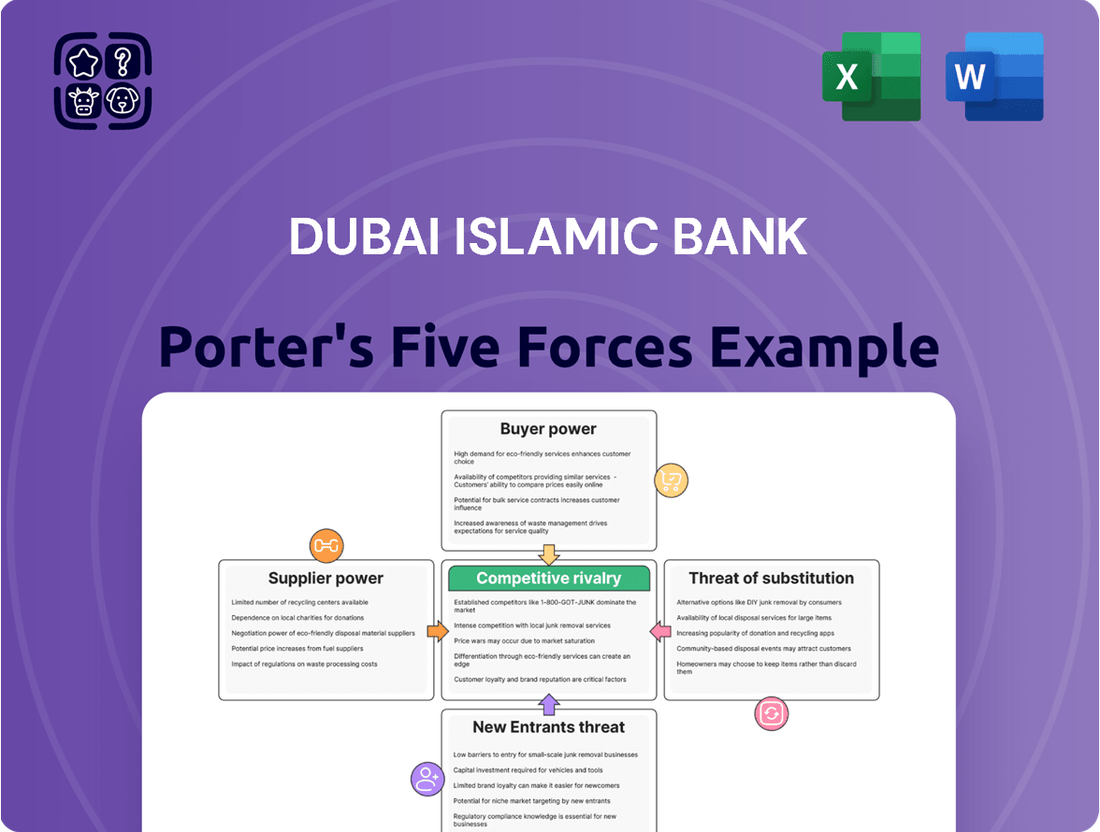
Dubai Islamic Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dubai Islamic Bank Bundle
Dubai Islamic Bank operates in a dynamic financial landscape where buyer power is significant due to readily available alternatives and a focus on competitive pricing. The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by regulatory hurdles and the capital-intensive nature of Islamic banking. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dubai Islamic Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) heavily depends on customer deposits, both from individuals and institutions, as its main funding source. The power these depositors hold is directly tied to how many other banking choices they have and the profit-sharing rates offered by competitors. For instance, in 2023, DIB saw its customer deposits grow significantly, reaching AED 274.5 billion, which shows strong trust from its customer base.
While this overall growth is positive, larger depositors, like institutional investors or government entities, can negotiate for better terms because of the substantial amounts they hold. This means DIB must remain competitive with its profit-sharing rates and services to attract and retain these crucial, high-volume depositors.
Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) relies heavily on technology for its digital banking services and robust cybersecurity. Specialized providers of banking software, IT infrastructure, and innovative fintech solutions, especially those adept at Sharia-compliant systems, hold potential leverage. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating the importance of these specialized suppliers.
However, DIB's ability to manage this supplier power is enhanced by the growing diversity of available tech solutions and its proactive investments in upgrading its technological infrastructure. This diversification reduces dependence on any single provider, thereby tempering their bargaining strength.
The availability of skilled professionals, particularly those with expertise in Islamic finance, Sharia compliance, and digital banking, is paramount for Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB). A scarcity of such specialized talent can significantly amplify their bargaining power, directly impacting recruitment and retention expenses. For instance, in 2023, the demand for fintech professionals in the UAE saw a substantial increase, driving up salary expectations.
DIB's commitment to cultivating its workforce is evident in its strategic investments, such as the DIB Academy. This initiative aims to develop and retain crucial human capital, proactively mitigating the potential for increased supplier power from specialized talent pools. By fostering internal expertise, DIB can better manage the costs associated with acquiring and keeping highly sought-after employees.
Regulatory Bodies (Central Bank of the UAE)
Regulatory bodies, such as the Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE), act as crucial suppliers of the operational framework and necessary licenses for banks like Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB). Their influence is immense, as they dictate critical parameters including capital adequacy, liquidity requirements, and risk management protocols. For instance, the CBUAE's ongoing focus on enhancing financial sector resilience, as seen in their prudential regulations updated throughout 2024, directly shapes DIB's strategic planning and compliance expenditures.
The CBUAE's power is further amplified by its ability to impose penalties for non-compliance, making adherence to their directives a top priority for DIB. New standards, such as those pertaining to the Sharia Compliance Function (SCF), introduce specific operational requirements and can increase the cost of doing business. In 2024, the CBUAE continued to emphasize robust governance and consumer protection, necessitating ongoing investment by DIB in compliance infrastructure and training.
- High Regulatory Authority: The CBUAE sets the rules for banking operations, including capital, liquidity, and risk management.
- Impact on Operations: Regulations directly influence DIB's business model and operational costs.
- Sharia Compliance: Specific standards like SCF add layers of complexity and cost for Islamic banks.
- Enforcement Power: The CBUAE can levy fines, reinforcing its significant bargaining power.
Sharia Scholars and Supervisory Boards
The Sharia Supervisory Board and the individual scholars advising Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) wield considerable influence due to the bank's foundational commitment to Sharia compliance. Their pronouncements are critical, shaping everything from new product creation to day-to-day operations, thereby validating the bank's adherence to Islamic financial principles.
This reliance on expert Sharia guidance grants these scholars significant bargaining power. Their interpretations directly impact DIB's ability to innovate and maintain its market position within the Islamic finance sector. For instance, in 2024, DIB continued to emphasize its Sharia-compliant product suite, which is a key differentiator in the competitive UAE banking landscape.
- Sharia Compliance as Core: DIB's business model is built upon adherence to Islamic law, making the guidance of Sharia scholars indispensable.
- Influence on Operations: Scholars' rulings dictate product development, investment strategies, and operational procedures, directly affecting the bank's offerings and legitimacy.
- Market Differentiation: The bank's commitment to Sharia principles, overseen by these scholars, is a significant factor in attracting its target customer base and maintaining a competitive edge in 2024.
Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) faces moderate bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly in specialized areas like technology and skilled human capital. While DIB's scale and diversified funding sources can mitigate some supplier leverage, the essential nature of certain inputs, especially Sharia-compliant technology and expert personnel, grants these suppliers a degree of influence. DIB's strategic investments in in-house capabilities and talent development aim to counter this by reducing reliance on external providers.
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Dubai Islamic Bank's operating environment, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Eliminate the guesswork of competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model for Dubai Islamic Bank, allowing for immediate identification of key threats and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
For fundamental banking services such as current and savings accounts, or straightforward loans, customers in the UAE, including those banking with Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB), generally encounter minimal costs and effort when switching between financial institutions. This ease of transition significantly amplifies customer leverage, allowing them to easily explore more favorable terms or superior services from rival banks if they perceive a lack of value. In 2023, the UAE banking sector saw a continued focus on digital onboarding and account opening, further reducing friction for customers looking to switch. For instance, many banks in the region offer fully digital account opening processes that can be completed in minutes, a trend that accelerated significantly post-2020 and continued through 2024, directly impacting switching costs.
Customers today have unprecedented access to information thanks to the internet and digital banking platforms. This means they can easily compare offerings from different banks, including profit rates and service fees, making it simpler than ever to find the best deal. For example, in 2024, a significant percentage of consumers actively used online comparison tools before making financial decisions, directly impacting how banks price their products.
While individual retail customers have limited sway, Dubai Islamic Bank's (DIB) bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by its large corporate and institutional clients. These entities, including government-backed organizations, often conduct substantial transaction volumes and require tailored financial solutions, granting them considerable negotiation leverage.
This concentration means these major clients can effectively negotiate for more favorable terms, customized product offerings, and reduced service fees, directly impacting DIB's revenue streams and profitability. For instance, if a large corporation shifts its substantial treasury operations or secures a significant financing deal elsewhere due to better terms, it represents a material loss for the bank.
Growth of Digital Banking Options
The proliferation of digital banking and fintech solutions significantly enhances customer bargaining power. These alternatives offer greater convenience and efficiency, allowing customers to easily switch between providers if dissatisfied with services or pricing. For instance, by mid-2024, the UAE's digital payments market was projected to reach over $20 billion, indicating a strong customer preference for digital channels.
This digital shift empowers customers, particularly the tech-savvy segment, to demand better services and more competitive rates. They are less tied to traditional branch networks and can readily explore options offering superior user experiences and lower fees. Dubai Islamic Bank's strategic investment in its digital infrastructure directly addresses this growing customer expectation for seamless online and mobile banking capabilities.
- Digital Adoption: In 2024, an estimated 85% of UAE banking customers were actively using digital channels for transactions.
- Fintech Growth: The UAE fintech sector saw a significant surge in new startups and funding rounds throughout 2023 and early 2024, offering diverse financial tools.
- Customer Expectations: Surveys in 2024 indicated that over 70% of UAE consumers prioritize ease of access and digital convenience when choosing a bank.
Sharia-Compliance Preference
For customers prioritizing Sharia-compliant financial services, Dubai Islamic Bank's (DIB) strong adherence to Islamic principles fosters a degree of loyalty. This preference can reduce the immediate inclination for these customers to switch to conventional banking alternatives. For instance, in 2023, Islamic banking assets globally continued their upward trajectory, underscoring the growing demand for Sharia-compliant products.
Despite this loyalty factor, the bargaining power of these customers isn't absolute. The market for Sharia-compliant finance is becoming increasingly competitive. Numerous Islamic banks and conventional financial institutions offering dedicated Islamic windows mean customers have a widening array of choices within their preferred segment. This increased competition provides customers with leverage, as they can more easily compare offerings and switch providers if better terms or services are available.
- Growing Islamic Banking Market: Global Islamic banking assets are projected to reach over $4.9 trillion by 2028, indicating a significant expansion of the Sharia-compliant financial sector.
- Customer Choice: The presence of multiple Islamic banks and Islamic finance divisions within conventional banks gives customers greater options and bargaining power.
- Service and Rate Sensitivity: Even within the Sharia-compliant segment, customers remain sensitive to service quality, profit rates, and product features, influencing their willingness to switch.
Customers in the UAE, especially those using digital channels, have significant bargaining power due to the ease of switching banks and readily available information for comparing services and rates. By mid-2024, over 70% of UAE consumers prioritized digital convenience, and an estimated 85% of banking customers actively used digital channels. The growing fintech sector, with numerous startups offering diverse financial tools, further empowers customers to seek better deals.
While individual retail customers have limited sway, large corporate and institutional clients at Dubai Islamic Bank wield considerable negotiation leverage due to their substantial transaction volumes and need for tailored solutions. This concentration means these major clients can negotiate for more favorable terms, impacting DIB's revenue. For instance, the UAE's digital payments market was projected to exceed $20 billion by mid-2024, highlighting the shift towards digital and the associated customer empowerment.
The bargaining power of customers seeking Sharia-compliant services is influenced by increasing competition within this segment. While DIB's adherence to Islamic principles fosters loyalty, the growing market for Islamic finance, with global assets projected to reach over $4.9 trillion by 2028, means customers have more choices and can negotiate for better terms or switch providers if dissatisfied.
| Factor | Impact on DIB | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
| Ease of Switching (Digital Onboarding) | High | 85% of UAE banking customers used digital channels; digital account opening processes completed in minutes. |
| Information Access & Comparison Tools | High | Significant percentage of consumers actively used online comparison tools for financial decisions. |
| Corporate Client Leverage | Moderate to High | Large clients can negotiate favorable terms, impacting revenue streams. |
| Fintech & Digital Alternatives | High | UAE digital payments market projected over $20 billion by mid-2024; surge in fintech startups. |
| Sharia-Compliant Loyalty vs. Competition | Moderate | Global Islamic banking assets projected to exceed $4.9 trillion by 2028; increased competition offers customer choice. |
What You See Is What You Get
Dubai Islamic Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the identical, professionally crafted Dubai Islamic Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis that you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring complete transparency and no hidden surprises. You're examining the exact, fully formatted document, ready for immediate download and application to your strategic planning needs. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file; what you're previewing is precisely what you get, with no mockups or samples involved.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Dubai Islamic Bank operates in a dynamic market characterized by the significant presence of multiple strong Islamic banks. This intense competition, exemplified by institutions like Emirates Islamic, forces each player to continuously innovate and refine their Sharia-compliant products and services to capture and retain market share. In 2023, the Islamic banking sector in the UAE continued its robust growth, with total assets reaching substantial figures, underscoring the crowded competitive landscape.
Conventional banks in the UAE, such as Emirates NBD and First Abu Dhabi Bank, increasingly offer Islamic banking services through dedicated windows. This strategy allows them to tap into the growing demand for Sharia-compliant finance without fully restructuring their operations. For instance, by the end of 2023, many of these conventional banks reported significant growth in their Islamic banking segments, capturing market share that might otherwise go to pure-play Islamic institutions.
This dual offering creates a complex competitive environment for Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB). DIB must contend not only with specialized Islamic banks but also with the broad customer base and extensive resources of these larger, diversified conventional banking groups. The ability of conventional banks to leverage their existing infrastructure and brand recognition, while simultaneously offering Islamic products, presents a formidable challenge.
The Islamic finance sector in the UAE is on a strong growth trajectory, with projections indicating a doubling of assets by 2031. This rapid expansion acts as a magnet for new entrants and spurs aggressive strategies from established institutions.
The UAE government's ambition to solidify its position as a global Islamic finance hub further intensifies this competitive landscape. This strategic push means banks like Dubai Islamic Bank face a dynamic environment where market share is fiercely contested.
Focus on Digital Innovation and Customer Experience
Competitive rivalry in the banking sector is intensifying as institutions prioritize digital innovation and customer experience. This means banks are pouring resources into technology to offer seamless online and mobile services, and personalized interactions. For Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB), staying competitive hinges on its ability to continually enhance these digital capabilities and ensure a superior customer journey.
Banks are no longer just competing on interest rates or product features; the digital storefront and the ease of interaction are paramount. This constant push for improvement fuels significant investment in areas like AI-driven customer service, intuitive mobile apps, and secure online platforms. DIB's strategic focus on digital transformation is therefore a crucial element in navigating this fierce competitive landscape.
- Digital Investment: In 2023, the UAE banking sector saw continued substantial investment in digital transformation initiatives, with many banks allocating over 20% of their IT budgets to digital projects.
- Customer Expectations: A recent survey indicated that over 75% of UAE consumers prefer digital banking channels for most transactions, highlighting the critical importance of a strong online presence.
- Innovation Focus: DIB has been actively promoting its digital offerings, including its mobile banking app which saw a significant increase in active users and transaction volumes throughout 2023.
Pricing Pressure and Profitability Dynamics
Intense competition within the banking sector often translates into significant pricing pressure, especially for more commoditized services. This pressure directly impacts net interest margins, a key indicator of a bank's profitability. DIB, like its peers, must navigate this challenge by strategically balancing competitive pricing to attract and retain customers with the imperative of maintaining robust profit margins.
Dubai Islamic Bank demonstrated its resilience in managing these competitive dynamics. For the full year 2024, the bank reported a net profit attributable to shareholders of AED 8.0 billion, a substantial 32% increase year-on-year. This strong performance, further evidenced by a net profit of AED 2.1 billion in Q1 2025, suggests DIB has effectively implemented strategies to mitigate pricing pressures and sustain healthy profitability.
- Competitive Pricing Strategy: DIB balances offering competitive rates on deposits and financing to attract a broad customer base.
- Profitability Management: The bank's ability to grow net profit by 32% in FY2024 to AED 8.0 billion highlights effective cost control and revenue generation despite competitive pressures.
- Margin Maintenance: Strong profitability in Q1 2025, with a net profit of AED 2.1 billion, indicates successful management of net interest margins.
Dubai Islamic Bank faces intense rivalry from both specialized Islamic banks and conventional banks offering Islamic windows, forcing a constant drive for innovation in Sharia-compliant products. The UAE's ambition to be a global Islamic finance hub further fuels this competition, with significant digital investments being made by all players to enhance customer experience and capture market share.
This competitive environment leads to pricing pressures, impacting profit margins. However, DIB's performance, including a 32% year-on-year net profit increase to AED 8.0 billion in FY2024 and a Q1 2025 net profit of AED 2.1 billion, demonstrates effective strategies in managing these challenges.
| Key Competitor Type | Examples | DIB's Response | Market Trend |
| Pure-play Islamic Banks | Emirates Islamic | Product innovation, digital enhancement | Growing demand for Sharia-compliant finance |
| Conventional Banks with Islamic Windows | Emirates NBD, First Abu Dhabi Bank | Leveraging existing infrastructure, brand recognition | Increased offering of Islamic banking services |
| Digital-first Challengers | Emerging fintechs | Investment in AI, mobile apps, seamless online platforms | Customer preference for digital channels (over 75% in UAE) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For customers who prioritize functionality over strict religious adherence, conventional banking products and services represent a significant threat of substitution. These traditional offerings, such as standard interest-based loans and credit cards, directly compete with Dubai Islamic Bank's (DIB) Sharia-compliant alternatives by providing similar financial solutions. In 2023, the global Islamic finance market was valued at an estimated $3.69 trillion, indicating a substantial portion of the financial landscape still operates on conventional models that could attract DIB's potential customers if Sharia compliance isn't their sole deciding factor.
The proliferation of fintech solutions, including digital wallets and peer-to-peer lending platforms, poses a significant threat to traditional banks like Dubai Islamic Bank. These innovative services offer convenient alternatives, especially for younger demographics who are increasingly embracing digital transactions. For instance, the global digital payments market is projected to reach $15.04 trillion by 2027, highlighting the substantial shift away from conventional banking methods.
Sophisticated investors, both individual and institutional, increasingly bypass traditional banking channels by directly investing in capital markets. For instance, the global Sukuk market, a key alternative investment avenue, saw significant growth, with issuance reaching an estimated USD 200 billion in 2024. This direct participation offers investors potentially higher returns and greater control over their assets, presenting a competitive threat to banks like Dubai Islamic Bank that rely on intermediation fees.
Alternative Lending Platforms
Alternative lending platforms, particularly those specializing in niche markets or employing innovative financing models, present a growing threat. These platforms can offer competitive terms and quicker approval processes compared to traditional banking, potentially drawing away both corporate and individual clients seeking financing solutions from Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB).
The rise of fintech and specialized lenders means that a wider array of options exist beyond conventional banking. For instance, in 2023, the global alternative lending market was valued at over $100 billion, demonstrating significant customer adoption and a clear substitutionary force against traditional financial institutions.
- Niche Lenders: Platforms focusing on specific sectors like SME financing or real estate development can offer tailored products that traditional banks might find less attractive or slower to adapt to.
- Digital Platforms: Online lending marketplaces and peer-to-peer lending sites often provide faster application and disbursement times, appealing to clients prioritizing speed and convenience.
- Alternative Financing Models: Options such as revenue-based financing or invoice discounting offer flexible repayment structures that can be more appealing than conventional loan terms for certain businesses.
Informal Financial Networks and Community-Based Finance
While Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) operates on a large, formal scale, the threat of substitutes from informal financial networks and community-based finance exists, especially in specific contexts. These informal channels often thrive on deep-seated trust and personal relationships, offering alternatives for certain financial needs where traditional banking might feel less accessible or personal.
These community-based models, such as savings and credit cooperatives or informal lending circles, can provide direct financial support, bypassing the regulatory and procedural layers of major banks. For instance, in emerging markets or within specific cultural enclaves, these networks can be quite robust. While DIB's 2024 financial reports focus on its institutional operations, understanding these smaller-scale substitutes is crucial for a complete market picture.
- Informal lending: Can offer quicker access to funds for small-scale needs, bypassing lengthy bank approval processes.
- Community savings groups: Provide a collective pool of capital for members, fostering local economic activity.
- Peer-to-peer lending platforms: Although digital, these can also be seen as a form of community finance, connecting borrowers and lenders directly.
The threat of substitutes for Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) primarily stems from conventional banking products and a growing array of fintech solutions. For customers not strictly adhering to Sharia principles, traditional interest-based banking offers a direct alternative, tapping into a market that, while Islamic finance was valued at $3.69 trillion in 2023, still represents a significant portion of global finance. Fintech platforms, including digital wallets and peer-to-peer lending, are particularly attractive to younger demographics, with the digital payments market expected to reach $15.04 trillion by 2027, indicating a strong shift towards digital and potentially non-Sharia compliant financial services.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Banking | Interest-based loans, credit cards, standard investment products | Global Islamic finance market valued at $3.69 trillion in 2023, highlighting the large conventional market share. |
| Fintech Solutions | Digital wallets, P2P lending, online payment platforms | Global digital payments market projected to reach $15.04 trillion by 2027. |
| Direct Capital Markets Access | Investors bypassing banks for direct investment in Sukuk, equities, etc. | Sukuk issuance reached an estimated USD 200 billion in 2024. |
| Alternative Lenders | Niche lenders, online marketplaces, specialized financing models | Global alternative lending market valued at over $100 billion in 2023. |
Entrants Threaten
The UAE banking sector, including Islamic banking, faces significant hurdles for new players due to stringent regulations from the Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE). These include demanding licensing processes, rigorous capital adequacy ratios, and strict adherence to anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing protocols.
For Islamic banks specifically, the requirement to comply with Sharia principles and evolving Sharia Certificate of Finance (SCF) standards adds another complex layer, making entry even more challenging.
Establishing a full-fledged bank, particularly one adhering to Sharia principles like Dubai Islamic Bank, necessitates a considerable upfront capital investment. This includes significant outlays for physical infrastructure, advanced technological systems, regulatory compliance, and initial operational setup. For instance, in 2024, the minimum capital requirements for new banks in many jurisdictions continue to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, presenting a substantial barrier.
This high capital threshold acts as a significant deterrent for potential new entrants. The sheer scale of financial commitment required to launch and sustain a banking operation, especially one needing to build trust and a robust digital presence, effectively limits the number of companies that can realistically consider entering the market. This protects incumbent players from immediate, widespread competition.
Existing banks, including Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB), have spent years building strong brand loyalty and customer trust. This deep-rooted connection makes it difficult for new players to attract customers who are comfortable with their current banking relationships.
For instance, DIB reported a customer base of over 2 million in 2023, demonstrating the significant existing trust and loyalty it commands. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and customer service to even begin to chip away at this established customer base.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
Established financial institutions like Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB) leverage significant economies of scale. This translates into lower per-unit costs for operations, technology investments, and marketing efforts. For example, DIB's extensive branch network and digital infrastructure allow it to spread fixed costs over a larger customer base, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
New entrants face substantial hurdles in matching the cost advantages enjoyed by incumbents. They must invest heavily in building a comparable infrastructure, acquiring customers, and developing brand recognition from scratch. This often means higher initial operating costs and potentially less competitive pricing, making it challenging to attract customers away from established players.
- Economies of Scale: DIB's large asset base, estimated at AED 307.4 billion as of Q1 2024, allows for efficient allocation of resources across its extensive operations.
- Cost Advantages: Incumbents benefit from established customer relationships and lower customer acquisition costs compared to new entrants needing to build trust and market presence.
- Technological Investment: Existing banks have already made substantial investments in digital platforms and security, creating a barrier for new entrants who must incur similar upfront costs.
Access to Talent and Distribution Networks
The threat of new entrants into Dubai Islamic Bank's market is significantly influenced by the substantial barriers related to accessing talent and established distribution networks. Building a comprehensive distribution network, encompassing both physical branches and robust digital platforms, demands considerable capital outlay and a lengthy developmental period. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to establish a new bank branch in the UAE can range from AED 5 million to AED 15 million, factoring in real estate, technology, and staffing.
Furthermore, attracting and retaining skilled banking professionals, especially those with specialized knowledge in Islamic finance principles, presents a considerable challenge for newcomers. The UAE's banking sector, as of early 2025, faces a shortage of experienced Sharia scholars and Islamic finance specialists, with demand outstripping supply. This talent scarcity can inflate recruitment costs and slow down operational readiness for any new player attempting to enter the market.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a physical branch network or a sophisticated digital banking infrastructure requires substantial upfront capital.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: Recruiting and retaining experienced personnel, particularly those with expertise in Islamic finance, is difficult and costly.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New entrants must navigate complex licensing and compliance requirements, adding to the time and expense of market entry.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Established banks like Dubai Islamic Bank benefit from years of building customer trust and brand loyalty, which new entrants must work hard to replicate.
The threat of new entrants for Dubai Islamic Bank is considerably low due to a combination of high capital requirements and stringent regulatory oversight from the Central Bank of the UAE. For instance, by 2024, minimum capital requirements for new banks often reach hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant barrier.
Furthermore, the need to comply with Sharia principles adds a unique layer of complexity and cost for any new Islamic bank. This, coupled with the established brand loyalty and economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like DIB, which reported over 2 million customers in 2023, makes market entry exceptionally challenging.
The substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and talent, alongside the difficulty in replicating DIB's AED 307.4 billion asset base as of Q1 2024, creates formidable entry barriers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High minimum capital needed for licensing and operations. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to CBUAE regulations and Sharia principles. | Increases complexity, time, and cost of market entry. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established customer relationships and reputation. | Difficult for newcomers to attract customers away from incumbents. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower operating costs due to large customer base and infrastructure. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies and competitive pricing. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Dubai Islamic Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data, including the bank's annual reports, financial statements, and investor relations disclosures. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry publications, market research reports, and macroeconomic data from sources like the World Bank and Bloomberg to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
