Deloitte & Touche LLP Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Deloitte & Touche LLP Bundle
Deloitte & Touche LLP operates within a complex professional services landscape, where the bargaining power of buyers and the threat of new entrants are significant considerations. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The intensity of rivalry among established firms, including Deloitte, directly impacts pricing and service innovation. We've analyzed how this competitive pressure shapes the market.
Furthermore, the availability of substitute services and the power of suppliers in the form of talent and technology present unique challenges. Our analysis delves into these critical areas.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Deloitte & Touche LLP’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Deloitte's most crucial suppliers are its highly skilled professionals, the consultants, auditors, and advisors who deliver its services. The ongoing scarcity of specialized talent, particularly in emerging fields like artificial intelligence and advanced data analytics, significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these individuals. For example, in 2024, the demand for AI specialists continued to outstrip supply, driving up compensation packages across the professional services sector.
This talent scarcity means that top performers can command higher salaries and better benefits, forcing firms like Deloitte to invest substantially in their development and offer attractive career pathways. The ability to attract and retain these in-demand professionals is directly linked to Deloitte's competitive advantage and its capacity to deliver high-quality client solutions.
The bargaining power of technology and software providers for a firm like Deloitte is shifting. While generic software suppliers typically have little leverage, those specializing in critical, cutting-edge areas like artificial intelligence, advanced analytics, and automation are gaining influence. These specialized tools are becoming essential for Deloitte's ability to deliver efficient and innovative client services, directly impacting their competitive edge.
Deloitte's increasing dependence on sophisticated technology means that providers of unique or proprietary solutions can exert a moderate degree of supplier power. For instance, the demand for AI-driven audit platforms or complex data analytics software, areas where specialized expertise is scarce, allows these vendors to negotiate more favorable terms. In 2023, spending on AI software alone was projected to reach over $62 billion globally, highlighting the growing importance and potential pricing power of these technology suppliers.
Deloitte's reliance on data and information providers is significant, as access to high-quality, real-time data and proprietary market insights is essential for their advisory and consulting services. Suppliers of specialized industry data, market intelligence, and analytical platforms can wield considerable bargaining power, particularly when their offerings are unique or challenging to replicate. For instance, specialized financial data providers often command premium pricing due to the scarcity and precision of their information, which directly impacts Deloitte's ability to deliver value-added analysis to its clients.
Real Estate and Infrastructure Providers
For a global firm like Deloitte, real estate lessors and infrastructure providers represent a crucial, yet typically low-power, supplier group. The sheer abundance of commercial office spaces available in most major markets significantly dilutes the individual bargaining leverage of any single landlord. For instance, in 2024, global commercial real estate vacancy rates saw varied trends, with some major business districts experiencing slightly higher availability, further constraining lessor power. However, securing prime locations in economically vital business hubs remains a strategic imperative for Deloitte, influencing client accessibility and the ability to attract top talent.
Deloitte’s extensive global footprint means its real estate needs are diverse, but the competitive nature of the leasing market generally keeps supplier power in check. The availability of multiple office buildings and colocation facilities across different cities provides ample choice, preventing any single provider from dictating terms. While the cost of prime real estate in sought-after financial centers can be substantial, the competitive landscape limits the ability of individual property owners to exert undue influence on lease agreements. This dynamic allows Deloitte to negotiate favorable terms, leveraging market conditions to its advantage.
- Market Saturation: Abundant commercial real estate options globally limit the bargaining power of individual lessors.
- Strategic Location Premium: While overall power is low, premium locations in key business hubs can command higher rents, reflecting their strategic importance for client access and talent acquisition.
- Negotiating Leverage: Deloitte’s scale and the competitive real estate market provide significant leverage in lease negotiations.
- Infrastructure Dependence: Reliable IT infrastructure and connectivity are critical, but often sourced from multiple providers, mitigating individual supplier power.
Subcontractors and Specialized Boutiques
Deloitte often partners with subcontractors and specialized boutiques to augment its capabilities, particularly for projects requiring niche expertise or to manage fluctuating demand. These smaller firms can wield moderate bargaining power if their specialization is in high demand or if they possess unique intellectual property. For instance, a cybersecurity firm with proprietary threat intelligence could negotiate higher fees.
The bargaining power of these specialized entities is influenced by the availability of alternatives and the importance of their contribution to Deloitte's overall project success. If a specific skill set is scarce across the broader market, these subcontractors can leverage that scarcity to their advantage. This dynamic creates a balanced relationship where Deloitte gains flexibility and access to specialized talent, while the subcontractors secure valuable engagements.
- Specialization Value: Boutique firms offering unique, in-demand skills like AI ethics consulting or quantum computing implementation can command higher rates, potentially influencing project costs.
- Market Scarcity: The limited supply of highly specialized talent means subcontractors in these areas have more leverage in fee negotiations.
- Project Dependence: If a subcontractor's contribution is critical to a large-scale Deloitte engagement, their bargaining power increases significantly.
The bargaining power of Deloitte's suppliers is notably influenced by the scarcity of specialized talent. Highly skilled professionals, particularly in emerging fields like AI and advanced analytics, can command higher compensation and benefits due to strong demand. For example, in 2024, the competition for AI specialists continued to drive up salaries across the professional services sector.
| Supplier Category | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors Influencing Power |
| Skilled Professionals (Consultants, Auditors) | High | Talent scarcity in AI/Data Analytics; High demand for specialized skills; Strong individual performance |
| Technology & Software Providers | Moderate to High | Proprietary/unique AI/analytics solutions; Increasing dependence on advanced tech; Scarcity of specialized tech expertise |
| Data & Information Providers | Moderate to High | Uniqueness and precision of data; Difficulty in replication; Essential for value-added analysis |
| Subcontractors & Boutiques | Moderate | Niche or in-demand expertise; Critical project contributions; Limited availability of alternatives |
| Real Estate Lessors | Low | Market saturation; Abundance of commercial spaces; Availability of alternative locations |
| Infrastructure Providers (IT, Connectivity) | Low | Multiple providers available; Standardized services; Little differentiation |
What is included in the product
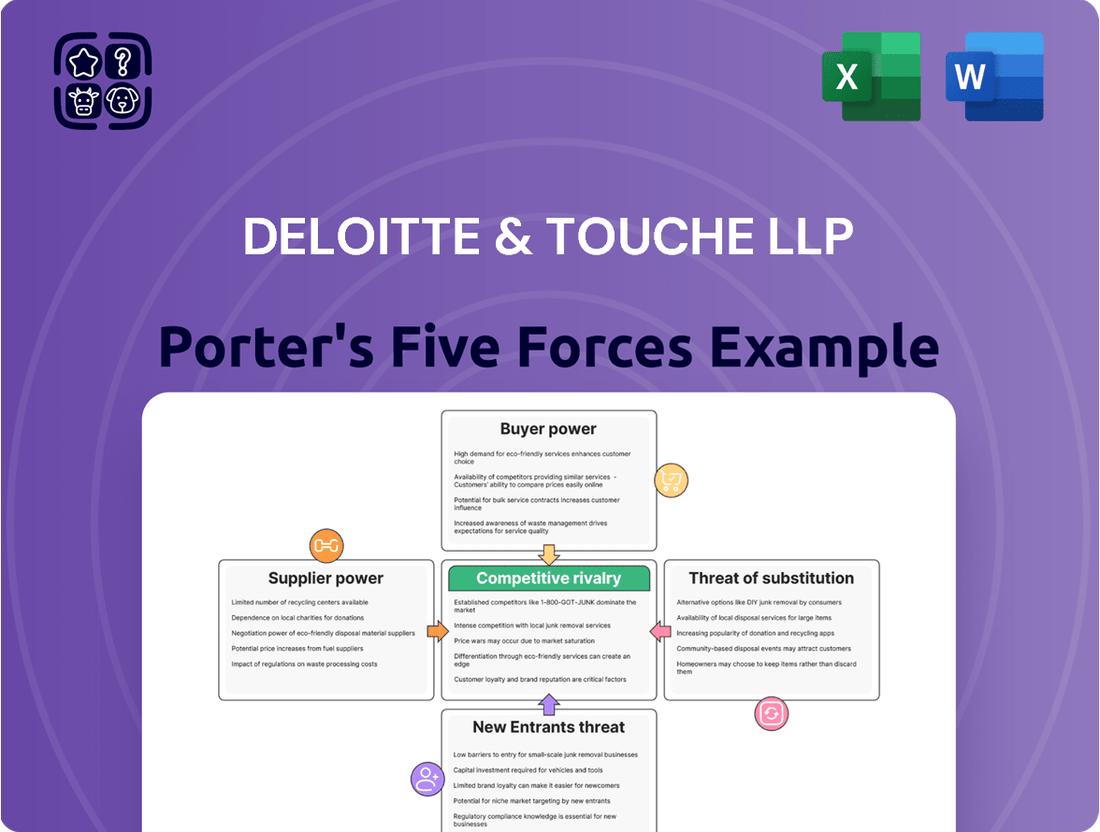
Explores the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the professional services industry, specifically for Deloitte & Touche LLP.
Deloitte & Touche LLP's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making and alleviating the pain of information overload.
Customers Bargaining Power
Deloitte's largest clients, often multinational corporations and Fortune Global 500 entities, wield considerable bargaining power. Their substantial contribution to Deloitte's revenue, estimated to be billions annually for such clients, grants them leverage in negotiations. For instance, a single Fortune 500 client could represent a significant percentage of a specific service line's annual income, making their retention a high priority.
These high-profile clients can effectively demand competitive pricing and highly customized service packages. They are well-informed about the market and aware of the limited number of globally recognized professional service firms capable of meeting their complex needs. This awareness allows them to pit major players, including Deloitte's peers within the Big Four, against each other to secure the best terms and service quality.
Public sector entities, like government agencies, wield significant bargaining power due to their procurement processes. These entities prioritize cost-effectiveness, compliance, and transparency in their dealings, which naturally leads to a focus on price negotiations.
Their substantial project sizes and the long-term nature of their contracts amplify this power. For instance, the U.S. federal government's annual spending on goods and services exceeds trillions of dollars, providing immense leverage in contract negotiations across various sectors.
Competitive bidding is a common mechanism that further empowers public sector customers. These processes often pit multiple suppliers against each other, driving down prices and allowing the public entity to secure more favorable terms and conditions.
In 2024, government contracting remained a significant market, with agencies continually seeking value. This dynamic means suppliers must be prepared to demonstrate not only quality but also competitive pricing to win and retain business.
For Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMEs), their individual bargaining power with a firm like Deloitte & Touche LLP is typically lower due to the smaller scale of their contracts. However, the sheer volume of the SME market represents a significant collective force. These businesses often exhibit a greater sensitivity to pricing and a strong focus on the perceived value of services rendered. For instance, in 2024, the SME sector continued to be a major contributor to economic activity, with many seeking cost-effective professional services to navigate complex regulatory environments.
Switching Costs and Client Stickiness
While clients can indeed switch professional service providers, especially for routine audit services where regulatory mandates might encourage periodic reviews, the landscape shifts dramatically for more intricate engagements. Think about long-term strategic consulting or highly specialized risk advisory; the investment in understanding a client's unique ecosystem, data, and operational nuances creates significant switching costs. These costs aren't just monetary; they encompass the time and resources needed for a new firm to get up to speed, the potential for project delays, and the inherent risks of disrupting established workflows.
Consider the client’s perspective: onboarding a new, unfamiliar firm requires extensive knowledge transfer, data migration, and system integration, all of which can be costly and time-consuming. For instance, a major financial institution engaging a new cybersecurity consultant would face substantial expenses in briefing the new team on their complex network architecture and existing security protocols. This inherent friction in switching providers, particularly for deeply embedded services, acts as a natural dampener on the bargaining power of customers in these segments.
- High Switching Costs: For complex, integrated services like long-term consulting or specialized risk advisory, switching costs can be substantial, involving significant effort in onboarding and knowledge transfer.
- Client Stickiness: The deep integration of a professional service provider's expertise and understanding of a client's business fosters client stickiness, making frequent switching less appealing.
- Disruption Risk: The potential for disruption to ongoing projects and business operations acts as a deterrent for clients considering a change in their professional service providers.
- Regulatory Influence: While regulations might encourage periodic review of audit services, this doesn't negate the switching costs associated with other, more integrated service offerings.
Access to Internal Expertise and Alternative Solutions
Clients increasingly possess strong internal capabilities, often bolstered by advanced technologies like AI. This allows them to automate functions previously outsourced to firms like Deloitte, directly reducing their need for external expertise. For instance, in 2024, many companies expanded their in-house data analytics teams, leveraging AI to process and interpret data internally.
The widespread availability of sophisticated off-the-shelf software and sophisticated internal data analytics tools empowers clients to handle tasks that were once the domain of professional services. This shift means clients can perform more functions themselves, significantly increasing their bargaining leverage. A 2024 survey indicated that 60% of large enterprises reported an increase in their ability to perform advanced analytics internally, a key factor in negotiating service contracts.
- Increased Internal Automation: AI and advanced analytics enable clients to handle more tasks in-house.
- Empowerment Through Technology: Off-the-shelf software reduces reliance on external specialized services.
- Negotiating Leverage: Clients with enhanced internal capabilities can demand more favorable terms.
- Reduced Outsourcing Dependence: Companies are strategically bringing functions back internally to control costs and expertise.
The bargaining power of customers for Deloitte & Touche LLP is a critical factor influencing pricing and service delivery. Large clients, like Fortune Global 500 companies, represent a significant portion of revenue, giving them considerable negotiation leverage. In 2024, the professional services market saw continued demand for cost-efficiency from these major players.
Public sector clients, such as government agencies, also exert strong bargaining power through their structured procurement processes and focus on value. Their massive spending, exemplified by the U.S. federal government's trillions in annual spending, necessitates competitive bidding and price sensitivity from service providers.
While individual SMEs have less direct power, their collective market size is substantial, and they often prioritize affordability. The increasing trend in 2024 for companies to build internal capabilities, particularly in areas like data analytics powered by AI, further enhances client leverage by reducing reliance on external expertise.
| Client Type | Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Market Trend Example |
| Large Corporations (e.g., Fortune Global 500) | High revenue contribution, significant spend, market awareness | Continued demand for customized, value-driven solutions. |
| Public Sector (e.g., Government Agencies) | Formal procurement, cost-effectiveness focus, large contract values | Emphasis on transparent pricing and demonstrable ROI in bids. |
| SMEs | Price sensitivity, volume of market presence | Seeking cost-effective solutions to navigate regulatory landscapes. |
| Clients with Enhanced Internal Capabilities | Increased in-house automation (AI), reduced reliance on external specialists | Growth in internal data analytics teams, impacting demand for outsourcing. |
What You See Is What You Get
Deloitte & Touche LLP Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Deloitte & Touche LLP Porter's Five Forces analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within an industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into industry attractiveness and strategic positioning. You are looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this comprehensive analysis, ready for your immediate use. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file; what you're previewing is precisely what you get, meticulously prepared for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The professional services landscape, particularly in audit and major consulting projects, is heavily influenced by the Big Four: Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG. This oligopolistic structure fuels fierce competition among these giants for clients, skilled professionals, and lucrative contracts.
These leading firms collectively achieved revenues exceeding $200 billion in 2024. This substantial financial power underscores their dominance and the intense rivalry that shapes the market, as they vie for a larger share of this vast economic pie.
The competitive rivalry within the accounting and consulting sector is significantly amplified as the Big Four, including Deloitte, aggressively diversify their service portfolios. This strategic move extends their reach from traditional audit and tax into high-growth areas like digital transformation, cybersecurity, and sustainability consulting. For instance, Deloitte's consulting revenue has seen robust growth, often outpacing its audit practice, directly challenging specialized firms across these new domains.
The competition for top talent, especially those skilled in AI, cybersecurity, and ESG, is a significant battleground for firms like Deloitte. In 2024, the demand for these specialized skills continues to outpace supply, driving up compensation and recruitment costs. Deloitte, like its peers, invests heavily in training and development to cultivate internal expertise, recognizing that human capital is its most crucial asset.
This intense rivalry for expertise directly impacts service quality and innovation. Firms that can attract and retain the best minds are better positioned to offer cutting-edge solutions to clients. For instance, the cybersecurity market alone was projected to reach over $230 billion globally in 2024, underscoring the immense value placed on professionals in this domain.
Pricing Pressure and Value Proposition
Clients are increasingly scrutinizing expenditures, demanding more bang for their buck. This has intensified pricing pressure across the consulting landscape, pushing firms like Deloitte & Touche LLP to move away from purely hourly billing towards value-based pricing models. In 2024, many consulting firms reported that clients were more insistent than ever on demonstrating clear ROI, directly impacting how services are quoted and delivered.
To stay competitive, firms must clearly articulate and prove the tangible outcomes and return on investment they deliver. This necessitates a constant drive for efficiency, often achieved through strategic investments in technology and the optimization of internal processes. For instance, the adoption of AI-powered analytics tools saw a significant uptick in 2024, as firms sought to streamline project delivery and enhance client value.
- Value-Based Pricing Growth: Many clients now expect pricing to be directly tied to the achieved business outcomes rather than just time spent.
- Technology Adoption for Efficiency: Consulting firms are investing heavily in AI and automation to reduce delivery costs and improve service quality.
- Demonstrating Tangible ROI: The ability to quantify and communicate the return on investment from consulting services is a key differentiator in 2024.
- Client Scrutiny on Fees: Client budgets are tighter, leading to more rigorous negotiation and a demand for greater transparency in billing.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Brand Reputation
Regulatory scrutiny, particularly around audit practices, remains a significant factor influencing competitive rivalry within the professional services sector. Firms like Deloitte & Touche LLP must navigate a complex web of regulations, which can lead to increased compliance costs and potential reputational damage if not managed effectively. For instance, in 2024, the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) continued its focus on audit quality, with inspection reports highlighting areas for improvement across major accounting firms, indirectly impacting all players.
Maintaining a sterling brand reputation for integrity, quality, and innovation is paramount. Any perceived lapse in these areas can severely erode client trust, a critical asset in this industry. This trust deficit can translate directly into lost business and market share. For example, a 2023 survey by Edelman found that trust in business remained fragile, emphasizing the importance of consistent ethical conduct and high-quality service delivery as key differentiators.
- Reputational Risk: Negative publicity from regulatory actions or service failures can significantly damage a firm's competitive standing.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to evolving regulatory requirements adds to operational expenses, impacting profitability and pricing strategies.
- Brand as Differentiator: Firms with a strong, trusted brand can command premium pricing and attract top talent.
- Trust Deficit: In 2024, client confidence in professional services remains sensitive to perceived ethical lapses or quality issues.
The competitive rivalry among the Big Four, including Deloitte & Touche LLP, is intense and multifaceted, driven by their significant market share and aggressive expansion into new service areas. This rivalry is evident in their pursuit of top talent, particularly in high-demand fields like AI and cybersecurity, where compensation and recruitment costs are escalating. Furthermore, firms are increasingly adopting value-based pricing models and leveraging technology to demonstrate tangible ROI to cost-conscious clients.
Regulatory scrutiny and the imperative to maintain a strong reputation for integrity are also key drivers of competition. Firms must navigate complex compliance landscapes and build unwavering client trust, as any perceived lapse can lead to significant business losses. This environment necessitates continuous innovation and a focus on delivering demonstrable value to clients, shaping the strategic priorities of all major players.
| Metric | Deloitte & Touche LLP (and peers) | Key Trend/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Combined Big Four Revenue (Est. 2024) | >$200 billion | Indicates significant market power and intense competition for market share. |
| Cybersecurity Market Growth (Est. 2024) | >$230 billion globally | Highlights the high value placed on specialized talent and services, fueling talent wars. |
| Client Demand for ROI | Increasingly stringent | Pushes firms towards value-based pricing and greater transparency in service delivery. |
| Investment in AI & Automation | Significant increase | Aims to improve efficiency, reduce delivery costs, and enhance client value in a competitive market. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Companies increasingly build out in-house capabilities for functions such as audit, tax, and advisory services, directly impacting the demand for external professional firms like Deloitte. Large enterprises, in particular, are leveraging their financial strength to create specialized internal departments. For instance, a significant number of Fortune 500 companies have been expanding their internal audit teams, with some increasing headcount by over 15% in the past two years to handle evolving regulatory landscapes and internal controls.
Technological advancements, particularly in AI and automation, present a substantial threat of substitution for traditional professional services. For instance, AI-powered platforms can now conduct complex data analysis and compliance checks at a fraction of the cost and time previously required by human experts.
The efficiency gains offered by robotic process automation (RPA) are particularly impactful in areas like basic accounting, payroll processing, and customer service, directly impacting the demand for human labor in these roles. Companies are increasingly adopting these technologies to streamline operations and reduce overhead.
In 2024, the global market for AI in professional services was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, with significant growth driven by the adoption of these automating technologies. This growth underscores the competitive pressure these technological solutions place on established service providers.
The rise of specialized software and platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional advisory services. For instance, advanced financial modeling software, like those offered by companies such as Anaplan or Oracle EPM Cloud, empowers businesses to conduct complex scenario planning and forecasting internally, potentially reducing the need for external consultants. Similarly, tax preparation software, with capabilities ranging from basic returns to intricate corporate filings, allows companies to manage their tax obligations with less reliance on accounting firms.
These tools democratize complex financial tasks, enabling clients to perform services themselves that were once exclusively the domain of full-service advisory firms. This self-service capability directly erodes the market for certain advisory engagements. Consider the growth in the fintech sector; in 2024, venture capital investment in fintech solutions, while experiencing some recalibration from peak years, continued to be substantial, indicating strong innovation and availability of powerful, albeit niche, software alternatives.
Freelance Professionals and Gig Economy Platforms
The burgeoning gig economy presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional employment models. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr connect businesses with freelance professionals, offering specialized skills on a project-by-project basis. This can be a more cost-effective and agile solution for tasks ranging from graphic design to software development. For example, in 2023, the global freelance platform market was valued at over $3.7 billion, indicating a substantial shift towards flexible work arrangements.
This trend allows companies to access a wider talent pool and avoid the overhead associated with full-time employees for specific needs. Consider the legal sector; many firms now utilize freelance paralegals or contract attorneys for overflow work, reducing the need for permanent staff. This flexibility means businesses can scale their workforce up or down rapidly in response to project demands.
The threat is amplified by the increasing professionalism and quality of freelance services. Many independent professionals offer expertise that rivals that of established agencies or in-house departments. This accessibility to high-quality, specialized talent at competitive rates directly challenges the necessity of traditional, longer-term hiring for many business functions.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Cost Savings: Businesses can often secure freelance talent at a lower overall cost compared to employing full-time staff, due to reduced benefits, office space, and training expenses.
- Flexibility and Scalability: The gig economy allows for rapid adjustments to staffing levels, aligning workforce capacity precisely with project needs.
- Access to Niche Expertise: Freelance platforms provide access to highly specialized skills that might be difficult or expensive to recruit internally.
- Increased Competition for Talent: Traditional employers now compete not only with each other but also with a vast network of independent professionals for skilled labor.
Educational Resources and Open-Source Knowledge
The threat of substitutes for traditional advisory services is growing as businesses can increasingly leverage readily available educational resources and open-source knowledge. For simpler advisory needs, companies can turn to online courses, webinars, and vast digital libraries to find solutions internally, thereby reducing the reliance on external consultants.
This shift is particularly evident in areas like basic financial planning, digital marketing strategy, and HR best practices, where a wealth of information is accessible. For instance, platforms like Coursera and edX offer a plethora of courses, with millions of users enrolling in business and finance-related programs annually. In 2024, the global e-learning market was projected to reach over $400 billion, demonstrating the significant adoption of self-directed learning.
- Increased Accessibility: Online platforms provide cost-effective access to specialized knowledge, empowering businesses to address common challenges without external fees.
- Skill Development: Employees can upskill through online courses, enabling companies to handle more tasks in-house, from data analysis to project management.
- Cost Savings: A 2023 survey indicated that 60% of small businesses reported cost savings by utilizing online resources instead of traditional consulting for specific tasks.
- Open-Source Solutions: The availability of open-source software and knowledge bases further reduces the need for specialized, paid advisory services for certain technological implementations.
The threat of substitutes is intensifying as technology offers increasingly capable alternatives to traditional professional services. AI and automation tools can now perform complex data analysis and compliance checks more affordably and swiftly than human experts. For example, AI in professional services is a rapidly expanding market, projected to reach tens of billions of dollars in 2024, highlighting the competitive pressure from these technological solutions.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the professional services arena, particularly aiming for a scale akin to Deloitte, demands considerable investment in talent, technology, and global operations. For instance, attracting and retaining top-tier talent in specialized fields like cybersecurity or AI requires competitive compensation packages, ongoing training, and a robust employer brand, all contributing to significant upfront and recurring costs.
Developing cutting-edge digital platforms and advanced analytics capabilities is another substantial hurdle. Firms need to invest heavily in software development, data infrastructure, and cybersecurity measures to offer competitive digital solutions and protect client data.
The need for a global presence, with offices and service capabilities in key markets, further escalates the capital requirements. Establishing and maintaining this international network involves substantial real estate, legal, and operational expenses.
These high capital and investment requirements act as a formidable barrier, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to challenge established firms like Deloitte without substantial backing and a long-term strategic vision.
The threat of new entrants in the professional services sector, particularly for firms like Deloitte & Touche LLP, is significantly mitigated by the paramount importance of brand reputation and trust. Building decades of proven expertise and client relationships is not something a newcomer can replicate overnight.
New firms struggle to establish the credibility and confidence necessary to attract large, sophisticated clients, especially in the corporate and public sectors where risk aversion is high. For instance, a 2024 survey by Edelman found that trust in professional services firms remains a critical differentiator, with 79% of respondents stating that trust is the most important factor when choosing a service provider.
This deep-seated reliance on established track records and verifiable performance creates a formidable barrier. New entrants must invest heavily in demonstrating reliability and competence, often through years of successful project delivery and positive client testimonials, a process that inherently limits their immediate competitive impact.
The audit and assurance sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles and licensing demands, acting as a formidable barrier for new entrants. Compliance with rigorous standards, such as those set by the PCAOB in the United States, requires significant investment in expertise and infrastructure. For instance, in 2023, firms seeking to audit publicly traded companies must adhere to a complex web of rules governing independence, quality control, and professional conduct, making it a costly and time-consuming process to establish a compliant operation.
Navigating these intricate regulations demands specialized knowledge and substantial financial resources, effectively deterring many potential competitors. The need for continuous training and adaptation to evolving legal frameworks, like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, adds another layer of difficulty. These requirements mean that any new firm must demonstrate a robust commitment to regulatory adherence from day one, a challenge that can be particularly daunting in the competitive landscape of 2024.
Talent Acquisition and Retention Challenges
Attracting and retaining highly specialized talent is a significant hurdle for new entrants looking to compete with established firms like Deloitte. These new players often find it difficult to match the comprehensive career development programs, the brand recognition, and the competitive compensation and benefits packages that are hallmarks of the Big Four accounting and consulting firms.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for experienced professionals in areas like cybersecurity, data analytics, and cloud computing remained exceptionally high. New firms face the challenge of offering incentives that can truly rival the long-term career trajectories and the perceived stability that larger, more established organizations can provide. This talent gap acts as a substantial barrier to entry.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Critical areas like AI, data science, and ESG consulting see intense competition for talent.
- Compensation Disparity: New entrants may struggle to match the salary, bonus, and equity structures offered by major players.
- Brand Prestige and Career Progression: Established firms offer a well-defined path for advancement and a recognized brand name, which is a powerful draw for ambitious professionals.
- Training and Development Investment: Deloitte invests heavily in continuous training, which new firms may find cost-prohibitive to replicate initially.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Established players like Deloitte leverage substantial economies of scale and scope, enabling them to deliver a broad spectrum of integrated services cost-effectively. For instance, Deloitte's global network allows for resource sharing and specialized expertise across various service lines, from audit to consulting, making their pricing highly competitive.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies and service breadth. Building a comparable infrastructure and talent pool to offer the comprehensive solutions demanded by large, diverse clients requires immense capital investment, often exceeding what a startup can readily access.
Consider the 2024 market landscape where major consulting firms reported substantial revenue growth, indicating their continued ability to capture market share through established client relationships and scaled operations. For example, firms are investing heavily in AI and digital transformation services, areas where incumbent firms have already built significant capabilities and client trust.
- Economies of Scale: Large firms can spread fixed costs over a greater volume of output, leading to lower per-unit costs.
- Economies of Scope: Offering a wider range of services allows firms to utilize shared resources and expertise, reducing costs.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants struggle to achieve comparable cost structures and service portfolios without significant upfront investment.
- Competitive Advantage: Incumbents benefit from established brand recognition and existing client relationships, further solidifying their market position.
The threat of new entrants is significantly dampened by the immense capital required to establish a credible presence in professional services, especially for firms aiming to rival Deloitte's scale. This includes substantial investments in talent, technology, and a global operational footprint, creating a high barrier to entry.
Furthermore, the critical importance of brand reputation and trust, built over years of proven expertise and client relationships, presents another major hurdle. New firms struggle to gain the necessary credibility to attract large clients, as evidenced by 2024 data showing trust as a paramount factor in service provider selection.
Regulatory complexities, particularly in areas like audit and assurance, demand significant investment in specialized knowledge and compliance infrastructure, making it difficult for newcomers to navigate these stringent requirements. The intense competition for highly specialized talent also poses a challenge, as new entrants may not be able to match the compensation and career development opportunities offered by established firms.
Finally, incumbent firms like Deloitte benefit from significant economies of scale and scope, allowing them to offer integrated services cost-effectively. New entrants would need considerable capital to replicate this cost efficiency and service breadth, making it difficult to compete on price and comprehensive offerings in the current market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
