Banco Davivienda Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Banco Davivienda Bundle
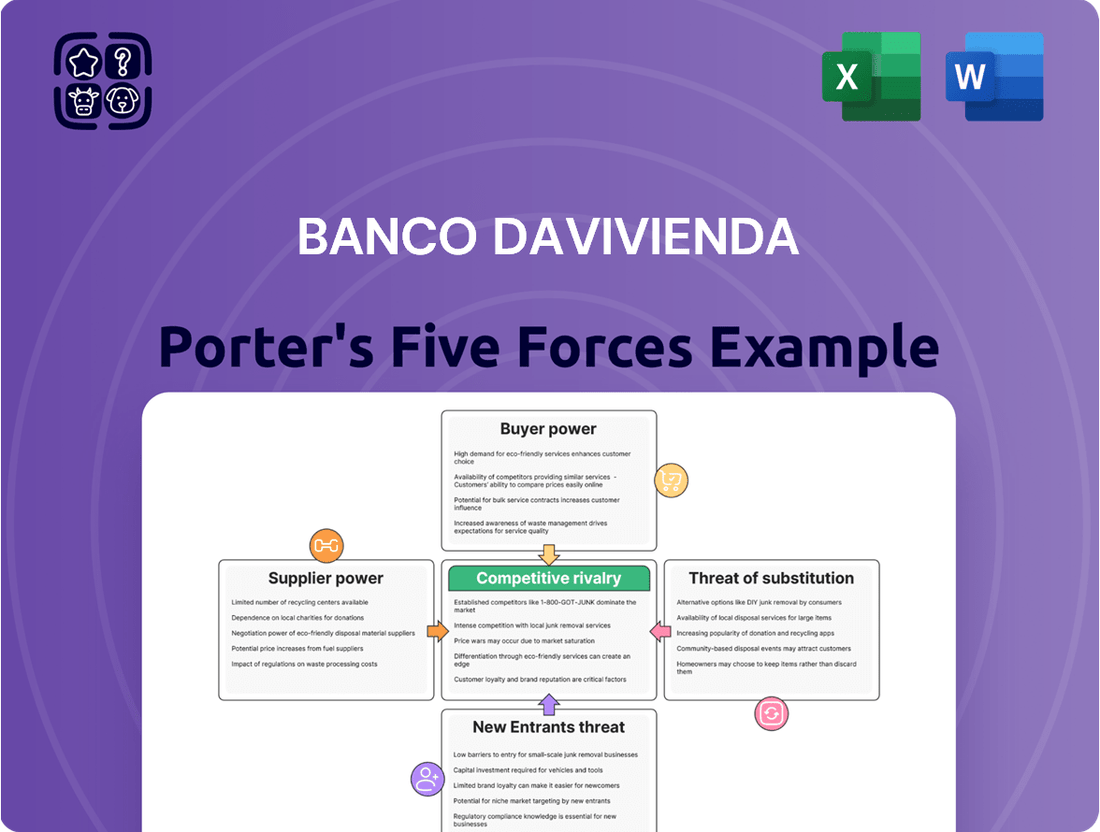
Banco Davivienda operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing significant pressures from various competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of its customers, and the influence of suppliers is crucial for strategic planning. Furthermore, the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute products can reshape the market significantly.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Banco Davivienda’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Banco Davivienda's reliance on a limited number of key technology providers for its core banking systems and cloud infrastructure significantly influences supplier bargaining power. If a few dominant vendors control essential software or cloud services, they can dictate pricing and terms, potentially increasing operational costs for Davivienda. For instance, the global market for core banking software is highly concentrated, with a few major players holding substantial market share, a trend that continued into 2024.
The financial sector, including institutions like Banco Davivienda, faces a growing challenge with the availability of skilled labor, particularly in high-demand areas such as cybersecurity, data analytics, and digital banking. A scarcity of these specialized professionals directly translates to increased bargaining power for employees, potentially driving up labor costs for the bank. For instance, a report from 2024 indicated a significant shortage of cybersecurity experts globally, with demand outstripping supply by a considerable margin.
This limited supply of talent means that skilled individuals can command higher salaries and better benefits, directly impacting Banco Davivienda's operational expenses and profitability. In 2024, the average salary for a senior data scientist in Latin America saw a notable increase, reflecting this competitive labor market. Consequently, the bargaining power of suppliers of these critical skills can exert upward pressure on the bank's cost structure.
Banco Davivienda's reliance on institutional funding, interbank lending, and central bank policies highlights a significant dependence on external sources for liquidity. The bargaining power of these funding providers, particularly concerning their interest rate policies and lending conditions, directly impacts Davivienda's cost of capital and overall profitability. For instance, ongoing monetary policy adjustments in Colombia, such as those implemented by the Banco de la República, can substantially alter the cost of funds available to the bank, affecting its ability to lend and generate returns.
Regulatory Compliance Vendors
In the banking sector, specialized vendors providing regulatory compliance, auditing, and legal services wield significant bargaining power. This is largely due to the highly regulated nature of financial institutions like Banco Davivienda, which require niche expertise. The limited number of qualified providers in this space means Davivienda has fewer alternatives, potentially driving up compliance costs, particularly as new regulations are anticipated to take effect in 2025.
- Specialized Expertise: Banks depend on a select group of vendors for critical functions like anti-money laundering (AML) software and Know Your Customer (KYC) solutions, areas demanding deep, evolving knowledge.
- Limited Supplier Pool: The scarcity of highly specialized and accredited compliance vendors in key markets grants them leverage in pricing and contract terms.
- Increasing Regulatory Burden: With new regulations, such as enhanced data privacy laws expected in 2025, the demand for these specialized services will likely intensify, further empowering suppliers.
- High Switching Costs: Migrating to new compliance systems or providers can be complex and costly for banks, reducing their willingness to switch and thus strengthening existing supplier relationships.
Infrastructure and Utility Providers
Infrastructure and utility providers, such as telecommunications and energy companies, hold significant bargaining power over Banco Davivienda. These essential services are critical for daily banking operations, and any disruption or price hike directly impacts the bank's ability to function and its operational expenses.
For instance, a substantial increase in internet service provider fees or electricity costs could directly affect Davivienda's profitability. While these services might seem commoditized, their critical nature means Davivienda has limited alternatives, especially for maintaining consistent and reliable service across its branches and digital platforms.
- Dependence on Reliable Connectivity: Davivienda relies heavily on telecommunications for inter-branch communication, ATM networks, and online banking services. Disruptions, even temporary ones, can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
- Escalating Utility Costs: Rising energy prices directly impact the operating costs of Davivienda’s physical branches and data centers. For example, in 2023, global energy prices saw volatility, which would have likely translated to higher utility bills for businesses operating large facilities.
- Limited Switching Options: In many regions, the number of providers for essential infrastructure like high-speed internet or stable power grids is limited, giving existing providers considerable leverage in negotiating rates and service level agreements with large corporate clients like Davivienda.
- Security Infrastructure: Physical security services are also crucial, and while perhaps less prone to dramatic price swings, maintaining robust security across numerous locations represents a substantial and ongoing cost, with providers having some power due to the sensitive nature of the services.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Banco Davivienda is notably influenced by the concentration within specialized technology markets. Providers of core banking software and cloud services, often dominated by a few large players, can dictate terms, impacting Davivienda's operational costs.
The scarcity of specialized talent, particularly in cybersecurity and data analytics, grants employees significant leverage, driving up labor costs for the bank. For instance, a 2024 report highlighted a global shortage of cybersecurity professionals, with demand far exceeding supply.
Funding sources, including interbank lending and central bank policies, also present supplier power. Adjustments in interest rates by entities like Colombia's Banco de la República directly affect Davivienda's cost of capital.
Vendors offering regulatory compliance and legal services hold considerable sway due to the highly regulated financial environment and the limited pool of specialized providers, a trend expected to intensify with new regulations anticipated in 2025.
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Banco Davivienda, this analysis dissects the five competitive forces shaping its industry, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart, simplifying complex competitive dynamics for Banco Davivienda.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer switching costs for Banco Davivienda are a key factor influencing customer bargaining power. High costs to switch, like early withdrawal penalties on certain savings products or the administrative burden of moving mortgages and direct deposits, tend to lock customers in, thereby reducing their ability to negotiate better terms. However, the increasing ease of digital account opening and management across various fintech platforms and traditional banks is gradually lowering these barriers.
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Banco Davivienda's market position. For instance, in 2024, a slight increase in interest rates on savings accounts could prompt depositors to move funds to institutions offering even a fractional higher yield, especially given the competitive landscape in Colombia where numerous banks vie for deposits.
This sensitivity is particularly acute for loan products. If Davivienda's loan origination fees or annual percentage rates (APRs) are perceived as less favorable than those of competitors like Bancolombia or Grupo Aval, borrowers will likely opt for the more cost-effective option. This forces Davivienda to constantly monitor and adjust its pricing strategies to remain competitive and retain its customer base.
Customers today have unprecedented access to information about financial products. Digital platforms and comparison websites allow individuals to easily research and compare offerings from various banks, including Banco Davivienda. This increased transparency means customers can readily see interest rates, fees, and service levels across the market, significantly boosting their bargaining power.
For instance, a 2024 report highlighted that over 70% of banking consumers actively use online tools to compare financial products before making a decision. This empowers them to seek better deals, whether it's a more competitive mortgage rate or a savings account with a higher yield. Davivienda must therefore remain competitive, as a dissatisfied customer can quickly find alternatives.
Customer Segmentation and Volume
Davivienda's customer base exhibits a wide range of bargaining power, heavily influenced by segmentation and transaction volume. Individual retail clients typically have minimal individual leverage, but their collective power can be significant through market trends and general sentiment.
Large corporate clients, however, represent a distinct segment where bargaining power is considerably higher. These entities, often managing substantial assets and complex financial requirements, can negotiate for customized solutions, preferential interest rates, and specialized services, directly impacting Davivienda's revenue and operational flexibility.
For instance, in 2024, while retail deposits formed the bulk of Davivienda's funding, large corporate clients often commanded more tailored pricing structures. This disparity means that while the sheer number of retail customers provides a stable base, the strategic importance and financial clout of major corporate accounts demand careful relationship management and competitive offerings.
- Retail Customers: High volume, low individual bargaining power, sensitive to general market conditions and pricing.
- SME Customers: Moderate volume, increasing bargaining power as size and complexity grow, seeking tailored solutions.
- Large Corporate Clients: Low volume of relationships but high transaction values, significant bargaining power, demanding customized services and preferential terms.
Availability of Alternative Channels
The increasing availability of alternative channels significantly bolsters customer bargaining power for Banco Davivienda. The proliferation of digital banking, mobile applications, and online platforms allows customers to conduct transactions and manage their finances with greater convenience, often bypassing traditional branch networks entirely. This enhanced accessibility and expanded choice empower customers to readily compare offerings and switch providers if Davivienda fails to meet their digital expectations. For instance, in Colombia, the rapid adoption of digital financial services, with a significant portion of the population now utilizing mobile banking, means customers have more leverage than ever to seek out the best digital experience.
Customers can now easily compare fees, interest rates, and service quality across multiple financial institutions, all accessible through their smartphones or computers. This ease of comparison directly translates into increased bargaining power, as banks like Davivienda must remain competitive in their digital offerings to retain their customer base. The growing digital ecosystem means that a bank’s physical presence is less of a barrier to entry for new competitors, further intensifying this dynamic.
- Digital Channel Adoption: In 2023, over 70% of banking transactions in Colombia were conducted through digital channels, highlighting the critical role of online and mobile platforms.
- Customer Expectations: A significant percentage of Colombian banking customers expect seamless digital onboarding and user-friendly mobile interfaces, with dissatisfaction leading to higher churn rates.
- Competitive Landscape: Fintech startups and neobanks are increasingly leveraging digital-first strategies, offering specialized services and attracting customers who prioritize digital convenience.
- Impact on Switching: The reduced friction in switching providers due to digital accessibility means that banks must continuously innovate their digital offerings to maintain customer loyalty.
The bargaining power of customers for Banco Davivienda is substantial, driven by increasing price sensitivity and easy access to information. In 2024, customers actively compare offerings, making them less tolerant of unfavorable rates or fees. This forces Davivienda to maintain competitive pricing, especially for loan products, as customers will readily switch to institutions like Bancolombia or Grupo Aval if better terms are available.
Customer segmentation also plays a crucial role; while individual retail clients have limited individual leverage, large corporate clients wield significant power due to their transaction volumes, enabling them to negotiate customized solutions and preferential rates. For example, in 2024, corporate accounts often secured more tailored pricing than the general retail market, highlighting the need for Davivienda to cater to these high-value relationships.
| Customer Segment | Transaction Value | Bargaining Power Influence | 2024 Market Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Low to Moderate | High volume, low individual leverage; sensitive to general market conditions. | High adoption of comparison tools, impacting deposit rate sensitivity. |
| SME Customers | Moderate to High | Growing power with increasing size; demand for tailored solutions. | Seeking bundled services and flexible loan terms. |
| Large Corporate Clients | Very High | Significant leverage; ability to negotiate customized services and preferential rates. | Commanding tailored pricing structures and dedicated relationship management. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Banco Davivienda Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Banco Davivienda Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape impacting Davivienda, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the Colombian banking sector. This detailed analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Banco Davivienda faces a competitive landscape in Colombia and Central America populated by several substantial players. For instance, Bancolombia and BBVA Colombia are significant institutions, often engaging in aggressive competition for market share and customer acquisition. Davivienda itself maintains a robust presence, particularly within the retail banking sector, which intensifies the rivalry.
The overall growth rate of the banking sector significantly influences how intensely competitors like Banco Davivienda vie for market share. In slower-growing or more mature markets, competition tends to intensify as banks fight harder for the same pool of customers. This can manifest as aggressive pricing strategies or increased spending on marketing and customer acquisition. For instance, the Colombian banking sector, where Davivienda operates, is anticipated to experience modest growth through 2024 and into 2025.
Banco Davivienda distinguishes itself through a strong emphasis on digital innovation and specialized financial solutions. For instance, its mobile banking app, DaviApp, consistently ranks high for user experience, offering features like biometric login and instant account opening, which sets it apart from competitors relying on more traditional platforms. This focus on digital convenience can significantly reduce direct price competition.
Beyond digital offerings, Davivienda has actively developed niche product lines, such as its pioneering range of sustainable financing options for homes and businesses. These specialized loans, which align with growing environmental consciousness, appeal to a specific customer segment and foster loyalty. In 2024, the bank reported a substantial increase in its green loan portfolio, demonstrating the market's positive reception to these differentiated products.
Superior customer service further bolsters Davivienda's competitive edge. The bank invests heavily in training its staff to provide personalized advice and efficient problem resolution, creating a tangible difference for its clientele. This commitment to service quality helps retain customers, making them less susceptible to switching based solely on minor price differences offered by rivals.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
Banco Davivienda faces competitive rivalry influenced by exit barriers for its competitors. Significant investments in technology, branch networks, and skilled personnel create substantial fixed costs for financial institutions operating in Colombia. These high sunk costs make it difficult for competitors to divest or exit the market without incurring substantial losses.
Furthermore, regulatory requirements and the need to maintain customer trust often tie competitors to their existing operations. The long-term nature of financial services, including mortgage and loan portfolios, also presents a challenge for competitors looking to quickly disengage. This can lead to a situation where even underperforming competitors remain active, intensifying the competitive landscape as they strive to survive.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Colombian banks have invested heavily in physical branches and digital infrastructure, representing millions in sunk costs.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Adhering to stringent financial regulations, such as capital adequacy ratios and anti-money laundering (AML) laws, imposes ongoing expenses that are difficult to abandon.
- Long-Term Customer Commitments: Contracts for mortgages, loans, and other financial products create long-term obligations that hinder rapid market exits.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: The financial services sector relies heavily on reputation; exiting abruptly can damage a brand's long-term standing, impacting future ventures.
Competitive Strategies and Innovation
Competitive rivalry is intense in Colombia's financial sector, with Banco Davivienda facing strong pressure from both traditional banks and emerging fintech players. Competitors are actively pursuing digital transformation, as evidenced by significant investments in mobile banking platforms and online services. For instance, many banks are enhancing their digital offerings to attract younger demographics and improve customer convenience.
Key strategic moves by rivals include launching innovative products and expanding their market reach. This often involves forging partnerships with fintech companies to leverage new technologies and offer specialized services, such as digital lending or payment solutions. Davivienda must remain agile, closely monitoring these advancements to maintain its competitive edge.
The rapid growth of fintech in Colombia means that innovation is a constant factor. Competitors are increasingly focusing on areas like personalized financial advice delivered through AI-powered tools and seamless mobile banking experiences. For example, the Colombian fintech market saw substantial growth in digital payment solutions and online lending platforms throughout 2023 and into early 2024, directly impacting traditional banking models.
- Digital Transformation: Competitors are heavily investing in digital channels and mobile banking to enhance customer experience and reach.
- Fintech Partnerships: Collaboration with fintech firms is a key strategy for rivals to introduce new technologies and specialized financial services.
- Product Innovation: Competitors are launching new products, particularly in areas like digital payments, personal finance management, and tailored credit solutions.
- Market Expansion: Strategic efforts include expanding digital footprints and exploring new customer segments, often through aggressive marketing and competitive pricing.
Banco Davivienda operates in a highly competitive market, characterized by aggressive pricing and innovation from both established banks like Bancolombia and BBVA Colombia, and a growing number of fintech disruptors. This rivalry intensifies during periods of moderate economic growth, such as the anticipated modest expansion of the Colombian banking sector through 2024 and 2025, forcing institutions to fight harder for customer acquisition and retention.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of non-bank digital payment platforms, including mobile wallets and peer-to-peer systems, presents a significant threat of substitution for Banco Davivienda. These services, like Daviplata itself and others such as Nequi, offer streamlined and often lower-cost alternatives for everyday transactions, directly challenging traditional bank-mediated transfers and card payments.
These platforms are increasingly bypassing conventional banking infrastructure, diminishing the necessity for some of Davivienda's core transaction services. For instance, by mid-2024, it's estimated that over 70% of the adult population in Colombia had access to at least one digital payment method, indicating a substantial shift in consumer behavior away from traditional banking channels for simple payments.
The convenience and user-friendliness of these fintech solutions are key drivers of their adoption, attracting a growing segment of users, particularly younger demographics. This trend directly impacts Davivienda's transaction fee income and its ability to maintain customer loyalty for basic financial services, as users opt for more specialized and agile digital payment providers.
The rise of fintech lending platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for Banco Davivienda. Online lenders, crowdfunding, and peer-to-peer services offer alternative financing options for both individuals and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
These digital alternatives often boast quicker application processes and more adaptable loan conditions compared to traditional banking. For instance, by mid-2024, the global fintech lending market was projected to reach over $1.8 trillion, indicating a substantial shift in borrowing behavior.
This increased accessibility and speed directly challenge Davivienda's established lending business. Many SMEs, in particular, are turning to these platforms for faster capital infusion, potentially eroding Davivienda's market share in crucial business segments.
The threat of substitutes for Banco Davivienda's investment and wealth management services is significant and growing. The rise of robo-advisors and online brokerage platforms, such as Robinhood and Wealthfront, offers lower-cost alternatives for individuals seeking to manage their portfolios. These digital solutions are attracting a younger demographic and those comfortable with self-directed investing, potentially diverting billions in assets away from traditional banking channels. For instance, by 2023, the global robo-advisor market was valued at over $30 billion and is projected to reach nearly $200 billion by 2029, indicating a substantial shift in how people approach investment management.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Solutions
The long-term threat posed by cryptocurrencies and blockchain solutions to traditional banking, including Banco Davivienda, warrants careful consideration. These technologies offer alternative pathways for transactions, remittances, and even lending, potentially bypassing established financial intermediaries. Colombia, for instance, has been proactive in developing regulations for crypto assets, indicating a growing recognition of their potential impact.
While still in their early stages, the increasing adoption of digital currencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms could disrupt core banking functions. Consider the potential for peer-to-peer lending or cross-border payments executed via blockchain, which could reduce reliance on traditional banking services.
- Growing Crypto Adoption: Global cryptocurrency adoption rates continue to climb, with an estimated 420 million users worldwide as of early 2024.
- Remittance Alternatives: Blockchain-based remittance services offer significantly lower fees compared to traditional methods, potentially attracting a substantial portion of the global remittance market.
- DeFi Growth: The total value locked in DeFi protocols reached over $100 billion in late 2023, showcasing the increasing scale of decentralized financial activities.
- Regulatory Landscape: As more jurisdictions, like Colombia, establish frameworks for digital assets, the legitimacy and usability of these alternatives are likely to increase.
Informal Financial Networks
Informal financial networks, such as family loans and community savings groups, pose a persistent threat, especially in emerging markets where Banco Davivienda has a significant presence. These alternatives, while lacking technological sophistication, effectively meet fundamental financial needs for a portion of the population, particularly in rural areas. For example, in many Latin American countries, a substantial percentage of the population relies on informal credit for small-scale transactions and emergencies.
The continued existence and even growth of these informal channels are driven by factors like accessibility, speed, and a perceived lack of stringent requirements compared to formal banking. This can divert a segment of potential customers, particularly those with lower incomes or limited credit histories, away from traditional financial institutions. In 2024, it's estimated that informal lending still plays a crucial role in the financial lives of millions across the region, underscoring the competitive pressure they represent.
- Accessibility: Informal networks often require less documentation and are more readily available, especially in underserved regions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While interest rates can vary wildly, some informal arrangements can be perceived as cheaper for small, short-term needs.
- Trust and Social Capital: Loans within families or communities are often based on existing social relationships, bypassing the need for formal credit assessments.
- Niche Market Fulfillment: These networks cater to financial needs not always met by formal banks, such as very small loan amounts or flexible repayment terms.
The threat of substitutes for Banco Davivienda is multifaceted, encompassing digital payment platforms, fintech lending, digital investment services, cryptocurrencies, and informal financial networks. These alternatives often offer greater convenience, lower costs, and faster processing, directly challenging traditional banking services.
By mid-2024, over 70% of Colombia's adult population had access to digital payments, highlighting a significant shift in consumer behavior. The global fintech lending market was projected to exceed $1.8 trillion by mid-2024, indicating substantial competition in financing. Furthermore, the robo-advisor market, valued at over $30 billion in 2023, demonstrates the growing appeal of digital investment solutions.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Davivienda | Market Trend Example (as of mid-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payment Platforms | Streamlined, low-cost transactions | Reduced transaction fee income, customer loyalty erosion | 70%+ adult population in Colombia with digital payment access |
| Fintech Lending | Faster applications, flexible terms | Erosion of market share in lending segments | Global fintech lending market projected >$1.8 trillion |
| Digital Investment Services | Lower fees, self-directed options | Diversion of assets under management | Robo-advisor market valued >$30 billion (2023) |
| Cryptocurrencies & DeFi | Alternative transaction and finance pathways | Potential disruption of core banking functions | DeFi total value locked >$100 billion (late 2023) |
| Informal Financial Networks | Accessibility, speed, fewer requirements | Diversion of potential customers, especially in underserved areas | Persistent reliance in many Latin American countries |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new bank, like Banco Davivienda, is heavily constrained by significant regulatory barriers. These include obtaining extensive licenses and adhering to strict operational guidelines set by financial authorities. For instance, in many Latin American markets, the minimum capital requirements for new banks can range from tens of millions to hundreds of millions of dollars, a substantial upfront investment that deters many potential entrants.
These stringent capital requirements and complex licensing processes serve as a formidable moat for established institutions. They effectively limit the pool of potential competitors to only those with substantial financial backing and the capacity to navigate intricate legal frameworks. This protective barrier ensures that incumbent banks, such as Davivienda, face a less crowded competitive landscape, allowing them to maintain market share and profitability.
Banco Davivienda benefits from decades of building strong brand loyalty and customer trust, a significant barrier for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, Davivienda continued to be recognized as one of the most trusted financial institutions in Colombia, with customer retention rates consistently above 90%.
New players struggle to replicate this deep-seated confidence, as customers often prefer established relationships and proven reliability over the unknown. This ingrained loyalty means potential new entrants must invest heavily in marketing and customer acquisition to even begin to chip away at Davivienda's established customer base.
Established banks like Banco Davivienda benefit significantly from economies of scale, creating a substantial barrier for new entrants. Their vast branch networks, numbering in the hundreds across Colombia, allow for widespread customer reach and lower per-transaction costs. For instance, in 2024, major Colombian banks processed billions of transactions annually, spreading fixed costs like technology infrastructure and compliance over a much larger volume than a startup could manage.
This scale translates into cost advantages in various operational areas, from loan processing to customer service. A new bank would struggle to replicate the efficiency gains Davivienda achieves through its mature systems and large customer base, making it challenging to compete on pricing for services like savings accounts or personal loans. For example, a new entrant might face significantly higher per-customer acquisition and servicing costs compared to an incumbent with an established, optimized infrastructure.
Access to Distribution Channels
New banks and fintech firms face a considerable hurdle in establishing robust distribution networks. Replicating Davivienda's extensive physical presence, which includes a vast network of branches and ATMs across six Latin American countries, is a significant capital and time investment for any new entrant. As of late 2024, Davivienda operates hundreds of branches and thousands of ATMs, offering unparalleled accessibility to its customer base.
The challenge extends to digital platforms as well; building a user-friendly, secure, and widely adopted digital banking experience requires substantial technological investment and marketing reach. Davivienda has invested heavily in its digital offerings, aiming to provide seamless online and mobile banking services. For instance, its mobile app regularly ranks highly for user engagement in its operating markets.
- Significant Capital Outlay: Establishing a physical branch network comparable to Davivienda's requires hundreds of millions of dollars in real estate, staffing, and operational costs.
- Time to Market: Building a trusted brand and widespread physical presence takes years, if not decades, creating a substantial barrier for new competitors.
- Digital Infrastructure Costs: Developing and maintaining sophisticated digital platforms, including robust cybersecurity measures, demands continuous and significant technological investment.
- Customer Inertia: Existing customers are often reluctant to switch from established institutions like Davivienda due to convenience and trust, making customer acquisition a costly endeavor for newcomers.
Technological Infrastructure and Data
The threat of new entrants in the banking sector, particularly concerning technological infrastructure, is significantly shaped by the substantial capital required to build and maintain advanced systems. Established institutions like Banco Davivienda have invested billions over years in sophisticated core banking platforms, robust cybersecurity measures to protect vast customer data, and cutting-edge data analytics capabilities. For instance, a new bank might need to allocate upwards of $500 million to $1 billion for initial technology build-out and ongoing upgrades, a figure that poses a considerable hurdle for aspiring players.
New entrants face the challenge of replicating the deep technological integration and data insights that incumbents like Davivienda have cultivated. This includes not only the initial setup costs but also the continuous investment in innovation and maintenance to stay competitive. As of 2024, major banks are dedicating substantial portions of their IT budgets to areas like AI-driven fraud detection and personalized customer experiences, further raising the bar for new entrants.
While the initial barrier is high, Open Finance initiatives are beginning to democratize access to customer data, potentially easing some of these entry barriers. However, translating this accessible data into actionable insights and integrated services still requires significant technological prowess and investment. For example, regulatory mandates for data sharing, while beneficial for competition, do not eliminate the need for a new entrant to develop its own analytical and operational infrastructure to leverage this data effectively.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants require substantial upfront capital to establish secure, scalable technological infrastructure, including core banking systems and advanced data analytics.
- Incumbent Data Advantage: Established banks like Davivienda possess vast, proprietary customer data, offering a significant competitive edge in personalization and risk assessment.
- Cybersecurity Costs: Meeting stringent cybersecurity standards and protecting sensitive financial data necessitates continuous, high-level investment, presenting a major cost for new players.
- Open Finance Evolution: While Open Finance initiatives enhance data accessibility, they do not negate the need for new entrants to build their own sophisticated technological and analytical capabilities to compete.
The threat of new entrants for Banco Davivienda is significantly mitigated by high regulatory barriers and substantial capital requirements. Obtaining banking licenses and complying with stringent financial regulations in markets like Colombia and Central America demands significant investment and expertise. For instance, in 2024, many Latin American countries maintained minimum capital requirements for new banks well into the tens of millions of dollars, creating a considerable hurdle.
Established brand loyalty and trust, cultivated over decades, also act as a powerful deterrent. Customers of Banco Davivienda, as evidenced by its consistent high customer retention rates, often prefer the reliability of an incumbent. In 2024, Davivienda's customer loyalty remained a cornerstone, with many clients demonstrating a strong preference for established relationships over newer, unproven entities.
Economies of scale achieved by Davivienda, through its extensive branch network and high transaction volumes, create cost advantages that are difficult for new entrants to match. This scale allows for lower per-unit costs in operations and service delivery. For example, in 2024, major banks processed billions of transactions, spreading substantial fixed costs over a much larger base than any new competitor could initially achieve.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Davivienda's Position | Example Data (2024) |
| Regulatory Requirements | Licenses, compliance, capital minimums | High initial investment, complex navigation | Established compliance infrastructure | Minimum capital requirements often $50M+ |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Customer preference for established names | High customer acquisition costs | Decades of relationship building | Customer retention >90% |
| Economies of Scale | Cost efficiencies from large operations | Higher per-unit costs for newcomers | Extensive branch/ATM network, high transaction volume | Billions of transactions processed annually |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Banco Davivienda leverages a comprehensive approach, drawing data from financial reports, industry-specific market research, and economic indicators. This ensures a robust understanding of competitive dynamics within the banking sector.
