CSW Industrials Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CSW Industrials Bundle
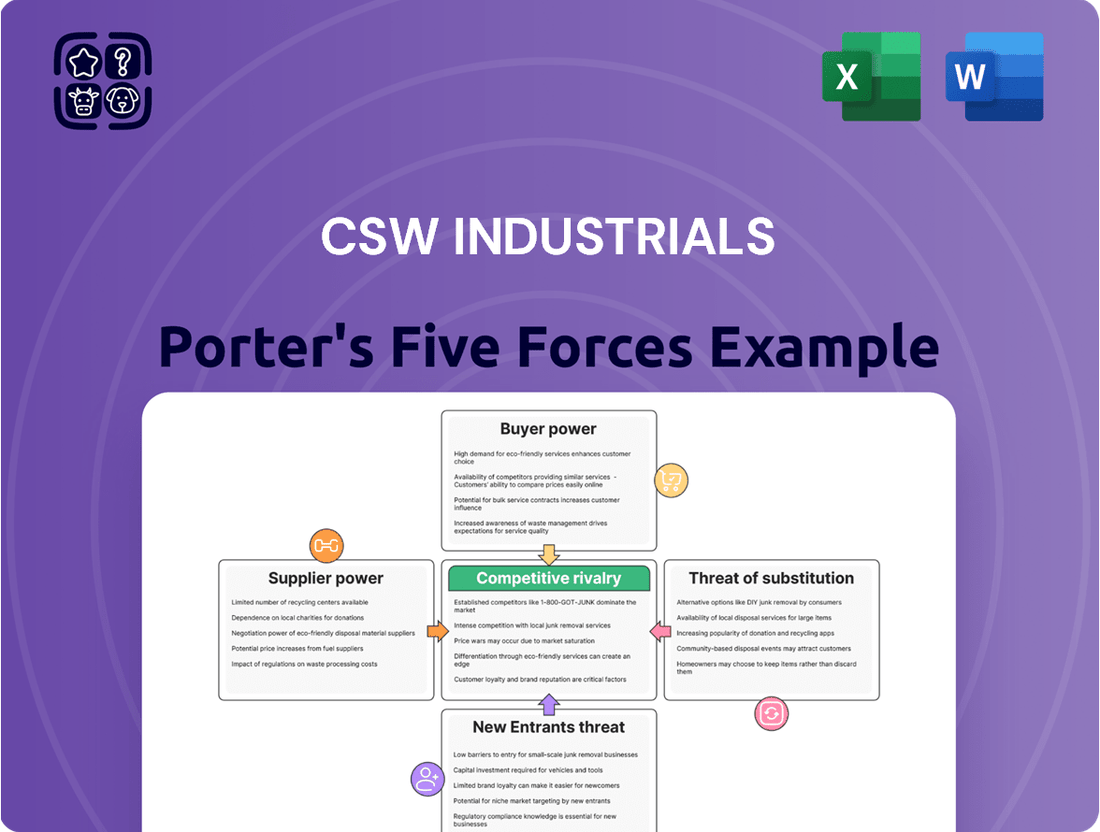
CSW Industrials operates within a landscape shaped by the bargaining power of its buyers and suppliers, the intense rivalry among existing competitors, and the ever-present threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic decision-making.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CSW Industrials’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CSW Industrials operates in diverse industrial sectors, including specialty chemicals and engineered products. A concentrated supplier base for critical raw materials or highly specialized components can significantly amplify supplier bargaining power. For instance, if a few key suppliers dominate the market for a unique chemical compound essential to CSWI's manufacturing processes, those suppliers can dictate terms, impacting CSWI's cost structure and production schedules.
CSW Industrials (CSWI) manufactures specialized industrial products, meaning the uniqueness of its inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. If the raw materials or components CSWI needs are proprietary, patented, or have a very limited number of suppliers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This scarcity restricts CSWI's options, making it harder to negotiate favorable terms or switch to alternative providers, thereby increasing costs and potentially impacting production schedules.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CSW Industrials is significantly influenced by switching costs. If CSW Industrials faces high expenses or considerable operational disruption when moving from one supplier to another, those suppliers gain leverage. This is especially true for specialized components where integration is deep.
For instance, if a supplier provides highly engineered solutions that require extensive retooling of CSW Industrials' manufacturing lines or necessitates costly re-certification processes for their products, the supplier's bargaining power increases. These substantial switching costs can make it prohibitive for CSW Industrials to seek alternative suppliers, thereby strengthening the supplier's position.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into CSW Industrials' product lines represents a significant leverage point. If a key supplier possesses the manufacturing capabilities and sees a strategic advantage, they could begin producing the specialized industrial products that CSW currently offers. This would transform a supplier into a direct competitor, thereby increasing their bargaining power substantially.
While forward integration by suppliers is not a universal concern for all industrial firms, its potential impact on CSW Industrials cannot be ignored. For instance, if a supplier of specialized metal components, a critical input for many of CSW's products, were to develop its own assembly and finishing operations, it could directly challenge CSW's market position. This scenario would allow the supplier to capture more of the value chain, potentially dictating terms or even absorbing CSW's customer base.
- Potential for Supplier Competition: Suppliers might enter CSW's market by producing similar industrial goods.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: This direct competition would give suppliers greater power over CSW.
- Value Chain Capture: Suppliers could aim to control more of the production and sales process.
Importance of CSWI to Supplier
The significance of CSW Industrials to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining the bargaining power of those suppliers. If CSW Industrials constitutes a minor fraction of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier might have less incentive to negotiate favorable terms or pricing for CSWI. This is because the supplier's revenue stream is not heavily reliant on CSW Industrials.
Conversely, if CSW Industrials is a substantial client for a supplier, the supplier's bargaining power diminishes. This reduced power stems from the supplier's increased dependence on CSWI for a significant portion of their business. In such scenarios, suppliers are often more amenable to offering competitive pricing and accommodating terms to retain CSWI as a customer.
For instance, if a key supplier's 2024 financial reports indicate that CSW Industrials accounted for only 2% of their total revenue, their leverage over CSWI would be considerable. However, if CSWI represented 15% of that same supplier's revenue in 2024, the supplier would be more motivated to maintain a positive relationship and be more flexible on pricing or delivery schedules.
- Supplier Dependence: A supplier's reliance on CSW Industrials for revenue directly impacts their leverage.
- Revenue Share: If CSWI is a small customer, suppliers have more power to dictate terms.
- Customer Significance: When CSWI is a major client, its purchasing volume reduces supplier power.
- 2024 Financial Impact: Examining 2024 revenue breakdowns can quantify this supplier dependence.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CSW Industrials is amplified when they provide unique or specialized inputs, as this limits CSWI's alternatives. High switching costs, whether financial or operational, further strengthen a supplier's position. Additionally, the threat of suppliers integrating forward into CSW's product markets can significantly increase their leverage.
For example, if a supplier of specialized adhesives, critical for CSWI's engineered products, holds patents on key formulations, their bargaining power is substantial. If CSWI's 2024 annual report highlights significant investment in custom-engineered components from a single supplier, this suggests high switching costs and thus increased supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on CSWI | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Uniqueness | High leverage for suppliers | Patented chemical compounds essential for CSWI's specialty coatings. |
| Switching Costs | Increased supplier power | Significant retooling costs for CSWI if changing a supplier of precision-machined parts. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for direct competition | A supplier of metal stampings developing their own finished industrial assemblies. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a deep dive into the competitive landscape surrounding CSW Industrials, examining the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the impact of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
CSW Industrials benefits from serving a wide array of end markets, including HVAC/R, plumbing, general industrial, and energy. This broad reach means that the company isn't overly reliant on any single sector for its sales.
A highly fragmented customer base is a significant advantage. Because no single customer represents a large chunk of CSWI's revenue, the bargaining power of any one customer is inherently diminished. For instance, in 2023, CSW Industrials reported net sales of $876.9 million, spread across numerous clients, preventing any one from wielding substantial influence.
In mature industrial markets, like those CSW Industrials (CSWI) operates in, customers often exhibit high price sensitivity, particularly for products that have become more standardized. This sensitivity is amplified when CSWI's offerings represent a substantial portion of a customer's overall expenses, leading them to actively seek out the best pricing. For instance, in 2024, the automotive sector, a key market for industrial suppliers, faced ongoing cost pressures, making buyers more inclined to negotiate aggressively on component prices.
The availability of substitutes significantly influences CSW Industrials' customer bargaining power. If customers can easily switch to alternative products or solutions offered by competitors, or even develop those solutions themselves, their leverage increases. For instance, in the HVAC sector where CSW Industrials operates, the presence of numerous manufacturers offering similar ventilation and air movement products means customers have a wide array of choices, enhancing their ability to negotiate prices and terms.
Switching Costs for Customers
If it's expensive or complicated for customers to switch from CSW Industrials' offerings to a competitor's, their ability to demand lower prices or better terms is diminished. These switching costs can include expenses related to re-engineering products, obtaining new certifications, or training personnel to use a different supplier's solutions.
CSW Industrials' emphasis on delivering strong performance, unwavering reliability, and competitive value is a strategic approach designed to foster customer loyalty and increase the perceived cost of switching. This focus aims to create what is often referred to as customer "stickiness."
For example, in the industrial sector, switching a critical component supplier can involve extensive re-testing and validation processes. If CSW Industrials' products meet stringent industry standards, like those in aerospace or defense, the cost and time to qualify an alternative supplier can be substantial, thereby reducing customer bargaining power.
- Reduced Switching Costs: High switching costs inherently limit a customer's ability to easily move to a competitor, thereby weakening their bargaining leverage.
- Investment in Performance and Reliability: CSW Industrials' commitment to performance and reliability directly contributes to higher switching costs by embedding their products deeply into customer operations.
- Value Proposition: The combination of performance, reliability, and value creates a compelling reason for customers to remain with CSW Industrials, even if competitors offer slightly lower prices.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of customers integrating backward, meaning they start producing the specialized industrial products themselves, poses a significant challenge to CSW Industrials. This is particularly true for large, well-resourced customers who possess the technical expertise to replicate CSWI's offerings.
For instance, major automotive manufacturers or large aerospace contractors, who are key clients for many industrial suppliers, often have the capital and engineering talent to develop in-house manufacturing capabilities for certain components. This can directly reduce their need to purchase from CSWI, thereby diminishing CSWI's pricing power.
- High Customer Concentration: If CSWI relies heavily on a few large customers, the bargaining power of those customers increases significantly.
- Customer Technical Sophistication: Customers with advanced R&D and manufacturing capabilities are more likely to consider backward integration.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers will weigh the cost of internal production against the price and quality offered by CSWI.
- Industry Trends: Observing whether competitors' major clients are bringing production in-house can signal a growing threat.
CSW Industrials benefits from a fragmented customer base, meaning no single client holds significant sway. In 2023, with net sales of $876.9 million, this broad customer distribution inherently limits the bargaining power of any individual buyer.
Customers in mature markets like HVAC/R and general industrial often seek competitive pricing, especially when CSWI's products represent a notable portion of their costs. For instance, in 2024, the automotive sector continued to face cost pressures, making buyers more aggressive in price negotiations.
The availability of substitutes and the ease with which customers can switch suppliers directly impact their leverage. In the HVAC sector, numerous competitors offering similar products empower customers to negotiate favorable terms.
CSW Industrials mitigates this by focusing on performance, reliability, and value, which increases switching costs for customers. For example, in industries with strict certifications, like aerospace, the expense and time to re-qualify a new supplier can be substantial, thus reducing customer bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on CSWI | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers individual customer power | 2023 Net Sales: $876.9 million, spread across many clients. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases customer power | 2024 automotive sector cost pressures encourage aggressive price negotiation. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer power | Numerous HVAC product manufacturers offer alternatives. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | High costs to re-engineer or re-certify products with new suppliers. |
Same Document Delivered
CSW Industrials Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CSW Industrials Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial products and solutions markets CSW Industrials operates within exhibit diverse growth trajectories. High-growth areas, such as the smart HVAC controls sector, which saw a global market size of approximately $6.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% through 2030, generally experience less intense competitive rivalry. This is because ample market opportunity allows multiple players to expand without directly cannibalizing each other's market share.
Conversely, segments experiencing slower growth or those considered mature can foster more aggressive competition. In these markets, companies often fight harder for every percentage point of market share, potentially leading to price wars or increased marketing spend. For instance, certain traditional specialty chemical markets might see slower growth, intensifying the battle for existing customers.
CSW Industrials competes in markets populated by significant, well-established players. This includes giants such as 3M, Honeywell, ITW, Stanley Black & Decker, and Parker Hannifin, all of which possess substantial market share and resources.
The presence of numerous competitors of comparable size and capability intensifies rivalry. These companies actively compete for the same customer segments, often leading to price pressures and increased marketing efforts as they strive to gain or maintain market position.
For instance, in the industrial adhesives and sealants market, where CSW Industrials has a presence, major competitors like 3M and Henkel reported revenues in the tens of billions of dollars in 2023, highlighting the scale of the competitive landscape CSW navigates.
CSW Industrials emphasizes niche, value-added products, aiming to deliver superior performance, reliability, and value to customers. This differentiation strategy is key to mitigating intense rivalry.
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, CSWI reported that its focus on specialized applications and quality in segments like HVAC and building solutions allowed it to command premium pricing, thereby reducing direct price competition with broader market players. The company's commitment to innovation, evidenced by its investment in R&D, further strengthens this differentiation.
However, if competitors manage to replicate CSWI's product features or if market demand shifts towards more standardized offerings, the products could become commoditized. This would likely lead to increased price-based competition, impacting profit margins and intensifying the rivalry within its operating segments.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry within the industrial sector. When it's difficult or costly for companies to leave a market, they tend to stay and compete, even if profitability is low. This persistence intensifies the struggle for market share among existing players.
For diversified industrial firms like CSW Industrials, asset specificity is a key exit barrier. Specialized machinery or facilities designed for a particular product line are hard to repurpose or sell, trapping capital and incentivizing continued operation. For instance, in 2024, many industrial manufacturers faced challenges divesting specialized production lines due to a lack of secondary market buyers for highly customized equipment.
- Asset Specificity: Industrial companies often invest in highly specialized assets that have limited alternative uses, making them difficult to sell or redeploy.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing commitments to customers or suppliers can create obligations that prevent a swift exit from the market.
- Emotional Attachment: While less quantifiable, the personal investment and history associated with a business can also act as an emotional barrier to closure.
- Government or Social Pressures: In some regions, there might be pressure to maintain employment or operations, further hindering exits.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
The strategic objectives of CSW Industrials' competitors significantly shape the competitive rivalry within the sector. When rivals prioritize aggressive market share expansion, rapid new product development, or a price leadership strategy, the intensity of competition naturally escalates. This means CSWI must constantly adapt its own plans, which currently include strategic acquisitions and a strong focus on product innovation, to counter these moves.
For instance, if a major competitor like Stanley Black & Decker (SWK) announces a significant capital expenditure aimed at increasing production capacity by 15% in 2024, this signals an intent to capture greater market share, directly impacting CSWI's growth prospects. Similarly, if Apex Tool Group launches a suite of new, technologically advanced tools, it forces CSWI to accelerate its own R&D and product launch timelines.
- Competitor Focus on Market Share: If competitors aim to increase their market share, it can lead to price wars or increased marketing spend, impacting CSWI's profitability.
- Competitor Focus on Innovation: A competitor's emphasis on new product development forces CSWI to invest more in R&D to maintain its competitive edge.
- Competitor Focus on Cost Leadership: If rivals pursue cost leadership, they might offer lower prices, putting pressure on CSWI's pricing strategies.
CSW Industrials operates in markets with a mix of growth rates, influencing competitive intensity. High-growth segments like smart HVAC controls, valued at $6.5 billion in 2023 and projected to grow over 12% annually, tend to have less fierce rivalry as opportunities abound. Conversely, mature markets can see heightened competition as players vie for existing market share, potentially leading to price wars.
The company faces formidable competition from large, established players such as 3M, Honeywell, and ITW, all possessing significant resources and market presence. This landscape is further complicated by numerous competitors of similar size, leading to intensified rivalry characterized by price pressures and increased marketing efforts to secure or maintain market positions.
CSW Industrials differentiates itself through niche, value-added products emphasizing performance and reliability, a strategy supported by its fiscal year 2023 focus on specialized HVAC and building solutions, allowing for premium pricing. However, the risk of product commoditization through competitor replication or market shifts towards standardization could escalate price-based competition and impact profit margins.
High exit barriers, such as asset specificity and long-term contracts common in the industrial sector, compel companies to remain competitive even in less profitable conditions. For instance, in 2024, many industrial firms struggled to divest specialized equipment, reinforcing ongoing competition.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Market Segments |
|---|---|---|
| 3M | $34.4 billion | Adhesives, Industrial Products |
| Honeywell | $36.7 billion | HVAC Controls, Building Solutions |
| ITW | $16.2 billion | Specialty Products, Industrial Components |
| Stanley Black & Decker | $16.0 billion | Tools, Industrial Equipment |
| Parker Hannifin | $15.8 billion | Motion & Control Technologies |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for CSW Industrials is significant, as customers can often find alternative products or technologies to meet their needs. For instance, in the HVAC/R sector, advancements in energy-efficient systems or the rise of smart home technologies could offer viable replacements for CSW's traditional offerings. In 2023, the global smart home market was valued at approximately $103.9 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a strong substitute trend.
Similarly, within specialty chemicals, the emergence of novel formulations or environmentally friendly alternatives presents a direct substitute threat. The demand for sustainable chemicals is rising; for example, the bio-based chemicals market reached an estimated $110 billion in 2023, showcasing a clear shift towards greener options that could impact CSW's market share.
Customers will readily shift to alternative solutions if those alternatives offer a more attractive combination of price and performance. For CSW Industrials (CSWI), this means if a competing product is substantially less expensive or delivers superior functionality, such as improved energy efficiency or greater durability, the threat posed by substitutes intensifies significantly.
In 2024, the industrial components market saw continued innovation in material science and manufacturing processes. For instance, advancements in composite materials have allowed some competitors to offer lighter, stronger alternatives to traditional metal components, potentially impacting CSWI's market share if these substitutes provide a compelling price-performance advantage.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives significantly impacts CSW Industrials. Factors such as established brand loyalty, the perceived risk associated with new solutions, and the simplicity of transitioning all play a part. For instance, in 2024, a survey indicated that 35% of industrial equipment buyers were willing to consider new suppliers if the cost savings were substantial, highlighting a degree of openness to substitution.
Technological Advancements
Rapid technological advancements in CSW Industrials' end markets, such as HVAC/R and plumbing, present a significant threat of substitutes. Innovations like smart plumbing technology and the increasing integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) can quickly introduce alternative solutions that bypass traditional product offerings. For instance, the smart home market, which heavily influences plumbing and HVAC, saw global revenue reach approximately $100 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% through 2030, indicating a fast-evolving landscape where new substitute technologies can emerge rapidly.
CSWI must therefore maintain a proactive stance on innovation to remain competitive. Failing to keep pace with these technological shifts could lead to market share erosion as consumers and businesses adopt newer, potentially more efficient or feature-rich substitute products. The company's ability to integrate similar smart technologies or offer complementary solutions will be crucial in mitigating this threat.
Key areas where substitutes are emerging include:
- Smart Water Leak Detection Systems: These can reduce the need for traditional plumbing components by offering early warnings and automated shut-offs.
- Energy-Efficient HVAC Alternatives: Advancements in heat pump technology and geothermal systems offer substitutes for traditional furnace and air conditioning units.
- IoT-Enabled Building Management Systems: These integrated systems can control and optimize plumbing and HVAC functions, potentially reducing reliance on individual component manufacturers.
Regulatory Changes and Environmental Concerns
New environmental regulations are a significant threat. For instance, the phasedown of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) in HVAC systems, as mandated by international agreements like the Kigali Amendment, directly encourages the adoption of alternative refrigerants or entirely new cooling technologies. This regulatory pressure can rapidly shift market demand away from established products.
The growing global emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly solutions further amplifies this threat. Consumers and businesses alike are increasingly seeking out products and services that align with environmental concerns, pushing demand towards alternatives that offer lower carbon footprints or are manufactured using more sustainable practices. By 2024, the market for green building materials, for example, has seen substantial growth, indicating a clear consumer preference for environmentally conscious options.
- Regulatory Pressure: Mandates like the HFC phasedown create an immediate need for substitute refrigerants and systems.
- Sustainability Demand: Consumer and corporate focus on eco-friendly alternatives drives innovation and adoption of substitutes.
- Market Shift: Environmental regulations can quickly alter market share by making older technologies less viable.
- Innovation Driver: The threat of regulation spurs the development of new, greener substitute products and services.
The threat of substitutes for CSW Industrials is considerable, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer preferences. For example, in the HVAC/R sector, smart home integration and energy-efficient alternatives pose a direct challenge. The global smart home market, valued at approximately $103.9 billion in 2023, demonstrates a strong substitute trend.
In specialty chemicals, the rise of bio-based and sustainable formulations presents another significant substitute. The bio-based chemicals market reached an estimated $110 billion in 2023, highlighting a clear shift towards greener options that could impact CSW's market position.
Customer willingness to switch is influenced by price and performance. If substitutes offer substantially lower costs or superior functionality, like enhanced energy efficiency, the threat intensifies. In 2024, industrial buyers showed a willingness to consider new suppliers for significant cost savings, with 35% open to alternatives.
Rapid technological shifts, such as IoT in plumbing and HVAC, create new substitute solutions. The smart home market's projected growth, with a CAGR over 10% through 2030, indicates a dynamic landscape where new technologies can quickly emerge as substitutes.
| Market Segment | Substitute Trend Example | Market Value (Approx.) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Home Technology (HVAC/R Influence) | Smart thermostats, integrated building management systems | $103.9 billion | 2023 |
| Specialty Chemicals | Bio-based and sustainable chemical formulations | $110 billion | 2023 |
| Industrial Components | Advanced composite materials | N/A (Innovation Trend) | 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the diversified industrial products market, particularly in areas like specialized chemicals and engineered solutions, demands substantial upfront capital. New players often need to invest heavily in state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, robust research and development capabilities, and extensive distribution channels. For instance, establishing a new chemical production facility can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, deterring many potential entrants.
CSW Industrials benefits significantly from economies of scale, particularly in its manufacturing and supply chain operations. For instance, in 2024, the company's substantial production volumes allowed for lower per-unit manufacturing costs compared to smaller, less established players. This cost advantage in production, coupled with bulk purchasing power for raw materials, creates a substantial barrier for any new entrant attempting to enter the market and match CSW's competitive pricing.
CSW Industrials benefits from its extensive portfolio of over 100 established brand names, fostering significant brand loyalty among its customer base. This deep-seated trust, built over years, makes it challenging for new entrants to attract customers away from familiar and reliable products. For instance, in the HVAC sector, a core market for CSW, brand perception plays a crucial role in contractor and end-user purchasing decisions.
Access to Distribution Channels
CSW Industrials benefits significantly from its established wholesale distribution network, a critical asset in the HVAC/R, plumbing, and general industrial sectors. Newcomers would find it difficult to replicate this reach, as securing shelf space and reliable partnerships with distributors is a major hurdle.
Gaining access to these vital channels requires substantial investment and time, creating a significant barrier for potential competitors looking to enter CSWI's markets. For instance, in 2024, the wholesale trade sector in the US generated over $5.5 trillion in sales, highlighting the sheer volume and importance of these established networks.
- Extensive Network: CSWI's existing relationships with distributors provide immediate market penetration.
- Cost Barrier: New entrants face high costs to build a comparable distribution infrastructure.
- Market Access: Established channels offer a direct route to a broad customer base, which is hard for new players to achieve.
Proprietary Product Technology and Patents
CSW Industrials' commitment to innovation and its focus on niche, value-added products are key differentiators. The company invests heavily in research and development, leading to proprietary product technologies and a robust patent portfolio. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, CSW Industrials reported approximately $18.5 million in R&D expenses, underscoring this dedication.
These proprietary technologies, coupled with specialized manufacturing processes, act as significant barriers to entry. New competitors would face substantial challenges in replicating CSWI's unique offerings and the expertise required to produce them efficiently. This technological moat makes it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
- Proprietary Technology: CSW Industrials holds numerous patents protecting its unique product designs and manufacturing methods.
- R&D Investment: The company consistently invests in innovation, as evidenced by its $18.5 million R&D spending in FY23.
- Specialized Manufacturing: Complex and specialized production techniques further deter potential entrants.
- Niche Market Focus: CSWI's strategy targets specific, often underserved, market segments where deep technical knowledge is paramount.
The threat of new entrants for CSW Industrials is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, coupled with established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, make it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. CSW's focus on proprietary technologies further solidifies its market position.
In 2024, the sheer scale of investment needed for advanced manufacturing, often in the hundreds of millions for specialized sectors, acts as a substantial deterrent. Furthermore, CSW's 2023 R&D expenditure of $18.5 million highlights a commitment to innovation that new entrants would struggle to match, creating a technological hurdle.
The company's established brand recognition, built over years, fosters customer loyalty that is hard for new players to overcome. This is particularly true in markets like HVAC, where trust in product reliability is paramount. Securing shelf space and partnerships within the wholesale distribution channels, which facilitated over $5.5 trillion in US sales in 2024, presents another formidable challenge for potential entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | CSW Industrials' Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for manufacturing, R&D, and distribution. | Significant financial hurdle. | Economies of scale in production and purchasing power. |
| Brand Loyalty | Customer trust built over time with established brands. | Difficult to attract customers away from known products. | Portfolio of over 100 established brand names. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to established wholesale networks. | Challenging to replicate reach and secure partnerships. | Extensive and well-established distribution infrastructure. |
| Proprietary Technology | Unique product designs and manufacturing processes protected by patents. | Difficult to replicate unique offerings and expertise. | Strong patent portfolio and consistent R&D investment ($18.5M in FY23). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CSW Industrials Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and economic databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
