Corebridge Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Corebridge Financial Bundle
Corebridge Financial operates within a dynamic insurance landscape, facing pressures from rivals, potential new entrants, and the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Corebridge Financial’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The financial services sector, including companies like Corebridge Financial, is becoming more reliant on specialized FinTech firms for essential technology, software, and data analysis. This reliance can shift power to these suppliers if they are few in number and offer critical, hard-to-replace solutions.
For instance, if only a handful of companies provide advanced AI-driven risk assessment tools or secure cloud infrastructure crucial for Corebridge's operations, these few providers can dictate terms and pricing. This concentration of key technology providers directly amplifies their bargaining power.
Corebridge Financial's reliance on reinsurance, exemplified by its significant modified coinsurance agreement with Fortitude Reinsurance Company Ltd., highlights the substantial bargaining power suppliers in this sector can wield. These partnerships are fundamental for managing the risk associated with Corebridge's long-term structured settlements portfolio.
The specialized nature and substantial scale required for such reinsurance arrangements mean that a select group of reinsurers can command considerable influence. The terms and availability of reinsurance directly affect Corebridge's capital efficiency and overall risk management strategy, underscoring the suppliers' leverage.
Switching costs for Corebridge, particularly concerning its core technology platforms, data providers, and significant reinsurance partners, are substantial. These expenses aren't limited to direct financial outlays; they encompass the potential for operational disruption, the complexities of data migration, and the necessity of retraining staff on new systems and processes.
For a major financial institution like Corebridge, these high switching costs effectively increase the bargaining power of its existing suppliers. This means suppliers can potentially demand more favorable terms, knowing that Corebridge faces significant hurdles and expenses if it decides to seek alternatives.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for Corebridge Financial. While the financial services industry broadly offers many options, highly specialized inputs such as proprietary actuarial software, advanced data analytics platforms, or unique investment management systems may have few, if any, readily available substitutes. For instance, if a particular data analytics provider offers a unique algorithm that is crucial for Corebridge's risk assessment models, and no other vendor can replicate its functionality, that supplier holds considerable leverage. This lack of alternatives means Corebridge has limited options if the supplier decides to increase prices or alter terms.
The degree to which Corebridge can easily switch suppliers for essential operational components directly impacts supplier power. If finding alternative providers for critical technologies or specialized services is difficult and time-consuming, existing suppliers are empowered. The uniqueness or proprietary nature of a supplier's offering is a key driver of this leverage. For example, in 2024, the market for AI-driven underwriting tools is still maturing, meaning a firm providing a cutting-edge, proven solution could command higher prices due to limited competition and the specialized expertise required.
- Limited Substitutes: Specialized actuarial software or unique data analytics platforms often lack direct, easily accessible alternatives in the financial services sector.
- Supplier Leverage: If Corebridge cannot readily find alternative suppliers for essential operational components, existing suppliers gain increased bargaining power.
- Proprietary Offerings: The uniqueness or proprietary nature of a supplier's product or service strengthens their negotiating position.
- Impact on Corebridge: A lack of substitutes can lead to higher costs or less favorable terms for Corebridge, affecting profitability and operational efficiency.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a notable risk to Corebridge Financial. If critical technology or data providers were to bypass Corebridge and offer retirement and insurance solutions directly to consumers, their leverage would escalate considerably. This scenario, though perhaps less probable for highly specialized tech firms, remains a possibility, especially if these suppliers form alliances with Corebridge's rivals.
This potential for suppliers to move into Corebridge's market space necessitates a proactive approach. Corebridge must cultivate robust supplier relationships and potentially allocate resources towards developing its own proprietary technologies and data capabilities. For instance, in the broader financial services sector, companies that have successfully integrated backward (e.g., a bank acquiring a payment processor) often see increased control and reduced costs, highlighting the strategic impact of such moves.
Consider the implications for Corebridge if a key data analytics provider, which might have generated substantial revenue from Corebridge in 2024, decided to launch its own direct-to-consumer wealth management platform. This would not only divert potential revenue streams but also give the supplier greater insight into customer behavior, which could then be used to further disadvantage Corebridge. The company's reliance on external data and technological infrastructure makes this a critical area to monitor and manage.
- Supplier Integration Risk: Key technology or data suppliers could directly offer retirement and insurance solutions, increasing their bargaining power against Corebridge.
- Competitive Alliances: Suppliers might partner exclusively with Corebridge's competitors, creating a significant disadvantage.
- Strategic Necessity: Corebridge needs to maintain strong supplier relationships and invest in proprietary solutions to mitigate this threat.
- Industry Precedents: Forward integration by suppliers is a recognized strategic move that can reshape competitive landscapes in financial services.
Corebridge Financial's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by the availability of substitutes and the switching costs involved. For highly specialized inputs like proprietary actuarial software or advanced data analytics platforms, direct substitutes are often scarce, granting these suppliers significant leverage. In 2024, the market for cutting-edge AI underwriting tools, for instance, saw providers with proven solutions commanding higher prices due to limited competition and the specialized expertise required.
The inability to easily switch providers for critical technologies or specialized services strengthens existing suppliers' negotiating positions. This leverage is amplified when offerings are unique or proprietary, as seen with specialized data analytics providers whose algorithms are crucial for risk assessment models, leaving Corebridge with few alternatives if pricing or terms change.
Suppliers may also pose a threat through forward integration, potentially offering retirement and insurance solutions directly to consumers, which would significantly escalate their bargaining power. This necessitates Corebridge cultivating strong supplier relationships and investing in proprietary technologies to mitigate such risks.
| Factor | Impact on Corebridge | 2024 Data/Example |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low for specialized tech/data, increasing supplier power. | Limited alternatives for unique AI risk assessment tools. |
| Switching Costs | High due to operational disruption, data migration, retraining. | Significant expenses and complexity in changing core platforms. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential threat if suppliers enter Corebridge's market. | Data analytics firms launching direct-to-consumer platforms. |
| Supplier Concentration | Few key FinTech or reinsurance providers can dictate terms. | Reliance on a limited number of specialized reinsurance partners. |
What is included in the product
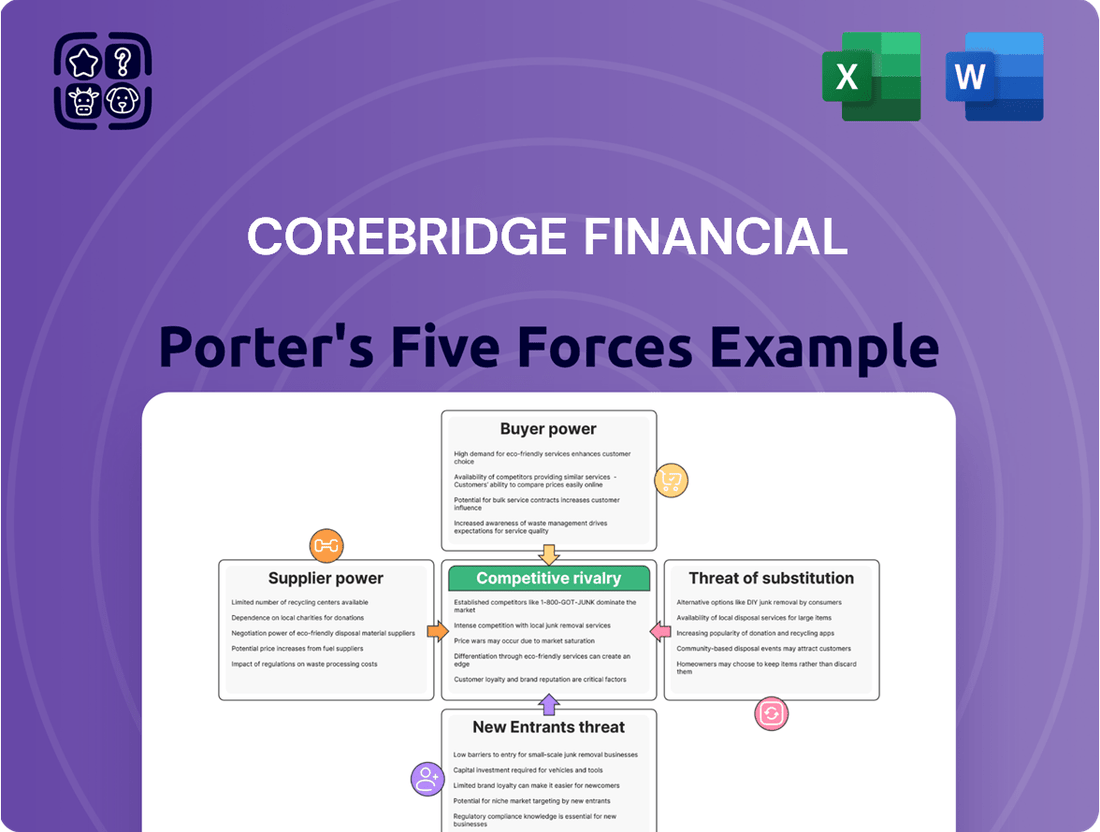
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Corebridge Financial, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the financial services industry.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard, allowing for rapid identification of strategic threats and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Corebridge Financial's broad customer base, encompassing individuals, institutions, and financial professionals, significantly tempers customer bargaining power. This diverse segmentation means no single customer group holds a disproportionate sway over the company's revenue streams, as evidenced by their varied product lines like individual retirement annuities and group retirement plans.
For Corebridge Financial's individual retirement and insurance products, customer switching costs are a significant factor. These can range from moderate to high, often involving surrender charges on existing policies, the administrative hassle of transferring assets, and the general effort required to move accounts. For instance, in 2024, many annuity products still carry surrender charges that can diminish the value of an investment if withdrawn prematurely, making a quick switch to a competitor less attractive purely on price.
These inherent costs do act as a deterrent, making it less likely for customers to switch to rivals solely based on minor price variations. However, the landscape is evolving. The increasing availability of digital tools and enhanced portability features across the industry in 2024 are gradually lowering these barriers, making it easier for customers to compare and move their business if a better offer arises.
Customers and financial professionals now have unprecedented access to information. Online platforms, financial advisors, and comparison tools provide detailed insights into product features, pricing, and historical performance. This heightened transparency directly impacts price sensitivity, especially for financial products that are largely standardized.
For Corebridge Financial, this means a constant need to differentiate beyond just price. In 2024, the average expense ratio for actively managed U.S. equity mutual funds was around 0.70%, a figure that continues to put pressure on providers to demonstrate superior value. Corebridge must focus on innovation and delivering tangible benefits, such as enhanced customer service, unique product offerings, or superior investment strategies, to maintain customer loyalty in such an informed market.
Influence of Financial Professionals and Institutions
Corebridge Financial's extensive distribution network, featuring financial professionals, consultants, and institutional investors, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. These intermediaries represent numerous clients, wielding considerable influence over product choices and pricing negotiations, particularly for large-scale transactions.
For instance, in 2023, the retirement services segment, a key area for Corebridge, saw substantial activity from institutional clients seeking competitive annuity and insurance solutions. The collective demand channeled through these powerful intermediaries can pressure Corebridge to offer more favorable terms.
- Financial Professionals: Act as gatekeepers, influencing client decisions and demanding competitive product features and pricing from providers like Corebridge.
- Institutional Clients: Large retirement plan sponsors or asset managers possess significant leverage due to the volume of business they represent, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms.
- Distribution Networks: The breadth and depth of Corebridge's relationships with broker-dealers and independent marketing organizations allow these entities to aggregate customer demand and negotiate collectively.
- Market Competition: The presence of numerous alternative providers means that intermediaries and their clients can readily switch if Corebridge's offerings are not perceived as competitive.
Availability of Alternative Financial Solutions
Customers seeking long-term financial security and goal achievement have a wide array of alternative solutions available beyond Corebridge Financial's offerings. These include direct investments in stocks and bonds, diverse mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), traditional savings and investment accounts offered by banks, and the option of building self-managed investment portfolios.
The proliferation of these substitutes significantly enhances customer bargaining power. If Corebridge's product terms, fees, or performance are perceived as unfavorable, customers can readily switch to or opt for these alternative financial vehicles, exerting pressure on Corebridge to remain competitive.
- Customer Choice: In 2024, the U.S. investment management industry saw assets under management in ETFs alone reach approximately $7.7 trillion, illustrating the substantial market share accessible to alternative providers.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of low-cost index funds and robo-advisors provides readily accessible and often cheaper alternatives for wealth accumulation compared to some structured products.
- Corebridge's Differentiation: To counter this, Corebridge must clearly articulate the unique advantages of its specialized retirement and insurance solutions, such as guaranteed income streams or estate planning benefits, which may not be replicated by simpler investment products.
The bargaining power of Corebridge Financial's customers is influenced by several factors, including switching costs and the availability of substitutes. While some products have moderate to high switching costs, such as surrender charges on annuities, the increasing ease of comparing offerings via digital tools in 2024 is gradually reducing these barriers. Furthermore, the wide array of alternative investment vehicles, from ETFs to self-managed portfolios, provides customers with significant leverage, pressuring Corebridge to maintain competitive terms and demonstrate unique value propositions.
| Factor | Impact on Corebridge | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High (e.g., surrender charges) | Surrender charges on annuities remain a deterrent, but digital portability is increasing. |
| Customer Information Access | High transparency pressures pricing | Online platforms and advisors offer extensive product comparisons. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Significant leverage for customers | ETFs alone held ~$7.7 trillion in U.S. AUM in 2024, highlighting alternatives. |
| Distribution Networks | Intermediaries amplify customer power | Financial professionals and institutional clients negotiate for better terms. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Corebridge Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Corebridge Financial, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally crafted report you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering no surprises or placeholders. You're viewing the actual, fully formatted analysis, ready for immediate download and use the moment you complete your transaction.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. retirement solutions and insurance market is vast, yet it's characterized by intense competition and a degree of fragmentation. This means Corebridge Financial, despite its size, contends with a multitude of established companies vying for market share across various product offerings.
Corebridge Financial stands as a significant player, overseeing more than $400 billion in client assets as of March 31, 2025. This substantial asset base underscores the competitive landscape Corebridge navigates, facing rivals with diverse strengths and market positions.
Corebridge Financial distinguishes itself with a broad range of products, encompassing individual retirement annuities, group retirement plans, and a variety of life insurance solutions. This diverse portfolio is designed to adapt to evolving customer demands, showcasing a commitment to staying relevant in a dynamic market.
The company's dedication to innovation is evident in new product launches, such as the Corebridge MarketLock® Annuity introduced in October 2024. This move highlights the industry's constant drive to develop enhanced features and benefits, directly fueling competitive rivalry.
Corebridge Financial benefits from a broad distribution network, touching customers directly, and also engaging with consultants, retirement plan sponsors, banks, broker-dealers, and independent agents. This expansive reach is a key differentiator, allowing them to access diverse market segments.
However, this advantage is tempered by the presence of other large financial institutions that also command robust distribution channels. For instance, in 2024, the retirement services market saw significant activity, with major players like Fidelity and Vanguard continuing to invest heavily in their advisor and institutional relationships, directly competing with Corebridge for both client acquisition and the loyalty of financial intermediaries.
Brand Reputation and Financial Strength
Corebridge Financial, post-spin-off from AIG, benefits from a robust financial strength rating, such as an A from AM Best. This is a significant asset in the insurance and retirement services industry, fostering customer trust for long-term financial commitments.
While Corebridge exhibits financial stability, its customer satisfaction scores have shown variability. This presents an opportunity for competitors to differentiate themselves by offering superior customer service and support, potentially attracting clients seeking a more consistent and positive experience.
- Financial Strength: Corebridge Financial holds an A rating from AM Best, underscoring its financial stability and capacity to meet obligations.
- Customer Satisfaction: Mixed customer satisfaction scores suggest a potential vulnerability that rivals can exploit through enhanced service offerings.
- Competitive Advantage: Competitors with higher customer satisfaction may leverage this to gain market share against Corebridge.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Costs
The insurance and retirement sectors are heavily regulated, leading to substantial compliance costs and operational hurdles for companies like Corebridge Financial. This regulatory landscape, while a deterrent for new entrants, intensifies competition among established players who must constantly adapt to evolving legislation. For instance, the SECURE 2.0 Act, enacted in late 2022, introduced numerous changes impacting retirement savings plans, requiring significant investment in updating systems and processes.
This ongoing need to comply with regulations such as those from the SEC and state insurance departments creates a competitive dynamic where firms with established, efficient compliance infrastructures are better positioned. It means that all players, including Corebridge, must allocate resources not just to product development and marketing, but also to ensuring adherence to a complex web of rules. This can favor larger, more established companies that can absorb these costs more readily, thereby influencing the intensity of rivalry.
- Regulatory Burden: Insurance and retirement industries face stringent regulations, increasing operational complexity and costs for all participants.
- SECURE 2.0 Act Impact: Legislation like SECURE 2.0 necessitates continuous adaptation and investment in compliance systems by firms like Corebridge.
- Barrier to Entry: The high cost of regulatory compliance acts as a significant barrier, limiting new competition but intensifying rivalry among existing players.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with robust compliance infrastructure gain an advantage, as they can more effectively navigate and adapt to legislative changes, influencing market share and profitability.
Competitive rivalry within the U.S. retirement solutions and insurance market is fierce, with Corebridge Financial facing numerous established competitors. The market's fragmentation means that while Corebridge is a significant player with over $400 billion in client assets as of March 31, 2025, it must constantly innovate and leverage its broad distribution network to stand out. Competitors like Fidelity and Vanguard, for example, continued substantial investments in their advisor relationships throughout 2024, directly challenging Corebridge's market penetration.
The intensity of this rivalry is further shaped by regulatory environments, such as the SECURE 2.0 Act, which mandates continuous adaptation and investment in compliance. Companies with strong compliance infrastructures, like Corebridge, can navigate these complexities more efficiently, but the overall burden increases operational costs for all, intensifying competition among existing firms.
| Competitor Example | Key Competitive Action (2024) | Corebridge's Counter/Area of Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Fidelity | Increased investment in advisor relationships and digital tools. | Leveraging broad distribution, product innovation (e.g., MarketLock Annuity). |
| Vanguard | Expansion of retirement plan services and low-cost investment options. | Focus on financial strength (A rating from AM Best) and diverse product portfolio. |
| Other Large Insurers (e.g., Prudential, Lincoln Financial) | Product development and marketing campaigns targeting specific segments. | Emphasis on customer service to address potential variability in satisfaction scores. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Individuals and institutions have a significant alternative to Corebridge Financial's offerings by directly managing their retirement savings. This includes investing in a wide array of stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). For instance, the total assets invested in U.S. equity ETFs alone reached approximately $5.6 trillion by the end of 2023, showcasing the scale of this direct investment market.
The increasing ease of access through online brokerage platforms and sophisticated financial planning tools further bolsters these direct investment substitutes. Many platforms now offer commission-free trading and robust research capabilities, making it simpler than ever for investors to build and manage their own portfolios. This accessibility pressures Corebridge to highlight the distinct advantages of its products, such as guaranteed income streams and potential tax deferral benefits, which are not always replicated in direct investment strategies.
Customers have a wide array of alternative savings vehicles beyond Corebridge Financial's formal retirement products. These include tangible assets like real estate, which has seen varied performance, with U.S. home prices increasing by approximately 5.4% year-over-year as of Q1 2024 according to the Federal Reserve. Traditional bank savings accounts and Certificates of Deposit (CDs) also serve as substitutes, offering lower but more liquid returns. For example, the national average savings account APY in early 2024 hovered around 0.46%, while 1-year CD rates were closer to 4.5%.
While these alternatives may not replicate the long-term income guarantees or the specific tax advantages of products like annuities, they represent viable options for wealth accumulation and preservation. The availability of these substitutes pressures Corebridge to effectively communicate the unique value proposition and benefits of its retirement solutions, such as guaranteed lifetime income and tax-deferred growth, to differentiate its offerings in the broader financial landscape.
Many employer-sponsored retirement plans, like 401(k)s, often lack built-in annuity options or guaranteed income features. This means participants primarily depend on their accumulated savings and withdrawal strategies, bypassing the need for a Corebridge annuity to secure retirement income.
The growing adoption of auto-enrollment in these plans, even without embedded annuity benefits, directly competes with Corebridge's standalone retirement income products. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of new 401(k) participants are automatically enrolled, increasing the pool of individuals managing their retirement solely through accumulated assets.
Government-Provided Social Security and Pensions
Government-provided Social Security and pensions represent a significant threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial. For many, Social Security serves as a crucial base for retirement income, and some individuals still benefit from traditional defined-benefit pension plans. While these sources are often not enough to cover all retirement expenses, they fulfill a substantial portion of an individual's income needs, making them direct substitutes for private retirement savings products.
Corebridge's offerings are designed to complement, not replace, these existing government or legacy corporate retirement provisions. In 2024, the Social Security Administration projected that the program would pay out approximately $1.3 trillion in benefits, highlighting its scale as a primary retirement income source for millions of Americans. This substantial government outlay directly competes with the market for private retirement solutions.
- Foundational Income: Social Security and traditional pensions provide a baseline retirement income for many, reducing the perceived need for entirely private solutions.
- Government Payouts: In 2024, Social Security was projected to disburse over $1.3 trillion, demonstrating its significant role in retirement planning.
- Supplement, Not Replace: Corebridge's strategy is to enhance, rather than substitute, these existing public and corporate retirement benefits.
- Market Competition: The existence and scale of these government programs create a competitive landscape for private retirement product providers like Corebridge.
Emerging Fintech Solutions
The increasing prevalence of FinTech firms offering robo-advisors, tailored financial planning applications, and economical investment platforms poses a significant threat of substitution. These digital alternatives provide accessible and often more affordable options for financial guidance and investment management, potentially diminishing reliance on conventional insurance or annuity offerings.
Corebridge is actively addressing this by introducing enhanced digital interfaces for its plan participants. For instance, as of 2024, the digital advice market is projected to manage trillions of dollars in assets, demonstrating the scale of this competitive shift.
- Robo-advisors offer automated, algorithm-driven investment management.
- Personalized financial planning apps provide customized budgeting and savings tools.
- Low-cost investment platforms enable easier access to diversified portfolios with reduced fees.
The threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial is substantial, as individuals can directly manage their retirement savings through various investment vehicles like ETFs, which saw approximately $5.6 trillion in assets by the end of 2023. Online platforms further simplify this, offering commission-free trading and research, making direct investment a compelling alternative that pressures Corebridge to emphasize its unique benefits such as guaranteed income.
Beyond formal retirement products, tangible assets like real estate and traditional savings accounts serve as substitutes, with U.S. home prices rising about 5.4% year-over-year in Q1 2024, while savings accounts offered around 0.46% APY. These alternatives, though varying in liquidity and return, compete for wealth accumulation, requiring Corebridge to clearly articulate the value of its tax-deferred growth and lifetime income features.
Government programs like Social Security and legacy pensions also act as significant substitutes. Social Security alone was projected to disburse over $1.3 trillion in benefits in 2024, establishing a foundational income for many that can reduce the perceived need for private retirement solutions. Corebridge's strategy acknowledges this by aiming to complement, rather than replace, these existing provisions.
FinTech innovations, including robo-advisors and personalized financial planning apps, present another layer of substitution. These digital platforms offer accessible and often more affordable financial guidance and investment management, potentially diverting customers from traditional annuity offerings. The digital advice market is projected to manage trillions in assets by 2024, highlighting this competitive shift.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Size/Activity (2023-2024 Data) | Impact on Corebridge |
| Direct Investment (ETFs, Stocks, Bonds) | Self-managed, diverse options, accessible platforms | U.S. Equity ETFs: ~$5.6 trillion (End of 2023) | Reduces need for managed retirement products; emphasizes Corebridge's value proposition |
| Tangible Assets & Savings Accounts | Real estate, bank savings, CDs; varying liquidity and returns | U.S. Home Price Growth: ~5.4% (Q1 2024); Savings APY: ~0.46% (Early 2024) | Competes for wealth accumulation; requires differentiation of Corebridge's benefits |
| Government & Legacy Pensions | Social Security, defined-benefit plans; provide baseline income | Social Security Payouts: ~$1.3 trillion projected (2024) | Fulfills a portion of retirement income needs, reducing reliance on private solutions |
| FinTech Robo-advisors & Apps | Automated advice, personalized planning, low-cost platforms | Digital Advice Market Assets: Trillions projected (2024) | Offers accessible, affordable alternatives to traditional offerings |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance and retirement solutions sector, where Corebridge Financial is positioned, demands considerable capital. This is necessary to maintain solvency, adhere to stringent regulations, and underwrite various products. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, U.S. life insurers reported total admitted assets of $7.4 trillion, highlighting the immense scale of financial resources required.
New companies entering this market must possess substantial financial backing to compete effectively and meet essential regulatory reserve requirements. This high barrier significantly restricts the pool of potential new entrants, thereby protecting established players like Corebridge Financial.
The financial services industry is a minefield of regulations, demanding extensive licensing and adherence to intricate laws like SECURE 2.0. Newcomers must navigate a lengthy and expensive path to secure approvals and build compliant operations, a significant barrier to entry.
Corebridge Financial, having already established its regulatory framework and amassed considerable expertise, is well-positioned to manage these complexities. This existing infrastructure provides a substantial advantage over potential new competitors.
Building brand recognition and trust in financial services, especially for long-term products like retirement and insurance, is a lengthy and costly endeavor. Newcomers find it challenging to quickly establish the credibility and market acceptance that established players enjoy. Corebridge Financial, with its roots in AIG, leverages existing trust and a substantial customer base of 4.4 million policyholders, creating a significant barrier.
Access to Distribution Channels
Corebridge Financial benefits from a vast and well-established distribution network. This includes a wide array of financial professionals, institutional partners, and independent marketing organizations, all vital for customer access.
New companies entering the market face a significant hurdle in replicating this reach. They would need substantial investment to build their own distribution channels or forge strategic alliances, a process that is both costly and time-consuming.
This barrier makes it exceptionally difficult for new entrants to achieve meaningful market share and compete effectively with established players like Corebridge.
- Established Network: Corebridge's access to financial professionals, institutions, and IMOs provides a significant advantage.
- High Entry Costs: New entrants require considerable capital to build or acquire similar distribution capabilities.
- Market Penetration Difficulty: The cost and complexity of distribution make it hard for newcomers to gain traction.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Corebridge Financial, as a major player in the insurance and retirement services sector, leverages significant economies of scale. This scale translates into lower operational costs per policy and more efficient investment management, giving them a pricing advantage. For instance, in 2023, Corebridge reported total assets of $1.4 trillion, a testament to its substantial operational capacity.
New entrants would struggle to match these cost efficiencies. They would need to invest heavily to build comparable scale in areas like claims processing, actuarial analysis, and distribution networks. The experience curve also plays a crucial role; Corebridge has accumulated decades of expertise in risk assessment and product innovation, which further reduces their costs and enhances their product offerings.
- Economies of Scale: Corebridge's vast asset base allows for cost reductions in operations and investment management, leading to more competitive pricing.
- Experience Curve Advantage: Decades of accumulated expertise in risk management and product development provide Corebridge with an efficiency and innovation edge.
- New Entrant Disadvantage: Start-ups face significant cost disadvantages due to the lack of scale and established experience, hindering their ability to compete effectively on price or profitability.
The threat of new entrants for Corebridge Financial is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for solvency and regulatory compliance, with U.S. life insurers holding $7.4 trillion in admitted assets as of Q1 2024. Navigating complex regulations and licensing, such as SECURE 2.0, presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. Building brand trust and an extensive distribution network, which Corebridge leverages through its 4.4 million policyholders and established partnerships, also requires considerable time and investment, further deterring new competition.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High solvency and regulatory capital needs. | Significant financial barrier; requires substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and compliance (e.g., SECURE 2.0). | Costly and time-consuming to establish compliant operations. |
| Brand & Trust | Building credibility in financial services. | New entrants struggle to match established trust and customer bases. |
| Distribution Network | Access to financial professionals and partners. | Replication requires extensive investment and time. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Corebridge Financial leverages data from SEC filings, investor relations reports, and industry-specific market research from firms like LIMRA and Fitch Ratings to assess competitive dynamics.
