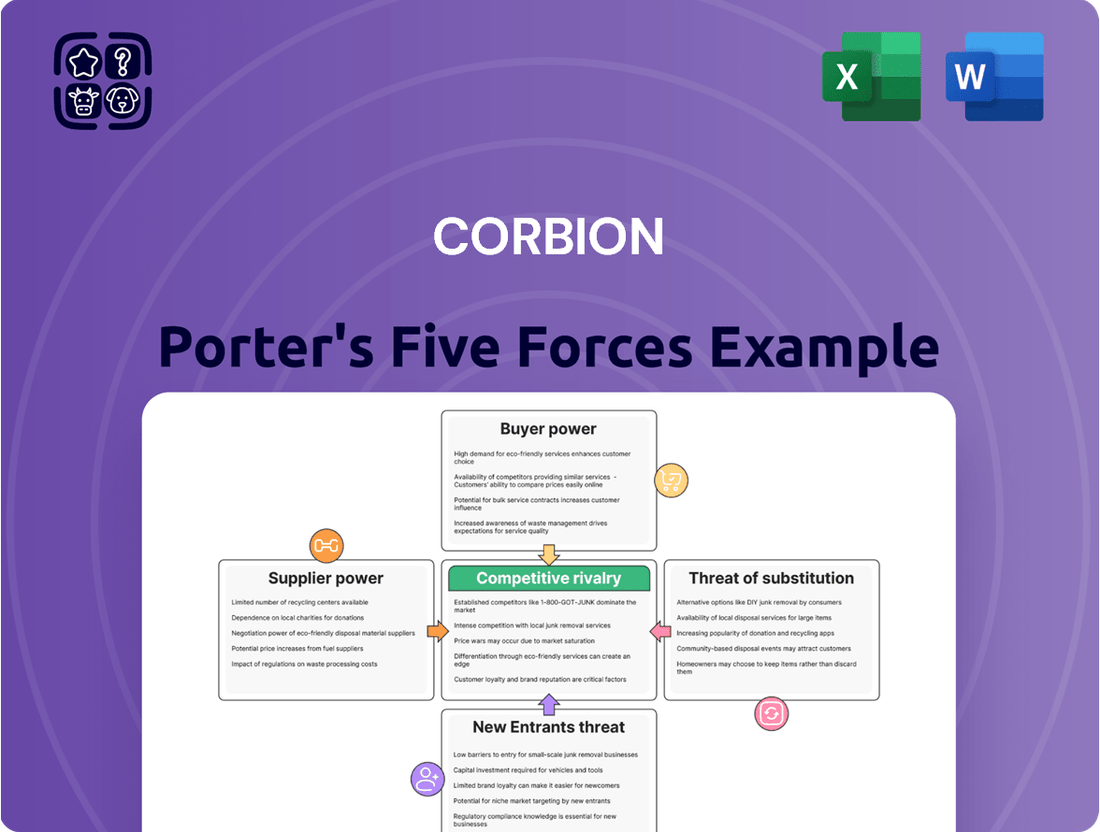
Corbion Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Corbion Bundle
Corbion's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the intense rivalry among existing players to the significant bargaining power of its buyers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this complex market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Corbion’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Corbion's reliance on agricultural inputs like sugarcane, soy, corn, wheat, and palm oil, which make up about 90% of its agricultural raw materials, highlights a key area of supplier bargaining power. The concentration of suppliers for these essential commodities can give them significant leverage.
If there are few suppliers for a critical raw material, or if switching to an alternative source is costly and time-consuming, these suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms. This concentration directly impacts Corbion's cost structure and operational flexibility.
The availability of substitutes for raw materials significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. For instance, Corbion's ability to utilize various agricultural feedstocks like corn, sugarcane, or cassava for lactic acid production means suppliers of any single feedstock have less leverage. This flexibility allows Corbion to shift sourcing based on price and availability, thereby reducing its dependence on any one supplier.
If Corbion encounters significant expenses when shifting from one supplier to another for its specialized bio-based ingredients, such as lactic acid or its derivatives, current suppliers gain leverage. These costs can encompass the rigorous process of qualifying new vendors, retooling production lines to accommodate different material specifications, or ensuring that the quality and consistency of the new ingredients meet Corbion's exacting standards.
Uniqueness or Specialization of Inputs
Suppliers offering highly specialized or unique ingredients, especially for Corbion's advanced bioplastics and biomedical polymers, can wield significant bargaining power. This is because readily available substitutes are scarce. For instance, if a supplier provides a proprietary fermentation strain crucial for Corbion's lactic acid production, their leverage increases substantially.
Corbion's strategic emphasis on innovation and natural ingredients necessitates specific, high-quality inputs. This focus means that suppliers who can consistently deliver these specialized materials, often with unique processing or purity standards, are in a strong position. For example, a supplier of sustainably sourced, high-purity algae for Corbion's algae-based ingredients would command greater influence.
- Specialized Inputs: Corbion's reliance on unique fermentation strains or specific natural extracts for its biopolymer and food ingredient lines grants suppliers of these inputs considerable bargaining power.
- Lack of Alternatives: The absence of readily available substitutes for key specialized ingredients limits Corbion's ability to switch suppliers without incurring significant costs or compromising product quality.
- Innovation Focus: Corbion's commitment to R&D in areas like advanced bioplastics and biomedical polymers means it often requires inputs with very specific, often patented, characteristics, further empowering specialized suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: In 2024, companies in specialty chemical sectors often saw input cost increases of 5-10% due to supply chain constraints and demand for unique materials, a trend likely impacting Corbion's specialized ingredient sourcing.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers of critical raw materials to Corbion possess the potential to integrate forward into producing lactic acid, derivatives, or other bio-based ingredients. This move could significantly enhance their bargaining power, directly impacting Corbion's competitive standing. For instance, a major agricultural producer supplying corn, a key feedstock for Corbion's fermentation processes, could invest in its own lactic acid production facilities.
However, the specialized and proprietary nature of Corbion's advanced fermentation technologies and downstream processing capabilities acts as a substantial barrier to such forward integration. Developing and operating these complex bio-manufacturing processes requires significant technical expertise and capital investment, which many raw material suppliers may lack. This technological moat helps to mitigate the threat.
In 2023, Corbion reported that its cost of goods sold was €827.3 million, highlighting the significant reliance on raw material suppliers. The threat of forward integration is therefore a crucial consideration, as a successful integration by a key supplier could lead to increased input costs or reduced availability of essential materials for Corbion.
- Supplier Integration Risk: If a major supplier of corn or other feedstocks were to integrate forward into lactic acid production, it could disrupt Corbion's supply chain and pricing.
- Technological Barriers: Corbion's proprietary fermentation technology and expertise in downstream processing create a competitive advantage, making it difficult for suppliers to replicate their value chain.
- Market Dynamics: The specialized nature of bio-based ingredients and the stringent quality requirements in end markets like food and pharmaceuticals further complicate potential supplier integration efforts.
Suppliers of Corbion's key agricultural inputs, like corn and sugarcane, hold considerable power due to the commodity nature of these materials and potential concentration among providers. If these suppliers face limited buyers or if Corbion's switching costs are high, they can influence pricing and terms, impacting Corbion's cost of goods sold, which stood at €827.3 million in 2023.
Corbion's ability to use various feedstocks, such as corn, sugarcane, or cassava, for lactic acid production mitigates supplier leverage by allowing shifts based on availability and price. However, specialized ingredients for advanced bioplastics or biomedical polymers, often with proprietary characteristics, empower those specific suppliers significantly, as alternatives are scarce.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Corbion's product lines, like lactic acid production, is a key concern, especially for large agricultural producers. While Corbion's advanced fermentation technology acts as a barrier, successful integration could lead to increased input costs or supply disruptions, a risk heightened by the 5-10% input cost increases seen in specialty chemicals in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Corbion | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Higher leverage for fewer suppliers | 90% of agricultural raw materials are key inputs |
| Switching Costs | Increased dependence on current suppliers | Costs for retooling, vendor qualification |
| Availability of Substitutes | Reduced supplier power | Flexibility in using corn, sugarcane, cassava |
| Supplier Specialization | Significant power for unique ingredient providers | Proprietary fermentation strains, specific biopolymer inputs |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for cost increases/supply disruption | Corbion's 2023 COGS: €827.3 million; 2024 specialty chemical input cost hikes |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Corbion's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the biochemicals industry.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model tailored for Corbion's unique market position.
Customers Bargaining Power
Corbion's extensive customer base, spanning industries like food, personal care, and bioplastics, generally dilutes individual customer bargaining power. This broad reach means no single client represents an overwhelming portion of their sales, limiting any one customer's ability to dictate terms.
Customer switching costs significantly influence their bargaining power. In sectors such as pharmaceuticals and biomedical polymers, stringent regulatory hurdles, extensive product validation, and the critical need for consistent ingredient performance create substantial barriers to switching suppliers. This often means customers in these areas have limited ability to easily move to a competitor, thereby diminishing their leverage.
For instance, the pharmaceutical industry’s rigorous approval processes for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can take years and cost millions, making a change in supplier a complex and expensive undertaking. This high barrier effectively locks in customers, strengthening the supplier's position. In contrast, some segments within the food ingredients market may present lower switching costs, allowing customers more flexibility to negotiate prices or explore alternative suppliers.
Corbion's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity depending on the industry they operate in. In fast-moving consumer goods sectors, where competition is often fierce, customers tend to be more attuned to price, which can amplify their bargaining power.
Conversely, in markets demanding specialized ingredients or high-performance applications, such as certain industrial or pharmaceutical segments, customers often place a greater emphasis on product quality, reliability, and unique functionalities rather than solely on cost. This prioritization can moderate their price sensitivity and, consequently, their bargaining power.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Customers possess greater bargaining power when readily available substitute products or alternative solutions exist. This is particularly relevant for companies like Corbion, a significant player in lactic acid and its derivatives. If customers can easily switch to different food preservation methods or alternative emulsifiers from competitors, their leverage increases.
For example, within the food ingredients sector, the availability of multiple suppliers for emulsifiers or preservatives can dilute a single company's pricing power. In 2024, the global food ingredients market continued to see innovation in alternative preservation techniques, offering consumers and food manufacturers a wider array of choices beyond traditional lactic acid-based solutions.
- Availability of Alternatives: Customers can switch to other food preservation ingredients or emulsifiers if Corbion's offerings become too expensive or less appealing.
- Market Dynamics: The presence of numerous suppliers for similar functional ingredients intensifies customer bargaining power.
- Innovation Impact: New product development in areas like natural preservatives or plant-based emulsifiers can create viable substitutes, thereby enhancing customer leverage.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant consideration for Corbion. If Corbion's major clients, particularly those in the food and biochemical sectors, possess the technical expertise and financial resources, they might explore producing bio-based ingredients or lactic acid derivatives internally. This would directly reduce their reliance on Corbion, thereby amplifying their bargaining power and potentially leading to price concessions.
However, the specialized nature of fermentation processes and the advanced production technologies employed by Corbion present a substantial barrier to entry for most customers. Developing and scaling these capabilities requires significant capital investment and deep scientific knowledge, making in-house production a complex and often unfeasible undertaking for many of Corbion's clientele. For instance, Corbion's expertise in lactic acid production, a core competency, involves intricate bioprocess engineering and quality control that are not easily replicated.
- Customer Integration Risk: Major customers in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals could potentially integrate backward into bio-based ingredient production, increasing their leverage.
- Technological Barriers: Corbion's proprietary fermentation and downstream processing technologies create significant hurdles for customers attempting backward integration.
- Corbion's Market Position: As of early 2024, Corbion holds a leading position in the global lactic acid market, indicating a strong competitive advantage that deters customer integration.
Corbion's customer bargaining power is generally moderate, influenced by factors like switching costs, price sensitivity, and the availability of alternatives. While a broad customer base dilutes individual power, high switching costs in sectors like pharmaceuticals, due to rigorous validation and regulatory requirements, limit customer leverage. In 2023, Corbion reported that specialized ingredients for these sectors represented a significant portion of their revenue, highlighting the value of these sticky customer relationships.
Price sensitivity varies; it's higher in competitive consumer goods markets, where customers might seek cost reductions. Conversely, in specialized applications, quality and reliability often outweigh price, reducing customer bargaining power. The availability of substitutes, such as alternative food preservation methods, can increase customer leverage, especially as new innovations emerge, as seen with the growing market for plant-based emulsifiers in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Corbion's Situation |
| Customer Base Size | Dilutes individual power | Extensive, diverse customer base |
| Switching Costs | High in specialized sectors (pharma, biomedical) | Significant barriers to switching due to regulation and validation |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by industry; higher in consumer goods | Lower in high-performance applications, higher in competitive segments |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increases power if substitutes are readily available | Moderate; new innovations in food preservation offer some alternatives |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for major clients to produce in-house | Limited by Corbion's specialized technology and scale; as of 2024, integration risk is low for most clients. |
What You See Is What You Get
Corbion Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Corbion Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Corbion faces intense competition across its core markets, including bio-based ingredients, lactic acid, and its derivatives. The landscape is populated by a mix of global chemical giants and specialized ingredient producers, creating a dynamic and challenging environment.
Major players like BASF, Cargill, DSM, and International Flavors & Fragrances (IFF) bring significant scale, R&D capabilities, and established market presence, directly challenging Corbion's market share. For instance, in 2024, BASF continued its expansion in bio-based materials, highlighting the ongoing investment by large competitors.
Furthermore, specialized companies such as NatureWorks, a leader in polylactic acid (PLA), and Tate & Lyle, a prominent player in food ingredients and sweeteners, also present formidable competition. NatureWorks, in particular, has been actively increasing its production capacity for PLA, a key bio-based polymer, further intensifying rivalry in that segment.
The markets for lactic acid and bio-based ingredients are booming. The lactic acid market, for example, is expected to see a CAGR of 8.0% between 2025 and 2035, indicating substantial expansion. This robust growth environment can temper competitive rivalry, as companies are more inclined to capture new market share than to engage in cutthroat competition for existing customers.
Corbion actively combats competitive rivalry by emphasizing unique, sustainable, and bio-based product offerings, a strategy reinforced by its strong capabilities in fermentation and preservation technologies. This focus on innovation, exemplified by their Verdad clean label preservation range and advancements in algae-based omega-3s, helps to insulate them from direct price-based competition.
Switching Costs for Customers
High switching costs for customers significantly dampen competitive rivalry, especially in specialized markets. For instance, in sectors like pharmaceuticals and biomedical polymers, the rigorous validation processes and regulatory approvals required for material changes mean that once a customer integrates a supplier's product, switching becomes a costly and time-consuming endeavor. This inertia effectively locks in existing customer relationships, making it difficult for new or existing competitors to gain market share through price wars or aggressive marketing.
These high switching costs are a critical factor for companies like Corbion, particularly in their advanced materials segments. The investment in research, development, and qualification for specific applications means that customers are hesitant to move away from established, proven suppliers. This can translate into more stable revenue streams and reduced pressure on pricing, as competitors face a higher barrier to entry when trying to attract these entrenched customers. For example, in the food ingredients sector, reformulation and consumer acceptance testing can add considerable expense and time for food manufacturers, reinforcing loyalty to existing suppliers.
- High switching costs in specialized segments like pharmaceuticals and biomedical polymers reduce competitive rivalry.
- Customers in these areas face significant time, cost, and regulatory hurdles when changing suppliers.
- This customer lock-in makes it harder for competitors to poach business, leading to more stable market dynamics.
- Corbion benefits from these high switching costs, particularly in its advanced materials and food ingredient businesses, by retaining customers and reducing pricing pressures.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can indeed prolong the presence of struggling competitors, thereby intensifying industry rivalry. For Corbion, this means that even if some players are performing poorly, specialized assets or existing long-term commitments might prevent them from leaving the market, keeping competitive pressure elevated.
Corbion's own strategic clarity and solid financial footing, as evidenced by its performance in the first half of 2025, position it well to navigate this competitive landscape. A strong financial position allows a company to weather periods of intense rivalry more effectively than its weaker counterparts.
Consider these factors regarding exit barriers and rivalry:
- Specialized Assets: Competitors with significant investments in highly specific machinery or technology may find it difficult and costly to divest or repurpose these assets, locking them into the market.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing contractual obligations with suppliers or customers can bind companies to operations even when they are no longer profitable, contributing to sustained rivalry.
- Corbion's Financial Strength: In H1 2025, Corbion demonstrated resilience. For instance, its reported revenue growth and stable margins indicate an ability to maintain market share and potentially absorb competitive pressures more effectively than less financially sound rivals.
- Strategic Focus: Corbion's clear focus on its core competencies and growth areas allows it to allocate resources efficiently, strengthening its competitive position against rivals who may be hampered by exit barriers and less focused strategies.
Corbion operates in a highly competitive arena, facing rivals like BASF, Cargill, and DSM, who possess considerable scale and R&D investment. For example, in 2024, BASF's ongoing expansion in bio-based materials underscored the significant capital deployment by major competitors.
The market growth for lactic acid, projected at an 8.0% CAGR from 2025-2035, can somewhat mitigate intense rivalry by offering opportunities for expansion. However, specialized players like NatureWorks in PLA continue to ramp up capacity, intensifying competition in specific segments.
| Competitor | Key Product Areas | 2024/2025 Developments |
| BASF | Bio-based materials, chemicals | Continued expansion in bio-based materials |
| Cargill | Food ingredients, bio-based products | Ongoing investment in sustainable ingredient solutions |
| DSM | Nutrition, health, bio-based materials | Focus on high-growth segments and innovation |
| NatureWorks | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Increased PLA production capacity |
| Tate & Lyle | Food ingredients, sweeteners | Strategic partnerships and product development |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of synthetic alternatives presents a significant threat to Corbion's bio-based ingredients. For instance, in the food preservation market, established chemical preservatives can directly compete with Corbion's natural solutions. While consumer demand for natural products is on the rise, the cost-effectiveness and familiarity of synthetic options remain a strong counter-argument for many food manufacturers.
The threat of substitutes for Corbion's products is heavily influenced by the price-performance trade-off. If alternative ingredients, particularly synthetic ones, can deliver similar functional benefits at a substantially lower price point, they represent a significant competitive pressure.
For instance, while Corbion's bio-based emulsifiers and preservatives offer performance advantages, if a synthetic alternative emerges that performs adequately for a much lower cost, customers might switch. This is especially true in price-sensitive market segments.
However, Corbion's strategic emphasis on 'clean label' and sustainability creates a value proposition that can mitigate this threat. Consumers and food manufacturers increasingly prioritize natural ingredients and environmentally friendly production methods, making Corbion's offerings more attractive even at a potential price premium. In 2023, the global clean label ingredients market was valued at approximately $45 billion and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong demand for such attributes.
Growing consumer demand for natural, sustainable, and eco-friendly products across sectors like food, personal care, and bioplastics significantly reduces the appeal of traditional, less environmentally sound substitutes. This shift directly benefits companies like Corbion whose business model is inherently aligned with these burgeoning trends.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements continuously introduce new substitutes for Corbion's bio-based ingredients. Innovations in non-bio-based alternatives or novel fermentation techniques could significantly impact market share. For instance, the development of synthetic biology for producing specific molecules bypasses traditional fermentation, potentially offering cost advantages or unique functionalities that compete directly with Corbion's offerings.
Corbion's strategic imperative is to maintain robust research and development to preemptively address these emerging threats. By investing in areas like advanced bioprocessing and exploring new bio-based platforms, the company can ensure its product pipeline remains competitive. For example, in 2024, Corbion reported investing €75 million in innovation, a significant portion allocated to exploring next-generation bio-based solutions.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the increasing accessibility of advanced manufacturing technologies. Companies can leverage these tools to develop and scale alternative ingredients more rapidly. This dynamic necessitates continuous monitoring of the competitive landscape and a proactive approach to product development. Examples include the rise of precision fermentation for producing proteins and enzymes, which could displace some of Corbion's existing product lines.
- Emerging Technologies: Synthetic biology and precision fermentation offer new pathways for ingredient production, potentially bypassing traditional bio-based methods.
- R&D Investment: Corbion's commitment to innovation, exemplified by its €75 million investment in 2024, is crucial for staying ahead of substitute threats.
- Competitive Landscape: Rapid advancements in manufacturing technologies allow competitors to quickly develop and scale alternative ingredients, increasing substitutability.
Regulatory Environment and Labeling Trends
The regulatory landscape significantly influences the threat of substitutes for Corbion's products. Favorable regulations that encourage bio-based ingredients, such as those promoting sustainable sourcing or offering tax incentives for bioplastics, directly diminish the appeal of synthetic alternatives. Conversely, stricter labeling requirements for synthetic ingredients can push consumers and manufacturers toward naturally derived options, which Corbion specializes in.
The burgeoning 'clean label' movement, emphasizing natural and recognizable ingredients, is a key factor. Initiatives by regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that streamline the Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) status for natural ingredients further bolster Corbion's position. For instance, in 2024, the FDA continued to review and approve new natural food additives, creating a more accessible market for Corbion's bio-based solutions.
- Regulatory Support for Bio-based Products: Government policies and incentives favoring sustainable and bio-based materials directly reduce the attractiveness of petrochemical-based substitutes.
- Labeling Regulations: Increased transparency requirements for ingredient sourcing and manufacturing processes can highlight the advantages of Corbion's natural offerings over synthetic ones.
- FDA GRAS Streamlining: The FDA's efforts to expedite the GRAS process for natural ingredients in 2024 made it easier for companies like Corbion to introduce and market their bio-based ingredients, thereby mitigating the threat from synthetic alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Corbion's bio-based ingredients is moderated by growing consumer preference for natural and sustainable products. While synthetic alternatives often offer cost advantages, the increasing demand for 'clean label' ingredients, driven by consumer awareness and regulatory shifts, makes Corbion's offerings more appealing. For example, the global market for natural food ingredients, a key area for Corbion, experienced significant growth, reflecting this trend.
Technological advancements in areas like synthetic biology and precision fermentation present potential substitutes that could challenge Corbion's market position. However, Corbion's substantial investment in research and development, such as its €75 million allocation in 2024 towards innovation, aims to preemptively counter these emerging threats by developing next-generation bio-based solutions.
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role, with policies favoring bio-based materials and streamlined approval processes for natural ingredients, like those seen with the FDA's GRAS status in 2024, directly diminishing the competitive threat from synthetic alternatives.
| Factor | Impact on Corbion | Supporting Data/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Demand for Natural/Sustainable | Reduces threat of synthetic substitutes | Global clean label ingredients market valued at ~$45 billion in 2023; growing demand for eco-friendly products. |
| Technological Advancements (Synthetic Biology, Precision Fermentation) | Potential for new, competitive substitutes | Corbion invested €75 million in innovation in 2024 to develop next-gen bio-based solutions. |
| Regulatory Landscape (Bio-based Incentives, Labeling) | Mitigates threat from synthetic alternatives | FDA's 2024 streamlining of GRAS for natural ingredients supports Corbion's market entry. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the bio-based ingredients and specialty chemicals market, like Corbion's lactic acid sector, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development to innovate, build specialized fermentation plants, and establish robust production lines. For example, setting up a new fermentation facility can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a substantial hurdle for newcomers.
Corbion's established position as a global leader in lactic acid and its derivatives grants it substantial economies of scale. This means they can produce, purchase raw materials, and distribute their products more cheaply than smaller, newer companies. For instance, in 2023, Corbion reported revenue of €1.1 billion, reflecting their significant operational footprint.
Newcomers would find it incredibly challenging to match Corbion's cost efficiencies. Building production facilities, securing reliable raw material suppliers, and establishing a widespread distribution network all require massive upfront investment. Without achieving similar production volumes, new entrants would likely face higher per-unit costs, making it difficult to compete on price against Corbion.
Corbion's formidable proprietary technology and deep expertise in fermentation and bio-based ingredients create a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. This unique knowledge base, including extensive intellectual property, is not easily replicated.
New companies would face immense challenges and significant investment to develop comparable technological capabilities and the nuanced application knowledge that Corbion has cultivated over years. For instance, Corbion's investments in R&D, which are crucial for maintaining its technological edge, are substantial and ongoing, making it difficult for newcomers to catch up quickly.
Access to Distribution Channels
The threat of new entrants regarding access to distribution channels for Corbion is moderate. Establishing robust distribution networks and gaining access to diverse markets such as food, pharmaceuticals, and home & personal care requires substantial time and significant capital investment. Corbion benefits from its established relationships with key distributors, including major players like Univar Solutions, which provides them with broad market reach.
New competitors would encounter considerable hurdles in replicating Corbion's existing market access. For instance, building a comparable distribution infrastructure, securing shelf space in retail, and establishing relationships with numerous B2B clients across various sectors are complex and costly endeavors. In 2024, the global distribution market for specialty ingredients, a key area for Corbion, continued to consolidate, making it even harder for new, smaller players to gain significant traction without substantial backing.
- Established Distribution Networks: Corbion leverages long-standing partnerships with global distributors, ensuring broad market penetration.
- High Capital Investment: Building a comparable distribution infrastructure and securing market access requires significant financial resources.
- Time-Consuming Market Entry: Developing the necessary relationships and logistical capabilities takes years, creating a barrier for new entrants.
- Market Consolidation: The ongoing consolidation in distribution channels, observed throughout 2024, further restricts entry opportunities for newcomers.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The food, pharmaceutical, and biomedical sectors Corbion operates in are heavily regulated, creating significant barriers for new competitors. Entering these markets requires substantial investment in time and resources to navigate complex approval processes and secure necessary certifications. For example, achieving Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) status for food ingredients or adhering to stringent Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical applications demands rigorous testing and documentation.
New entrants must also contend with the need for various certifications that validate product quality and safety. These can include ISO standards for quality management and environmental practices, as well as sustainability certifications like EcoVadis Gold, which Corbion has achieved. These established compliance and sustainability credentials provide a significant competitive advantage, making it difficult for newcomers to match Corbion's level of trust and market acceptance.
In 2024, the global regulatory landscape for food and health products continued to tighten, with increased scrutiny on ingredient sourcing, production processes, and environmental impact. Companies like Corbion, with decades of experience in maintaining high compliance standards and a strong track record of certifications, are better positioned to adapt and thrive. For instance, Corbion’s commitment to sustainability, often reflected in its EcoVadis ratings, is increasingly becoming a prerequisite for doing business with major global customers, further deterring potential new entrants who lack this established framework.
- Regulatory complexity in food, pharma, and biomedical industries requires extensive compliance efforts.
- Key certifications such as GRAS, ISO, and EcoVadis Gold are essential market entry requirements.
- Corbion's established compliance and sustainability ratings serve as a significant barrier to new entrants.
- Increasing regulatory scrutiny in 2024 further solidifies the advantage of experienced, certified players.
The threat of new entrants into Corbion's bio-based ingredients and specialty chemicals market is generally low. Significant capital investment for R&D, specialized production facilities, and navigating stringent regulatory landscapes create substantial barriers. Furthermore, Corbion's established economies of scale, proprietary technology, and strong distribution networks make it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on price and market access.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Corbion's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for R&D, fermentation plants, and production lines. | Significant financial hurdle. | Established infrastructure and operational scale. |
| Proprietary Technology & Expertise | Unique knowledge in fermentation and bio-based ingredients. | Difficult to replicate unique capabilities. | Extensive IP and years of cultivated knowledge. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower production and purchasing costs due to high volume. | Higher per-unit costs for new entrants. | Cost efficiencies from global operations. |
| Distribution Channels | Established relationships with global distributors. | Challenges in replicating market access and shelf space. | Broad market reach via established partnerships. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex approval processes and certifications in food, pharma, etc. | Time-consuming and costly to achieve compliance. | Decades of experience in regulatory adherence. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Corbion is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and trade publications to capture nuanced competitive dynamics.
