Anhui Conch Cement Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Anhui Conch Cement Bundle
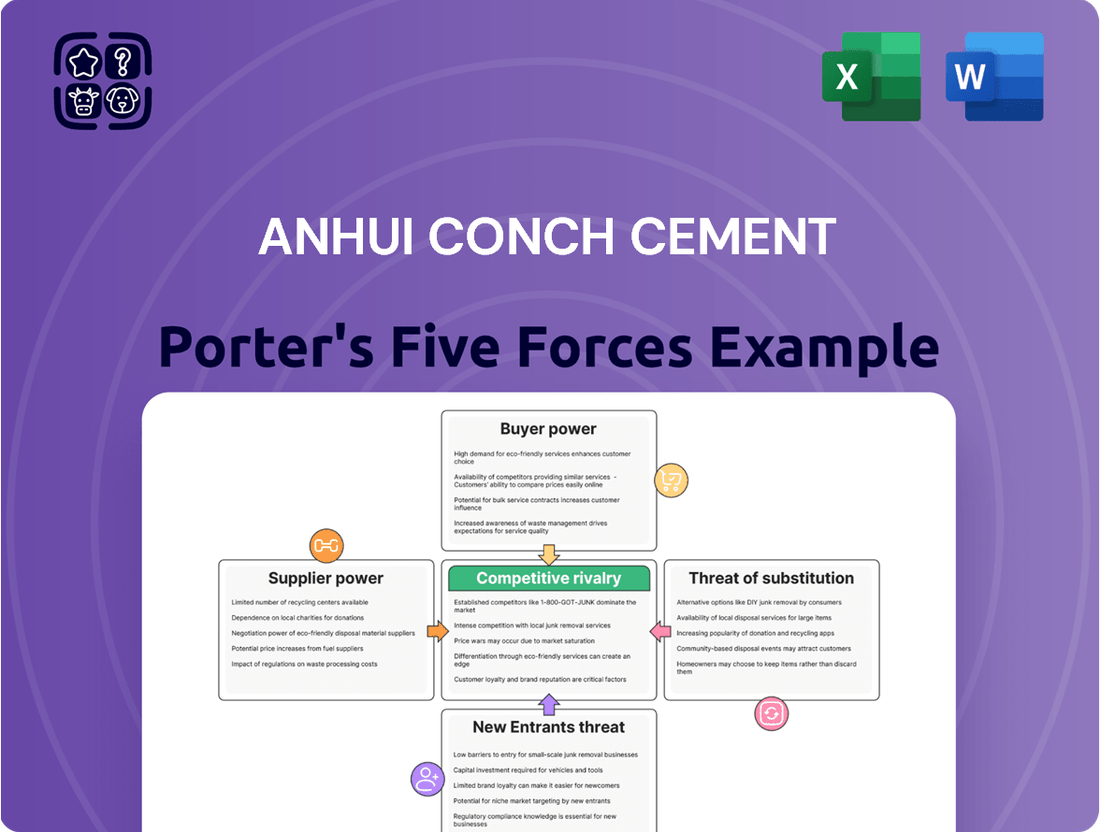
Anhui Conch Cement faces a moderately intense competitive landscape, with significant rivalry from existing players. The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by high capital requirements and established distribution networks. Buyer power, while present, is tempered by product standardization and the sheer scale of demand in the construction sector. Suppliers of raw materials like limestone and coal hold some leverage, but Conch Cement's size often allows for favorable terms.
The threat of substitutes, such as alternative building materials, is a growing concern, especially with advancements in green construction. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for anyone looking to grasp Anhui Conch Cement's strategic position. The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Anhui Conch Cement’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration in the cement industry, particularly for Anhui Conch Cement, is somewhat mitigated by the localized nature of key raw materials. Limestone, clay, and gypsum, the foundational components of cement, are often abundant and sourced from captive mines or local quarries by major players like Anhui Conch. This vertical integration significantly diminishes the bargaining power of external raw material suppliers.
However, the equation changes for critical inputs like energy. Coal and electricity represent substantial cost drivers for cement production, and their supply chains are far more susceptible to supplier concentration and global market dynamics. Fluctuations in international coal prices, for instance, directly impact Anhui Conch's operational costs and can therefore exert considerable influence on the company.
For example, as of early 2024, global coal prices have seen volatility due to geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions. While specific figures for Anhui Conch's energy procurement are proprietary, the general trend of rising energy costs in 2023 and early 2024, driven by these broader market forces, indicates that energy suppliers do hold significant bargaining power. This can translate to increased production expenses for cement manufacturers if they are not adequately hedged or if their energy contracts are subject to market price adjustments.
For a major player like Anhui Conch Cement, the cost of switching suppliers for specialized machinery or critical raw materials can be substantial. Imagine the expense and time involved in retooling production lines or obtaining new certifications for incoming materials.
These significant switching costs, which can include logistical adjustments and extensive testing, directly empower Anhui Conch's current suppliers. For instance, if a supplier provides a unique additive crucial for specific cement grades, Conch might face millions in costs to find and integrate an alternative.
The availability of alternative inputs significantly impacts the bargaining power of traditional cement clinker suppliers. For Anhui Conch, the presence of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) like fly ash and ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS) offers a viable alternative. In 2024, the global market for SCMs continued to expand, driven by environmental regulations and the desire for lower-carbon concrete. This growing accessibility to substitutes inherently weakens the leverage of suppliers who solely depend on traditional clinker production.
Supplier's Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into cement production, thereby competing directly with companies like Anhui Conch Cement, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital outlay and specialized operational expertise needed to establish and run cement manufacturing facilities. For instance, building a new cement plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier most raw material suppliers cannot easily overcome.
While most suppliers of raw materials like limestone and coal lack the resources or inclination to become cement producers, there can be exceptions. Very large, diversified conglomerates in sectors like energy or mining might possess the financial muscle and existing infrastructure to explore such a strategic move downstream. However, this remains a niche concern for major cement players.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing a cement production facility requires significant investment, often exceeding $500 million for a modern plant, deterring most raw material suppliers.
- Specialized Expertise: Cement manufacturing involves complex processes, logistics, and regulatory compliance that suppliers may not possess.
- Limited Diversification Incentives: Most suppliers focus on their core competencies rather than venturing into a capital-intensive industry like cement production.
- Potential for Large Conglomerates: Exceptionally large mining or energy firms might have the capacity to consider forward integration, though this is not a widespread threat.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Anhui Conch
For Anhui Conch, the bargaining power of suppliers is a significant factor due to the critical nature of its key inputs. Coal and electricity are the lifeblood of cement production, an inherently energy-intensive process. Suppliers of these essential resources wield considerable influence.
The direct correlation between energy price fluctuations and Anhui Conch's production expenses cannot be overstated. Volatility in the cost of coal and electricity directly impacts the company's profitability, making supplier relationships paramount for cost control.
Anhui Conch actively pursues strategies to mitigate this supplier power. These efforts are focused on reducing procurement costs, which is vital for maintaining competitive pricing and healthy profit margins in the cement industry. For example, in 2023, Anhui Conch reported that its cost of sales increased by 3.4% year-on-year, highlighting the ongoing challenge of managing input costs.
- Critical Inputs: Coal and electricity are essential for Anhui Conch's energy-intensive cement manufacturing.
- Cost Impact: Fluctuations in energy prices directly affect production costs and profitability.
- Mitigation Strategies: Anhui Conch focuses on cost management, including procurement optimization, to counter supplier influence.
- 2023 Cost Data: The company's cost of sales rose 3.4% in 2023, underscoring the importance of managing supplier costs.
Anhui Conch Cement's supplier bargaining power is most pronounced with energy providers, particularly for coal and electricity, which are significant cost drivers. While raw material suppliers like limestone have less leverage due to localized availability and Conch's vertical integration, energy markets are more volatile. For instance, global coal prices experienced notable fluctuations in early 2024 due to geopolitical events and supply chain issues, directly impacting Anhui Conch's operational expenses.
The company's mitigation strategies focus on procurement optimization to manage these rising input costs. In 2023, Anhui Conch's cost of sales increased by 3.4%, underscoring the persistent challenge of supplier influence on profitability. This highlights the critical need for effective cost management in an energy-intensive industry.
High switching costs for specialized machinery and critical additives further empower existing suppliers, as finding and integrating alternatives can be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming for Anhui Conch. Conversely, the growing availability of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) like fly ash in 2024 provides alternatives, weakening the power of traditional clinker suppliers.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into cement production is generally low due to the immense capital and expertise required, though large conglomerates could pose a theoretical risk. Overall, while raw material suppliers have limited influence, energy suppliers wield considerable power over Anhui Conch due to the critical nature of their products.
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Anhui Conch Cement, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape, this Porter's Five Forces analysis identifies the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on the cement industry.
Anhui Conch Cement's Five Forces Analysis offers a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive pressures—perfect for quick decision-making and identifying key vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Anhui Conch Cement's customer base is heavily concentrated among large construction firms and government bodies undertaking substantial infrastructure developments. These entities, responsible for projects like high-speed rail, extensive highway networks, and major airport expansions, are significant buyers.
The sheer volume of cement these customers procure grants them considerable leverage. This scale enables them to negotiate more favorable pricing and contractual conditions, directly impacting Anhui Conch Cement's revenue and profit margins.
For instance, in 2023, Anhui Conch Cement reported that its top ten customers accounted for a substantial portion of its sales volume, highlighting the influence these large buyers wield.
Product standardization in the cement industry significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Standard Portland cement, the most common type, is largely indistinguishable between manufacturers, meaning buyers can easily comparison shop. This lack of product differentiation forces producers to compete primarily on price, giving customers substantial leverage, particularly when the market experiences overcapacity.
Customer price sensitivity in the Chinese cement market is currently elevated. This is largely due to an economic slowdown and a significant downturn in the property sector, which has led to weaker demand and declining prices across the industry. For Anhui Conch Cement, this translates directly into customers actively seeking the most competitive prices, directly impacting the company's ability to set prices and maintain its gross profit margins. In 2023, the average selling price for cement in China saw a notable decline compared to previous years, reflecting this intensified price competition.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of backward integration by customers for Anhui Conch Cement is notably low. Major buyers, such as large construction firms, typically lack the immense capital investment and specialized knowledge needed to build and run their own cement manufacturing facilities. For instance, establishing a modern cement plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, making it an unfeasible venture for most construction companies. This barrier effectively neutralizes their ability to produce cement in-house, thereby diminishing their bargaining power.
The significant barriers to entry for cement production mean that construction companies are unlikely to engage in backward integration. These barriers include:
- High Capital Requirements: The cost of land, kilns, grinding mills, and pollution control equipment is substantial.
- Technical Expertise: Operating a cement plant requires specialized knowledge in quarrying, raw material preparation, clinker production, and quality control.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining permits and complying with environmental regulations for cement production is complex and time-consuming.
- Economies of Scale: Existing large cement producers, like Anhui Conch Cement, benefit from economies of scale that smaller, integrated operations would struggle to match.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers
The bargaining power of customers in the Chinese cement market, even for a dominant player like Anhui Conch, is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers. In 2024, China continued to grapple with substantial cement overcapacity, estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of tons annually. This surplus means customers have a wide array of choices when sourcing cement.
This abundance of suppliers directly translates into heightened customer leverage. Buyers can readily compare pricing, product specifications, and delivery terms across multiple companies. For instance, a large construction project could easily solicit quotes from several regional cement manufacturers, creating a competitive environment that drives down prices and improves service conditions for the customer.
- High Market Saturation: China's cement industry, while led by giants like Anhui Conch, features a fragmented landscape with numerous smaller and regional producers.
- Overcapacity as a Driver: Persistent overcapacity in the Chinese cement sector, a trend continuing into 2024, amplifies customer choice and weakens supplier pricing power.
- Price Sensitivity: Cement is often viewed as a commodity, making price a primary decision factor for many buyers, especially in large-scale infrastructure and real estate development.
- Switching Costs: For many customers, the costs associated with switching cement suppliers are relatively low, further empowering their negotiation stance.
Anhui Conch Cement faces considerable bargaining power from its customers, primarily large construction firms and government bodies. These major buyers, responsible for vast infrastructure projects, procure immense volumes of cement. This scale allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Conch Cement's profitability, especially given the industry's commodity nature and the persistent overcapacity in China, which remained a significant factor in 2024. The low switching costs for customers further bolster their negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on Anhui Conch Cement | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High influence from large buyers | Top customers accounted for a significant sales volume in 2023. |
| Product Standardization | Price becomes the primary differentiator | Cement is largely a commodity, forcing price competition. |
| Price Sensitivity | Weakened pricing power | Economic slowdown and property sector downturn increased customer demand for lower prices. |
| Overcapacity | Amplified customer choice and leverage | China's cement overcapacity, estimated in hundreds of millions of tons annually, continued in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Anhui Conch Cement Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The preview you see is the exact Anhui Conch Cement Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces within the industry. This detailed document meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You can be confident that this preview accurately reflects the thoroughness and quality of the final analysis, ensuring no surprises and immediate usability for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive rivalry within China's cement industry is fierce, with Anhui Conch Cement navigating a landscape dominated by a few substantial players. In 2024, Anhui Conch Cement stands as a colossal entity, recognized as the second-largest cement producer in China based on its impressive production capacity. This intense competition is further exemplified by the presence of other major industry giants like China National Building Material (CNBM) and Jidong Cement, all vying for market share in this massive, yet highly contested, sector.
The Chinese cement market is grappling with a substantial decline in demand, a trend that has persisted since 2021. This downturn is largely attributed to the ongoing struggles within the real estate sector and a noticeable slowdown in infrastructure investment. Consequently, the industry is burdened by significant overcapacity.
This imbalance between supply and demand has intensified competitive rivalry. By 2024, cement utilization rates have reportedly fallen to approximately 50%. Such low utilization forces companies to aggressively compete for market share in an increasingly constrained market, putting considerable pressure on pricing and profitability.
Anhui Conch Cement faces intense competition primarily due to the largely homogenous nature of cement. Differentiation beyond standard quality and service is challenging, meaning rivals often compete on price. For instance, in 2023, domestic cement prices in China, a key market for Conch Cement, experienced fluctuations driven by supply-demand dynamics and regional cost pressures, underscoring the price-sensitive environment.
The low switching costs for buyers further intensify this rivalry. Customers can readily shift to alternative suppliers with minimal effort or expense if a better price is offered. This dynamic forces Anhui Conch Cement and its competitors to constantly vie for market share through competitive pricing strategies, impacting overall profitability.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The cement industry, including players like Anhui Conch Cement, is characterized by significant capital intensity. Operating and maintaining cement plants requires substantial, ongoing investment, creating high fixed costs. For instance, building a new cement plant can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a massive upfront commitment.
These high fixed costs, combined with substantial exit barriers, intensify competitive rivalry. Specialized machinery and the significant social impact of plant closures mean that companies find it difficult and costly to leave the market. This often leads to persistent overcapacity, especially when demand falters, forcing companies to compete aggressively on price to utilize their expensive assets.
- High Capital Investment: Cement production facilities are extremely capital-intensive, requiring massive upfront investment.
- Specialized Assets: Plant and equipment are highly specialized, limiting resale value and increasing exit costs.
- Social Costs: Layoffs and community impact make plant closures a sensitive and often prohibitive decision.
- Capacity Underutilization: High fixed costs pressure firms to maintain production even in downturns, leading to price wars.
Government Policies and Environmental Regulations
Government policies are significantly reshaping the cement industry. Initiatives like capacity reduction schemes are designed to tackle overcapacity, a persistent issue in China's cement market. For instance, the government has been actively promoting consolidation to create a more efficient and environmentally sound industry structure.
The inclusion of the cement sector in China's Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) by the end of 2024 is a critical development. This policy is expected to incentivize companies to reduce their carbon footprint, potentially leading to higher operating costs for less efficient producers. Anhui Conch, as a major player, will need to adapt its strategies to comply with these new emissions regulations.
These regulatory shifts can foster industry consolidation, as smaller, less compliant, or less efficient firms may struggle to meet new environmental standards. This dynamic could lead to a more concentrated market, potentially benefiting larger, well-capitalized companies like Anhui Conch that can invest in cleaner technologies and operational improvements.
- Capacity Reduction Schemes: Government-mandated or encouraged reductions in cement production capacity to address market imbalances.
- Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS): By the end of 2024, cement companies in China will participate in an ETS, creating a market for carbon allowances and driving emission reductions.
- Industry Consolidation: Regulations are expected to encourage mergers and acquisitions, leading to fewer, larger players in the market.
- Competitive Impact: Companies that adapt to environmental regulations and efficiency standards will gain a competitive advantage.
The competitive landscape for Anhui Conch Cement is characterized by intense rivalry, driven by significant overcapacity and declining demand in China. With cement utilization rates around 50% in 2024, companies are forced into aggressive price competition. The homogenous nature of cement and low buyer switching costs further exacerbate this pressure.
The industry's high capital intensity and substantial exit barriers mean that firms are reluctant to scale back production, even when demand is weak. This persistent overcapacity fuels price wars, directly impacting profitability for all major players, including Anhui Conch Cement.
Government policies, such as capacity reduction schemes and the impending inclusion of cement in China's Emissions Trading Scheme by the end of 2024, are expected to drive consolidation. Companies that can adapt to stricter environmental regulations and improve efficiency are likely to gain an advantage.
| Metric | 2023 (Approximate) | 2024 (Projected/Early Data) | Impact on Rivalry |
| Cement Utilization Rate | Below 50% | Continued low utilization (approx. 50%) | Intensifies price competition due to excess supply |
| Domestic Cement Price Trend | Fluctuating, generally under pressure | Continued pressure from overcapacity | Forces cost efficiencies and aggressive pricing |
| Industry Consolidation Initiatives | Ongoing government focus | Increased focus with ETS implementation | May reduce number of competitors, but competition remains fierce among survivors |
| Anhui Conch Cement Market Share (China) | Second largest producer | Maintains strong position but faces intense competition | Requires strategic pricing and operational efficiency to defend market share |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of direct substitutes for cement is quite low, particularly for its core function as a binding agent in concrete for large-scale construction projects. Concrete's unique properties, combining strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, make it difficult to replace in applications demanding structural integrity. Globally, cement production reached approximately 4.1 billion metric tons in 2023, highlighting its continued dominance in infrastructure development.
The threat of substitutes for Anhui Conch Cement's core product, concrete, is a significant factor. Alternative building materials can replace concrete in various applications, impacting demand. For instance, mass timber is gaining traction due to its sustainability credentials, and steel remains a strong competitor in structural applications.
The construction industry's increasing focus on environmental impact and efficiency fuels the adoption of these alternatives. For example, the global market for mass timber products was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, presenting a direct substitution threat in certain building segments.
Furthermore, advancements in modular construction techniques and the use of precast concrete elements can also reduce the need for traditional cast-in-place concrete, offering faster build times and potentially lower costs in specific projects. Asphalt continues to be a primary substitute for concrete in road construction, a major market for cement producers.
The growing urgency around environmental issues is accelerating the development of sustainable building materials, presenting a significant threat of substitution for traditional cement. Innovations such as graphene-enhanced concrete, hempcrete, and ferrock, which captures CO2 during its curing process, offer compelling alternatives with reduced environmental impact. Mycelium composites are also gaining traction as a biodegradable option. These emerging materials, supported by increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for greener construction, could erode cement's market share.
Relative Price and Performance of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for cement, particularly for Anhui Conch Cement, is significantly influenced by the price and performance characteristics of alternative building materials. If materials like engineered wood, advanced composites, or even certain types of recycled aggregates can match cement's structural integrity and durability while offering comparable or lower costs, they become more appealing. The perceived value increases if these alternatives also provide additional benefits, such as a reduced carbon footprint or quicker installation times, directly impacting demand for traditional cement.
In 2024, the global construction market continues to explore and adopt new materials. For instance, cross-laminated timber (CLT) has seen growing adoption in mid-rise and even some high-rise construction, offering a lighter, renewable alternative to concrete. While CLT's upfront cost can sometimes be higher than traditional concrete, its faster construction cycle and lower embodied energy can offset these initial expenses, making it a competitive substitute in specific applications. The ongoing innovation in material science means that the performance-to-price ratio of these substitutes is constantly improving, posing a dynamic challenge to established players like Anhui Conch Cement.
- Price Competitiveness: The cost of alternative materials relative to cement is a primary driver of substitution.
- Performance Parity: Substitutes achieving similar or better strength, durability, and fire resistance diminish cement's advantage.
- Added Benefits: Materials offering environmental advantages (lower CO2 emissions) or construction efficiencies (faster build times) increase their substitution threat.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing R&D in alternative materials like engineered wood and advanced composites continuously improves their price-performance ratio.
Demand for Green Construction
The increasing global demand for green construction presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional cement. As environmental consciousness grows, so does the market for alternative building materials with lower embodied carbon footprints. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with strong sustainability regulations and incentives. For example, by 2024, the global green building market is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a clear shift in material preferences.
Anhui Conch Cement is actively addressing this threat. The company has been investing in developing and promoting low-carbon technologies and blended cements. These products are designed to offer comparable performance to traditional cement but with a reduced environmental impact. By doing so, Anhui Conch aims to retain its market share by aligning its offerings with the evolving demands of the construction industry.
- Market Demand: Global green building market growth signals a strong preference for sustainable materials.
- Carbon Footprint: The embodied carbon in construction materials is a key factor driving substitute adoption.
- Industry Response: Anhui Conch's investments in low-carbon cement technologies aim to counter this threat.
- Product Innovation: Blended cements offer a viable alternative to traditional Portland cement, meeting environmental criteria.
While cement's core strength as a binder is hard to replace, alternative materials pose a growing threat to Anhui Conch Cement. Mass timber, for instance, is gaining traction due to its sustainability, with its global market valued around $50 billion in 2023. Steel also remains a strong competitor in structural applications. These alternatives are becoming more appealing as they offer environmental benefits and faster construction times, directly impacting demand for traditional cement in certain building segments.
The construction industry's focus on sustainability and efficiency is accelerating the adoption of substitutes. In 2024, cross-laminated timber (CLT) is seeing increased use in mid-rise buildings, offering a lighter, renewable option. While CLT can have a higher upfront cost, its quicker construction cycle and lower embodied energy make it competitive. Innovations in material science are constantly improving the price-performance ratio of these substitutes, presenting a dynamic challenge.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by a growing demand for green construction, particularly in regions with strong sustainability regulations. By 2024, the global green building market is projected to reach significant figures, signaling a clear shift towards more environmentally friendly materials. Anhui Conch Cement is responding by investing in low-carbon technologies and blended cements to meet these evolving market demands.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantage | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) | Anhui Conch Cement's Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Timber | Sustainability, Lighter Weight | $50 billion | Investing in low-carbon technologies |
| Steel | Structural Strength | N/A (Broad Market) | Developing blended cements |
| Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) | Renewable, Faster Construction | Growing segment | Focus on product innovation |
Entrants Threaten
The cement industry demands substantial upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in land for quarries, sophisticated kilns for production, grinding mills, and extensive distribution networks. For instance, building a new, large-scale cement plant in 2024 could easily cost upwards of $300 million to $500 million, depending on capacity and technology.
This high capital requirement serves as a formidable barrier to entry. Potential new competitors must secure significant financing to even begin operations, let alone achieve the scale necessary to compete with established players like Anhui Conch Cement. The sheer financial commitment deters many from entering the market.
Anhui Conch Cement benefits from formidable economies of scale, meaning their massive production volumes allow them to spread fixed costs over more units, significantly lowering per-unit expenses. For instance, in 2023, Anhui Conch's production capacity reached approximately 370 million tons per year, a scale that new entrants would find incredibly difficult and costly to replicate. This cost advantage in production, coupled with bulk purchasing power for raw materials and optimized logistics networks, creates a substantial barrier.
Newcomers face significant hurdles in securing access to high-quality, abundant limestone reserves, a primary raw material for cement production. Established players, like Anhui Conch Cement, often possess long-term control over prime quarry sites, giving them a cost advantage and supply security that is difficult for new entrants to replicate. For instance, in 2023, Anhui Conch Cement's extensive reserve base provided a stable foundation for its production, a critical factor in maintaining competitive pricing.
Developing efficient and cost-effective distribution channels is another substantial barrier. The cement industry relies on robust logistics, including trucking, rail, and shipping, to transport bulk materials to construction sites. New entrants must invest heavily in building or acquiring these networks, which are often already optimized by incumbents, creating a significant capital expenditure requirement and operational complexity that deters potential new competitors.
Stringent Environmental Regulations
China's tightening environmental regulations, particularly the inclusion of the cement sector in its emissions trading scheme, present a substantial hurdle for new entrants. These regulations translate into significant compliance costs and necessitate advanced technological investments.
For any new company aiming to enter the cement market, the need to adopt state-of-the-art pollution control equipment and embrace sustainable operational practices creates a formidable financial barrier. This can divert crucial capital away from production and market penetration efforts.
Consider the following implications:
- Increased Capital Expenditure: New entrants must allocate substantial funds towards meeting stringent emission standards, potentially adding millions to initial setup costs.
- Technological Sophistication Required: Companies need to implement advanced technologies for dust suppression, NOx reduction, and CO2 capture, which are costly to acquire and maintain.
- Operational Cost Burden: Ongoing costs associated with emissions monitoring, reporting, and potential carbon credit purchases can impact profitability from day one.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Existing players, especially those who have already invested in upgrades, may have a cost advantage over newcomers burdened by immediate compliance requirements.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
While cement is largely seen as a commodity, Anhui Conch Cement has cultivated deep-seated loyalty and established strong relationships with its key clientele. These long-standing partnerships are particularly prevalent with significant buyers such as government infrastructure projects and large-scale construction conglomerates. For new companies entering the market, replicating this level of trust and securing substantial contracts from these influential entities presents a formidable hurdle, given their absence of a proven track record and established market reputation.
These established connections act as a significant barrier, as demonstrated by Anhui Conch's consistent ability to win major tenders. For instance, in 2023, Anhui Conch Cement secured a significant portion of contracts for China's Belt and Road Initiative infrastructure projects, highlighting the advantage of its established relationships. New entrants would struggle to displace these entrenched partnerships without offering a significantly disruptive value proposition or demonstrating exceptional reliability over time.
- Established Client Base: Anhui Conch Cement benefits from long-term relationships with government agencies and major construction firms, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
- Trust and Reputation: A proven track record and established reputation are crucial for securing large contracts, a significant advantage for incumbent players.
- Contractual Advantages: Existing relationships often translate into favorable long-term supply agreements, locking in demand and making it harder for newcomers to compete on price or volume.
- Market Inertia: Large buyers are often hesitant to switch suppliers due to the risks associated with unproven entities, preferring the reliability offered by established brands like Anhui Conch.
The threat of new entrants in the cement industry, particularly for a player like Anhui Conch Cement, is significantly mitigated by several factors. High capital requirements, estimated at $300 million to $500 million for a new plant in 2024, coupled with the need to replicate Anhui Conch's 370 million tons per year capacity, create substantial financial barriers. Furthermore, securing prime limestone reserves and establishing efficient distribution networks are critical challenges for newcomers. Stringent environmental regulations in China also add to the initial investment and operational costs for potential new competitors.
Established client relationships and a strong reputation, exemplified by Anhui Conch's success in securing large infrastructure project contracts in 2023, further deter new entrants. The industry's reliance on trust and proven reliability means that newcomers struggle to displace incumbents. This creates a high switching cost for major buyers, effectively locking in demand for established players.
| Barrier to Entry | Estimated Cost/Requirement | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (New Plant) | $300M - $500M (2024 Estimate) | Prohibitive for many potential competitors. |
| Economies of Scale | Anhui Conch's 370M Tons/Year Capacity (2023) | New entrants cannot match cost efficiency. |
| Raw Material Access (Limestone) | Control over prime quarry sites | Supply security and cost advantage for incumbents. |
| Distribution Networks | Investment in logistics infrastructure | High upfront cost and operational complexity. |
| Environmental Compliance | Advanced pollution control technology | Increased capital expenditure and operating costs. |
| Client Relationships/Reputation | Securing major infrastructure contracts (e.g., BRI 2023) | Difficulty displacing established trust and loyalty. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Anhui Conch Cement leverages data from company annual reports, industry association publications, and government economic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
