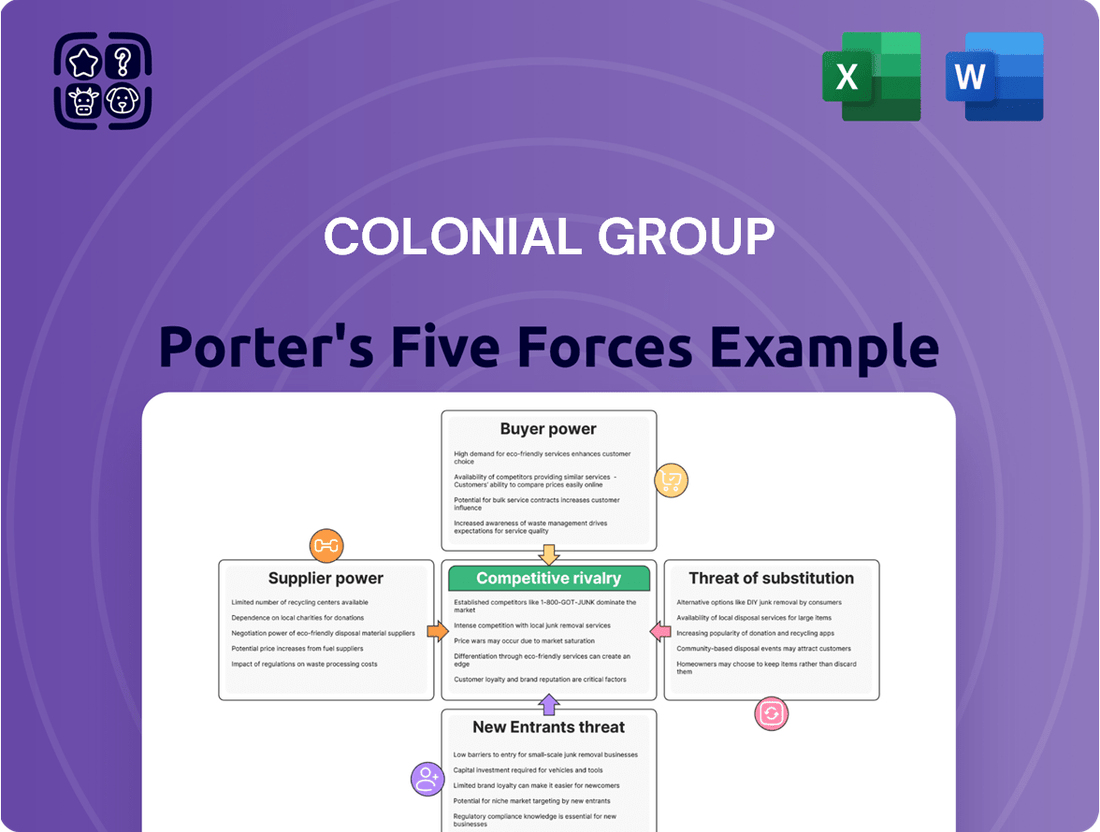
Colonial Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Colonial Group Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and Colonial Group is no exception. By examining the five key forces—threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors—we can uncover the dynamics shaping Colonial Group's industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Colonial Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Colonial Group's reliance on a small number of large crude oil and refined product suppliers grants these entities considerable bargaining power. This concentration means suppliers can dictate terms, impacting Colonial's operational costs and product availability, particularly when market conditions favor sellers.
In 2024, global crude oil prices experienced significant volatility, influenced by geopolitical events and production decisions by major oil-producing nations. This environment amplifies the leverage of dominant suppliers, as disruptions or supply cuts can rapidly escalate costs for downstream entities like Colonial Group.
The ability of these few suppliers to control output and pricing directly affects Colonial's profitability and competitive positioning. Managing these supplier relationships and exploring alternative sourcing strategies are therefore critical for mitigating risks associated with this concentrated supply base.
The price of crude oil and refined products, key inputs for many industries, is highly susceptible to global market shifts and geopolitical events. For instance, in early 2024, oil prices experienced significant volatility, with Brent crude fluctuating between $75 and $85 per barrel due to ongoing supply concerns and demand outlooks. This volatility means suppliers' pricing power is less about their individual negotiation strength and more about their ability to pass on these external cost increases to Colonial Group.
Political events, such as conflicts in oil-producing regions, and decisions by organizations like OPEC, can dramatically impact supply and, consequently, prices. Colonial Group’s procurement costs are therefore directly influenced by these external market dynamics. This situation underscores the critical need for the company to implement sophisticated hedging strategies and maintain flexible supply agreements to mitigate the impact of supplier pricing power driven by global energy market instability.
Suppliers of specialized marine vessels, port equipment, and sophisticated logistics software often wield moderate bargaining power. This is due to the niche nature of their products and the substantial costs associated with switching to alternative providers. For instance, a company like Colonial Group might find that the specialized nature of its fleet or port handling machinery means limited alternative suppliers, thereby strengthening the position of existing vendors.
Colonial Group's investment in specific, proprietary technologies or infrastructure can create significant lock-in effects. This makes it difficult and expensive to transition to new systems, effectively increasing the bargaining power of these specialized technology vendors. For example, if Colonial Group has integrated a particular port management software deeply into its operations, replacing it could involve extensive retraining and system overhauls, giving the software provider more leverage.
To mitigate this supplier power, Colonial Group can leverage long-term contracts and cultivate strategic partnerships. These arrangements can help secure favorable pricing and terms, while also fostering collaboration that might lead to innovation. In 2024, many logistics firms focused on strengthening supplier relationships to ensure supply chain resilience, a trend likely to continue as companies aim to de-risk operations.
Labor market dynamics for skilled and unskilled workers
The availability and cost of both skilled and unskilled labor significantly impact the bargaining power of workers as suppliers of services to Colonial Group. A constrained labor market, where demand for specific skills outstrips supply, can empower employees to negotiate higher wages and better benefits. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. experienced persistent labor shortages in critical sectors, leading to average hourly earnings growth for private nonfarm payrolls, which can directly influence operational costs for companies like Colonial Group.
Strong unionization or a high concentration of skilled workers in specific geographic areas can further amplify this supplier power. When a significant portion of the workforce is represented by unions, collective bargaining can lead to standardized wage increases and benefit packages that are harder for individual companies to resist. Conversely, a surplus of available labor tends to diminish this power, allowing companies more flexibility in setting compensation and terms.
To mitigate the impact of strong labor bargaining power, Colonial Group must focus on competitive compensation strategies and robust training and development programs. Offering attractive benefits and opportunities for career advancement can help retain skilled employees and reduce reliance on external hiring, thereby lessening the leverage of the labor market as a supplier.
- Skilled Labor: Demand for specialized roles like marine engineers and logistics managers can lead to higher wage pressures in tight labor markets.
- Unskilled Labor: Even retail staff can exert influence if there's a widespread shortage of available workers, driving up entry-level wages.
- Unionization: The presence and strength of labor unions can consolidate worker bargaining power, leading to more standardized and potentially higher labor costs.
- Market Conditions: In 2024, reports indicated that certain industries faced significant challenges in finding qualified personnel, a trend that can directly translate to increased labor costs for businesses.
Real estate and land developers for expansion and operations
Colonial Group's reliance on real estate and land developers for its retail gasoline stations, convenience stores, and port facilities grants these suppliers considerable leverage. The availability and cost of prime locations in sought-after areas directly influence Colonial Group's expansion capabilities and ongoing operational expenses. For instance, in 2024, prime commercial real estate prices in many high-traffic urban centers saw continued appreciation, potentially increasing lease or purchase costs for new site acquisitions.
The bargaining power of real estate suppliers is amplified in markets with limited supply or high demand. This scarcity can force Colonial Group to accept less favorable terms or pay a premium for essential land or lease agreements. Such situations directly impact the company's ability to execute strategic growth initiatives and manage its cost structure effectively.
- Location Scarcity: Limited availability of prime real estate in key markets increases supplier power.
- Cost of Land/Leases: Fluctuations in property values directly impact Colonial Group's expansion and operational costs.
- Strategic Importance: Access to desirable locations is critical for retail gasoline stations and port operations, enhancing supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Colonial Group is a significant factor, particularly concerning crude oil and refined product providers. With a concentrated supply base, these entities can exert considerable influence over pricing and availability. This was evident in 2024, a year marked by substantial volatility in global oil markets, driven by geopolitical tensions and OPEC+ production adjustments. For example, Brent crude prices saw fluctuations, impacting procurement costs for downstream players like Colonial Group.
Specialized suppliers, such as those providing marine vessels or advanced logistics software, also hold moderate leverage due to the niche nature of their offerings and the high switching costs involved. Colonial Group's investment in proprietary technologies further solidifies this vendor power, creating lock-in effects that make transitions costly and complex. To counter this, strategic partnerships and long-term contracts are key, a trend observed in 2024 as firms prioritized supply chain resilience.
Labor also acts as a supplier, and in 2024, tight labor markets in various sectors, including those relevant to Colonial Group's operations, led to increased wage pressures. Shortages in skilled roles like marine engineers and logistics managers, coupled with unionization, can consolidate worker bargaining power, directly affecting operational expenses.
Furthermore, real estate developers represent another supplier group with significant bargaining power, especially in markets with limited prime locations. The rising cost of commercial real estate in high-traffic areas in 2024 directly impacted Colonial Group's ability to acquire new sites and manage expansion costs, underscoring the critical need for effective negotiation and strategic site acquisition planning.
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape for Colonial Group, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual consumers at Colonial Group's gas stations and convenience stores exhibit significant price sensitivity, particularly for gasoline. This sensitivity is amplified by the commodity nature of fuel, where brand loyalty is often secondary to the lowest price at the pump.
The ease with which consumers can switch between competitors, given the minimal differentiation in gasoline products, grants them considerable bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, average gasoline prices fluctuated significantly, with consumers actively seeking out the cheapest options, impacting sales volumes for stations not offering competitive pricing.
To counteract this, Colonial Group relies on loyalty programs and the overall convenience and service offered at its locations. These factors aim to build a degree of stickiness, encouraging repeat business even when minor price differences exist elsewhere.
Large commercial and industrial clients are major purchasers of petroleum products, and their substantial order volumes grant them considerable negotiating leverage. These clients can often dictate terms, pushing for competitive pricing, adaptable delivery arrangements, and tailored service contracts. For instance, in 2024, major industrial consumers of refined fuels might represent 10-20% of a distributor's total sales volume, making their demands impactful.
Colonial Group's presence across energy, marine, and retail sectors means its customer base is inherently diversified. This broad reach significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer or customer group. For instance, while a large energy client might hold some sway, the company's reliance on this sector is tempered by its relationships with numerous entities in the marine and retail industries.
This diversification acts as a natural buffer against concentrated customer demands. In 2024, Colonial Group's revenue streams reflected this balance, with no single sector accounting for an overwhelming majority of its income, thereby reducing the leverage individual customers could exert.
Availability of alternative suppliers for petroleum products and logistics services
Customers for petroleum products and logistics services often have numerous choices available. This abundance of alternatives, especially for standardized products like fuel, significantly enhances their ability to negotiate. For instance, in 2024, the global oil and gas logistics market was valued at approximately $2.5 trillion, indicating a highly competitive landscape with many service providers.
The ease with which customers can switch to competing suppliers, particularly for commoditized offerings, directly amplifies their bargaining power. Colonial Group must consistently prove its value through exceptional service, operational efficiency, and attractive pricing to retain its customer base and mitigate the risk of customer churn.
- High Availability of Alternatives: Customers can readily access multiple suppliers for both petroleum products and the associated logistics.
- Low Switching Costs: For many petroleum products, the cost and effort for a customer to change suppliers are minimal, empowering them to seek better deals.
- Competitive Pressure: In 2024, the average price per gallon of gasoline in the US fluctuated, demonstrating the intense price competition driven by customer choice.
Impact of digital platforms and online price comparison tools on customer choices
The increasing availability of digital platforms and online price comparison tools has dramatically shifted the bargaining power of customers in the gasoline and convenience store sector. Consumers can now effortlessly compare prices for items like gasoline across numerous retailers in real-time. For instance, in 2024, apps like GasBuddy reported millions of users actively seeking the lowest fuel prices, directly impacting retailer pricing strategies.
This transparency significantly reduces information asymmetry, allowing customers to make swift, price-driven purchasing decisions. Colonial Group, like its competitors, faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing. Failing to do so can lead to immediate customer defection to rivals offering better deals, a trend amplified by the ease of digital discovery.
- Price Transparency: Digital tools enable instant price comparisons, empowering consumers.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Customers have access to more data than ever before.
- Enhanced Customer Choice: Easy access to information facilitates quick switching between retailers.
- Competitive Pressure: Retailers must offer competitive pricing to retain customers in this digital environment.
Colonial Group faces substantial customer bargaining power due to the commoditized nature of gasoline and the low switching costs for consumers. The widespread availability of alternatives and increasing price transparency through digital platforms in 2024 further empower customers to seek the lowest prices, forcing Colonial Group to maintain competitive pricing strategies and leverage loyalty programs to foster retention.
| Factor | Impact on Colonial Group | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity (Retail) | High | Average US gasoline prices fluctuated, with consumers actively seeking cheaper options. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Global oil and gas logistics market valued at ~$2.5 trillion, indicating a competitive landscape. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal effort for customers to change fuel suppliers. |
| Price Transparency (Digital) | High | Apps like GasBuddy used by millions to compare real-time fuel prices. |
| Bargaining Power of Large Clients | Moderate to High | Industrial consumers can represent 10-20% of a distributor's sales volume. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Colonial Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for The Colonial Group, offering a detailed examination of competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. This comprehensive report provides actionable insights into the industry landscape, enabling strategic decision-making for The Colonial Group.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The petroleum distribution landscape is crowded, with many regional and national companies actively competing. Colonial Group operates within this dynamic, facing significant rivalry from both large-scale distributors and smaller, localized players. This intense competition often drives down prices, impacting profitability and requiring a strong focus on cost management and efficient operations.
Major integrated oil companies, such as ExxonMobil and Shell, wield considerable power due to their extensive retail networks and substantial financial resources. These giants can absorb price fluctuations and invest heavily in marketing and brand building, creating a challenging environment for smaller players like Colonial Group. Their economies of scale in purchasing and distribution allow them to offer competitive pricing, forcing independent distributors to focus on service and niche markets to differentiate themselves.
Colonial Group's convenience stores encounter intense rivalry from numerous local and regional chains. These competitors often vie for market share by offering comparable product selections, service levels, and price points. For instance, in 2024, the convenience store sector saw continued expansion, with many smaller chains focusing on hyper-local market penetration and unique product offerings to differentiate themselves.
Competition within the marine transportation and logistics sector
The marine transportation and logistics sector is indeed a bustling arena, characterized by a diverse array of companies vying for market share. Colonial Group faces robust competition from other marine operators, freight forwarders, and comprehensive logistics providers, all offering similar shipping, port services, and supply chain solutions.
Key differentiators in this competitive landscape are critical for success. These include the sheer size and modernity of a company's fleet, the development of specialized capabilities for niche markets, unwavering reliability in service delivery, and the strategic advantage of offering seamless, integrated logistics solutions that encompass the entire supply chain.
- Fleet Size and Specialization: Companies like Maersk, MSC, and CMA CGM dominate global container shipping with vast fleets, while smaller, specialized operators focus on bulk carriers, tankers, or regional routes.
- Integrated Logistics: Major players are increasingly offering end-to-end services, from port handling to warehousing and final-mile delivery, aiming to capture more value and customer loyalty.
- Technological Adoption: Investments in digital platforms for tracking, booking, and supply chain management are becoming a significant competitive edge, enhancing efficiency and customer experience.
Strategic positioning and diversification across multiple energy and logistics segments
Colonial Group's strategic positioning across diverse segments like petroleum distribution, retail, marine transport, and real estate means it encounters varied competitive pressures. For instance, in the highly fragmented petroleum distribution sector, competition is often price-driven, with numerous regional players vying for market share. In 2024, the U.S. gasoline market, a key area for Colonial, saw continued volatility, with retail margins fluctuating significantly based on crude oil prices and regional demand.
This diversification, while spreading risk, also necessitates managing distinct competitor sets in each arena. The marine transport segment, for example, faces competition from global shipping lines and specialized carriers, each with unique operational strengths and cost structures. Colonial's ability to integrate these diverse operations, offering bundled services from fuel supply to logistics and property management, can create a unique competitive advantage. This integrated approach allows them to potentially capture more value and offer more comprehensive solutions than single-segment competitors.
- Petroleum Distribution: Intense competition from regional distributors and national brands, often focused on price and supply reliability.
- Retail Operations: Competition from convenience stores, supermarkets, and other fuel retailers, with differentiation often coming from location, product assortment, and loyalty programs.
- Marine Transport: Faces competition from global and regional shipping companies, with factors like fleet size, efficiency, and route networks being critical.
- Real Estate: Competitive landscape varies by market, with competition from local developers and national property management firms.
Colonial Group faces intense competition across its various business segments, from petroleum distribution to marine transport. In the petroleum sector, numerous regional and national players, including integrated oil giants, drive price competition, making cost efficiency crucial. The convenience store market is similarly crowded, with local and regional chains differentiating through unique offerings and hyper-local strategies. In 2024, the U.S. gasoline market experienced significant price volatility, impacting retail margins for distributors like Colonial.
| Segment | Key Competitors | Competitive Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Petroleum Distribution | ExxonMobil, Shell, Regional Distributors | Price, Supply Reliability, Economies of Scale |
| Retail Operations | Local/Regional Chains, Supermarkets | Location, Product Assortment, Loyalty Programs |
| Marine Transport | Maersk, MSC, Specialized Carriers | Fleet Size, Efficiency, Route Networks, Integrated Logistics |
| Real Estate | Local Developers, National Firms | Market Specific Factors, Location, Property Management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a substantial long-term challenge to Colonial Group's primary operations in petroleum distribution and gasoline retail. As consumer preference shifts towards EVs, the demand for conventional gasoline is projected to decrease.
For instance, in 2024, EV sales are expected to continue their upward trajectory, with projections indicating a significant market share increase globally. This trend directly impacts the volume of gasoline Colonial Group distributes and sells.
To address this, Colonial Group should explore strategic diversification into areas like EV charging infrastructure or other alternative fuel solutions. This proactive approach is crucial for mitigating the impact of declining gasoline demand and ensuring future business sustainability.
The burgeoning growth of online retail and rapid delivery services poses a significant substitution threat to Colonial Group's traditional convenience store model. Consumers now have readily available alternatives for purchasing many convenience items, from snacks and beverages to household essentials, directly through e-commerce platforms and specialized delivery apps.
This shift is underscored by the increasing consumer preference for convenience and speed, with many online services offering delivery within hours or even minutes. For instance, in 2024, the online grocery market continued its upward trajectory, with many consumers opting for the ease of having goods delivered directly to their doorstep, bypassing the need for a physical store visit.
To counter this, Colonial Group must innovate by differentiating its in-store offerings, perhaps through exclusive products or enhanced customer experiences, or by strategically partnering with or developing its own delivery capabilities. Failure to adapt could see a substantial portion of their customer base migrate to these more convenient digital channels.
The increasing adoption of public transportation and ride-sharing platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for Colonial Group. For instance, in 2024, cities globally saw continued expansion of metro systems and bus rapid transit, with billions invested in upgrades. This trend directly diminishes the need for personal vehicle usage, impacting demand for gasoline.
Ride-sharing services, like Uber and Lyft, further erode reliance on private cars. By 2024, these platforms facilitated billions of rides annually in major urban centers, offering a convenient and often cost-effective alternative to personal car ownership and, by extension, fuel purchases. Colonial Group must closely track these evolving mobility patterns.
Development and deployment of renewable energy sources for commercial and industrial use
The growing adoption of renewable energy for commercial and industrial applications presents a significant threat of substitution for Colonial Group's petroleum business. As businesses increasingly look to reduce their carbon emissions and long-term operating expenses, they are exploring alternatives like solar and wind power for their energy needs. For instance, in 2024, global investment in renewable energy reached record highs, with the International Energy Agency reporting over $1.7 trillion deployed, signaling a strong market shift.
This trend directly impacts Colonial Group's commercial and industrial petroleum clients, who may opt to transition their power generation and industrial processes away from fossil fuels. The economic viability of renewables continues to improve; the levelized cost of electricity for utility-scale solar PV dropped by an estimated 8% in 2024 compared to 2023, making it more competitive with traditional energy sources.
To mitigate this threat, Colonial Group could strategically explore opportunities within the renewable energy sector, such as providing logistics or distribution services for renewable energy components or infrastructure. The expansion of renewable energy capacity is substantial; by the end of 2024, solar and wind power were projected to account for over 70% of new renewable capacity additions globally, indicating a robust and growing market for related services.
- Renewable Energy Investment Growth: Global investment in renewables exceeded $1.7 trillion in 2024, highlighting a significant market shift.
- Cost Competitiveness: The levelized cost of solar PV saw an estimated 8% decrease in 2024, enhancing its appeal against fossil fuels.
- Market Share of New Capacity: Solar and wind power are expected to constitute over 70% of new renewable capacity additions by the close of 2024.
- Strategic Adaptation: Colonial Group can leverage its existing infrastructure and expertise to support the burgeoning renewable energy logistics and distribution sector.
Innovation in supply chain logistics reducing reliance on traditional marine transport
Innovation in supply chain logistics presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional marine transport. Advances such as optimized multimodal transport networks, the burgeoning use of drone delivery for smaller, time-sensitive goods, and the futuristic potential of hyperloop systems could offer viable alternatives for specific cargo types and transit routes. For instance, in 2024, the global drone delivery market was valued at approximately $2.4 billion and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a tangible shift in logistics capabilities.
While marine transport undeniably retains its dominance for the movement of bulk commodities and large volumes of goods, the continuous evolution of logistics technologies could gradually erode demand for certain Colonial Group marine services. This is particularly true for high-value or time-critical shipments where speed and direct point-to-point delivery become paramount. The increasing efficiency and cost-effectiveness of land-based and air-based alternatives are key factors here.
The critical imperative for Colonial Group, therefore, lies in its ability to adapt and integrate these emerging technologies. Proactive investment in and strategic adoption of advanced logistics solutions will be crucial to mitigate the threat of substitutes and maintain a competitive edge in the evolving global supply chain landscape. This could involve exploring partnerships or developing in-house capabilities for integrated logistics offerings.
- Market Shift: Drone delivery market valued at $2.4 billion in 2024, signaling a growing alternative for certain logistics needs.
- Cargo Specialization: Marine transport remains dominant for bulk goods, but substitutes threaten niche, time-sensitive cargo segments.
- Strategic Adaptation: Colonial Group must integrate new logistics technologies to counter the threat of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Colonial Group's petroleum products is multifaceted, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) directly challenges gasoline demand, with EV sales continuing their significant global growth in 2024. Similarly, the convenience of online retail and rapid delivery services offers a substitute for Colonial Group's convenience stores, as evidenced by the continued expansion of the online grocery market in 2024. Furthermore, increased public transportation and ride-sharing platforms reduce reliance on personal vehicles, impacting fuel consumption. The growing adoption of renewable energy for industrial and commercial use, supported by over $1.7 trillion in global investment in 2024, also presents a substitution threat to traditional petroleum energy sources.
Entrants Threaten
The energy distribution sector, especially for petroleum storage, pipelines, and retail networks, necessitates massive capital outlays. For instance, constructing a new, modern pipeline can easily cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This significant financial hurdle effectively discourages many aspiring companies from entering the market.
These substantial capital requirements act as a formidable barrier to entry. Potential new competitors must secure vast sums to acquire land, build or purchase storage facilities, lay pipelines, and establish a retail presence, making it an unattractive proposition for those without deep pockets.
Colonial Group benefits greatly from its established infrastructure, which represents a significant sunk cost for any new entrant. This existing network provides a strong competitive advantage, as replicating it would involve immense time and financial commitment, further solidifying Colonial Group's market position.
The petroleum and marine transportation industries face formidable regulatory hurdles and demanding environmental compliance standards. New companies must secure numerous permits and licenses, a process that is both time-consuming and costly, requiring significant legal expertise. For example, compliance with the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap on fuel oil, implemented in January 2020, necessitated substantial investments in new technologies or cleaner fuels for existing fleets, a burden that can deter smaller, less capitalized entrants.
Established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks pose a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to compete with incumbents like Colonial Group. For instance, in 2024, major players in the financial services sector often reported customer retention rates exceeding 90%, a testament to years of building trust and providing consistent service. Newcomers would need substantial investment in marketing and customer acquisition to even begin chipping away at this ingrained loyalty.
Furthermore, the logistical infrastructure and established relationships that companies like Colonial Group have cultivated over decades are incredibly difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate. Think about the widespread branch networks or the sophisticated digital platforms that are already deeply integrated into customer workflows. Building such a comprehensive and trusted distribution channel from scratch in 2024 would likely require hundreds of millions of dollars in upfront capital, making it a daunting prospect for any new competitor.
Difficulty in securing prime real estate locations for retail and port operations
The difficulty in securing prime real estate locations presents a substantial barrier for new entrants in the retail gasoline and port operations sectors. Access to strategically positioned sites is paramount for customer convenience and operational efficiency, yet these desirable locations are often scarce and already controlled by established players.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost of acquiring a prime retail location for a gas station could range from $1 million to $5 million or more, depending on the market. New companies must contend with high acquisition costs or long-term leases that can significantly impact initial capital outlay and ongoing operational expenses, making it tough to establish a competitive foothold.
- Limited Availability: Prime real estate for high-traffic retail gasoline stations and essential port facilities is a finite resource.
- High Acquisition Costs: Securing these sought-after locations often involves substantial upfront investment, potentially exceeding $5 million in major metropolitan areas in 2024.
- Incumbent Advantage: Existing businesses have already secured many of the most advantageous sites, leaving fewer options for newcomers.
- Zoning and Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex zoning laws and obtaining necessary permits for new retail or port operations can further complicate site acquisition.
Economies of scale and experience curve advantages enjoyed by existing players
Incumbent financial institutions like Colonial Group often leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs, such as technology infrastructure and regulatory compliance, over a larger volume of business, leading to lower per-unit costs for services like wealth management or transaction processing. For instance, a large bank might negotiate better rates with data providers or suppliers due to its sheer purchasing power, a benefit a new entrant would struggle to match initially.
Furthermore, Colonial Group benefits from an experience curve, having refined its operational processes and customer service strategies over years, or even decades, of operation. This accumulated knowledge allows for greater efficiency and potentially higher quality service delivery. New entrants would face a steep learning curve, likely incurring higher initial operating costs and potentially making costly mistakes as they build their own expertise, making it challenging to compete on price or service quality.
Consider the financial services sector in 2024. Major players often have operating margins that are several percentage points higher than newer, smaller firms, partly due to these scale and experience advantages. For example, a report from S&P Global Market Intelligence in late 2023 indicated that the largest global banks generally maintained stronger net interest margins compared to smaller regional banks, a trend often attributable to their scale.
- Economies of Scale: Colonial Group can achieve lower per-unit costs in procurement, operations, and logistics due to its large transaction volumes.
- Experience Curve: Years of operation have allowed Colonial Group to optimize processes and build institutional knowledge, leading to greater efficiency.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New competitors face higher initial costs and operational inefficiencies, hindering their ability to compete on price.
- Competitive Barrier: These advantages create a significant barrier, making it difficult for new players to enter and gain market share profitably.
The threat of new entrants for Colonial Group is significantly low due to immense capital requirements, estimated in the hundreds of millions to billions for infrastructure like pipelines. This financial barrier, coupled with established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, makes market entry exceptionally challenging for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to acquire prime real estate for a gas station could range from $1 million to $5 million, further deterring potential competitors.
Colonial Group's existing infrastructure represents a substantial sunk cost for any new entrant, requiring immense time and financial commitment to replicate. Regulatory hurdles and stringent environmental compliance standards, such as the IMO 2020 sulfur cap, also impose significant costs and complexities. These factors collectively create a formidable barrier, protecting Colonial Group's market position.
Furthermore, Colonial Group benefits from economies of scale and an experience curve, allowing for lower per-unit costs and optimized operations. In 2024, larger financial institutions typically maintained higher operating margins than smaller firms due to these advantages. New entrants face a steep learning curve and higher initial costs, making it difficult to compete on price or service quality.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Colonial Group is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and expert commentary from financial analysts. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and company press releases to capture the nuances of the competitive landscape.
