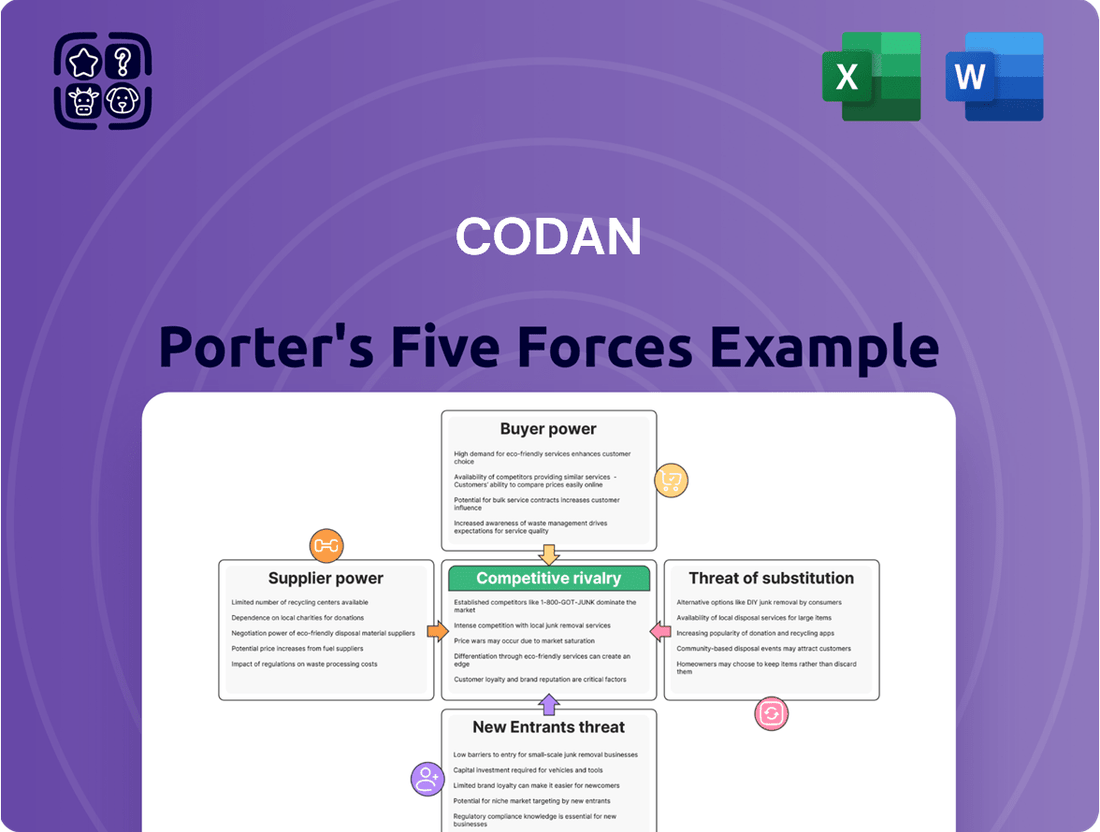
Codan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Codan Bundle
Codan operates in a dynamic market, facing significant pressures from rivals and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any strategic decision.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Codan’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Codan's reliance on a vast network of 1,050 direct suppliers across 32 countries suggests a generally fragmented supplier landscape, which typically dilutes the bargaining power of any single supplier.
However, the strategic outsourcing of a significant portion of its manufacturing to world-leading electronics manufacturers like Plexus Services Corp and Venture International Pte Ltd in Malaysia introduces a degree of concentration. This means that while the overall supplier base is broad, key manufacturing partners could wield more influence due to their specialized capabilities and importance to Codan's production.
Codan's switching costs with its suppliers are likely moderate to high. This is particularly true for highly specialized components or manufacturing services that are integral to their complex product lines.
Given Codan's emphasis on intellectual property-sensitive and high-complexity products, often manufactured at their head office or through select subcontractors, changing these critical suppliers could necessitate substantial re-tooling and rigorous qualification processes. This transition period could also lead to significant disruptions in their production schedules, impacting delivery timelines and overall operational efficiency.
Codan's reliance on specialized components for its mission-critical communication solutions and advanced metal detectors significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, the sophisticated electronics and proprietary materials needed for military-grade radios or high-sensitivity detection coils are often sourced from a limited number of specialized manufacturers.
This uniqueness means suppliers of these critical inputs hold considerable sway. If Codan’s products, like their secure tactical communication systems, depend on a single-source supplier for a vital microchip or a unique alloy, that supplier can dictate terms, potentially leading to higher input costs for Codan.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Codan's business, while generally low for specialized electronics, could emerge if a supplier holds unique technology or manufacturing expertise critical to Codan's operations. This would allow them to directly compete with Codan by offering finished products instead of just components.
Codan's significant investment in research and development, representing approximately 10% of its group sales in FY24, acts as a crucial countermeasure. This focus on internal capabilities helps Codan reduce reliance on any single supplier and explore alternative technological pathways, thereby diminishing the leverage suppliers might otherwise gain from potential forward integration.
Key considerations regarding this threat include:
- Supplier's technological advantage: The extent to which a supplier possesses proprietary technology or manufacturing processes that are difficult for Codan to replicate internally.
- Codan's R&D investment: The ongoing commitment to innovation and the development of in-house expertise as a buffer against supplier dependency.
- Component criticality: The degree to which Codan's product performance and market position depend on specific components supplied by a limited number of sources.
Importance of Codan to Suppliers
Codan's considerable material supplier expenditure, exceeding AUD 196 million in FY23, positions it as a crucial client for numerous suppliers. This substantial spend grants Codan a degree of negotiation power, especially when dealing with smaller or less diversified suppliers whose revenue could be significantly impacted by the loss of Codan's business.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key factor in Codan's industry analysis. Given Codan's large procurement volumes, suppliers are often incentivized to maintain favorable terms to secure this consistent revenue stream.
- Significant Customer: Codan's FY23 material supplier spend of over AUD 196 million highlights its importance to its supply chain partners.
- Leverage for Codan: This substantial spend provides Codan with leverage, particularly over smaller suppliers who rely heavily on its business.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers who depend on Codan for a significant portion of their revenue may be more willing to negotiate on price and terms to retain Codan as a customer.
While Codan's broad supplier base generally limits individual supplier power, the reliance on specialized components for its high-complexity products, such as military-grade radios, concentrates leverage with a few key manufacturers. Codan's significant R&D investment, around 10% of group sales in FY24, helps mitigate this by fostering internal capabilities and reducing dependency. The company's substantial FY23 material supplier expenditure exceeding AUD 196 million also provides considerable negotiation leverage, particularly with smaller suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Codan's Supplier Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High for specialized components | Reliance on world-leading electronics manufacturers for significant portions of manufacturing. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High | Specialized components and rigorous qualification processes for critical inputs. |
| Supplier Differentiation | High for unique technologies | Dependence on single-source suppliers for vital microchips or unique alloys in mission-critical systems. |
| Codan's Spend | Lowers supplier power | FY23 material supplier expenditure exceeded AUD 196 million, making Codan a crucial client. |
| Codan's R&D | Lowers supplier power | Approximately 10% of group sales invested in R&D in FY24 to reduce reliance. |
What is included in the product
Codan's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity of its operating environment by examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Pinpoint and neutralize competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Codan's customer base is quite spread out across various sectors like commercial, defense, government, humanitarian aid, and even individual consumers for their metal detection products. This diversity generally means that no single customer or small group of customers holds significant sway over Codan's pricing or terms.
While there might be instances where a very large government or defense contract could temporarily concentrate power, the overall wide reach of Codan's customers across these different markets helps to diffuse that potential power. This broad market penetration is a key factor in managing customer bargaining power.
Switching costs for Codan's customers present a varied landscape. For its defense and public safety segments, where communication systems are mission-critical, these costs are notably high. This is due to the deep integration with existing infrastructure, the extensive training required for personnel, and the sheer importance of uninterrupted operations. For instance, a government agency relying on Codan's secure radio systems would face significant expense and disruption in retraining staff and reconfiguring networks if they were to switch to a competitor.
Conversely, for customers in the recreational metal detector market, the barriers to switching are generally lower. While brand loyalty and the perceived performance of Codan's products can influence decisions, the financial and operational hurdles are less substantial compared to the professional sectors. A hobbyist might switch to a different brand for a new detector if a competitor offers a compelling feature set or a more attractive price point, with minimal impact on their operations.
The availability of substitute products significantly influences customer bargaining power. If customers can easily switch to alternatives offering similar benefits, their power increases.
In the radio communications sector, while other providers exist, Codan's niche in rugged, reliable solutions for demanding environments, particularly for military and emergency services, may reduce the number of direct substitutes for its high-end offerings. This specialization can lessen customer power by limiting readily available alternatives.
For metal detectors, Codan's Minelab brand enjoys a strong market position, especially in specialized areas like gold prospecting. This dominance in specific segments suggests that for these particular customers, the availability of effective substitutes is limited, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity within Codan's markets varies significantly by segment. For instance, defense and public safety sectors, where operational continuity and equipment failure are unacceptable, tend to exhibit lower price sensitivity. These customers prioritize robust performance and reliability, often overlooking marginal cost differences for superior product assurance. In contrast, commercial and recreational users, while still valuing quality, may be more inclined to compare prices and seek the most cost-effective solutions.
However, it's crucial to recognize that even in specialized markets, price sensitivity can emerge. Budgetary limitations and the prevalence of competitive bidding processes, particularly in government contracts, can exert considerable pressure on pricing. For example, in 2024, many government procurement cycles emphasized value for money, leading to increased scrutiny of unit costs across all suppliers, including those in the defense and public safety technology sectors.
This dynamic means that while Codan's core defense and public safety clients might accept higher prices for critical functionality, they are not immune to cost-consciousness. The company must balance the need to invest in advanced, reliable technology with the market realities of budget constraints and competitive pressures. This is evident in tender processes where even the most critical equipment requires justification of its cost-benefit ratio.
The bargaining power of customers is thus influenced by these differing sensitivities:
- Defense/Public Safety: Lower price sensitivity due to critical operational needs, but increasing budget awareness.
- Commercial/Recreational: Higher price sensitivity, actively seeking competitive pricing.
- Procurement Processes: Competitive bidding and value-for-money mandates can amplify price sensitivity across all segments.
- Technological Advancements: While driving demand, the cost of adopting new technologies can also introduce price considerations for customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by Codan's customers is generally low. For instance, government agencies or individual consumers purchasing specialized communications equipment or metal detectors lack the substantial capital, intricate technical knowledge, and proprietary intellectual property needed to establish their own manufacturing operations. These high barriers effectively deter such integration.
The complexity and specialized nature of Codan's product lines, such as advanced radio communications systems and sophisticated metal detection technology, require significant investment in research and development, specialized manufacturing facilities, and a highly skilled workforce. These factors make it economically unfeasible for most customers to consider producing such equipment in-house.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing manufacturing capabilities for advanced electronics and communication systems requires millions in specialized machinery and facilities.
- Technical Expertise: Designing and producing high-frequency radio components or sensitive metal detection circuitry demands deep engineering and scientific knowledge.
- Intellectual Property: Codan's proprietary designs and patented technologies present a significant hurdle for potential imitators or backward integrators.
Codan's diverse customer base, spanning commercial, defense, government, and recreational sectors, generally limits the bargaining power of any single customer. While high switching costs exist for critical defense and public safety systems due to integration and training, recreational users face lower barriers. Price sensitivity also varies, with defense clients showing less concern for cost than commercial users, though budget constraints in 2024 increased price scrutiny across all segments, especially in government procurement.
The threat of backward integration by Codan's customers is minimal due to the high capital investment, specialized technical expertise, and proprietary intellectual property required to manufacture advanced communications and metal detection equipment. These barriers make it economically unfeasible for most customers to produce such goods in-house.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Switching Costs | Backward Integration Threat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defense/Public Safety | Lower, but increasing budget awareness | High (mission-critical integration, training) | Very Low |
| Commercial/Recreational | Higher, competitive pricing sought | Low to Moderate | Very Low |
| Government (Procurement) | Amplified by value-for-money mandates | Moderate (contract-specific) | Very Low |
Same Document Delivered
Codan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Codan Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can confidently proceed with your acquisition, knowing you'll gain immediate access to this comprehensive strategic tool.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Codan faces a dynamic competitive landscape. In its radio communications segment, it contends with giants like Motorola Solutions and Thales, alongside significant players such as Hytera, and a multitude of smaller, specialized providers. This broad spectrum, from global behemoths to niche specialists, means Codan must constantly innovate and differentiate itself to maintain its market standing.
The metal detection market also presents a diverse competitive set, featuring numerous brands catering to various user needs, from hobbyists to professional security and mining operations. While Codan holds a strong position in its core competencies, the sheer number of competitors across its operating segments underscores a healthy degree of rivalry, demanding continuous strategic focus and operational excellence.
The industry growth rate for Codan's key segments, particularly communications, shows a positive outlook. This is largely fueled by increased military spending and significant government investment in public safety initiatives. For instance, global defense spending was projected to reach $2.4 trillion in 2024, a substantial increase that directly benefits companies like Codan providing critical communication systems.
Codan itself experienced robust revenue growth in its fiscal year 2024, with both its communications and metal detection divisions performing strongly. The company is actively pursuing further organic growth, indicating confidence in market expansion and its ability to capture new opportunities. This growth trajectory suggests a favorable environment for the business.
A burgeoning market, characterized by a healthy growth rate, can often temper intense, price-focused competition. When demand is on the rise, companies tend to prioritize expanding their market share by meeting new customer needs rather than engaging in aggressive price wars. This dynamic can lead to a more stable competitive landscape for established players.
Codan's strategy heavily relies on differentiating its electronic solutions by focusing on ruggedness and reliability, specifically for harsh environments. This approach positions their products as superior for demanding applications.
This differentiation is particularly evident in their military and humanitarian demining product lines, where failure is not an option. By excelling in these niche, high-stakes markets, Codan can effectively sidestep direct price-based competition from less specialized rivals.
For instance, in 2023, Codan's revenue reached AUD 357.7 million, with a significant portion likely driven by these specialized, differentiated products that command premium pricing due to their proven performance in extreme conditions.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers in specialized markets like defense and public safety are notably high. This is largely due to the significant investment in integration and extensive training required for operating sophisticated equipment. For instance, a government agency adopting a new communication system might face costs associated with retraining personnel, recalibrating existing infrastructure, and ensuring interoperability with other critical systems. These factors create a substantial barrier to switching, directly impacting competitive rivalry.
These elevated switching costs can dampen the intensity of competitive rivalry. When customers face considerable expense and operational disruption to change providers, they are less inclined to explore alternative options. This sticky customer base allows established players like Codan to maintain a more stable market position, as the effort and cost involved in switching to a competitor deter frequent customer churn. This dynamic is crucial for understanding Codan's competitive landscape.
- High Integration Costs: Specialized equipment often requires deep integration into existing operational frameworks, making a switch complex and expensive.
- Training Investment: Significant resources are typically allocated to training personnel on new systems, adding to the overall cost of changing vendors.
- Reduced Customer Churn: The financial and operational hurdles associated with switching discourage customers from moving to competitors, fostering customer loyalty.
- Market Stability: For companies like Codan, these high switching costs contribute to a more predictable revenue stream and a less volatile competitive environment.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for companies like Codan, operating in specialized technology solutions, are often substantial. This is primarily due to the significant capital commitment required for research and development, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and the protection of intellectual property. For instance, in the defense technology sector, where Codan has a presence, R&D spending can represent a considerable portion of revenue; in 2023, major defense contractors globally saw R&D investments ranging from 5% to over 10% of their sales.
The highly specialized nature of Codan's assets and its deep technical expertise further complicate market exit. Divesting or repurposing these unique assets without incurring significant losses can be challenging. This difficulty in exiting the market can compel existing players to remain engaged and continue competing, even in less favorable conditions, to avoid realizing those substantial exit costs.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized technology often requires substantial upfront investment in R&D and manufacturing, making it costly to abandon.
- Asset Specificity: Codan's unique technology and equipment may have limited alternative uses, increasing losses upon exit.
- Intellectual Property: Significant investment in patents and proprietary knowledge creates a barrier to simply walking away.
- Market Commitment: Once a company has established a presence and reputation in a niche, exiting can be seen as a failure, impacting future ventures.
Competitive rivalry within Codan's operating segments is significant, featuring both large multinational corporations and numerous smaller, specialized entities. This broad competitive base necessitates continuous innovation and differentiation to maintain market share. For instance, in the radio communications sector, Codan competes with established players like Motorola Solutions and Thales, alongside agile niche providers.
Despite the presence of strong competitors, the growth potential in Codan's key markets, such as defense and public safety communications, helps to moderate intense price competition. Global defense spending, projected to reach $2.4 trillion in 2024, provides a growing demand pool. Codan's strategy of focusing on rugged, reliable solutions for harsh environments, particularly in military and demining sectors, allows it to command premium pricing and sidestep direct price wars.
High switching costs for customers in specialized fields, driven by integration complexity and training requirements, further stabilize the competitive landscape. These costs encourage customer loyalty and reduce churn, benefiting established providers like Codan. For example, the significant investment in retraining personnel and recalibrating infrastructure when adopting new communication systems creates a substantial barrier to switching vendors.
Exit barriers for companies in specialized technology sectors are also considerable, stemming from high R&D investments and the specificity of assets. Codan's commitment to these high-barrier markets, coupled with its differentiated product strategy, contributes to a less volatile competitive environment, allowing it to focus on value-based competition rather than solely price.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Codan's specialized radio communications hinges on whether alternatives can match its performance at a lower price or offer superior performance at a comparable cost. For mission-critical applications where reliability and specific functionalities are paramount, generic consumer devices like smartphones or standard Wi-Fi systems are generally not viable substitutes.
However, the landscape of communication technology is constantly evolving. Emerging technologies, such as advanced satellite communication solutions or highly integrated mesh networks, could potentially offer comparable or even enhanced capabilities in the future, presenting a long-term threat to Codan's market position if they become more cost-effective.
Customer propensity to substitute is generally low in Codan's core mission-critical segments, such as defense and public safety. In these areas, the need for unwavering reliability, robust security, and highly specialized features significantly reduces the likelihood of customers switching to alternative solutions, even if those alternatives are less expensive. This is particularly true for critical communications equipment where failure is not an option.
For Codan's recreational metal detection segment, specifically under the Minelab brand, the threat of substitutes varies. While cheaper, less advanced detectors are available and may appeal to casual users, serious prospectors and dedicated hobbyists often prioritize the superior performance, depth, and discrimination capabilities offered by specialized brands like Minelab. This segmentation means that while some substitution exists, it's less impactful among the most valuable customer base.
Codan's perceived level of product differentiation is a key factor in mitigating the threat of substitutes. Its high-frequency radios, designed for rugged, demanding environments, and advanced metal detectors for specialized uses like gold prospecting or demining, stand out from more generic offerings.
Customers frequently opt for Codan due to its established reputation for reliability and superior performance in conditions where less specialized alternatives would likely falter. This focus on niche, high-performance applications creates a barrier against readily available, lower-quality substitutes.
Availability of Alternative Technologies
The threat of substitutes for Codan's offerings is significant due to the rapid pace of technological advancement. New communication and detection technologies are constantly emerging, potentially serving as alternatives to Codan's current product lines. For instance, advancements in satellite communication and the expansion of high-speed cellular networks could offer comparable or superior functionality in certain applications.
Codan's proactive approach includes substantial investment in research and development. In 2024, the company continued to prioritize innovation to stay ahead of these evolving alternatives. This commitment to R&D is crucial for maintaining product competitiveness and relevance in a dynamic market landscape.
Key areas where substitutes pose a threat include:
- Satellite Communication: Increasingly affordable and accessible satellite internet and communication solutions can bypass traditional terrestrial networks.
- Advanced Cellular Networks: The ongoing rollout of 5G and future cellular technologies offers higher bandwidth and lower latency, potentially replacing some specialized communication needs.
- Emerging Detection Technologies: Innovations in sensor technology and data analytics could provide alternative methods for detection and monitoring, impacting Codan's security and surveillance segments.
Cost of Switching to a Substitute
The cost for customers to switch to a substitute for Codan's communication systems can be substantial. For sectors like defense and emergency services, this involves not just the price of new hardware but also extensive retraining of personnel, ensuring interoperability with existing infrastructure, and managing potential disruptions to critical operations. For instance, a government agency might spend millions on new radios, software licenses, and a year-long training program to transition from one system to another.
These switching costs significantly reduce the attractiveness of substitutes. Codan's integrated solutions, often tailored for demanding environments, create a high barrier to entry for competitors. The complexity and mission-critical nature of these systems mean that reliability and proven performance are paramount, often outweighing minor cost savings from alternative providers. In 2024, the defense sector alone saw significant investment in secure communication upgrades, with many nations prioritizing established vendors like Codan due to these high switching costs.
- High Monetary Investment: Acquiring new communication hardware and software can run into millions of dollars for large organizations.
- Training and Skill Development: Equipping staff with the knowledge to operate and maintain new systems is a significant, ongoing expense.
- Interoperability Challenges: Ensuring new systems can communicate seamlessly with existing networks and equipment is crucial and often complex.
- Operational Disruption Risk: The transition period can lead to temporary reductions in efficiency or communication breakdowns, impacting critical services.
The threat of substitutes for Codan's specialized communication and metal detection products is moderate but growing, driven by technological advancements and increasing affordability of alternatives. While mission-critical applications in defense and public safety have low propensities to substitute due to high reliability needs and switching costs, segments like recreational metal detecting see more competition from lower-priced, less sophisticated devices. Codan's differentiation through performance and ruggedness in specialized niches helps mitigate this threat, but ongoing R&D is crucial to counter emerging technologies like advanced satellite communication and 5G networks.
Codan's commitment to innovation, including significant R&D investment in 2024, aims to stay ahead of potential substitutes. For instance, advancements in satellite communication offer alternatives to terrestrial radio systems, and the expanding 5G network provides higher bandwidth for certain communication needs. Emerging detection technologies also present a long-term challenge across its business segments.
The high cost associated with switching to substitute communication systems for Codan's core customers, particularly in defense and emergency services, acts as a significant deterrent. These costs encompass not only new hardware but also extensive retraining and ensuring interoperability, making Codan's integrated and reliable solutions highly valuable.
In 2024, Codan reported robust performance in its communication segment, driven by demand for its specialized, high-frequency radios. This demand is partly fueled by the significant switching costs customers face when considering alternatives, which can easily reach millions of dollars for large organizations due to training, integration, and operational disruption risks.
| Technology Area | Potential Substitutes | Impact on Codan (2024) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Communications | Satellite Communication, 5G Networks | Moderate Threat (growing) | Reliability, security, specialized features remain key differentiators; switching costs are high for core customers. |
| Metal Detection | Lower-priced generic detectors | Moderate Threat (segment-specific) | Serious users prioritize performance and depth, mitigating substitution for high-end Minelab products. |
| R&D Investment | N/A | Mitigation Strategy | Continued investment in 2024 to maintain technological edge against evolving alternatives. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering Codan's specialized markets, like defense communications or advanced metal detection, demands significant upfront investment. Think about the costs for cutting-edge research and development, building state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and establishing robust global distribution channels. For instance, companies in the defense sector often face R&D budgets in the tens of millions of dollars annually, and setting up production lines for sophisticated electronics can easily run into hundreds of millions.
Established players like Codan leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, creating a substantial cost advantage. For instance, in 2024, large telecommunications equipment manufacturers often achieve production costs per unit that are 20-30% lower than smaller competitors due to bulk purchasing and optimized production lines.
New entrants would face immense difficulty replicating these cost efficiencies without a substantial initial sales volume. This barrier makes it challenging for them to compete effectively on price against incumbents who have already amortized their fixed costs over a much larger output.
Codan's significant investment in proprietary product technology, particularly in specialized radio communications and metal detection, acts as a formidable barrier to new entrants. This intellectual property (IP) requires substantial upfront R&D expenditure to replicate, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on technological parity.
For instance, the development cycle for advanced communication systems can span several years and cost millions. In 2023, Codan reported significant R&D investments, underscoring their commitment to maintaining a technological edge. New players would face a steep climb, needing to either match these R&D outlays or acquire expensive existing IP, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive.
Access to Distribution Channels
Codan's established global distribution network, reaching over 150 countries through a mix of direct sales, dealers, distributors, and agents, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. Building a comparable reach requires immense capital and time to cultivate the necessary relationships and market penetration.
For instance, in 2024, a new entrant attempting to replicate Codan's distribution footprint would likely face upfront investment costs exceeding tens of millions of dollars, considering the logistical infrastructure, partner onboarding, and marketing required to secure shelf space and customer access in diverse international markets.
- Extensive Global Reach: Codan operates in over 150 countries.
- Diverse Sales Channels: Utilizes direct sales, dealers, distributors, and agents.
- High Entry Barrier: Significant investment and time needed to replicate this network.
- Market Access Challenge: Newcomers struggle to gain comparable market penetration.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations present a significant hurdle for new entrants in sectors like defense and public safety, where Codan operates. These industries are characterized by complex certifications, lengthy approval processes, and strict procurement protocols. Codan's long-standing compliance and established relationships with governmental bodies create a substantial competitive moat, making it difficult for newcomers to navigate these requirements. For instance, in 2024, the defense sector continued to see increased regulatory scrutiny, with many nations prioritizing domestic suppliers and adhering to national security frameworks that favor established players.
Export controls and national security considerations further exacerbate the threat of new entrants. These regulations can restrict market access for companies that do not meet specific governmental standards or have established trust with national security agencies. Codan's experience in managing these international compliance requirements provides a distinct advantage, limiting the pool of potential competitors capable of operating in these sensitive markets.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Defense and public safety sectors demand adherence to stringent certifications and procurement processes, acting as a barrier to entry.
- Established Relationships: Codan benefits from its existing ties with government agencies, a key advantage over new competitors.
- National Security & Export Controls: These factors limit market access and competition, favoring companies with proven compliance records like Codan.
The threat of new entrants for Codan is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, especially in specialized sectors like defense communications. For example, establishing advanced electronics production lines can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. Furthermore, Codan's established economies of scale in 2024, where larger manufacturers often achieve 20-30% lower unit costs, make it difficult for newcomers to compete on price without significant initial sales volume.
Codan's strong intellectual property and years of R&D investment, running into millions annually as seen in their 2023 reports, create a high barrier. New entrants would need to either match these R&D expenditures or acquire costly IP to achieve technological parity. Additionally, Codan's extensive global distribution network, covering over 150 countries, requires tens of millions in upfront investment to replicate, further deterring new competition.
Government regulations and national security considerations in Codan's operating sectors, such as defense, pose significant hurdles. The lengthy certification processes and strict procurement protocols favor established players with proven compliance records and existing government relationships. Export controls also limit market access for companies lacking this established trust and experience, effectively reducing the pool of potential new entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for R&D and manufacturing. | Electronics production lines: Hundreds of millions USD. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages for established players. | Large manufacturers: 20-30% lower unit costs. |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary technology requiring significant R&D. | Codan's R&D investment: Millions annually (2023). |
| Distribution Network | Established global reach and sales channels. | Replication cost: Tens of millions USD. |
| Government Regulations | Certifications, approvals, and procurement protocols. | Defense sector: Increased regulatory scrutiny. |
| Export Controls | Restrictions based on national security and compliance. | Favors companies with proven compliance and trust. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Codan Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial statements to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
