CNH Industrial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CNH Industrial Bundle
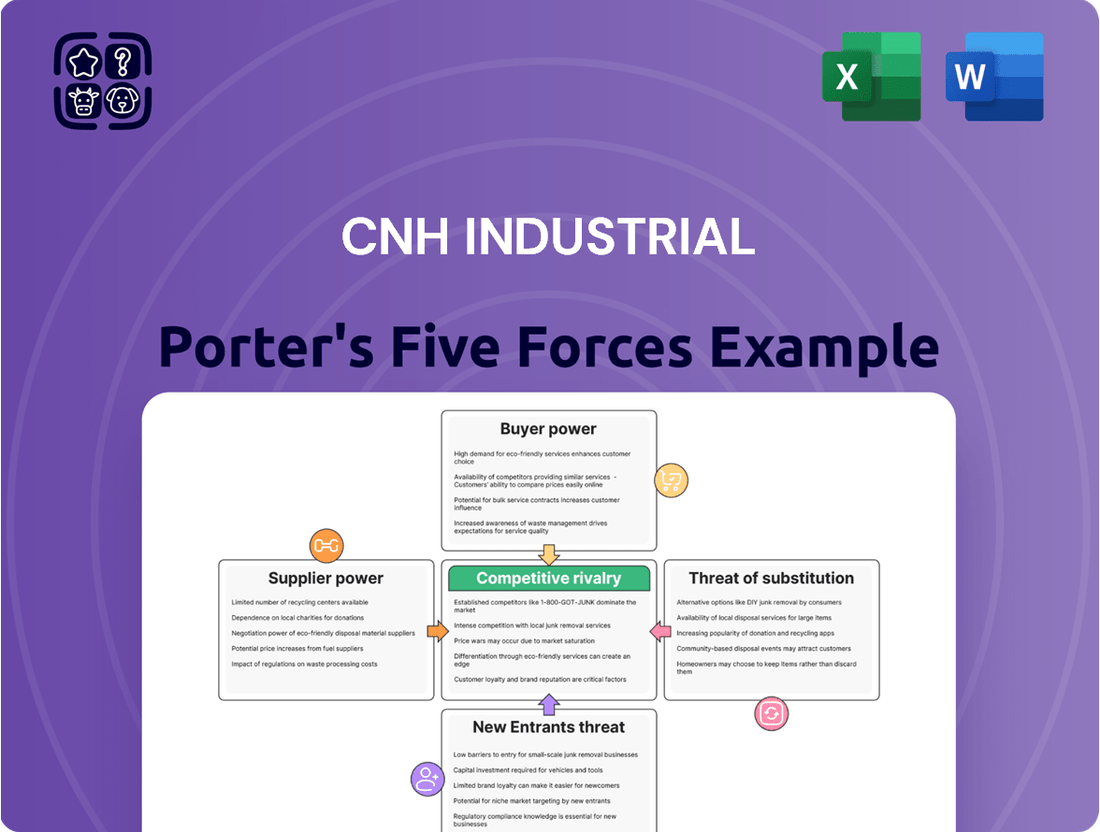
CNH Industrial navigates a competitive landscape shaped by significant buyer power and the constant threat of substitutes in the agricultural and construction equipment sectors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic positioning.
The full report reveals the real forces shaping CNH Industrial’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CNH Industrial depends on a vast global supply chain for essential parts like steel, engines, and sophisticated electronics, crucial for its agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and vehicles. When a few suppliers dominate the market for specialized components, such as unique engine parts or high-tech sensors for precision farming, their leverage over CNH Industrial naturally grows.
CNH Industrial faces substantial switching costs when changing suppliers, especially for critical, integrated components or proprietary technologies. These costs can include re-engineering existing systems, the lengthy process of requalifying new suppliers, and the inherent risk of supply chain disruptions. Such barriers significantly bolster the bargaining power of CNH Industrial’s current suppliers.
Suppliers providing unique, patented, or highly specialized components for CNH Industrial's diverse product lines, like advanced powertrain systems or proprietary digital farming technologies, wield significant bargaining power. This distinctiveness restricts CNH Industrial's ability to switch suppliers, thereby heightening its dependence. For instance, in 2024, the agricultural machinery sector saw continued innovation in precision farming technology, with a few key players holding patents on critical sensor and data analytics modules.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If CNH Industrial's key suppliers possess the ability and motivation to move into producing components or even complete sub-assemblies that CNH currently makes, their leverage would grow. This risk is especially significant for components that are high in value or involve critical technologies.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers could enter CNH Industrial's value chain by producing parts or finished goods CNH currently handles.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Such a move would directly increase supplier leverage over CNH Industrial.
- Critical Components: The threat is most pronounced for high-value, technologically advanced components.
Importance of CNH Industrial to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers to CNH Industrial is significantly shaped by how crucial CNH Industrial is as a customer to them. If CNH Industrial accounts for a substantial percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier will likely be more amenable to offering competitive pricing and favorable contract terms. This is because losing CNH Industrial as a client could have a considerable impact on their financial performance.
Conversely, if CNH Industrial represents only a minor portion of a supplier's business, the supplier's leverage increases. In such scenarios, the supplier may feel less pressure to concede on price or other contract stipulations, as their overall revenue is not heavily dependent on CNH Industrial. This dynamic can lead to less favorable terms for CNH Industrial.
For instance, in 2023, CNH Industrial's total cost of goods sold was approximately $23.6 billion. The distribution of this spending across its various suppliers dictates the relative importance of CNH Industrial to each. Suppliers who provide critical, specialized components and for whom CNH Industrial is a primary customer will wield less bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which a supplier relies on CNH Industrial for its revenue directly impacts its bargaining power.
- CNH Industrial's Scale: CNH Industrial's substantial purchasing volume can provide leverage, but this is diluted if the supplier serves many large customers.
- Component Specificity: Suppliers of highly specialized or proprietary components may have more power, regardless of CNH Industrial's overall importance to them.
- Market Concentration: If only a few suppliers can provide a necessary component, their bargaining power is inherently higher.
CNH Industrial's suppliers, particularly those providing specialized components like advanced engine parts or precision farming electronics, hold significant bargaining power due to high switching costs and the proprietary nature of their offerings. For example, in 2024, the agricultural sector saw continued innovation in precision farming, with a few key players holding patents on critical sensor modules, directly increasing their leverage.
The bargaining power of CNH Industrial's suppliers is influenced by CNH's importance as a customer. If CNH represents a small portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier has more leverage. In 2023, CNH Industrial's cost of goods sold was approximately $23.6 billion, but the distribution of this spending across its supplier base determines the relative power dynamics.
| Factor | Impact on CNH Industrial | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High power for few dominant suppliers | Patented precision farming sensors (2024) |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier leverage | Re-engineering, requalification processes |
| CNH's Customer Importance | Less power if CNH is a minor customer | CNH's COGS: ~$23.6 billion (2023) |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within the agricultural and construction equipment sectors, detailing supplier and buyer power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and CNH Industrial's strategic positioning.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting CNH Industrial.
Customers Bargaining Power
CNH Industrial caters to a broad range of customers, from individual farmers to large construction firms and government agencies. The bargaining power of these buyers is significantly shaped by their concentration and the sheer volume of their purchases. For instance, major agricultural cooperatives or large construction companies that buy in bulk can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms.
In 2023, CNH Industrial's net sales for its Agriculture segment reached $16.4 billion, and its Construction segment generated $5.3 billion in net sales. This indicates substantial purchase volumes from various customer groups, with larger entities likely holding more sway in negotiations due to the scale of their commitments.
For CNH Industrial customers, the investment in their current fleet of agricultural and construction equipment represents a significant barrier to switching. This includes the capital already spent on machinery, the ongoing costs of maintenance and parts, and the established network of dealerships that provide essential service and support.
The familiarity operators have with CNH Industrial's operating systems and the specialized training required to use and maintain different brands also contribute to higher switching costs. For instance, a farmer deeply invested in a particular brand's precision agriculture technology will face considerable expense and disruption to adopt a competitor's system.
These substantial switching costs, often involving significant capital outlay for new equipment and the retraining of personnel, generally diminish the bargaining power of CNH Industrial's customers. In 2023, CNH Industrial reported revenues of approximately $24.4 billion, indicating a large installed base of equipment where switching costs play a crucial role.
Customers in CNH Industrial's agricultural and construction markets are typically very knowledgeable. They conduct thorough research on equipment specs, performance, and pricing, especially given the significant capital investment required for these purchases. This deep understanding and the availability of competitive alternatives empower them to negotiate favorable terms, increasing their bargaining power.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers integrating backward and producing their own agricultural and construction machinery, trucks, and powertrain solutions is generally low for CNH Industrial. This is due to the significant capital investment, complex manufacturing processes, and specialized technical expertise required, which are substantial barriers for most customers.
This limited threat directly curbs the bargaining power of customers. They are unlikely to possess the scale or capabilities to effectively replicate CNH Industrial's integrated operations, thus maintaining CNH's competitive advantage in production and innovation.
- Low Likelihood of Backward Integration: Customers typically lack the extensive capital and specialized knowledge needed to vertically integrate into manufacturing heavy machinery, limiting their ability to produce equipment in-house.
- High Barriers to Entry for Customers: The sheer complexity and cost of establishing manufacturing facilities comparable to CNH Industrial's global footprint present a formidable challenge for potential customer integration.
- Reduced Customer Bargaining Power: Because customers cannot easily produce their own equipment, their leverage to negotiate lower prices or demand specific features from CNH Industrial is significantly diminished.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly amplifies customer bargaining power for CNH Industrial. When customers can easily find alternative brands or types of equipment that perform similar functions, their leverage to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms rises. For instance, in the agricultural sector, a farmer can choose between CNH's Case IH tractors and John Deere tractors, or even consider smaller, specialized manufacturers, directly influencing price sensitivity.
This abundance of choices means CNH Industrial must remain competitive on price and features to retain its customer base. In 2024, the construction equipment market, a key segment for CNH, saw increased competition with new entrants and established players expanding their product lines, further empowering buyers. For example, reports indicated that the global construction equipment market was projected to reach over $200 billion in 2024, with a significant portion driven by product innovation and competitive pricing strategies from various manufacturers.
- High Availability of Alternatives: Customers can readily source comparable equipment from numerous competitors, diminishing CNH's pricing control.
- Impact on Pricing: The presence of substitutes forces CNH to offer competitive pricing to avoid losing market share.
- Customer Choice and Flexibility: A wide array of options provides customers with the flexibility to switch suppliers based on price, quality, or service.
CNH Industrial's customers, particularly large agricultural cooperatives and construction firms, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchase volumes. In 2023, CNH Industrial's net sales for its Agriculture segment were $16.4 billion and for its Construction segment were $5.3 billion, highlighting the scale of customer commitment and the leverage this provides.
The high switching costs associated with CNH Industrial's equipment, including capital investment in existing fleets and specialized training, generally reduce customer bargaining power. However, the availability of numerous substitute products from competitors in the global construction equipment market, projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, empowers customers to negotiate more aggressively on price and terms.
| Factor | CNH Industrial's Position | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration & Volume | High concentration among large buyers | Increases bargaining power |
| Switching Costs | High due to capital investment and training | Decreases bargaining power |
| Availability of Substitutes | High, with many competitors | Increases bargaining power |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low due to high capital and expertise requirements | Decreases bargaining power |
Full Version Awaits
CNH Industrial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details CNH Industrial's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products within the agricultural and construction machinery sectors.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The capital goods sector, especially for agricultural and construction equipment, sees a moderate number of significant global companies like John Deere, AGCO, and Caterpillar. This group is complemented by various regional and niche producers, creating a dynamic competitive landscape.
This mix of large, international players and smaller, specialized firms intensifies rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the global agricultural machinery market was valued at approximately $200 billion, with these major players holding substantial market share but facing constant pressure from emerging competitors and technological advancements.
The agricultural and construction equipment sectors, where CNH Industrial primarily operates, have seen a noticeable slowdown in demand and a dip in sales recently. This cooling market trend, with a projected industry growth rate that is either flat or negative for 2024, naturally escalates the competitive intensity among established companies.
CNH Industrial distinguishes its agricultural and construction equipment through significant investments in technological innovation. For instance, their AI-powered precision agriculture solutions and advancements in electric vehicle technology set them apart. Brand recognition, particularly with established names like Case IH and New Holland, also plays a crucial role in customer loyalty and perceived product value.
While CNH Industrial boasts strong brand equity and technological advancements, the competitive landscape is fierce. Competitors like John Deere and AGCO are also heavily investing in research and development, continually pushing the boundaries of innovation in areas such as autonomous farming and sustainable power sources. This ongoing R&D arms race means that maintaining a distinct product advantage requires constant effort and substantial capital outlay.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly intensify competitive rivalry within the agricultural and construction equipment sectors. These barriers include substantial investments in specialized machinery and manufacturing facilities, which are difficult to repurpose or sell. For instance, CNH Industrial, a major player, has extensive global manufacturing footprints dedicated to specific product lines, making divestment costly.
The presence of significant fixed costs, such as R&D, distribution networks, and brand building, further entrenches companies in the market. Contractual obligations with suppliers and dealers also create hurdles for exiting. These factors compel companies to persist in competing, even when profitability is low, leading to prolonged periods of intense price competition and market share battles.
For example, in 2024, the agricultural machinery market faced headwinds due to fluctuating commodity prices and interest rates. Despite these challenges, major manufacturers like CNH Industrial continued to invest in new technologies and maintain production levels, a testament to the high exit barriers that prevent a rapid contraction of supply.
- Specialized Assets: CNH Industrial's factories are highly specialized for producing tractors and construction equipment, with limited alternative uses, increasing the cost of exiting.
- Significant Fixed Costs: High ongoing investments in R&D for autonomous farming and electric construction vehicles lock companies into these markets.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term agreements with dealer networks and component suppliers create financial penalties for early termination, deterring market exit.
- Emotional Factors: Management's commitment to established brands and market presence can also act as a psychological exit barrier, encouraging continued competition.
Strategic Commitments of Rivals
Rivals such as John Deere and Caterpillar are heavily investing in precision agriculture, electrification, and digital solutions, signaling long-term strategic commitments. These significant investments are designed to secure future market leadership and enhance their competitive standing within the agricultural and construction equipment sectors.
CNH Industrial's strategic plan mirrors this focus, emphasizing technology leadership, a refined go-to-market strategy, and product innovation. For instance, CNH Industrial announced a plan to invest over $2 billion in electrification and autonomous technologies through 2026, aiming to bolster its product portfolio and market competitiveness.
- John Deere's investment in autonomous technology: John Deere has been a leader in precision agriculture, with its autonomous tractor technology being a key differentiator.
- Caterpillar's electrification push: Caterpillar is investing heavily in electric and hybrid-powered equipment, aiming for zero-emission solutions in its construction machinery.
- CNH Industrial's technology focus: CNH Industrial's commitment to technology leadership includes advancements in connected services and advanced farming solutions, as seen in its 2024 product launches.
The competitive rivalry within the capital goods sector, particularly for agricultural and construction equipment where CNH Industrial operates, is intense. This is driven by a moderate number of large global players like John Deere and Caterpillar, alongside numerous regional and niche competitors, all vying for market share in a sector valued at around $200 billion globally in 2024.
The current market conditions, with a slowdown in demand and flat to negative industry growth projected for 2024, further exacerbate this rivalry, forcing companies to compete aggressively on price and innovation to maintain sales.
CNH Industrial and its rivals are heavily investing in R&D for areas like autonomous farming and electrification, with CNH Industrial planning to invest over $2 billion through 2026, highlighting the continuous innovation arms race. High exit barriers, including specialized assets and significant fixed costs, also compel companies to remain in the market, perpetuating fierce competition.
| Company | Key Focus Areas | 2024 Market Activity Example |
|---|---|---|
| CNH Industrial | Electrification, Autonomous Tech, Connected Services | Continued investment in technology leadership, new product launches |
| John Deere | Autonomous Tractors, Precision Agriculture | Leader in autonomous technology, significant R&D investment |
| Caterpillar | Electrification, Hybrid Power | Investing heavily in zero-emission construction machinery |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for CNH Industrial's agricultural and construction equipment is significant, stemming from alternative technologies that can achieve similar outcomes. For instance, advancements in precision agriculture, like drone-based crop monitoring and automated weeding systems, can reduce the reliance on traditional heavy machinery for certain tasks. In construction, innovative building materials and prefabrication techniques might lessen the demand for specific types of earthmoving or lifting equipment.
Customers meticulously weigh the price against the performance capabilities when considering substitute products or services. For instance, if advanced equipment rental services offer comparable functionality at a lower overall cost than purchasing CNH Industrial machinery, this presents a strong competitive pressure. In 2024, the increasing accessibility of specialized rental fleets, particularly for short-term or project-specific needs, directly challenges the traditional ownership model for construction and agricultural equipment.
Customer propensity to substitute for CNH Industrial's agricultural and construction equipment is influenced by several factors. For smaller operations or those facing economic headwinds, a shift towards less technologically advanced, more affordable machinery or even increased reliance on manual labor can become a viable alternative. This willingness to switch is often tied to the perceived risk and tangible economic benefits of adopting new solutions.
Regulatory or Environmental Shifts
Changes in regulations or heightened environmental awareness can significantly boost the appeal of substitute products. For instance, more stringent emissions mandates could push manufacturers and end-users towards electric or alternative-fuel machinery, potentially hastening a move away from conventional diesel engines if CNH Industrial is slow to innovate.
CNH Industrial, for example, faces increasing pressure from evolving environmental standards globally. In 2024, many regions are tightening emission controls on off-road and agricultural machinery. This regulatory push directly impacts the cost and viability of traditional internal combustion engine products, making cleaner alternatives more attractive.
- Stricter Emissions Standards: Regulations like Tier 5 in Europe and EPA Tier 4 Final in the US continue to evolve, increasing the complexity and cost of diesel engine technology.
- Government Incentives for Green Tech: Many governments are offering subsidies and tax credits for electric and alternative-fuel vehicles, making these substitutes more cost-competitive.
- Consumer and Corporate ESG Goals: Growing emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors by customers and investors incentivizes the adoption of more sustainable equipment options.
- Advancements in Alternative Fuels: Developments in hydrogen, biogas, and advanced biofuels are making these energy sources more practical and efficient for heavy-duty applications.
Emergence of Service-Based Models
The increasing prevalence of equipment-as-a-service (EaaS) models and shared economy platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for CNH Industrial. Customers are increasingly opting to rent or share heavy machinery instead of purchasing it outright, directly impacting the demand for new equipment sales.
This shift towards access over ownership could erode CNH Industrial's traditional revenue streams. For instance, in 2024, the global equipment rental market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating further expansion as businesses prioritize flexibility and reduced capital expenditure.
- EaaS models offer customers lower upfront costs and predictable operational expenses.
- Shared economy platforms provide access to a wider range of equipment without the burden of ownership and maintenance.
- This trend directly competes with CNH Industrial's core business of selling new agricultural and construction equipment.
- The growing acceptance of these alternative models signals a potential long-term reduction in the need for outright equipment purchases.
The threat of substitutes for CNH Industrial is amplified by the growing popularity of equipment-as-a-service (EaaS) and shared economy models. These alternatives offer customers flexibility and lower upfront costs compared to outright ownership, directly impacting CNH Industrial's traditional sales. In 2024, the global equipment rental market continued its strong upward trajectory, demonstrating a clear customer preference for access over ownership.
This trend challenges CNH Industrial's core business by offering comparable functionality at potentially lower overall costs, particularly for short-term or project-specific needs. Customers are increasingly weighing the benefits of renting or sharing against the capital expenditure and maintenance associated with owning heavy machinery.
The accessibility of specialized rental fleets in 2024 directly competes with the purchase of new equipment. This shift towards service-based models can erode CNH Industrial's revenue streams as businesses prioritize operational flexibility and reduced capital outlay.
CNH Industrial faces pressure from evolving environmental regulations, such as stricter emissions standards in Europe and the US, which increase the cost of traditional diesel technology. Government incentives for electric and alternative-fuel machinery further bolster the appeal of these substitutes, as customers and corporations increasingly focus on ESG goals.
| Factor | Impact on CNH Industrial | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS) | Reduces demand for new equipment sales | Strong growth in rental market |
| Shared Economy Platforms | Offers alternative access to machinery | Increasing customer adoption |
| Stricter Emissions Standards | Increases cost of traditional engines | Driving interest in electric/alternative fuels |
| Government Incentives | Makes green alternatives more competitive | Supporting adoption of new technologies |
Entrants Threaten
CNH Industrial operates in the capital goods sector, which inherently requires massive upfront investment. Think about the costs for cutting-edge research and development, building and maintaining advanced manufacturing plants, and establishing widespread distribution and service networks. These aren't small figures; they represent significant financial hurdles.
For instance, in 2023, CNH Industrial reported significant capital expenditures, reflecting the ongoing need to invest in its operational capabilities and product innovation. These investments, often in the billions of dollars annually across the industry, create a formidable barrier for any new player looking to enter the market. The sheer scale of capital needed to even begin competing effectively is a major deterrent.
Established players like CNH Industrial leverage substantial economies of scale across production, procurement, and research and development. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, driving down per-unit costs significantly.
For instance, CNH Industrial's global manufacturing footprint and vast supply chain network enable them to negotiate better terms with suppliers, further enhancing cost efficiencies. In 2023, CNH Industrial reported net sales of $24.7 billion, reflecting the scale of their operations.
New entrants would find it exceedingly difficult to replicate these cost advantages, making it challenging to compete on price and achieve profitability from the outset. The initial investment required to build comparable production capacity and establish a robust supply chain would be immense.
CNH Industrial benefits from significant brand loyalty, cultivated through its prominent brands such as Case IH, New Holland, and CASE. This deep-seated customer preference, developed over decades of operation, makes it challenging for newcomers to attract market share.
The company's commitment to innovation and product differentiation further solidifies its market position. By consistently introducing advanced features and tailored solutions, CNH Industrial creates a high barrier to entry, requiring substantial investment and unique value propositions from potential competitors.
Access to Distribution Channels
CNH Industrial commands a significant advantage through its extensive and deeply entrenched global dealer network. This network is not merely for selling equipment; it's vital for after-sales service, maintenance, and the crucial distribution of spare parts, forming a comprehensive support system for customers.
New entrants would find it exceptionally difficult and prohibitively expensive to replicate this established infrastructure. Dealers often have years, even decades, of loyal relationships with established manufacturers like CNH Industrial, making it hard for newcomers to secure comparable partnerships. For instance, as of 2024, CNH Industrial reported having over 4,000 dealers across more than 170 countries.
- Established Global Dealer Network: CNH Industrial benefits from a vast and loyal dealer network, critical for sales, service, and parts.
- High Barriers to Entry for New Entrants: Building a comparable dealer network requires substantial investment and time, facing established relationships.
- Cost and Complexity of Network Replication: New competitors must overcome significant financial and logistical hurdles to establish a comparable distribution and service footprint.
- CNH Industrial's 2024 Dealer Presence: The company operates over 4,000 dealerships worldwide, underscoring the scale of its distribution advantage.
Regulatory and Policy Barriers
The agricultural and construction equipment sectors are heavily regulated, with new entrants facing significant hurdles due to safety standards, environmental mandates, and intricate trade policies. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to implement stringent emissions standards like Stage V for off-road machinery, requiring substantial investment in compliant engine technology. This complexity, coupled with diverse international standards, acts as a formidable barrier.
Navigating these regulatory landscapes demands considerable expertise and financial resources. New companies must invest heavily in research and development to meet evolving environmental regulations, such as those impacting particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. In 2024, many manufacturers were still adapting to the full implications of these standards, which can add millions to product development costs.
- Regulatory Complexity: Safety, environmental, and trade regulations create significant compliance burdens for new entrants.
- Investment in Compliance: Meeting standards like EU Stage V emissions requires substantial R&D and capital expenditure.
- International Standards Variance: Differing regulations across global markets increase the complexity and cost of market entry.
The threat of new entrants for CNH Industrial is generally considered low due to substantial capital requirements for manufacturing, research, and distribution, coupled with strong brand loyalty and established dealer networks. The sheer scale of investment needed to compete effectively, estimated in the billions for new facilities and product development, presents a significant deterrent. For example, CNH Industrial's 2023 capital expenditures underscore the ongoing need for substantial investment in operational capabilities.
Furthermore, the complex regulatory environment, including evolving emissions standards like EU Stage V, demands significant R&D investment and expertise, adding another layer of difficulty for newcomers. Navigating these diverse international regulations can add millions to product development costs, as seen in 2024 as companies adapted to these requirements.
CNH Industrial's established global dealer network, boasting over 4,000 locations as of 2024, is a critical advantage that is exceptionally costly and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate. These dealers not only facilitate sales but also provide essential after-sales service and parts distribution, creating a robust support system that new competitors struggle to match.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CNH Industrial Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including CNH's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld. This blend ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
