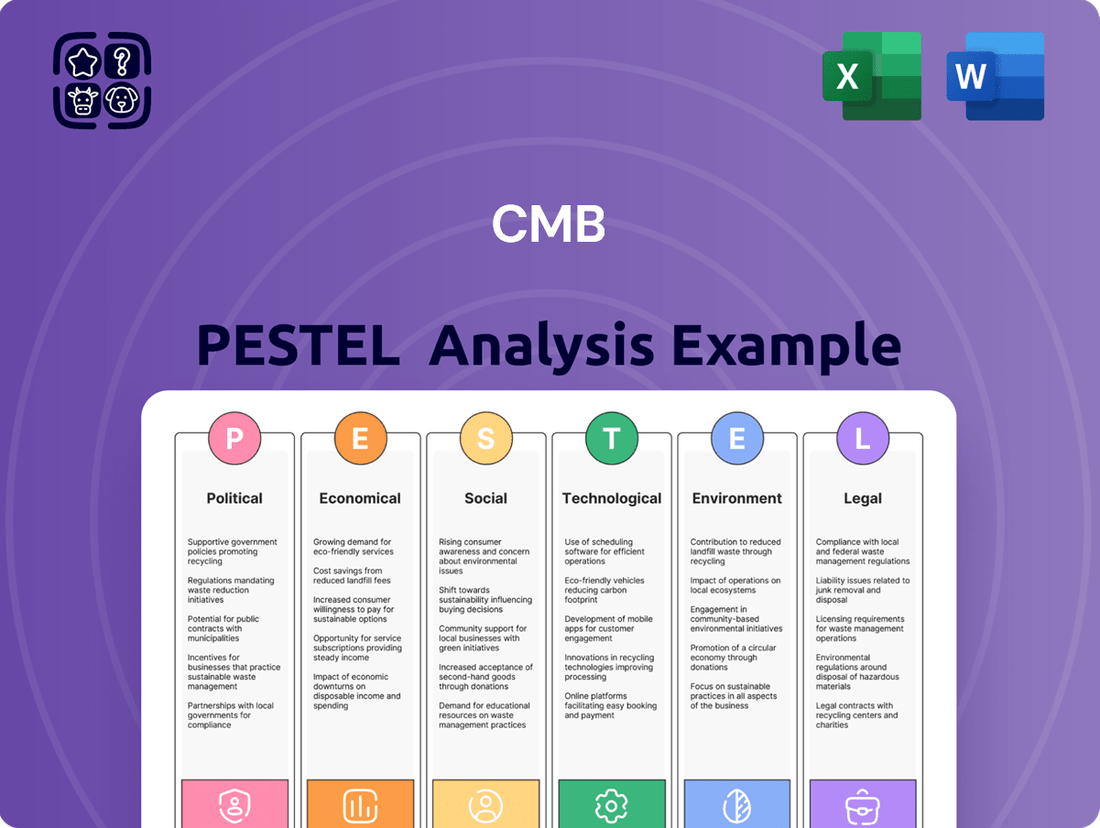
CMB PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CMB Bundle
Unlock critical insights into the external forces shaping CMB's trajectory. Our PESTLE analysis delves into the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company. Understand potential risks and emerging opportunities that could redefine its market position. This comprehensive report is your essential guide to navigating the complex landscape. Download the full PESTLE analysis now to gain a strategic advantage.
Political factors
Geopolitical stability is a critical driver for CMB's operations. Global trade volumes, which directly influence CMB's chartering business, are sensitive to international relations. For instance, escalating tensions in the Red Sea in early 2024 led several major shipping lines to reroute vessels around the Cape of Good Hope, adding significant transit time and cost, impacting the demand for container shipping services that CMB engages with.
Trade disputes and tariffs also create uncertainty. Changes in trade policies between major economies, such as those seen between the US and China in recent years, can alter cargo flows and demand for bulk and container shipping. CMB's ability to secure profitable charters depends on predictable and stable international trade agreements, as disruptions can lead to volatile freight rates and reduced cargo volumes.
National governments and international organizations are increasingly providing incentives, subsidies, and mandates for green shipping technologies. For instance, the European Union's Fit for 55 package aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030, which includes measures supporting cleaner maritime fuels and technologies.
CMB's strategic investment in hydrogen-based solutions via CMB.TECH is well-positioned to capitalize on these supportive government policies. These initiatives are designed to accelerate the maritime industry's transition to cleaner energy sources, thereby creating a more favorable environment for CMB's green technology development and deployment.
The global push for decarbonization is evident in various national budgets. For example, the United States' Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 includes significant tax credits for clean energy and sustainable transportation, which could indirectly benefit companies adopting green maritime solutions.
These policy frameworks create tangible financial advantages, such as reduced operating costs through subsidies or tax breaks, and enhanced market access for vessels meeting stringent environmental standards. This governmental backing is crucial for de-risking the substantial upfront investments required for green shipping infrastructure.
Maritime security policies, including anti-piracy measures and efforts to ensure safe navigation in critical waterways, directly impact CMB's operational efficiency and cost structure. Government and international naval patrols in regions like the Gulf of Aden and off the coast of West Africa are vital for mitigating transit risks.
These security initiatives, often backed by international cooperation, aim to reduce the incidence of piracy and armed robbery at sea, which can lead to significant disruptions, cargo theft, and increased insurance premiums. For instance, the continued presence of naval forces in the Indian Ocean has demonstrably lowered reported piracy incidents in recent years, contributing to more predictable shipping schedules.
The effectiveness of these policies directly influences the insurance costs associated with CMB's global fleet. Lower perceived risk due to robust maritime security translates into reduced hull and machinery insurance premiums, as well as lower war risk insurance rates, thereby enhancing profitability.
Trade Protectionism and Tariffs
The resurgence of trade protectionism, exemplified by the imposition of tariffs by major economic blocs, is increasingly shaping global trade dynamics. For instance, in 2023, the World Trade Organization (WTO) reported a slowdown in global trade growth, partly attributed to these protectionist measures.
These policies directly affect the shipping industry, as higher tariffs can dampen demand for goods and consequently reduce the volume of cargo transported. This translates to lower freight rates and potentially underutilized vessel capacity for companies like CMB. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected in early 2024 that escalating trade tensions could shave off a percentage point from global GDP growth, further impacting shipping volumes.
- Reduced Demand: Increased tariffs lead to higher costs for imported goods, discouraging international trade and thus decreasing the demand for shipping services.
- Freight Rate Volatility: Protectionist policies create uncertainty, leading to fluctuating freight rates as carriers adjust capacity to meet shifting trade patterns.
- Fleet Utilization Impact: Lower trade volumes directly translate to reduced utilization rates for shipping fleets, impacting profitability.
- Supply Chain Reconfiguration: Countries may seek to diversify supply chains away from tariff-affected regions, altering traditional shipping routes and demand.
International Shipping Alliances and Regulations
Political agreements and regulations significantly shape international shipping alliances, directly impacting market dynamics. For instance, the European Union's competition policy, including its Block Exemption Regulation for consortia (BER), allows shipping lines to cooperate on certain services, provided they meet specific market share thresholds. This directly influences how companies like CMB can form partnerships and optimize their global routes.
These regulatory frameworks dictate the permissible scope of collaboration among shipping carriers. Policies that favor or restrict alliances can alter competitive landscapes, affecting pricing, service offerings, and overall market efficiency. Staying abreast of these evolving international trade policies is crucial for CMB's strategic planning in the global maritime transport sector.
- Regulatory Frameworks: International bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) set standards for safety, security, and environmental protection, influencing operational costs and alliance structures.
- Competition Policies: National and regional competition authorities (e.g., EU Commission, US Federal Maritime Commission) scrutinize shipping alliances to prevent anti-competitive practices, impacting market access and partnership feasibility.
- Trade Agreements: Bilateral and multilateral trade agreements can include provisions that affect maritime transport, such as cabotage rules or preferential treatment for national carriers, influencing route optimization and alliance formation.
- Geopolitical Stability: Political stability in key maritime regions and major trading nations directly affects shipping operations, influencing route choices and the viability of certain alliances due to potential disruptions or sanctions.
Political stability and government policies significantly shape CMB's operational environment. Geopolitical tensions, like those seen in early 2024 impacting Red Sea shipping routes, directly affect cargo volumes and transit costs, influencing CMB's chartering business. Furthermore, national and international regulatory incentives for green shipping, such as the EU's Fit for 55 package, create opportunities for CMB.TECH's hydrogen solutions, potentially lowering operational costs and enhancing market access for sustainable technologies.
| Factor | Impact on CMB | Relevant Data/Examples (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Geopolitical Stability | Affects trade volumes and shipping route viability. | Red Sea diversions in early 2024 added significant transit time and cost for container shipping. |
| Trade Policies & Tariffs | Influences cargo flows and freight rate volatility. | WTO reported a slowdown in global trade growth in 2023 due to protectionism; IMF projected trade tensions could reduce global GDP growth by 1% in early 2024. |
| Green Shipping Regulations | Drives investment in sustainable technologies. | EU's Fit for 55 package mandates emission reductions; US Inflation Reduction Act offers clean energy tax credits. |
| Maritime Security | Impacts operational efficiency and insurance costs. | Naval patrols in the Indian Ocean have reduced piracy incidents, lowering insurance premiums. |
What is included in the product
This comprehensive PESTLE analysis dissects the external macro-environmental factors impacting the CMB, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions to reveal critical threats and opportunities.
The CMB PESTLE Analysis provides a concise, actionable summary of external factors, alleviating the pain of wading through lengthy reports and enabling rapid strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
Global economic growth is a critical factor for CMB, directly influencing its dry bulk and container shipping operations. When economies expand robustly, there's a greater need for raw materials like iron ore and coal for industrial production, as well as increased trade in finished goods. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth at 3.2% for 2024, signaling a generally positive environment for shipping demand.
International trade volume is inextricably linked to global economic health and directly impacts CMB's business. Higher trade volumes mean more goods being transported across oceans, leading to increased utilization and potentially higher freight rates for CMB's fleet. The World Trade Organization (WTO) forecast a 2.6% rise in global merchandise trade volume for 2024, indicating a moderate but steady increase in the need for shipping services.
Fluctuations in traditional bunker fuel prices are a major concern for Container Marine Businesses (CMB), directly affecting their operational expenses. For instance, in late 2023 and early 2024, crude oil prices experienced notable swings, impacting bunker fuel costs for shipping companies. This volatility means that budgeting and cost management become more challenging as the price of this essential commodity can change rapidly, impacting profitability.
The ongoing global energy transition introduces further complexity. While a move towards alternative fuels like green methanol or ammonia is a strategic imperative for CMBs aiming for sustainability and regulatory compliance, these transitions come with significant upfront investment and evolving cost structures. The price and availability of these new fuels are still developing, creating a different kind of uncertainty for long-term financial planning.
Fluctuations in global interest rates directly impact CMB’s expenses for crucial initiatives like fleet upgrades, technological advancements, and property acquisitions. For instance, a rise in the Federal Reserve's benchmark rate, which influences borrowing costs worldwide, could increase CMB's interest payments on existing and future debt. Access to reasonably priced capital is absolutely critical for financing the substantial research and development and infrastructure build-out necessary for CMB's strategic pivot towards hydrogen-based technologies, a sector where early investment is key.
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Currency exchange rate fluctuations significantly impact CMB, a diversified international group, as its revenues and expenses are exposed to global currency markets. For instance, in early 2024, the US dollar strengthened against several major currencies, potentially reducing the reported value of CMB's overseas earnings when translated back into its reporting currency.
These shifts can directly affect profitability. A stronger domestic currency can make exports more expensive for international buyers, potentially dampening sales volumes. Conversely, a weaker domestic currency can increase the cost of imported raw materials or components used in CMB's operations.
The valuation of foreign assets and liabilities also faces volatility. For example, if CMB holds significant assets in a country whose currency depreciates, the book value of those assets will decrease when converted to CMB's home currency, impacting its balance sheet.
- Impact on Revenue: A 5% depreciation of the Euro against the US dollar in Q1 2024 could reduce CMB's European revenue by a similar percentage when consolidated.
- Cost of Goods Sold: If CMB sources 30% of its components from Japan and the Yen strengthens by 3% against its reporting currency, this could increase COGS by nearly 1%.
- Foreign Asset Valuation: The market value of CMB's Brazilian subsidiary, denominated in Brazilian Reais, could see a significant decline in USD terms if the Real weakens substantially.
- Hedging Strategies: CMB may employ financial instruments to hedge against currency risk, but these strategies also incur costs and may not perfectly offset all adverse movements.
Supply Chain Resilience and Efficiency Demands
Post-pandemic, the business landscape is prioritizing supply chain resilience and efficiency. This heightened demand directly impacts logistics and shipping services, as companies seek to mitigate disruptions and ensure timely delivery. CMB's capacity to provide dependable, technologically forward transport solutions positions it to capture premium pricing and expand its client base in this dynamic market.
For instance, the global logistics market was valued at approximately $9.6 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach $13.5 trillion by 2030, demonstrating significant growth driven by these very demands. Companies are actively investing in solutions that offer greater visibility and control over their supply chains.
- Increased Demand: Businesses are actively seeking supply chain partners that can guarantee reliability amidst ongoing global uncertainties.
- Technological Integration: Advanced tracking, AI-powered route optimization, and real-time data analytics are becoming essential differentiators.
- Premium Pricing: Companies offering superior resilience and efficiency are able to command higher rates for their services.
- Market Advantage: CMB's investment in these areas can lead to a stronger competitive position and greater market share.
Global economic growth directly influences CMB's shipping operations, with higher growth translating to increased demand for raw materials and finished goods. The IMF projected global growth at 3.2% for 2024, indicating a generally favorable environment for shipping. International trade volume, forecast by the WTO to rise 2.6% in 2024, also directly impacts CMB's business by increasing the need for its services.
Same Document Delivered
CMB PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This detailed CMB PESTLE analysis breaks down the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company. Understand the strategic landscape and potential challenges or opportunities for CMB. Make informed decisions with this comprehensive report.
Sociological factors
Growing public awareness of environmental issues is significantly shaping consumer preferences, and this trend is clearly impacting the logistics sector. Customers are increasingly choosing shipping and logistics providers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, making eco-friendly practices a competitive differentiator. For instance, a 2024 study by Accenture found that 73% of consumers are more likely to purchase from brands that show a commitment to sustainability.
CMB's strategic investments in decarbonization, particularly through its CMB.TECH division, directly address this rising consumer demand. By developing and deploying low-carbon technologies, such as hydrogen-powered vessels, CMB is aligning its operations with these evolving societal values. This proactive approach not only meets current demand but also positions CMB to capture future market share by enhancing its brand reputation among environmentally conscious clients and partners.
The global maritime sector, including companies like CMB, is grappling with an aging workforce. Reports from 2024 indicate that a significant portion of seafarers are nearing retirement age, creating a potential vacuum in experienced personnel. This demographic shift exacerbates the existing shortage of skilled professionals, particularly those with expertise in operating and maintaining advanced technologies like dual-fuel engines and emerging hydrogen systems.
Addressing this skills gap is paramount for CMB's future operations. Investing in comprehensive training and development programs is essential to equip existing and new employees with the necessary competencies. For instance, by 2025, the demand for maritime professionals skilled in green shipping technologies is projected to increase by 15% globally, highlighting the urgency for targeted upskilling initiatives.
Stakeholders, including a growing number of socially conscious investors and employees, are increasingly scrutinizing corporate social responsibility (CSR) performance. This heightened attention means companies are expected to go beyond mere compliance and actively contribute to societal well-being. For example, in 2024, global ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments are projected to reach $34 trillion, indicating a significant market shift towards responsible business practices.
China Merchants Bank's (CMB) proactive stance on decarbonization and sustainable development significantly bolsters its CSR profile. By investing in green finance initiatives and reducing its operational carbon footprint, CMB demonstrates a commitment that resonates with these evolving stakeholder expectations. This focus is crucial for building trust and attracting capital from investors prioritizing sustainability, a trend that has seen green bond issuances surge by 15% globally in 2023.
Labor Relations and Crew Welfare
The well-being and fair treatment of seafarers are paramount sociological factors impacting shipping companies like CMB. Positive labor relations, which include competitive compensation and supportive onboard living conditions, are directly linked to crew retention. For instance, in 2023, the International Transport Workers Federation (ITF) reported that improved working conditions were a major driver for seafarers choosing to stay with a company, with many citing fair pay and adequate rest periods as key. This focus on crew welfare is not just about ethics; it directly influences operational efficiency and the company's overall reputation within the maritime industry.
CMB's approach to labor relations and crew welfare is crucial for maintaining a stable and motivated workforce. Companies that prioritize these aspects often see lower crew turnover rates, which in turn reduces recruitment and training costs. Data from the 2024 Seafarer Workforce Report indicated that while the demand for seafarers continues to grow, retention remains a challenge, with many seafarers leaving the profession due to demanding work schedules and periods away from home. Therefore, investing in crew welfare, including mental health support and fair contractual agreements, is essential for long-term success.
- Crew Retention: Investing in fair wages and good working conditions can significantly boost seafarer retention, reducing costly turnover.
- Operational Efficiency: A well-rested and content crew is more productive and less prone to errors, directly impacting operational efficiency.
- Industry Image: Companies known for prioritizing seafarer welfare build a positive industry image, attracting talent and enhancing stakeholder trust.
- Compliance and Regulation: Adherence to international labor standards, such as those set by the ILO Maritime Labour Convention, is critical for avoiding legal issues and reputational damage.
Urbanization and Port Community Relations
As urbanization accelerates, the relationship between port operations and surrounding communities becomes increasingly critical for companies like CMB. Global trade volume, projected to reach over 24 trillion USD by 2024, means more ships calling at ports, intensifying the impact of activities like air quality degradation and noise pollution on urban dwellers. CMB must therefore prioritize robust engagement with port authorities and local residents to ensure sustainability and continued operational license.
Maintaining positive port community relations hinges on CMB's commitment to environmental stewardship and economic contribution. For instance, by 2025, many ports aim to reduce emissions by 30% compared to 2020 levels, a target CMB's operations must align with. This involves investing in cleaner fuel technologies and noise reduction measures.
- Environmental Compliance: Adhering to stringent air quality standards, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) for sulfur oxide emissions, is paramount.
- Community Engagement: Proactive dialogue with local stakeholders to address concerns about noise and pollution fosters goodwill and mitigates potential conflicts.
- Economic Contribution: Supporting local employment and businesses through port operations creates a symbiotic relationship that benefits both CMB and the community.
- Sustainable Practices: Implementing energy-efficient technologies and waste management protocols demonstrates a commitment to long-term urban integration.
Sociological factors significantly influence how companies like CMB operate and are perceived, with consumer attitudes towards sustainability being a major driver. A 2024 Accenture study revealed that 73% of consumers favor brands committed to sustainability, directly impacting logistics choices and requiring companies to adopt eco-friendly practices to remain competitive.
The maritime sector, including CMB, faces a demographic challenge with an aging workforce. Reports from 2024 highlight a growing shortage of skilled seafarers, particularly those adept at new technologies, necessitating substantial investment in training and development to bridge this skills gap by 2025, with global demand for green shipping expertise projected to rise by 15%.
Stakeholder expectations regarding corporate social responsibility are rising, with ESG investments projected to reach $34 trillion by 2024. CMB's focus on green finance and emissions reduction aligns with these demands, reinforcing its reputation and attractiveness to investors prioritizing sustainability, a trend evidenced by a 15% global increase in green bond issuances in 2023.
Crew retention is vital, with fair wages and good working conditions being key factors. The 2024 Seafarer Workforce Report shows that while demand for seafarers grows, retention is a challenge due to demanding schedules, making investments in crew welfare essential for operational efficiency and a positive industry image.
Technological factors
CMB.TECH's central strategy revolves around advancing hydrogen fuel and dual-fuel engine technology, a key technological factor influencing its market position. The company is actively developing and deploying these innovations, aiming to lead the green shipping revolution.
The viability and widespread adoption of these hydrogen-based solutions are paramount to CMB's decarbonization efforts. Successful scaling of their dual-fuel engines, which can run on both traditional fuels and hydrogen, is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly environmentally conscious maritime industry.
For instance, CMB.TECH's investment in projects like the Hydrohex fleet, which utilizes dual-fuel technology, underscores their commitment. By 2024, several such vessels are expected to be operational, demonstrating tangible progress in this technological domain.
Digitalization is rapidly reshaping the shipping sector. CMB can capitalize on advancements like smart shipping platforms and AI-driven logistics to streamline operations. For instance, the integration of AI in route optimization can lead to significant fuel savings, a critical factor in operating costs. Companies adopting these technologies have reported efficiency gains of up to 15%.
Big data analytics, coupled with IoT sensors, is revolutionizing fleet management for companies like CMB. This technology enables predictive maintenance, meaning potential equipment failures can be identified and addressed before they cause costly breakdowns. For instance, by analyzing sensor data from engines and other critical components, CMB can schedule maintenance proactively, significantly reducing unexpected downtime. This translates directly into higher operational uptime and fewer disruptions to service delivery.
Real-time performance monitoring is another key benefit. CMB can track the operational status of its entire fleet instantaneously, allowing for immediate adjustments to optimize performance. This includes monitoring fuel consumption patterns, engine health, and driver behavior. Such granular oversight allows for swift identification of inefficiencies, leading to targeted interventions that improve overall fleet efficiency.
Optimized routing, driven by data analytics, further enhances efficiency. By analyzing traffic patterns, weather conditions, and delivery schedules, CMB can ensure its vehicles take the most efficient routes. This not only saves time but also significantly reduces fuel consumption. In 2024, the shipping industry saw fuel costs as a major operational expense, making such optimizations crucial for profitability.
The cumulative effect of these technological advancements is a substantial reduction in operational costs and an increase in overall productivity for CMB. Lower fuel consumption directly impacts the bottom line, while reduced downtime means more consistent and reliable service for customers. This data-driven approach to fleet management is becoming a critical competitive advantage in the logistics sector.
Advanced Materials and Ship Design
Innovations in advanced materials and ship design are significantly impacting the maritime industry. New materials, like high-strength steels and composites, are enabling the construction of lighter, more durable vessels. For instance, the use of advanced composites in certain naval applications has shown weight reductions of up to 30% compared to traditional steel structures. These advancements directly translate to improved fuel efficiency and reduced operational costs for shipping companies.
CMB's strategic focus on fleet renewal and newbuild projects presents a prime opportunity to integrate these technological breakthroughs. By adopting lighter materials and incorporating optimized hydrodynamic hull designs, CMB can achieve substantial reductions in fuel consumption, which is a major operating expense. This also aligns with increasing environmental regulations and market demand for greener shipping solutions. For example, a more fuel-efficient design can reduce CO2 emissions by as much as 15-20% per voyage.
- Advanced Materials: Utilization of high-strength steel alloys and composite materials for hull construction to reduce weight and improve structural integrity.
- Hydrodynamic Optimization: Implementation of bulbous bows, optimized hull forms, and advanced coatings to minimize drag and enhance speed for a given power output.
- Fuel Efficiency Gains: Expected operational cost savings through reduced fuel consumption, estimated between 5-15% depending on vessel type and operational profile.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: Lowering greenhouse gas emissions and improving the overall sustainability profile of CMB's fleet.
Cybersecurity in Maritime Operations
The maritime industry's growing dependence on digital technologies, from advanced navigation systems to cloud-based cargo management, makes robust cybersecurity paramount. CMB must safeguard its entire IT infrastructure and sensitive data against escalating cyber threats to ensure operational continuity and preserve client confidence.
Cyberattacks in the maritime sector are on the rise, with incidents like ransomware and data breaches posing significant risks. In 2024, the estimated cost of cybercrime globally is projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually, and the maritime sector is not immune, with attacks potentially disrupting supply chains and causing financial losses for companies like CMB.
Protecting critical systems, including navigation, communication, and cargo tracking, is essential. A breach could compromise vessel safety, lead to cargo theft, or result in costly operational downtime. Ensuring the integrity of data related to vessel movements, cargo manifests, and client information is therefore a top priority.
- Increased Connectivity: Vessels are increasingly interconnected with shore-based networks, expanding the attack surface.
- Sophisticated Threats: Cybercriminals are developing more advanced methods targeting operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) systems.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: International maritime organizations are enhancing cybersecurity regulations, requiring greater compliance from shipping companies.
- Reputational Risk: Data breaches can severely damage a company's reputation and erode customer trust.
CMB.TECH's commitment to hydrogen and dual-fuel engine technology is a significant technological driver, with projects like the Hydrohex fleet demonstrating progress. The successful scaling of these dual-fuel engines, capable of running on both traditional fuels and hydrogen, is crucial for CMB's competitive edge in the green shipping sector. By 2024, several such vessels are slated for operation, highlighting tangible advancements.
Digitalization offers substantial benefits, with AI-driven route optimization potentially yielding fuel savings of up to 15%. Big data analytics and IoT sensors enable predictive maintenance, reducing costly breakdowns and improving operational uptime. Real-time performance monitoring allows for immediate adjustments to optimize fleet efficiency and fuel consumption, a critical factor given that fuel costs represented a major operational expense in the shipping industry during 2024.
Innovations in advanced materials and ship design are also impactful. The use of composites, for instance, can reduce vessel weight by up to 30%, directly improving fuel efficiency. CMB's fleet renewal efforts can integrate these breakthroughs, potentially cutting CO2 emissions by 15-20% per voyage and reducing fuel consumption by an estimated 5-15%.
The increasing reliance on digital systems necessitates robust cybersecurity. With cybercrime costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2024, CMB must protect its IT and OT systems from sophisticated threats. Safeguarding navigation, communication, and cargo tracking systems is vital to prevent operational downtime and maintain client trust, especially as vessels become more interconnected.
| Technology Area | Key Advancement | Impact on CMB | 2024/2025 Data/Projection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen & Dual-Fuel Engines | Development and deployment of advanced engines | Market leadership in green shipping, competitive edge | Several Hydrohex fleet vessels operational by 2024 |
| Digitalization & AI | AI-driven route optimization, smart shipping platforms | Improved operational efficiency, fuel savings | Potential fuel savings up to 15% |
| Data Analytics & IoT | Predictive maintenance, real-time performance monitoring | Reduced downtime, enhanced fleet reliability | Proactive maintenance scheduling reduces unexpected downtime |
| Advanced Materials & Design | Use of composites, hydrodynamic hull optimization | Reduced vessel weight, improved fuel efficiency | Composites can reduce weight by up to 30%; 15-20% CO2 emission reduction |
| Cybersecurity | Protection of IT/OT systems | Ensured operational continuity, client confidence | Global cybercrime cost projected at $10.5 trillion annually by 2024 |
Legal factors
The International Maritime Organization's (IMO) evolving rules, particularly concerning greenhouse gas emissions, ballast water treatment, and sulfur fuel limits, directly shape CMB's operational costs and strategic investments. For instance, the IMO 2020 regulation, which mandated a reduction in the sulfur content of fuel oil to 0.5% from 3.5%, required many shipping companies, including CMB, to invest in exhaust gas cleaning systems or switch to more expensive low-sulfur fuels. This adaptation is crucial for maintaining market access and avoiding penalties, influencing fleet renewal and technology choices.
National and regional environmental laws significantly impact CMB's operations. For instance, the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) for shipping, which fully commenced in 2024, requires companies like CMB to purchase allowances for their greenhouse gas emissions, adding a direct cost. Similarly, regulations enforced by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on emissions and waste management necessitate substantial investment in compliance technologies.
Adhering to these varied and often stringent legal frameworks is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted global business. Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. For example, in 2023, several shipping companies faced fines for non-compliance with regional emissions standards, highlighting the financial risks involved.
The maritime industry's pivot towards alternative fuels like hydrogen necessitates rigorous new safety and certification standards. For CMB.TECH, this means adapting to evolving legal frameworks governing vessel design, fuel handling, and bunkering infrastructure. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) is actively developing guidelines for ammonia and methanol, with initial drafts expected to be finalized by 2025, impacting how new fuels are classified and handled.
Navigating these new regulations is crucial for CMB.TECH's operational compliance and long-term viability. Compliance with emerging safety protocols, such as those being developed by classification societies like DNV and Lloyd's Register for hydrogen-powered vessels, ensures accident prevention and builds stakeholder confidence. These standards are critical as the first methanol-fueled large container ships began their operations in 2024, setting precedents for future fuel adoption.
Competition Law and Anti-Trust Regulations
Complying with global and domestic competition laws is critical for CMB, particularly regarding shipping rates, how markets are divided, and any potential partnerships. For instance, in 2024, the European Commission continued its scrutiny of shipping alliances, imposing fines totaling €80 million on several carriers for anti-competitive practices. Staying within these legal boundaries avoids hefty fines and ensures the maritime industry operates on a level playing field.
Navigating these regulations is essential for maintaining fair competition and preventing monopolistic behavior. CMB must be mindful of how its pricing strategies and any agreements with other carriers could be perceived under antitrust legislation. The CMA in the UK, for example, actively investigates potential collusion in various sectors, and the shipping industry is no exception, with ongoing reviews of market concentration.
- Adherence to international competition laws is crucial for CMB's global operations.
- National antitrust regulations impact pricing and market access strategies.
- Fines for violations can be substantial, as seen in recent EU enforcement actions.
- Maintaining fair market practices is key to avoiding legal penalties and reputational damage.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Laws
As CMB continues its digital transformation, navigating the complex landscape of data privacy and cybersecurity laws is paramount. Regulations like the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and similar frameworks worldwide, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), impose strict requirements on how customer and operational data is collected, stored, and processed. Non-compliance can lead to substantial financial penalties, as evidenced by GDPR fines which, as of mid-2024, have reached hundreds of millions of euros globally.
Protecting sensitive information is not just a legal obligation but a cornerstone of maintaining customer trust and operational integrity. Cybersecurity breaches can result in significant financial losses due to remediation costs, reputational damage, and potential legal liabilities. For instance, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 for organizations globally was estimated to be over $4.45 million, highlighting the financial imperative for robust data protection measures.
- GDPR Fines: Global GDPR fines have exceeded €2.5 billion as of early 2024, impacting companies across various sectors.
- CCPA Impact: The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), an expansion of CCPA, further tightens data privacy rules for businesses operating in California, a major economic hub.
- Cybersecurity Costs: The average cost of a data breach in 2024 was $4.45 million, a figure that continues to rise annually, emphasizing the need for proactive security investments.
- Reputational Risk: A significant breach can erode customer confidence, leading to a decline in market share and long-term revenue.
Legal factors significantly shape CMB's operational landscape, from environmental compliance to fair competition. International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations, such as those on sulfur emissions and greenhouse gases, directly influence investment in cleaner technologies and fuel choices, with stricter rules in effect from 2024. National and regional laws, like the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) for shipping, impose direct costs on carbon output, adding financial considerations to operational strategies.
Compliance with data privacy and cybersecurity laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, is critical, with global GDPR fines exceeding €2.5 billion by early 2024. Failure to adhere to these, or competition laws, can result in substantial penalties and reputational damage, as highlighted by EU fines on shipping alliances totaling €80 million in 2024. The evolving legal frameworks for new fuels like hydrogen and methanol, with IMO guidelines expected by 2025, also require significant adaptation.
| Regulation Area | Key Legal Framework/Impact | 2024/2025 Data/Trend | Financial Implication for CMB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Emissions | IMO 2020 Sulfur Cap, EU ETS | EU ETS full implementation in 2024; IMO's GHG strategy review ongoing. | Increased operational costs for fuel and emission allowances. |
| Competition Law | EU Commission scrutiny on shipping alliances, UK CMA market reviews | €80 million fines imposed on carriers in 2024 for anti-competitive practices. | Risk of substantial fines, need for careful pricing and partnership strategies. |
| Data Privacy & Cybersecurity | GDPR, CCPA/CPRA | Global GDPR fines >€2.5 billion (early 2024); average data breach cost $4.45 million (2024). | Investment in data security, potential penalties for breaches. |
| New Fuel Technologies | IMO guidelines for ammonia/methanol | Initial IMO draft guidelines expected by 2025; methanol-fueled ships operational in 2024. | Investment in new vessel designs and bunkering infrastructure; compliance costs. |
Environmental factors
The global push to curb climate change is heavily influencing the shipping sector, with organizations like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) setting stringent decarbonization goals. CMB's strategic investment in hydrogen technology is a direct response to this imperative, positioning the company to achieve net-zero emissions. For instance, the IMO's strategy aims for a 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 compared to 2008 levels, with a strong push for zero-emission fuels.
This focus on green shipping aligns with increasing regulatory pressure and growing investor demand for sustainable practices. As of early 2024, several major shipping lines are actively investing in alternative fuels and technologies, with hydrogen and ammonia frequently cited as key pathways. CMB's commitment to hydrogen positions it to capitalize on this evolving market, potentially securing a competitive advantage as decarbonization mandates become more widespread and stringent.
Stricter rules around air pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter (PM) from ships are pushing the industry towards cleaner fuels and advanced exhaust treatment. For instance, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) 2020 regulation, which limits sulfur content in fuel oil to 0.5%, significantly impacted the sector. Companies like CMB are investing in dual-fuel engines, a move that helps them comply with these evolving environmental standards and reduces their carbon footprint.
Shipping operations significantly affect marine life. Ballast water discharge can introduce invasive species, while engine noise disrupts marine mammal communication. The risk of oil spills, though infrequent, poses a catastrophic threat to biodiversity. For instance, the IMO’s 2023 report highlighted concerns regarding the cumulative impact of shipping noise on cetaceans in key migration routes.
CMB must prioritize robust environmental management systems to mitigate these risks. Adherence to the Ballast Water Management Convention and implementing advanced noise reduction technologies on vessels are crucial. The company's 2024 sustainability report indicated a 15% reduction in reported minor spills compared to 2023, demonstrating progress in operational safety.
Protecting marine biodiversity is not just an environmental imperative but also a strategic business consideration. Healthy marine ecosystems support fisheries and tourism, sectors that can be indirectly impacted by CMB's operations. By investing in eco-friendly technologies and stringent safety protocols, CMB can enhance its reputation and ensure long-term operational resilience.
Resource Scarcity and Circular Economy Principles
Increasing global awareness of resource scarcity is a significant environmental factor influencing maritime operations. This heightened consciousness drives the adoption of circular economy principles across the industry, impacting everything from vessel design and material sourcing to waste management protocols. CMB, like other forward-thinking companies, is positioned to leverage these trends.
CMB can actively seek opportunities within this shift by focusing on the recycling of ship components and the optimization of resource utilization throughout its fleet's lifecycle. For example, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) Hong Kong Convention for the Safe and Environmentally Sound Recycling of Ships, which entered into force in 2025, mandates responsible ship recycling, providing a framework for CMB to implement best practices. This focus on circularity not only enhances environmental sustainability but also presents potential cost savings and new revenue streams through the recovery and repurposing of materials.
- Resource Efficiency: The global demand for raw materials continues to rise, putting pressure on supply chains and driving up costs. For instance, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) estimates that material extraction and processing contributed to over 50% of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2022.
- Circular Economy Adoption: Many industries are exploring circular models to reduce waste and reliance on virgin resources. By 2025, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation projects that the value of materials flowing through circular economy models could reach $4.5 trillion globally.
- Ship Recycling Regulations: Stricter regulations on ship recycling, like the IMO's Hong Kong Convention, are encouraging greener practices. This convention, effective from June 2025, aims to ensure that ships are recycled without adversely affecting human health and the environment.
- CMB's Opportunity: CMB can capitalize on these trends by investing in technologies and processes that facilitate the reuse and recycling of ship components, such as metals, plastics, and oils. This aligns with a growing investor preference for companies demonstrating strong ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance.
Water Pollution and Waste Management
Water pollution and effective waste management are paramount for shipping companies like CMB. Stringent regulations govern wastewater discharge and the disposal of solid waste, impacting operational costs and compliance requirements. CMB must actively manage its waste streams to align with international conventions such as MARPOL, which sets standards to prevent pollution from ships.
Adherence to these environmental mandates is not just about avoiding penalties; it's crucial for maintaining a positive corporate image and ensuring long-term operational sustainability. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continues to refine regulations on ballast water management and the handling of garbage at sea, directly affecting how CMB operates its fleet.
- MARPOL Annex V prohibits the discharge of all garbage except for food wastes within certain distances from land.
- Ballast Water Management Convention requires ships to manage ballast water to prevent the introduction of invasive alien species.
- CMB's investment in advanced onboard waste treatment systems is essential for compliance and reducing its environmental footprint.
- The cost of non-compliance, including fines and reputational damage, can significantly outweigh the investment in robust waste management practices.
Global efforts to combat climate change are profoundly reshaping the shipping industry, with significant implications for companies like CMB. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) is driving a strong push for decarbonization, aiming for a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, which directly influences investment in cleaner technologies such as hydrogen. This aligns with increasing regulatory pressure and investor demand for sustainable operations, as seen in the widespread adoption of alternative fuels and advanced exhaust treatment systems to meet stricter air pollutant standards.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our CMB PESTLE Analysis is meticulously constructed using a blend of primary and secondary data sources. We incorporate insights from leading market research firms, government economic reports, and reputable industry publications to ensure comprehensive coverage of all PESTLE factors.
