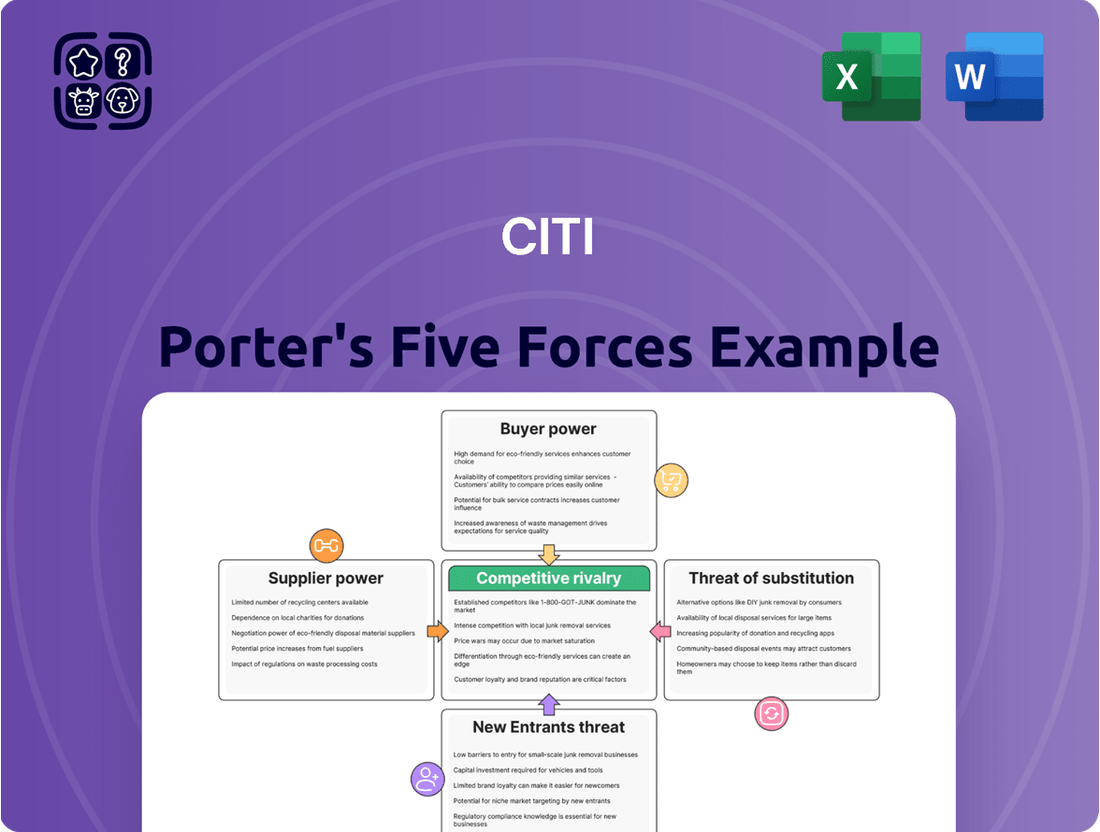
Citi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Citi Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for Citi is crucial for any strategic decision. Porter's Five Forces provides a powerful framework to dissect these pressures, from the bargaining power of customers to the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Citi’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Technology and software providers hold considerable sway over financial institutions like Citi. Citi's operations, from managing risk to serving clients, depend on sophisticated tech infrastructure and software. Suppliers of unique fintech or enterprise software can exert moderate to significant bargaining power, particularly when their products are proprietary and require complex integration.
Citi's significant commitment to technology, evidenced by its annual investment of over $8.5 billion in digital transformation initiatives, underscores its reliance on these external tech partners. This substantial expenditure highlights the critical nature of these solutions and, consequently, the suppliers' leverage.
The financial services sector, especially for a global powerhouse like Citi, relies heavily on a specialized workforce. This includes experts in finance, cutting-edge technology, robust cybersecurity, and intricate regulatory compliance. When there's a shortage of these in-demand professionals, or when competitors aggressively pursue them, the bargaining power of these skilled employees significantly rises.
Citi itself has acknowledged internal skill gaps, particularly in areas like compliance and data governance. This highlights a continuous need for strategic investment in employee development and a proactive approach to attracting and retaining top-tier talent in these critical fields.
The bargaining power of suppliers in data and information services significantly impacts financial institutions like Citi. Access to real-time market data, economic indicators, and credit ratings is absolutely essential for Citi's core operations, including trading, investment banking, and risk management. For instance, in 2024, the global financial data market was valued at over $40 billion, with a few dominant players holding substantial sway over pricing and access.
Key providers of specialized or exclusive datasets can wield considerable power. Citi's reliance on accurate and timely information means that suppliers with unique data streams or proprietary analytics platforms can command higher prices or dictate terms. This dependence is fundamental to maintaining a competitive edge and making sound financial decisions across all of Citi's diversified services.
Regulatory and Compliance Consultants
The bargaining power of regulatory and compliance consultants for Citi is significant, driven by the complexity and ever-changing nature of global financial regulations. These specialized firms possess unique expertise crucial for navigating intricate legal landscapes and addressing consent orders, allowing them to command premium fees and favorable terms. Citi's history of substantial fines, such as the $400 million penalty in 2022 related to risk management and data deficiencies, highlights the critical need for and influence of these expert advisors.
These consultants often operate in a niche market where deep knowledge of specific financial regulations, like those pertaining to anti-money laundering or consumer protection, is paramount. Their ability to interpret and implement compliance measures can directly impact a financial institution's operational continuity and avoid costly penalties.
- Specialized Expertise: Consultants offer deep knowledge of evolving financial regulations, a necessity for large institutions like Citi.
- High Switching Costs: The intensive nature of compliance work and the need for continuity make switching consultants costly and time-consuming.
- Impact of Non-Compliance: Significant fines, such as Citi's $400 million penalty in 2022, underscore the critical role and leverage of compliance consultants.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Ongoing and stringent regulatory oversight by bodies like the Federal Reserve grants consultants considerable influence over financial firms' operations.
Payment Network Operators
Payment network operators like Visa and Mastercard hold substantial bargaining power over Citi's consumer banking and credit card operations. These networks dictate transaction fees and processing standards, essential infrastructure for Citi's core business. For instance, Visa reported processing 200 billion transactions in 2023, highlighting their immense scale and leverage.
Citi's reliance on these established payment rails means they have limited ability to negotiate favorable terms, as these networks are critical intermediaries. Even strategic partnerships, such as Citi's co-branded credit cards with airlines, must operate within the fee structures and rules set by these dominant payment processors.
- Network Dominance: Visa and Mastercard control the vast majority of global payment transactions, giving them significant pricing power.
- Essential Infrastructure: Citi cannot bypass these networks for credit card processing, creating a dependency.
- Fee Structures: Payment networks set interchange fees and other charges that directly impact Citi's profitability.
Suppliers of critical technology and data services possess considerable bargaining power over Citi. This is due to the essential nature of their offerings for Citi's operations and the often proprietary or specialized capabilities they provide. For example, in 2024, the global financial data market, a key area for Citi, was valued at over $40 billion, indicating the significant economic weight of these suppliers.
The reliance on specialized talent also strengthens supplier power, particularly when there are shortages in areas like cybersecurity or advanced analytics. Citi's acknowledgment of internal skill gaps further emphasizes this dependence. Similarly, payment network operators like Visa and Mastercard, processing billions of transactions annually, dictate terms due to their essential role in credit card processing.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Citi | 2024 Data/Example |
| Technology & Software Providers | Proprietary solutions, integration complexity | Moderate to Significant leverage on pricing and terms | Citi's $8.5B+ annual digital investment highlights reliance. |
| Data & Information Services | Exclusive datasets, real-time market access | High leverage on pricing and access control | Global financial data market > $40B in 2024. |
| Skilled Workforce Providers | Shortage of specialized talent (e.g., cybersecurity) | Increased wage demands and retention challenges | Citi's internal skill gap acknowledgments. |
| Payment Network Operators | Network dominance, essential infrastructure | Significant control over transaction fees | Visa processed 200B+ transactions in 2023. |
| Regulatory & Compliance Consultants | Specialized expertise, high switching costs | Premium fees, influence on operational terms | Citi's $400M penalty in 2022 highlights consultant importance. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Citi by examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each Porter's Five Force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Citi's large institutional clients, including major corporations and governments, wield significant bargaining power. These entities often manage vast sums and require highly specialized financial services, giving them leverage to negotiate better pricing and terms. For instance, in 2023, the global investment banking market saw intense competition for large deals, with fees often being a key negotiation point.
These sophisticated clients typically maintain relationships with several financial institutions, creating a competitive environment where Citi must offer compelling value. Their ability to easily shift business to a competitor if unsatisfied with Citi's offerings or pricing directly enhances their bargaining strength. This dynamic is particularly evident in areas like treasury management and capital markets, where client switching costs can be relatively low for large players.
Wealth management clients, particularly high-net-worth individuals and family offices, wield significant bargaining power. They demand highly personalized services, competitive investment returns, and specialized advisory expertise. These clients possess substantial assets, making them mobile enough to shift their funds to institutions offering superior performance, lower fees, or enhanced client experiences. For instance, in 2024, the global wealth management market saw continued competition, with firms actively adjusting fee structures and service packages to retain and attract these valuable clients.
Retail and consumer banking customers wield significant bargaining power due to the proliferation of choices. In 2024, the banking landscape continues to be shaped by a diverse range of institutions, from established banks to nimble neobanks, all vying for customer attention. This competitive environment means consumers can readily switch providers for services like checking accounts or savings, often with minimal friction.
The ease of switching is further amplified by digital tools. Mobile banking apps allow customers to compare interest rates, fees, and service offerings with unprecedented speed. Data from early 2024 suggests that a substantial percentage of consumers actively monitor their banking options, contributing to pressure on banks to offer competitive pricing and enhanced digital experiences to retain their customer base.
Digital-First Expectations
Digital-first expectations are reshaping the banking landscape, giving customers more leverage. The proliferation of fintech and digital banking means consumers now anticipate constant, convenient access to their finances, often through mobile apps. They’re looking for personalized services, quick transactions, and integrated financial tools, much like they experience with other digital services.
By mid-2024, reports indicated that over 70% of banking customers preferred digital channels for most interactions, a significant jump from previous years. This shift means banks that don't offer intuitive, mobile-first solutions risk alienating a large portion of their customer base. For instance, the demand for instant payment options has surged, with many consumers expecting transfers to be completed in seconds rather than days.
- Digital Channel Preference: A significant majority of banking customers now favor digital channels for their transactions and inquiries.
- Mobile-First Demand: Customers expect seamless mobile banking experiences, including personalized insights and instant transaction capabilities.
- Fintech Influence: The rise of agile fintech companies has set a high bar for digital user experience, increasing customer power over traditional banks.
- Personalization Expectations: Consumers are increasingly looking for tailored financial advice and product offerings delivered through digital platforms.
Regulatory Protections and Transparency
Increased regulatory scrutiny, particularly in the financial sector, significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) continued to enforce regulations mandating clearer disclosures for financial products, directly impacting how easily customers can compare offerings. This transparency reduces information asymmetry, a key factor in customer leverage.
These regulations empower customers by granting them more rights and simplifying dispute resolution processes. For example, regulations enacted in the lead-up to and during 2024 have made it easier for consumers to contest erroneous charges or unfair fees. This increased ease of recourse makes customers less tolerant of poor service or unfavorable terms.
- Enhanced Disclosure Requirements: Regulations like the CFPB's oversight ensure clearer, upfront information on fees and terms for financial services.
- Streamlined Dispute Resolution: Consumers benefit from more accessible and effective mechanisms for resolving complaints.
- Protection Against Unfair Practices: Laws are in place to safeguard customers from predatory or deceptive business conduct.
- Facilitated Provider Switching: Transparency and standardized information make it simpler for customers to compare and switch between financial institutions.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to increased choice and ease of switching, particularly in retail banking where digital options abound. By mid-2024, over 70% of banking customers preferred digital channels, highlighting the demand for seamless mobile experiences and personalized services. This shift, influenced by fintech competition, pressures institutions to offer competitive pricing and superior digital engagement to retain clients.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Example (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Clients | Volume, specialized needs, multiple provider relationships | Negotiating lower fees on large capital markets deals; intense competition for mandates. |
| Wealth Management Clients | Asset size, demand for personalization, performance expectations | Shifting assets to firms offering better returns or lower advisory fees; fee adjustments by firms. |
| Retail/Consumer Banking Customers | Abundant choices, low switching costs, digital convenience | Switching accounts for better interest rates or lower fees; comparison shopping via mobile apps. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Citi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Citi. You'll gain immediate access to this fully formatted and professionally written analysis, providing deep insights into the competitive landscape of the banking industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Citi operates in a highly competitive landscape, facing significant rivalry from other global universal banks. Major players such as JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, HSBC, and Goldman Sachs offer a comparable breadth of services, encompassing consumer, corporate, and investment banking. This intense competition is particularly evident in the lucrative investment banking sector, where Citi is actively seeking to expand its market presence.
Citi faces intense competition from powerful regional and domestic banks that possess intimate knowledge of local markets and loyal customer relationships. These institutions often excel in consumer and small business banking, where personalized service and deep community ties are paramount.
For instance, in the United States, while Citi is a global player, it directly contends with banks like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo, which boast extensive branch networks and deeply entrenched customer bases. In 2024, these domestic giants continue to leverage their scale and local presence to capture market share.
Citi's strategic decision to divest certain international consumer banking operations underscores its focus on core markets where it can more effectively compete against these formidable local rivals. This shift aims to concentrate resources on areas where its global strengths can be best leveraged against strong domestic competition.
Fintech companies and digital challengers are dramatically reshaping the financial industry. These agile players, including neobanks, are introducing specialized, cost-effective, and user-friendly services by effectively leveraging technology. They are directly disrupting core banking areas such as payments, lending, and wealth management.
This intense competition compels established institutions like Citi to accelerate their digital transformation and innovation strategies to remain competitive. The growth rate of fintechs is striking; they are expanding at a pace three times faster than incumbent banks, presenting a substantial challenge to traditional business models.
Product and Service Innovation
Competitive rivalry in the financial sector is intensely fueled by a relentless pursuit of innovation in products and services. This includes the integration of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and embedded finance solutions. Banks are channeling substantial resources into these advancements to elevate customer experiences, streamline operations, and carve out unique market positions.
Citi's commitment to technological advancement, demonstrated by its substantial annual tech spending, underscores the pressure to innovate. For instance, in 2023, Citi announced plans to invest approximately $10 billion in technology, a significant portion of which is directed towards innovation and digital transformation initiatives. This investment is crucial for staying ahead in a landscape where competitors are rapidly deploying new digital tools and platforms to attract and retain customers.
The drive for innovation impacts competitive rivalry in several key ways:
- AI and Machine Learning: Banks are leveraging AI for personalized customer service, fraud detection, and risk management. For example, many institutions are using AI-powered chatbots to handle customer inquiries, reducing wait times and improving efficiency.
- Blockchain Technology: The adoption of blockchain is streamlining cross-border payments and trade finance, offering faster settlement times and reduced costs. Citi has been actively exploring and piloting blockchain solutions for various financial services.
- Embedded Finance: The trend of embedding financial services directly into non-financial platforms is creating new revenue streams and customer touchpoints. This allows for seamless transactions within everyday applications, shifting the competitive battleground.
- Digital Banking Platforms: Continuous upgrades to mobile banking apps and online platforms are essential for meeting evolving customer expectations for convenience and accessibility.
Regulatory and Compliance Burden
The banking sector's highly regulated environment intensifies competitive rivalry. Evolving compliance requirements and substantial penalties for non-adherence force banks to dedicate significant resources, potentially impacting profitability and growth investments. For instance, Citi's ongoing efforts to address regulatory consent orders have involved billions of dollars in investments for technology and risk management overhauls.
This regulatory burden creates a competitive disadvantage for smaller institutions less equipped to handle the compliance costs. Banks must navigate a complex web of rules, including those related to capital adequacy, anti-money laundering (AML), and consumer protection.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Banks face constant oversight from bodies like the Federal Reserve, OCC, and CFPB.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting stringent regulatory demands requires significant investment in technology, personnel, and training.
- Penalties for Lapses: Fines for non-compliance can be substantial, impacting financial performance and reputation.
- Impact on Innovation: Resources diverted to compliance may limit investment in new products and services, affecting competitive positioning.
Citi faces fierce competition from a broad spectrum of financial institutions, from global behemoths like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America to nimble fintech disruptors. This rivalry is intensified by rapid technological advancements, with banks investing heavily in AI, blockchain, and digital platforms to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. For example, Citi's reported $10 billion technology investment in 2023 highlights the pressure to innovate.
The banking sector’s stringent regulatory environment further fuels competitive rivalry. Compliance costs and the risk of substantial penalties for non-adherence necessitate significant resource allocation, impacting profitability and potentially limiting investment in innovation. This creates a challenging landscape where staying ahead requires not only financial strength but also adaptability and a keen focus on technological integration.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Citi |
| Global Universal Banks | Broad service offerings, extensive global reach | Direct competition across all business lines, pressure on market share |
| Regional/Domestic Banks | Local market knowledge, strong customer relationships | Challenges in consumer and small business banking, need for localized strategies |
| Fintech & Digital Challengers | Agile, technology-driven, specialized services | Disruption of core banking services, necessitates digital transformation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Digital payment platforms and mobile wallets represent a growing threat of substitutes for Citi's traditional payment services. Consumers and businesses alike are embracing options like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay, which offer enhanced convenience and speed for everyday transactions. This shift diminishes the necessity of relying solely on bank accounts and credit cards, directly impacting Citi's transaction volumes and fee income.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for Citi's traditional lending business. These platforms offer alternative avenues for individuals and small businesses to secure funding, bypassing conventional banking channels. For instance, by mid-2024, the P2P lending market globally was projected to reach over $150 billion, demonstrating a substantial and growing alternative to bank loans.
These fintech solutions often boast faster approval times and more adaptable repayment structures compared to traditional bank offerings. This increased accessibility and flexibility make them compelling substitutes, particularly for consumer and small business credit needs where speed and ease of access are paramount. As of early 2024, crowdfunding platforms alone facilitated billions in funding for various projects and businesses, highlighting their impact as a viable alternative financing source.
Direct investment platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat to traditional wealth management. These digital alternatives offer considerably lower fees, often a fraction of what human advisors charge, making them attractive to a broad range of investors. For instance, many robo-advisors manage portfolios for annual fees around 0.25%, a stark contrast to the 1% or more often seen with human advisors.
These platforms democratize investing, providing access to sophisticated portfolio management and rebalancing tools that were once exclusive to high-net-worth individuals. The convenience and user-friendly interfaces appeal especially to younger, tech-savvy demographics who are comfortable managing their finances online. This shift in investor preference means that Citi's wealth management division faces increased pressure to demonstrate its value proposition beyond basic investment execution.
The accessibility and low cost of these substitutes can divert significant assets, particularly from clients who may not require complex financial planning. As of early 2024, assets under management for robo-advisors have reached hundreds of billions of dollars globally, a figure that continues to grow rapidly, indicating a substantial and expanding competitive force within the industry.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Finance
The rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based finance presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offer alternative avenues for value storage, fund transfers, and financial services, bypassing traditional intermediaries. For example, stablecoins are gaining traction for their potential to simplify cross-border payments, with the global stablecoin market cap reaching over $150 billion in early 2024.
While established institutions like Citi are actively exploring blockchain technology, the inherent disintermediation offered by these digital assets could erode market share. The continued development and adoption of these technologies could lead to significant shifts in how financial transactions are conducted and value is stored.
- DeFi Growth: The total value locked in DeFi protocols surpassed $100 billion in 2023, indicating substantial user adoption and a growing alternative financial ecosystem.
- Cross-Border Payments: Stablecoins aim to reduce transaction fees and settlement times, potentially disrupting traditional remittance markets which saw over $800 billion in global flows in 2023.
- Technological Exploration: Major financial institutions are investing in blockchain research and development, acknowledging the potential impact of these technologies on future financial infrastructure.
Embedded Finance
Embedded finance is increasingly offering alternative ways for consumers and businesses to access financial services, directly within their preferred non-financial applications. For instance, many e-commerce platforms now seamlessly integrate buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) options at checkout, bypassing traditional credit applications. This trend is projected to grow significantly, with some estimates suggesting the embedded finance market could reach $7 trillion globally by 2030, according to reports from late 2023 and early 2024.
This integration represents a threat of substitutes because it provides convenient, often more tailored, financial solutions outside of traditional banking institutions. As more companies embed payment processing, lending, and even insurance into their user experiences, customers may find less need to engage with banks directly for these services. For example, ride-sharing apps offering instant driver payouts or accounting software with integrated payment solutions demonstrate this shift.
- Market Growth: The embedded finance market is anticipated to expand rapidly, with projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years.
- Convenience Factor: Financial services are becoming accessible within non-financial platforms, enhancing user convenience and potentially reducing reliance on traditional banks.
- Blurring Industry Lines: The distinction between financial and non-financial sectors is diminishing as financial functionalities become embedded in everyday digital experiences.
- Competitive Pressure: Traditional financial institutions face increased competition from technology companies and fintechs that leverage embedded finance strategies.
The threat of substitutes for Citi is substantial, stemming from digital payment platforms, P2P lending, direct investment platforms, cryptocurrencies, and embedded finance. These alternatives offer enhanced convenience, lower costs, and faster access to financial services, directly challenging Citi's traditional revenue streams and customer relationships.
Entrants Threaten
Regulatory barriers significantly deter new entrants in the banking sector. For instance, in 2024, capital adequacy ratios, like Basel III requirements, demand substantial financial reserves, making it incredibly costly for new banks to establish themselves. Obtaining necessary licenses and navigating complex compliance frameworks, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, further escalate the initial investment and operational complexity.
These stringent requirements effectively limit the number of new full-service banks that can realistically enter the market. Citi, as a Global Systemically Important Bank (G-SIB), faces even more rigorous oversight and higher capital requirements, reinforcing the high entry barriers that protect established players from new competition.
The sheer capital needed to launch and sustain a global financial institution like Citi presents a formidable barrier. Think about the billions required for cutting-edge technology, extensive branch networks, and robust regulatory compliance. For instance, in 2024, major banks reported trillions in assets, underscoring the scale of investment necessary to even enter the playing field.
This massive capital outlay effectively deters most potential new entrants, particularly those looking to offer a comprehensive suite of financial services. Smaller, niche players might emerge, but challenging established global banks across multiple product lines is incredibly difficult without comparable financial muscle. The global banking landscape demands significant scale, making it a tough market for newcomers to penetrate.
Established financial institutions, such as Citi, leverage decades of brand loyalty and deeply ingrained customer trust, a formidable barrier for newcomers. Citi's founding in 1812 underscores its extensive history in building these relationships. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating this trust, particularly in critical financial services like wealth management, where customer confidence is paramount.
Technological and Infrastructure Investment
The threat of new entrants in the financial services sector, particularly concerning technological and infrastructure investment, remains moderate for established players like Citi. While fintech startups can be agile, replicating the vast, secure, and globally integrated technology infrastructure of a diversified financial giant demands immense capital and expertise. Newcomers would face the daunting task of building out robust IT systems, state-of-the-art cybersecurity defenses, and sophisticated data management capabilities to even approach Citi's current operational framework.
For instance, a new entrant aiming to offer a comparable suite of services would need to invest billions in technology. In 2023, major banks like JPMorgan Chase reported technology spending in the tens of billions of dollars, a significant portion of which goes towards maintaining and upgrading existing infrastructure and enhancing cybersecurity. This level of investment creates a substantial barrier, as replicating Citi's established technological backbone, which supports everything from retail banking to complex investment services, is a monumental and costly undertaking.
- Substantial Capital Outlay: New entrants require significant upfront investment in IT systems, cloud infrastructure, and data analytics platforms, often running into billions of dollars to match incumbent capabilities.
- Cybersecurity Demands: Building and maintaining a world-class cybersecurity infrastructure to protect against sophisticated threats is a continuous and extremely expensive endeavor, with global cybersecurity spending projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024.
- Regulatory Compliance: New entrants must also invest heavily in systems to ensure compliance with a complex web of global financial regulations, adding another layer of cost and complexity to infrastructure development.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
New entrants face a significant hurdle in attracting and retaining the highly specialized talent required for a complex financial institution. This includes professionals ranging from investment bankers to cybersecurity experts, whose skills are in high demand across the industry.
Established firms, such as Citi, possess established networks and competitive compensation packages that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in 2024, the average base salary for a financial analyst in major financial hubs often exceeded $90,000, with bonuses and other incentives pushing total compensation much higher, a benchmark that startups struggle to meet globally.
- Talent Scarcity: Critical roles in areas like AI and blockchain in finance saw an estimated 15% year-over-year increase in demand in 2024, outstripping supply.
- Compensation Gaps: Startups may offer equity, but the immediate cash compensation and benefits packages of incumbents are a strong retention tool.
- Brand Recognition: A well-known financial institution's brand name itself acts as a magnet for top talent, providing a perceived stability and prestige that new entrants lack.
- Training & Development: Large organizations invest heavily in ongoing training and career development programs, which are attractive to ambitious professionals.
The threat of new entrants for established financial institutions like Citi is generally low due to significant barriers. These include immense capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the need for deep-seated customer trust built over decades. For example, in 2024, global cybersecurity spending was projected to exceed $200 billion, illustrating the substantial investment required for infrastructure and security, a cost that deters many potential new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for technology, licenses, and operations. | Formidable; requires billions to compete. | Trillions in assets for major banks. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex global financial regulations (KYC, AML, capital adequacy). | Costly and time-consuming; increases operational complexity. | Basel III capital adequacy ratios. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established reputation and customer relationships. | Difficult to replicate; takes years to build. | Citi's founding in 1812. |
| Technology & Infrastructure | Need for advanced, secure, and integrated IT systems. | Massive investment needed to match incumbents. | JPMorgan Chase's annual tech spending in tens of billions. |
| Talent Acquisition | Attracting and retaining specialized financial and tech talent. | Challenging due to competition and compensation demands. | Average financial analyst salary exceeding $90,000 plus bonuses. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also leverage data from reputable business news outlets and regulatory filings to capture a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
