Cincinnati Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cincinnati Financial Bundle
Cincinnati Financial operates within a highly competitive insurance landscape, where buyer power and the threat of substitutes can significantly impact profitability. Understanding the nuances of supplier relationships and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview only scratches the surface of these complex dynamics.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Cincinnati Financial’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you with a comprehensive understanding of its market position.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cincinnati Financial, like other insurers, relies on key suppliers such as reinsurers, technology providers, and data analytics firms. The global reinsurance market, a critical supplier of risk transfer capacity, demonstrated robust capital levels and favorable pricing conditions through 2024 and into 2025. This stability suggests that reinsurers generally hold moderate to high bargaining power, as primary insurers depend heavily on their services for managing large risks and maintaining solvency.
Technology and software providers, particularly those in AI and machine learning, are becoming indispensable for insurers like Cincinnati Financial. The ongoing digital transformation in the insurance sector fuels a strong demand for these advanced solutions. This rising demand can significantly amplify the bargaining power of prominent insurtech companies, especially those with proprietary technologies.
Cincinnati Financial relies heavily on data and analytics providers for critical functions like underwriting and fraud detection. The exclusivity and sophistication of these data sets and analytical tools grant these suppliers significant bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the market for Insurtech data analytics saw substantial investment, with companies like Verisk Analytics, a major player, continuing to innovate its offerings, potentially increasing its leverage with insurers.
Supplier Power 4
Cincinnati Financial's bargaining power of suppliers is generally moderate, though it can be influenced by the availability of specialized insurance products. While the overall insurance market is competitive with many providers, niche insurers offering unique coverage or proprietary products can exert greater influence. For instance, if Cincinnati Financial relies on a specific reinsurer for a specialized line of business, that reinsurer may hold significant leverage.
This dynamic is particularly relevant for unique or hard-to-underwrite risks where the pool of capable suppliers is limited. The company's ability to negotiate terms with these specialized suppliers is crucial for managing costs and ensuring product availability.
- Supplier Concentration: The insurance industry, while broad, can have concentrated pockets of suppliers for highly specialized lines of coverage, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: High switching costs for specialized insurance products or reinsurance can further empower suppliers by making it difficult for Cincinnati Financial to change providers.
- Availability of Alternatives: The general availability of standard insurance products keeps supplier power in check for those lines, but niche offerings present a different dynamic.
Supplier Power 5
The financial markets themselves can exert significant power over insurers like Cincinnati Financial. This power manifests through the cost of capital, which is directly influenced by external factors such as prevailing interest rates and broader financial market conditions. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions, including potential adjustments to the federal funds rate, directly impact the borrowing costs for insurance companies and the returns they can expect on their investment portfolios.
High interest rates, while potentially boosting investment income for insurers, also increase the cost of doing business by making it more expensive to raise capital. This dynamic creates a form of supplier power, as the financial markets dictate the cost of a crucial input for insurance operations. For example, if interest rates rise significantly, the cost of issuing new debt or equity to fund growth or manage liabilities will increase, impacting profitability.
- Financial Market Influence: Interest rates and overall market stability are external forces that suppliers of capital (financial markets) control.
- Cost of Capital Impact: Fluctuations in market conditions directly affect Cincinnati Financial's cost of borrowing and equity.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: While higher rates can boost investment income, they also increase operational costs for insurers.
- 2024 Context: Anticipated shifts in interest rate policy by central banks in 2024 will continue to shape the bargaining power of financial markets.
Cincinnati Financial's reliance on reinsurers, technology providers, and data analytics firms means these suppliers can wield significant influence. The stability and capital strength of the global reinsurance market in 2024 indicated moderate to high bargaining power for reinsurers, essential for managing large risks. Similarly, the increasing demand for advanced insurtech solutions in 2024, particularly in AI and machine learning, amplifies the leverage of leading tech firms with proprietary offerings.
The bargaining power of specialized data analytics providers, such as Verisk Analytics, is amplified by the exclusivity and sophistication of their tools, crucial for underwriting and fraud detection. While general insurance markets offer alternatives, niche suppliers for unique risks can command greater leverage, impacting Cincinnati Financial's cost management and product availability.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | 2024/2025 Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Capital levels, risk transfer capacity, pricing | Robust capital, favorable pricing, moderate to high power |
| Technology Providers (Insurtech) | Proprietary technology, demand for digital solutions | Strong demand, increasing power for leading firms |
| Data Analytics Providers | Exclusivity of data, sophistication of tools | Significant investment, innovation increasing leverage |
| Financial Markets (Capital Providers) | Interest rates, market stability, cost of capital | Interest rate sensitivity, cost of capital impact |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Cincinnati Financial, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining rivalry, buyer power, supplier influence, new entrants, and substitutes.
Effortlessly identify competitive pressures within the insurance industry, allowing Cincinnati Financial to proactively address potential threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the insurance sector, including those engaging with Cincinnati Financial, are experiencing a notable increase in their bargaining power. This shift is driven by a heightened awareness of available policy options and the proliferation of online comparison tools, making it easier for consumers to shop around.
Today's insurance buyers expect a smooth digital journey, quick quotes, and tailored services. For instance, in 2024, the ease of obtaining multiple insurance quotes online within minutes has become a standard expectation, directly influencing how insurers like Cincinnati Financial must adapt their offerings and pricing to remain competitive.
Cincinnati Financial faces increasing buyer power due to the ease with which customers can compare insurance policies online. This transparency allows consumers to readily identify and switch to providers offering more competitive pricing and customized coverage, directly impacting Cincinnati Financial's ability to maintain pricing power.
The growing prevalence of embedded insurance, where insurance is bundled with other products or services, further amplifies customer power. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers are open to purchasing insurance directly through non-insurance channels, suggesting a shift in how and where insurance is bought, often driven by convenience and perceived value.
Customers' ability to easily switch providers if their expectations for price and tailored solutions aren't met puts pressure on Cincinnati Financial to continuously innovate and offer compelling value propositions. This dynamic necessitates a focus on customer retention through superior service and product differentiation to mitigate the impact of heightened buyer power.
In 2024, the insurance industry saw a significant shift towards hyper-personalization, directly increasing customer bargaining power. Consumers increasingly demand tailored policies and exceptional service experiences, making it easier for them to switch providers if their needs aren't met.
Cincinnati Financial, like its peers, must invest heavily in data analytics and customer relationship management to offer these personalized solutions. The ability to anticipate and cater to individual client needs is becoming a crucial differentiator, empowering customers to seek out the best value and service.
Buyer Power 4
Cincinnati Financial's customers, particularly in the personal lines segment, wield significant bargaining power. The growing reliance on mobile platforms for policy management and claims processing means customers expect seamless, convenient, and accessible digital experiences. Insurers who fail to meet these expectations risk customer attrition.
This digital shift empowers buyers by providing them with more information and easier comparison tools. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of insurance interactions, from quotes to claims updates, are expected to occur digitally, placing a premium on user-friendly interfaces and prompt service delivery. Cincinnati Financial must continually invest in its digital infrastructure to maintain customer loyalty.
- Digital Expectations: Customers increasingly demand mobile-first solutions for policy management and claims handling, driving the need for intuitive digital platforms.
- Information Accessibility: The ease of comparing insurance products online amplifies customer bargaining power, forcing insurers to offer competitive pricing and superior service.
- Service Delivery Pressure: Insurers prioritizing mobile interactions face heightened pressure to deliver efficient and satisfactory digital experiences to retain customers.
Buyer Power 5
For commercial clients, especially smaller businesses, the emphasis on cost-effectiveness and highly specific risk assessments significantly enhances their bargaining leverage. Insurers capable of showcasing tangible cost reductions and bespoke policy designs will naturally hold a stronger appeal.
This dynamic is particularly evident in the property and casualty insurance market. For instance, in 2024, small businesses continued to seek out insurers offering competitive premiums, often comparing quotes from multiple providers. A study by the National Federation of Independent Business indicated that over 60% of small business owners consider price a primary factor when selecting insurance.
- Cost Sensitivity: Small commercial clients are highly sensitive to premium costs, driving them to seek out the most economical coverage options.
- Customization Demand: The need for tailored risk profiles, matching specific business operations and exposures, gives buyers more power to demand specialized solutions.
- Information Availability: Increased access to comparative data and online quoting tools empowers buyers to easily assess and negotiate terms.
- Switching Costs: While some switching costs exist, they are often perceived as manageable for smaller enterprises, further bolstering their bargaining position.
Cincinnati Financial customers, especially in the personal lines, benefit from increased bargaining power due to readily available online comparison tools and a demand for digital-first experiences. This allows them to easily switch providers if pricing or service expectations aren't met, as seen in 2024 where digital interactions for insurance were paramount.
For commercial clients, particularly small businesses, cost sensitivity and the need for customized risk assessments are key drivers of their bargaining power. In 2024, over 60% of small business owners prioritized price when choosing insurance, highlighting the pressure on insurers like Cincinnati Financial to offer competitive premiums and tailored solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Comparison Tools | Increases buyer power by enabling easy price and service comparison. | Consumers expect seamless online quoting and policy management. |
| Demand for Personalization | Empowers customers to seek tailored policies and service. | Insurers investing in data analytics to meet individual needs. |
| Cost Sensitivity (Commercial) | Drives demand for competitive premiums and cost-effective solutions. | Over 60% of small businesses prioritize price in insurance selection. |
| Switching Ease | Low perceived switching costs for many customer segments. | Customers readily switch for better value or service. |
What You See Is What You Get
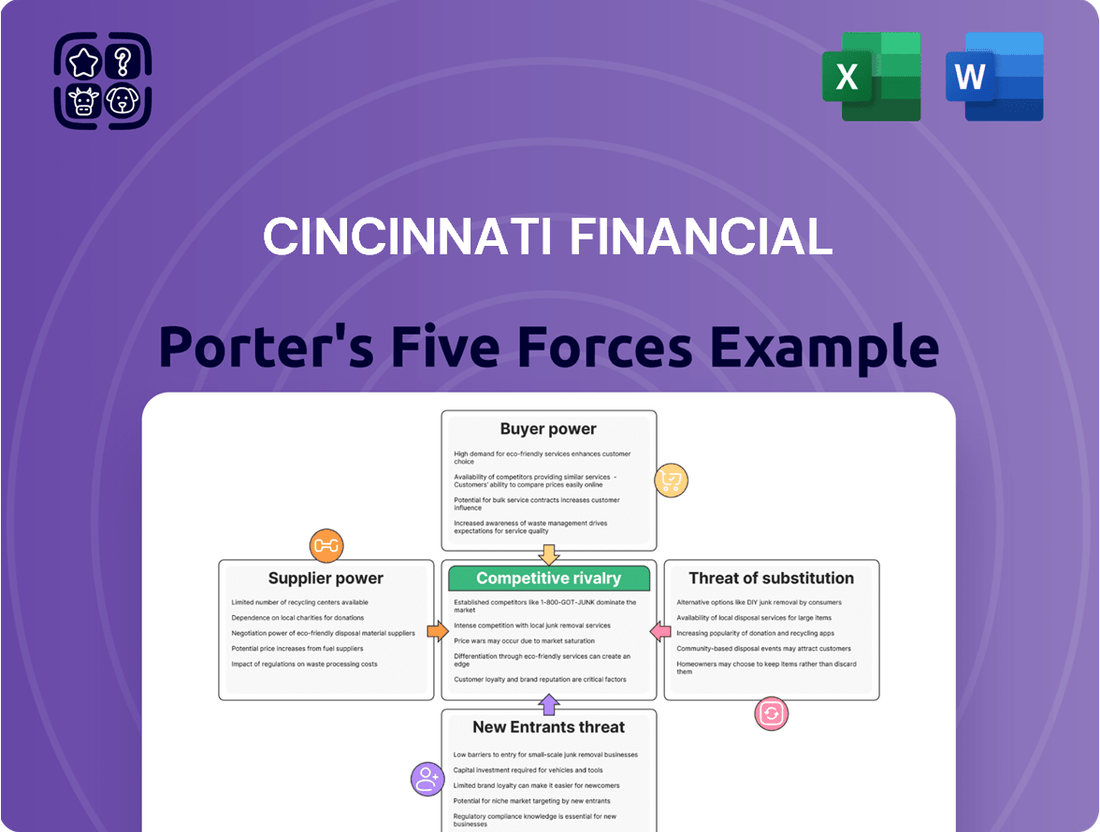
Cincinnati Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Cincinnati Financial, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the insurance industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing valuable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Cincinnati Financial faces significant competitive rivalry within the property and casualty insurance market. This sector is crowded with both long-standing, well-capitalized insurers and agile new entrants, all vying for market share.
This intense competition directly influences pricing strategies, forcing companies like Cincinnati Financial to remain competitive on premiums. For instance, in 2024, the industry continued to see aggressive pricing from major players, particularly in commercial lines, putting pressure on profit margins.
Furthermore, the need for product innovation is paramount. Insurers are constantly developing new coverage options and digital tools to attract and retain customers, making it a dynamic landscape where staying ahead requires continuous investment in technology and service offerings.
Competitive rivalry within Cincinnati Financial's operating environment is intensifying, especially in personal auto insurance, where a resurgence of competition is evident. This is occurring even as growth in commercial lines begins to moderate, indicating a mixed competitive landscape.
In 2023, for instance, the personal auto segment continued to face pricing pressures and increased customer acquisition costs for many insurers, including those competing with Cincinnati Financial. This heightened rivalry can lead to reduced profitability if not managed effectively through superior underwriting and operational efficiency.
Technological advancements, particularly in AI and automation, are significantly shaping competitive rivalry within the insurance sector. Companies are actively integrating these tools to refine operations, elevate customer interactions, and boost the precision of their underwriting, creating a more dynamic and innovation-driven market. For instance, by mid-2024, many insurers reported efficiency gains of up to 15% in claims processing through AI-powered automation.
This technological race intensifies competition as insurers strive for differentiation by offering superior digital experiences and more accurate risk assessments. Those who effectively adopt AI and automation can gain a crucial edge in pricing and service delivery, putting pressure on less technologically advanced competitors to keep pace or risk losing market share.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry in the insurance sector, particularly for companies like Cincinnati Financial, is intensifying as customer experience emerges as a key differentiator. Insurers are investing heavily in digital platforms and personalized services to streamline interactions and claims processing. For instance, in 2024, many leading insurers reported significant increases in customer satisfaction scores directly linked to improved digital engagement and faster claims resolution times, indicating a strong correlation between tech investment and competitive advantage.
Companies that successfully integrate seamless digital journeys, from policy inception to claim settlement, are capturing market share. This focus on customer-centricity means that traditional pricing strategies alone are no longer sufficient to win and retain business. The ability to offer a superior, hassle-free experience is becoming paramount, driving innovation across the industry.
- Digital Transformation: Insurers are prioritizing investments in user-friendly mobile apps and online portals to enhance customer interaction.
- Personalized Service: Tailoring offerings and communication based on individual customer needs is becoming a critical competitive element.
- Efficient Claims Processing: Streamlining the claims handling process through technology and dedicated support is a major focus for retaining customer loyalty.
- Customer Satisfaction Metrics: Improvements in customer satisfaction, often directly tied to these experience enhancements, are a key indicator of competitive success in 2024.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Cincinnati Financial's competitive rivalry is shaped by its distinctive agent-centric approach. This model fosters deep relationships with independent agencies, creating a significant advantage in local markets where trust and personalized service are paramount. This localized strength contrasts with the presence of larger, more diversified insurance conglomerates.
These industry giants often employ broader strategies, leveraging scale and varied product offerings to compete. For instance, in 2024, the property and casualty insurance sector saw continued consolidation and intense competition, with major players like State Farm and Berkshire Hathaway (through its insurance subsidiaries) maintaining substantial market share and employing aggressive pricing and marketing tactics.
- Agent Relationships: Cincinnati Financial's reliance on independent agents provides a strong distribution network and local market penetration.
- Industry Giants: Large insurers with vast resources and diverse strategies present a significant competitive challenge.
- Market Dynamics: The ongoing evolution of the insurance landscape, including technological advancements and changing consumer preferences, necessitates continuous adaptation for all players.
- Adaptation Necessity: To maintain its edge, Cincinnati Financial must consistently refine its offerings and service model in response to broader market trends and competitor actions.
Competitive rivalry within Cincinnati Financial's property and casualty insurance market is intense, fueled by both established players and emerging digital insurers. This forces a constant focus on pricing and product innovation. For instance, in 2024, the personal auto segment experienced a notable resurgence in aggressive pricing strategies, impacting profit margins for many insurers.
Technological advancements, particularly in AI, are a significant driver of this rivalry, enabling companies to improve underwriting accuracy and customer experience. By mid-2024, insurers leveraging AI reported efficiency gains of up to 15% in claims processing, creating a competitive edge.
Cincinnati Financial's agent-centric model provides a strong differentiator, fostering local market trust, though it competes against larger, diversified insurers like State Farm and Berkshire Hathaway's subsidiaries, which utilize broader market strategies and aggressive tactics.
Customer experience is increasingly becoming a key battleground, with insurers investing in digital platforms for seamless interactions. In 2024, improved digital engagement directly correlated with higher customer satisfaction scores, highlighting the importance of a superior, hassle-free experience in retaining market share.
| Key Competitors | 2024 Market Share (Est.) | Key Competitive Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| State Farm | ~10% (P&C) | Broad product offerings, aggressive pricing, strong agent network |
| Berkshire Hathaway (Insurance Subsidiaries) | ~7% (P&C) | Diversified insurance operations, strong financial backing, decentralized management |
| Allstate | ~5% (P&C) | Focus on brand recognition, digital transformation, product innovation |
| Progressive | ~5% (P&C) | Direct-to-consumer model, telematics, aggressive marketing |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for traditional insurance products is a significant consideration. Alternative risk transfer mechanisms, such as large corporations choosing to self-insure or establish captive insurance companies, can bypass conventional insurers. While specific data for Cincinnati Financial's exposure to these substitutes isn't publicly detailed, the broader insurance industry faces this challenge as businesses seek more control over their risk financing.
The threat of substitutes for Cincinnati Financial is growing as new insurance models emerge. Peer-to-peer insurance, where groups pool risk, and usage-based policies, which price premiums on actual driving or usage, offer consumers more personalized and potentially cost-effective alternatives to traditional coverage. For instance, usage-based insurance programs, like those offered by Progressive with its Snapshot program, have seen significant adoption, with millions of customers participating, demonstrating consumer interest in policies tied to behavior rather than broad risk categories.
Non-insurance platforms are increasingly embedding insurance directly into their customer workflows, presenting a significant substitute threat to traditional insurers like Cincinnati Financial. This trend, fueled by the growing popularity of embedded insurance, allows customers to seamlessly acquire coverage through channels they already use, bypassing conventional insurance providers.
For instance, in 2024, the embedded insurance market is projected to reach substantial figures, with some estimates suggesting it could account for a significant portion of the global insurance premium. This means customers might opt for insurance bundled with their purchases or services, such as travel insurance with flight bookings or extended warranties with electronics, rather than seeking it independently from an insurer.
4
The threat of substitutes for Cincinnati Financial's offerings is moderate. As consumers become more informed about insurance options, they may explore alternative risk management strategies or direct-to-consumer platforms. For instance, the rise of insurtech companies in 2024 offers more accessible and potentially lower-cost alternatives for certain types of coverage, putting pressure on traditional insurers. This increased consumer awareness empowers individuals to compare policies more readily and consider self-insuring for smaller risks.
The availability of comprehensive online information and comparison tools in 2024 allows customers to easily research and switch providers, increasing the substitutability of insurance products. This trend is particularly evident in personal lines like auto and homeowners insurance. Furthermore, the growth of the gig economy has led to an increased demand for specialized, on-demand insurance solutions that may not be readily available through traditional channels.
- Increased consumer awareness: Customers actively research and compare insurance policies online, leading to a greater consideration of alternatives.
- Rise of Insurtech: New technology-driven insurance providers offer innovative and potentially cheaper solutions, directly competing with established players.
- Self-insurance: Individuals and small businesses may opt to self-insure for certain lower-impact risks, reducing the need for traditional insurance policies.
- Gig economy impact: The growth of flexible work arrangements drives demand for specialized insurance products that traditional providers might not easily accommodate.
5
The threat of substitutes for Cincinnati Financial is growing, primarily from the rapid expansion of financial technology (FinTech). These digital solutions offer innovative ways for individuals and businesses to manage their financial well-being, potentially bypassing traditional insurance products. For instance, robo-advisors and automated financial planning platforms can provide investment and risk management guidance, acting as an alternative to certain advisory services offered by insurers.
FinTech platforms are increasingly offering tools that allow users to directly manage and diversify their risks through alternative investments or self-insurance strategies. This can reduce the perceived need for conventional insurance policies, especially for simpler risk exposures. In 2024, the FinTech sector saw significant investment, with global FinTech funding reaching over $100 billion, indicating a strong push towards these alternative solutions.
- FinTech's Impact: Digital platforms are enabling individuals and businesses to manage financial risks through alternative means, potentially reducing reliance on traditional insurance.
- Robo-Advisors and Planning: Automated financial planning and investment tools offer guidance that can substitute for some advisory services.
- Direct Risk Management: FinTech allows for direct management and diversification of risks, sometimes bypassing insurance altogether.
- Market Growth: Global FinTech funding in 2024 exceeded $100 billion, highlighting the sector's rapid development and its potential to disrupt established industries.
The threat of substitutes for Cincinnati Financial is moderate but growing, driven by increased consumer awareness and the rise of insurtech. Customers are more empowered than ever in 2024 to research and compare policies online, leading them to consider alternatives like self-insuring for smaller risks or utilizing specialized on-demand solutions emerging from the gig economy.
FinTech innovations, including robo-advisors and direct risk management platforms, also present a significant substitute threat. With over $100 billion invested globally in FinTech in 2024, these digital solutions offer increasingly sophisticated ways for individuals and businesses to manage their financial well-being, potentially reducing the perceived need for traditional insurance products.
Embedded insurance, where coverage is seamlessly integrated into other purchases, further diminishes the direct interaction with traditional insurers. This trend, projected to capture a substantial portion of insurance premiums in 2024, means customers might opt for bundled insurance rather than seeking it independently.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the insurance sector, including for Cincinnati Financial, is generally considered moderate to low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital needed to start an insurance company, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, to meet solvency requirements and underwrite risk effectively. For instance, in 2023, property and casualty insurers typically needed at least $100 million in surplus to operate comfortably, a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Furthermore, the industry is heavily regulated, requiring extensive licensing and compliance with state-specific laws, which adds considerable time and cost to market entry. Cincinnati Financial benefits from its long-standing relationships with independent agents, a crucial distribution channel that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly. In 2024, agent relationships remain a cornerstone of customer acquisition, making it difficult for unestablished players to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants in the insurance sector, particularly for a company like Cincinnati Financial, is amplified by the rise of InsurTech startups. These digital-first companies are challenging traditional models by offering innovative, streamlined customer experiences and often lower overheads. For instance, in 2023, venture capital funding for InsurTech reached over $10 billion globally, indicating significant investment in new players entering the market.
The threat of new entrants in the property and casualty insurance sector, which Cincinnati Financial operates within, remains moderate. While significant capital is required to establish an insurance company, technology and digital platforms are lowering some entry barriers. For instance, insurtech startups can focus on specific, underserved market segments or utilize data analytics to offer more competitive pricing, potentially siphoning off profitable business lines. In 2023, the property and casualty insurance industry in the U.S. saw a combined ratio of 101.7%, indicating a slight underwriting loss, which could deter some new entrants but also present opportunities for leaner, more efficient newcomers.
4
The threat of new entrants for Cincinnati Financial is generally low. The insurance industry, particularly property and casualty, demands substantial capital to cover potential claims and regulatory compliance. Building a trusted brand and acquiring customers is a lengthy and expensive process, acting as a significant barrier. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to acquire a new customer in the insurance sector can be quite high, often running into hundreds of dollars, especially for specialized lines of business that Cincinnati Financial operates in.
Cincinnati Financial benefits from its established reputation and deep customer relationships, cultivated over decades. This brand loyalty makes it difficult for new companies to lure away existing policyholders. The company's consistent financial performance and strong underwriting practices, evident in its stable profitability over the years, further solidify its market position. For example, Cincinnati Financial has a history of strong returns on equity, often outperforming industry averages, which signals stability and reliability to customers.
- High Capital Requirements: Significant upfront investment is needed for licensing, reserves, and marketing, deterring many potential entrants.
- Brand Loyalty and Trust: Cincinnati Financial's long-standing reputation for reliability and customer service creates a formidable hurdle for new, unproven competitors.
- Distribution Networks: Established insurers have robust networks of agents and brokers, which are difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex insurance regulations in various states requires specialized expertise and resources, adding to the cost of entry.
5
The threat of new entrants for Cincinnati Financial, a player in the insurance sector, is generally moderate to low. The insurance industry is characterized by significant capital requirements, extensive regulatory compliance, and the need for established brand trust and distribution networks, all of which act as substantial barriers. For instance, in 2024, obtaining the necessary licenses and approvals to operate as an insurer in most jurisdictions involves complex and time-consuming processes, demanding substantial upfront investment in systems, personnel, and actuarial expertise.
While some regulatory shifts, like the UK's initiative to streamline entry for new financial firms, might theoretically lower some barriers, the highly regulated nature of insurance, particularly in property and casualty or life insurance, means that stringent oversight remains a constant. This oversight includes solvency requirements and consumer protection measures, which new entrants must meticulously adhere to from inception. The established reputation and customer loyalty that companies like Cincinnati Financial have cultivated over years also present a formidable challenge for newcomers seeking market share.
New entrants would need to overcome significant hurdles:
- High Capital Requirements: Insurers need substantial capital reserves to meet regulatory solvency standards and underwrite policies effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex licensing, reporting, and consumer protection laws across different states and countries is a major undertaking.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Building a trusted brand in a sector where policyholders rely on financial stability is a long-term endeavor.
- Distribution Networks: Establishing effective sales channels, whether through agents or direct-to-consumer models, requires significant investment and time.
The threat of new entrants for Cincinnati Financial is generally low due to high capital requirements, stringent regulations, and the need for established distribution networks. New companies must secure significant funding, often in the hundreds of millions, to meet solvency standards and navigate complex state-specific licensing. For instance, in 2024, the average capital needed to launch a new property and casualty insurer in the U.S. can easily exceed $100 million.
Cincinnati Financial's long-standing reputation and deep agent relationships are also significant barriers. Building brand trust and replicating a robust agency network takes years and substantial investment, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share. In 2023, independent agents remained a dominant force in insurance distribution, a channel that new entrants struggle to access effectively.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for licensing, reserves, and operations. | Deters many potential entrants; estimated $100M+ for P&C in 2024. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and compliance across multiple states. | Time-consuming and costly; requires specialized expertise. |
| Brand & Trust | Established reputation for reliability and financial strength. | New entrants need years to build comparable trust. |
| Distribution Networks | Existing relationships with independent agents and brokers. | Difficult and expensive for new players to replicate quickly. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cincinnati Financial Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and analyst reports to capture the dynamic competitive landscape.
