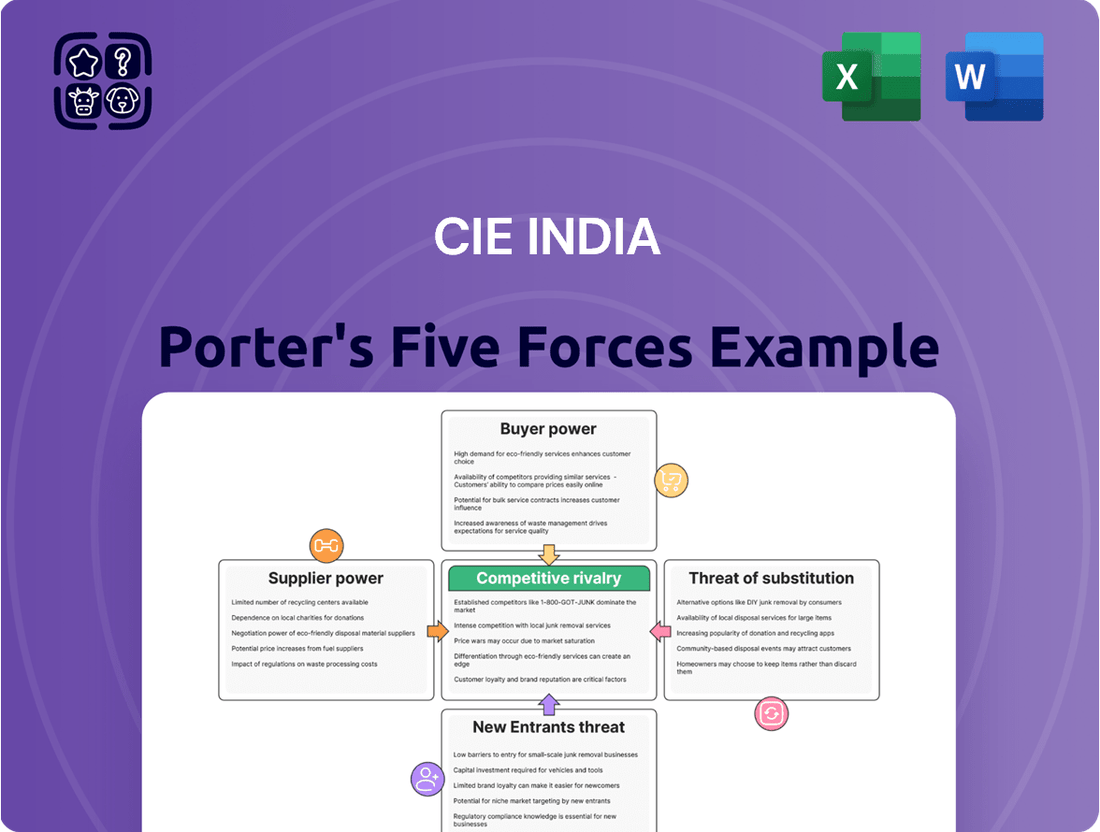
CIE India Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CIE India Bundle
CIE India navigates a dynamic automotive component landscape, facing intense rivalry and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding the leverage of suppliers and buyers is crucial for strategic planning.
The bargaining power of CIE India's suppliers can significantly impact its cost structure and profitability. Similarly, the power of its buyers, often large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), demands competitive pricing and product innovation.
The threat of new entrants, while present, is moderated by high capital requirements and established relationships within the industry. However, agile competitors can disrupt established market positions.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore CIE India’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for commodity raw materials like steel and aluminum is generally weak for automotive component companies such as Mahindra CIE. The global steel market, for instance, saw significant production volumes exceeding 1.8 billion metric tons in 2023, indicating a large number of manufacturers. This abundance provides Mahindra CIE with multiple sourcing options, reducing its dependence on any single supplier. The ability to easily switch between providers for these standardized inputs limits the pricing power of individual raw material suppliers, ensuring competitive procurement in 2024.
Suppliers of specialized and technologically advanced components, crucial for modern automotive applications, wield moderate bargaining power. This is particularly evident for inputs vital to emerging technologies like electric vehicles and advanced driver-assistance systems. For instance, the global ADAS market was projected to reach over $30 billion in 2024, highlighting the demand for these critical systems. The technical expertise required and the often-limited number of qualified suppliers for these intricate parts, such as specific semiconductor chips or battery chemistries, grant them significant leverage in negotiations with manufacturers like CIE India.
Global events and supply chain disruptions can temporarily boost supplier power for CIE India. For instance, geopolitical tensions, like those seen impacting global shipping routes in early 2024, create logistical bottlenecks and increase raw material costs, shifting bargaining power to suppliers ensuring reliable delivery. Companies are actively diversifying their supply chains away from single-country dependence, a trend evident in 2024 with a 40% increase in nearshoring investments, aiming to mitigate this supplier leverage long-term.
Long-Term Relationships and Partnerships
Mahindra CIE, like many major automotive component manufacturers, cultivates deep, long-term relationships with its core suppliers. This collaborative model, often involving joint development initiatives and multi-year contracts, fosters mutual dependence between the parties. While such partnerships can temper extreme supplier bargaining power by aligning interests, the significant costs and operational disruptions associated with switching established suppliers grant them considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, the automotive supply chain continues to prioritize stability and reliability, making supplier transitions particularly challenging due to complex qualification processes and production integration requirements.
- Long-term contracts reduce immediate supplier switching flexibility.
- Joint development initiatives increase mutual dependency.
- Supply chain stability prioritizes existing, qualified relationships.
- Switching costs, including re-tooling and qualification, are substantial.
Parent Company and Group Sourcing Influence
Being part of the global CIE Automotive group significantly enhances Mahindra CIE's sourcing power. The ability to pool procurement volumes across the group, which reported revenues of approximately €3.86 billion in 2023, greatly weakens individual suppliers' bargaining power. This scale allows Mahindra CIE to secure better pricing and more favorable terms than it could achieve alone, leveraging global relationships for key raw materials and components. The group's extensive supplier base, exceeding 6,000 global suppliers, further diversifies sourcing options and reduces dependency on any single vendor.
- CIE Automotive Group's 2023 revenue: Approximately €3.86 billion.
- Global supplier base: Over 6,000 suppliers.
- Sourcing volume leverage: Reduces per-unit costs for Mahindra CIE.
- Improved terms: Negotiates favorable payment and delivery conditions.
Mahindra CIE's supplier bargaining power is low for commodity materials, given global abundance like over 1.8 billion metric tons of steel produced in 2023. However, it is moderate for specialized components vital for technologies such as ADAS, a market projected to exceed $30 billion in 2024, due to fewer qualified suppliers. Global supply chain disruptions can temporarily increase supplier leverage. Nevertheless, being part of the CIE Automotive Group, with 2023 revenues of approximately €3.86 billion and over 6,000 global suppliers, significantly enhances Mahindra CIE's procurement power.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Materials | Low | Global steel production >1.8B tons (2023) |
| Specialized Components | Moderate | ADAS market >$30B projected (2024) |
| CIE Group Leverage | Reduced Supplier Power | CIE Auto 2023 revenue ≈€3.86B; >6,000 global suppliers |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for CIE India dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes, providing a strategic overview of the industry's profitability drivers.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of CIE India's market landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
The primary customers for Mahindra CIE are major Original Equipment Manufacturers in the automotive sector, who possess substantial bargaining power. These are large, concentrated buyers such as Tata Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra, and Maruti Suzuki, which collectively dominated a significant portion of India's passenger vehicle market share in 2024. Their immense purchase volumes allow them to exert considerable pressure on pricing and supply terms. This high customer concentration means that even a single OEM can significantly impact Mahindra CIE's revenues and profitability.
While establishing new supplier relationships involves qualification, the switching costs for OEMs are not prohibitively high for many auto components. India's auto component sector boasts numerous capable suppliers, with over 700 Tier 1 and 2 players in 2024, enabling OEMs to easily shift sourcing. This broad supplier base means OEMs frequently switch to optimize costs, quality, and delivery, directly impacting Mahindra CIE's pricing flexibility. For instance, major OEMs continuously evaluate their supply chains, fostering intense competition among component manufacturers. Such competitive pressure inherently limits Mahindra CIE's ability to dictate prices.
Automotive OEMs operate within an intensely competitive market, which consistently drives them to demand significant cost reductions from suppliers like Mahindra CIE. These manufacturers expect ongoing value engineering and process improvements, aiming to lower costs across a vehicle model's entire lifecycle. In 2024, this pressure intensified as OEMs navigated fluctuating demand and supply chain challenges, pushing for greater efficiency. This relentless pricing scrutiny is a defining characteristic of the global automotive component industry, directly impacting supplier margins.
Long-Term Contracts and Customer Diversification
Mahindra CIE strategically mitigates customer bargaining power by securing long-term contracts, which provide revenue stability. The company diversifies its customer base across various vehicle segments, including passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and tractors, both in India and Europe, reducing dependence on any single original equipment manufacturer (OEM). This broad customer portfolio, including major global OEMs, lessens concentration risk. As of 2024, Mahindra CIE continues to onboard new customers, further strengthening its market position and reducing reliance on a few key clients.
- Diversified customer base across passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and tractors.
- Geographical presence spans India and Europe, reducing regional market dependence.
- Focus on securing long-term contracts to ensure stable revenue streams.
- Active customer acquisition strategy continues to broaden its client portfolio.
Quality and Technology as a Differentiator
A supplier's ability to provide high-quality, technologically advanced components significantly reduces the bargaining power of customers. For critical and complex automotive parts, where reliability is paramount, original equipment manufacturers are less inclined to switch suppliers based solely on price. The robust technological expertise and support provided by the parent CIE Automotive group, which reported consolidated revenues of €3.87 billion in 2023, further amplifies this competitive advantage for CIE India. This ensures that customers prioritize proven quality over marginal cost savings, as seen with major OEM partnerships in India in 2024.
- CIE India leverages global parent's R&D, which invested €118 million in 2023.
- OEMs often sign multi-year contracts for critical components, limiting negotiation frequency.
- The automotive sector's increasing focus on advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicle (EV) components elevates demand for specialized, high-quality parts.
- Supplier switching costs for validated components can be substantial, including re-tooling and re-certification expenses.
Major automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers exert significant bargaining power due to their concentrated purchasing volumes and the availability of over 700 alternative auto component suppliers in India as of 2024. These large buyers, including key players dominating India's passenger vehicle market, continuously demand cost reductions, limiting Mahindra CIE's pricing flexibility. However, Mahindra CIE strategically mitigates this pressure by securing long-term contracts, diversifying its customer base across vehicle segments and geographies, and leveraging its parent company's robust R&D investments, which totaled €118 million in 2023, for technologically advanced components.
| Factor | 2024 Data / Impact | Mitigation by Mahindra CIE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM Concentration | Major OEMs dominate India's passenger vehicle market share. | Diversified customer base across India and Europe. | |
| Supplier Availability | Over 700 Tier 1 and 2 auto component suppliers in India. | Focus on high-quality, technologically advanced components. | |
| R&D Investment | CIE Automotive's R&D investment was €118 million in 2023. | Leverages parent's expertise for critical parts. |
Preview Before You Purchase
CIE India Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CIE India Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden surprises. Our meticulously crafted analysis details the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the Indian market. You're looking at the actual, professionally formatted document, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian automotive component industry is highly fragmented, leading to intense competitive rivalry. Mahindra CIE faces significant competition from numerous domestic and international players, all vying for business from the same OEM customers. Key domestic competitors include giants like Bharat Forge, which reported a 2024 market capitalization exceeding INR 60,000 crore, along with Ramkrishna Forgings and Endurance Technologies, further intensifying the landscape.
Price-based competition significantly impacts the Indian auto components sector. With numerous suppliers offering similar, often commoditized, components, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) possess considerable leverage. This intense rivalry allows OEMs to consistently push for lower prices, directly impacting supplier margins. For instance, the Automotive Component Manufacturers Association of India (ACMA) noted continued pressure on profitability in their 2024 outlook due to input cost volatility and pricing demands. This environment forces companies like CIE India to relentlessly focus on cost efficiency and operational excellence to maintain competitiveness.
Mahindra CIE faces intense competitive rivalry from both Indian companies and global auto component giants operating within India. These international players, such as Bosch and ZF, often leverage advanced technology and established global OEM relationships, intensifying market competition. Their significant financial resources allow for substantial R&D investments, further challenging domestic firms. The competitive landscape is also broadened by the presence of numerous organized and unorganized sector players, particularly in segments like castings, where Mahindra CIE has a strong footprint, contributing to pricing pressures and market fragmentation in 2024.
Competition in Export Markets
Competition in export markets is fierce, with Indian auto component manufacturers contending with rivals from other low-cost countries. Global trade dynamics, including recent tariff adjustments, significantly shift competitive advantages, prompting companies to seek new markets. The increasing adoption of a 'China Plus One' sourcing strategy by global OEMs offers both opportunities and heightened competitive pressures for Indian players. India's auto component exports were projected to reach approximately $22 billion by FY25, reflecting this competitive landscape.
- India's auto component exports are expected to grow by 12-15% in FY24.
- Global OEMs are actively diversifying supply chains away from single-country reliance.
- The push for 'China Plus One' has increased inquiries for Indian manufacturers in 2024.
- Indian firms compete intensely with low-cost producers from countries like Vietnam and Mexico.
Technological Advancement as a Competitive Edge
Competitive rivalry in the automotive components sector is increasingly driven by technological capabilities, particularly with the industry's significant shift towards electric vehicles and more sophisticated vehicle electronics. Companies investing heavily in research and development to offer advanced components for new energy vehicles and complex systems gain a crucial competitive advantage. Mahindra CIE Automotive’s connection with its global parent, CIE Automotive, provides essential access to cutting-edge technology and innovation, which is vital for staying competitive in this evolving landscape. This strategic advantage helps them address the rising demand for EV components, projected to grow substantially by 2024.
- The Indian EV component market is expected to reach USD 5 billion by 2024, highlighting the focus on technological readiness.
- Companies are increasing R&D spending, with some major players allocating over 3-5% of their revenue towards new product development in 2024.
- Mahindra CIE's global collaboration facilitates knowledge transfer in areas like lightweighting and advanced material technologies.
- The ability to supply integrated electronic modules is a key differentiator, influencing procurement decisions from OEMs in 2024.
Competitive rivalry is intense due to market fragmentation and price pressure, with OEMs leveraging numerous suppliers. Key players like Bharat Forge, with a 2024 market cap exceeding INR 60,000 crore, and global firms like Bosch, intensify competition. The shift to EVs drives R&D, with the Indian EV component market projected to reach USD 5 billion by 2024. Export markets are also competitive, fueled by a 'China Plus One' strategy.
| Metric | 2024 Data | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bharat Forge Mkt Cap | >INR 60,000 Cr | Intense Competition |
| Indian EV Comp. Mkt | ~$5 Billion | Tech-driven Rivalry |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Mahindra CIE, a key supplier of forgings, castings, and stampings, faces a low threat from direct product substitutes in the short to medium term. These components are fundamental to vehicle architecture and function, essential for structural integrity and performance. While the automotive industry, as seen in 2024 trends, is exploring lighter materials like aluminum and advanced composites, these largely represent material shifts rather than outright elimination of the need for such foundational components. For instance, even with the push towards electric vehicles, the underlying chassis and powertrain still require robust, precisely engineered metal parts. The capital intensity and specialized manufacturing processes for these components also create high barriers for new, truly disruptive direct product substitutes.
The rise of Electric Vehicles (EVs) poses the most significant substitution threat to CIE India. This industry-wide shift makes many components for internal combustion engines (ICE) obsolete, including forgings and castings for engines and transmissions. India's EV market saw sales reach 1.7 million units in FY2024, a 37.1% increase from the prior fiscal year. To survive this long-term threat, auto component manufacturers must pivot product portfolios towards EV-specific components, like parts for electric motors and battery systems.
Advancements in manufacturing processes present a potential substitute threat to CIE India's traditional forging and casting methods. New technologies like 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, are evolving rapidly, capable of producing complex components. While still niche for high-volume automotive parts, the global additive manufacturing market, estimated at over $30 billion in 2024, indicates its growing capacity. This trend could eventually substitute certain low-volume or intricate parts currently made through conventional processes, impacting demand for traditional manufacturing services.
Changes in Vehicle Usage and Ownership Models
The evolving landscape of mobility, marked by the rise of ride-sharing services like Ola and Uber, alongside significant improvements in public transportation infrastructure, poses a long-term threat to personal vehicle ownership in India. This shift could lead to a reduction in the overall demand for new vehicles, directly impacting the automotive component industry. For instance, India's ride-sharing market is projected to continue its strong growth trajectory through 2024, influencing consumer choices. This represents a macro-level substitution threat to the volume of demand for all automotive parts.
- India's public transport ridership is expanding, with metro networks growing in major cities.
- Ride-sharing gross bookings in India are forecast to exceed $5 billion in 2024.
- A decline in new vehicle sales directly reduces demand for components.
- This macro trend challenges the traditional automotive supply chain.
Component Integration and System-Level Solutions
The automotive industry is seeing a significant shift towards component integration, where multiple functions are combined into more complex modules. This trend poses a direct threat to companies like Mahindra CIE, as these integrated units can substitute the need for several individual components they traditionally produce. For instance, integrated powertrain modules or advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) units reduce demand for separate parts, directly impacting component suppliers. Suppliers are increasingly expected to deliver system-level solutions rather than just discrete parts, requiring significant R&D investment and a shift in production capabilities.
- The global automotive module market is projected to reach over $300 billion by 2024, highlighting the shift towards integrated solutions.
- Mahindra CIE's 2024 focus on lightweighting and new material technologies aims to counter this by offering value-added integrated solutions.
- Automakers are consolidating their supplier base, favoring those who can provide complete systems, reducing opportunities for single-component suppliers.
- Companies not adapting to this system-level solution demand risk obsolescence in the evolving automotive supply chain.
Mahindra CIE faces substitution threats from electric vehicles making ICE components obsolete, highlighted by India's 1.7 million EV sales in FY2024. Advanced manufacturing like 3D printing, a $30 billion market in 2024, could replace traditional parts. Moreover, the shift to integrated modules, a market exceeding $300 billion by 2024, reduces demand for individual components.
| Threat Type | 2024 Market Data | Impact on CIE India |
|---|---|---|
| EV Adoption | 1.7M EV sales in FY2024 (India) | Obsolescence of ICE components |
| Additive Manufacturing | >$30B global market | Substitution of traditional parts |
| Component Integration | >$300B global automotive modules | Reduced demand for discrete parts |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in India's automotive component manufacturing sector, including for precision parts like forgings and castings, remains moderate to low. This is primarily due to the high capital investment requirements for establishing advanced production facilities. Setting up state-of-the-art machinery and implementing stringent quality control systems demands substantial financial resources, often exceeding INR 150-200 crore for a new forging plant in 2024. Such significant upfront costs act as a formidable barrier, deterring potential new market participants from entering this specialized industry.
New entrants into the automotive components sector face a significant barrier in establishing credibility and relationships with major Original Equipment Manufacturers. OEMs, particularly in 2024, demand stringent quality standards and often require extensive, multi-year qualification processes for new suppliers, making market entry challenging. Incumbent players like Mahindra CIE, with its deep roots in the Indian automotive supply chain, benefit from decades-long alliances with key automakers. This entrenched trust and proven track record are exceedingly difficult for any new company to replicate quickly or efficiently.
Large, established players like Mahindra CIE benefit significantly from economies of scale in procurement and production, allowing them to offer competitive pricing. With consolidated revenue from operations at Rs 2,900.5 crore in Q1 2024, their sheer volume enables substantial cost efficiencies. A new entrant would likely operate at a smaller scale initially, facing a considerable cost disadvantage in acquiring raw materials and optimizing manufacturing. The global sourcing power of the broader CIE Automotive group further amplifies Mahindra CIE's ability to secure favorable terms, making market entry challenging. This scale barrier effectively deters potential competitors from easily penetrating the automotive components sector.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies, such as India's Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme with an outlay of over INR 1.97 lakh crore, are designed to boost domestic manufacturing and attract significant investment. While these policies aim to encourage new players, they often benefit established companies that possess the scale and capability to meet the stringent investment and production targets required to receive incentives. This dynamic effectively raises the entry barrier for new, smaller entrants, making it challenging for them to compete effectively in 2024. The PLI scheme for the auto sector, for instance, has an allocation of INR 25,938 crore, primarily attracting large-scale players.
- PLI scheme outlay: Over INR 1.97 lakh crore across 14 sectors.
- Auto sector PLI allocation: INR 25,938 crore.
- Benefit: Primarily to established companies meeting high investment thresholds.
- Impact: Raises capital and production barriers for new entrants.
Technological Expertise and Access to R&D
The increasing technological complexity of automotive components, particularly with the advent of electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced electronics, significantly raises the barrier to entry for new players. Potential new entrants face the formidable challenge of acquiring or developing extensive technological expertise and investing heavily in research and development. Mahindra CIE's strategic advantage lies in its access to the global R&D capabilities and cutting-edge technology of its parent company, CIE Automotive, which reported a consolidated net sales of EUR 4,008 million in 2023. This deep integration and shared knowledge base make it exceptionally difficult for new competitors to match their innovation pace and product sophistication in the Indian market.
- CIE Automotive's 2023 consolidated net sales: EUR 4,008 million.
- Mahindra CIE's R&D expenditure for the year ended December 31, 2023, was INR 153.11 Crores.
- The company has a strong focus on advanced materials and processes, critical for EV components.
- Access to global patents and proprietary manufacturing techniques from CIE Automotive.
The threat of new entrants in India's automotive component sector, including for Mahindra CIE, remains low due to high capital requirements for advanced facilities, often exceeding INR 150-200 crore for a new forging plant in 2024. Establishing credibility with OEMs and overcoming deep-rooted relationships and qualification processes, which can take years, also presents a formidable barrier. Furthermore, incumbent players benefit from significant economies of scale and access to global R&D, making competitive entry challenging.
| Barrier | Description | 2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High cost for modern facilities | INR 150-200 Cr for new forging plant |
| Credibility/OEM Trust | Long qualification processes | Decades-long incumbent alliances |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantage for large players | Mahindra CIE Q1 2024 revenue: Rs 2,900.5 Cr |
| Technological Complexity | R&D and advanced materials | CIE Automotive 2023 sales: EUR 4,008 Mn |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CIE India Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from official government statistics, reputable industry associations, and financial reports from key players in the Indian market.
We leverage a combination of market research reports, trade publications, and company disclosures to thoroughly assess the competitive landscape, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes in India.
