China Mobile Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Mobile Bundle
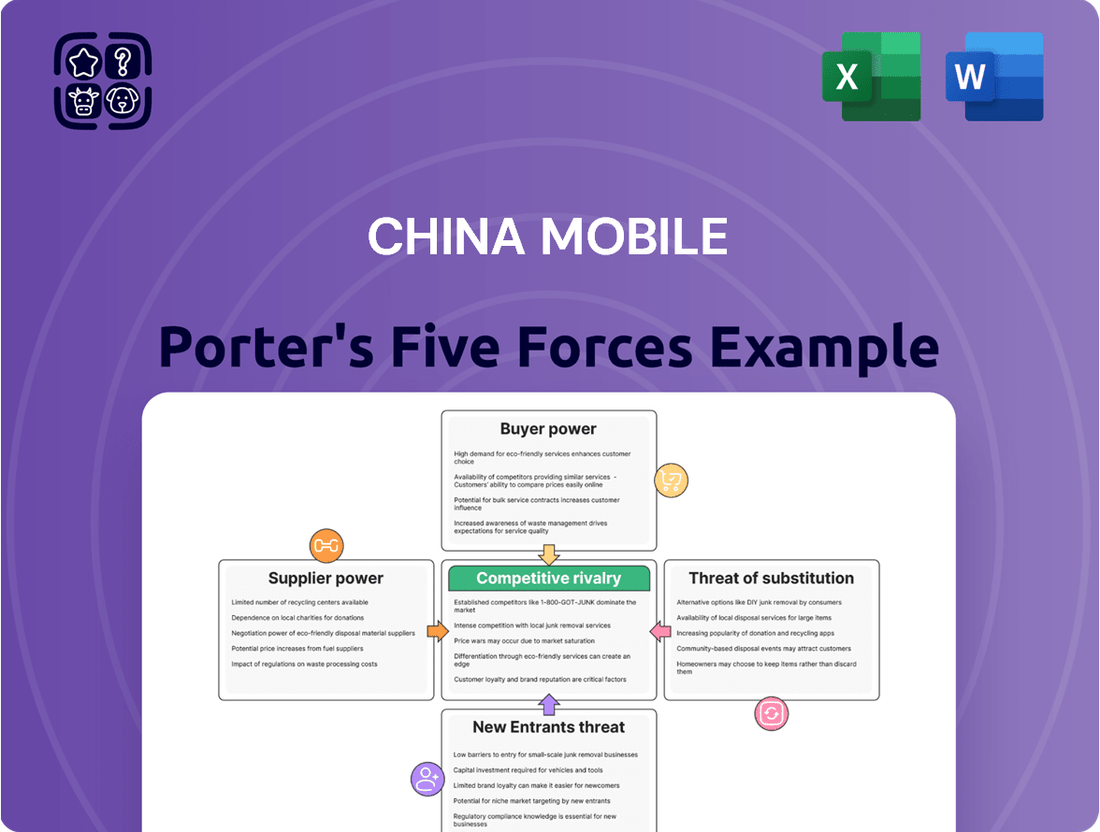
China Mobile navigates intense rivalry from domestic and international competitors, a key factor in its market position. The threat of new entrants, while moderated by high capital requirements, remains a persistent consideration.
Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers is crucial for China Mobile's profitability. The availability of substitutes, particularly in emerging technologies, also shapes its strategic landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore China Mobile’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The telecommunications sector, including giants like China Mobile, depends on a select group of global equipment manufacturers for essential network infrastructure. Companies such as Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia dominate the supply of critical components like 5G base stations and core network systems.
This limited supplier base grants these vendors considerable bargaining power. China Mobile faces substantial switching costs and integration complexities when considering alternative suppliers for its network infrastructure, effectively locking it into existing relationships.
The highly specialized and proprietary nature of telecommunications technology further restricts China Mobile's choices, amplifying the supplier's leverage. For instance, in 2023, Huawei continued to be a leading global supplier of 5G network equipment, underscoring its significant market presence.
China Mobile's reliance on advanced networking equipment, specialized software, and critical chipsets underscores the significant bargaining power of its suppliers. These inputs are not merely components; they are the bedrock upon which China Mobile builds and maintains its expansive network infrastructure, directly influencing service quality and customer experience.
In 2023, China Mobile invested heavily in 5G network expansion, with capital expenditures reaching approximately RMB 184.5 billion. This substantial investment highlights the critical need for high-quality, reliable components from suppliers, giving those suppliers considerable leverage in negotiations.
The quality and reliability of these essential inputs directly translate into China Mobile's operational capabilities and its ability to meet subscriber demands. Consequently, suppliers of these critical technologies hold a strong position, as any disruption or compromise in supply can have a material impact on China Mobile's service performance and market standing.
Switching core network equipment suppliers for China Mobile presents significant hurdles. The financial outlay for new hardware, coupled with rigorous testing and the potential for service interruptions, creates very high switching costs. This inherent difficulty in changing vendors reinforces the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
China Mobile's reliance on legacy infrastructure and proprietary technologies further entrenches its ties to current equipment providers. Transitioning to new systems is not only complex but also financially burdensome, limiting the company's flexibility and strengthening the leverage of its current partners.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While less common in the telecom equipment sector, the theoretical threat of key technology suppliers integrating forward into direct service provision could enhance their bargaining power. However, the immense scale and regulatory landscape of China's telecommunications market make direct competition from equipment vendors improbable. Despite this, suppliers' influence over technological roadmaps and their ability to dictate advancements can indirectly shape China Mobile's strategic decisions and operational capabilities.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a critical supplier to telecom infrastructure, continued to experience supply chain complexities. Companies like TSMC, a major chip manufacturer, hold significant leverage due to their advanced manufacturing capabilities. Any shift in their pricing or production priorities could directly impact the cost and availability of essential components for China Mobile's network expansion and upgrades.
- Supplier Integration Risk: The potential for telecom equipment suppliers to move into direct service provision, though unlikely in China's regulated market, represents a theoretical increase in their power.
- Technological Leverage: Suppliers' control over the development and rollout of new technologies, such as 5G-Advanced and future 6G standards, grants them indirect influence over China Mobile's strategic planning and investment cycles.
- Market Realities: The sheer scale and governmental oversight of China's telecom sector act as significant deterrents to equipment vendors attempting direct service competition, limiting this threat to indirect influence through technology.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
Suppliers offering highly specialized and often proprietary technologies, particularly in advanced areas like 5G and future network architectures, hold significant sway. For instance, in 2024, the development and deployment of next-generation network equipment often rely on unique intellectual property from a limited number of global vendors, making direct substitution difficult.
The uniqueness of certain components or software solutions means China Mobile cannot easily find alternative sources for specific critical functionalities. This technological differentiation grants considerable bargaining power to suppliers who hold patents or unique expertise in these vital areas, impacting cost and availability.
- Specialized 5G Components: Suppliers of advanced chipsets and radio frequency modules for 5G infrastructure often possess unique manufacturing processes or patented designs.
- Proprietary Software: Network management and orchestration software developed by specific vendors can be critical for China Mobile's operations, limiting switching options.
- Limited Alternative Sources: The high barrier to entry for developing and manufacturing cutting-edge telecommunications hardware means few companies can offer comparable products.
China Mobile's suppliers of critical network infrastructure, such as Huawei and Ericsson, possess substantial bargaining power due to the specialized nature of their products and the high switching costs involved. For example, in 2024, the ongoing demand for advanced 5G equipment, coupled with supply chain constraints in the semiconductor industry, further amplified supplier leverage. This dependence on a limited number of technologically advanced vendors means China Mobile has less flexibility in negotiating prices or terms.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on China Mobile | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology | Limits alternative sourcing options | Continued reliance on proprietary 5G components |
| High Switching Costs | Entrenches existing relationships | Complex integration of new network hardware |
| Limited Supplier Base | Increases supplier negotiation leverage | Dominance of key vendors like Huawei in 5G |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to China Mobile's dominant position in the Chinese telecommunications market.
Instantly visualize China Mobile's competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, making complex market dynamics easily digestible for strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
China Mobile faces significant customer price sensitivity due to the presence of strong competitors like China Telecom and China Unicom. This intense competition means customers can easily switch providers based on price, forcing China Mobile to maintain competitive pricing strategies. For instance, as of late 2023 and early 2024, the telecommunications market saw ongoing promotional activities and bundled offers from all major players, highlighting the pressure on pricing.
Customers of China Mobile face significant bargaining power due to the readily available substitutes. China Telecom and China Unicom offer comparable mobile, broadband, and enterprise services, presenting direct alternatives that dilute China Mobile's market dominance.
The proliferation of Over-The-Top (OTT) applications like WeChat and QQ further amplifies customer choice. These platforms provide alternative communication channels, diminishing customer dependence on traditional voice and SMS services, which are core revenue streams for mobile operators.
In 2023, China's telecom market saw intense competition, with China Mobile serving approximately 985 million mobile users, while China Unicom and China Telecom also commanded substantial user bases, each exceeding 300 million. This competitive landscape allows customers to easily switch providers or reduce their reliance on specific services if pricing or quality expectations are not met.
For most individual users of mobile services in China, switching between providers like China Mobile is quite straightforward. The ability to keep their phone number, a feature widely available, removes a significant barrier. Furthermore, contract termination fees are generally not prohibitive, especially for prepaid plans. This ease of movement means customers can readily explore better pricing or service offerings from competitors.
This low friction in switching directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers. In 2023, China's mobile market saw intense competition, with operators vying for subscribers through various promotions and service bundles. For instance, the average revenue per user (ARPU) for Chinese mobile operators remained a key metric, and the ability for customers to switch easily puts pressure on providers to maintain competitive pricing and service quality to retain their customer base.
Customer Concentration
China Mobile serves a vast and highly fragmented customer base, encompassing hundreds of millions of individual consumers and a wide array of enterprise clients throughout mainland China. This broad distribution means that no single customer, or even a small group of customers, possesses significant leverage to dictate terms or pricing to the company.
The lack of significant customer concentration directly diminishes the collective bargaining power of China Mobile's customer base. This fragmentation generally translates into less power for customers to demand lower prices or higher quality services.
- Customer Fragmentation: China Mobile's customer base is characterized by its sheer size and diversity, with over 980 million mobile subscribers reported as of the end of 2023.
- Limited Individual Leverage: Due to the immense number of users, individual customer influence on pricing or service offerings is negligible.
- Reduced Collective Power: While large enterprise clients exist, their numbers relative to the total subscriber base do not create a concentrated bloc capable of exerting significant collective bargaining power.
- Market Dominance Impact: China Mobile's leading market position, with a subscriber market share often exceeding 35% in 2023, further dilutes individual customer power.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers in China are increasingly well-informed about mobile service plans, pricing, and network quality. This surge in transparency, fueled by online forums, comparison sites, and competitor ads, significantly boosts their bargaining power. Armed with this knowledge, consumers can readily compare offerings and push for better deals, particularly as core mobile services become increasingly standardized.
This heightened transparency directly impacts China Mobile by intensifying price competition. For instance, by mid-2024, reports indicated that the average revenue per user (ARPU) for Chinese mobile operators remained under pressure, reflecting this customer demand for value. Customers can easily identify and switch to providers offering superior price-to-performance ratios, forcing China Mobile to remain competitive on pricing to retain its subscriber base.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers leverage readily available data to compare service features, network coverage maps, and pricing structures across different providers.
- Negotiating Leverage: Increased transparency allows customers to negotiate more effectively for lower monthly bills, bundled services, or upgraded plans.
- Commoditization Effect: As basic mobile services become more similar across providers, customers focus more on price and perceived value, amplifying their bargaining power.
- Switching Behavior: Easy access to information facilitates customer switching, compelling operators like China Mobile to offer attractive retention incentives and competitive new customer deals.
China Mobile's customers possess considerable bargaining power, primarily driven by the availability of close substitutes from competitors like China Telecom and China Unicom. The ease with which customers can switch providers, often retaining their phone numbers and facing minimal switching costs, further amplifies this power. This dynamic forces China Mobile to engage in competitive pricing and service enhancements to retain its vast subscriber base.
| Factor | Description | Impact on China Mobile |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | China Telecom and China Unicom offer comparable mobile, broadband, and enterprise services. | Forces competitive pricing and service differentiation. |
| Switching Costs | Low, with number portability and manageable contract termination fees. | Increases customer mobility and pressure on China Mobile to retain users. |
| Customer Information | High transparency due to online comparison tools and competitor advertising. | Empowers customers to seek better deals and value. |
| Customer Concentration | Vast and fragmented customer base with no single dominant customer. | Limits individual customer leverage, but collective power is still significant due to market dynamics. |
Same Document Delivered
China Mobile Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details China Mobile's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, and the threat of substitute products or services. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning of China Mobile within the telecommunications industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape in China's telecommunications sector is an oligopoly, characterized by three dominant state-owned enterprises: China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom. China Mobile stands as the largest operator, boasting a substantial subscriber base. However, China Telecom and China Unicom are significant rivals, each holding considerable market share and possessing extensive, well-developed network infrastructure across the nation.
China's mobile subscriber penetration rate is already quite high, suggesting a mature market with slowing growth. This means companies like China Mobile are looking for new ways to expand, rather than just adding more customers.
The real growth opportunities now lie in encouraging existing users to upgrade to more advanced services, such as 5G plans, business-focused solutions, and the Internet of Things (IoT). For instance, by the end of 2023, China Mobile reported over 330 million 5G users, showcasing a significant shift towards higher-value services.
This slower overall growth rate naturally makes the competition fiercer. With fewer new customers to attract, companies must work harder to win over market share and increase the revenue they get from each user in this crowded landscape.
While China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom offer similar core services, differentiation hinges on network quality and coverage, particularly 5G. China Mobile's vast network scale and extensive coverage remain a significant advantage, though competitors are closing the gap. For instance, in 2023, China Mobile reported over 3.3 million 5G base stations, a substantial lead but one that Unicom and Telecom are actively expanding.
Customer service and innovative bundled offerings also play a crucial role in distinguishing the operators. However, the true challenge lies in moving beyond basic connectivity to offer genuinely innovative services. This is where the competitive rivalry intensifies, as operators seek to capture market share through value-added services and unique customer experiences.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The telecommunications sector, including players like China Mobile, faces intense competition driven by substantial fixed costs. Building and maintaining vast network infrastructure, from cell towers to fiber optics, requires billions of dollars. For instance, the ongoing 5G network build-out is a significant capital expenditure. This necessitates continuous investment to remain competitive, creating a high barrier to entry and exit.
These immense upfront and ongoing investments act as significant exit barriers. Companies are essentially locked into the market, compelled to operate and compete aggressively to recover their substantial capital outlays, even when profit margins are thin. This dynamic forces operators to fight harder for market share, intensifying the rivalry among existing players.
- Massive Infrastructure Investment: Telecom operators invest heavily in network infrastructure, such as 5G deployment, which involves substantial capital.
- High Exit Barriers: The sunk costs in infrastructure make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market, forcing them to compete even in challenging economic conditions.
- Intensified Rivalry: The inability to easily exit the market leads to sustained, fierce competition among the remaining players as they strive to achieve a return on their investments.
- Compulsory Competition: Operators are compelled to stay and compete to recoup their investments, leading to aggressive pricing and service strategies.
Strategic Stakes and Government Influence
The competitive landscape for China Mobile is deeply intertwined with government objectives, as all major telecom operators are state-owned. This means strategic stakes extend beyond simple profit motives to encompass national infrastructure development and achieving technological supremacy. For instance, the government's push for 5G deployment saw significant investment across all carriers, with China Mobile investing ¥185.5 billion in 5G in 2023, underscoring this national priority.
Government policies and directives play a pivotal role in shaping competitive dynamics. These can include mandates for infrastructure sharing, which can reduce individual company investment burdens but also alter competitive intensity, and directives on pricing strategies to ensure affordability. In 2024, ongoing discussions around spectrum allocation and network build-out continue to be influenced by these national strategic aims, impacting how operators like China Mobile compete.
- State Ownership: All major Chinese telecom operators are state-owned, aligning their strategies with national goals.
- Infrastructure Investment: China Mobile's substantial 5G investment in 2023 (¥185.5 billion) highlights the focus on national technological leadership.
- Government Directives: Policies on infrastructure sharing and pricing significantly influence market competition.
- National Strategic Objectives: Competition is often driven by broader national aims rather than solely market forces.
The competitive rivalry among China's major telecom operators, including China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom, is intense. This is largely due to the mature market with high subscriber penetration, forcing companies to focus on gaining market share from each other and increasing revenue per user through services like 5G and IoT. China Mobile's significant 5G user base, exceeding 330 million by the end of 2023, demonstrates this shift towards higher-value offerings.
The substantial fixed costs associated with building and maintaining vast network infrastructure, such as 5G deployment, create high barriers to entry and exit. China Mobile's investment of ¥185.5 billion in 5G in 2023 exemplifies this, locking operators into continuous competition to recoup these massive capital outlays. This financial commitment compels aggressive strategies to secure market share and revenue.
| Operator | Subscribers (End of 2023, Millions) | 5G Subscribers (End of 2023, Millions) | 5G Base Stations (End of 2023, Millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Mobile | 999.7 | 330.7 | 3.3 |
| China Telecom | 409.5 | 249.7 | 1.5 |
| China Unicom | 327.7 | 218.7 | 1.4 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Over-the-top (OTT) communication services represent a significant threat of substitutes for China Mobile. Applications such as WeChat and QQ offer free messaging and voice calls over data networks, directly competing with China Mobile's traditional SMS and voice revenue streams. In 2024, a substantial portion of China's mobile data traffic is generated by these OTT platforms, indicating their widespread adoption and the corresponding decline in usage of legacy services.
The widespread availability of Wi-Fi and fixed broadband internet presents a significant threat of substitutes for China Mobile's core services. In 2024, the penetration of fixed broadband in China continued to grow, with over 600 million household broadband connections reported. This ubiquity means users can easily access the internet without consuming their mobile data allowances, particularly for data-intensive tasks like streaming video or downloading large files.
This substitution effect directly impacts China Mobile's revenue streams, as users opt for Wi-Fi offloading rather than relying on their mobile data plans. For instance, in urban areas where Wi-Fi is readily available in homes, offices, and public hotspots, the demand for mobile data can be significantly reduced. This competitive pressure from alternative connectivity solutions necessitates that China Mobile continuously innovate its data offerings and pricing strategies to retain subscribers.
The rise of smart devices like smartwatches and tablets, often utilizing Wi-Fi or LPWAN, presents a subtle but growing threat. These devices can fulfill some communication needs without a primary reliance on traditional mobile subscriptions, thereby chipping away at China Mobile's exclusive hold on connectivity for certain user segments.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and International Calling Apps
The threat of substitutes for China Mobile's international voice services is significant, primarily from virtual private networks (VPNs) and international calling applications. These internet-based services often provide cheaper, or even free, international call options by bypassing traditional carrier infrastructure. For instance, services like Skype, WhatsApp Calling, and dedicated VPNs with calling features allow users to connect globally at a fraction of the cost of traditional IDD, directly impacting China Mobile's revenue streams in this segment.
These substitutes are particularly attractive for consumers and businesses seeking cost-effective international communication solutions. The ease of use and accessibility of these apps, often available on smartphones, further amplifies their competitive pressure. While China Mobile's IDD services remain a reliable option, the growing preference for digital communication channels presents a clear substitution threat, especially for high-volume international callers.
- VPNs and Calling Apps: Offer cheaper or free international calls via internet protocols.
- Impact on Revenue: Directly substitute China Mobile's traditional international voice revenue.
- Target Segment: Affects a potentially high-margin service niche for carriers.
On-Demand Content and Streaming Services
The rise of on-demand content and streaming services presents a significant threat of substitutes for China Mobile. While these services drive data consumption, they also offer an alternative to traditional bundled content packages. For instance, by mid-2024, China Mobile's extensive user base, exceeding 900 million mobile subscribers, increasingly accesses entertainment through platforms like Tencent Video and iQiyi, which provide vast libraries of movies, TV shows, and live events.
This shift means users might perceive less value in content offerings directly from China Mobile if they can access a wider variety of entertainment elsewhere. The convenience and personalization of streaming platforms can directly siphon demand away from operator-provided content. This dynamic potentially redirects revenue streams towards content creators and platforms, diminishing the network operator's ability to capture value from content delivery.
- Growth of Streaming Platforms: Services like Tencent Video and iQiyi saw substantial user growth in 2023, with millions of daily active users, indicating a strong preference for on-demand content.
- Data Consumption vs. Content Value: While streaming boosts data usage, a key metric for China Mobile, it doesn't necessarily translate to increased value capture for the operator's own content services.
- User Preference Shift: Surveys in late 2023 showed a significant portion of Chinese consumers prefer subscription-based streaming for entertainment over bundled telecom content.
- Revenue Diversion: The increasing spend on third-party streaming subscriptions by consumers represents revenue that could otherwise be captured by China Mobile through its own content bundles.
The threat of substitutes for China Mobile is substantial, primarily from Over-the-Top (OTT) communication services and the widespread availability of Wi-Fi. Applications like WeChat and QQ offer free messaging and voice calls, directly impacting China Mobile's traditional SMS and voice revenue. By mid-2024, over 900 million mobile subscribers were increasingly using these platforms for communication and entertainment.
The ubiquity of Wi-Fi, with over 600 million household broadband connections in China by 2024, allows users to bypass mobile data, especially for data-intensive activities. This offloading reduces demand for China Mobile's data plans. Furthermore, internet-based international calling apps and VPNs provide cheaper alternatives to traditional IDD services, impacting a potentially high-margin segment for the company.
The growth of streaming services also presents a substitution threat, as users opt for third-party content over operator bundles. While these services drive data consumption, they divert revenue from China Mobile's own content offerings. In 2023, platforms like Tencent Video saw millions of daily active users, indicating a strong preference for on-demand content over bundled telecom packages.
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a nationwide telecommunications network, particularly for advanced services like 5G, demands immense capital. China Mobile, for instance, has invested billions in its infrastructure. In 2023 alone, China Mobile's capital expenditure was approximately RMB 180 billion (around $25 billion USD), primarily for 5G network construction and upgrades. This staggering financial commitment creates a formidable barrier for any new entrant aiming to replicate such a comprehensive network from the ground up, effectively deterring competition.
The telecommunications sector in China operates under stringent government oversight, particularly concerning spectrum allocation and operating licenses. This heavy regulation significantly restricts new entrants by making the process of obtaining the necessary permits to run a nationwide mobile network incredibly complex and often politically influenced, thereby limiting the number of authorized participants.
China Mobile's immense subscriber base, exceeding 980 million by the end of 2023, creates significant economies of scale. This vast network allows for lower per-unit costs in operations and service delivery, a hurdle for any new entrant aiming to compete on price.
New competitors would face substantial capital investment to build a network infrastructure comparable to China Mobile's, making it difficult to achieve similar cost efficiencies. This inherent cost disadvantage acts as a strong deterrent, limiting the threat of new entrants substantially.
Established Brand Loyalty and Network Effects
China Mobile benefits from decades of established brand loyalty in China, a critical barrier for any new competitor. This loyalty is reinforced by powerful network effects; the more people use China Mobile's services, the more valuable those services become to every user, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain traction. By the end of 2023, China Mobile boasted over 1.1 billion mobile subscribers, illustrating the sheer scale of its entrenched user base.
The challenge for new entrants isn't just about offering competitive pricing or technology; it's about overcoming the ingrained trust and recognition that China Mobile has cultivated over many years. This deep customer loyalty translates into a significant hurdle for new players aiming to capture even a small percentage of the market share. For instance, in 2023, China Mobile maintained a dominant market share, underscoring the difficulty of dislodging established players.
- Established Brand Loyalty: China Mobile's long history has fostered deep customer trust and recognition.
- Network Effects: The value of China Mobile's network increases with its vast user base, discouraging switching.
- Subscriber Dominance: With over 1.1 billion mobile subscribers by the end of 2023, China Mobile possesses a significant advantage.
- Market Inertia: High customer loyalty creates inertia, making it challenging for new entrants to attract and retain users.
Access to Distribution Channels and Infrastructure
China Mobile's formidable presence in distribution channels and infrastructure presents a significant barrier to new entrants. The company boasts an extensive network of retail stores, direct sales channels, and a vast physical infrastructure, including cell towers and fiber optic cables, strategically placed across China.
Replicating this nationwide reach and the associated capital expenditure would be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming for any newcomer. For instance, as of the end of 2023, China Mobile operated over 2.5 million base stations, a figure that underscores the sheer scale of investment required to compete.
- Extensive Retail Footprint: China Mobile maintains thousands of physical retail outlets nationwide, offering direct customer interaction and sales.
- Dominant Infrastructure: The company controls a vast network of cell towers and fiber optic infrastructure, essential for service delivery.
- High Capital Requirements: New entrants would need billions of dollars to build comparable distribution and network infrastructure.
- Established Brand Recognition: Decades of operation have built significant brand loyalty and market awareness, further complicating entry for new players.
The threat of new entrants in China's mobile market is significantly low, primarily due to the colossal capital investment required to build a comparable network infrastructure. China Mobile's 2023 capital expenditure alone was around $25 billion USD, highlighting the immense financial barrier. Furthermore, stringent government regulations and licensing processes create substantial hurdles for any new player seeking to enter the market, effectively limiting competition.
| Factor | China Mobile's Position | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Billions invested in 5G infrastructure (e.g., RMB 180 billion in 2023) | Extremely high barrier; prohibitive cost to replicate nationwide network. |
| Government Regulation | Strict licensing and spectrum allocation | Complex and politically influenced entry process, limiting authorized participants. |
| Economies of Scale | Over 980 million subscribers (end of 2023) | New entrants face higher per-unit costs, making price competition difficult. |
| Brand Loyalty & Network Effects | Over 1.1 billion subscribers (end of 2023), established trust | Significant customer inertia; difficult for newcomers to attract users. |
| Distribution & Infrastructure | 2.5 million+ base stations (end of 2023), extensive retail network | Prohibitively expensive and time-consuming to match nationwide reach. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our China Mobile Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including China Mobile's official annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IDC and Counterpoint, and government regulatory filings from MIIT.
