CES Energy Solutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CES Energy Solutions Bundle
CES Energy Solutions operates within an industry shaped by significant buyer power and the constant threat of substitutes, impacting pricing and product differentiation. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CES Energy Solutions’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CES Energy Solutions depends on a variety of raw chemicals for its blending processes. When these specialized chemicals come from only a handful of producers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This can translate into increased costs for CES, especially if finding other sources is difficult or expensive.
The bargaining power of these concentrated raw material suppliers is further strengthened if CES faces substantial costs or quality issues when trying to switch to different chemical providers. For instance, in 2023, the global chemical industry experienced price volatility due to supply chain disruptions, impacting companies like CES that rely on consistent access to key inputs.
CES Energy Solutions might face significant supplier power from providers of highly specialized equipment used in chemical blending, delivery, and application. This power is amplified when the technology is proprietary or requires substantial capital investment from the supplier, thereby limiting the availability of alternative vendors for CES.
The reliance on specific intellectual property or patented processes from external suppliers can further enhance their bargaining leverage. For instance, if a key component for CES's advanced chemical injection systems is only available from a single patented source, that supplier can dictate terms more effectively. This situation can lead to higher input costs for CES, impacting its overall profitability and competitive positioning.
CES Energy Solutions' reliance on timely chemical delivery to demanding oil and gas locations means logistics and transportation are critical. Suppliers of specialized transport, particularly for hazardous goods, can leverage their position by controlling prices, especially where specialized carriers are scarce or infrastructure is challenging. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of trucking a ton of freight in North America saw an increase, impacting CES's operational expenses and supplier leverage.
Skilled Labor and Talent Pool
The availability of highly skilled chemists, engineers, and field service personnel is crucial for CES Energy Solutions, particularly given its emphasis on technically advanced chemical solutions. A constrained supply of specialized talent, especially when demand in the oil and gas sector surges, can significantly amplify the bargaining power of employees and recruitment agencies. This heightened power can lead to increased labor costs and potentially affect CES's operational efficiency and profitability.
In 2024, the demand for specialized oilfield services personnel remained robust, contributing to wage pressures. For instance, the average salary for petroleum engineers in the US saw an upward trend, reflecting the competitive landscape for talent. This scarcity directly impacts companies like CES, as securing and retaining top-tier technical expertise becomes a key factor in maintaining their competitive edge and delivering advanced solutions.
- Talent Scarcity: Limited availability of specialized chemists and engineers in the energy sector.
- Demand Impact: High demand in oil and gas increases the bargaining power of skilled workers.
- Cost Pressures: Rising labor costs can affect CES's operational expenses and profitability.
- Recruitment Challenges: Reliance on recruitment agencies may further inflate talent acquisition costs.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance Inputs
Suppliers providing essential services for regulatory and environmental compliance can wield considerable bargaining power over CES Energy Solutions. Their specialized knowledge in areas like emissions monitoring, waste disposal, and safety protocols is crucial for maintaining operational legality.
Failure to meet these stringent requirements, often dictated by bodies like Environment and Climate Change Canada, can result in hefty fines or even temporary suspensions of operations, making these suppliers' services a necessity rather than a discretionary expense for CES. For instance, in 2023, Canadian businesses faced an estimated $2.7 billion in regulatory compliance costs, highlighting the significant financial impact of adhering to governmental mandates.
- Critical Expertise: Suppliers offer indispensable knowledge of complex environmental and safety regulations.
- Non-Compliance Penalties: CES faces substantial financial and operational risks if compliance standards are not met.
- Inelastic Demand: The necessity of these services means CES has limited ability to negotiate lower prices without risking compliance.
- Industry Standards: Adherence to evolving environmental standards, such as those related to greenhouse gas emissions, necessitates specialized supplier involvement.
CES Energy Solutions faces significant supplier power from providers of highly specialized equipment and proprietary chemical formulations. This leverage is amplified when there are few alternative vendors or when switching suppliers involves substantial costs or risks, impacting CES's operational flexibility and input prices.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also evident in the market for specialized talent, such as chemists and engineers. In 2024, the demand for these skilled professionals in the oil and gas sector remained high, leading to increased labor costs for companies like CES. For instance, average salaries for petroleum engineers saw an upward trend, reflecting this competitive talent landscape.
Furthermore, suppliers of essential regulatory and environmental compliance services hold considerable sway. CES's need to adhere to complex regulations, such as those concerning emissions, makes these services critical. The potential for substantial fines or operational disruptions due to non-compliance underscores the inelastic demand for such expertise, giving these suppliers significant pricing power.
| Supplier Type | Factors Enhancing Power | Impact on CES Energy Solutions | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Chemical Formulations | Proprietary nature, limited alternatives | Higher input costs, reduced negotiation flexibility | Continued demand for performance chemicals |
| Advanced Blending Equipment | High capital investment for suppliers, specialized technology | Increased equipment acquisition costs, potential maintenance dependencies | Ongoing investment in optimizing production technology |
| Skilled Technical Personnel | Scarcity of specialized chemists and engineers | Elevated labor costs, challenges in talent acquisition and retention | Robust demand for oilfield services personnel, wage pressures |
| Regulatory Compliance Services | Critical expertise, high penalties for non-compliance | Inelastic demand for services, limited price negotiation | Increasing focus on ESG compliance and reporting |
What is included in the product
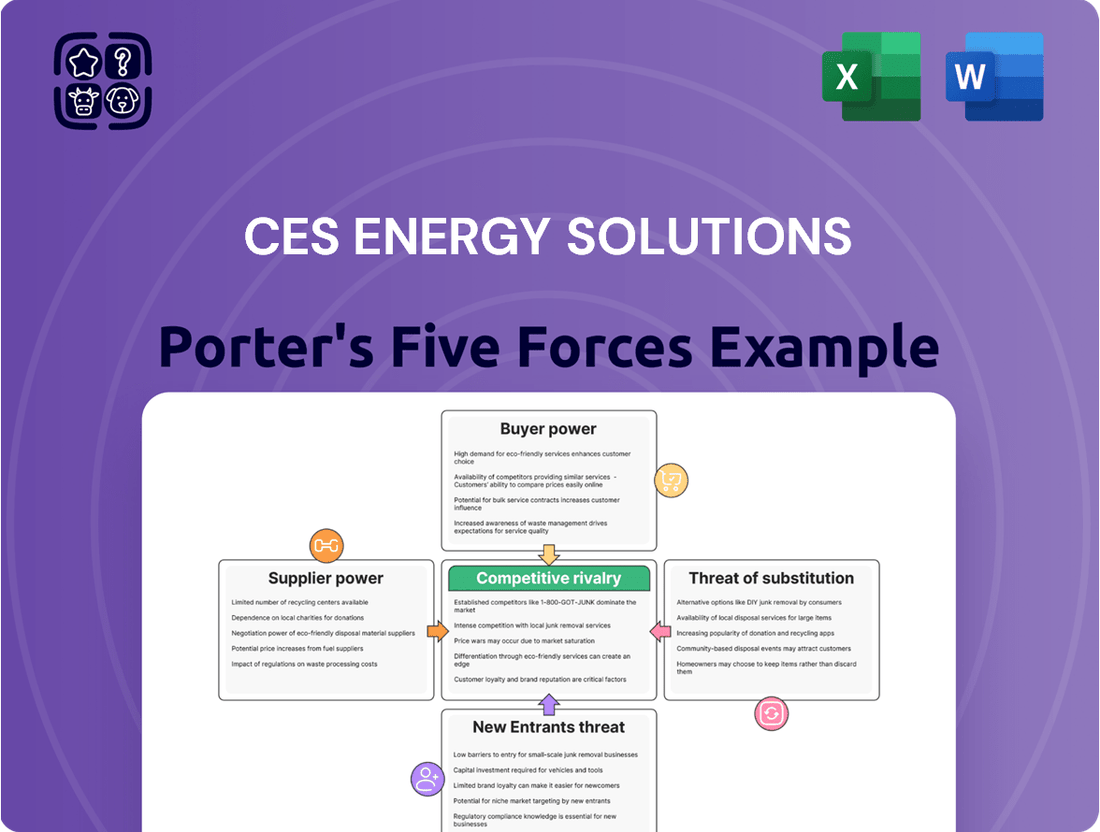
This analysis of CES Energy Solutions examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes within the energy services sector.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures and customer leverage with a visual representation of CES Energy Solutions' Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
CES Energy Solutions' customers, primarily oil and gas producers, are often large, consolidated entities. In 2024, many of these producers operate with significant scale, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms. This consolidation means fewer, but larger, buyers, increasing their collective bargaining power.
The substantial purchasing volumes of these major oil and gas producers give them considerable leverage. They can influence pricing and contract conditions, especially when issuing large tenders for services like those CES provides. For instance, a major producer might secure lower rates by committing to a multi-year, high-volume contract.
This robust customer purchasing power directly impacts CES Energy Solutions' revenue and profitability. Their ability to command better pricing or more favorable contract terms means CES must remain competitive to secure and retain these key accounts, a dynamic evident throughout the 2024 market.
Oil and gas producers are inherently price-sensitive because their own profitability hinges on volatile commodity prices. When crude oil prices, for instance, are low, like the WTI average of around $78 per barrel in early 2024, these customers exert greater pressure on their suppliers, including CES Energy Solutions, to reduce costs for essential services.
This sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. If oil prices dip, producers will actively seek out cheaper chemical solutions or negotiate harder on existing contracts, forcing CES to compete more aggressively on price to retain business.
The bargaining power of CES Energy Solutions' customers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers. While CES provides technically advanced chemical solutions, customers can often find comparable services from other established providers in the oil and gas sector. For instance, competitors like Schlumberger or Halliburton offer a broad range of chemical and well services, providing customers with viable alternatives.
Furthermore, some customers, particularly larger integrated energy companies, possess the internal capabilities to handle certain basic chemical treatment and supply needs themselves. This internal capacity acts as a significant check on CES's pricing and service terms. In 2024, the energy services market remained competitive, with companies like ChampionX and NexTier Oilfield Services also vying for market share, further amplifying customer choice.
The existence of multiple credible competitors offering similar or substitutable solutions empowers customers. This ability to switch suppliers easily means CES must consistently innovate and differentiate its offerings to retain business and avoid being commoditized. This dynamic forces CES to focus on unique value propositions and superior service delivery to maintain its competitive edge.
Low Switching Costs for Standard Products
For standard chemical solutions, CES Energy Solutions customers often face low switching costs. This means if a competitor offers a comparable product at a more attractive price or with superior service, customers can easily move their business. For instance, in 2024, the chemical distribution market saw increased price competition, particularly for widely available products, making it easier for buyers to shift suppliers.
This ease of switching directly impacts CES Energy Solutions' bargaining power with these customers. When switching is simple and inexpensive, customers gain leverage, pushing for better pricing and terms. This dynamic is especially pronounced in segments where the chemical solutions are less specialized and readily available from multiple providers.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily switch to competitors for standard chemical products.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased price competition in 2024 for commoditized chemicals pressures CES Energy Solutions.
- Customer Leverage: Simple transitions empower customers to negotiate better terms.
- Impact on Margins: This can lead to reduced profit margins on less specialized offerings.
Customer's Technical Expertise and In-house Capabilities
Large oil and gas firms often boast substantial in-house technical expertise, sometimes even capable of developing their own chemical solutions. This capacity for backward integration, or at least a profound grasp of chemical processes, empowers these customers. They can critically assess CES Energy Solutions' products and negotiate from a stronger position, insisting on precise performance metrics and cost savings. For instance, a major operator might leverage its internal R&D to benchmark CES's new stimulation fluid, directly impacting pricing discussions.
This technical acumen translates into a heightened ability for customers to demand customized solutions and competitive pricing. They understand the underlying chemistry and can articulate specific performance requirements, making it harder for CES to command premium prices without clear differentiation. This is particularly true for commodity chemicals where performance differences are marginal.
- Customer Technical Expertise: Large oil and gas companies often possess significant in-house technical expertise and may have the capacity to develop or produce certain chemical solutions themselves.
- Backward Integration Potential: This capability allows customers to critically evaluate CES's offerings and negotiate more effectively.
- Negotiating Power: Customers can demand specific performance criteria and cost efficiencies due to their understanding of chemical processes.
- Benchmarking: In-house R&D allows clients to benchmark CES's products, influencing pricing and contract terms.
The bargaining power of CES Energy Solutions' customers is considerable, driven by the consolidated nature of the oil and gas industry. In 2024, major producers, often operating at significant scale, wield substantial influence due to their large purchasing volumes, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms.
Customers' price sensitivity, directly linked to volatile commodity prices like the WTI average of around $78 per barrel in early 2024, further amplifies their leverage. This sensitivity compels CES to maintain competitive pricing, especially for commoditized chemical solutions where switching costs are low.
| Factor | Impact on CES Energy Solutions | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Consolidation | Increased leverage for fewer, larger buyers | Major oil and gas producers operate with significant scale |
| Purchasing Volume | Ability to influence pricing and contract conditions | Large tenders allow for negotiation of multi-year, high-volume contracts |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure for cost reduction from suppliers | Low crude oil prices (e.g., WTI ~$78/bbl in early 2024) increase customer pressure |
| Availability of Alternatives | Limits CES's pricing power and necessitates differentiation | Competitors like Schlumberger, Halliburton, ChampionX, and NexTier offer comparable services |
| Low Switching Costs | Customers can easily move business for standard products | Price competition in the chemical distribution market for widely available products |
| Customer Technical Expertise | Enables critical assessment and negotiation from a stronger position | Large operators can benchmark CES's products, influencing pricing |
Preview Before You Purchase
CES Energy Solutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for CES Energy Solutions, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the energy services sector. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted analysis. This includes in-depth evaluations of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, all ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The oil and gas chemical solutions market, particularly in North America, is characterized by a robust mix of large, established companies and a multitude of smaller, specialized businesses. This creates a highly competitive environment where global leaders and regional specialists actively compete for market dominance.
CES Energy Solutions operates within this dynamic landscape, facing intense rivalry from both broad-service providers and niche players. For instance, in 2024, the market saw significant activity from companies like Baker Hughes and ChampionX, alongside numerous smaller, regional chemical suppliers, each vying for contracts and contracts.
This diversity of competitors necessitates continuous innovation and strategic differentiation for CES Energy Solutions to maintain and grow its market share. Companies must focus on unique product offerings, superior service, and cost-effectiveness to stand out in this crowded field.
The oil and gas sector, where CES Energy Solutions operates, is inherently cyclical and prone to substantial swings driven by commodity prices and global political events. This volatility means that periods of intense competition can quickly follow times of relative calm.
In 2024, the oil and gas industry experienced a complex environment. While demand remained robust, supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions in regions like Eastern Europe continued to influence pricing. For instance, Brent crude oil prices fluctuated significantly throughout the year, impacting the capital expenditure budgets of exploration and production companies, which directly affects demand for services like those offered by CES Energy Solutions.
When the industry faces slower growth or contraction, the rivalry among service providers intensifies. Companies are forced to compete more aggressively for a smaller pool of available work, often leading to price wars and a heightened struggle to secure contracts. This dynamic was evident in certain segments of the North American oilfield services market during periods of price downturns in 2024, where margins were squeezed.
CES Energy Solutions highlights its technically advanced and customized solutions, but the actual level of differentiation in the energy services sector can be inconsistent. When products or services become similar, price competition escalates, increasing rivalry among players.
In 2024, the oilfield services market, particularly in North America, experienced significant pricing pressures in certain segments due to oversupply of certain equipment and services, impacting companies that couldn't clearly differentiate. CES's focus on proprietary chemical formulations and demonstrating tangible performance improvements is crucial for them to stand out and avoid being solely judged on price.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The oil and gas chemical solutions sector, including companies like CES Energy Solutions, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These investments span research and development, advanced manufacturing facilities, specialized blending plants, and extensive distribution networks. For instance, building and maintaining these operational assets requires significant capital outlay, creating a high barrier to entry and a strong incentive for existing players to maximize their operational efficiency.
Given these high fixed costs, companies are driven to achieve high capacity utilization to spread these expenses over a larger volume of production. This pursuit of efficiency can intensify competitive rivalry, particularly during periods of reduced demand or industry downturns. Companies may resort to aggressive pricing tactics to secure market share and maintain production levels, putting pressure on profit margins across the industry.
- High Capital Investment: The oil and gas chemical sector demands significant upfront investment in R&D, manufacturing, and logistics infrastructure.
- Capacity Utilization Drive: Companies aim for high operational capacity to amortize fixed costs, potentially leading to price competition.
- Impact on Rivalry: The need to maintain volume can result in aggressive pricing strategies, especially when demand falters, intensifying direct competition among players.
Exit Barriers and Asset Specificity
CES Energy Solutions operates in an environment where high exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry. Specialized assets, such as unique chemical blending facilities or dedicated transportation fleets, are difficult and costly to repurpose, trapping companies in the market even when unprofitable.
These specialized assets, coupled with long-term contractual obligations, can prevent competitors from exiting, leading to persistent market overcapacity. This overcapacity directly fuels intense price competition, making it a struggle for all participants, including CES Energy Solutions, to maintain healthy profit margins.
- Specialized Assets: Difficult to repurpose, increasing the cost of exiting the market.
- Long-Term Contracts: Lock companies into operations, even if they become unprofitable.
- Market Overcapacity: Created by companies unable to exit, leading to price wars.
- Margin Pressure: Sustained overcapacity forces down prices, impacting profitability for all players.
The competitive rivalry for CES Energy Solutions is intense, fueled by a fragmented market with both large, established players and smaller, agile competitors. In 2024, the oil and gas chemical sector saw significant competition from companies like ChampionX and Baker Hughes, alongside numerous regional suppliers, all vying for market share.
This rivalry is exacerbated by high fixed costs and the drive for capacity utilization, pushing companies toward aggressive pricing strategies to maintain production levels. For example, in 2024, pricing pressures were evident in certain North American oilfield services segments due to oversupply, squeezing profit margins.
CES Energy Solutions must continually innovate and differentiate its offerings, focusing on technically advanced and customized solutions to avoid competing solely on price. The presence of specialized assets and long-term contracts also creates high exit barriers, trapping companies in the market and perpetuating overcapacity and price wars.
| Competitor Type | 2024 Market Activity Example | Impact on CES Energy Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Large Established Players | Baker Hughes, ChampionX | Intensified competition for major contracts, pressure on pricing |
| Regional Specialists | Numerous smaller suppliers | Fragmented market, competition for localized contracts, potential for price erosion |
| Niche Product Providers | Companies with unique chemical formulations | Need for CES to highlight proprietary advantages and performance benefits |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Technological advancements in drilling and completion, like extended reach drilling and novel fracturing methods, can diminish the need for specific chemical solutions or drastically change their requirements. For instance, innovations reducing fluid volumes in hydraulic fracturing could directly substitute CES Energy Solutions' chemical offerings. CES must maintain robust research and development to counter this threat.
Mechanical alternatives pose a potential threat to CES Energy Solutions' chemical treatment business. For certain applications, physical processes might substitute for chemical interventions. For example, advanced filtration technologies could lessen the reliance on production chemicals, and novel downhole tools might offer alternatives to chemical wellbore cleanouts.
These mechanical innovations represent a latent threat, as they could reduce the demand for traditional chemical solutions. While the exact market share impact is still developing, the trend towards more sustainable and potentially cost-effective mechanical solutions is evident across various industrial sectors.
The global shift towards renewable energy sources presents a significant long-term substitute threat to CES Energy Solutions. As nations commit to decarbonization goals, the demand for fossil fuels, and consequently the services supporting them, is expected to decrease.
For instance, in 2024, renewable energy capacity additions are projected to reach record levels, with solar and wind power leading the charge. This trend directly impacts the oil and gas sector, CES's primary market, potentially reducing the need for their chemical solutions and services over time.
This macro-economic transition to cleaner energy fundamentally alters the industry landscape, influencing the future growth and sustainability of companies like CES that are heavily reliant on traditional energy markets.
Improved Operational Practices and Well Design
The threat of substitutes for CES Energy Solutions is influenced by advancements in operational practices and well design within the oil and gas industry. Operators are constantly looking for ways to boost efficiency and reduce costs. For instance, in 2024, many upstream companies focused on optimizing drilling fluid formulations and completion techniques to minimize chemical usage throughout the well's life. This drive for efficiency can directly impact the demand for specialized chemicals and services that CES provides.
Improved well design and enhanced reservoir management can lead to a direct reduction in the volume of chemicals needed. For example, innovations in hydraulic fracturing, such as the use of more effective proppants or reduced water volumes, could lessen the reliance on traditional chemical additives. This trend suggests that as the industry adopts more sophisticated methods, the need for certain chemical solutions might diminish, posing a substitution threat.
- Optimized Drilling Fluids: Advances in drilling fluid technology aim to reduce the overall volume of chemicals required per well, potentially impacting demand for traditional chemical suppliers.
- Enhanced Well Completion: Innovations in completion techniques, such as improved proppant selection and placement, can decrease the necessity for certain specialized chemical treatments.
- Reservoir Management: Better understanding and management of reservoirs can lead to more efficient production, potentially lowering the chemical input needed for production optimization.
In-house Development or Generic Chemical Production
Large integrated oil and gas companies possess the resources to develop certain chemical solutions in-house or procure generic chemicals directly from manufacturers, bypassing specialized service providers like CES Energy Solutions. This poses a threat, particularly for standard or high-volume chemicals where customers might see a cost benefit in direct sourcing.
While CES's proprietary and complex blends are more insulated, the availability of off-the-shelf chemical alternatives or the capability of major players to manufacture them internally limits pricing power. For instance, if a large producer can achieve economies of scale in producing a common drilling fluid additive, they may reduce their reliance on external suppliers.
- In-house Production: Major oil companies can leverage their existing infrastructure and R&D capabilities to produce chemicals internally, potentially reducing costs.
- Generic Chemical Sourcing: Direct procurement of widely available chemicals from bulk manufacturers offers an alternative to specialized service providers.
- Cost Advantage: Customers may switch to in-house or generic options if they perceive a significant cost saving compared to CES's offerings.
Technological advancements and operational efficiencies within the oil and gas sector present a significant threat of substitution for CES Energy Solutions. Innovations in drilling and completion, such as extended reach drilling and new fracturing methods, can reduce the need for specific chemical solutions or alter their requirements. For example, in 2024, upstream companies are focusing on optimizing drilling fluid formulations to minimize chemical usage, directly impacting demand for CES's offerings.
Mechanical alternatives also pose a threat, with advanced filtration technologies and novel downhole tools potentially substituting for chemical interventions in wellbore cleanouts and production treatments. Furthermore, the global energy transition, with record renewable energy capacity additions projected for 2024, signals a long-term shift away from fossil fuels, which could diminish the overall market for oilfield services and chemicals.
| Substitution Threat Area | Description | Example Impact | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Innovations reducing chemical usage in drilling and completion. | More efficient proppants in hydraulic fracturing decrease additive needs. | Focus on optimizing drilling fluid formulations to minimize chemical input. |
| Mechanical Alternatives | Physical processes replacing chemical treatments. | Advanced filtration reducing reliance on production chemicals. | Development of novel downhole tools for wellbore cleanouts. |
| Energy Transition | Shift towards renewable energy sources. | Decreased demand for fossil fuels impacts oilfield services. | Record renewable capacity additions in 2024 impacting oil & gas sector. |
| In-house/Generic Sourcing | Large companies producing chemicals internally or sourcing generically. | Cost savings for standard chemicals bypassing specialized providers. | Major players leveraging economies of scale for common additives. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the advanced chemical solutions market for the oil and gas sector demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development to create innovative products, alongside specialized blending facilities and a reliable distribution network. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art chemical blending plant can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, creating a substantial hurdle for newcomers.
CES Energy Solutions operates in a sector where creating and distributing technically advanced chemical solutions requires significant scientific acumen, robust research and development infrastructure, and often protected intellectual property like patents and unique formulations. This high bar for specialized knowledge and proprietary assets acts as a substantial deterrent for potential newcomers.
The oil and gas sector thrives on deeply ingrained customer relationships and a strong reputation, particularly for essential services like chemical solutions where operational efficiency and safety are paramount. CES Energy Solutions, for instance, has cultivated these vital connections over many years.
This history translates into a significant barrier for newcomers. New entrants face a considerable challenge in building the trust and credibility necessary to displace established providers and win substantial contracts, a process that can take considerable time and investment.
Stringent Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
The oil and gas sector, particularly concerning chemical handling and application, is heavily regulated in both Canada and the United States. These stringent environmental, health, and safety (EHS) regulations create substantial barriers for potential new entrants.
Navigating the complex web of permitting processes and adhering to rigorous compliance standards demands significant investment and expertise. For instance, in 2024, companies operating in this space must contend with evolving EHS frameworks, which can include updated reporting requirements and stricter waste management protocols.
The financial burden associated with meeting these regulatory demands, including specialized training, equipment, and ongoing compliance monitoring, can deter new companies from entering the market. This high cost of entry effectively limits the number of new players who can realistically compete.
- Complex Permitting: New entrants must secure numerous permits for chemical handling, storage, and disposal, often involving lengthy review periods.
- EHS Compliance Costs: Adherence to regulations like Canada's Environmental Protection Act and the U.S. EPA standards requires substantial capital for compliant infrastructure and operational procedures.
- Operational Standards: Meeting industry-specific safety standards, such as those mandated by the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers (CAPP) for chemical usage, adds another layer of complexity and cost.
Economies of Scale in Production and Distribution
Economies of scale significantly deter new entrants in the energy services sector, including for companies like CES Energy Solutions. Established players leverage their large operational volumes to achieve lower per-unit costs in raw material procurement, manufacturing, and logistics. For instance, in 2023, CES Energy Solutions reported total revenues of approximately CAD 2.2 billion, indicating a substantial scale of operations that would be difficult for a newcomer to replicate quickly.
This scale advantage translates into a considerable cost disadvantage for potential new competitors. Without the ability to match the purchasing power and distribution efficiency of incumbents, new entrants would struggle to offer competitive pricing. This barrier makes it challenging for them to gain market share and achieve profitability in the initial stages of operation.
- Existing players benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high production and distribution volumes.
- CES Energy Solutions' 2023 revenue of ~CAD 2.2 billion exemplifies this scale.
- New entrants face a cost disadvantage, hindering price competitiveness.
- Achieving comparable economies of scale is a significant hurdle for market entry.
The threat of new entrants for CES Energy Solutions is moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for specialized chemical production, research and development, and distribution networks. Furthermore, established customer relationships and a strong reputation for reliability and safety in the oil and gas sector present significant barriers. Navigating complex and stringent environmental, health, and safety regulations, along with achieving economies of scale in procurement and operations, also deters new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023/2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High investment for R&D, production facilities, and distribution. | Significant deterrent. | Chemical blending plant costs in the tens of millions USD. |
| Customer Relationships & Reputation | Long-standing trust and proven performance are crucial. | Difficult to displace incumbents. | Years of service required to build credibility. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict EHS regulations and permitting processes. | Adds substantial cost and complexity. | Evolving EHS frameworks in Canada and the US. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established, high-volume players. | Creates a cost disadvantage for newcomers. | CES Energy Solutions' ~CAD 2.2 billion in 2023 revenue. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CES Energy Solutions Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of credible data, incorporating information from CES Energy Solutions' annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research reports and energy sector publications. We also leverage public regulatory filings and economic data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
