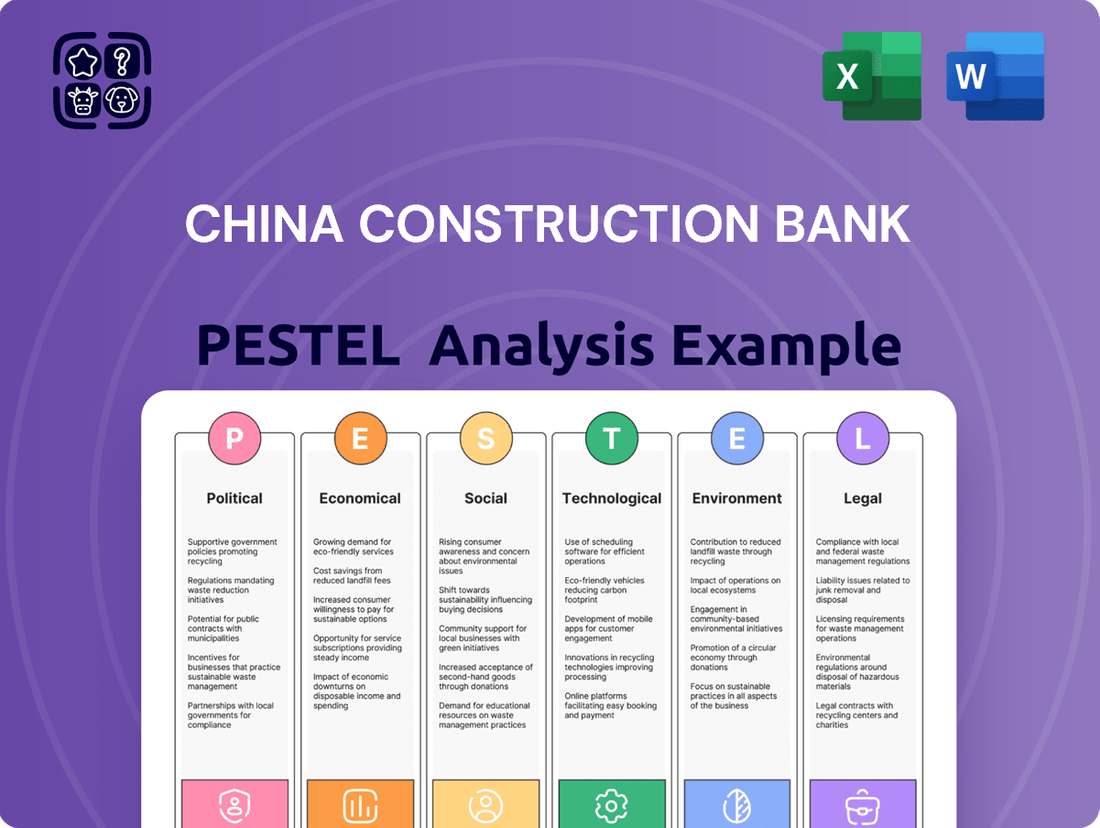
China Construction Bank PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Construction Bank Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping China Construction Bank's trajectory. Our meticulously researched PESTLE analysis provides the strategic foresight you need to navigate this dynamic landscape. Don't get left behind; download the full version now for actionable intelligence that empowers smarter decisions.
Political factors
China Construction Bank (CCB), as a major state-owned institution, is significantly shaped by government directives. Policies enacted in late 2024, targeting property market stability, stock market revitalization, and consumption growth, are anticipated to benefit CCB, particularly due to its substantial mortgage loan exposure.
The bank expects continued government support to stimulate economic activity. This could include measures like reductions in reserve requirement ratios and loan prime rates, aimed at reducing borrowing costs and increasing market liquidity.
China's banking sector is subject to rigorous regulatory control, with 2024 seeing the implementation of new rules aimed at improving loan business operations. These updates include greater adaptability in how loan funds are disbursed and defined parameters for loan durations.
The National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) has also issued guidelines concerning syndicated loans and data security for financial institutions. These measures underscore a commitment to prudent regulation and maintaining stability within the financial system.
China's commitment to financial stability remains a cornerstone of its economic policy, with significant efforts in 2024 aimed at mitigating risks in the real estate sector and managing local government debt. These initiatives are expected to continue into 2025, focusing on enhancing the banking sector's resilience and risk management capabilities.
The government's proactive approach, potentially formalized by the PRC Financial Stability Law, signals a robust strategy to safeguard the financial system. This focus is crucial given the banking sector's role in supporting economic growth, with total assets of Chinese banks reaching approximately $33.4 trillion by the end of 2023, according to the National Financial Regulatory Administration.
Geopolitical Landscape and International Relations
Global geopolitical tensions and ongoing trade disputes, particularly between major economies, present a significant factor influencing China's economic trajectory and, by extension, its banking sector. These international dynamics can directly affect trade flows and investment patterns, creating a more uncertain operating environment for financial institutions.
China Construction Bank (CCB), despite its strong domestic focus, is not immune to these shifts. Its international operations and engagement in cross-border financial services expose it to the ripple effects of geopolitical realignments. For instance, in 2023, global trade growth slowed, impacting the volume of international transactions that banks like CCB facilitate.
- Trade Tensions: Continued trade friction between China and the United States, for example, can dampen export-oriented growth, affecting corporate clients and their borrowing needs.
- Supply Chain Realignments: Geopolitical factors are driving a restructuring of global supply chains, which can alter investment destinations and the demand for financing in different regions.
- Sanctions and Regulations: The increasing use of economic sanctions by various nations can create compliance challenges and limit CCB's ability to conduct business in certain markets.
- Foreign Investment Flows: Shifts in global investor sentiment due to geopolitical instability can lead to volatility in foreign direct investment into China, impacting the banking sector's asset growth.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) Efforts
China is significantly bolstering its anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations, with the amended Anti-Money Laundering Law set to take effect in January 2025. This updated legislation expands the definition of money laundering to encompass proceeds from a wider range of criminal activities and specifically targets terrorism financing. Financial institutions, including China Construction Bank (CCB), must now adopt more rigorous compliance measures, such as a beneficial ownership filing system, which elevates their regulatory burden.
These evolving AML/CTF requirements directly impact CCB's operations by necessitating enhanced due diligence and reporting mechanisms. The expanded scope means CCB must scrutinize transactions more broadly, potentially increasing operational costs associated with compliance. Furthermore, the introduction of a beneficial ownership filing system requires the bank to implement robust processes for identifying and verifying the ultimate beneficial owners of its clients, adding a layer of complexity to customer onboarding and ongoing monitoring.
- Expanded Scope: The amended Anti-Money Laundering Law, effective January 2025, broadens AML to include proceeds from 'other crimes'.
- Terrorism Financing Focus: Explicitly includes terrorism financing activities within the scope of AML regulations.
- Enhanced Due Diligence: Financial institutions like CCB must implement a beneficial ownership filing system.
- Increased Compliance Burden: These changes necessitate greater investment in compliance technology and personnel for CCB.
Government policies in 2024 and projected into 2025 are crucial for CCB, with directives aimed at stabilizing the property market and boosting economic activity. These include potential interest rate adjustments and reserve requirement changes, designed to inject liquidity and lower borrowing costs for businesses and individuals. The government's commitment to financial stability, particularly in managing real estate risks and local debt, underpins the banking sector's operational environment.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors influencing China Construction Bank, covering political stability, economic growth, social trends, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks.
It offers strategic insights into how these forces create both challenges and opportunities for the bank's operations and future growth.
A concise PESTLE analysis for China Construction Bank offers a clear, summarized version of complex external factors, simplifying strategic discussions and ensuring all stakeholders grasp key market dynamics.
Economic factors
China's economic growth trajectory significantly impacts China Construction Bank's (CCB) operations. Despite a recovery observed in 2024, the nation's economy grappled with subdued domestic demand and ongoing pressures on businesses.
CCB's financial results for 2024 illustrate this dynamic. The bank reported a 5.86% increase in total assets, reaching approximately 33.5 trillion yuan, while net profit saw a modest rise of 1.15% to 332.1 billion yuan, underscoring a period of stable but challenging economic conditions.
China's prevailing low-interest-rate environment has significantly compressed banks' net interest margins (NIMs). This pressure contributed to a noticeable decline in net interest income for many publicly traded banks during 2024.
China Construction Bank (CCB) has not been immune to this trend, with its NIMs also experiencing a downturn, directly linked to the ongoing interest rate cut cycles. This challenging environment is projected to persist into 2025, compelling CCB to explore strategic shifts in its operations to safeguard profitability.
The real estate sector is a significant driver for China Construction Bank (CCB), as a substantial portion of its loan portfolio is tied to mortgages and infrastructure development. CCB's exposure to real estate means its performance is closely linked to the health of this market.
In late 2024, Chinese authorities implemented new policies designed to stabilize the property market. These measures are anticipated to ease concerns about asset quality within the banking sector, including CCB. This stabilization is crucial as CCB experienced a rise in its non-performing loan (NPL) ratio in the early part of 2024, partly due to real estate sector pressures.
Credit Demand and Asset Quality
Weak credit demand from both businesses and individuals has been a significant factor, leading to a slowdown in loan growth across China's banking industry. This trend directly impacts profitability for institutions like China Construction Bank (CCB).
Despite the softer demand, the overall asset quality within the Chinese banking sector has shown resilience. For instance, the non-performing loan (NPL) ratio for listed banks generally held steady through 2024. This stability is partly attributed to banks actively working to manage and dispose of existing NPLs.
Looking ahead, CCB's asset quality is anticipated to see improvement. This positive outlook is bolstered by ongoing policy interventions designed to support economic growth and financial stability, which are expected to translate into a healthier loan portfolio.
- Slowing Loan Growth: Weak credit demand from corporations and consumers has resulted in decelerating loan growth for Chinese banks.
- Stable NPL Ratios: The non-performing loan ratio for listed banks remained generally stable in 2024, supported by active NPL disposal.
- CCB's Outlook: China Construction Bank's asset quality is projected to improve, aided by supportive policy measures.
Consumer Spending and Household Debt
China's economic strategy heavily emphasizes expanding domestic demand and stimulating consumption. China Construction Bank (CCB) plays a crucial role in this by supporting retail credit and initiatives like trade-in programs. This focus is evident in CCB's performance, with a notable rise in individual consumption loans and credit card lending observed in 2024.
CCB's efforts extend to bridging urban-rural divides, a strategy aimed at unlocking broader domestic consumption potential. By providing financial support to improve living standards across different regions, the bank aims to create a more robust consumer base. This approach aligns with national goals to foster sustainable economic growth driven by internal demand.
- CCB's retail credit growth: Experienced a significant increase in individual consumption loans and credit card lending in 2024, supporting domestic demand.
- Trade-in program support: CCB actively finances trade-in initiatives to encourage consumer spending on durable goods.
- Urban-rural development: The bank focuses on reducing living standard disparities to stimulate consumption in less developed areas.
China's economic landscape in 2024 presented a mixed bag for China Construction Bank (CCB). While the nation's GDP growth was projected to be around 5% for the year, the bank navigated challenges like subdued domestic demand and pressures on the property sector.
CCB's financial performance reflected these dynamics; by the end of 2024, its total assets reached approximately 33.5 trillion yuan, a 5.86% increase year-on-year, with net profit growing by a more modest 1.15% to 332.1 billion yuan.
The prevailing low-interest-rate environment significantly compressed net interest margins (NIMs) across the banking sector, impacting CCB's net interest income, a trend expected to continue into 2025, necessitating strategic adjustments.
CCB's substantial exposure to the real estate sector meant its asset quality was closely watched, especially after a rise in its non-performing loan (NPL) ratio in early 2024, though government stabilization policies for the property market in late 2024 offered some relief.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Approx.) | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Assets (Trillion Yuan) | 31.65 | 33.50 | Increasing |
| Net Profit (Billion Yuan) | 328.3 | 332.1 | Slightly Increasing |
| Net Profit Growth (%) | -2.1% | 1.15% | Improving |
| NPL Ratio (%) | 0.40% | 0.41% | Slightly Increasing (early 2024), expected stabilization |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
China Construction Bank PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of China Construction Bank delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations. Gain valuable insights into the strategic landscape for one of the world's largest financial institutions.
Sociological factors
China's rapid urbanization continues, with projections indicating that by 2030, over 70% of its population will reside in cities, up from around 65% in 2023. This demographic shift fuels demand for mortgages, consumer loans, and wealth management services, areas where China Construction Bank (CCB) is actively expanding its offerings.
Simultaneously, China faces a significant demographic challenge with an aging population; by 2035, it's estimated that over 30% of the population will be aged 60 or older. CCB is strategically addressing this by bolstering its pension finance business, aiming to capture a larger share of the growing retirement savings market and provide comprehensive financial solutions for seniors.
Chinese consumers are rapidly embracing digital platforms, with mobile banking transactions surging. By the end of 2024, over 90% of China Construction Bank's (CCB) retail customers were actively using digital channels, reflecting a significant shift in banking behavior. This trend underscores the growing demand for seamless online experiences and innovative digital financial products.
CCB's strategic focus on a customer-centric model is evident in its continuous investment in digital transformation. The bank is enhancing its mobile app and online services to offer personalized financial solutions and improve overall customer satisfaction. This commitment aims to meet the evolving needs of a digitally savvy customer base, ensuring CCB remains competitive in the rapidly changing financial landscape.
Recognizing the importance of empowering its customers, CCB is actively involved in initiatives to boost financial and technological literacy. These programs are crucial for helping consumers navigate the complexities of digital finance and make informed decisions. By fostering greater understanding, CCB aims to build trust and deepen relationships with its customers, promoting responsible financial management in the digital age.
China Construction Bank (CCB) actively addresses wealth distribution and promotes inclusive finance, aligning with national objectives. By extending financial services to previously underserved segments and small businesses, CCB facilitates economic participation. In 2023, CCB reported a 10.3% increase in loans to small and micro enterprises, demonstrating its commitment to supporting the real economy.
Trust and Reputation
Trust and reputation are foundational for China Construction Bank (CCB), a major state-owned enterprise. Its public image directly impacts customer loyalty and market confidence. CCB's commitment to transparency, evidenced by its regular publication of sustainability reports and rigorous internal control assessments, is vital for maintaining this trust. For instance, in 2023, CCB continued to emphasize its corporate social responsibility initiatives, aiming to bolster its reputation among its extensive customer base.
Maintaining a strong reputation is critical for CCB's continued success in the competitive Chinese financial landscape. Adherence to stringent regulatory standards, such as those set by the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), reinforces its credibility. The bank’s proactive approach to risk management and its consistent performance, as reflected in its robust financial results, contribute significantly to its standing.
- Public Trust: As a state-owned bank, public trust is a cornerstone of CCB's operations, influencing deposit growth and lending activities.
- Reputational Risk: Negative publicity or perceived ethical lapses could severely damage CCB's standing and lead to customer attrition.
- Sustainability Reporting: CCB's detailed sustainability reports highlight its commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles, enhancing its corporate image.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict adherence to banking regulations is paramount for maintaining a clean reputation and avoiding penalties.
Workforce Dynamics and Talent Development
The evolving financial landscape, driven by technological advancements, increasingly demands a workforce equipped with specialized digital and data-analysis skills. China Construction Bank (CCB) actively addresses this by investing significantly in talent development programs. These initiatives focus on cultivating expertise in areas like inclusive finance and the strategic application of artificial intelligence across various banking operations, ensuring CCB remains competitive in a digital-first environment.
CCB's commitment to workforce development is evident in its continuous training initiatives. For instance, in 2023, the bank reported a substantial investment in employee training hours, with a notable emphasis on digital literacy and AI integration. This proactive approach aims to bridge the skills gap and foster innovation, enabling CCB to effectively navigate the complexities of a rapidly digitizing financial sector.
- Digital Skills Enhancement: CCB prioritizes upskilling its employees in areas such as data analytics, cybersecurity, and digital customer service to meet the demands of modern banking.
- AI Integration Training: The bank is actively training staff on the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in risk management, customer relationship management, and operational efficiency.
- Inclusive Finance Expertise: CCB develops specialists in inclusive finance, aiming to broaden access to financial services for underserved populations, a key strategic objective.
- Talent Pipeline Development: The bank invests in programs to attract and nurture young talent, ensuring a future pipeline of skilled professionals capable of driving technological innovation.
China's rapidly aging demographic, with over 30% of the population expected to be 60+ by 2035, presents both challenges and opportunities for China Construction Bank (CCB). The bank is proactively expanding its pension finance business to cater to the growing retirement savings market, aiming to provide comprehensive financial solutions for seniors.
CCB's focus on digital transformation is evident in its customer-centric approach, with over 90% of retail customers actively using digital channels by the end of 2024. This reflects a significant shift in consumer behavior, driving demand for seamless online experiences and innovative digital financial products.
The bank is also committed to enhancing financial and technological literacy among its customers, recognizing the importance of empowering them to navigate digital finance. This initiative aims to build trust and foster responsible financial management in an increasingly digital world.
CCB actively supports inclusive finance, extending services to underserved segments and small businesses, as demonstrated by a 10.3% increase in loans to small and micro enterprises in 2023. This aligns with national objectives to promote economic participation and support the real economy.
Technological factors
China Construction Bank (CCB) is heavily invested in digital transformation, aiming to build robust, secure, and efficient digital finance infrastructures. This initiative saw the complete distributed transformation of its core systems, significantly boosting the performance of all customer touchpoints.
CCB's strategic roadmap, including its Digital Strategy (2022-2025) and FinTech Strategic Plan (2021-2025), underscores its dedication to integrating cutting-edge technologies. For instance, by the end of 2023, CCB had achieved over 99% of its core system distributed transformation, enhancing operational agility and customer experience.
China Construction Bank (CCB) is actively integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data analytics across its operations. By 2024, the bank had implemented 168 unique AI use cases, deploying over 7,000 AI models and 193 AI-driven scenarios into production. This technological adoption is transforming core banking processes, with sixteen key functions now utilizing AI tools to enhance efficiency and decision-making.
CCB employs AI for intelligent customer service, targeted marketing, streamlined credit approval, and robust risk management. The bank also harnesses the power of big data to generate actionable insights, enabling it to deliver highly personalized financial services to both individual and corporate clients, thereby improving customer engagement and operational effectiveness.
China's ambition to cultivate a 'digitalized, intelligent, green, and fair' fintech sector by 2025 is a significant technological driver. China Construction Bank (CCB) is at the forefront of this, embedding fintech into its operations through advanced mobile banking and app functionalities, aiming to boost customer engagement and streamline processes. This strategic integration is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly digitizing financial environment.
Cybersecurity and Data Security
The accelerating digital transformation within China's financial sector places immense importance on cybersecurity and data security for institutions like China Construction Bank (CCB). Stringent regulations, notably the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) and the Data Security Law (DSL), mandate rigorous data handling practices. These laws require comprehensive data classification, robust security protocols, and well-defined emergency response frameworks for all banking and insurance entities.
CCB, like its peers, must adhere to these evolving data security mandates. For instance, the PIPL, effective November 1, 2021, imposes significant obligations on how personal information is collected, processed, and stored, with potential penalties for non-compliance. The DSL, implemented September 1, 2021, further categorizes data based on its importance to national security and public interest, dictating specific security measures for each tier.
- Increased Digitalization: CCB's expanded online and mobile banking services heighten the attack surface for cyber threats.
- PIPL and DSL Compliance: Adherence to China's data protection laws is paramount, impacting data collection, storage, and cross-border transfer.
- Data Security Management: New measures require banks to implement detailed data classification, access controls, and incident response plans.
- Cybersecurity Investments: CCB likely invests heavily in advanced threat detection, encryption, and employee training to safeguard sensitive customer data.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
China Construction Bank (CCB) has actively invested in blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), deploying a sophisticated blockchain system to boost transaction security and operational efficiency. This strategic move places CCB at the vanguard of digital banking advancements within China.
This adoption aligns with China's overarching national strategy to integrate and leverage emerging technologies like DLT across its financial landscape. CCB's commitment to blockchain is demonstrated by its participation in pilot programs and the development of blockchain-based platforms for various financial services.
CCB's blockchain initiatives are designed to streamline cross-border payments, enhance supply chain finance, and improve the transparency of financial transactions. For instance, CCB has been involved in projects utilizing DLT for trade finance, aiming to reduce processing times and associated risks.
- Blockchain Investment: CCB has allocated significant resources to research and development in blockchain technology, aiming to build robust and scalable DLT solutions.
- Enhanced Security: The implementation of blockchain technology fortifies transaction security by utilizing cryptographic principles and decentralized record-keeping, reducing vulnerabilities to fraud.
- Efficiency Gains: CCB's DLT platforms are engineered to expedite financial processes, such as clearing and settlement, thereby lowering operational costs and improving customer experience.
- Digital Yuan Integration: CCB is also a key player in the testing and rollout of China's central bank digital currency (CBDC), the digital yuan, which leverages DLT principles for its operations.
China Construction Bank (CCB) is heavily invested in AI and big data, deploying over 7,000 AI models and 193 AI-driven scenarios by 2024 to enhance efficiency and personalize services.
The bank's commitment to digitalization is further evidenced by its core system transformation, achieving over 99% distributed transformation by the end of 2023, significantly improving customer touchpoints.
CCB's strategic focus on FinTech, including its 2022-2025 Digital Strategy, positions it to leverage advancements like blockchain for improved security and efficiency in financial transactions.
Adherence to China's stringent data security laws, such as the PIPL and DSL, necessitates significant investment in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive customer information.
| Key Technological Initiatives | Status/Data Point | Impact |
| AI Model Deployment | 193 AI-driven scenarios in production by 2024 | Enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency |
| Core System Transformation | Over 99% distributed transformation by end of 2023 | Improved performance and customer experience |
| Blockchain Adoption | Development of DLT platforms for various financial services | Increased transaction security and cross-border payment efficiency |
| Data Security Compliance | Adherence to PIPL (effective Nov 2021) and DSL (effective Sep 2021) | Mandatory robust data handling and security protocols |
Legal factors
China Construction Bank (CCB) navigates a robust and evolving regulatory landscape. In 2024, significant updates were introduced to measures governing fixed-asset loans, working capital loans, and personal loans, aiming to simplify procedures and bolster risk management. The National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) is the primary body overseeing the banking and insurance industries, ensuring compliance and stability.
China's data protection landscape is increasingly rigorous, with the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) and the Data Security Law (DSL) setting clear mandates for handling sensitive information. These regulations, further clarified by the Network Data Regulations effective January 2025, require institutions like China Construction Bank (CCB) to implement robust data security measures and conduct thorough assessments, especially for cross-border data transfers.
China's amended Anti-Money Laundering Law, effective January 1, 2025, broadens its reach to encompass proceeds from 'other crimes' and specifically targets terrorism financing. This updated legislation places significant compliance burdens on financial institutions like China Construction Bank (CCB).
CCB must now implement more rigorous procedures to identify and verify beneficial ownership for all clients, a key component in preventing illicit financial activities. Failure to adhere to these strengthened AML/CTF regulations could result in substantial penalties, impacting the bank's reputation and financial standing.
Consumer Protection Regulations
Consumer protection regulations are a growing focus within China's financial sector. The Administrative Measures for Consumer Finance Companies, effective March 2024, specifically mandated enhanced data security obligations and stricter debt collection practices. These measures underscore a commitment to safeguarding financial consumers. China Construction Bank's proactive stance in developing a customer-centric approach and continuously improving its service offerings directly supports compliance with these evolving consumer protection imperatives.
These regulations impact CCB through:
- Data Security: Increased responsibility for protecting customer financial data, requiring robust cybersecurity measures.
- Debt Collection Practices: Adherence to fair and transparent debt collection protocols, preventing predatory behavior.
- Customer Service Standards: A mandate for improved transparency and fairness in financial product and service delivery.
- Regulatory Compliance: The need for ongoing adaptation of internal policies and procedures to align with new legal frameworks.
Corporate Governance and Disclosure Requirements
As a publicly traded entity, China Construction Bank (CCB) operates under stringent corporate governance and disclosure mandates. Its adherence to these regulations is overseen by its Board of Supervisors, which reviews and approves key documents like annual reports, sustainability reports, and internal control assessments. This process underscores CCB's dedication to transparency and accountability within the established legal framework.
CCB’s commitment to robust corporate governance is further exemplified by its compliance with China's Securities Law and Banking Supervision Law, which dictate extensive reporting and operational standards. For instance, in its 2023 annual report, CCB detailed its corporate governance structure, board composition, and risk management framework, providing stakeholders with comprehensive insight into its operations. The bank's proactive approach to disclosure ensures it meets the expectations of regulators and investors alike, fostering trust and confidence in its financial dealings.
Key aspects of CCB's legal compliance include:
- Adherence to the Corporate Governance Code: CCB follows guidelines set by the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) and the Shanghai Stock Exchange, ensuring best practices in board independence, executive compensation, and shareholder rights.
- Mandatory Financial Disclosures: The bank regularly publishes detailed financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, in compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. In 2023, CCB reported total assets of approximately RMB 32.3 trillion.
- Sustainability Reporting: CCB publishes annual sustainability reports, aligning with national and international standards for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, reflecting a growing emphasis on responsible business practices.
- Internal Control Assessments: The Board of Supervisors rigorously reviews internal control systems to ensure operational efficiency, asset safety, and compliance with laws and regulations, a critical component of its legal obligations.
China Construction Bank (CCB) operates within a legal framework that prioritizes data protection and anti-money laundering efforts. The Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) and the amended Anti-Money Laundering Law, effective January 2025, impose strict requirements on data handling and financial crime prevention. These regulations necessitate robust cybersecurity measures and diligent client verification processes for CCB to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
Environmental factors
China's commitment to green finance intensified in 2024, with policies aimed at steering capital towards sustainable development, a trend expected to continue through 2025. China Construction Bank (CCB) is at the forefront, actively expanding its Green Credit Development Strategy by boosting loans for environmentally sound projects and assisting industries in their transition to greener operations.
CCB's strategic engagement includes underwriting and investing in a diverse range of ESG-focused financial instruments. Notably, the bank has been instrumental in the issuance of green bonds and carbon neutrality bonds, demonstrating its role in facilitating the growth of sustainable finance within the Chinese economy.
Climate change presents a substantial environmental challenge, driving a heightened focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors within financial reporting. China Construction Bank (CCB) actively incorporates ESG principles into its business model, with its ESG-oriented investments reaching over RMB 500 billion by the close of 2024.
CCB's commitment to environmental sustainability is further underscored by its regular issuance of sustainability reports and active participation in green bond investments, reflecting a strategic approach to addressing climate-related risks and opportunities.
China's ambitious goals to peak carbon emissions before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 are significantly reshaping its financial landscape. This presents both challenges and opportunities for institutions like China Construction Bank (CCB).
CCB actively supports this low-carbon transition by developing and expanding its green finance offerings. This includes facilitating the issuance of green bonds, which raised over $70 billion globally in 2023, and channeling funds into projects focused on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure.
Furthermore, CCB is investing in technological advancements to support its green initiatives. This includes the development of green data centers and the integration of advanced technologies into its systems, aiming to reduce its own environmental footprint and enhance its capacity to finance sustainable development.
Resource Efficiency and Sustainable Operations
China Construction Bank (CCB), beyond its role in financing green initiatives, is also concentrating on making its own operations more sustainable. This includes a focus on resource efficiency within the bank's infrastructure and daily activities. While precise data on CCB's internal resource use isn't readily available in public summaries, the national drive for greener development in China means major financial institutions are under increasing expectation to implement more efficient operational practices.
The broader environmental policy landscape in China significantly influences CCB's approach to sustainability. For instance, China's commitment to peaking carbon emissions before 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 creates a strong incentive for financial institutions to align their operations and lending portfolios with these goals. This national agenda encourages banks like CCB to integrate environmental considerations into their core business strategies, pushing for greater resource efficiency across the board.
CCB's commitment to sustainable operations is likely to manifest in several key areas:
- Energy Consumption: Implementing measures to reduce electricity usage in branches and data centers through energy-efficient equipment and smart building technologies.
- Waste Management: Enhancing recycling programs and reducing paper consumption by promoting digital services and internal processes.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Encouraging or requiring suppliers to adopt environmentally friendly practices in their own operations.
- Digital Transformation: Leveraging technology to reduce the need for physical resources and travel, thereby lowering the bank's environmental footprint.
Biodiversity Protection and Environmental Risk Management
China's environmental policies are evolving to include biodiversity protection, with a significant push for financial institutions to integrate these considerations. This shift is evident in initiatives like the China Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2023-2030), which actively encourages banks to factor biodiversity into their financing and investment choices. For a major player like China Construction Bank (CCB), this translates into a growing imperative to embed comprehensive environmental risk management into its core lending and investment operations, moving beyond traditional climate-related risks.
The implications for CCB are substantial, requiring a proactive approach to understanding and mitigating risks associated with biodiversity loss in its project financing and portfolio management. For instance, projects in ecologically sensitive areas will face increased scrutiny, potentially impacting loan approvals and investment returns. CCB's 2023 annual report, for example, detailed its ongoing efforts in green finance, which will likely expand to encompass biodiversity metrics as these policies mature.
- Growing Regulatory Focus: China's commitment to biodiversity conservation, as outlined in its 2023-2030 action plan, directly influences financial sector regulations.
- Financial Institution Responsibility: Banks are increasingly expected to assess and manage biodiversity-related risks within their lending and investment portfolios.
- Integration of Environmental Risk: CCB must enhance its environmental risk management frameworks to incorporate biodiversity considerations alongside climate change.
- Impact on Lending and Investment: Projects with significant biodiversity impacts may face greater due diligence, potentially affecting financing accessibility and cost.
China's environmental policies, particularly its ambitious carbon peak and neutrality goals, are driving significant changes for financial institutions like China Construction Bank (CCB). The bank is actively expanding its green finance offerings, including underwriting green bonds which saw global issuance exceed $70 billion in 2023, to support the low-carbon transition. CCB's ESG-oriented investments surpassed RMB 500 billion by the end of 2024, reflecting a strategic alignment with national sustainability objectives.
Furthermore, CCB is integrating biodiversity protection into its risk management frameworks, responding to national strategies like the China Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2023-2030). This means greater scrutiny for projects in ecologically sensitive areas, potentially impacting financing. CCB's commitment extends to its own operations, with efforts focused on energy efficiency and waste reduction, aligning with the broader national drive for greener development.
| Environmental Factor | CCB's Response/Action | Relevant Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Carbon Goals | Expanding green credit and ESG investments. | China aims to peak carbon emissions before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. CCB's ESG investments exceeded RMB 500 billion by end of 2024. |
| Green Finance Growth | Underwriting and investing in green bonds. | Global green bond issuance surpassed $70 billion in 2023. CCB actively facilitates this market. |
| Biodiversity Protection | Integrating biodiversity risk into financial operations. | China Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2023-2030) guides financial institutions. |
| Resource Efficiency | Focus on energy consumption and waste management in own operations. | National drive for greener development pressures major institutions to improve operational sustainability. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for China Construction Bank is built on a robust foundation of data from official Chinese government publications, reports from international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank, and leading economic and market research firms. We also incorporate insights from reputable news outlets and industry-specific publications to ensure comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors.
