CBRE Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CBRE Group Bundle
CBRE Group operates in a dynamic real estate services landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is crucial for success. Our analysis highlights how buyer power and the threat of substitutes significantly shape market strategies.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CBRE Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CBRE Group's extensive service offerings, from property leasing and sales to project management and advisory, mean it engages with a vast and fragmented supplier network. This widespread distribution of suppliers generally dilutes the bargaining power of any individual vendor, allowing CBRE to source alternatives for common needs like cleaning or office supplies.
While the overall fragmentation limits supplier leverage, certain specialized services or proprietary technology solutions can indeed empower specific suppliers. For instance, a unique software platform for property management or a highly specialized engineering firm might command greater negotiating power due to the lack of readily available substitutes.
Technology providers are becoming increasingly crucial for CBRE Group, especially as the real estate sector embraces digital transformation. The demand for sophisticated data analytics, AI-driven insights, and smart building management systems is on the rise, directly impacting CBRE's operational efficiency and market positioning.
In 2024, the global proptech market was valued at approximately $25 billion and is projected to grow substantially. This increasing reliance on specialized tech solutions means that suppliers of these critical technologies can wield greater bargaining power. Their ability to offer unique, high-performance solutions that drive value for CBRE and its clients enhances their leverage in negotiations.
Suppliers offering advanced property management software and data analytics platforms are particularly well-positioned. As CBRE continues to integrate these technologies to optimize asset performance and client services, the demand for these niche solutions will only intensify, further solidifying the bargaining power of these technology vendors.
The availability of substitutes for suppliers significantly dilutes their bargaining power when it comes to standard services CBRE utilizes. For instance, in 2024, the commercial real estate services market saw numerous providers offering general property management and maintenance, meaning CBRE isn't reliant on a single entity.
This abundance of alternatives allows CBRE to readily switch suppliers if one tries to impose unfavorable terms or a decline in service quality. This is particularly true for commoditized services that don't demand unique expertise, presenting a clear advantage for CBRE in its procurement processes.
Switching Costs for CBRE
Switching costs for CBRE's suppliers vary significantly. While basic services might have low switching costs, suppliers providing integrated technology platforms or highly specialized consulting services can command greater bargaining power. This is because the expense and disruption involved in migrating away from these deeply embedded solutions can be substantial for CBRE.
For instance, a supplier offering a proprietary property management software that CBRE has heavily integrated across its operations presents a high switching cost. The effort to transition to a new system, retrain staff, and ensure data integrity can be considerable, giving the incumbent supplier more leverage in negotiations.
- High Switching Costs: Suppliers of specialized technology platforms and customized consulting services often benefit from high switching costs for CBRE.
- Operational Integration: Suppliers deeply embedded in CBRE's operational infrastructure, providing critical, customized solutions, gain increased bargaining power.
- Disruption Factor: The potential disruption and cost associated with changing suppliers for these specialized services can be significant, impacting CBRE's ability to easily switch.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
Suppliers offering highly specialized or unique services, especially in areas like sophisticated data center management or advanced property technology (PropTech), can exert considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true when few alternatives exist for these critical inputs.
CBRE's strategic acquisitions, such as its 2023 purchase of J&J Worldwide Services, a provider of facilities management and logistics, and Direct Line Global, a data center services firm, highlight a strategy to internalize specialized capabilities. This integration aims to mitigate reliance on external suppliers who might otherwise hold significant leverage, especially in these technically demanding sectors.
For instance, in the burgeoning PropTech market, companies developing proprietary software for building management or sustainability tracking can command higher prices if their solutions are integral to a firm like CBRE's service delivery and difficult to replicate. The bargaining power of such suppliers is directly tied to the indispensability and uniqueness of their offerings within CBRE's operational framework.
- Niche Expertise: Suppliers in specialized fields like advanced building automation systems or unique sustainability consulting services possess higher bargaining power due to limited alternatives.
- Proprietary Technology: Firms offering unique PropTech solutions, critical for CBRE's service differentiation, can leverage their technology to negotiate more favorable terms.
- Strategic Acquisitions: CBRE's acquisitions, like J&J Worldwide Services and Direct Line Global, demonstrate an effort to gain control over specialized services, thereby reducing supplier bargaining power in those acquired areas.
- Integration Value: The value of integrating specialized supplier capabilities into CBRE's broader service offering can increase the supplier's leverage if these capabilities are essential for competitive advantage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CBRE Group is generally moderate, largely due to the company's scale and the fragmented nature of many supplier markets. However, this power increases significantly for providers of specialized technology and unique, integrated services.
In 2024, the global PropTech market, a key area for specialized suppliers, was valued at approximately $25 billion and is expected to see robust growth. This expansion means that suppliers of advanced software for property management, data analytics, and sustainability solutions can exert considerable leverage due to the critical role these technologies play in CBRE's operations and client offerings.
CBRE's strategic acquisitions, such as its 2023 purchase of facilities management provider J&J Worldwide Services, aim to internalize specialized capabilities, thereby reducing reliance on external suppliers and mitigating their bargaining power in those specific service areas.
Suppliers of commoditized services, like general office supplies or basic maintenance, face low bargaining power due to the abundance of alternative providers available to CBRE. This allows CBRE to readily switch suppliers for these non-critical inputs, ensuring favorable terms.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Example | Impact on CBRE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commoditized Services | Low | Office supplies, general cleaning services | Minimal leverage; easy to switch |
| Specialized Technology | High | Proprietary property management software, AI analytics platforms | Significant leverage due to integration and lack of substitutes |
| Integrated Solutions | High | Facilities management with advanced tech (e.g., post-acquisition) | Reduced leverage for external providers after CBRE acquisition |
What is included in the product
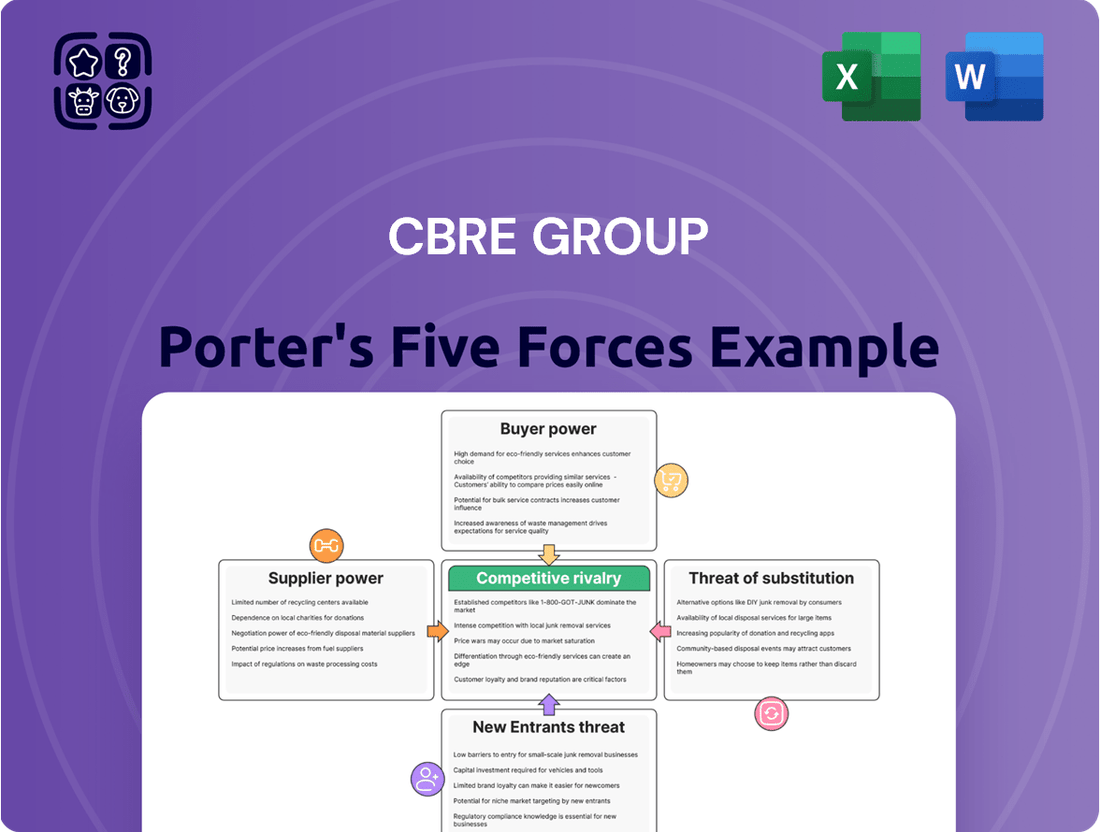
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting CBRE Group, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the commercial real estate services industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, allowing for targeted strategic responses.
Customers Bargaining Power
CBRE Group's large and diverse customer base significantly diminishes the bargaining power of individual customers. Serving a global clientele that spans from individual investors to major corporations, including real estate owners, investors, and occupiers, means no single client represents an overwhelming portion of their revenue. This broad reach, coupled with their extensive expertise and network, allows CBRE to cater to a wide array of needs, further diluting any single customer's leverage.
Customers in commercial real estate often place a high value on the quality of service and the expertise of their providers, frequently prioritizing these factors over mere cost. This focus on superior delivery and proven capability significantly diminishes their ability to exert downward price pressure.
CBRE Group's robust global brand reputation, a cornerstone of its market leadership, directly translates into enhanced customer loyalty. This loyalty means clients are less likely to switch providers based solely on minor price differences, thereby curbing their bargaining power.
In 2024, CBRE's commitment to service excellence was reflected in its consistent client retention rates, which remained strong across its diverse service lines. This demonstrates that the tangible benefits of expertise and reliability often outweigh price considerations for commercial real estate clients.
Customers considering CBRE Group have a robust selection of alternative service providers. Major global competitors like JLL, Cushman & Wakefield, and Colliers International offer comparable commercial real estate services, presenting clients with readily available choices.
This abundance of alternatives directly enhances customer bargaining power. If clients are unhappy with CBRE's offerings or pricing, they can easily switch to a competitor, forcing CBRE to remain competitive in its service delivery and cost structures.
The market is actively shifting towards technology-integrated and data-driven service models. This evolution means customers expect more sophisticated solutions, and providers who fail to adapt risk losing clients to those who embrace innovation, further empowering the customer.
Customer Price Sensitivity
CBRE Group's customer price sensitivity varies. While large institutional clients might negotiate harder on price, especially during competitive bidding for services, they often prioritize CBRE's extensive service offerings, deep market intelligence, and global presence. These factors frequently make the overall value proposition more important than minor price variations.
However, for services that are more standardized or commoditized, customers are likely to exhibit greater price sensitivity. This means that in segments where CBRE's differentiation is less pronounced, price becomes a more significant factor in client decision-making.
- Price Sensitivity Drivers: For commoditized services, price is a key differentiator.
- Value Proposition: Comprehensive services, market insights, and global reach mitigate price sensitivity for institutional clients.
- Competitive Bidding: Large clients may exert more price pressure in competitive procurement processes.
- Market Conditions: Economic downturns or increased competition can heighten customer price sensitivity across all service segments.
Impact of Economic Cycles on Customer Power
In a robust real estate market, CBRE's customer bargaining power tends to diminish. This is because high demand for services like property management and brokerage means clients are more willing to accept standard terms. For instance, in 2024, a strong market often saw fewer concessions offered by firms like CBRE.
However, during economic slowdowns, customer leverage increases significantly. With fewer transactions and greater competition among real estate service providers, clients can negotiate more favorable rates and contract conditions. This was evident in 2023 when market uncertainty gave buyers and tenants more negotiating power.
Looking ahead to 2025, the commercial real estate market is anticipated to experience a revival. This projected improvement suggests a potential shift back towards reduced customer bargaining power as demand for CBRE's services is expected to rise, potentially leading to less price sensitivity among clients.
- Economic Cycle Impact: Customer bargaining power is inversely related to market strength; higher demand equals less power for customers.
- Downturn Leverage: In weaker markets, reduced transaction volumes and increased competition empower customers to negotiate better terms.
- 2025 Outlook: An expected revival in the commercial real estate market in 2025 indicates a likely decrease in customer bargaining power.
- Market Data: 2023 saw increased customer leverage due to market uncertainty, contrasting with the stronger negotiating position of service providers in 2024.
CBRE's extensive client base and global reach limit the bargaining power of individual customers, as no single client represents a dominant share of revenue. The company's strong brand reputation and focus on service quality further reduce customer price sensitivity, particularly for institutional clients who value expertise and comprehensive offerings over minor cost differences.
While commoditized services may see higher price sensitivity, CBRE's ability to offer integrated, data-driven solutions in 2024 helped maintain client loyalty. The availability of strong competitors like JLL and Cushman & Wakefield means customers have choices, but CBRE's value proposition often mitigates the impact of these alternatives on its pricing power.
| Factor | Impact on CBRE | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Lowers individual customer power | Diverse global client base; no single client dominates revenue. |
| Service Differentiation | Reduces price sensitivity | Emphasis on expertise, market intelligence, and global presence. |
| Brand Reputation & Loyalty | Decreases customer power | Strong brand fosters client retention, reducing reliance on price alone. |
| Competitive Landscape | Increases customer power | Presence of JLL, Cushman & Wakefield offers alternatives. |
| Market Conditions | Variable impact | Strong 2024 market saw reduced customer concessions; economic downturns increase leverage. |
Full Version Awaits
CBRE Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details CBRE Group's Porter's Five Forces Analysis, covering the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products or services. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into the competitive landscape of the commercial real estate services industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The commercial real estate services sector is densely populated, featuring a multitude of global and regional entities vying for market share. This intense competition is a defining characteristic of the industry, impacting strategic decisions and operational efficiency for all participants, including CBRE.
CBRE directly contends with formidable rivals like Jones Lang LaSalle (JLL), Cushman & Wakefield, Colliers International, and Newmark Group. These major players provide a comparable breadth of services across diverse real estate segments, intensifying the competitive landscape.
For instance, in 2023, the global commercial real estate services market was valued at approximately $120 billion, with these key competitors holding substantial portions of this market, underscoring the high degree of rivalry.
CBRE Group stands as the undisputed leader in the commercial real estate services sector, boasting the largest revenue globally. This dominant position, as of the first quarter of 2025, translates into a substantial market share that outpaces its nearest competitors, underscoring its industry leadership.
This scale and brand recognition offer CBRE significant leverage in negotiations and client acquisition, further solidifying its competitive advantage. The firm’s consistent performance in maintaining this leadership highlights its ability to navigate and thrive within a highly competitive landscape.
CBRE's extensive range of services, encompassing property leasing, sales, management, project management, valuation, and investment management, significantly dampens competitive rivalry. This diversification shields the company from downturns in any single sector, allowing it to leverage strengths across various business lines. For instance, in 2023, CBRE reported revenue of $31.9 billion, demonstrating its substantial market presence and ability to generate income from multiple sources.
Technological Advancements and Data-Driven Insights
The competitive rivalry within the commercial real estate sector is intensifying due to rapid technological advancements and a strong demand for data-driven insights. CBRE is actively investing in PropTech, artificial intelligence, and sophisticated data analytics platforms. These investments are crucial for CBRE to offer strategic advisory services and boost its operational efficiency, setting it apart in a crowded market.
Competitors are not standing still; they are also channeling significant resources into similar technological areas. This arms race in technology means that staying ahead requires continuous innovation and adaptation. For instance, many firms are developing proprietary AI tools for property valuation and market trend prediction.
- CBRE's 2023 Technology Investment: CBRE reported significant spending on technology, including AI and data analytics, to enhance client services and internal operations.
- PropTech Adoption: The adoption of PropTech solutions across the industry is growing, with companies leveraging technology for everything from property management to investment analysis.
- Data Analytics in Real Estate: A 2024 industry survey indicated that over 70% of real estate firms are increasing their investment in data analytics to gain competitive advantages.
Global Reach and Brand Reputation
CBRE's extensive global reach, spanning over 100 countries, coupled with its robust brand reputation, acts as a significant barrier to entry for competitors. This vast network enables CBRE to effectively manage complex, cross-border real estate transactions, a capability that smaller or regionally focused firms struggle to replicate.
The company's strong brand equity translates into client trust and loyalty, particularly for multinational corporations with diverse real estate portfolios. This trust is a powerful differentiator, often outweighing price considerations for clients seeking reliable and experienced service providers. For instance, in 2023, CBRE maintained its position as a leading global commercial real estate services firm, a testament to its enduring brand strength.
- Global Operations: CBRE operates in over 100 countries, providing a comprehensive service offering worldwide.
- Brand Recognition: CBRE is consistently ranked among the top global brands in commercial real estate services.
- Client Trust: Its reputation fosters deep trust, especially among large, international clients with complex needs.
The competitive rivalry within the commercial real estate services sector is exceptionally high, characterized by a crowded field of global and regional players. CBRE, while a market leader, faces intense competition from firms like JLL and Cushman & Wakefield, all vying for market share in a sector valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023. This rivalry is further fueled by a technological arms race, with companies heavily investing in PropTech and AI to gain an edge.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Service Areas |
|---|---|---|
| CBRE Group | $31.9 billion | Leasing, Sales, Management, Project Management, Valuation, Investment Management |
| Jones Lang LaSalle (JLL) | $20.8 billion | Similar to CBRE, with a strong focus on corporate solutions |
| Cushman & Wakefield | $10.5 billion | Leasing, Capital Markets, Property Management, Facilities Management |
| Colliers International | $4.5 billion | Investment Management, Leasing, Project Management, Advisory Services |
| Newmark Group | $2.6 billion | Capital Markets, Leasing, Property Management, Consulting |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large corporations and significant property owners increasingly consider bringing their real estate management functions in-house. This trend offers a direct substitute for services provided by firms like CBRE, especially for entities possessing substantial internal expertise and dedicated resources. For instance, a major retail chain with a vast portfolio might develop its own leasing and property management division to cut costs and gain tighter control.
The burgeoning PropTech sector, encompassing digital platforms for listings, AI-driven valuations, and streamlined transaction systems, poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional real estate services. These innovations can automate and simplify many core functions, potentially diminishing the perceived value of conventional brokerage and advisory roles for a segment of the market. For instance, by mid-2024, the global PropTech market was projected to reach over $50 billion, indicating substantial investment and adoption of these alternative solutions.
The rise of direct transactions and peer-to-peer platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for CBRE Group. In 2024, the increasing adoption of digital tools and online marketplaces allows buyers and sellers, especially in simpler or smaller real estate deals, to connect directly. This bypasses the need for traditional brokerage services, directly impacting CBRE's transactional revenue streams.
Alternative Investment Vehicles
For investors looking for real estate exposure without direct property management, alternative investment vehicles present a significant threat. Options like direct real estate investment funds or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) offer a more passive way to gain exposure, potentially bypassing the need for a firm like CBRE for individual property acquisitions or investment management services. This is particularly relevant for individuals seeking to diversify their portfolios with real estate assets.
While CBRE provides comprehensive real estate services, other financial products can satisfy similar investment objectives. For instance, the global REIT market capitalization reached approximately $2.4 trillion in early 2024, indicating a substantial pool of capital accessible through these vehicles. This broad availability of alternatives means investors can achieve real estate investment goals through channels that do not necessarily involve CBRE’s direct services.
- REITs: Offer liquid, diversified exposure to real estate portfolios, often with attractive dividend yields.
- Real Estate Funds: Provide access to professionally managed portfolios of properties, catering to various risk appetites.
- Private Equity Real Estate: Targets specific property types or development projects, offering potentially higher returns for accredited investors.
- Crowdfunding Platforms: Enable smaller investors to participate in real estate deals, democratizing access to the asset class.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Blockchain in Real Estate
The rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional real estate services. These innovations are fundamentally altering how property is transacted and owned, offering alternative pathways that bypass established intermediaries.
Blockchain enables tokenization, allowing real estate assets to be represented as digital tokens. This can facilitate fractional ownership, making real estate investment more accessible to a broader range of investors. For instance, platforms are emerging that allow fractional investment in commercial properties, potentially drawing capital away from traditional direct ownership or REITs.
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, automate many aspects of real estate transactions, such as escrow, payments, and title transfers. This disintermediation can reduce the reliance on traditional legal, brokerage, and administrative services, thereby lowering transaction costs and increasing efficiency. By 2024, the global real estate tokenization market is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating growing adoption and a tangible substitute offering.
- Fractional Ownership: Blockchain allows for the division of real estate into smaller, tokenized units, democratizing access to property investment.
- Smart Contracts: Automation of transaction processes, including payments and title transfers, reduces the need for intermediaries.
- Disintermediation: Direct peer-to-peer transactions are becoming more feasible, cutting out traditional brokers and legal facilitators.
- Market Growth: The increasing investment in and adoption of real estate tokenization platforms signal a growing competitive threat.
The threat of substitutes for CBRE Group is significant, driven by technological advancements and evolving investor preferences. In-house real estate management by large corporations and the rise of PropTech platforms offer direct alternatives, potentially reducing the need for external brokerage and advisory services. By mid-2024, the global PropTech market was projected to exceed $50 billion, underscoring the growing adoption of these digital solutions.
Direct transactions facilitated by online marketplaces and alternative investment vehicles like REITs and real estate funds also pose a substantial threat. These options provide investors with accessible ways to gain real estate exposure, often bypassing traditional intermediaries. The global REIT market capitalization reached approximately $2.4 trillion in early 2024, highlighting the scale of these substitute investment avenues.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on CBRE | Market Indicator (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Management | Large corporations managing their own real estate portfolios. | Reduces demand for CBRE's property and facility management services. | Growing trend among Fortune 500 companies. |
| PropTech Platforms | Digital tools for listings, valuations, and transactions. | Automates core brokerage functions, potentially lowering service fees. | Global market projected over $50 billion. |
| Direct Transactions | Peer-to-peer platforms bypassing brokers for property deals. | Directly competes with CBRE's transactional revenue streams. | Increasing adoption for simpler real estate transactions. |
| REITs & Real Estate Funds | Passive investment vehicles offering real estate exposure. | Attracts capital that might otherwise be invested directly via CBRE. | Global REIT market cap ~$2.4 trillion. |
| Real Estate Tokenization | Blockchain-based fractional ownership and automated transactions. | Disintermediates traditional brokerage and administrative services. | Emerging market with significant growth potential. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global commercial real estate services and investment arena at CBRE's scale demands immense capital. This includes building a worldwide network of offices, investing heavily in advanced technology, and securing top-tier talent, creating a significant financial hurdle for newcomers.
CBRE's financial strength, evidenced by its substantial revenue, which reached approximately $31.7 billion in 2023, and its vast assets under management, highlights the sheer scale of investment needed to compete effectively. These figures act as a powerful deterrent for potential entrants lacking comparable financial backing.
CBRE's formidable brand reputation and deeply entrenched client relationships present a significant barrier to new entrants. The commercial real estate sector thrives on trust and a proven track record, elements that take years, if not decades, to cultivate. For instance, CBRE's consistent ranking among the top global commercial real estate services firms, as evidenced by their repeated inclusion in the Fortune 500, underscores this established credibility.
CBRE's status as the world's largest commercial real estate services firm grants it substantial economies of scale and scope. This means they can operate more efficiently and offer a wider range of services globally than smaller competitors. For instance, in 2023, CBRE reported revenue of $31.3 billion, demonstrating their massive operational footprint.
New companies entering this market would face immense difficulty replicating CBRE's cost advantages and integrated service model. Building a comparable global network and achieving similar operational efficiencies would require massive upfront investment and a significant amount of time, creating a high barrier to entry.
Regulatory Hurdles and Licensing
The commercial real estate sector faces significant regulatory hurdles. New entrants must contend with a complex web of licensing requirements and compliance standards that vary by location, demanding substantial investment in legal and administrative infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, obtaining the necessary permits and adhering to zoning laws across multiple jurisdictions can add months and significant costs to market entry.
These regulatory complexities act as a substantial barrier to entry, deterring potential competitors who may lack the specialized knowledge or financial capacity to navigate them. CBRE Group, as an established player, has already built the necessary compliance frameworks, giving it an advantage.
- Licensing and Permits: Obtaining necessary real estate brokerage licenses and project-specific permits is a time-consuming and costly process.
- Zoning and Land Use Regulations: Compliance with diverse local zoning laws and land use policies requires expert legal counsel.
- Environmental Standards: Adherence to evolving environmental regulations, such as those related to energy efficiency and sustainability, adds another layer of complexity.
- Financial Compliance: Meeting financial reporting standards and anti-money laundering regulations are critical for operating legally.
Access to Talent and Data
Access to experienced real estate professionals and crucial market data presents a significant barrier for new entrants. CBRE Group's established network, cultivated over decades, allows them to attract and retain top talent in the industry. This deep bench of expertise is difficult for newcomers to replicate swiftly.
Furthermore, CBRE's substantial investments in data analytics and proprietary insights provide a competitive edge. For instance, CBRE's data platforms offer comprehensive market intelligence, which is essential for effective decision-making in the real estate sector. New companies would face considerable challenges in amassing comparable data repositories and developing sophisticated analytical capabilities in a timely manner.
- CBRE's global workforce of over 130,000 employees (as of early 2024) represents a vast pool of specialized talent.
- The company's commitment to data and analytics is demonstrated through its continuous investment in technology and research, providing a significant advantage in market understanding.
- Replicating CBRE's extensive network and data infrastructure would require substantial capital and time, making the threat of new entrants in this specific area relatively low.
The threat of new entrants in the commercial real estate services sector is generally low for CBRE Group due to significant barriers. These include the massive capital required for global operations, the need for extensive technology investment, and the challenge of building a strong brand reputation and client relationships, which takes considerable time and proven performance.
CBRE's substantial financial resources, demonstrated by its 2023 revenue of $31.3 billion, and its established global network of over 130,000 employees as of early 2024, create significant economies of scale and scope. New entrants would struggle to match these operational efficiencies and integrated service offerings without immense upfront investment and time, making it difficult to compete on cost or breadth of services.
Navigating complex regulatory environments, including licensing, zoning, and environmental standards across various jurisdictions, presents another substantial hurdle. Furthermore, acquiring specialized talent and developing sophisticated data analytics capabilities, which CBRE has invested heavily in, are critical differentiators that are difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate quickly.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building a global network, investing in technology, and securing talent requires billions. | Extremely high barrier; deters most potential entrants. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Relationships | Trust and a proven track record take decades to build. | Significant barrier; requires substantial time and consistent performance to overcome. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | CBRE's size allows for cost efficiencies and a wide service range. | New entrants cannot match cost advantages or service breadth easily. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating diverse licensing, zoning, and compliance rules is costly and time-consuming. | High barrier; requires specialized legal and administrative infrastructure. |
| Talent & Data Access | Attracting top talent and accessing advanced market data is challenging. | Difficult to replicate CBRE's expertise and data-driven insights. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CBRE Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including CBRE's annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms, real estate market data providers, and economic indicators to capture the competitive landscape.
