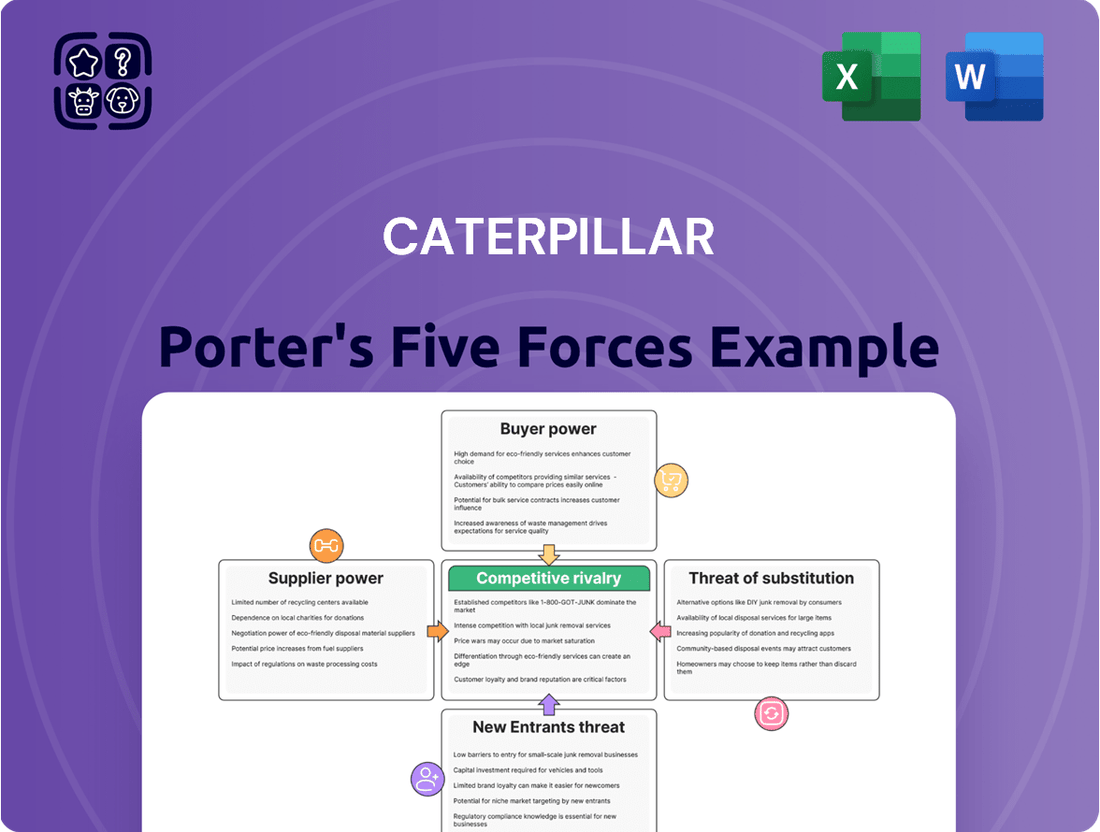
Caterpillar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Caterpillar Bundle
Caterpillar operates in a highly competitive heavy machinery market, where intense rivalry among existing players significantly impacts profitability. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as high capital requirements and established brand loyalty create barriers. However, the bargaining power of buyers, particularly large construction firms, can exert downward pressure on prices.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Caterpillar’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Caterpillar's reliance on a vast global supplier network means that the concentration of suppliers for highly specialized components, like advanced electronics or specific engine parts, can significantly amplify their bargaining power. This is a key factor in assessing supplier leverage.
While Caterpillar's immense purchasing volume and established, long-term relationships with many suppliers help to dilute individual supplier power, the strategic importance of certain niche suppliers cannot be overlooked. For instance, in 2024, the automotive and industrial sectors experienced ongoing supply chain challenges, particularly for semiconductor chips, which saw supplier concentration leading to increased pricing power for those few providers.
Switching suppliers for critical components can be a significant undertaking for Caterpillar, involving costs for product redesign, retooling manufacturing lines, and rigorous requalification of new vendors. These expenses can bolster the bargaining power of existing suppliers. However, Caterpillar's substantial investments in research and development, alongside its advanced manufacturing infrastructure, likely mitigate its dependence on highly specialized external parts, thereby potentially lessening supplier leverage.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for companies like Caterpillar. If there are numerous readily available alternatives for raw materials or essential components, a supplier's ability to dictate terms or raise prices diminishes considerably. For instance, in 2024, Caterpillar's strategic focus on advanced material science and additive manufacturing continues to explore and integrate alternative materials, reducing reliance on any single source.
Supplier's Product Differentiation
Suppliers who provide highly unique or patented parts, especially in areas like specialized engine technology or sophisticated control systems, can wield substantial influence. When few substitutes exist for these critical components, suppliers can command higher prices and dictate terms, impacting Caterpillar's cost structure and production flexibility.
Caterpillar's own robust research and development efforts, coupled with its strategic focus on creating integrated solutions, serve as a crucial countermeasure. By developing proprietary technologies and maintaining strong internal capabilities, Caterpillar can reduce its reliance on external suppliers for highly differentiated products, thereby mitigating supplier power.
- Supplier Differentiation Impact: Suppliers of specialized engine components or advanced electronics can command higher prices due to limited alternatives.
- Caterpillar's Mitigation: Caterpillar's investment in R&D for proprietary technologies lessens dependence on unique external supplier offerings.
- Example Scenario: A supplier of a unique, high-efficiency engine cooling system could leverage its differentiation to negotiate more favorable terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers could realistically integrate forward and become competitors, their bargaining power would significantly increase. This would mean they could potentially offer finished products directly to Caterpillar's customers, bypassing Caterpillar itself.
However, in the heavy equipment industry, the capital intensity and the need for complex, established distribution networks make this a low threat for most of Caterpillar's suppliers. For example, a supplier of specialized engine components would face immense challenges in setting up manufacturing, global logistics, and dealer networks comparable to Caterpillar's established infrastructure.
- Low Likelihood of Supplier Forward Integration: The substantial capital investment and intricate global distribution systems required to compete in the heavy machinery market deter most suppliers from attempting forward integration.
- High Barriers to Entry for Suppliers: Establishing manufacturing facilities, extensive service networks, and brand recognition akin to Caterpillar's presents a formidable barrier, limiting the practical threat of suppliers becoming direct competitors.
- Caterpillar's Scale Advantage: Caterpillar's massive scale of operations and entrenched customer relationships further solidify its position, making it difficult for any supplier to gain traction through forward integration.
The bargaining power of Caterpillar's suppliers is generally moderate, influenced by factors like supplier concentration for specialized parts and the cost of switching. While Caterpillar's scale provides leverage, suppliers of unique, high-value components can exert significant influence. For instance, in 2024, ongoing global supply chain disruptions, particularly for advanced electronics and specialized alloys, continued to empower certain niche suppliers, leading to price increases that Caterpillar had to absorb or pass on.
Caterpillar's ability to mitigate supplier power lies in its substantial R&D investments, fostering proprietary technologies and exploring alternative materials, as seen with its 2024 focus on advanced manufacturing techniques. This reduces reliance on single-source, highly differentiated components. The high capital requirements and complex distribution networks needed to compete directly in the heavy equipment sector also limit the threat of suppliers integrating forward into becoming direct competitors.
| Factor | Impact on Caterpillar's Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Data |
| Supplier Concentration (Specialized Components) | Increases power | Continued challenges in sourcing semiconductor chips and advanced engine parts due to limited providers. |
| Switching Costs | Increases power | High costs for redesign, retooling, and requalification of new vendors for critical parts. |
| Caterpillar's Scale & Purchasing Volume | Decreases power | Leverage through large order volumes and long-term relationships. |
| Availability of Substitute Inputs | Decreases power | Exploration of advanced materials and additive manufacturing in 2024 to reduce reliance on single sources. |
| Supplier Differentiation/Uniqueness | Increases power | Suppliers of patented or unique technologies (e.g., engine systems) can command higher prices. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low | High capital intensity and established distribution networks deter suppliers from direct competition. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Caterpillar dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within the heavy equipment industry, examining buyer and supplier power, new entrant threats, substitute products, and existing rivalry.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Caterpillar's customer base is vast and spread across critical sectors like construction, mining, agriculture, and power generation. This broad reach means that while individual large clients might possess some sway, the sheer number of customers generally dilutes the collective bargaining power of any single segment.
In 2023, Caterpillar reported total revenue of $67.1 billion, underscoring the breadth of its market penetration. While major mining operations or large infrastructure projects represent significant individual sales, they are part of a much larger, diversified customer pool, thereby limiting the overall bargaining leverage of its customers as a group.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in Caterpillar's favor, effectively limiting customer bargaining power. These costs are substantial, encompassing the need to re-establish maintenance networks, retrain operators on new equipment, and ensure compatibility with existing machinery fleets. This creates a sticky environment for customers, making a switch to a competitor a costly and disruptive undertaking.
For instance, a construction company deeply invested in Caterpillar's integrated fleet management systems and dealer support infrastructure would face considerable expense and operational downtime to transition to a rival brand. This inherent stickiness means customers are less likely to exert downward price pressure or demand significant concessions from Caterpillar, as the alternative is often more complex and expensive in the short to medium term.
While the initial sticker price for heavy machinery matters, customers in sectors like construction and mining are far more concerned with the total cost of ownership. This includes ongoing expenses such as fuel consumption, the frequency and cost of maintenance, and the equipment's long-term durability. For instance, a slightly higher upfront investment in a fuel-efficient Caterpillar machine can lead to significant savings over its operational life, making it a more attractive option despite the initial price difference.
Caterpillar's strong brand equity and its reputation for producing robust, reliable equipment significantly temper customer price sensitivity. The company's extensive dealer network and comprehensive aftermarket support, including readily available parts and skilled service technicians, further reduce the perceived risk associated with purchasing their products. This focus on reliability and support means customers are often willing to pay a premium for the assurance of less downtime and lower unexpected repair costs.
Availability of Substitute Products
The availability of substitute products significantly influences customer bargaining power. Caterpillar faces competition from major players like Komatsu, Volvo, and Hitachi, offering customers viable alternatives in the heavy equipment market. This competitive landscape means customers can switch suppliers if Caterpillar's pricing or offerings become unfavorable.
While substitutes exist, Caterpillar leverages its strengths to mitigate this pressure. Its extensive global dealer network, providing robust support and service, and its integrated solutions, which combine equipment with technology and financing, create switching costs and differentiate its value proposition. For instance, Caterpillar's Cat Connect technology offers fleet management solutions that enhance efficiency, making it harder for customers to simply switch to a competitor without losing these integrated benefits.
- Competition from Major Manufacturers: Companies like Komatsu, Volvo Construction Equipment, and Hitachi Construction Machinery offer comparable heavy equipment, providing customers with direct alternatives.
- Customer Choice and Switching: The presence of these alternatives empowers customers by giving them choices and the ability to switch suppliers based on price, features, or service.
- Caterpillar's Differentiation Strategy: Caterpillar counters this by emphasizing its vast dealer network for superior service and support, alongside integrated solutions that bundle equipment with advanced technology and financial services.
- Impact on Pricing and Margins: The threat of substitutes can limit Caterpillar's ability to raise prices significantly, as customers may opt for more cost-effective alternatives if price increases are not matched by perceived value increases.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating into heavy equipment manufacturing for Caterpillar is remarkably low. The sheer scale of capital investment, estimated in the billions of dollars for a new manufacturing facility, coupled with the intricate technological expertise and established supply chains required, presents an almost insurmountable barrier. For instance, establishing a production line comparable to Caterpillar's, which involves advanced robotics, specialized tooling, and extensive R&D, would demand resources far beyond the typical operational scope of even large customers.
This low likelihood of backward integration significantly diminishes the bargaining power of customers. Caterpillar's customers, such as construction companies or mining operations, are focused on their core competencies, not on producing the heavy machinery they utilize. The cost and complexity of replicating Caterpillar's manufacturing capabilities would likely outweigh any perceived benefits, making it an economically unviable strategy for most.
- Massive Capital Outlay: Establishing a heavy equipment manufacturing plant requires billions in investment, a prohibitive cost for most customers.
- Technological Sophistication: Producing complex machinery demands advanced engineering, specialized skills, and significant R&D capabilities.
- Economies of Scale: Caterpillar benefits from immense production volumes, allowing for cost efficiencies that are difficult for new entrants to match.
- Focus on Core Business: Customers prioritize their primary operations, making backward integration into manufacturing a distraction and an inefficient use of resources.
Caterpillar's bargaining power with its customers is generally moderate, influenced by several factors including customer switching costs, the total cost of ownership, and brand loyalty. While individual large clients can exert some pressure, the sheer diversity of Caterpillar's customer base, spanning construction, mining, and agriculture, dilutes the collective bargaining power of any single segment.
In 2023, Caterpillar's revenue reached $67.1 billion, reflecting its broad market reach. Although significant sales occur with large entities, their impact is tempered by the vast number of smaller customers, limiting the overall leverage of the customer base.
Customer switching costs remain a significant barrier for customers looking to change suppliers. These costs involve retraining staff, integrating new machinery with existing fleets, and establishing new service and maintenance networks, often making a switch a complex and expensive endeavor.
Customers are increasingly focused on the total cost of ownership, which includes fuel efficiency, maintenance, and durability, rather than just the initial purchase price. For instance, Caterpillar's fuel-efficient machines can offer substantial long-term savings, making them attractive despite potentially higher upfront costs.
| Factor | Caterpillar's Position | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Switching Costs | High due to integrated systems, dealer support, and retraining needs. | Reduces customer power; makes switching costly and disruptive. |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Focus | Emphasis on fuel efficiency, durability, and maintenance reduces TCO. | Shifts focus from initial price to long-term value, potentially increasing customer loyalty. |
| Brand Equity & Reliability | Strong reputation for robust and reliable equipment. | Customers often willing to pay a premium for perceived lower risk and higher uptime. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Competition from Komatsu, Volvo, Hitachi. | Provides customers with alternatives, limiting Caterpillar's pricing power. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Extremely low due to massive capital, technology, and scale requirements. | Significantly diminishes customer bargaining power. |
What You See Is What You Get
Caterpillar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Caterpillar Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the heavy equipment industry. You're viewing the exact, professionally formatted document you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The heavy equipment sector is a battleground with a concentrated group of major global contenders. Companies like Komatsu, Volvo Construction Equipment, Hitachi Construction Machinery, and Sany Heavy Industry are all vying for market share. These giants offer a wide array of similar products, from excavators to loaders, intensifying the direct competition.
This similarity in product offerings fuels aggressive rivalry, as each player strives to differentiate through innovation, price, and service. For instance, in 2023, the global construction equipment market was valued at approximately $230 billion, with these key players holding significant portions of that revenue, indicating the scale of the competitive landscape.
The global construction and mining equipment markets are projected to experience moderate growth, though this expansion isn't uniform across all regions and might see some temporary slowdowns. For instance, Mordor Intelligence forecasts the global construction equipment market to grow from $207.67 billion in 2024 to $265.72 billion by 2029, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.02%.
When industry growth is slower, companies tend to compete more fiercely for existing market share. This heightened rivalry can lead to price wars, increased marketing spend, and a greater focus on product differentiation as businesses vie for customer attention and loyalty.
While many heavy equipment manufacturers offer similar core functionalities, the competitive rivalry intensifies through product differentiation. Companies distinguish themselves by investing in advanced technology, superior fuel efficiency, cutting-edge automation, and integrated digital solutions that enhance operational performance and reduce costs for end-users. Caterpillar, for instance, heavily emphasizes its commitment to innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of integrated solutions designed to optimize job site productivity. In 2023, Caterpillar reported $67.1 billion in total sales and revenues, reflecting significant market presence built on such differentiators.
Exit Barriers
Caterpillar, like many heavy equipment manufacturers, faces significant exit barriers. The sheer scale of investment required for specialized manufacturing facilities, including advanced robotics and assembly lines, represents a massive sunk cost. For instance, establishing a new, state-of-the-art manufacturing plant can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This immense capital outlay makes it incredibly difficult for companies to simply walk away from the industry, even when facing financial difficulties.
Furthermore, the reliance on highly specialized labor, from engineers with expertise in hydraulics and diesel engines to skilled technicians for complex machinery assembly, adds another layer to these exit barriers. Training and retaining such a workforce is costly and time-consuming. The extensive research and development (R&D) necessary to stay competitive in areas like emissions technology, autonomous operation, and fuel efficiency also represents a substantial, ongoing investment that is difficult to recoup if a company decides to exit.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up and maintaining advanced manufacturing plants for heavy machinery requires billions in capital, making divestment a significant financial challenge.
- Specialized Workforce: The need for highly skilled engineers and technicians in areas like powertrain and hydraulics creates a valuable but difficult-to-disassemble asset.
- R&D Commitments: Continuous investment in innovation, such as developing more fuel-efficient engines or autonomous operating systems, locks companies into the industry.
- Brand and Reputation: Established brands in the heavy equipment sector have built decades of trust and a global service network, which are costly to abandon and difficult for new entrants to replicate.
Brand Identity and Loyalty
Caterpillar's brand identity is a formidable barrier to entry, cultivated over a century of delivering robust and reliable equipment. This enduring reputation fosters significant customer loyalty, as buyers often prioritize proven performance and extensive aftermarket support. For instance, Caterpillar's brand equity is a key factor in its ability to command premium pricing in a competitive market.
- Brand Equity: Caterpillar's century-long history has built a strong association with durability and performance, translating into substantial brand equity.
- Customer Loyalty: Repeat purchases are driven by trust in Caterpillar's product longevity and the comprehensive service network.
- Competitive Advantage: The brand's strength allows Caterpillar to maintain market share and pricing power against rivals.
- Perceived Reliability: Customers consistently associate the Caterpillar brand with high reliability, a critical factor in heavy equipment purchasing decisions.
Competitive rivalry within the heavy equipment sector is intense, characterized by a few dominant global players like Komatsu, Volvo, and Hitachi, all offering similar products. This similarity drives aggressive competition, often centered on innovation, price, and service, as seen in the global construction equipment market, valued around $230 billion in 2023.
When industry growth slows, such as the projected 5.02% CAGR for the construction equipment market from 2024 to 2029, rivalry escalates. Companies fight harder for market share, leading to price wars and increased marketing efforts to capture customer attention and loyalty.
Differentiation is key, with companies like Caterpillar focusing on advanced technology, fuel efficiency, and integrated digital solutions to stand out. Caterpillar's 2023 revenue of $67.1 billion highlights the success of its strategy to optimize job site productivity through innovation.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Product Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Caterpillar | $67.1 billion | Construction, Mining, Energy & Transportation |
| Komatsu | ~$28 billion (converted from JPY) | Construction & Mining Equipment |
| Volvo Construction Equipment | ~$12 billion (converted from SEK) | Construction Equipment |
| Hitachi Construction Machinery | ~$7 billion (converted from JPY) | Construction & Mining Equipment |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While diesel engines have long powered heavy equipment, the threat of substitutes is intensifying. Electrification and hybrid technologies are gaining traction, offering lower emissions and potentially reduced operating costs, directly challenging traditional diesel solutions.
Caterpillar recognizes this shift and is actively investing in and developing alternative power sources. For instance, by 2024, the company had already introduced electric versions of some of its smaller equipment and was showcasing prototypes of hydrogen-powered machines, demonstrating a proactive approach to mitigating this substitution threat.
The growing trend of equipment rental, particularly in North America, presents a significant threat of substitutes for Caterpillar. As businesses opt for renting over purchasing, especially for smaller jobs or when economic conditions are uncertain, this directly impacts the demand for new equipment sales.
The used equipment market presents a significant threat of substitution for Caterpillar. Buyers can opt for pre-owned machinery, often at a considerably lower price point, especially when new equipment costs are elevated or delivery times stretch out. For instance, in late 2023 and early 2024, supply chain disruptions continued to impact new equipment availability, driving demand and prices for used alternatives higher.
Manual Labor or Less Mechanized Methods
In certain niche applications, particularly in less developed economies or for very small, specialized projects, manual labor or less mechanized construction methods can indeed serve as a substitute for Caterpillar's heavy machinery. These alternatives might involve more traditional building techniques that rely heavily on human effort and simpler tools.
However, for the vast majority of large-scale construction, infrastructure development, and mining operations where Caterpillar excels, manual labor is not a practical or efficient substitute. The sheer scale, speed, and precision required in these sectors make advanced mechanization essential. For instance, a single Caterpillar excavator can move hundreds of tons of earth in a day, a feat impossible to replicate with manual labor within a reasonable timeframe or cost structure.
- Limited Applicability: Manual labor is only a viable substitute for Caterpillar's products in very specific, low-volume, or labor-abundant markets.
- Efficiency Gap: The productivity difference between mechanized and manual methods is enormous; for example, a modern hydraulic excavator can perform the work of dozens of laborers.
- Cost Inefficiency: While labor might be cheaper per hour in some regions, the overall project cost and timeline become prohibitive when relying on manual methods for large tasks.
- Technological Advancement: The ongoing trend in construction and mining is towards greater automation and efficiency, further diminishing the role of manual labor as a true substitute for advanced machinery.
Advancements in Existing Equipment Capabilities
Improvements in the efficiency, versatility, and longevity of existing heavy equipment can reduce the need for customers to purchase new units as frequently. For instance, Caterpillar's 2024 product updates often focus on fuel efficiency gains, which directly impact operating costs and can extend the useful life of older machines by making them more competitive. This means a customer might keep a machine running longer if it's retrofitted or upgraded to meet new efficiency standards, thereby delaying a new purchase.
Caterpillar continually innovates to enhance its products, which can also contribute to this effect. For example, advancements in telematics and predictive maintenance software, widely adopted by Caterpillar customers in 2024, allow for better management of existing fleets. This proactive maintenance reduces unexpected downtime and extends the operational life of equipment, lessening the immediate pressure to replace machines that are still functional but might have previously been retired due to reliability concerns.
- Enhanced Durability: Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes are leading to heavier equipment that lasts longer, reducing the replacement cycle for customers.
- Retrofit and Upgrade Options: Caterpillar's ability to offer significant upgrades for older models means customers can improve performance and efficiency without buying entirely new machines.
- Fuel Efficiency Gains: In 2024, Caterpillar reported average fuel efficiency improvements of up to 15% on certain new models compared to previous generations, making older, less efficient machines less appealing and potentially extending the life of newer, more efficient ones by comparison.
- Technological Integration: The integration of advanced digital technologies, like remote monitoring and diagnostics, allows for better maintenance of existing equipment, pushing out the need for replacement.
The threat of substitutes for Caterpillar's heavy machinery is multifaceted, encompassing alternative power sources, equipment rental, the used equipment market, and even manual labor in specific contexts. Electrification and hybrid technologies are emerging as key substitutes, promising reduced emissions and operational costs. Caterpillar's investment in electric and hydrogen prototypes by 2024 highlights their awareness of this evolving landscape.
The rental market and the robust used equipment sector also present significant substitution threats. Economic uncertainty and supply chain issues, prevalent in late 2023 and early 2024, amplified demand for used machinery, making it a more attractive alternative to new purchases. Furthermore, while manual labor is not a viable substitute for large-scale operations, it remains a factor in niche markets.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the heavy equipment manufacturing sector, like Caterpillar's, demands substantial financial backing. Think billions for research and development, state-of-the-art factories, and establishing a worldwide sales and service infrastructure. For instance, in 2023, Caterpillar reported capital expenditures of $3.4 billion, highlighting the ongoing investment needed just to maintain and grow operations.
Caterpillar, a giant in the heavy equipment industry, enjoys massive economies of scale. This means they can produce goods at a much lower cost per unit than a smaller, newer company. For instance, Caterpillar's global manufacturing footprint allows for bulk purchasing of raw materials, driving down input costs significantly.
These scale advantages extend to research and development. Caterpillar invests billions annually in innovation, a cost that new entrants would struggle to absorb. In 2023 alone, Caterpillar reported R&D expenses of $1.3 billion, a figure that new competitors would find incredibly challenging to match while simultaneously trying to establish production capabilities.
Consequently, the threat of new entrants is somewhat dampened by Caterpillar's entrenched cost advantages. A new player would need substantial capital to achieve similar production volumes and R&D investment, making it difficult to compete on price and technological advancement from the outset.
Caterpillar's century-long history has cultivated formidable brand loyalty and deep-seated customer relationships. This established trust, bolstered by an extensive global dealer network, presents a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to replicate such deep connections and brand recognition. For instance, in 2023, Caterpillar's revenue reached $67.1 billion, a testament to its enduring market presence and customer commitment.
Access to Distribution Channels
Caterpillar's extensive and deeply entrenched global dealer network presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. This network is not merely about sales; it encompasses vital after-sales support, parts availability, and service expertise, all crucial for heavy equipment customers. In 2024, Caterpillar continued to leverage this advantage, with its dealers providing essential support across its vast product lines.
Establishing a comparable distribution and service infrastructure would require immense capital investment and years of dedicated effort. New competitors would struggle to match the reach and reliability of Caterpillar's established channels, which are critical for customer retention and market penetration in the construction and mining industries.
- Global Dealer Network: Caterpillar operates through over 175 dealers worldwide.
- Service & Parts Infrastructure: Dealers provide essential maintenance, repair, and parts supply, ensuring uptime for customers.
- High Investment Barrier: Replicating this comprehensive network requires significant financial and time commitment, deterring potential new entrants.
- Customer Loyalty: The established network fosters strong customer relationships and loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
Regulatory and Environmental Hurdles
The heavy equipment sector is burdened by significant regulatory and environmental hurdles. Caterpillar, for instance, must navigate complex global standards for emissions and operational safety. New companies entering this arena face substantial upfront costs to meet these requirements, making it a challenging barrier.
- Stringent Environmental Regulations: Companies must comply with evolving emissions standards, such as those set by the EPA in the United States or similar bodies internationally, impacting engine design and manufacturing processes.
- Safety Compliance Costs: Meeting rigorous safety certifications for heavy machinery requires significant investment in testing, design modifications, and quality control, adding to the overall cost of market entry.
- Capital Intensive Compliance: For example, developing Tier 4 Final compliant engines for off-road machinery involved substantial R&D and retooling costs for established players, a burden new entrants would also face.
The threat of new entrants into the heavy equipment manufacturing sector is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required for operations and research. For instance, Caterpillar's 2023 capital expenditures reached $3.4 billion, underscoring the substantial investment needed to simply maintain and grow existing operations, let alone establish a new global presence.
Furthermore, Caterpillar's established economies of scale, driven by its global manufacturing and purchasing power, create a cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to overcome. In 2023, the company's R&D spending alone was $1.3 billion, a figure that new competitors would find exceedingly difficult to match while simultaneously building production capabilities.
Brand loyalty and an extensive dealer network, built over a century, also act as powerful deterrents. Caterpillar's 2023 revenue of $67.1 billion reflects this deep market penetration. Replicating the service and parts infrastructure provided by its over 175 global dealers would demand immense capital and time, making it challenging for newcomers to gain market share.
| Factor | Caterpillar's Position | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Billions required for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution | Extremely high barrier to entry |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to massive production volumes | New entrants face higher initial costs |
| R&D Investment | $1.3 billion in 2023 | Difficult for new firms to match technological advancement |
| Brand Loyalty & Dealer Network | Established trust and extensive global support infrastructure | Significant challenge to replicate reach and customer relationships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Caterpillar leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate information from trade publications and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
