Casey's General Stores Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Casey's General Stores Bundle
Casey's General Stores navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the persistent threat of substitutes, particularly from larger convenience store chains and grocery stores. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp their market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Casey's General Stores’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
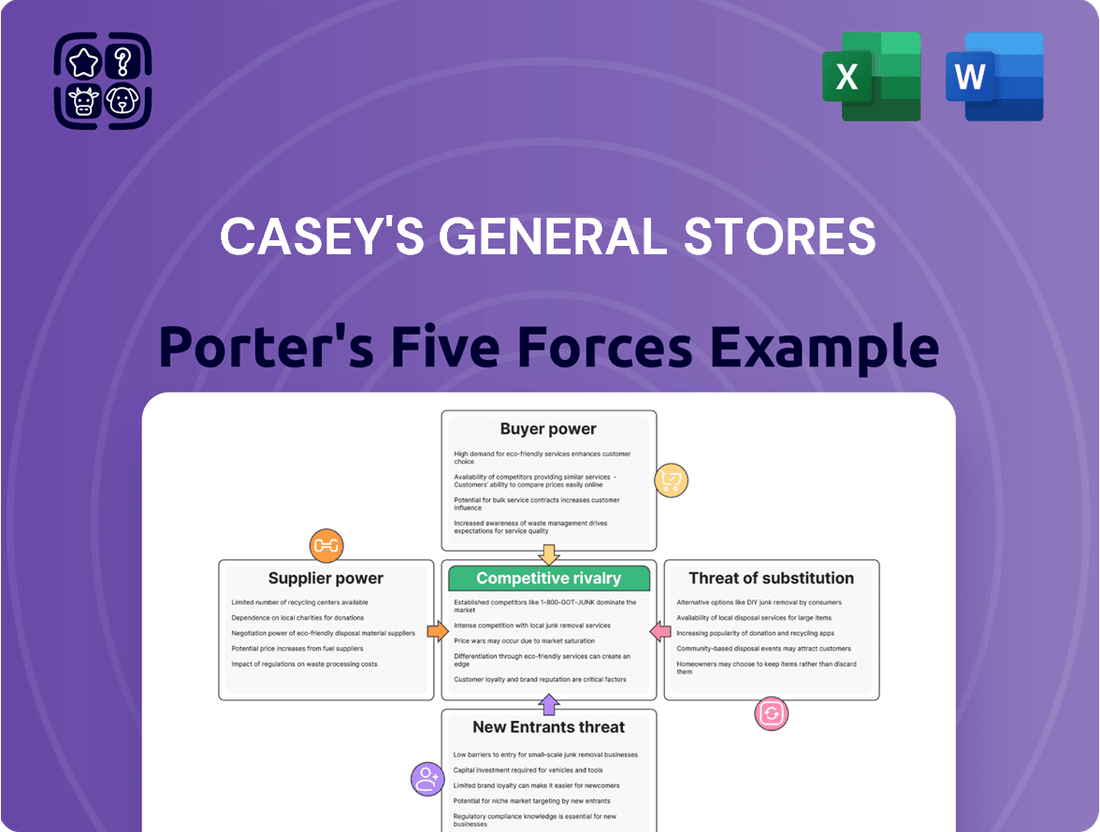
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for essential items like fuel, packaged goods, and ingredients for prepared foods significantly impacts their leverage over Casey's General Stores. If a small number of suppliers control a critical input, they can dictate pricing and terms, potentially squeezing Casey's margins.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Casey's General Stores is significantly influenced by switching costs. For critical inputs like fuel, the logistical complexities and contractual obligations associated with changing suppliers can be substantial, thereby strengthening supplier leverage. For instance, a disruption in fuel supply could directly impact Casey's ability to operate its extensive network of convenience stores and gas stations.
Conversely, for many of the generic grocery and convenience items Casey's stocks, the costs and effort involved in switching suppliers are considerably lower. This allows Casey's greater flexibility in sourcing these products, thereby reducing supplier power in those categories. In fiscal year 2024, Casey's reported that approximately 40% of its sales were from fuel, highlighting the importance of managing supplier relationships in this key segment.
The uniqueness of supplier offerings significantly impacts their bargaining power with Casey's General Stores. If suppliers provide proprietary food ingredients crucial for Casey's popular prepared foods, like their well-regarded pizza, this differentiation grants them considerable leverage. For example, a supplier holding exclusive rights to a specific cheese blend or a unique pizza sauce could command higher prices or more favorable terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Casey's operations, essentially becoming competitors, is generally quite low within the convenience store sector. This is primarily due to the high capital investment and established brand loyalty required to effectively operate a large chain of convenience stores. Suppliers in this industry typically focus on their core competencies of manufacturing or distribution rather than retail operations.
However, for certain niche or specialized product categories, a supplier might explore direct-to-consumer sales or supplying other retail channels. This could potentially increase their bargaining power by offering alternatives to Casey's. For instance, a local bakery supplying fresh goods to Casey's might consider opening its own retail outlets or partnering with smaller independent stores, thereby bypassing Casey's as an intermediary for some of its output.
The overall impact of this threat on Casey's General Stores is mitigated by the diverse range of products they offer and the scale of their operations. While individual suppliers might have some leverage with unique products, the vast majority of suppliers to a company like Casey's are unlikely to possess the resources or strategic inclination to undertake forward integration into the highly competitive convenience retail market. For example, in 2023, Casey's reported over 2,500 stores, a scale that presents a significant barrier to entry for most suppliers looking to replicate such a footprint.
- Low Likelihood of Broad Forward Integration: The convenience store industry requires significant capital and established infrastructure, making it difficult for most suppliers to directly compete with a large chain like Casey's.
- Niche Product Exception: For specialized or unique product lines, suppliers might consider direct sales or alternative retail partnerships, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
- Scale as a Deterrent: Casey's extensive network of over 2,500 stores in 2023 presents a substantial barrier to entry for suppliers contemplating forward integration.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most suppliers in this sector concentrate on manufacturing and distribution, rather than venturing into the complexities of retail operations.
Importance of Casey's to Suppliers
The significance of Casey's General Stores as a customer plays a crucial role in determining the bargaining power of its suppliers. For suppliers whose products are a small fraction of their overall sales, Casey's might not hold substantial sway, allowing them to exert more influence over pricing and terms.
Conversely, if Casey's represents a substantial portion of a supplier's business, that supplier's bargaining power is diminished. This is particularly true for smaller, specialized suppliers who rely heavily on Casey's for their revenue.
For instance, in 2024, Casey's reported total revenue of approximately $13.9 billion. The impact of this revenue on any given supplier's business can vary dramatically.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers who derive a larger percentage of their revenue from Casey's have less bargaining power.
- Market Share of Supplier: Larger, more diversified suppliers may have more leverage with Casey's, as Casey's represents a smaller portion of their total sales.
- Product Specialization: Suppliers offering unique or specialized products to Casey's might find themselves with more negotiating strength.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Casey's General Stores is influenced by the concentration of suppliers for critical inputs like fuel, where a few dominant players can dictate terms. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, fuel constituted about 40% of Casey's sales, underscoring the importance of fuel suppliers.
Switching costs are a key factor; high logistical hurdles for fuel suppliers strengthen their position, while lower costs for common grocery items give Casey's more flexibility. The uniqueness of offerings, such as proprietary ingredients for prepared foods, also grants suppliers leverage.
While forward integration by suppliers is generally low due to high barriers to entry, niche suppliers might explore alternative sales channels. Casey's substantial revenue, approximately $13.9 billion in 2024, means its importance as a customer varies, impacting supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example for Casey's |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Dominant fuel suppliers |
| Switching Costs | High costs increase power | Logistical complexity for fuel |
| Product Uniqueness | Unique products increase power | Proprietary pizza ingredients |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low threat generally | High capital needed for retail |
| Customer Importance | Less importance for supplier = more power | Casey's is a large customer, reducing power |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive landscape for Casey's General Stores, examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Easily identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Casey's General Stores' Porter's Five Forces, simplifying strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of convenience stores, particularly for essential items like fuel and basic groceries, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is especially noticeable in smaller towns and rural areas where Casey's has a strong presence. In these locations, consumers might not have many other choices, but they are still keenly aware of their budget, especially when economic conditions are tight.
The ease with which customers can find alternative places to purchase fuel, groceries, or prepared foods directly impacts their bargaining power. While Casey's strategically targets small towns, the presence of supermarkets, dollar stores, or even other small independent retailers can give customers options, potentially driving down prices or demanding better service.
For instance, in 2024, convenience store sales continued to see competition from traditional grocery stores and even online delivery services expanding their offerings. This broadens the competitive landscape, giving consumers more choices beyond the typical quick-stop options, thereby increasing their leverage.
Individual customers at Casey's General Stores generally buy in small quantities, which means their individual ability to negotiate prices or terms is quite limited. This fragmented purchasing behavior inherently reduces their direct bargaining power.
However, the sheer number of these individual customers creates a different kind of influence. Casey's Rewards program, for instance, has over 9 million members, demonstrating the collective impact of its customer base. This loyalty program allows Casey's to leverage customer data for personalized offers, effectively engaging a large group and shaping their purchasing decisions through tailored incentives and discounts.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, making price comparisons and online reviews readily available. This transparency significantly amplifies their bargaining power, even for seemingly small purchases like convenience store items. For instance, readily available fuel price apps allow consumers to quickly identify the cheapest options nearby, putting pressure on Casey's to remain competitive.
The increasing ease with which consumers can research and compare offerings directly impacts their willingness to pay. This is evident across various sectors, and convenience stores are not immune. Casey's General Stores, like its competitors, must consider this informed customer base when setting prices and developing loyalty programs.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Customers can easily compare fuel prices across multiple stations within a small radius, influencing their choice of where to fill up.
- Influence of Online Reviews: While more common for larger purchases, customer reviews on service and product quality can still sway decisions for convenience items and food offerings.
- Fuel Price Volatility: In 2024, fuel prices experienced fluctuations, making customers more vigilant in seeking out the best deals, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Switching Costs for Customers
The bargaining power of customers for Casey's General Stores is influenced by low switching costs. Customers can readily switch to a competitor for fuel or prepared food items without incurring significant expense or effort. This means Casey's must continually provide competitive pricing, quality products, and convenient service to keep customers loyal.
In 2024, the convenience store sector remains highly competitive, with numerous national and regional chains vying for market share. For instance, major competitors like Circle K, 7-Eleven, and regional players often offer similar product assortments and loyalty programs. This ease of substitution amplifies customer power.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers face minimal barriers when choosing an alternative convenience store or a different retail channel for their purchases.
- Price Sensitivity: Fuel prices, in particular, are a significant driver for many customers, making them highly sensitive to price differences between competing stations.
- Convenience Factor: While convenience is a draw, it's also a factor that can be replicated by competitors, further empowering customers to switch if another location is more convenient or offers better value.
Customers' bargaining power at Casey's General Stores is moderate, primarily due to low switching costs and increasing price sensitivity, especially for fuel. While individual customers have little leverage, their collective presence, amplified by loyalty programs like Casey's Rewards with over 9 million members, grants them influence. The ease of comparing prices, particularly for gasoline, and the availability of numerous competitors in 2024, such as Circle K and 7-Eleven, empower consumers to seek better value.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Evidence/Data (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal cost or effort for customers to choose a competitor for fuel or snacks. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High | Customers actively compare fuel prices using apps; 2024 saw fuel price volatility increasing this vigilance. |
| Information Availability | High | Easy access to competitor pricing and online reviews influences purchasing decisions. |
| Customer Volume | Moderate (Collective) | Over 9 million members in Casey's Rewards program demonstrate collective influence through loyalty and data. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Numerous convenience stores and supermarkets offer similar products, increasing customer options. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Casey's General Stores Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for Casey's General Stores, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning. You're viewing the exact document you'll receive, offering a thorough examination of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes. Once purchased, you'll gain immediate access to this professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The convenience store sector is a crowded arena, featuring a wide array of competitors. These range from national giants such as 7-Eleven and Circle K, which boast extensive store networks, to smaller regional operators and independent, single-location stores. This broad spectrum of players means Casey's faces competition from entities of all sizes and operational models.
Casey's General Stores, holding its position as the third-largest convenience store retailer in the United States, navigates this intensely competitive environment. Its significant scale, however, is juxtaposed against a market populated by many smaller, often locally focused, businesses. This dynamic creates a complex competitive landscape where market share can be influenced by factors beyond sheer store count.
Further intensifying the rivalry is Casey's dual identity as the fifth-largest pizza chain in the U.S. This means it competes not only within the convenience retail space but also against dedicated quick-service restaurants and other pizza providers. The company's strategy to integrate prepared food offerings, particularly its popular pizza, places it in direct competition with a different set of businesses, increasing the overall competitive pressure.
The convenience store sector is expanding, with a projected market size of USD 2.39 trillion in 2025, anticipated to climb to USD 3.11 trillion by 2030. This robust growth fuels intense competition among established players and new entrants vying for market dominance.
Companies are actively pursuing store expansion and innovative service offerings to capture a larger share of this expanding market. This competitive drive, intensified by industry growth, directly impacts the rivalry among convenience store operators like Casey's General Stores.
Casey's General Stores stands out in the convenience store landscape by heavily emphasizing its prepared food offerings, particularly its popular made-to-order pizza and freshly baked donuts. This strategic focus on quality food items helps to differentiate Casey's from competitors who primarily rely on undifferentiated fuel and snack sales. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Casey's reported that its prepared foods and beverages category generated over $2.3 billion in revenue, highlighting the significance of this differentiator.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, particularly significant fixed assets like real estate and specialized equipment, can trap companies like Casey's General Stores in the market. This means even when profitability wanes, these substantial investments make it difficult and costly to leave, forcing them to continue operating and thus intensifying competition. For instance, the cost of divesting or repurposing a large network of convenience stores and their associated fuel infrastructure can be prohibitive.
While Casey's has demonstrated growth, the broader convenience store sector often experiences consolidation. Smaller, less efficient operators facing these high exit barriers may struggle to adapt or sell their assets, leading them to continue competing even in a weakened state. This can further fuel rivalry as these businesses fight to survive.
The implications for competitive rivalry are clear:
- Sticky Investments: Significant capital tied up in physical locations and equipment discourages exiting the market, keeping more players active.
- Forced Competition: Companies may operate at lower margins or even losses to avoid the sunk costs of exiting, leading to prolonged competitive pressure.
- Consolidation Dynamics: High exit barriers can slow down consolidation, allowing weaker players to persist and maintain a competitive presence longer than might otherwise occur.
Strategic Commitments and Acquisitions
Casey's General Stores exhibits intense competitive rivalry, underscored by its aggressive strategic commitments. In fiscal year 2025, the company achieved its highest-ever annual store acquisition total, bringing on board 270 new locations. This expansion included the significant acquisition of 198 CEFCO stores from Fikes Wholesale.
This proactive growth strategy directly escalates competitive pressures. By substantially increasing its market footprint, Casey's is positioned to exert greater influence and potentially marginalize smaller, less resourced competitors within the convenience store sector.
- Aggressive Expansion: Casey's acquired 270 stores in fiscal year 2025, a record for the company.
- Key Acquisition: The CEFCO deal added 198 stores to Casey's portfolio.
- Market Impact: This rapid growth intensifies competition and challenges smaller players.
Competitive rivalry at Casey's General Stores is fierce, amplified by the sheer number of players in the convenience store sector, from national chains to local independents. Casey's, as the third-largest convenience store operator in the U.S., faces constant pressure from its peers who are also expanding and innovating.
The company's dual role as a major pizza provider, ranking fifth nationally, further intensifies this rivalry by placing it in direct competition with quick-service restaurants. This broad competitive landscape is further heated by the sector's projected growth, with the market expected to reach USD 3.11 trillion by 2030, encouraging aggressive expansion and service differentiation.
Casey's strategic emphasis on prepared foods, like its popular pizza, helps it stand out against competitors focused mainly on fuel and snacks. In fiscal year 2024, this category alone brought in over $2.3 billion in revenue, demonstrating its importance in a crowded market.
High exit barriers, due to substantial investments in real estate and equipment, mean that even struggling businesses remain in the market, prolonging competitive intensity. This is evident in Casey's own aggressive expansion, acquiring a record 270 stores in fiscal year 2025, including the significant purchase of 198 CEFCO locations, which directly increases market pressure on smaller rivals.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Casey's Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| National Chains | Extensive store networks, strong brand recognition (e.g., 7-Eleven, Circle K) | Direct competition for market share and customer loyalty. |
| Regional/Local Operators | Targeted customer base, localized offerings | Compete on convenience and community connection. |
| Quick-Service Restaurants | Focus on prepared food, dining experience (e.g., pizza chains) | Indirect competition for food spending, especially with Casey's pizza offerings. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers have numerous alternatives for purchasing fuel, ranging from supermarket fuel stations to big-box retailers, and even standalone gas stations. This broad availability increases the threat of substitutes for Casey's. For instance, in 2024, Walmart continued to expand its fuel offerings at many locations, often providing competitive pricing that directly impacts convenience store fuel sales.
The long-term threat from electric vehicles (EVs) is also significant, as consumers increasingly adopt them. While many convenience stores, including Casey's, are investing in EV charging infrastructure, the fundamental shift away from gasoline-powered vehicles represents a substantial substitute. By the end of 2023, EV sales in the US had already surpassed 1.2 million units, a trend expected to accelerate through 2024 and beyond.
Casey's faces significant threats from substitutes across its product categories. For its popular prepared foods, alternatives like McDonald's, Subway, and local delis offer convenient meal options. Even the option of preparing meals at home presents a substitute, especially with the rising popularity of meal kit services and readily available grocery items.
In the grocery and beverage sector, the substitutes are even more numerous. Traditional supermarkets, discount retailers like Dollar General, and large mass merchandisers such as Walmart provide a wider selection and often lower prices on staple goods and drinks. Furthermore, the growth of online grocery delivery services, like Instacart and Amazon Fresh, directly competes by offering doorstep convenience, further eroding the unique value proposition of a convenience store for these items.
The growing popularity of online retail and food delivery services presents a significant threat of substitutes for convenience stores like Casey's General Stores. Consumers can now easily order groceries, snacks, and even prepared meals directly to their homes through various e-commerce platforms and delivery apps, bypassing the need for a physical visit. This shift in consumer behavior is particularly impactful as these digital channels offer convenience and often a wider selection, directly competing with the core offerings of convenience retailers.
The convenience store sector itself is responding to this threat by integrating their own digital strategies. For instance, many are developing or enhancing their own mobile apps and online ordering systems, often partnering with third-party delivery services. This adaptation is crucial for survival, as failing to offer comparable digital convenience could lead to a substantial loss of market share. In 2024, the online grocery market continued its robust growth, with a significant portion of consumers demonstrating a preference for the ease of home delivery, underscoring the ongoing pressure from this substitute channel.
'Do-It-Yourself' Options
The threat of do-it-yourself (DIY) substitutes for convenience store offerings is significant, particularly for price-sensitive consumers. Many customers can opt to prepare meals at home, brew their own coffee, or purchase snacks in bulk from larger retailers, often at a lower overall cost than buying individual items from a convenience store. This DIY trend represents a readily available alternative that bypasses the convenience factor, directly impacting demand for pre-packaged foods and beverages.
For instance, the average American household spends approximately $3,500 annually on groceries, with a portion of that dedicated to items often found in convenience stores. However, the convenience premium charged by these stores can mean a single meal or coffee costs considerably more than its homemade equivalent. In 2024, the average price of a cup of coffee at a convenience store could range from $2.50 to $4.00, whereas brewing at home might cost less than $0.50 per cup. Similarly, a pre-made sandwich might cost $6-$8, while ingredients for a homemade sandwich could be as low as $2-$3.
- DIY Meal Preparation: Consumers can save significantly by preparing meals at home instead of purchasing ready-to-eat options from convenience stores.
- Home Coffee Brewing: The cost difference between brewing coffee at home and buying it from a convenience store is substantial, making it an attractive substitute.
- Bulk Snack Purchases: Buying snacks in larger quantities from supermarkets or wholesale clubs offers a more economical alternative to convenience store single-serving options.
- Cost Savings Focus: Price-sensitive consumers are more likely to adopt DIY habits to reduce their overall spending on food and beverages.
Changing Consumer Lifestyles and Health Trends
The growing emphasis on health and wellness, alongside the increasing adoption of GLP-1 medications, presents a significant threat of substitutes for convenience stores like Casey's. Consumers may increasingly opt for healthier food alternatives, potentially bypassing traditional convenience store fare. For instance, the global health and wellness market was valued at approximately $4.5 trillion in 2023, indicating a strong consumer shift towards healthier choices.
This trend could lead consumers to reduce their overall food consumption or seek out specialized healthier options not readily available in many convenience store formats. This dynamic pressures convenience retailers to adapt their product mix. In response, many convenience chains are expanding their fresh food and healthier snack offerings to meet evolving consumer demands.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Growing health consciousness drives demand for fresh, unprocessed foods.
- Impact of GLP-1 Medications: These drugs can lead to reduced appetite, potentially decreasing overall food purchases from convenience stores.
- Retailer Adaptation: Convenience stores are increasing offerings of fresh produce, salads, and healthier grab-and-go options.
- Market Value: The global health and wellness market's substantial size underscores the significant shift in consumer priorities.
The threat of substitutes for Casey's extends beyond direct competitors to include alternative consumption methods. Consumers can choose to prepare meals at home, brew their own coffee, or buy snacks in bulk from supermarkets, often at a lower cost. For example, the average price of a convenience store coffee in 2024 might be $3.50, while home-brewed coffee could cost under $0.50. This DIY approach directly challenges the convenience premium Casey's charges.
Furthermore, the rise of online grocery delivery services and meal kit subscriptions offers significant substitution opportunities. Platforms like Instacart and Amazon Fresh provide doorstep convenience and a wider selection of goods, directly competing with Casey's core offerings. The online grocery market continued its robust growth in 2024, with many consumers prioritizing the ease of home delivery.
The increasing consumer focus on health and wellness, coupled with the adoption of medications like GLP-1s that can reduce appetite, also presents a substitute threat. Consumers may shift towards healthier options or simply consume less, impacting sales of traditional convenience store fare. The global health and wellness market, valued at approximately $4.5 trillion in 2023, highlights this significant consumer shift.
Casey's faces a multitude of substitutes across its product lines, from fuel to prepared foods and groceries. These substitutes range from direct competitors like other convenience stores and supermarkets to alternative consumption methods such as home preparation and online delivery services. The evolving consumer preferences towards health and the potential impact of appetite-reducing medications further broaden this threat landscape.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Casey's | 2024 Trend/Data |
| Fuel | Supermarket fuel stations, Big-box retailers | Price competition, potential loss of traffic | Walmart's continued expansion of fuel offerings |
| Prepared Foods | Fast-food chains (McDonald's, Subway), Home cooking, Meal kits | Competition for meal occasions | Continued popularity of fast-casual dining |
| Groceries & Beverages | Supermarkets, Discount retailers (Dollar General), Online grocery delivery | Price sensitivity, wider selection, convenience | Robust growth in online grocery market |
| Convenience Services | Online ordering platforms, Delivery apps | Bypassing physical store visits | Increased consumer preference for home delivery |
| Health & Wellness | Health food stores, Home-prepared healthy meals, GLP-1 medication impact | Shift away from traditional convenience store offerings | Global health and wellness market valued at $4.5 trillion (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to launch a new convenience store chain, particularly one featuring prepared foods like Casey's, is considerable. This includes expenses for acquiring land, building new stores, purchasing necessary equipment, and stocking initial inventory. For instance, a new store build can easily range from $1 million to $5 million, depending on size and location, making the upfront investment a significant hurdle for potential competitors.
For new competitors looking to enter the convenience store market, securing reliable access to distribution channels presents a significant hurdle. Casey's General Stores, for instance, operates three company-owned distribution centers, a substantial investment that ensures a consistent supply of a vast majority of its products and fuel. This integrated system is not easily replicated.
The sheer complexity and expense involved in building out a comparable network of warehouses and logistics operations are formidable barriers. New entrants would struggle to achieve the same level of efficiency and cost-effectiveness as Casey's established infrastructure, making it difficult to compete on product availability and delivery speed.
Established convenience store chains like Casey's General Stores benefit significantly from strong brand loyalty, a factor that erects a substantial barrier for potential new entrants. Their well-recognized brands and effective customer loyalty programs, such as Casey's Rewards which boasts over 9 million members, cultivate a dedicated customer base. This loyalty means newcomers must undertake considerable marketing expenditure and offer compelling incentives to persuade customers to switch from familiar and trusted providers.
Regulatory Hurdles and Permits
The convenience store sector faces significant regulatory challenges that act as a barrier to new entrants. These include stringent rules governing fuel sales, which often require specialized permits and adherence to environmental standards. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a new business license in the United States can range from several weeks to months, depending on the state and specific industry requirements.
Furthermore, regulations concerning food safety, alcohol sales, and zoning laws add layers of complexity. New businesses must invest considerable resources in understanding and complying with these diverse requirements. Obtaining all necessary permits can be a lengthy and expensive process, diverting capital and attention away from core business operations.
- Fuel Sales Regulations: Compliance with environmental and safety standards for underground storage tanks and dispensing equipment.
- Food Safety Standards: Adherence to health department regulations for food handling, preparation, and storage.
- Alcohol and Tobacco Sales: Obtaining specific licenses and complying with age verification and sales restrictions.
- Zoning and Land Use: Meeting local government requirements for business location and operation, impacting site selection and expansion.
Economies of Scale and Experience
Economies of scale significantly deter new entrants in the convenience store sector. Established players like Casey's General Stores, with their extensive network, leverage bulk purchasing power, reducing per-unit costs for inventory and supplies. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Casey's reported over $15 billion in revenue, enabling substantial negotiation leverage with suppliers that a new, smaller competitor could not match.
The operational experience gained by Casey's over decades allows for optimized supply chains, efficient store layouts, and refined marketing strategies. These efficiencies translate into better pricing and service, creating a high barrier for newcomers who would need substantial investment to replicate such operational sophistication. Without achieving similar scale, new entrants would likely face higher operating costs per unit, impacting their ability to compete on price or service.
- Economies of Scale: Casey's fiscal year 2024 revenue of over $15 billion highlights its significant purchasing power, allowing for lower input costs compared to potential new entrants.
- Operational Experience: Decades of experience enable Casey's to optimize logistics, inventory management, and customer service, creating an efficiency gap that is costly for new competitors to bridge.
- Marketing Efficiencies: Established brands benefit from widespread recognition and more cost-effective marketing campaigns due to their scale, making it harder for new entrants to build brand awareness.
- Capital Requirements: The substantial capital needed to establish a network of stores, achieve comparable scale, and gain operational experience acts as a major deterrent to new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Casey's General Stores is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. Building a new convenience store chain involves significant upfront costs for real estate, construction, and inventory, often ranging from $1 million to $5 million per store. Additionally, replicating Casey's integrated distribution network, which includes three company-owned distribution centers, requires substantial investment and operational expertise.
New competitors also face challenges in overcoming Casey's strong brand recognition and loyalty programs, such as Casey's Rewards, which has over 9 million members as of 2024. This established customer base necessitates considerable marketing investment and attractive incentives for newcomers to gain market share. Furthermore, navigating complex regulations related to fuel sales, food safety, and alcohol licensing adds further barriers, demanding significant time and resources for compliance.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for land, construction, equipment, and initial inventory (estimated $1M-$5M per store). | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Distribution Network | Casey's operates three company-owned distribution centers, ensuring efficient supply. | Replicating this integrated system is costly and complex for new players. |
| Brand Loyalty & Rewards Programs | Over 9 million members in Casey's Rewards program foster customer retention. | New entrants need substantial marketing to attract customers away from established brands. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict rules for fuel sales, food safety, alcohol, and zoning add complexity. | Requires significant investment in legal, compliance, and licensing processes. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Casey's General Stores is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, including annual filings and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific market research from reputable firms and news from trade publications to capture competitive dynamics.
