Cadence Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cadence Bank Bundle
Cadence Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the forces of buyer power, supplier influence, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for navigating this environment effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Cadence Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cadence Bank, like many financial institutions, depends on technology providers for essential services like core banking software, cybersecurity, and digital customer interfaces. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be substantial when their offerings are unique, costly to replace, or when there's a limited pool of comparable providers. For instance, the global market for specialized financial technology (FinTech) solutions saw significant investment in 2024, with venture capital funding reaching billions, indicating the critical nature and potential leverage of key technology partners.
Financial data and analytics providers hold significant bargaining power over Cadence Bank. The reliance on accurate, real-time information for critical functions like risk assessment and investment strategy means switching providers can be costly and disruptive. For instance, in 2024, the financial data market, including analytics, was valued at over $30 billion globally, highlighting the scale and importance of these services.
The uniqueness and comprehensiveness of data offerings, coupled with the integration challenges, further amplify supplier power. Banks like Cadence often depend on specialized datasets or proprietary algorithms that are not easily replicated. The cost and time required to migrate data and retrain personnel can deter banks from switching, effectively locking them into existing relationships.
The availability of skilled professionals in banking, technology, and wealth management significantly impacts Cadence Bank's supplier power. A tight labor market, especially for specialized roles like AI engineers or cybersecurity experts, can empower employees and recruitment agencies, driving up compensation and benefits costs. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals continued to outstrip supply, with average salaries for these roles seeing substantial increases.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, while not typical suppliers, exert significant influence by providing operating licenses and setting compliance standards for Cadence Bank. Their mandates for increased capital reserves and enhanced risk management directly affect operational flexibility and profitability. For instance, in 2024, the banking sector continued to navigate evolving capital adequacy ratios and liquidity coverage requirements, adding to the cost of doing business.
These bodies can increase costs by imposing stricter compliance measures and higher capital requirements. For Cadence Bank, this means allocating more resources to meet these demands, potentially reducing funds available for lending or investment. The ongoing evolution of regulations, such as those related to cybersecurity and consumer protection, necessitates continuous adaptation and investment in compliance infrastructure.
- Increased Capital Requirements: Regulators often mandate higher capital ratios, forcing banks like Cadence to retain more earnings or seek additional capital, impacting return on equity.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to complex and evolving regulations, including anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) rules, incurs substantial operational expenses.
- Operational Restrictions: Regulatory frameworks can limit certain business activities or impose specific operational procedures, affecting the bank's agility and product offerings.
- Risk Management Mandates: Enhanced requirements for stress testing and risk mitigation strategies demand significant investment in technology and personnel.
Interbank Lending Market
Cadence Bank, like many financial institutions, taps into the interbank lending market to manage its short-term liquidity needs. This market acts as a crucial source of funds, and the terms available there directly impact the bank's cost of operations.
The bargaining power of suppliers in this context is significant. Conditions within the interbank market, often shaped by central bank monetary policy and broader economic stability, dictate the interest rates at which banks can borrow. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve's policy rate, which influences interbank lending, remained a key factor for banks like Cadence.
- Interbank Lending as a Supplier Source: Banks rely on this market for immediate funding, making lenders in this space powerful suppliers.
- Interest Rate Influence: Central bank policies, such as the Federal Funds Rate, directly affect interbank lending rates, impacting Cadence Bank's cost of funds.
- Economic Stability Factor: Overall economic health and perceived risk in the financial system can amplify or diminish the bargaining power of interbank lenders.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cadence Bank is notably influenced by technology providers and data analytics firms. These entities can command significant leverage due to the specialized nature of their services and the high costs associated with switching. For example, global spending on financial technology solutions continued to rise in 2024, underscoring the critical reliance of banks on these partners.
Furthermore, the interbank lending market acts as a crucial supplier of liquidity for Cadence Bank. The terms of these short-term loans, heavily influenced by central bank policies and overall economic stability, directly impact the bank's cost of operations. In 2024, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions significantly shaped the rates available in this market.
| Supplier Type | Impact on Cadence Bank | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, Cybersecurity) | High switching costs, reliance on specialized solutions | Billions invested in FinTech globally; critical for operations |
| Data & Analytics Providers | Essential for risk assessment and strategy; integration challenges | Global financial data market valued over $30 billion |
| Interbank Lenders | Source of short-term liquidity; cost of funds influenced by policy | Federal Reserve policy rates a key determinant of borrowing costs |
What is included in the product
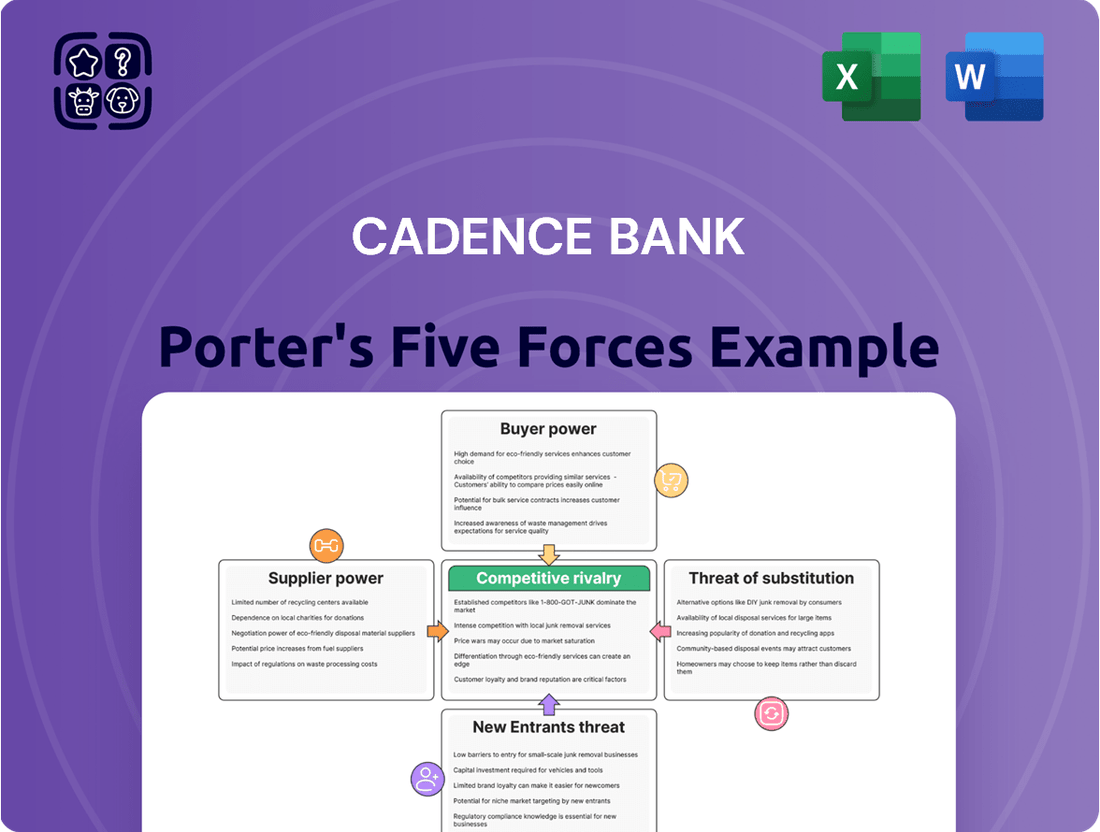
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Cadence Bank, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
Instantly understand competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, allowing for rapid identification of key challenges and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual retail customers typically wield limited bargaining power. This is largely because many core banking products like checking accounts, savings accounts, and mortgages are fairly standardized. The increasing ease of switching banks, particularly with the growth of digital banking platforms, means customers can move relatively easily if they find better offers elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, many neobanks and traditional banks continued to compete aggressively on interest rates for savings accounts, with some offering APYs exceeding 4.5%, directly impacting customer retention.
Commercial clients, especially larger enterprises with intricate banking requirements like substantial lending or sophisticated treasury management, wield considerable bargaining power. These clients frequently engage in negotiations over interest rates, service fees, and the customization of banking solutions to meet their specific operational demands. For instance, in 2024, large corporate clients of banks like Cadence Bank often have the leverage to seek out and secure better terms from competing institutions, given the relatively low switching costs for many core banking services.
Wealth management clients, particularly high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors, wield considerable bargaining power. Their ability to shift substantial assets means they can demand highly competitive fees and customized investment solutions. For instance, in 2024, the average assets under management for ultra-high-net-worth individuals globally exceeded $30 million, giving them significant leverage.
These sophisticated clients require personalized attention and tailored strategies, further amplifying their bargaining position. They expect bespoke financial planning, access to exclusive investment opportunities, and a high degree of responsiveness from wealth management firms. This demand for specialized service means firms must compete not only on performance but also on the quality and depth of their client relationships.
Digital-Savvy Customers
Digitally-savvy customers are increasingly demanding seamless online experiences and innovative digital tools from their banks. This trend puts pressure on institutions like Cadence Bank to continually invest in advanced technology to meet these expectations. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 70% of U.S. bank customers reported using mobile banking apps, highlighting the widespread adoption of digital channels.
These customers wield significant indirect power by their willingness to switch to fintech companies or challenger banks if traditional banks fail to keep pace with digital offerings. This competitive pressure forces established banks to enhance their digital platforms, offering features like intuitive mobile interfaces, easy online account opening, and robust digital payment solutions. A 2024 survey indicated that nearly 40% of consumers would consider switching banks for a superior digital experience.
- Increased demand for digital channels: Customers expect 24/7 access and self-service options.
- Threat of switching to fintechs: A significant portion of customers are open to alternative financial providers offering better digital experiences.
- Pressure for technological investment: Banks must allocate resources to upgrade digital infrastructure and develop new online tools.
- Focus on user experience: The ease of use and functionality of digital platforms are becoming key differentiators.
Depositors (Core vs. Wholesale)
Depositors represent a significant force for Cadence Bank, particularly when distinguishing between core and wholesale customers. Core deposits, excluding brokered and public funds, are a bedrock of stability for the bank. While individual depositors generally wield little individual bargaining power, larger institutional depositors or those with substantial balances can exert influence, especially when interest rates are climbing. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, the average interest rate paid on interest-bearing deposits for U.S. commercial banks saw an increase, reflecting this dynamic.
- Core depositors provide a stable, low-cost funding base.
- Wholesale depositors, often large institutions, possess greater bargaining power.
- Negotiation leverage increases for depositors in a rising interest rate environment.
- The Federal Reserve's policy rate hikes in 2023 and early 2024 directly influenced deposit pricing.
The bargaining power of customers for Cadence Bank is multifaceted, influenced by customer segment and the evolving financial landscape. While individual retail customers have limited power due to standardized products, larger commercial and wealth management clients can negotiate favorable terms. The increasing demand for digital services also empowers customers to switch providers for better online experiences, forcing banks to invest in technology.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power | Key Drivers | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Retail | Low | Standardized products, ease of switching | High competition on savings APYs, some exceeding 4.5% |
| Commercial Clients (Large) | High | Complex needs, negotiation on rates/fees, low switching costs for core services | Ability to secure better terms from competing institutions |
| Wealth Management | High | Substantial asset shifts, demand for customization and personalized service | Average global UHNW assets exceeded $30 million |
| Digitally-Savvy | High (Indirect) | Expectation of seamless digital experience, willingness to switch to fintechs | Nearly 40% would switch for a superior digital experience |
Same Document Delivered
Cadence Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Cadence Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the banking industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This detailed analysis is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, providing valuable strategic intelligence.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Cadence Bank faces intense competition from a multitude of regional and community banks concentrated in its Southern and Texas operating areas. This rivalry is particularly fierce as these institutions vie for customer deposits and actively seek to expand their loan books.
The competition manifests through aggressive pricing strategies on loans and deposits, alongside a constant push for product differentiation and superior customer service. For instance, in 2024, many community banks in Texas continued to offer highly competitive rates on savings accounts, often exceeding national averages by 50 basis points, directly challenging larger players like Cadence.
Cadence Bank faces intense competition from large national and global banks. These behemoths boast vast financial resources, allowing them to invest heavily in technology and talent, often offering more attractive rates and a wider array of sophisticated financial products. For instance, as of early 2024, major players like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America reported trillions in assets under management, dwarfing smaller regional banks and enabling them to absorb market fluctuations and invest aggressively in digital transformation initiatives that enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Fintech companies and neobanks are intensifying competition for Cadence Bank. These agile digital players, like Chime and SoFi, are capturing market share by offering streamlined, low-cost digital banking and specialized financial services. For instance, Chime reported over 14 million customers by late 2023, highlighting the significant customer migration away from traditional institutions.
Merger and Acquisition Activity
Merger and acquisition (M&A) activity is a significant factor shaping competitive rivalry within the banking industry, particularly for regional players like Cadence Bank. This trend is driven by a desire for scale, efficiency, and expanded market reach.
The banking sector, including the regional segment where Cadence operates, has seen a notable uptick in M&A. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. banking sector witnessed a considerable number of deals, with many focusing on consolidation to achieve greater economies of scale and broader geographic footprints. This consolidation inherently intensifies competition by creating larger, more resource-rich entities that can challenge existing market dynamics. These combined entities often boast enhanced technological capabilities and a wider array of financial products and services, putting pressure on smaller or less integrated competitors.
- Increased Consolidation: The banking industry continues to consolidate, with regional banks frequently involved in M&A to gain market share and operational efficiencies.
- Larger Competitors Emerge: Successful mergers create larger, more formidable competitors with expanded branch networks, customer bases, and service offerings.
- Diversification of Offerings: Acquired banks often bring complementary services, allowing the merged entity to offer a more comprehensive suite of financial products, thereby increasing competitive pressure.
- Impact on Regional Banks: For regional banks like Cadence, this heightened M&A activity means facing rivals that are often larger, more technologically advanced, and possess greater financial muscle.
Product and Service Differentiation
Competitive rivalry in banking is significantly fueled by how institutions differentiate their products and services. This often translates into specialized lending options, robust treasury management solutions, and comprehensive wealth management services. For instance, many banks are investing heavily in digital banking tools, aiming to provide seamless online and mobile experiences that set them apart.
Banks actively seek to offer unique value propositions to capture and keep customers in a highly competitive landscape. This differentiation is key to standing out. For example, in 2024, many regional banks are focusing on personalized customer service and community engagement as a way to differentiate from larger national institutions.
- Specialized Lending: Offering niche loan products tailored to specific industries or customer needs.
- Treasury Management: Providing advanced tools for businesses to manage cash flow, payments, and liquidity.
- Wealth Management: Delivering personalized financial planning, investment advice, and estate planning services.
- Digital Banking Tools: Enhancing mobile apps and online platforms for user-friendly account management, payments, and customer support.
Cadence Bank operates in a highly competitive environment, facing pressure from numerous regional and community banks, particularly in its core Southern and Texas markets. These smaller institutions actively compete for deposits and loans, often employing aggressive pricing and focusing on personalized customer service to attract clients. Furthermore, large national and global banks, with their extensive resources and advanced digital capabilities, present a significant competitive challenge, as do agile fintech companies and neobanks that are rapidly gaining traction with streamlined, low-cost offerings.
Merger and acquisition activity further intensifies this rivalry, as successful consolidations create larger, more powerful competitors with broader reach and enhanced service portfolios. This dynamic landscape necessitates continuous innovation and strategic differentiation for Cadence Bank to maintain its market position.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Actions | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Regional & Community Banks | Aggressive pricing on loans/deposits, personalized service | Community banks in Texas offering savings rates 50 bps above national average |
| National & Global Banks | Heavy investment in technology, wider product range, attractive rates | JPMorgan Chase & Bank of America's trillions in AUM enabling aggressive digital investment |
| Fintech & Neobanks | Streamlined digital offerings, low costs, specialized services | Chime's reported 14M+ customers by late 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies present a significant threat of substitutes for Cadence Bank, particularly in payments and lending. Digital payment platforms like PayPal and Square, along with peer-to-peer lending services such as LendingClub, offer convenient and often cheaper alternatives for consumers and businesses. In 2023, the global digital payments market was valued at over $2.5 trillion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift away from traditional banking channels for many transactions.
These fintech solutions can directly siphon revenue from Cadence Bank by facilitating payments and loan origination outside of the bank's ecosystem. For instance, online loan aggregators can connect borrowers with multiple lenders, bypassing the need for a bank loan application. This competitive pressure forces traditional banks to innovate and adapt their offerings to remain relevant in an increasingly digitized financial landscape.
The increasing prevalence of non-bank lenders, such as online platforms and specialized financing companies, presents a significant threat of substitution for Cadence Bank. These entities offer alternative credit avenues, potentially siphoning off market share from traditional banking services.
For instance, the alternative lending market in the U.S. saw substantial growth, with estimates suggesting it could reach hundreds of billions of dollars in annual origination by 2024, providing a clear alternative for borrowers seeking faster or more flexible financing options than those offered by conventional banks.
For wealth management and investment services, online brokerage platforms and automated robo-advisors present significant substitutes to Cadence Bank's offerings. These digital alternatives frequently boast lower fee structures and enhanced accessibility, attracting a wider spectrum of investors, from those just starting out to seasoned individuals seeking cost-effective solutions.
The rise of platforms like Robinhood and Betterment exemplifies this threat. In 2024, the robo-advisor market alone was projected to manage trillions of dollars in assets globally, demonstrating their substantial market penetration and appeal. Many of these platforms offer fractional share trading and user-friendly interfaces, further lowering the barrier to entry and making them attractive alternatives to traditional banking wealth management services.
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets present a nascent but potentially significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. While their primary adoption is for speculative investment, the underlying technology could eventually enable them to function as alternatives for payment processing and value storage, bypassing conventional financial intermediaries.
The ongoing evolution of digital asset infrastructure and regulatory clarity will be key determinants of their substitutive power. For instance, by the end of 2023, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies fluctuated significantly, reaching highs of over $2.5 trillion at certain points, indicating substantial investor interest and the growing scale of this alternative asset class.
- Growing Adoption: Increased retail and institutional interest in cryptocurrencies suggests a potential shift in how some individuals and businesses manage and transact value.
- Technological Advancements: Developments in blockchain technology and stablecoins aim to improve transaction speed and reduce volatility, making digital assets more viable for everyday use.
- Regulatory Landscape: Evolving regulations globally will shape the accessibility and legitimacy of cryptocurrencies as payment and storage alternatives.
- Long-Term Disruption: While not an immediate widespread substitute, the long-term disruptive potential for traditional banking services remains a considerable threat as digital assets mature.
In-House Corporate Treasury Management
Larger commercial clients, particularly those with sophisticated financial operations, might opt to manage their treasury functions and liquidity internally. This trend is driven by a desire for greater control and customization, potentially leading them to bypass traditional banking treasury management services. For instance, in 2024, many large corporations continued to invest in advanced treasury management systems (TMS) that offer real-time visibility and automated workflows, reducing their need for external treasury support.
The availability of specialized corporate treasury solutions, often provided by fintech firms or dedicated treasury service providers, presents a significant substitute. These solutions can offer highly tailored services, including advanced cash forecasting, risk management, and payment processing, which may exceed the standard offerings of a commercial bank like Cadence. This competitive landscape means that banks must continually innovate to retain clients seeking specialized treasury capabilities.
The threat of substitutes in corporate treasury management is amplified by technological advancements. Companies can leverage sophisticated software and platforms to streamline their treasury operations, from cash pooling and reconciliation to foreign exchange management. This in-house capability or reliance on specialized third-party solutions directly competes with the treasury services offered by Cadence Bank.
Consider the following factors influencing the threat of substitutes:
- Technological Advancements: The increasing sophistication and accessibility of treasury management software enable companies to bring functions in-house.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: For large clients, the long-term cost savings and enhanced control from in-house management can outweigh the fees associated with bank services.
- Specialized Providers: The growth of fintech and dedicated treasury solution providers offers specialized expertise and tools that can be more attractive than generic banking services.
- Regulatory Environment: Evolving regulations might also encourage or necessitate certain treasury functions to be managed more directly by corporations.
Fintech companies and digital platforms offer compelling substitutes for Cadence Bank's services, particularly in payments, lending, and wealth management. These alternatives often provide lower fees, greater convenience, and enhanced accessibility, drawing customers away from traditional banking channels.
The global digital payments market, valued at over $2.5 trillion in 2023, highlights a significant shift. Similarly, the projected growth of the robo-advisor market, expected to manage trillions in assets globally by 2024, underscores the appeal of these digital substitutes for investment services.
Moreover, the alternative lending market in the U.S. is expected to reach hundreds of billions in annual origination by 2024, presenting a direct substitute for traditional bank loans.
| Service Area | Substitute Offering | Key Differentiator | Market Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payments | Digital Payment Platforms (e.g., PayPal, Square) | Convenience, Speed | Global digital payments market > $2.5 trillion (2023) |
| Lending | Online Lenders, Peer-to-Peer Platforms (e.g., LendingClub) | Faster Approval, Flexibility | U.S. alternative lending market ~$100s of billions annually (2024 projection) |
| Wealth Management | Robo-Advisors, Online Brokerages (e.g., Betterment, Robinhood) | Lower Fees, Accessibility | Robo-advisor market trillions in AUM globally (2024 projection) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces substantial regulatory barriers that significantly deter new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve's capital adequacy ratios, such as the Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) requirement, which for larger banks can exceed 9%, necessitate considerable upfront investment. This, coupled with complex licensing processes and ongoing compliance mandates like the Bank Secrecy Act, creates a formidable challenge for any new institution seeking to establish itself.
Establishing a new bank, like Cadence Bank, demands significant capital. For instance, in 2024, regulatory bodies like the Federal Reserve often mandate minimum capital ratios, such as a Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio of at least 4.5% of risk-weighted assets. This translates into billions of dollars for a sizable institution, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
Beyond regulatory capital, new entrants must fund extensive operational infrastructure. This includes investing in secure IT systems, physical branch networks, and skilled personnel. The sheer scale of these upfront costs, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars, effectively deters many potential competitors from even attempting to enter the banking sector.
Brand reputation and trust are significant barriers for new entrants in banking. Cadence Bank, like other established institutions, has cultivated decades of customer loyalty and a perception of reliability. For instance, in 2023, Cadence Bank reported a customer satisfaction score of 82%, a testament to its established trust.
Technological Investment and Infrastructure
The constant need for substantial technological investment acts as a significant hurdle for potential new entrants into the banking sector. Developing and maintaining cutting-edge digital platforms, robust cybersecurity measures, and advanced data analytics capabilities requires immense capital outlay and specialized knowledge.
For instance, in 2024, the global banking sector's spending on IT is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, reflecting the scale of investment required. New banks would need to match or exceed these expenditures to offer competitive services.
- High Capital Requirements: New entrants must invest heavily in core banking systems, digital channels, and cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Rapid Technological Evolution: Continuous upgrades are necessary to keep pace with advancements in AI, blockchain, and cloud computing, demanding ongoing R&D and capital.
- Talent Acquisition: Securing skilled IT professionals and data scientists in a competitive market adds to operational costs and complexity for new players.
Fintech Companies Expanding into Banking
Fintech companies are increasingly moving beyond their initial niche services to offer a broader range of banking products, directly challenging traditional institutions like Cadence Bank. This expansion means that what were once specialized tech providers are now becoming direct competitors in core banking areas such as lending and payments.
Their agility and digital-first approach allow them to innovate rapidly and attract customers with user-friendly interfaces and often lower fees. For instance, by mid-2024, several prominent fintechs had secured significant funding rounds, enabling them to scale operations and invest heavily in customer acquisition and technological development, thereby increasing the competitive pressure on established banks.
- Fintech Expansion: Many fintechs are broadening their services to include traditional banking functions, acting as new entrants.
- Agility and Technology: Their inherent flexibility and tech focus enable swift innovation and customer acquisition.
- Competitive Pressure: This trend intensifies competition, potentially impacting market share and profitability for incumbent banks.
- Funding Growth: Significant venture capital flowing into fintechs in 2024 fuels their ability to challenge established players.
The threat of new entrants for Cadence Bank remains moderately low, largely due to the substantial capital and regulatory hurdles inherent in the banking industry. Established trust and brand loyalty also serve as significant deterrents for newcomers. While fintechs present a growing challenge, their ability to fully replicate the comprehensive service offerings and regulatory standing of traditional banks is still developing.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Minimum capital ratios and upfront infrastructure investment | CET1 ratio requirements (e.g., 4.5% of risk-weighted assets) necessitate billions for large banks. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Licensing, ongoing compliance (e.g., Bank Secrecy Act) | Complex and costly to navigate, demanding significant legal and operational resources. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Customer loyalty and perceived reliability | Established banks like Cadence Bank benefit from decades of trust; e.g., 82% customer satisfaction in 2023. |
| Technological Investment | IT systems, cybersecurity, digital platforms | Global banking IT spending projected in hundreds of billions in 2024; requires continuous, substantial investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cadence Bank leverages data from financial statements, investor relations reports, and industry-specific market research to assess competitive intensity.
We integrate insights from regulatory filings, analyst reports, and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the banking industry's competitive landscape.
