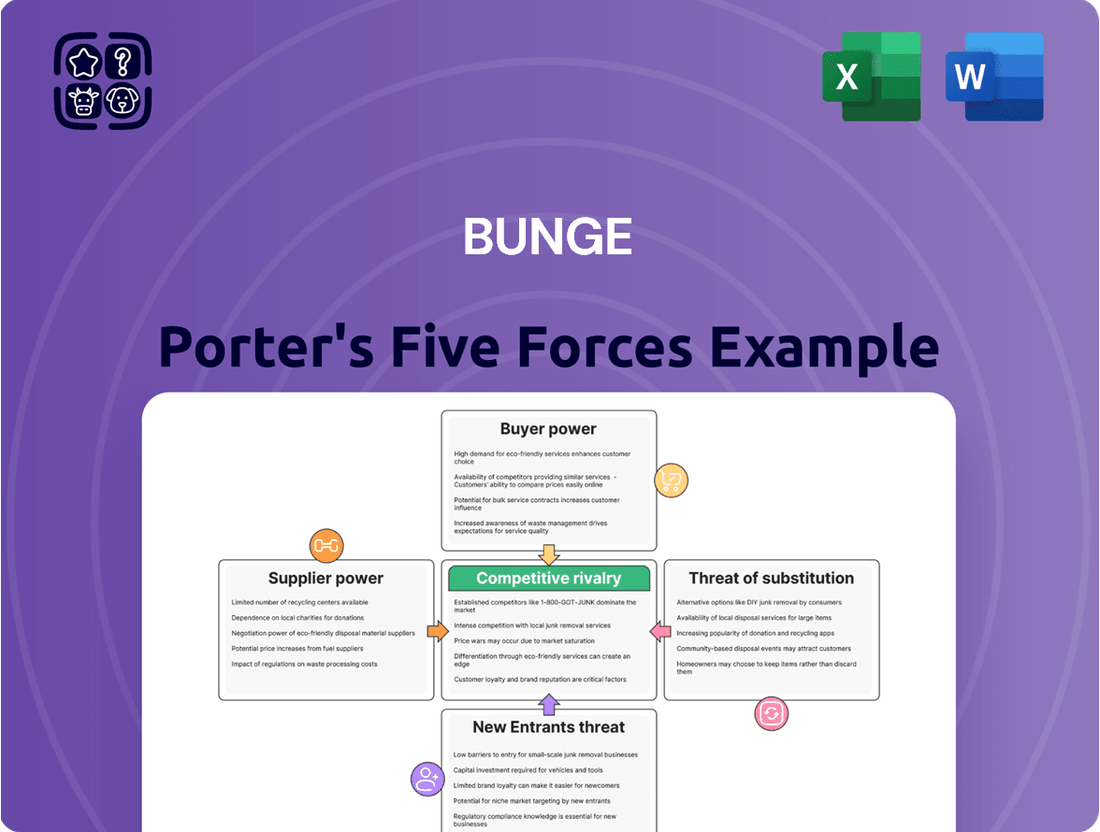
Bunge Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bunge Bundle
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intricate competitive landscape Bunge operates within, detailing the power of buyers, suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the agricultural and food processing industries effectively.
The complete report unlocks a deeper understanding of Bunge's strategic positioning and the underlying pressures shaping its profitability. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making by exploring the full analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bunge experiences considerable supplier concentration, especially for crucial agricultural inputs such as seeds and fertilizers. A handful of dominant companies control these essential markets, granting them significant influence over pricing and contract conditions. In 2024, for example, the four largest seed providers held more than 60% of the worldwide market share.
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly amplified by input price volatility. For instance, the agricultural sector, a key area for companies like Bunge, often experiences sharp fluctuations in the cost of essential inputs such as fertilizers.
This volatility directly impacts a company's operational expenses and profit margins. In 2022, a notable surge in fertilizer prices, driven by factors like supply chain disruptions and geopolitical events, placed considerable pressure on Bunge's cost structure.
Such price swings empower suppliers, as they can leverage periods of high demand or limited supply to dictate terms and increase prices, thereby strengthening their position in negotiations with buyers like Bunge.
Bunge's reliance on specific agricultural regions, like the Americas for soybeans and corn in 2024, grants significant leverage to suppliers within those concentrated areas. This geographic focus means that disruptions or shifts in production in these key territories can disproportionately impact Bunge's supply chain.
Supplier Switching Costs
Supplier switching costs present a significant challenge for Bunge. For instance, shifting from one agricultural supplier to another requires substantial investment in building new relationships, reconfiguring logistics chains, and rigorously verifying the quality and consistency of incoming goods. These expenditures directly limit Bunge's ability to easily change suppliers.
These high switching costs effectively bolster the bargaining power of Bunge's existing, established suppliers. When it's costly and time-consuming to find and onboard new suppliers, Bunge is more likely to accept the terms offered by current partners, potentially leading to higher input costs.
- High Switching Costs: Bunge faces significant expenses when changing agricultural suppliers, encompassing relationship building, logistical adjustments, and quality assurance protocols.
- Reduced Flexibility: These costs diminish Bunge's operational flexibility, making it harder to respond to price changes or seek alternative sourcing options.
- Supplier Leverage: Established suppliers can leverage these switching costs to negotiate more favorable terms, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into processing and distribution, thereby becoming competitors, is generally low for Bunge, particularly concerning raw agricultural commodities. While theoretically possible, the substantial capital investment and established infrastructure required for large-scale processing and global logistics present a significant barrier to entry for most suppliers.
This forward integration threat is mitigated by Bunge's extensive and complex global supply chain and processing capabilities. For instance, in 2024, Bunge operated numerous crushing plants and strategically located distribution hubs worldwide, handling millions of tons of soybeans, corn, and other oilseeds annually. Building a comparable network would demand immense resources, making it an unlikely move for most upstream suppliers.
- Low Likelihood: Suppliers typically lack the scale and capital to replicate Bunge's processing and distribution network.
- High Barriers: Establishing global logistics, crushing facilities, and marketing channels requires significant investment, estimated in the billions for a comparable operation.
- Bunge's Advantage: Bunge's integrated model, from sourcing to delivering finished products, creates a competitive moat against potential supplier encroachment.
Bunge's suppliers hold considerable power due to market concentration, particularly in seeds and fertilizers, where a few major players controlled over 60% of the global market share in 2024. This concentration, coupled with input price volatility and Bunge's reliance on specific geographic regions, empowers suppliers to dictate terms and influence pricing, directly impacting Bunge's operational costs and profit margins.
High switching costs for Bunge, involving new relationships, logistics, and quality verification, further solidify supplier leverage. While the threat of suppliers integrating forward is low due to Bunge's extensive global infrastructure, established suppliers can capitalize on these barriers to negotiate more favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on Bunge | Supplier Power Level |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Seeds/Fertilizers) | Limited sourcing options, price sensitivity | High |
| Input Price Volatility (e.g., Fertilizers) | Increased operational costs, margin pressure | High |
| Geographic Reliance (e.g., Americas for Soybeans) | Vulnerability to regional disruptions | Moderate to High |
| Supplier Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility, higher costs to change providers | High |
| Forward Integration Threat | Minimal due to Bunge's infrastructure scale | Low |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the five key competitive forces impacting Bunge's industry, analyzing supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing rivalry to inform strategic decisions.
Pinpoint and mitigate competitive threats with a visual representation of each force, enabling proactive strategy development.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bunge's substantial industrial customer base, including major food manufacturers and bioenergy producers, wields significant bargaining power. These large-volume buyers frequently negotiate for better pricing and contract terms due to their purchasing scale. For instance, in 2024, the agricultural commodity sector saw intense price negotiations driven by these key industrial players, impacting Bunge’s margins.
Bunge's diverse customer base, spanning food processors, animal feed producers, and bioenergy companies, significantly dilutes the bargaining power of individual customers. This broad reach means that no single customer segment holds enough sway to dictate terms, as Bunge can readily shift focus or supply to other segments if one becomes too demanding. For instance, in 2024, Bunge reported that its agribusiness segment, which serves a wide array of industrial and food customers, remained a robust contributor to its overall revenue, underscoring the benefit of this widespread demand.
Customer switching costs for Bunge, while generally lower than supplier switching costs, can still influence their bargaining power. For instance, a food manufacturer might incur expenses related to retooling production lines or qualifying new ingredient suppliers, particularly if Bunge offers specialized or proprietary ingredients. In 2024, the agricultural commodity sector saw ongoing volatility, meaning the effort to find equally reliable global suppliers with consistent quality could be a significant deterrent for some Bunge customers.
Information Availability
Customers in the agribusiness and food sectors often possess a wealth of market intelligence, particularly concerning commodity prices and the availability of various suppliers. This increased transparency directly enhances their negotiation leverage. For instance, in 2024, global soybean prices fluctuated significantly, providing buyers with ample data points to secure favorable terms.
- Informed Negotiation: Buyers can readily compare prices and quality across multiple agribusinesses, making it harder for any single supplier to dictate terms.
- Price Sensitivity: With easy access to pricing data, customers become more sensitive to price variations, pushing for lower costs.
- Supplier Switching: readily available information on alternative suppliers lowers the cost and risk associated with switching, further empowering customers.
Downstream Integration Threat
The threat of downstream integration by large customers, while present, is somewhat mitigated by the substantial capital and specialized knowledge required for backward integration into commodity processing. This means Bunge must continually focus on delivering value and competitive pricing to retain these crucial relationships.
For instance, a major food manufacturer considering processing its own soybeans would face immense logistical hurdles and significant investment in infrastructure. In 2024, the global agricultural processing sector demands sophisticated supply chain management and risk mitigation strategies, making such a move a considerable undertaking.
This potential for customers to move upstream underscores the importance for Bunge to maintain:
- Competitive Pricing: Offering attractive price points to deter customers from seeking in-house solutions.
- Superior Service: Providing reliable and efficient processing and logistics that are difficult for individual customers to replicate.
- Innovation: Continuously improving processing techniques and product offerings to maintain a competitive edge.
Bunge's customers, particularly large industrial buyers, possess considerable bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volumes and access to market information. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, impacting Bunge's profitability. For example, in 2024, intense price negotiations within the agricultural commodity market, driven by these key players, exerted pressure on Bunge’s margins.
The wide array of customers Bunge serves, from food manufacturers to bioenergy producers, helps to fragment customer power. This diversification means that no single customer segment can dominate negotiations, as Bunge can reallocate resources to other segments. In 2024, Bunge's agribusiness segment demonstrated resilience, contributing substantially to revenue, highlighting the advantage of its broad customer base.
While switching costs for Bunge's customers are not prohibitively high, they can still influence bargaining power, especially when Bunge offers specialized ingredients or reliable global supply chains. The volatility in agricultural commodities during 2024 made it challenging for customers to find equally dependable alternative suppliers, thus reinforcing their reliance on established relationships.
Customers' access to real-time market data, particularly on commodity prices and supplier availability, significantly amplifies their negotiation leverage. The fluctuations in global soybean prices throughout 2024 provided buyers with ample data to secure advantageous terms.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Bunge (2024 Example) |
| Large Food Manufacturers | High volume purchasing, price sensitivity, market intelligence | Negotiated lower prices for commodities, potentially squeezing Bunge's margins. |
| Bioenergy Producers | Bulk purchasing, long-term contracts, alternative feedstock options | Could leverage alternative energy sources or suppliers to negotiate favorable terms for agricultural inputs. |
| Animal Feed Producers | Price sensitivity, availability of substitute ingredients | Focused on cost-effective sourcing, increasing pressure on Bunge for competitive pricing. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Bunge Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Bunge Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can confidently acquire this professionally formatted analysis, ready for immediate application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global agribusiness sector is characterized by significant industry concentration, with a handful of dominant companies like Bunge, Archer Daniels Midland (ADM), Cargill, and Louis Dreyfus Company controlling a substantial portion of the market. This limited number of major players intensifies the competitive rivalry, as each seeks to capture market share and secure lucrative customer contracts.
Bunge's extensive global footprint, spanning over 30 countries, and its diversified portfolio across the entire agricultural value chain, from sourcing to processing and distribution of oilseeds, grains, and fertilizers, significantly shapes competitive rivalry. This broad operational presence allows Bunge to effectively manage seasonal cycles, weather disruptions, and geopolitical risks, thereby strengthening its competitive stance. In 2023, Bunge reported net sales of $60.1 billion, underscoring its substantial market reach and influence.
Commodity price volatility is a major force in the agribusiness sector, directly impacting companies like Bunge. For instance, in 2024, soybean prices experienced significant fluctuations due to weather patterns and geopolitical events, directly affecting Bunge's cost of goods sold and, consequently, its profit margins. This inherent price instability forces companies to constantly manage risk and compete fiercely for every percentage point of margin.
This volatility intensifies competitive rivalry. When prices are high, margins expand, attracting new entrants and encouraging aggressive expansion from existing players. Conversely, during price downturns, companies scramble to maintain profitability, often leading to price wars and consolidation. Bunge's 2023 revenue of $54.2 billion, while substantial, is directly exposed to these market swings, highlighting the pressure to operate efficiently and strategically hedge against price fluctuations.
Mergers and Acquisitions
The agribusiness sector, particularly in the realm of crop inputs and processing, has seen substantial consolidation through mergers and acquisitions. This trend significantly impacts competitive rivalry by altering market structures and the concentration of power among key players.
A prime example is Bunge's merger with Viterra, finalized in July 2025. This transaction created a global agribusiness powerhouse, combining Bunge's processing capabilities with Viterra's extensive origination and distribution network. The combined entity, with operations spanning over 40 countries, is now a formidable competitor, influencing pricing and supply chains.
- Bunge-Viterra Merger: Created one of the largest agribusiness companies globally, enhancing market concentration.
- Industry Consolidation: Drives increased market power for merged entities, potentially leading to higher barriers to entry.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: Reshapes how companies compete on price, scale, and geographic reach.
Sustainability and Innovation Focus
Competitive rivalry in the agribusiness sector is intensifying due to a pronounced shift towards sustainability, enhanced traceability, and groundbreaking innovation. This is particularly evident in burgeoning markets for plant-based oils, fats, and proteins, as well as in the development of feedstocks with a reduced carbon footprint.
Companies like Bunge are strategically channeling investments into these crucial areas. For instance, Bunge's 2024 sustainability report highlighted a 15% increase in R&D spending focused on alternative protein sources and sustainable sourcing technologies. This proactive approach aims to secure a competitive advantage and effectively cater to the growing consumer preference for environmentally conscious products.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Bunge's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 25% by 2030 is a key differentiator.
- Innovation in Plant-Based Foods: Investments in plant-based ingredient processing are expanding Bunge's portfolio in this high-growth segment.
- Traceability Technologies: Adoption of blockchain technology for supply chain transparency is enhancing trust and meeting regulatory demands.
- Low-Carbon Feedstocks: Research into advanced biofuels and bio-based materials signifies a move towards a more sustainable operational model.
The competitive rivalry within the agribusiness sector, particularly for companies like Bunge, is characterized by intense competition among a few dominant global players and significant consolidation. This rivalry is further fueled by commodity price volatility, which necessitates efficient operations and strategic risk management to maintain profitability.
The recent merger between Bunge and Viterra, finalized in July 2025, exemplifies this trend, creating a larger, more powerful entity that will likely reshape market dynamics and competitive strategies. Companies are also investing heavily in sustainability and innovation, especially in plant-based foods and low-carbon feedstocks, to gain a competitive edge.
| Company | 2023 Net Sales (USD Billions) | Key Business Segments | 2024 Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bunge (Pre-Merger) | 60.1 | Agribusiness, Food Ingredients | Sustainability, Plant-based innovation |
| Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) | 97.9 | Nutrition, Origination & Processing | Growth in alternative proteins |
| Cargill | 176.4 | Food, Agriculture, Financial & Industrial Products | Supply chain resilience, Digitalization |
| Louis Dreyfus Company | 47.0 | Merchandising, Processing, Finance | Sustainable sourcing, Value-added products |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Bunge is significant, primarily stemming from the interchangeability of various agricultural commodities. For instance, in the oilseed sector, soybeans, palm oil, and rapeseed (canola) can often be swapped depending on market prices and specific industrial needs. In 2024, global soybean production was projected to reach over 400 million metric tons, while palm oil production hovered around 80 million metric tons, illustrating the scale of these potential substitutions.
The food ingredients sector faces a significant threat from emerging plant-based alternatives and novel proteins, including cultured meat and insect-based options. Consumer demand for ethical, sustainable, and healthier choices is driving this shift, directly challenging traditional protein sources.
For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $4.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear substitution threat to conventional ingredients. This trend is amplified by increasing investment in alternative protein research and development, with venture capital funding reaching billions in recent years, further solidifying the competitive pressure on established players.
Evolving consumer dietary preferences significantly impact the threat of substitutes. Shifts towards functional nutrition, personalized diets, and clean label ingredients create demand for alternative food components. For instance, the plant-based protein market, driven by health and sustainability concerns, offers a direct substitute for traditional animal-based proteins.
This evolving landscape fuels innovation, leading to the development of new ingredients and product formulations. In 2024, the global plant-based food market was valued at over $40 billion, demonstrating a substantial shift in consumer choices and the growing viability of substitutes for conventional food products.
Technological Advancements in Food Production
Technological advancements are rapidly creating new avenues for food production, posing a significant threat of substitution for companies like Bunge. Innovations such as precision fermentation and cellular agriculture allow for the creation of ingredients or even entire food products that can directly compete with traditional offerings. For instance, plant-based protein alternatives, often produced using these advanced methods, are gaining substantial market share, directly impacting demand for conventional agricultural commodities that Bunge processes.
These emerging technologies can bypass traditional agricultural supply chains, potentially offering cost efficiencies and novel product attributes. Vertical farming, for example, can produce certain crops with less land and water, presenting a substitute for conventionally grown produce. The global market for alternative proteins, a key area impacted by these technologies, was projected to reach over $160 billion by 2030, highlighting the scale of this disruptive potential.
- Precision Fermentation: Capable of producing proteins, fats, and flavors that can substitute for dairy, egg, and meat components.
- Cellular Agriculture: Cultivated meat and dairy offer direct replacements for animal-based products, bypassing traditional farming.
- Vertical Farming: Enables localized, efficient production of certain produce, reducing reliance on traditional agricultural regions and potentially offering fresher, more consistent alternatives.
- Plant-Based Innovations: Continued advancements in plant-based ingredients create increasingly sophisticated substitutes for meat, dairy, and other animal-derived foods.
Renewable Fuel Source Diversification
The threat of substitutes in the renewable fuel source sector, particularly for companies like Bunge that supply agricultural feedstocks, is a significant consideration. While Bunge is a key player in providing ingredients for biofuels, the broader renewable energy landscape is constantly evolving.
Technological breakthroughs and shifting government policies can accelerate the adoption of non-agricultural substitutes or entirely different types of feedstocks for renewable fuels. For instance, advancements in cellulosic ethanol production, which uses non-food plant matter, or the development of synthetic fuels, could reduce reliance on traditional agricultural inputs. In 2023, the global biofuels market was valued at approximately $150 billion, with projections indicating continued growth, but the specific mix of feedstocks is subject to change.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in areas like algae-based biofuels or waste-to-energy processes present alternatives to agricultural feedstocks.
- Policy and Regulatory Shifts: Government incentives or mandates can favor specific types of renewable fuels or feedstocks, impacting demand for Bunge's offerings.
- Feedstock Competition: Increased demand for agricultural products for food, feed, and industrial uses can divert resources away from biofuel production, increasing costs and potentially driving the search for substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Bunge is substantial across its diverse business segments. In the edible oils market, consumers and industrial users can switch between various vegetable oils like soybean, palm, and sunflower oil based on price and availability. For instance, in 2024, global soybean oil production was estimated to be around 60 million metric tons, offering a direct alternative to other oils.
The rise of plant-based alternatives in the food industry presents a significant substitution threat to Bunge's traditional ingredient offerings. Products mimicking meat, dairy, and eggs are increasingly sophisticated and gaining consumer acceptance. The global plant-based food market, valued at over $40 billion in 2024, underscores this trend.
Technological innovations in food production, such as precision fermentation and cellular agriculture, are creating new substitutes that can bypass traditional agricultural supply chains. These advancements offer potential cost efficiencies and novel product attributes, directly challenging conventional ingredients. The alternative protein market alone is projected to exceed $160 billion by 2030.
In the renewable fuels sector, alternative feedstocks and technologies pose a substitution risk to agricultural commodities used for biofuels. Advancements in cellulosic ethanol or synthetic fuels could reduce demand for crops like corn and soybeans. The global biofuels market, valued around $150 billion in 2023, is dynamic and subject to these evolving technologies and policies.
| Segment | Key Substitute(s) | 2024/2023 Data Point | Market Size/Projection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edible Oils | Palm oil, Sunflower oil, Rapeseed oil | Soybean oil production ~60 million metric tons | Global edible oils market is vast and highly interchangeable. |
| Food Ingredients (Proteins) | Plant-based meat/dairy, Cultured meat, Insect protein | Plant-based food market >$40 billion | Alternative protein market projected >$160 billion by 2030. |
| Renewable Fuels | Cellulosic ethanol, Synthetic fuels, Algae-based biofuels | Global biofuels market ~$150 billion (2023) | Technological shifts can alter feedstock demand. |
Entrants Threaten
The agribusiness and food processing sector demands significant upfront capital. Building state-of-the-art processing plants, establishing robust logistics and supply chains, and developing global operational infrastructure can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. For instance, a new large-scale grain processing facility alone can cost upwards of $100 million.
This immense financial requirement acts as a substantial deterrent for aspiring new companies. It means that only well-funded corporations or those with access to significant debt financing can even consider entering the market. In 2024, the average capital expenditure for major food processing companies globally exceeded $500 million, highlighting the scale of investment needed.
Bunge operates a vast, deeply entrenched global network for sourcing, processing, and distributing agricultural products. This intricate web of relationships and infrastructure, built over decades, represents a formidable barrier.
Replicating Bunge's established global networks and supply chains would require immense capital investment and considerable time, making it exceptionally difficult for new entrants to compete effectively. For instance, in 2023, Bunge's integrated operations spanned over 40 countries, underscoring the scale of this advantage.
The threat of new entrants into the agribusiness sector, particularly for a company like Bunge, is significantly mitigated by the sheer complexity of global regulatory environments. Operating across numerous countries means navigating a dense web of international trade regulations, stringent environmental standards, and rigorous food safety compliance protocols. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to tighten its regulations on agricultural imports, focusing on deforestation-free supply chains and pesticide residue limits, which would require substantial investment and adaptation from any newcomer.
Brand Recognition and Customer Relationships
Bunge benefits from strong brand recognition and deeply established relationships with farmers and industrial customers worldwide. For instance, in 2023, Bunge reported revenues of $60.4 billion, showcasing its significant market penetration. New competitors would require substantial time and investment to build comparable trust and market presence in this established landscape.
Building brand loyalty in the agribusiness sector is a long-term endeavor. Bunge's history, dating back to 1818, has allowed it to cultivate a reputation for reliability and quality. New entrants face the challenge of overcoming this ingrained customer preference, a hurdle that typically demands years of consistent performance and marketing expenditure.
- Brand Equity: Bunge's established brand name reduces customer price sensitivity and fosters loyalty.
- Farmer Relationships: Decades of working with agricultural producers create strong, often exclusive, supply chains.
- Industrial Partnerships: Long-standing contracts with food processors and manufacturers provide a stable demand base.
- Investment Barrier: Replicating Bunge's global network and brand trust would necessitate billions in capital investment and years of operational experience.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing giants in the agribusiness sector, such as Bunge, leverage substantial economies of scale across their operations, from global sourcing and advanced processing techniques to extensive logistics networks. This cost efficiency, built over decades, presents a formidable challenge for newcomers aiming to compete on price and volume. For instance, in 2023, Bunge reported revenues exceeding $60 billion, a testament to its operational scale.
The steep experience curve in commodity trading and sophisticated risk management further erects a significant barrier to entry. New entrants lack the established expertise and the deep understanding of market volatilities and hedging strategies that seasoned players possess. This accumulated knowledge allows incumbents to navigate price fluctuations and secure favorable contracts more effectively.
- Economies of Scale: Bunge's massive global footprint in sourcing and processing agricultural commodities allows for significant cost advantages over smaller, less established firms.
- Experience Curve: Decades of experience in commodity trading and risk management provide incumbents with superior market insights and hedging capabilities.
- Capital Requirements: The substantial investment needed to build comparable infrastructure and operational capacity deters many potential new entrants.
- Supplier and Customer Relationships: Established players have built long-term, trusted relationships that are difficult for new companies to replicate quickly.
The threat of new entrants in the agribusiness sector is generally low due to the immense capital required for infrastructure, global supply chains, and regulatory compliance. New players must overcome significant hurdles related to established relationships, brand loyalty, and economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like Bunge. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to build a new, large-scale food processing plant globally remained well over $100 million, a substantial barrier.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for facilities, logistics, and technology. | Deters smaller players; requires significant funding. | Bunge's 2023 revenue: $60.4 billion. New plant costs: $100M+. |
| Brand Equity & Relationships | Established trust with farmers and industrial customers. | Difficult to replicate; requires time and marketing investment. | Bunge's operational history dates back to 1818. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale global operations. | New entrants struggle to compete on price and volume. | Bunge's integrated network spans over 40 countries. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating diverse international trade and food safety laws. | Requires specialized expertise and compliance investment. | EU tightening import regulations on deforestation-free supply chains in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial reports, market research studies, and industry-specific publications to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.
