Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel Bundle
Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel faces significant competitive pressures, with a moderate threat from new entrants and substantial bargaining power from buyers in the steel industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel Union Co., Ltd. is heavily shaped by the concentration of sources for crucial raw materials like iron ore and coking coal. A limited number of suppliers for these essential inputs, especially if they are large and well-established entities, can dictate terms and prices, thereby increasing Baotou Steel's operational expenses.
In 2024, China's domestic iron ore production was approximately 1.1 billion tonnes, with a significant portion concentrated in regions like Inner Mongolia. Similarly, the coking coal market, vital for steel production, also exhibits supplier concentration, allowing dominant players to influence pricing and availability for companies like Baotou Steel.
Baotou Steel's significant control over the Bayan Obo rare earth deposit, one of the world's largest, positions it as a primary internal supplier for its rare earth operations. This unique advantage substantially diminishes the bargaining power of external suppliers for raw rare earth ores, as the company can largely self-supply. In 2024, China, where Baotou is located, continued to dominate global rare earth production, accounting for approximately 70% of the world's supply.
However, for specialized processing chemicals, advanced refining agents, or high-tech equipment crucial for rare earth extraction and separation, Baotou Steel might still encounter suppliers with considerable market leverage. The global rare earth processing industry is complex, with a limited number of specialized chemical producers and equipment manufacturers holding significant market share. This concentration means that while Baotou controls the ore, its reliance on these niche suppliers for critical inputs can still exert some influence on its costs and operational efficiency.
Switching suppliers for critical raw materials like iron ore and coking coal presents significant hurdles for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel. Reconfiguring extensive supply chains, the rigorous process of qualifying new materials to meet stringent quality standards, and adapting complex production processes all incur substantial costs and operational disruptions. These switching costs effectively lock Baotou Steel into relationships with its current suppliers, diminishing its bargaining leverage and empowering suppliers to dictate pricing and terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers represents a significant concern for Baotou Steel. If key raw material providers, such as iron ore or coking coal producers, were to move into steel manufacturing, they could exert considerable influence. This would allow them to dictate terms or even bypass Baotou Steel, thereby diminishing the latter's bargaining power.
For instance, if a major iron ore supplier in Inner Mongolia, which is rich in such resources, decided to establish its own steel production facilities, it would fundamentally alter the supply chain dynamics. This hypothetical scenario would empower the supplier by giving them direct access to the end market, making Baotou Steel more reliant on their pricing and availability.
- Suppliers integrating forward into steel production could directly compete with Baotou Steel.
- This integration would increase supplier leverage by allowing them to control both raw material supply and finished steel output.
- The potential for forward integration by suppliers of critical inputs like iron ore and coking coal heightens their bargaining power over Baotou Steel.
Importance of Raw Materials to Production
The criticality of specific raw materials to Baotou Steel's continuous production and the quality of its final products directly impacts supplier power. For instance, high-grade iron ore or specific rare earth concentrates are indispensable, meaning suppliers of these crucial inputs have substantial influence due to the lack of viable alternatives or the severe impact of supply disruptions.
In 2024, Baotou Steel's reliance on key inputs like high-grade iron ore, which is essential for steel quality, highlights the bargaining power of its primary ore suppliers. Any disruption or price increase from these suppliers can significantly affect Baotou Steel's production costs and output capacity.
- Criticality of Inputs: Baotou Steel's production heavily depends on specific raw materials, making the suppliers of these materials powerful.
- Rare Earth Dependence: The company's significant role in rare earth processing means suppliers of high-purity rare earth concentrates wield considerable influence.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Disruptions in the supply of these critical raw materials can halt production, underscoring the suppliers' leverage.
- Lack of Alternatives: The absence of readily available substitutes for essential inputs further strengthens the bargaining position of Baotou Steel's suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel is significant, particularly for essential raw materials like iron ore and coking coal, where market concentration allows key providers to influence pricing and terms. While Baotou Steel benefits from internal rare earth supply, its reliance on specialized chemicals and equipment for processing still leaves it vulnerable to powerful niche suppliers.
Switching costs for critical inputs are high, creating supplier lock-in and limiting Baotou Steel's negotiation leverage. Furthermore, the threat of suppliers integrating forward into steel production poses a substantial risk, potentially shifting power dynamics and increasing Baotou Steel's dependence on their pricing strategies.
| Factor | Impact on Baotou Steel | 2024 Data/Context |
| Supplier Concentration (Iron Ore/Coking Coal) | Increases supplier leverage, potentially raising costs. | China's 2024 domestic iron ore production ~1.1 billion tonnes, with regional concentration. |
| Baotou Steel's Rare Earth Control | Reduces external supplier power for raw rare earth ores. | China's 2024 global rare earth production share ~70%. |
| Reliance on Specialized Chemicals/Equipment | Maintains leverage for niche suppliers in processing. | Complex global rare earth processing industry with few specialized producers. |
| Switching Costs | Locks Baotou Steel into existing supplier relationships. | High costs associated with reconfiguring supply chains and qualifying new materials. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Potential for suppliers to directly compete, increasing their power. | Hypothetical scenario of major ore suppliers establishing steel facilities. |
What is included in the product
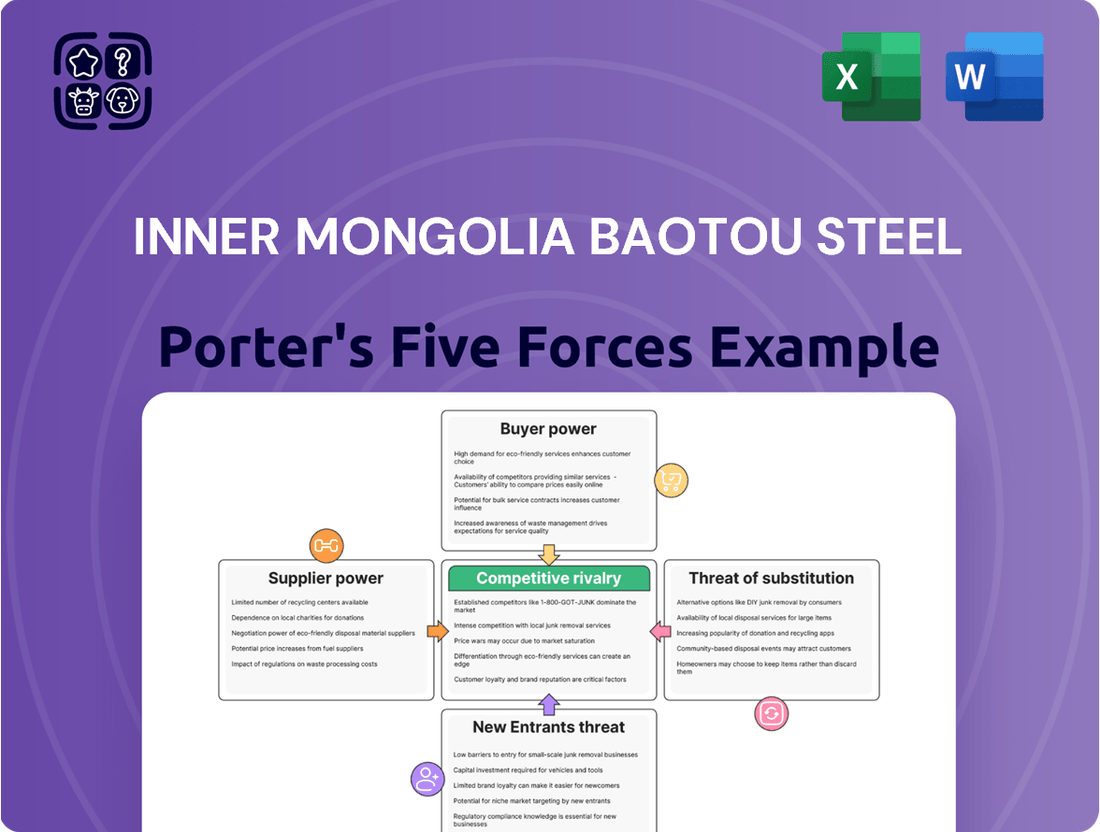
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel dissects the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on the steel industry.
Navigate the competitive landscape of Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel Porter's Five Forces with a visually intuitive dashboard, instantly highlighting key pressure points for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel's customers is significantly influenced by customer concentration and the volume of their purchases. Major industries like construction, machinery, automotive, and railway represent key client bases, and their collective demand shapes Baotou Steel's pricing power.
When a small number of large customers represent a substantial portion of Baotou Steel's revenue, these clients gain considerable leverage. This allows them to negotiate for reduced prices, more favorable payment schedules, or specific product customizations, directly impacting Baotou Steel's profitability and operational flexibility.
For instance, if a single major automotive manufacturer procures a significant percentage of Baotou Steel's output, their ability to switch suppliers, or even threaten to do so, grants them substantial bargaining power. This is especially true if Baotou Steel has limited alternative buyers for those specific steel grades.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly amplified due to the standardization of many of Baotou Steel's core products, including plates, sections, rods, and wires. These are largely commodity items, meaning buyers can readily switch to competitors if prices are more favorable, as there's little to differentiate one supplier's basic steel from another's. This ease of substitution means customers hold considerable sway.
Customers' ability to substitute steel with materials like aluminum, advanced composites, concrete, or timber significantly impacts their bargaining power. As these alternatives become more cost-competitive or offer enhanced performance for specific applications, buyers have more choices, allowing them to push for lower prices from Baotou Steel.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, especially large automotive and construction firms, is a key factor influencing Baotou Steel. These major clients could potentially establish their own steel production facilities, thereby reducing their reliance on external suppliers like Baotou Steel.
This capability, though requiring substantial capital investment, grants customers significant bargaining power. It forces Baotou Steel to be more competitive on pricing and terms to secure and maintain these crucial relationships.
- Automotive Industry Dependence: In 2024, the automotive sector remained a significant consumer of steel, with global vehicle production expected to reach approximately 85 million units. A major automaker integrating backward could significantly impact Baotou Steel's order book.
- Construction Sector Leverage: The construction industry, a large steel consumer, often operates on tight margins. The potential for large construction companies to explore in-house steel production, particularly for large infrastructure projects, represents a credible threat.
- Capital Investment Threshold: While backward integration is capital-intensive, the growing trend of vertical integration across industries, driven by supply chain resilience concerns, makes this a viable long-term consideration for large customers.
Price Sensitivity of End Markets
The price sensitivity of industries relying on steel, such as construction and automotive, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. These sectors often operate on thin margins, making them highly attuned to fluctuations in raw material costs. For instance, in 2024, the construction sector, a major consumer of steel, faced rising labor and material costs, intensifying pressure on steel suppliers like Baotou Steel to offer competitive pricing.
When end markets are highly competitive, customers are more inclined to switch suppliers if they perceive a better deal. This forces steel producers to be more accommodating in their pricing strategies. In 2024, the global steel market experienced overcapacity in certain segments, further empowering buyers to demand lower prices to protect their own profitability.
- High Price Sensitivity in Construction: The construction industry, a key Baotou Steel customer, is acutely sensitive to steel prices, as it represents a substantial portion of project costs.
- Automotive Sector's Cost Pressure: The automotive industry, also a significant steel consumer, faces intense global competition, driving a strong demand for cost-effective steel inputs.
- Impact of Market Competition: In 2024, increased competition among steel manufacturers globally provided end-users with more options, strengthening their negotiating position for lower prices.
The bargaining power of Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel's customers is substantial due to product standardization and the availability of substitutes. In 2024, industries like construction and automotive, which are highly price-sensitive, exerted significant pressure on steel suppliers for lower prices. This is exacerbated by global market overcapacity, giving buyers more leverage.
Key customer industries, such as automotive and construction, are increasingly exploring vertical integration to control costs and supply chains. This threat of backward integration, while capital-intensive, forces Baotou Steel to maintain competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain these crucial relationships.
The concentration of major buyers, particularly in sectors like automotive, amplifies their negotiation power. If a few large clients account for a significant portion of Baotou Steel's revenue, they can demand concessions on pricing, payment terms, or product specifications, directly impacting profitability.
| Customer Segment | 2024 Steel Consumption (Estimated) | Key Bargaining Factors |
| Automotive | Significant portion of global steel demand | Price sensitivity, potential for backward integration, switching to alternative materials |
| Construction | Major steel consumer, especially for infrastructure | High price sensitivity due to project margins, threat of in-house production for large projects |
| Machinery & Manufacturing | Consistent demand for various steel grades | Standardized product nature, availability of competing suppliers |
Full Version Awaits
Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel, providing an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering immediate strategic insights. This detailed analysis covers the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry, all crucial for understanding Baotou Steel's competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The steel sector in China, where Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel operates, is highly fragmented with a substantial number of significant companies. This includes a mix of large state-owned enterprises and rapidly growing private firms, all vying for dominance.
Baotou Steel contends with numerous domestic competitors, many of whom possess considerable scale and market influence. For instance, in 2023, China's crude steel output reached an estimated 1.02 billion tonnes, underscoring the sheer volume and the competitive landscape it navigates.
This intense rivalry, fueled by the sheer number and size of players, often translates into aggressive pricing strategies and a constant battle for market share. Global steel producers also represent a competitive force, though the domestic market remains the primary arena for Baotou Steel's competitive struggles.
The steel and rare earth sectors are experiencing varied growth trajectories, directly impacting how fiercely companies like Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel compete. When demand is sluggish or supply outstrips it, the rivalry intensifies. Companies often resort to price reductions, higher marketing budgets, and pushing production to its limits to spread fixed costs, all in an effort to gain or maintain market share.
For instance, the global steel market saw a modest growth of around 1.5% in 2023, with expectations for a similar pace in 2024, according to industry reports. This relatively slow expansion means that any gains by one player often come at the expense of another, driving up the intensity of competition. Similarly, while the rare earth market is crucial for many high-tech applications and generally sees robust demand, periods of oversupply can quickly turn a healthy market into a battleground for market share.
Baotou Steel's competitive landscape is significantly shaped by product differentiation and switching costs. While the company does offer some specialized rare earth products, a substantial portion of its steel output consists of largely undifferentiated commodity items. This lack of unique features in many of its core products means customers have little incentive to remain loyal to Baotou Steel if a competitor offers a better price.
The low product differentiation, coupled with minimal customer switching costs, directly fuels intense price-based competition. Customers can readily shift their business to other steel suppliers without incurring significant penalties or disruptions. This forces Baotou Steel to prioritize cost efficiency and operational excellence to remain competitive in a market where price is often the primary deciding factor.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
The steel industry, including players like Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel, faces significant exit barriers. These include the substantial capital tied up in fixed assets, such as blast furnaces and rolling mills, which are highly specialized and difficult to repurpose. For instance, the global steel industry saw capital expenditures exceeding $100 billion annually in the years leading up to 2024, highlighting the scale of these investments.
Specialized labor and management expertise are also critical components that make exiting the market challenging. The closure of a large steel plant can also have considerable social implications, including job losses and impacts on local communities, which often leads to government intervention or pressure against closures. This was evident in various regions where steel plant closures faced strong opposition in the 2020s.
These high exit barriers mean that even struggling or inefficient steel producers may remain in the market longer than economically optimal. This persistence can contribute to ongoing overcapacity within the industry, a situation that has been a recurring theme, particularly in China, where excess steel production capacity has been a persistent concern for years, impacting global steel prices and profitability.
- High Capital Investment: Steel plants require billions in upfront investment, making divestment difficult.
- Specialized Workforce: Skilled labor in steel production is not easily transferable to other industries.
- Social and Political Factors: Plant closures can lead to significant unemployment and community backlash, influencing decisions.
- Industry Overcapacity: Persistent overcapacity, a known issue in the steel sector, discourages exits by keeping firms operational, albeit often at low margins.
Strategic Stakes of Competitors
The strategic importance of market share and specific product lines for Baotou Steel and its competitors significantly fuels competitive rivalry. For instance, major Chinese steel producers like Ansteel Group and HBIS Group often prioritize maintaining high production volumes to leverage economies of scale, a crucial factor in the cost-sensitive steel industry. This drive for volume can lead to aggressive pricing strategies. In 2023, China's crude steel output reached approximately 1.02 billion tonnes, underscoring the sheer scale and competitive nature of the market.
Competitors with high strategic stakes, such as those operating under government mandates to ensure regional steel supply or those aiming for national dominance, are likely to engage in more aggressive competitive tactics. These players might tolerate lower short-term profit margins to secure or expand their market position. Baotou Steel, as a significant player in North China, faces intense competition from these strategically motivated rivals who are crucial for regional economic stability and employment.
- Market Share Focus: Competitors may aggressively pursue market share, impacting pricing and profitability for all players.
- Economies of Scale: The need to maintain production volumes for cost efficiency drives intense competition, especially in a high-volume industry like steel.
- Regional Dominance: Companies with regional dominance goals may engage in price wars or strategic investments to solidify their position.
- Government Mandates: State-owned enterprises, common in China's steel sector, may be directed to maintain production, influencing competitive behavior.
The competitive rivalry within China's steel sector, where Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel operates, is extremely intense due to a large number of players, including state-owned giants and private firms. This fierce competition is evident in the sheer volume of production; China produced approximately 1.02 billion tonnes of crude steel in 2023, a testament to the scale of operations and the battle for market share.
The market's fragmentation and the presence of numerous large-scale competitors often lead to aggressive pricing and a constant struggle for dominance. While global players exist, the domestic Chinese market remains the primary battleground for Baotou Steel. This high level of rivalry is further exacerbated by relatively slow market growth, estimated at around 1.5% for 2023 and projected similarly for 2024, meaning gains for one company often come at another's expense.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Projected) | Impact on Rivalry |
| China Crude Steel Output | 1.02 billion tonnes | Similar to 2023 | High volume indicates intense competition and potential oversupply. |
| Global Steel Market Growth | ~1.5% | ~1.5% | Slow growth forces companies to fight harder for market share. |
| Capital Expenditure (Global Steel) | >$100 billion (annual avg. pre-2024) | N/A | High fixed assets create high exit barriers, keeping less efficient firms in the market. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of alternative materials presents a substantial threat to Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel's traditional steel offerings. For instance, in the automotive sector, the drive for lightweighting means materials like aluminum alloys are increasingly favored over steel, with global aluminum demand projected to grow steadily, impacting steel consumption in vehicle manufacturing.
In construction, while steel remains dominant, the use of advanced composites, high-strength concrete, and even engineered timber in certain structural applications offers viable substitutes, potentially eroding Baotou Steel's market share in these segments.
The growing adoption of carbon fiber composites in aerospace and high-performance vehicles, despite their higher initial cost, highlights a long-term trend where advanced materials can displace steel in applications demanding superior strength-to-weight ratios.
The performance of substitute materials for steel continues to improve, with advancements in areas like aluminum alloys and advanced composites offering better strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced corrosion resistance. For instance, the automotive industry is increasingly adopting aluminum, with its use in vehicles projected to rise significantly in the coming years, driven by fuel efficiency demands. This trend directly impacts steel demand.
Concurrently, the cost of these substitutes is becoming more competitive. While steel prices can fluctuate based on global commodity markets, the production costs for some alternative materials have seen a steady decline due to technological innovation and economies of scale. This makes them a more attractive option for manufacturers seeking to optimize their product costs and appeal to price-sensitive consumers.
As these alternatives become more viable and cost-effective, they pose a direct challenge to steel's traditional market dominance. This erosion of steel's appeal in specific applications, such as construction and manufacturing, could lead to a reduction in Baotou Steel's potential market share if the company doesn't adapt its product offerings or pricing strategies.
Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel faces a significant threat from substitutes, particularly as industries like automotive increasingly seek lighter, more fuel-efficient materials. For instance, the global automotive industry's push for reduced emissions and improved mileage directly fuels the demand for aluminum and advanced composites as steel alternatives. In 2024, the automotive sector continued its strong adoption of these materials, with many manufacturers setting ambitious targets for increasing the use of lightweight components, thereby directly impacting steel demand.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Ongoing advancements in material science are a significant threat to Baotou Steel. For instance, the development of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) offers superior performance characteristics compared to traditional steel grades, potentially luring away customers in the automotive sector. In 2024, the global automotive industry continued its push for lighter and more fuel-efficient vehicles, driving demand for materials like AHSS and aluminum alloys, which directly substitute conventional steel.
Innovations in manufacturing processes also introduce new substitutes. Composite materials, for example, are becoming increasingly cost-effective and versatile, finding applications in construction and infrastructure where steel has traditionally dominated. The global advanced composites market was projected to reach over $20 billion in 2024, indicating a growing competitive landscape for traditional materials like steel.
These technological shifts mean Baotou Steel must continually invest in research and development to either improve its existing steel products or explore the integration of new materials into its offerings. Failure to adapt could lead to a decline in market share as customers opt for more advanced or cost-effective substitutes.
- Technological advancements in material science introduce new substitutes for steel.
- Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) are a direct substitute, particularly in the automotive industry, which saw continued demand for lighter materials in 2024.
- Composite materials are becoming more competitive in construction and infrastructure, challenging steel's traditional dominance.
- Baotou Steel's ability to innovate and adapt to these material substitutions is crucial for its long-term competitiveness.
Substitution for Rare Earth Products
While rare earth elements are often critical for high-tech applications like magnets and catalysts, the threat of substitutes is present. Research is ongoing into alternative materials and technologies that can reduce or eliminate the need for specific rare earths. Even partial substitution or a decrease in the quantity of rare earths used in finished goods could affect the demand for Baotou Steel's rare earth products.
For example, advancements in electric vehicle motors are exploring designs that utilize fewer or no rare earth permanent magnets, potentially impacting a significant market for these elements. Furthermore, the development of new catalyst formulations in industries such as petroleum refining aims to reduce reliance on rare earth components.
- Research into alternative magnet materials: Efforts are underway to develop high-performance magnets using materials like ferrite or advanced alloys that do not require rare earths.
- Catalyst innovation: New catalytic converters are being designed to achieve desired chemical reactions with reduced or no rare earth content.
- Substitution in electronics: Some consumer electronics are exploring alternative display technologies or component designs that lessen dependence on rare earth phosphors and other materials.
The threat of substitutes for Baotou Steel's products is significant, driven by material science advancements and evolving industry demands. In the automotive sector, the push for lighter vehicles to improve fuel efficiency means aluminum alloys and advanced composites are increasingly replacing steel. For instance, the global automotive industry's commitment to sustainability and emissions reduction continued to drive the adoption of lightweight materials throughout 2024, with many manufacturers setting ambitious targets for increasing the use of aluminum and high-strength composites.
In construction, while steel remains a primary material, the growing use of engineered timber, advanced concrete formulations, and composite materials presents viable alternatives for certain structural applications. The global advanced composites market, for example, was projected to exceed $20 billion in 2024, underscoring the expanding competitive landscape for traditional materials like steel.
These material shifts, coupled with potential cost competitiveness of substitutes, necessitate continuous innovation from Baotou Steel. The company must adapt by enhancing its product offerings or exploring new material integrations to maintain market share against these encroaching alternatives.
| Substitute Material | Key Applications | 2024 Market Trend Impact on Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive (lightweighting), Aerospace | Increased demand in automotive for fuel efficiency, directly impacting steel consumption in vehicle manufacturing. |
| Advanced Composites | Aerospace, Automotive, Construction | Growing adoption in high-performance applications and infrastructure, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. |
| Engineered Timber | Construction (structural elements) | Viable alternative in certain building segments, challenging steel's dominance in traditional construction. |
| Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) | Automotive (structural components) | While a steel variant, AHSS performance can displace conventional steel grades in demanding applications. |
Entrants Threaten
The steel and rare earth mining sectors demand colossal upfront investments, often running into billions of dollars for essential infrastructure like mines, smelters, and advanced rolling mills. For example, establishing a new greenfield steel plant in 2024 can easily cost upwards of $5 billion, while rare earth processing facilities require hundreds of millions. These immense capital requirements create a significant hurdle, effectively discouraging many potential new players from entering the market.
The threat of new entrants in the steel industry, particularly for companies like Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel, is significantly mitigated by substantial economies of scale. Existing giants benefit from lower per-unit production costs due to their massive output, a hurdle for newcomers.
For instance, in 2024, major steel producers often operate plants with capacities exceeding 10 million tons per year. A new entrant would need to invest billions to achieve comparable production volumes and cost efficiencies, making it exceptionally challenging to compete on price in this commodity-focused sector.
New entrants to the steel industry, like those looking to compete with Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel, face significant hurdles in securing crucial raw materials. Established companies often have long-term supply contracts for iron ore, coking coal, and energy, making it difficult and expensive for newcomers to gain comparable access. For instance, in 2023, global iron ore prices fluctuated, with benchmarks like the Singapore benchmark for fines averaging around $115 per tonne, demonstrating the cost sensitivity of this essential input.
Developing robust distribution channels is another major barrier for potential new entrants. Building out the necessary logistics infrastructure, including transportation networks and warehousing, requires substantial capital and time. This is particularly true in a market where established players like Baotou Steel have already optimized their supply chains over many years, giving them a significant cost and efficiency advantage.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations in China act as a substantial deterrent to new entrants in the steel industry, impacting companies like Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel. Stringent environmental regulations, for instance, require significant upfront investment in pollution control technology, making it difficult for smaller or less capitalized firms to enter the market. In 2024, China continued its push for industrial upgrades and environmental protection, with the Ministry of Ecology and Environment emphasizing stricter enforcement of emissions standards for heavy industries, including steel production.
The process of obtaining permits and licenses in China's steel sector is notoriously complex and time-consuming. New companies must navigate a web of national and provincial regulations, which can add years and considerable expense to their establishment timeline. This administrative burden, coupled with ongoing industry consolidation efforts aimed at creating larger, more efficient, and environmentally compliant enterprises, effectively caps the number of new players entering the market.
- Environmental Compliance Costs: New steel plants in China face substantial costs for meeting emissions standards, often requiring advanced filtration and waste treatment systems.
- Permitting Complexity: Securing all necessary operating permits and licenses can be a multi-year process, involving numerous governmental agencies.
- Industry Consolidation: Government-backed initiatives to merge and restructure the steel sector favor established players and discourage fragmentation from new entrants.
- Capital Requirements: The high capital expenditure needed to meet regulatory and operational standards creates a significant barrier for potential new steel producers.
Brand Loyalty and Switching Costs for Customers
While basic steel products can appear as commodities, deep-seated brand loyalty and significant switching costs pose a substantial barrier for new entrants targeting Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel. Baotou Steel has cultivated robust, long-term relationships with key industrial clients, often through integrated supply chains and tailored product offerings. For instance, in 2024, major automotive manufacturers rely on Baotou Steel for specific grades of steel crucial for their production lines, a relationship built over years of consistent quality and delivery.
These established ties, coupled with the implicit costs associated with re-qualifying suppliers, vetting new product specifications, and potentially disrupting existing production processes, make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Customers often value the predictability and reliability offered by established players like Baotou Steel, which can translate into a reluctance to switch even if marginal price differences exist.
- Established Customer Relationships: Baotou Steel's long-standing partnerships with major industrial consumers in sectors like automotive and construction create a strong incumbent advantage.
- Integrated Supply Chains: Many clients are integrated into Baotou Steel's supply chain, making the logistical and operational shift to a new supplier costly and complex.
- Customized Solutions: Baotou Steel provides customized steel grades and specifications, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate immediately, increasing switching costs for clients.
- Perceived Reliability: The proven track record and consistent quality from Baotou Steel foster customer trust, creating a preference that new entrants must actively overcome.
The threat of new entrants for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel is considerably low due to several formidable barriers. The steel industry, especially in China, is characterized by immense capital requirements, with new greenfield steel plants in 2024 costing upwards of $5 billion. Furthermore, securing essential raw materials like iron ore, where prices in 2023 averaged around $115 per tonne for fines, is challenging for newcomers due to established long-term contracts held by incumbents.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing a modern steel plant requires billions in investment for infrastructure and technology. | Extremely high, deterring most potential entrants. |
| Raw Material Access | Securing consistent and cost-effective supply of iron ore, coal, and energy is crucial. | Difficult for new players without pre-existing supply agreements. |
| Economies of Scale | Large-scale producers benefit from lower per-unit costs. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies without massive output. |
| Government Policy & Regulation | Strict environmental standards and complex permitting processes add significant costs and time. | Increases upfront investment and operational complexity for new firms. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Inner Mongolia Baotou Steel leverages data from official company filings, industry-specific market research reports, and government economic databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
