Bridgestone Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bridgestone Bundle
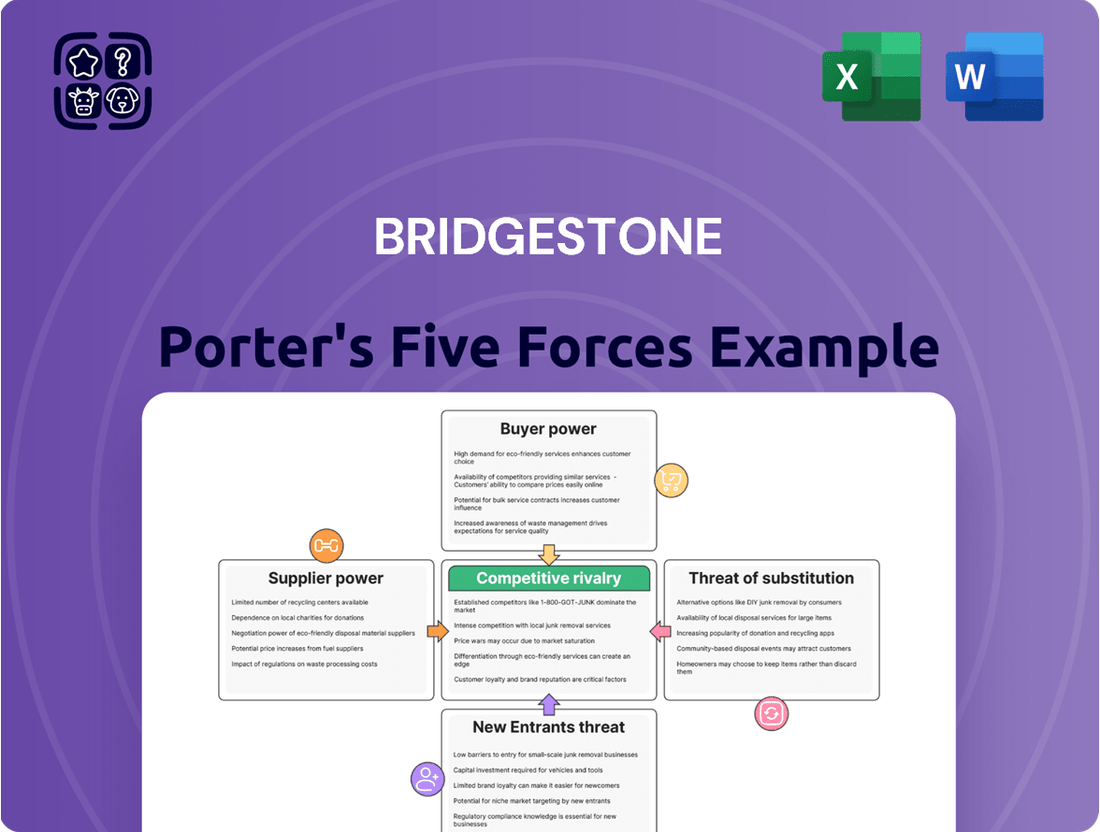
Bridgestone operates in a dynamic automotive industry, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the interplay of rivalry among existing firms, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic success.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Bridgestone’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bridgestone's reliance on a few critical raw materials, such as natural rubber, synthetic rubber, carbon black, and steel cord, positions concentrated suppliers of these inputs to exert significant bargaining power. This concentration can translate into higher input costs for Bridgestone, directly impacting its profitability. For instance, fluctuations in the price of natural rubber, a key component, can have a substantial effect on overall production expenses.
To mitigate this risk, Bridgestone is actively pursuing strategies to optimize its local sourcing of raw materials. The company aims to achieve 80-90% local sourcing for all raw materials, with the notable exception of natural rubber, where global supply chains are more prevalent. This focus on local procurement aims to reduce transportation costs and potentially offer greater control over supply, thereby lessening supplier leverage.
The costs Bridgestone incurs when switching suppliers for crucial raw materials, like synthetic rubber or carbon black, can be substantial. These expenses often involve significant investment in re-tooling manufacturing equipment, rigorous re-certification processes for new materials to meet quality standards, and establishing entirely new logistical and supply chain networks, all of which bolster supplier leverage.
Suppliers of highly specialized or unique components, or those critical to Bridgestone's production, hold significant bargaining power. This is particularly true as Bridgestone emphasizes premium tires and advanced technologies such as ENLITEN, potentially increasing its dependence on these specialized suppliers.
Bridgestone's initiative to enhance traceability in its natural rubber supply chain is a key factor. By the end of 2024, the company aims to achieve approximately 42% traceability for its global natural rubber volume, indicating a strategic effort to manage and potentially influence supplier relationships in this crucial raw material segment.
Forward Integration Threat by Suppliers
Suppliers might threaten Bridgestone by integrating forward into tire manufacturing, effectively becoming competitors. This scenario, while possible, is generally considered a lesser threat due to the substantial capital investment and advanced technical know-how required for tire production. The automotive industry, for instance, demands significant R&D and manufacturing capabilities, making it difficult for many raw material suppliers to make such a leap.
Bridgestone's strong supplier relationships are a testament to its operational strength. For example, Bridgestone was honored as a 'Supplier of the Year' by General Motors, highlighting its consistent delivery of quality products and innovative solutions. This recognition suggests that Bridgestone is adept at managing its supply chain and mitigating potential threats from its suppliers.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers could enter tire manufacturing, directly competing with Bridgestone.
- Barriers to Entry: High capital and technical expertise needed for tire manufacturing limit this threat.
- Supplier Recognition: Bridgestone's 'Supplier of the Year' award from General Motors indicates strong supplier management.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly curtails supplier bargaining power. If Bridgestone can readily source alternative raw materials or develop innovative material technologies, it lessens reliance on any single supplier. This flexibility allows Bridgestone to negotiate more favorable terms, as suppliers face competition from other material providers or from Bridgestone's own technological advancements.
Bridgestone's strategic investments in research and development are crucial in this regard. By exploring and implementing sustainable materials and advanced technologies like ENLITEN, the company actively broadens its material sourcing options. This diversification directly weakens the leverage of traditional suppliers, as Bridgestone gains the ability to switch to or develop new material solutions, thereby reducing its dependence on existing supply chains.
Bridgestone's 2024 Integrated Report underscores this commitment, detailing initiatives focused on nature positivity and fostering a circular economy. These efforts are not just about environmental responsibility but also about securing long-term material availability and reducing vulnerability to supply disruptions or price hikes from specific suppliers.
Key aspects impacting substitute input availability for Bridgestone include:
- Diversification of Raw Materials: Bridgestone's exploration of materials beyond traditional rubber, such as recycled plastics or bio-based polymers, directly counters supplier dominance.
- Technological Innovation: Investments in R&D for new tire compounds and manufacturing processes can create internal substitutes or reduce the need for specialized inputs.
- Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with multiple suppliers for critical materials ensures competitive pricing and reduces the impact of any single supplier's pricing power.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Efforts to recycle and reuse materials within the production cycle create internal sources of supply, diminishing reliance on external raw material providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Bridgestone is moderate, influenced by the concentration of key raw material producers and the costs associated with switching suppliers. While Bridgestone aims for 80-90% local sourcing by 2024 to mitigate these pressures, natural rubber remains a global commodity with price volatility. The company's investment in tracing 42% of its natural rubber by the end of 2024 signals a strategic move to better manage these supplier relationships and their associated costs.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into tire manufacturing is low due to the high capital and technical expertise required. However, suppliers of specialized components, particularly those for Bridgestone's premium and advanced technology tires, hold considerable leverage. Bridgestone's own R&D, including its focus on sustainable materials and circular economy initiatives, aims to broaden material options and reduce dependence on any single supplier.
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Bridgestone, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitute products.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces on a dynamic radar chart.
Customers Bargaining Power
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) such as General Motors are substantial clients for Bridgestone, driving a significant portion of its revenue. The sheer volume of their purchases grants these large buyers considerable leverage, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and product specifications.
Bridgestone's ongoing partnership with General Motors was highlighted when the company was named a GM Supplier of the Year for the tenth year running in 2024. This consistent recognition underscores the deep, collaborative relationship Bridgestone maintains with a key OEM, demonstrating the mutual benefit derived from these large-scale customer relationships.
Individual consumers often show significant price sensitivity when purchasing replacement tires, particularly in the more affordable segments of the market. This sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for these customers, compelling manufacturers like Bridgestone to maintain competitive pricing strategies to remain attractive.
Bridgestone's premium-priced tire offerings are not immune to this dynamic; they face pressure from brands that deliberately target the lower-priced end of the spectrum. This competitive landscape intensifies customer bargaining power, as consumers have a wider range of options to consider based on price alone.
In 2024, the automotive aftermarket, where replacement tires are a key component, continued to see robust demand, but also intense price competition. For instance, while the global tire market was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, a significant portion of this value is driven by replacement sales where price is a primary decision factor for many consumers.
The cost for consumers to switch between tire brands is generally low. This is largely because tires are often standardized in terms of dimensions and basic specifications, making it easy for buyers to find comparable alternatives. For instance, a consumer needing a 225/60R17 tire can find options from numerous manufacturers that fit their vehicle.
This low switching cost significantly enhances consumer bargaining power. They can readily compare prices, features, and promotions from different tire companies, forcing manufacturers to compete more aggressively on these factors. In 2023, the average price for a standard all-season tire in the US ranged from $100 to $200, illustrating the price sensitivity within the market.
Bridgestone actively works to mitigate this by fostering brand loyalty through programs and emphasizing superior product quality and innovation. Their investments in research and development, aiming for better fuel efficiency and durability, are key strategies to retain customers even when switching is financially simple.
Availability of Information
The increased availability of information significantly boosts customer bargaining power in the tire market. Consumers can now easily access detailed data on tire performance metrics, competitive pricing, and peer reviews across numerous online platforms. This transparency allows them to thoroughly research and compare options, leading to more informed purchasing decisions and a greater ability to negotiate favorable terms or seek out lower-cost alternatives.
Bridgestone's strategic emphasis on 'growth with quality' and strengthening its premium tire segment directly addresses this evolving customer landscape. By providing superior product performance and clear value propositions, the company aims to build brand loyalty and differentiate itself beyond price alone. This focus is crucial as customers, armed with more data, can readily identify and demand higher quality and better value.
For instance, in 2024, online tire retailers reported a substantial increase in customer engagement with product comparison tools and review sections, indicating a heightened reliance on readily available information. This trend empowers buyers to exert more pressure on manufacturers like Bridgestone to offer competitive pricing and demonstrate clear product superiority.
- Increased Online Research: Customers in 2024 spent an average of 30% more time researching tire options online compared to 2022, utilizing review sites and manufacturer specifications.
- Price Transparency: Online price comparison tools are now used by over 65% of tire purchasers, making it harder for brands to maintain significant price discrepancies without justification.
- Performance Data Accessibility: Independent testing data and user-generated performance reviews are readily available, allowing customers to directly compare tire durability, fuel efficiency, and handling.
- Bridgestone's Premium Focus: Bridgestone's investment in R&D for its premium lines, such as the Potenza and Turanza series, aims to provide tangible performance benefits that justify higher price points in an information-rich environment.
Customer Segmentation
Bridgestone caters to a broad range of customers, from individual car owners to large commercial operators in trucking, aviation, and mining. The bargaining power of these customer groups differs significantly. For instance, large commercial fleets and airlines, due to their substantial order volumes and specialized tire requirements, often possess greater leverage than individual consumers.
Bridgestone's strategic focus on expanding its B2B commercial solutions, particularly for sectors like mining, aviation, and heavy-duty trucking, directly addresses this dynamic. This expansion is driven by a co-creation approach with these key clients, aiming to build stronger relationships and potentially mitigate some of the intense bargaining power exerted by these high-volume customers.
- Passenger Vehicles: High volume, but fragmented, leading to lower individual bargaining power.
- Commercial Trucks & Buses: Significant volume and potential for fleet-level negotiations, increasing bargaining power.
- Aviation & Mining: Highly specialized needs and large, concentrated orders grant these segments substantial bargaining power.
- B2B Solutions: Bridgestone's co-creation strategy in commercial sectors aims to manage and potentially reduce customer bargaining power through tailored offerings.
The bargaining power of customers in the tire market is substantial, driven by several key factors. Large Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) like General Motors wield significant influence due to their massive order volumes, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and specifications. This is evident in Bridgestone's consistent recognition as a GM Supplier of the Year, highlighting the importance of these relationships.
Individual consumers also exert considerable power, particularly in the replacement tire market where price sensitivity is high. The ease with which consumers can switch between brands, due to product standardization and readily available online information and comparison tools, further amplifies their leverage. In 2023, the average price for a standard all-season tire in the US was between $100 and $200, reflecting this price-conscious environment.
Bridgestone actively works to counter this by focusing on brand loyalty through programs and emphasizing product quality and innovation. Their investments in R&D for premium lines like Potenza and Turanza aim to justify higher price points by offering superior performance, a strategy increasingly important as customers in 2024 spent 30% more time researching tires online compared to 2022.
| Customer Segment | Influence Factors | Bridgestone's Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| OEMs (e.g., GM) | High volume, long-term contracts | Co-creation, supplier recognition programs |
| Commercial Fleets (Trucks, Buses) | Large order volumes, specialized needs | B2B solutions, fleet-specific offerings |
| Individual Consumers | Price sensitivity, low switching costs, information access | Brand loyalty programs, R&D for premium products, value proposition |
| Specialized Sectors (Aviation, Mining) | Concentrated orders, critical performance requirements | Tailored solutions, direct client engagement |
What You See Is What You Get
Bridgestone Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Bridgestone Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of industry competition. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global tire market is intensely competitive, featuring giants like Michelin, Goodyear, and Continental, all battling for significant market share. This intense rivalry is further amplified by the presence of many regional and smaller tire manufacturers, creating a crowded and dynamic landscape.
Bridgestone held the position of the second-largest global tire company by market share in 2022, trailing closely behind industry leader Michelin. This close ranking underscores the fierce competition among the top players and the constant effort to gain or maintain dominance in this sector.
The tire industry's growth rate significantly impacts how fiercely companies compete. When the market expands quickly, there's often enough business for everyone, which can temper rivalry. However, a slower growth environment typically intensifies competition as businesses vie more aggressively for market share.
Looking at the numbers, the global tire industry is expected to see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% from 2023 through 2032. This moderate growth suggests that while opportunities exist, established players and new entrants will likely still engage in considerable competition to capture demand and expand their presence.
Bridgestone actively pursues product differentiation to stand out in the competitive tire market. This strategy focuses on advanced technology, superior performance, and enhanced durability, aiming to lessen direct price wars. For instance, Bridgestone's ENLITEN technology is a key differentiator, offering benefits like reduced rolling resistance and lighter weight.
The company is making significant strides in integrating this technology. By 2025, Bridgestone plans to equip 170 car models with OE tires featuring ENLITEN. This push for technological advancement and brand recognition helps to build customer loyalty and justify premium pricing, thereby mitigating the intensity of rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can trap companies in the tire industry, even when they are not profitable. These barriers, like specialized machinery that's hard to sell or substantial severance packages for employees, mean that exiting the market is often very costly. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition as these companies continue to operate, potentially at reduced capacity or with aggressive pricing strategies, to recoup some of their investments.
Bridgestone itself has demonstrated an awareness of restructuring needs due to these dynamics. In 2024, the company confirmed plans to close its tire manufacturing facility in La Vergne, Tennessee, with operations ceasing by 2025. This move is part of a broader business restructuring effort, signaling that even major players face pressures that necessitate difficult decisions regarding capacity and operational footprint.
- Specialized Assets: Tire manufacturing plants often contain highly specialized equipment, making resale or repurposing difficult and costly.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements or leases can create financial penalties for early termination, acting as an exit barrier.
- Workforce Restructuring Costs: Severance pay, retraining, and outplacement services for a significant workforce can represent substantial exit expenses.
- Bridgestone's 2025 Tennessee Plant Closure: This action highlights the real-world impact of restructuring in response to market conditions and the costs associated with exiting certain operations.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
Competitors' strategic aims, whether for market dominance, enhanced profitability, or pioneering technological advancements, significantly shape the competitive landscape. For example, a competitor aggressively pursuing market share through lower prices can create considerable pressure on other players in the industry.
Goodyear, a key rival, is channeling significant investment into 2025 for new product development and the modernization of its manufacturing facilities. This strategic focus is geared towards capturing a larger share of the premium tire market and bolstering its presence in high-margin segments.
- Market Share Focus: Competitors prioritizing market share may engage in aggressive pricing strategies, potentially eroding industry profitability.
- Profitability Drive: Companies aiming for profitability might concentrate on higher-value products or cost-efficiency measures, influencing market segmentation.
- Technological Leadership: A focus on innovation can lead to product differentiation and create barriers to entry for less technologically advanced rivals.
- Goodyear's 2025 Strategy: Goodyear's investments in new products and plant modernization underscore a strategic objective to strengthen its position in premium and high-profit tire categories.
The competitive rivalry within the tire industry is considerable, with Bridgestone facing strong opposition from major global players like Michelin and Goodyear. These companies are not only vying for market share but also investing heavily in innovation and operational upgrades, as seen with Goodyear's strategic focus on new product development and plant modernization for 2025. This intense competition is further fueled by a global market expected to grow at a 5% CAGR through 2032, creating opportunities but also intensifying the battle for customers.
Bridgestone's strategy of product differentiation, particularly through its ENLITEN technology, aims to mitigate direct price competition. The company's commitment to equipping 170 car models with ENLITEN by 2025 highlights this effort to build brand loyalty and command premium pricing. However, high exit barriers in the industry mean that even struggling competitors may remain active, potentially leading to sustained aggressive pricing and market pressure.
| Competitor | 2022 Market Share (approx.) | Key 2025 Strategic Focus | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Michelin | Largest | Continued innovation and premium product offerings | Sets a high benchmark for performance and quality |
| Goodyear | Second Largest (alongside Bridgestone) | New product development, manufacturing modernization | Aggressive pursuit of premium market segments |
| Continental | Significant Global Player | Technological advancement, especially in EV tires | Increased competition in emerging tire technologies |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The long-term threat of substitutes for traditional pneumatic tires looms with the ongoing development of airless tire technology and other novel mobility concepts. While these alternatives are not yet mainstream for passenger cars, significant progress could eventually diminish the market for conventional tires.
For instance, Michelin and General Motors had plans to introduce their Uptis (Unique Puncture-proof Tire System) airless tire for commercial passenger vehicles as early as 2024. Concurrently, Goodyear is actively developing non-pneumatic tires (NPTs) designed to eliminate the issues of flats and the need for regular air pressure checks, further pushing the boundaries of tire innovation.
For commercial vehicle operators, re-treaded tires present a significant threat of substitution for new tires, offering a considerably lower price point. This cost advantage makes them an attractive alternative, particularly for fleets focused on operational efficiency and managing expenses.
Bridgestone actively addresses this threat by integrating retread services into its broader commercial vehicle solutions. This strategy not only mitigates the impact of substitutes but also transforms a potential threat into a competitive advantage by offering a comprehensive package of mobility and maintenance services.
In 2024, Bridgestone's focus on reinforcing its truck and bus radial (TBR) replacement business underscores the importance of this integrated approach. By combining retreading with advanced mobility solutions and dedicated maintenance, Bridgestone aims to provide a compelling value proposition that competes effectively with the lower cost of substitute products.
The rise of public transportation and ride-sharing services presents a significant threat of substitutes for individual vehicle owners. For instance, in 2024, cities worldwide are seeing a continued surge in ride-sharing adoption, with platforms like Uber and Lyft reporting millions of daily rides. This trend could directly impact the demand for replacement tires as fewer people opt for personal vehicle ownership, relying instead on these more flexible and often cost-effective mobility solutions.
Furthermore, the potential widespread adoption of centrally managed autonomous vehicle fleets, a concept gaining traction in 2024 development cycles, could further diminish the need for privately owned cars. If these fleets become a dominant mode of transport, the market for replacement tires for personal vehicles might shrink considerably. While the global automotive tire market is still robust, driven by new vehicle production and demand for specialized tires, this shift in personal mobility directly challenges the traditional replacement tire segment.
Durability and Longevity of Tires
Improvements in tire technology are making tires last longer, which means consumers don't need to buy new ones as often. This increased durability acts as a substitute for frequent purchases, potentially impacting tire manufacturers like Bridgestone.
Bridgestone's ENLITEN technology is a prime example of this trend. It's designed to enhance both the durability and overall performance of their tires. For instance, ENLITEN technology can contribute to a longer tire lifespan, reducing the need for replacements.
- Extended Tire Lifespan: Innovations like ENLITEN aim to push the boundaries of how long tires can last, directly substituting for more frequent purchase cycles.
- Reduced Replacement Frequency: As tires become more durable, the demand for new tires from consumers who prioritize longevity will naturally decrease.
- Technological Advancement: Bridgestone's focus on technologies that improve wear resistance and structural integrity is a direct response to, and a driver of, this substitute threat.
Low-priced and Used Tires
Consumers, especially those focused on cost savings, often consider lower-priced new tires from emerging brands or even used tires as viable alternatives to premium options like those from Bridgestone. This dynamic forces manufacturers to clearly articulate the value proposition of their higher-priced products, emphasizing superior quality, durability, and performance to retain market share.
The availability of these budget-friendly substitutes directly impacts pricing power. For instance, while Bridgestone enjoys strong brand recognition and a reputation for quality, the increasing presence of affordable alternatives in the market, particularly in segments like replacement tires, necessitates continuous innovation and marketing efforts to reinforce brand loyalty and justify premium pricing.
- Price Sensitivity: A significant portion of the tire market, particularly for replacement vehicles, exhibits high price sensitivity, making lower-cost alternatives attractive.
- Used Tire Market: The used tire market, though often overlooked, represents a direct substitute for new tires, especially for consumers prioritizing minimal expenditure.
- Brand Differentiation: Bridgestone's strategy to counter this threat relies on highlighting its technological advancements, safety features, and longer lifespan, which can offset the initial cost difference for discerning buyers.
The threat of substitutes for traditional tires is multifaceted, encompassing technological advancements, alternative mobility solutions, and cost-effective options. Innovations like airless tires, exemplified by Michelin's Uptis and Goodyear's NPTs, aim to eliminate common tire issues and could significantly disrupt the market by 2024 and beyond. Ride-sharing services and potential autonomous vehicle fleets also reduce the demand for personal vehicle tires. Furthermore, the availability of retreaded and lower-priced new tires presents a constant challenge, forcing manufacturers like Bridgestone to emphasize value through durability and performance, such as with their ENLITEN technology.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Tire Market | Bridgestone's Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airless/Non-Pneumatic Tires | Puncture-proof, reduced maintenance | Potential long-term disruption of pneumatic tire demand | Development and integration of advanced tire technologies |
| Retreaded Tires | Lower cost, environmentally friendly | Significant price-based competition for new tires | Offering retreading services as part of commercial solutions |
| Ride-Sharing & Autonomous Fleets | Reduced personal vehicle ownership | Decreased demand for replacement tires in personal vehicles | Focus on fleet solutions and mobility services |
| Budget Tire Brands/Used Tires | Lower initial price | Price pressure on premium tire segments | Highlighting superior quality, durability, and performance |
Entrants Threaten
The tire manufacturing industry, where Bridgestone operates, demands immense capital. Building modern factories, acquiring advanced machinery, and investing heavily in research and development for new tire technologies easily run into billions of dollars. For instance, establishing a new, state-of-the-art tire plant can cost upwards of $500 million to over $1 billion, depending on scale and automation.
This substantial financial requirement acts as a formidable barrier, significantly deterring potential new entrants. New companies would need to secure massive funding just to get started, a challenge that few can overcome. Consequently, the threat of new companies entering the market and challenging established players like Bridgestone is considered weak.
Established tire manufacturers like Bridgestone leverage significant economies of scale in production, raw material procurement, and global distribution networks. This allows them to achieve substantially lower per-unit production costs compared to potential new entrants. For instance, Bridgestone's vast manufacturing footprint and bulk purchasing power enable cost advantages that are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
New entrants would face immense challenges in matching these cost efficiencies, particularly in areas like research and development for advanced tire technologies and extensive marketing campaigns. The capital investment required to build comparable production capacity and establish a global supply chain is a major barrier.
Bridgestone's strategic focus on reinforcing earning power and improving capital efficiency further solidifies its competitive position. By optimizing operations and investing in high-return projects, the company enhances its ability to withstand price competition and invest in future growth, making the threat of new entrants with comparable cost structures less impactful.
Bridgestone benefits from formidable brand loyalty, cultivated through decades of premium product offerings and significant investment in global motorsports, such as its Formula 1 presence. This strong brand equity makes it difficult for newcomers to capture market share. For instance, in 2024, Bridgestone continued to leverage its reputation for quality and performance, which resonates deeply with consumers and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) alike.
The company also boasts deeply entrenched distribution channels, encompassing direct relationships with major automotive manufacturers for OEM fitments and an extensive network of retail outlets worldwide. New entrants would struggle to replicate this reach, facing substantial costs and time investment to establish comparable access to customers. Bridgestone's established partnerships ensure consistent sales volume and market presence, a barrier that is hard to overcome.
Technological Expertise and R&D
The tire industry demands substantial investment in research and development, particularly in material science, product design, and advanced manufacturing techniques. New companies entering this space face a steep learning curve and the need for considerable capital to match existing players' technological capabilities. Bridgestone's commitment to innovation, exemplified by its ENLITEN technology, acts as a significant deterrent for potential entrants lacking similar levels of expertise and financial backing.
Bridgestone is actively enhancing its value proposition by integrating its ENLITEN technology with its Business Capability Management Architecture (BCMA). This fusion streamlines operations and fosters further innovation, creating a more formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, ENLITEN technology, which focuses on reducing tire weight and rolling resistance, can lead to significant fuel savings for consumers, a benefit that requires substantial R&D to replicate.
- Technological Intensity: The tire manufacturing process is highly technical, requiring specialized knowledge in polymer chemistry, aerodynamics, and manufacturing engineering.
- R&D Investment: Bridgestone consistently invests heavily in R&D; for example, in 2023, the company allocated significant resources to develop next-generation tire technologies and sustainable materials.
- Innovation as a Barrier: Proprietary technologies like ENLITEN, which optimizes tire performance and sustainability, are difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate, raising the barrier to entry.
- Integration for Advantage: The strategic fusion of ENLITEN with BCMA further solidifies Bridgestone's competitive edge by enhancing operational efficiency and accelerating future product development cycles.
Regulatory Requirements and Environmental Standards
The tire industry faces significant hurdles for newcomers due to stringent regulatory requirements and environmental standards. For instance, the European Union's Tire and Rubber Products Regulation mandates specific performance and safety criteria, alongside comprehensive lifecycle assessments. New entrants must invest heavily in research and development to meet these evolving demands, which can be a substantial barrier.
Compliance with manufacturing standards, waste disposal protocols, and detailed product labeling adds layers of complexity and expense. Bridgestone, as a major player, consistently emphasizes its dedication to sustainability and adherence to global environmental regulations in its integrated reports, demonstrating the ongoing commitment required to operate within the sector.
These regulatory burdens translate into higher initial capital outlays for new companies, impacting their ability to compete on price or innovation from the outset. For example, meeting the stringent emissions standards for manufacturing processes can require substantial upfront investment in new technologies.
- Safety Regulations: Compliance with standards like ECE R117 (noise and wet grip) necessitates advanced testing and production capabilities.
- Environmental Standards: Adherence to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) in Europe impacts material sourcing and chemical usage.
- Disposal Requirements: Regulations concerning end-of-life tire management, such as those in North America, require investment in recycling infrastructure or partnerships.
- Labeling: EU tire labeling, detailing fuel efficiency, wet grip, and noise, demands precise product data and consistent manufacturing.
The threat of new entrants in the tire industry is generally considered weak, largely due to the immense capital required to establish a competitive presence. Building modern manufacturing facilities, acquiring advanced machinery, and investing in research and development for new tire technologies can easily cost billions. For instance, a new, high-tech tire plant can cost between $500 million and over $1 billion to construct, a significant barrier for any aspiring competitor.
Existing players like Bridgestone benefit from substantial economies of scale, allowing for lower per-unit production costs through bulk purchasing and efficient global distribution. Newcomers would struggle to match these cost efficiencies, especially when factoring in the need for extensive R&D and marketing to build brand recognition. Bridgestone's continued focus on operational efficiency and innovation, such as its ENLITEN technology, further solidifies its cost advantage.
Brand loyalty and established distribution networks also pose significant challenges for new entrants. Bridgestone's decades of premium product offerings and its involvement in motorsports have cultivated strong brand equity. Furthermore, its deep relationships with automotive manufacturers for original equipment fitments and its widespread retail presence are difficult and costly for new companies to replicate, limiting their market access.
The tire sector is also characterized by high technological intensity and rigorous regulatory compliance. New companies must invest heavily in specialized knowledge and meet stringent safety and environmental standards, such as those mandated by the EU's Tire and Rubber Products Regulation. Bridgestone's ongoing commitment to sustainability and adherence to global regulations, as highlighted in its integrated reports, demonstrates the continuous investment required to operate successfully in this market.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing modern tire manufacturing facilities costs upwards of $500 million to over $1 billion. | Significant financial hurdle, requiring substantial funding for basic operations. |
| Economies of Scale | Bridgestone's large-scale production and procurement lead to lower per-unit costs. | New entrants face higher initial production costs, making price competition difficult. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Decades of brand building and established OEM and retail networks. | Difficult for newcomers to gain market share and reach customers effectively. |
| R&D and Technology | High investment in material science, design, and proprietary technologies like ENLITEN. | Requires significant expertise and capital to match technological advancements. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting stringent safety and environmental standards (e.g., EU regulations). | Adds complexity and cost to product development and manufacturing processes. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Bridgestone Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Bridgestone's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and broader economic indicators from sources like the World Bank.
