BOK Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BOK Financial Bundle
BOK Financial navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer demands. Understanding the power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the influence of suppliers is crucial for its sustained success.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BOK Financial’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BOK Financial, like many banks, depends on specialized technology for core operations and security. The market for these critical banking software providers is concentrated, meaning a few key vendors hold significant influence.
For instance, in 2024, the global banking software market was valued at approximately $30 billion, with a significant portion driven by core banking solutions. The limited number of vendors offering highly specialized, compliant, and secure core banking systems can grant them considerable bargaining power. This necessitates careful relationship management by BOK Financial to secure favorable terms and avoid dependency.
The demand for skilled professionals in finance, especially in wealth management, investment services, and digital innovation, is exceptionally high. These specialized talents are essential for BOK Financial to deliver its comprehensive range of services effectively.
This scarcity of specialized skills directly translates to increased bargaining power for these employees. Consequently, BOK Financial experienced a notable rise in personnel expenses during the first half of 2025, reflecting the competitive landscape for top talent.
Depositors, acting as suppliers of capital, wield growing influence, particularly as they become more attuned to interest rate differentials and the simplicity of moving their money. If BOK Financial fails to provide competitive deposit yields, it risks seeing customers shift their balances to banks offering better returns, compelling BOK to meticulously manage its funding expenses.
Low Switching Costs for General Services
For general services like office supplies or basic administrative support, BOK Financial benefits from a wide array of potential suppliers. This broad supplier market typically means suppliers have less leverage. If one supplier’s terms aren’t ideal, BOK Financial can readily find another, keeping supplier bargaining power in check.
The ease with which BOK Financial can switch providers for non-specialized needs directly impacts supplier negotiation. For instance, in 2024, the market for business process outsourcing (BPO) services, which can include administrative tasks, remained highly competitive with numerous providers offering flexible contracts. This competition limits the ability of any single BPO supplier to dictate terms to a large financial institution like BOK Financial.
- Diverse Supplier Base: BOK Financial can choose from many vendors for standard operational needs.
- Low Switching Costs: Moving between suppliers for general services is typically straightforward and inexpensive.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: This ease of switching diminishes the power of individual suppliers to demand higher prices or less favorable terms.
- Competitive Market for Services: The broad availability of services like IT support or stationery keeps supplier demands in check.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Suppliers of services to the banking sector, especially in crucial areas like software development and data management, face significant regulatory hurdles. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions continued to navigate evolving data privacy laws and cybersecurity mandates, such as those influenced by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in the US and GDPR in Europe. These compliance demands mean suppliers must invest heavily in security protocols and data handling practices, which can limit their flexibility and thus their bargaining power.
BOK Financial, like other banks, can leverage these stringent regulatory requirements to its advantage. By demanding suppliers meet specific, often costly, compliance benchmarks and security standards, BOK Financial effectively raises the barrier to entry and ensures a baseline level of service quality. This dynamic can reduce the number of qualified suppliers and, in turn, diminish their ability to dictate terms, thereby lowering their overall bargaining power.
Key compliance areas impacting suppliers in 2024 included:
- Data Security and Encryption Standards: Suppliers must demonstrate robust data protection measures to prevent breaches.
- Regulatory Reporting Capabilities: Software providers need to ensure their systems can facilitate accurate and timely regulatory reporting for banks.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Banks are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers' own risk management frameworks and compliance adherence.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Suppliers must have resilient operations to ensure uninterrupted service, a critical factor for financial institutions.
Suppliers of specialized technology, like core banking software providers, hold significant bargaining power due to market concentration. For instance, the global banking software market in 2024 was valued around $30 billion, with a few key vendors dominating critical solutions. This limited vendor pool means BOK Financial must manage these relationships carefully to secure favorable terms and avoid over-reliance.
The scarcity of highly skilled financial professionals, particularly in areas like wealth management and digital innovation, also enhances supplier bargaining power. This demand directly impacts BOK Financial's operational costs, as evidenced by the rise in personnel expenses observed in the first half of 2025 due to the competitive talent landscape.
Depositors, as suppliers of capital, are increasingly influential, especially with readily available information on interest rate differentials and ease of account transfers. BOK Financial must offer competitive yields to retain deposits, directly influencing its funding expenses.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on BOK Financial | 2024/2025 Data Point |
| Core Banking Software Vendors | Market Concentration, High Specialization | Requires careful relationship management, potential for higher costs | Global banking software market ~$30 billion (2024) |
| Specialized Financial Talent | Scarcity of Skills | Increased personnel expenses, competitive hiring landscape | Notable rise in personnel expenses (H1 2025) |
| Depositors | Interest Rate Sensitivity, Ease of Switching | Pressure to offer competitive yields, impacts funding costs | N/A (market-driven) |
| General Service Providers (e.g., office supplies) | Numerous Suppliers, Low Switching Costs | Limited leverage for suppliers, competitive pricing | Highly competitive BPO market (2024) |
What is included in the product
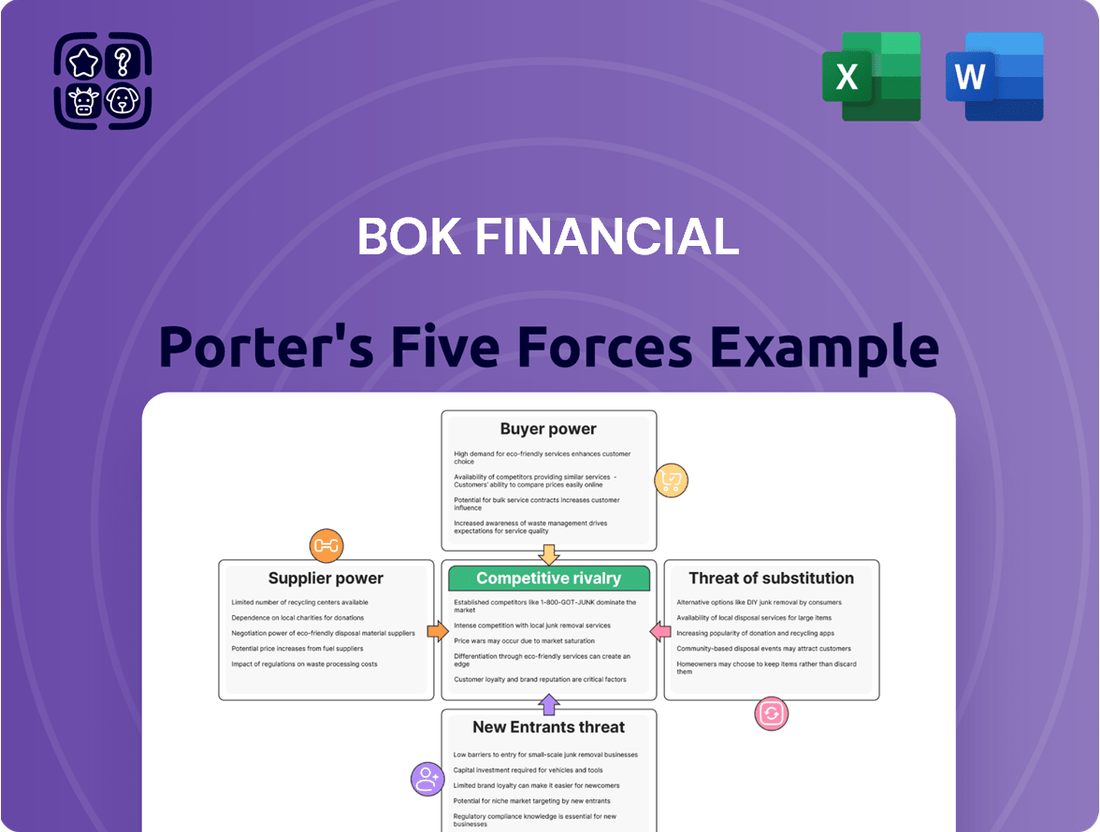
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for BOK Financial dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products impacting its banking operations.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a clear, actionable overview of BOK Financial's Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of financial services, both individuals and businesses, generally encounter minimal costs and effort when switching banks or financial providers. This is particularly true given the advancements in digital banking, which simplify account transfers and management across different institutions. For instance, in 2023, the average time to open a new bank account online was reported to be under 10 minutes for many leading digital banks, highlighting the low friction involved.
This ease of switching empowers customers, granting them considerable leverage to select institutions that offer more attractive interest rates, reduced fees, or enhanced service quality. In 2024, data from consumer surveys indicated that over 35% of banking customers actively compare offers from different providers at least once a year, driven by the low switching barriers and the potential for cost savings.
Customers today have an unprecedented array of digital financial tools at their fingertips. The rise of mobile banking apps and fintech solutions means BOK Financial's clients can effortlessly compare services, fees, and interest rates across multiple institutions. This ease of access and comparison significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, as they can quickly switch to providers offering better terms or more convenient digital experiences.
Modern banking customers increasingly demand financial products and services that are precisely tailored to their individual circumstances and financial well-being. This shift in expectation significantly influences the bargaining power of customers, pushing institutions like BOK Financial to adapt.
For instance, a significant portion of consumers, particularly younger demographics, are actively seeking out financial technology (fintech) companies that specialize in delivering highly personalized banking experiences. This trend was highlighted in a 2024 survey where over 60% of respondents indicated a preference for financial institutions offering customized digital tools and advice.
Consequently, if traditional banks fail to meet these evolving needs for personalization, customers are more likely to switch to alternative providers, often fintechs, that excel in this area. This creates a direct pressure on BOK Financial to continually innovate its service offerings and leverage data analytics to provide more bespoke solutions, thereby mitigating the risk of customer attrition.
Transparency in Fees and Rates
Transparency in fees and rates significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers in the financial sector. With a wealth of online resources, consumers can effortlessly compare pricing, interest rates, and product conditions from various banks and credit unions. This easy access to information levels the playing field, diminishing information asymmetry and empowering customers to select the most advantageous offerings.
For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate for a new car loan hovered around 7.25%, but this varied significantly based on creditworthiness and lender. Customers armed with this knowledge could readily identify institutions offering rates below this average, effectively leveraging this transparency to negotiate better terms or switch providers.
- Informed Comparisons: Customers can easily benchmark fees and rates across numerous financial institutions.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Online accessibility democratizes financial product knowledge.
- Negotiation Leverage: Transparency empowers customers to seek and secure more favorable terms.
- Provider Choice: Consumers can readily switch to institutions offering superior value.
Diverse Customer Segments with Varying Needs
BOK Financial's customer base is quite diverse, encompassing commercial enterprises, individual consumers, and large institutional investors. Each of these segments has unique financial needs and, consequently, different levels of influence. For instance, major corporations or investment funds often possess substantial bargaining power due to the sheer volume of business they bring, allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms and pricing.
However, the collective strength of numerous smaller clients, such as individual depositors or small business owners, also contributes significantly to overall customer bargaining power. These customers, while individually less influential, can collectively drive demand and influence market offerings by seeking better value, competitive rates, and superior service. This dynamic means BOK Financial must balance the demands of its large clients with the aggregated preferences of its retail and small business segments to maintain competitiveness.
- Diverse Customer Base: BOK Financial serves commercial, consumer, and institutional clients, each with distinct financial requirements.
- Varying Bargaining Power: Large institutional clients typically wield more negotiation leverage than individual customers.
- Cumulative Customer Impact: The aggregated needs and preferences of numerous small clients can significantly influence market offerings and pricing.
- Focus on Value: Customers across segments increasingly seek better value, competitive rates, and enhanced financial services.
The bargaining power of customers for BOK Financial is significant, driven by low switching costs and readily available information. Customers can easily compare rates and fees across institutions, with many actively seeking better deals. This empowers them to demand more favorable terms, influencing BOK Financial's pricing and service strategies.
| Factor | Description | Impact on BOK Financial | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Minimal effort and cost to change financial providers. | Increases customer leverage. | Average online account opening time < 10 minutes. |
| Information Availability | Easy online access to compare rates, fees, and services. | Reduces information asymmetry, empowers informed choices. | >35% of banking customers compare offers annually. |
| Personalization Demand | Customers seek tailored digital experiences and advice. | Pressures BOK Financial to innovate and offer bespoke solutions. | >60% of consumers prefer personalized digital tools. |
Same Document Delivered
BOK Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete BOK Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the actual, professionally formatted report you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your strategic planning needs without any alterations or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
BOK Financial faces significant competition from a multitude of regional banks concentrated in the Southwestern and Midwestern United States, where it primarily operates. These regional players often have deep community ties and a strong understanding of local market nuances.
Adding to this competitive pressure are larger national banks, which boast substantial financial resources, broader geographic footprints, and often more advanced technological capabilities. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the largest national banks by assets held trillions of dollars in deposits, dwarfing the scale of many regional institutions.
This crowded marketplace intensifies competition for crucial banking services, including attracting deposits, originating loans, and offering a full suite of financial products. BOK Financial must therefore continually innovate and differentiate itself to maintain and grow its market share against these diverse competitors.
Fintechs and challenger banks are aggressively competing, offering specialized services and enhanced digital experiences that attract customer segments away from traditional institutions. These agile newcomers often boast lower operating costs, enabling them to offer more competitive pricing. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, demonstrating its substantial growth and disruptive potential.
The banking sector faces significant pressure on its net interest margin (NIM) and loan growth, directly influenced by fluctuating interest rates and overall economic momentum. For BOK Financial, this translates into a challenging environment for its core lending operations. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, the average NIM for U.S. commercial banks hovered around 3.15%, a figure that can be squeezed by increased funding costs and competitive pricing for loans.
BOK Financial has navigated these pressures, with its net interest margin showing resilience amidst economic shifts. While specific loan growth figures vary by quarter, the broader industry trend in 2024 indicated a moderating pace of commercial and industrial loan expansion compared to prior periods, reflecting the competitive landscape and cautious economic outlook.
Consolidation and M&A Activity
The U.S. banking sector is experiencing a notable uptick in merger and acquisition (M&A) activity, signaling a potential shift towards a more consolidated industry. This trend could see the emergence of larger, more dominant competitors, thereby intensifying the competitive rivalry for BOK Financial. For instance, in 2024, there were significant M&A announcements within regional banking, such as the proposed acquisition of KeyCorp by another major player, indicating this consolidation is actively reshaping the landscape.
This heightened M&A environment necessitates strategic adaptation for BOK Financial to effectively navigate the evolving competitive dynamics and sustain its market position. The increased scale of potential rivals, driven by these consolidations, could translate into greater market power and enhanced resources for competitors.
- Increased M&A activity in U.S. banking in 2024.
- Potential for larger, more consolidated competitors.
- Need for BOK Financial to adapt strategically.
- Reshaping of the competitive landscape.
Diversified Service Offerings
BOK Financial's broad range of services, encompassing commercial and consumer banking, investment services, and wealth management, places it in direct competition with a multitude of specialized financial institutions. This diversification means BOK Financial contends with not only other large, diversified banks but also with niche players excelling in specific areas.
For instance, in commercial banking, BOK Financial competes with national giants and regional banks, each with established client bases and tailored offerings. Simultaneously, its wealth management division faces off against dedicated private banks and independent wealth advisors who often cater to a more exclusive clientele. This broad competitive landscape intensifies rivalry across all its business segments.
The bank's diversified approach means it must maintain competitive pricing and service quality across all its offerings. For example, as of the first quarter of 2024, BOK Financial reported total assets of $51.6 billion, demonstrating its significant scale. However, this scale also exposes it to competition from firms that may have a more focused and potentially more agile approach within a specific financial service niche.
- Broad Competition: BOK Financial's diverse offerings mean it competes with a wide spectrum of financial firms, from large, diversified banks to specialized boutique firms in areas like investment banking or wealth management.
- Segment-Specific Rivals: In commercial lending, it faces competition from institutions like JPMorgan Chase and Wells Fargo, while its wealth management arm competes with firms such as Charles Schwab and Fidelity.
- Asset Scale vs. Niche Focus: While BOK Financial's total assets reached approximately $51.6 billion in Q1 2024, it must still contend with specialized competitors who may offer deeper expertise or more tailored solutions within their specific service areas.
- Maintaining Competitiveness: The need to remain competitive across multiple financial segments requires BOK Financial to continuously innovate and adapt its strategies to counter the strengths of its more specialized rivals.
BOK Financial operates in a highly competitive banking environment, facing pressure from both large national institutions and numerous regional banks concentrated in its primary operating areas. The landscape is further complicated by agile fintech companies and the ongoing trend of consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, which is creating larger, more formidable competitors. This dynamic requires BOK Financial to constantly innovate and adapt its strategies to maintain its market position and attract customers across its diverse service offerings.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on BOK Financial |
|---|---|---|
| Regional Banks | Deep community ties, local market knowledge | Intense competition for deposits and loans in specific geographic areas. |
| National Banks | Vast financial resources, broad geographic reach, advanced technology | Significant competition across all service lines; ability to offer wider product suites and potentially lower pricing due to scale. (e.g., Top 5 U.S. banks by assets held over $10 trillion in Q1 2024). |
| Fintechs/Challenger Banks | Specialized services, enhanced digital experiences, lower operating costs | Attract specific customer segments, particularly younger demographics; pressure on traditional fee structures and service delivery models. (Global fintech market valued over $1.1 trillion by end of 2023). |
| Consolidated Entities (Post-M&A) | Increased scale, market power, and resources | Potential for heightened competitive intensity and reduced market fragmentation. (e.g., significant regional bank M&A activity in 2024). |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of fintech solutions, particularly in payments and lending, presents a substantial threat of substitutes for BOK Financial. Companies offering streamlined mobile payment apps and accessible peer-to-peer lending platforms are directly competing for customer transactions. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at over $2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift towards these alternative channels.
These fintech innovations, like 'Buy Now, Pay Later' (BNPL) services which saw a surge in adoption, allow consumers to bypass traditional banking infrastructure for many everyday purchases and credit needs. This directly erodes the transaction-based revenue streams that BOK Financial, like other incumbent banks, relies upon. The convenience and often lower fees associated with these digital alternatives make them increasingly attractive to a broad customer base.
The rise of direct investment platforms and robo-advisors presents a significant threat of substitutes for BOK Financial's traditional investment and trust services. These online platforms offer lower fees and greater accessibility, making it easier for customers to manage their own investments or use automated advisory services.
For instance, the robo-advisor market has seen substantial growth, with assets under management projected to reach over $3 trillion by 2026, according to industry reports. This trend directly competes with BOK Financial by providing a cost-effective and user-friendly alternative for wealth management, potentially siphoning assets and advisory revenue away from the bank.
Embedded finance, a significant trend where non-financial platforms integrate financial services, presents a potent threat of substitutes. For instance, e-commerce giants like Amazon offer their own credit cards and payment processing, directly competing with traditional banks. This seamless integration provides customers with convenient alternatives, blurring the lines between financial and non-financial sectors.
The growth of embedded finance is substantial, with projections indicating a significant market expansion. For example, the global embedded finance market was valued at approximately $4.2 trillion in 2023 and is expected to reach over $10 trillion by 2030, according to various industry reports. This rapid growth signifies a direct challenge to established financial institutions as customers increasingly opt for integrated financial solutions within their preferred platforms.
Shift to Cryptocurrency and Digital Assets
The rise of cryptocurrencies and digital assets poses a growing threat of substitution for traditional banking services. These evolving technologies offer alternative methods for payments, fund transfers, and even wealth storage, potentially bypassing established financial institutions.
While still in development, the increasing adoption and evolving regulatory landscape for digital assets suggest they could significantly disrupt conventional financial services. For instance, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.6 trillion in early 2024, indicating substantial user engagement and a growing alternative financial ecosystem.
- Growing Adoption: Global cryptocurrency ownership is estimated to be over 420 million people as of early 2024, demonstrating a significant shift in user behavior.
- Payment Innovation: Companies like Visa and Mastercard are exploring blockchain technology and stablecoins for faster, cheaper cross-border payments, directly competing with traditional wire transfers.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The DeFi sector, which allows lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries, saw total value locked (TVL) exceed $100 billion in early 2024, showcasing a viable alternative to traditional banking products.
Credit Unions and Community Banks as Alternatives
For consumers and small businesses, credit unions and community banks frequently act as viable substitutes for larger financial institutions. These alternatives often compete effectively by offering more personalized service, lower fees, and a strong community-centric approach. This can draw in customers who value relationship banking over the scale of major banks.
The appeal of these substitutes is evident in their growing market share. For instance, in 2024, credit unions continued to demonstrate robust membership growth, often attracting individuals and small businesses seeking tailored financial solutions. Many community banks also reported increased deposits in the first half of 2024, indicating a sustained preference among certain customer segments.
- Personalized Service: Credit unions and community banks often provide a higher level of individual attention, fostering stronger customer relationships.
- Lower Fees and Better Rates: These institutions may offer more competitive pricing on loans, accounts, and transaction fees compared to larger national banks.
- Community Focus: A commitment to local economic development and community involvement can resonate strongly with customers who wish to support local initiatives.
- Membership Benefits: Credit unions, in particular, often provide member-exclusive benefits and profit-sharing opportunities, enhancing their attractiveness as substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for BOK Financial is amplified by the increasing accessibility and appeal of alternative financial solutions. Fintech innovations, cryptocurrencies, and even traditional credit unions and community banks offer compelling alternatives that can siphon customers and revenue away from incumbent banks.
These substitutes often provide greater convenience, lower costs, and more personalized experiences, directly challenging BOK Financial's traditional business models. The rapid growth in areas like digital payments and decentralized finance underscores the dynamic nature of this competitive landscape.
For instance, the global digital payments market's continued expansion and the growing adoption of cryptocurrencies, with over 420 million global owners by early 2024, highlight a significant shift in consumer preferences. Furthermore, credit unions' consistent membership growth in 2024 indicates their ongoing strength as viable substitutes for larger financial institutions.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2023-2024 Impact/Growth | BOK Financial Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Solutions (Payments, Lending) | Convenience, lower fees, streamlined processes | Digital payments market > $2 trillion (2023); BNPL surge | Erodes transaction revenue, customer acquisition |
| Robo-Advisors & Direct Investment Platforms | Lower fees, accessibility, automated management | Robo-advisor AUM projected > $3 trillion (by 2026) | Threatens wealth management and advisory fees |
| Embedded Finance | Financial services integrated into non-financial platforms | Embedded finance market ~$4.2 trillion (2023) | Blurs industry lines, offers integrated alternatives |
| Cryptocurrencies & Digital Assets | Alternative payment, transfer, and storage methods | Global crypto market cap ~$2.6 trillion (early 2024) | Potential bypass of traditional financial infrastructure |
| Credit Unions & Community Banks | Personalized service, lower fees, community focus | Consistent membership growth (2024); increased deposits | Attracts customers seeking tailored, relationship-based banking |
Entrants Threaten
The digital-first nature of challenger banks and neobanks dramatically lowers entry barriers. These agile, tech-focused startups bypass the substantial overheads associated with traditional brick-and-mortar branches, enabling them to enter the market with less capital. For instance, by Q1 2024, neobanks globally had secured over $25 billion in funding, showcasing their ability to attract investment despite not having physical infrastructure.
These new entrants can rapidly gain traction by targeting underserved market segments or by providing a demonstrably superior digital customer experience. Their ability to innovate quickly and offer specialized services, often with lower fees, directly challenges incumbents. Reports from 2024 indicate that digital-only banks are seeing customer acquisition rates that far outpace traditional banks in many developed markets.
The banking sector, while historically shielded by substantial capital requirements and stringent oversight, faces a dynamic regulatory landscape that can influence the threat of new entrants. For instance, in 2024, discussions around potential fintech sandbox expansions and revised capital adequacy frameworks could lower entry barriers for innovative financial service providers.
Changes in supervisory focus, such as increased emphasis on cybersecurity or consumer data protection, can also reshape the competitive environment. New entrants adept at navigating these evolving compliance demands might find a more accessible market, while established institutions may need to adapt their existing structures.
The increasing availability of cloud computing, open banking APIs, and ready-to-use fintech solutions significantly reduces the technological hurdles for new players entering the financial services sector. This means startups can launch new products and services rapidly, bypassing the substantial upfront costs associated with building and maintaining traditional, extensive IT infrastructure.
For instance, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, a substantial increase from previous years, highlighting the accessibility of scalable technology. This readily available tech stack allows new entrants to BOK Financial’s market to innovate and compete on par with established institutions, thereby increasing the threat of new competition.
Niche Market Focus and Customer-Centricity
New entrants are increasingly targeting underserved customer segments or specific financial needs, often developing highly customer-centric models that can quickly gain market share. For instance, neobanks and specialized fintech firms frequently focus on particular demographics or service gaps, allowing them to build strong customer loyalty without immediately confronting the broad product suites of established institutions. This niche focus enables them to innovate rapidly and offer tailored solutions.
The threat of new entrants is amplified by their ability to bypass legacy systems and regulatory hurdles that can slow down larger, incumbent banks. By concentrating on a specific niche, these new players can offer specialized services and a more agile customer experience. For example, in 2024, several fintechs focused on small business lending or international money transfers saw significant growth by offering streamlined digital platforms and competitive pricing, directly addressing pain points for those specific customer groups.
- Niche Targeting: New entrants often succeed by focusing on specific customer segments or financial needs, avoiding direct competition with established banks.
- Customer-Centric Models: These new players build highly customer-centric approaches, fostering rapid traction and strong loyalty.
- Agility and Innovation: By avoiding legacy systems, new entrants can innovate quickly and offer tailored, efficient services.
- Market Penetration: In 2024, specialized fintechs, particularly in areas like small business lending, demonstrated significant growth by addressing specific market gaps.
Capital Requirements and Brand Trust as Remaining Barriers
Despite the increasing digitalization of financial services, the threat of new entrants for established institutions like BOK Financial remains moderated by significant capital requirements. Launching a fully regulated bank necessitates substantial upfront investment in technology, compliance, and operational infrastructure, a hurdle that many new players find difficult to clear.
Furthermore, cultivating brand trust and customer loyalty is a lengthy and resource-intensive process. While agile fintechs can disrupt niche markets or specific services, replicating the comprehensive offerings and established reputation of a full-service financial holding company like BOK Financial presents considerable challenges.
- Capital Investment: Establishing a new bank can require hundreds of millions of dollars in initial capital, with regulatory minimums often exceeding $50 million for a de novo bank in the US.
- Brand Reputation: Building trust in financial services, especially for handling customer deposits and investments, is crucial. Incumbents like BOK Financial benefit from years of established relationships and a proven track record.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex banking regulations, such as those from the Federal Reserve and OCC, demands significant expertise and ongoing compliance costs, acting as a substantial barrier to entry for new firms.
- Scale and Scope: While fintechs can offer specialized digital solutions, becoming a comprehensive financial holding company with diverse product lines (commercial banking, wealth management, etc.) requires a scale of operations and capital that is difficult for newcomers to achieve quickly.
The threat of new entrants for BOK Financial is significant due to the digital-first approach of challenger banks and neobanks. These entities bypass traditional overheads, entering the market with less capital and rapidly gaining traction by targeting underserved segments or offering superior digital experiences. For instance, by Q1 2024, neobanks globally had secured over $25 billion in funding, demonstrating their ability to attract investment despite lacking physical infrastructure.
New players leverage readily available cloud computing, open banking APIs, and fintech solutions, drastically reducing technological hurdles and upfront costs. This accessibility allows startups to launch new products and services swiftly. The global cloud computing market was projected to exceed $1.3 trillion in 2024, underscoring the ease with which new entrants can access scalable technology to compete effectively.
While digitalization lowers barriers, substantial capital requirements, complex regulatory navigation, and the need for established brand trust remain significant hurdles for new entrants aiming to replicate the comprehensive offerings of established institutions like BOK Financial. For example, establishing a de novo bank in the US can require initial capital exceeding $50 million, a substantial barrier for many startups.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Digitalization & Fintech | Lowers entry barriers significantly | Neobank funding exceeded $25 billion globally by Q1 2024 |
| Technology Accessibility | Reduces IT infrastructure costs | Global cloud computing market projected over $1.3 trillion |
| Capital Requirements | High barrier for full-service banking | US de novo bank capital minimums often >$50 million |
| Brand Trust & Reputation | Difficult for newcomers to replicate | Incumbents benefit from years of established customer relationships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our BOK Financial Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data from BOK Financial's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with industry-specific research from reputable sources and macroeconomic data to capture the broader competitive landscape.
