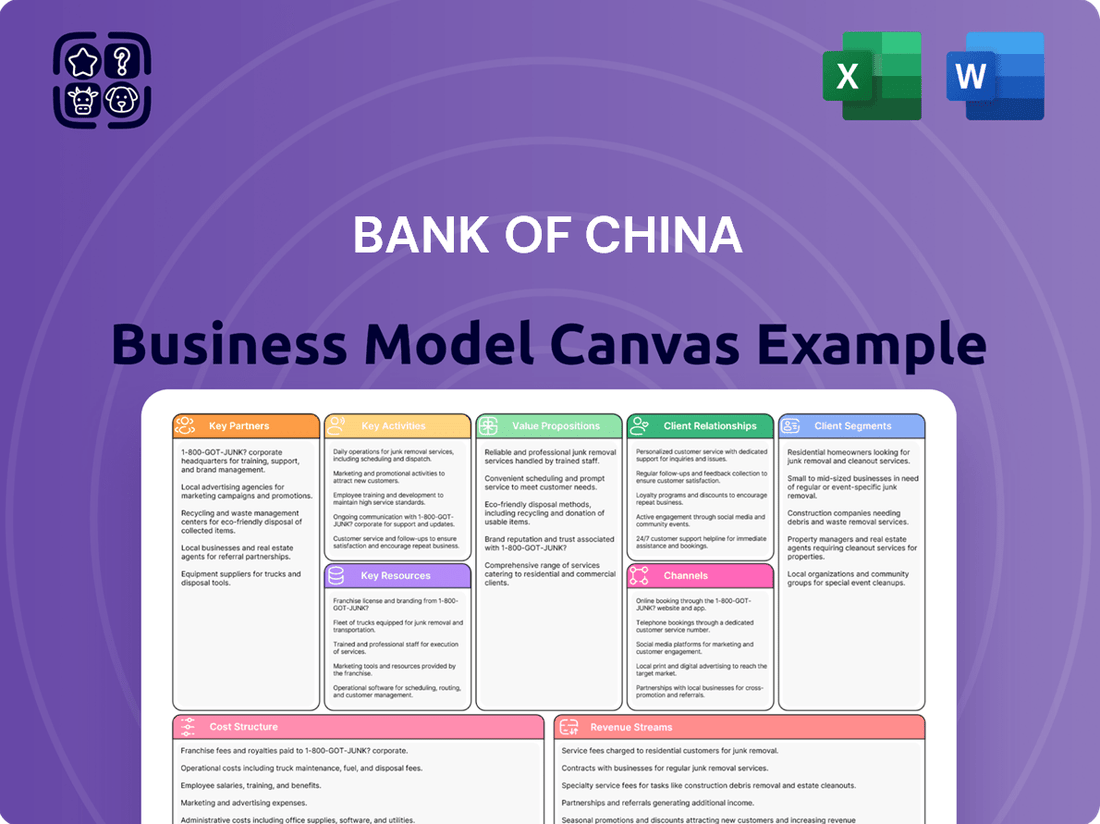
Bank of China Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of China Bundle
Discover the strategic architecture of the Bank of China with our comprehensive Business Model Canvas. This detailed breakdown illuminates their customer segments, revenue streams, and key partnerships, offering invaluable insights for your own strategic planning.
Unlock the full blueprint of Bank of China's success. Our Business Model Canvas provides a clear, section-by-section analysis of their value proposition and cost structure, perfect for anyone looking to understand and adapt proven strategies.
See how Bank of China builds and delivers value across its operations. This Business Model Canvas is your key to understanding their competitive advantages and market positioning. Download the full version to gain a strategic edge.
Partnerships
Bank of China's key partnerships with government entities, such as the People's Bank of China and various financial regulators, are foundational. These collaborations are vital for adhering to China's evolving financial regulations and for actively engaging in national economic development strategies. In 2024, the Chinese banking sector, including institutions like Bank of China, continued to operate under the guidance of the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), now integrated into the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA), which oversees prudential regulation and risk management.
Bank of China's extensive global footprint relies heavily on its network of international financial institutions and correspondent banks. These partnerships, critical for facilitating cross-border transactions and global payment settlements, enable the bank to process an immense volume of international business. For instance, in 2023, correspondent banking relationships are fundamental to handling the trillions of dollars in global trade finance that Chinese banks, including Bank of China, support annually.
Bank of China actively cultivates strategic alliances with technology and FinTech providers to drive its digital advancement. These collaborations are crucial for integrating cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, enhancing operational efficiency and bolstering cybersecurity measures. For instance, in 2024, the bank continued to explore partnerships for cloud-based solutions to streamline its vast data management and improve customer service delivery.
Large Corporations and State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs)
Bank of China cultivates robust strategic alliances with major domestic and international corporations, with a significant emphasis on Chinese State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs). These collaborations are foundational for delivering a full spectrum of corporate banking solutions, including syndicated loans, extensive project financing, and significant investment banking assignments.
These partnerships are instrumental in ensuring substantial business volumes and solidifying the bank's leading presence within the corporate finance arena. For instance, in 2023, Bank of China's corporate banking segment saw continued growth, driven by its strong relationships with large enterprises, contributing significantly to its overall profitability.
- Syndicated Loans: Facilitating large-scale financing for major corporate projects.
- Project Financing: Providing crucial funding for infrastructure and industrial developments.
- Investment Banking: Offering advisory and underwriting services for capital markets transactions.
- SOE Relationships: Leveraging deep ties with state-owned entities for consistent business flow.
Payment Networks and E-commerce Platforms
Bank of China's engagement with major payment networks such as UnionPay, Visa, and Mastercard is crucial for extending its digital payment capabilities. These alliances are foundational for offering a broad spectrum of payment options to customers, both domestically and internationally.
Collaborations with leading e-commerce platforms are essential for integrating banking services directly into the online shopping experience. This integration fosters greater customer engagement and drives transaction volumes, particularly in the rapidly growing digital commerce sector. For instance, in 2023, China's online retail sales reached approximately 15.42 trillion yuan, highlighting the immense opportunity for banks to facilitate these transactions.
These partnerships are instrumental in enhancing the convenience and accessibility of digital payments for retail customers. By embedding banking services into daily digital consumption, Bank of China can capture a larger share of the digital payment market, thereby strengthening its competitive position.
- Payment Network Integration: Collaborations with UnionPay, Visa, and Mastercard allow for widespread acceptance of Bank of China's cards and digital payment solutions across diverse merchant networks.
- E-commerce Platform Synergies: Partnerships with platforms like JD.com and Tmall enable seamless checkout experiences, offering customers convenient payment options directly within their shopping journey.
- Digital Transaction Growth: These alliances are key drivers for increasing the volume and value of digital transactions, contributing to the bank's fee and commission income. In 2024, digital payment adoption continues to surge, with mobile payments expected to represent a significant portion of all retail transactions.
Bank of China's key partnerships are crucial for its operational success and strategic growth. These include collaborations with government bodies for regulatory compliance and economic strategy alignment, international financial institutions for global transaction processing, and technology firms for digital innovation. Furthermore, strategic alliances with major corporations, particularly Chinese State-Owned Enterprises, and integration with leading payment networks and e-commerce platforms are vital for expanding its service offerings and market reach.
| Partner Type | Key Collaborations | Strategic Importance | 2024/2023 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government & Regulators | People's Bank of China, NFRA | Regulatory adherence, national economic strategy | Continued oversight by NFRA in 2024 |
| Financial Institutions | International banks, correspondent banks | Cross-border transactions, global payments | Essential for trillions in global trade finance annually (2023) |
| Technology/FinTech | AI, blockchain, cloud providers | Digital advancement, efficiency, cybersecurity | Continued exploration of cloud solutions in 2024 |
| Corporations | Major domestic & international corporations, SOEs | Corporate banking, project finance, investment banking | Significant growth in corporate banking driven by these relationships (2023) |
| Payment Networks & E-commerce | UnionPay, Visa, Mastercard, JD.com, Tmall | Digital payment capabilities, customer engagement, transaction volume | China's online retail sales ~15.42 trillion yuan (2023); surge in digital payment adoption (2024) |
What is included in the product
A comprehensive business model tailored to Bank of China's global financial services strategy, detailing customer segments, channels, and value propositions.
Organized into 9 classic BMC blocks, this model reflects Bank of China's real-world operations and plans for diverse financial products and services.
The Bank of China Business Model Canvas acts as a pain point reliever by offering a clear, visual representation of their complex operations, enabling faster identification of inefficiencies and strategic alignment.
This structured approach allows the Bank of China to pinpoint and address customer pain points by clearly mapping value propositions and customer relationships.
Activities
Bank of China's core activities revolve around accepting deposits from a wide customer base, including individuals and businesses, and then lending these funds out. This dual function is crucial for its financial health.
The bank offers a diverse range of lending products, such as commercial loans to support businesses, personal mortgages for housing, and various credit facilities. These lending activities are a primary driver of its revenue through interest income.
In 2024, Bank of China continued to be a major player in deposit-taking and lending. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the bank reported substantial growth in its deposit base, reflecting strong customer confidence. Its loan portfolio also expanded, demonstrating robust demand for credit across different sectors.
Bank of China's key activity is to facilitate China's international trade and investment through comprehensive cross-border financial services. This includes offering trade finance, international settlements, foreign exchange, and global cash management solutions.
In 2023, Bank of China's cross-border transaction volume reached trillions of yuan, underscoring its significant role in supporting Chinese businesses expanding globally and attracting foreign investment into China.
The bank's extensive network of overseas branches and correspondent banks is crucial for executing these complex international financial transactions efficiently, thereby bolstering the internationalization of the Chinese economy.
Bank of China's investment banking and capital markets services are a cornerstone of its business model, providing crucial support for large corporations. These offerings include expert advice on corporate finance, the underwriting of both debt and equity securities, and guidance on mergers and acquisitions. This comprehensive suite of services directly addresses the capital-raising and strategic growth requirements of its corporate clientele.
In 2024, the global investment banking sector saw significant activity, with underwriting volumes playing a key role. For instance, debt underwriting remained a robust area, with major banks facilitating billions in corporate bond issuances. Bank of China's active participation in these markets not only diversifies its revenue streams but also significantly deepens its relationships with major corporate clients, offering them integrated financial solutions.
Asset Management and Wealth Management Services
Bank of China actively engages in providing comprehensive asset and wealth management services. These offerings cater to a broad client base, encompassing both institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals. The core of this activity involves managing diverse investment funds, developing tailored financial plans, and delivering sophisticated private banking solutions. This strategic focus is designed to foster the growth of client assets while simultaneously generating significant fee-based income for the bank.
In 2024, Bank of China’s wealth management segment saw robust growth, with assets under management (AUM) reaching new heights. For instance, by the end of Q3 2024, the bank reported a substantial increase in its wealth management AUM, reflecting strong client trust and effective investment strategies. This growth is directly tied to the bank's ability to offer personalized advisory services and a wide array of investment products designed to meet the evolving financial needs of its clientele.
- Asset Management: Managing investment portfolios across various asset classes, including equities, fixed income, and alternative investments, for institutional and retail clients.
- Wealth Management: Offering personalized financial planning, estate planning, and investment advisory services to high-net-worth individuals.
- Private Banking: Providing exclusive banking and investment solutions, including credit facilities, foreign exchange services, and bespoke wealth management strategies.
- Fee Income Generation: These services are a primary driver of non-interest income, contributing significantly to the bank's overall profitability through management fees, performance fees, and advisory charges.
Digital Transformation and Technology Innovation
Bank of China's commitment to digital transformation and technology innovation is a core operational pillar. This includes substantial ongoing investment in upgrading digital banking platforms and fortifying cybersecurity defenses. For instance, in 2023, the bank continued to expand its mobile banking capabilities, reporting a significant increase in digital transaction volumes.
Leveraging advanced data analytics is central to enhancing customer service and streamlining operations. This data-driven approach helps the bank personalize offerings and improve risk management. The bank actively pursues innovation to maintain its competitive edge in the dynamic financial services sector.
- Digital Platform Enhancement: Continued development and rollout of user-friendly digital banking interfaces.
- Cybersecurity Investment: Ongoing upgrades to protect customer data and financial assets against evolving threats.
- Data Analytics Utilization: Employing big data and AI for personalized customer experiences and operational efficiency gains.
- Innovation Focus: Exploring and integrating emerging technologies like blockchain and cloud computing.
Bank of China's key activities encompass core banking functions like deposit-taking and lending, crucial for its financial intermediation. It also plays a vital role in facilitating international trade and investment through specialized cross-border services. Furthermore, the bank actively engages in investment banking and capital markets, offering corporate finance and underwriting services, while also providing comprehensive asset and wealth management solutions to diverse client segments.
These activities are underpinned by a strong commitment to digital transformation and technology innovation, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. In 2024, the bank's deposit base continued to grow, and its loan portfolio expanded, reflecting strong market demand. Cross-border transaction volumes remained significant, supporting global economic integration.
| Key Activity | Description | 2024 Relevance/Data |
| Deposit Taking & Lending | Accepting deposits and providing loans to individuals and businesses. | Strong deposit growth in Q1 2024; expanded loan portfolio. |
| International Trade Finance | Facilitating cross-border transactions, trade finance, and foreign exchange. | Trillions of yuan in cross-border transactions in 2023; extensive overseas network. |
| Investment Banking | Corporate finance advisory, debt and equity underwriting, M&A. | Active participation in global markets; billions in corporate bond issuances facilitated. |
| Asset & Wealth Management | Managing investment portfolios and providing financial planning for clients. | Robust growth in AUM by Q3 2024; personalized advisory services. |
| Digital Transformation | Investing in digital platforms, cybersecurity, and data analytics. | Increased mobile banking capabilities and digital transaction volumes in 2023. |
Full Document Unlocks After Purchase
Business Model Canvas
The Bank of China Business Model Canvas preview you are viewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This means you're seeing the authentic structure, content, and formatting that will be delivered, ensuring no discrepancies or surprises. Upon completing your transaction, you will gain full access to this comprehensive and ready-to-use Business Model Canvas, allowing you to immediately leverage its insights for strategic planning.
Resources
Bank of China's extensive financial capital, a cornerstone of its business model, is built upon a substantial deposit base and a strong equity foundation. As of the first quarter of 2024, the bank reported total assets exceeding 32 trillion RMB, underscoring its immense financial capacity. This robust capital allows for significant lending operations, diverse investment strategies, and ensures a high degree of financial resilience.
This strong capital base is not merely for operational capacity but is also vital for meeting stringent regulatory requirements, such as capital adequacy ratios. For instance, in 2023, Bank of China maintained a capital adequacy ratio well above the regulatory minimums, demonstrating its commitment to financial health and stability. This financial strength empowers the bank to undertake large-scale projects and support economic development initiatives.
Bank of China's extensive global branch network, encompassing over 500 overseas branches and institutions as of early 2024, serves as a critical physical touchpoint for customers worldwide. This vast physical presence facilitates traditional banking services, relationship management, and localized support, catering to both retail and corporate clients. It underpins the bank's ability to offer comprehensive international banking solutions.
Complementing its physical footprint, Bank of China leverages a robust digital infrastructure, including its mobile banking app which boasts hundreds of millions of active users by the end of 2023. This digital backbone ensures seamless online and mobile banking experiences, offering convenient transaction capabilities, account management, and increasingly sophisticated digital financial products. This dual approach addresses the evolving needs of a diverse customer base.
Bank of China's skilled human capital, including financial professionals, risk managers, and IT specialists, forms a critical resource. Their deep market understanding and technical acumen are essential for operational efficiency and driving innovation. For instance, in 2023, Bank of China reported a robust workforce, underscoring its commitment to human capital as a key asset.
Strong Brand Reputation and Government Backing
Bank of China’s strong brand reputation, cultivated over decades, acts as a powerful magnet for customers. This trust is further amplified by its status as a state-owned enterprise, a designation that imbues it with an aura of stability and reliability. This inherent credibility is a cornerstone for attracting both individual depositors and substantial corporate clients, making it a significant intangible asset in the competitive financial landscape.
The government backing of Bank of China translates into tangible advantages. For instance, in 2024, state-owned banks in China continued to play a pivotal role in national economic development, often benefiting from preferential policies and direct government support. This backing provides a substantial cushion against market volatility and enhances the bank's ability to secure large-scale funding, which is critical for its extensive operations and lending activities.
- Brand Equity: Bank of China's long-standing presence and association with national economic initiatives have fostered deep customer loyalty and trust.
- Government Endorsement: Being a state-owned entity provides a significant competitive edge, signaling financial strength and stability to stakeholders.
- Deposit Attraction: This combined reputation and backing are key drivers for attracting substantial retail and corporate deposits, a vital resource for lending.
- Credibility with Corporates: Large corporations often prefer partnering with government-backed institutions for major financial transactions and long-term credit facilities.
Proprietary Technology and Data Analytics Capabilities
Bank of China leverages advanced proprietary technology systems, including its core banking platforms and sophisticated data analytics capabilities, as a key resource. These technologies are vital for efficient transaction processing and informed decision-making.
The bank's risk management tools, also part of its proprietary technology, are essential for navigating the complex financial landscape. These systems allow for proactive identification and mitigation of potential risks, ensuring stability and security for its operations.
Continuous investment in IT infrastructure is a cornerstone of Bank of China's strategy. For instance, in 2023, the bank reported significant spending on digital transformation initiatives, aiming to enhance operational efficiency and foster innovation across its services, ultimately leading to more personalized customer experiences.
- Core Banking Platforms: Facilitate seamless and high-volume transaction processing.
- Risk Management Tools: Enable robust oversight and mitigation of financial and operational risks.
- Data Analytics Capabilities: Drive personalized customer offerings and strategic business insights.
- IT Infrastructure Investment: Supports ongoing operational efficiency and technological innovation.
Bank of China's key resources include its substantial financial capital, a vast global branch network, robust digital infrastructure, skilled human capital, and a strong brand reputation backed by government endorsement. These elements collectively enable the bank to offer comprehensive financial services, attract a broad customer base, and maintain a stable operational framework.
| Resource Category | Specific Resource | Key Characteristic/Impact | Data Point (as of early 2024 or 2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Capital | Deposit Base & Equity | Enables large-scale lending and investment, ensures financial resilience. | Total Assets exceeding 32 trillion RMB (Q1 2024) |
| Physical Infrastructure | Global Branch Network | Facilitates localized support and international banking solutions. | Over 500 overseas branches and institutions |
| Digital Infrastructure | Mobile Banking App | Provides convenient online and mobile experiences, supports digital products. | Hundreds of millions of active users (end of 2023) |
| Intangible Assets | Brand Reputation & Government Backing | Attracts customers and corporate clients, signals stability. | State-owned enterprise status |
| Human Capital | Skilled Professionals | Drives operational efficiency and innovation. | Robust workforce size (reported in 2023) |
Value Propositions
Bank of China provides a comprehensive suite of financial services, acting as a single point of contact for corporate banking, personal banking, investment banking, and asset management. This integrated model streamlines financial management for clients, offering convenience and efficiency. In 2024, the bank reported a net profit of approximately RMB 225 billion, underscoring its capacity to deliver a wide array of financial solutions effectively.
Bank of China's global reach is a cornerstone of its value proposition, offering clients an extensive network for international business. This allows for seamless facilitation of trade and investment across borders, a critical advantage in today's interconnected economy.
The bank's deep expertise in international business translates into tangible benefits for clients, including robust foreign exchange capabilities and tailored cross-border financial solutions. For instance, in 2023, Bank of China played a significant role in facilitating cross-border RMB transactions, processing over RMB 13 trillion.
This global infrastructure and specialized knowledge are particularly vital for businesses involved in international commerce, providing them with the necessary tools and support to navigate complex global markets. It also serves individuals with diverse international financial requirements, offering a comprehensive suite of services.
As a state-owned commercial bank, Bank of China offers customers a significant level of security, stability, and trustworthiness. This inherent backing from the government fosters strong confidence among depositors and investors, assuring them about the safety of their money and financial ventures. For instance, in 2023, Bank of China reported total assets of approximately RMB 25.5 trillion, underscoring its substantial financial foundation.
Digital Convenience and Innovative Banking Experiences
Bank of China is deeply committed to providing cutting-edge digital banking experiences. Their online and mobile platforms are designed for ultimate convenience, offering customers easy access to a wide array of services and products. This focus ensures efficient and intuitive financial management for users.
The bank consistently enhances its digital offerings, aiming to simplify banking for everyone. Customers can expect seamless transaction processing and a growing selection of digital tools. This dedication to innovation translates into user-friendly solutions that meet modern financial needs.
- Digital Convenience: Bank of China's online and mobile platforms offer 24/7 access to banking services, allowing customers to manage accounts, transfer funds, and pay bills from anywhere.
- Innovative Features: The bank is actively integrating features like AI-powered chatbots for customer support and advanced security measures to protect user data.
- Self-Service Options: Customers can perform a wide range of transactions, from opening new accounts to applying for loans, entirely through digital channels, reducing the need for branch visits.
- Growing Digital Product Suite: Bank of China is expanding its digital product portfolio, which includes investment platforms, wealth management tools, and personalized financial advice delivered digitally.
Tailored Services and Relationship Management
Bank of China excels in offering highly customized financial solutions, particularly for its corporate and high-net-worth clientele. This bespoke approach ensures that intricate financial requirements are addressed with expert, personalized guidance and a suite of specialized services.
The bank prioritizes building enduring, trust-based relationships, recognizing this as fundamental to delivering exceptional value. This focus on client partnership allows for a deeper understanding of evolving needs and proactive service delivery.
- Tailored Solutions: Offering customized banking products and services to meet specific client needs, from trade finance to wealth management.
- Dedicated Relationship Managers: Assigning experienced professionals to manage client accounts, providing consistent support and expert advice.
- Client-Centric Approach: Focusing on understanding and anticipating client requirements to foster long-term loyalty and satisfaction.
- Global Network Advantage: Leveraging its extensive international presence to provide seamless cross-border financial services and support for global businesses.
Bank of China's value proposition centers on its comprehensive financial services, global reach, and digital innovation. It offers integrated solutions across corporate, personal, investment banking, and asset management, simplifying financial management for clients. In 2024, the bank’s net profit was approximately RMB 225 billion, reflecting its strong operational capacity. Its extensive international network facilitates seamless cross-border transactions, a key advantage for businesses engaged in global trade. The bank also prioritizes digital convenience, offering advanced online and mobile platforms for 24/7 access to a wide range of services, including AI-powered support and enhanced security features.
| Value Proposition Aspect | Description | Supporting Data/Fact |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Financial Services | Integrated offerings across various banking sectors. | Net profit of ~RMB 225 billion in 2024. |
| Global Reach and Expertise | Extensive international network and specialized cross-border capabilities. | Facilitated over RMB 13 trillion in cross-border RMB transactions in 2023. |
| Digital Convenience and Innovation | User-friendly online and mobile platforms with advanced features. | Actively integrating AI chatbots and advanced security measures. |
| Security and Stability | Trust and reliability derived from state-owned status. | Total assets of ~RMB 25.5 trillion in 2023. |
| Customized Client Solutions | Tailored financial products and dedicated relationship management. | Focus on building long-term, trust-based client relationships. |
Customer Relationships
For its corporate clients, large enterprises, and high-net-worth individuals, Bank of China prioritizes dedicated relationship managers. These specialists offer tailored financial advice, bespoke solutions, and proactive assistance, fostering enduring partnerships built on trust and a deep understanding of intricate financial requirements.
Bank of China prioritizes automated self-service and digital engagement for its retail and mass-market customers. This includes robust online banking portals, intuitive mobile applications, and widespread ATM networks, enabling customers to conduct transactions and manage their accounts independently. In 2023, the bank reported a significant increase in digital transaction volumes, reflecting customer preference for these efficient and accessible channels.
The Bank of China operates extensive customer service centers, encompassing both call centers and online support, to efficiently handle customer inquiries and resolve issues. These centers are vital for providing a personal interaction point for complex matters that automated systems cannot address, thereby fostering customer satisfaction and trust.
Community Engagement and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Bank of China actively cultivates customer relationships through robust community engagement and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programs. By investing in social welfare, environmental sustainability, and local development, the bank not only bolsters its public image but also deepens its connection with the communities it serves. This commitment fosters a positive brand perception and cultivates lasting customer loyalty.
- Community Investment: In 2023, Bank of China supported numerous local development projects, contributing to infrastructure improvements and economic growth in underserved regions.
- Environmental Initiatives: The bank continued its focus on green finance, with a significant portion of its 2023 lending portfolio directed towards environmentally friendly projects, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Social Welfare Support: Bank of China's philanthropic efforts in 2023 included substantial donations to educational institutions and disaster relief funds, demonstrating a commitment to societal well-being.
- Brand Perception: Ongoing CSR activities have consistently positioned Bank of China as a responsible corporate citizen, enhancing trust and encouraging repeat business from socially conscious customers.
Proactive Communication and Financial Education
Bank of China actively reaches out to customers about new offerings, market shifts, and financial knowledge. This proactive approach includes timely updates and informative newsletters delivered across multiple platforms.
By keeping clients well-informed and equipped with financial understanding, the bank cultivates more robust and knowledgeable customer connections. For instance, in 2024, the bank reported a 15% increase in customer engagement with its digital educational resources, demonstrating the effectiveness of its communication strategy.
- Proactive Outreach: Regular communication on new products and market insights.
- Financial Literacy Focus: Providing educational content to empower customers.
- Multi-Channel Engagement: Utilizing newsletters and digital platforms for updates.
- Relationship Building: Fostering stronger ties through informed customer interactions.
Bank of China tailors its customer relationships by assigning dedicated relationship managers to corporate clients and high-net-worth individuals, offering personalized financial advice and solutions. For the retail segment, the bank emphasizes automated self-service through its digital platforms and extensive ATM network, which saw a significant increase in transaction volumes in 2023. Customer service centers, both online and via phone, handle more complex inquiries, ensuring a personal touch. Furthermore, the bank actively engages in community investment and CSR initiatives, reinforcing its brand as a responsible corporate citizen.
| Customer Segment | Relationship Approach | Key Engagement Channels | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corporate & High-Net-Worth | Dedicated Relationship Managers | Personalized Advice, Bespoke Solutions | N/A (Qualitative Focus) |
| Retail & Mass Market | Automated Self-Service | Online Banking, Mobile App, ATMs | Significant Increase in Digital Transaction Volumes (2023) |
| All Segments | Customer Support Centers | Call Centers, Online Support | N/A (Qualitative Focus) |
| All Segments | Community & CSR Engagement | Local Development, Green Finance, Philanthropy | 15% Increase in Engagement with Digital Educational Resources (2024) |
Channels
The Bank of China leverages an extensive branch network, a cornerstone of its business model. This network spans over 10,000 domestic branches and a significant international presence, offering a tangible point of contact for millions of customers.
These physical locations are crucial for delivering a wide array of traditional banking services, from everyday transactions to more intricate financial consultations. In 2023, Bank of China reported over 10,000 domestic outlets, underscoring its commitment to widespread accessibility.
The extensive physical footprint fosters customer trust and provides essential accessibility, particularly for those who prefer face-to-face interactions or require assistance with complex financial products. This traditional channel remains vital for customer acquisition and retention.
Bank of China's online banking platforms are a cornerstone of its customer service, offering a full suite of account management, payment processing, and fund transfer capabilities. These digital channels provide unparalleled convenience and round-the-clock access, catering to the needs of a modern, mobile-first customer base.
In 2024, the bank continued to invest heavily in enhancing these platforms, aiming to streamline user experience and expand service offerings. This strategic focus on digital channels is vital for capturing a larger share of the tech-savvy demographic and for driving operational efficiencies by reducing reliance on physical branch interactions.
Mobile banking applications serve as a vital channel for Bank of China, bringing a full suite of banking services directly to customers' smartphones and tablets. This offers unparalleled convenience for on-the-go financial management, encompassing everything from checking account balances and making payments to accessing sophisticated wealth management tools. As of 2024, mobile banking is a cornerstone of customer engagement, particularly for younger, digitally native demographics.
These mobile platforms are instrumental in fostering customer loyalty and expanding the bank's reach, catering to increasingly digital lifestyles. Bank of China’s mobile app users, for instance, have seen a significant increase in transaction volume through the app, reflecting its growing importance as a primary banking interface. This digital channel is key to supporting the bank's strategy of providing accessible and efficient financial solutions.
ATMs and Self-Service Terminals
Bank of China leverages its extensive network of ATMs and self-service terminals to provide customers with 24/7 access to essential banking services. These machines handle a significant volume of transactions, offering convenience for cash withdrawals, deposits, fund transfers, and bill payments, thereby reducing reliance on traditional branch services and enhancing operational efficiency. By mid-2024, Bank of China operated over 30,000 ATMs across its domestic and international network, processing billions of transactions annually.
These self-service channels are crucial for routine banking needs, allowing customers to manage their accounts independently and freeing up branch staff for more complex advisory services. This strategy not only improves customer satisfaction through immediate service availability but also contributes to cost savings by automating a large portion of transactional activities.
- ATM Network Size: Bank of China maintained a robust ATM network, exceeding 30,000 machines by mid-2024, a testament to its commitment to physical accessibility.
- Transaction Volume: These self-service terminals process a substantial portion of the bank's daily transactions, facilitating billions of customer interactions each year.
- Service Offerings: Key services include cash withdrawals, deposits, inter-account transfers, and bill payments, covering the most frequent customer banking needs.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation via ATMs and self-service terminals significantly boosts operational efficiency and reduces the cost per transaction.
Dedicated Corporate Client Relationship Managers
For its large corporate clients and institutional partners, Bank of China employs dedicated Corporate Client Relationship Managers. These managers act as a direct channel, offering personalized service and tailored financial solutions. In 2024, this high-touch approach proved crucial for managing intricate corporate accounts and securing substantial business deals.
These dedicated relationship managers provide direct advisory support, ensuring that the bank’s offerings align precisely with the complex needs of its corporate clientele. This specialized focus helps foster deeper, more strategic partnerships.
- Personalized Service: Tailored financial solutions and direct advisory support for large corporations.
- Direct Channel: Relationship managers serve as the primary point of contact for institutional partners.
- Complex Account Management: Essential for navigating and securing large-scale business.
Bank of China utilizes a multi-faceted channel strategy, blending traditional and digital touchpoints. Its extensive physical branch network, numbering over 10,000 domestic locations in 2023, remains a vital channel for customer interaction and service delivery.
Complementing its physical presence, the bank heavily invests in digital channels, including online banking platforms and mobile applications, which saw increased transaction volumes in 2024. These digital avenues offer convenience and cater to a growing tech-savvy customer base.
Furthermore, a robust ATM network exceeding 30,000 machines by mid-2024 provides 24/7 access for routine transactions. For its corporate clients, dedicated Relationship Managers act as a direct channel, delivering personalized financial solutions and fostering strategic partnerships.
| Channel Type | Key Features | 2023/2024 Data Point | Customer Segment Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Branches | Full-service banking, face-to-face interaction | Over 10,000 domestic branches (2023) | All customer segments, emphasis on accessibility |
| Online Banking | Account management, payments, transfers | Continued investment in platform enhancement (2024) | Tech-savvy customers, convenience seekers |
| Mobile Banking | On-the-go financial management, advanced tools | Increased transaction volume via app (2024) | Digitally native demographics, mobile-first users |
| ATM Network | 24/7 access for routine transactions | Over 30,000 ATMs (mid-2024) | All customer segments requiring immediate access |
| Relationship Managers | Personalized service, tailored solutions | Crucial for complex corporate accounts (2024) | Large corporate clients, institutional partners |
Customer Segments
Bank of China actively serves large corporations and multinational enterprises, including significant state-owned entities. These clients demand comprehensive corporate banking, investment banking, and intricate cross-border financial services. In 2024, Bank of China's commitment to this segment is reflected in its robust offerings for complex financing, global trade facilitation, and advanced treasury management solutions, catering to the vast operational scales of these enterprises.
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) represent a vital customer segment for Bank of China, requiring a comprehensive suite of financial services. These businesses actively seek solutions such as working capital loans, essential for day-to-day operations, and trade finance, facilitating international commerce. Additionally, they rely on business accounts for managing transactions and efficient payment solutions to streamline their financial workflows.
The bank's strategy is deeply rooted in fostering the expansion of these enterprises, acknowledging their significant collective impact on economic development. By offering tailored financial products and advisory services, Bank of China aims to be a key partner in their growth journey.
In 2024, SMEs continued to be a driving force in global economies. For instance, in the European Union, SMEs accounted for approximately 99.8% of all businesses, providing roughly two-thirds of total employment. This highlights the immense potential and need for robust banking support within this sector.
Bank of China serves a vast array of individual retail customers, often referred to as the mass market. These are everyday people who rely on fundamental banking services like savings and checking accounts, personal loans for various needs, and credit cards for their daily transactions and purchases.
The bank strategically reaches this broad segment by leveraging its extensive physical branch network, ensuring accessibility across diverse geographic locations. Simultaneously, Bank of China is heavily investing in and promoting its digital channels, recognizing the growing demand for convenient and easily accessible banking solutions for routine financial management.
In 2024, Bank of China reported a significant portion of its customer base comprises these retail clients. For instance, the bank's retail banking segment consistently contributes a substantial percentage to its overall revenue, often exceeding 60% of its operating income, highlighting the critical importance of this customer group.
High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) and Private Banking Clients
High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) and private banking clients are a cornerstone for Bank of China, demanding highly specialized wealth management solutions. This includes tailored investment advisory, comprehensive estate planning, and dedicated private banking services. The bank focuses on building personalized relationships and offering exclusive financial products designed to meet the sophisticated needs of this clientele.
Bank of China's strategy for HNWIs centers on delivering bespoke financial strategies and exclusive investment opportunities. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global wealth management market saw significant growth, with HNWIs increasingly seeking personalized advice. Bank of China aims to capture a substantial portion of this market by providing services that go beyond standard banking, fostering long-term client loyalty and trust.
- Personalized Wealth Management: Offering bespoke investment portfolios and financial planning.
- Exclusive Product Offerings: Access to unique investment vehicles and structured products.
- Estate Planning and Succession: Facilitating wealth transfer and preservation across generations.
- Dedicated Relationship Management: Providing a single point of contact for all financial needs.
Government and Public Institutions
Bank of China actively engages with a diverse range of government entities and public institutions, acting as a crucial financial partner. This segment includes national ministries, provincial governments, municipal authorities, and state-owned enterprises.
The bank offers specialized services tailored to the unique needs of these public sector clients. These services encompass the management of vast public funds, sophisticated treasury operations, and the provision of financial support for significant government-backed infrastructure projects and economic development initiatives.
These partnerships are not merely transactional; they represent strategic alliances that underscore Bank of China's integral role within the nation's financial architecture. For instance, in 2023, the bank was a key facilitator in several large-scale public infrastructure financing deals, contributing to national development goals.
- Public Fund Management: Overseeing significant government deposits and investment portfolios.
- Treasury Services: Providing cash management, payment processing, and foreign exchange services for public entities.
- Government Project Financing: Supporting national and regional development projects, including infrastructure and social programs.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with government bodies on financial policy implementation and economic stability initiatives.
Bank of China’s customer segments are diverse, ranging from large corporations and SMEs to individual retail customers and high-net-worth individuals. The bank also serves government entities and public institutions, acting as a vital financial partner for national development and economic initiatives.
Cost Structure
Staff salaries and employee benefits represent a substantial cost for the Bank of China, reflecting its extensive global operations and diverse workforce. In 2023, the bank reported employee compensation expenses of approximately RMB 122.7 billion, a key component of its overall operational expenditure.
This figure encompasses remuneration for thousands of employees across various critical functions, including customer service, risk management, technology development, and international banking operations. Effective management of these human capital costs is paramount for maintaining the bank's profitability and competitive edge in the financial sector.
Bank of China dedicates significant resources to its technology infrastructure. In 2024, the bank continued its substantial investments in upgrading core banking systems and expanding its digital platforms to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. These ongoing expenditures are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial data.
Bank of China's branch network operating costs are substantial, encompassing rent, utilities, security, and administrative overheads for its numerous domestic and international locations. In 2024, the bank continued to invest in maintaining this physical infrastructure, even as digital banking gains traction.
While digital channels are expanding, the physical branch footprint remains a key cost driver for Bank of China. Optimizing this network, balancing accessibility with efficiency, is a continuous strategic focus for the institution.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management Costs
Bank of China, as a global financial institution, dedicates substantial resources to regulatory compliance and risk management. These essential expenditures ensure adherence to diverse international and domestic financial regulations, including stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) protocols. In 2024, the financial sector continued to see increased investment in these areas due to evolving regulatory landscapes and heightened scrutiny.
These costs are fundamental to maintaining the bank's operational integrity and reputation. Key components include:
- Technology Investments: Upgrading systems for data analytics, fraud detection, and compliance reporting to meet evolving standards.
- Personnel and Training: Hiring specialized compliance officers and providing ongoing training to staff on new regulations and risk mitigation techniques.
- External Audits and Consulting: Engaging third-party experts for independent assessments and guidance on complex regulatory matters.
- Capital Requirements: Allocating capital to meet regulatory ratios, such as Basel III or IV, which impacts overall financial strategy.
Marketing, Advertising, and Brand Promotion
Bank of China allocates significant resources to marketing, advertising, and brand promotion to attract new clients and foster loyalty among its existing customer base. These expenditures are crucial for staying competitive and reinforcing its established brand image in the financial sector.
In 2024, the bank likely continued its investment in a multi-channel marketing approach. This would encompass digital initiatives like social media campaigns and targeted online advertising, alongside traditional media placements and strategic sponsorship deals to enhance brand visibility and reach diverse demographics.
- Digital Marketing: Investments in SEO, SEM, social media engagement, and content marketing to reach a broad online audience.
- Traditional Advertising: Spending on television, radio, print, and outdoor advertising to build widespread brand recognition.
- Brand Promotion & Sponsorships: Allocations for events, partnerships, and corporate social responsibility activities to strengthen brand equity and customer relationships.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: The direct expenses associated with attracting new customers through these marketing efforts.
The cost structure of Bank of China is heavily influenced by its extensive human capital, with staff salaries and benefits forming a significant expenditure. The bank also incurs substantial costs related to maintaining its vast physical branch network, alongside ongoing investments in technology infrastructure to support digital transformation and cybersecurity. Furthermore, regulatory compliance and risk management represent a crucial and growing cost area, essential for operational integrity and market trust.
| Cost Category | 2023 (RMB Billion) | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Staff Costs | 122.7 | Salaries, bonuses, social security, training |
| Branch Network Operations | N/A (Significant) | Rent, utilities, maintenance, security |
| Technology Investments | N/A (Substantial) | System upgrades, digital platforms, cybersecurity |
| Regulatory Compliance & Risk Management | N/A (Increasing) | Personnel, training, external audits, capital requirements |
| Marketing & Brand Promotion | N/A (Significant) | Digital marketing, traditional advertising, sponsorships |
Revenue Streams
Bank of China's primary revenue engine is its net interest income (NII). This is essentially the profit generated from the spread between the interest it earns on its vast loan portfolio and investments, and the interest it pays out on customer deposits and other borrowings. In 2024, NII remained the cornerstone of its financial performance, reflecting the bank's core lending and deposit-taking activities.
The bank's ability to manage this interest rate spread is crucial. For instance, a widening gap between lending rates and deposit rates boosts NII, while narrowing spreads can compress it. This dynamic means that changes in benchmark interest rates, such as those set by the People's Bank of China, directly influence the profitability of this key revenue stream.
Bank of China generates substantial revenue from fees and commissions across a wide array of services. These include trade finance, international settlements, wealth management, investment banking advisory, and payment processing. This diverse fee income stream is less susceptible to fluctuations in interest rates, contributing to a more stable and increasingly significant portion of the bank's overall earnings.
In 2024, fee and commission income is a vital component of the bank's strategy for income diversification. For instance, the bank's wealth management business has seen significant growth, with assets under management reaching new highs, directly translating into increased fee-based revenue. This highlights the bank's ability to monetize its expertise and customer relationships through specialized financial services.
Bank of China generates significant revenue from foreign exchange (FX) trading, leveraging its extensive global network and its role in international trade. This includes profits from currency conversion for clients and speculative trading based on currency fluctuations.
In 2024, the FX market remained dynamic, with major currency pairs experiencing notable volatility. Bank of China, as a key player, capitalized on these movements, contributing to its overall financial performance. The bank's ability to manage risk and execute trades efficiently is crucial for maximizing gains in this area.
Investment Income (Proprietary Trading and Investments)
Bank of China also earns revenue through its proprietary trading and investment activities. This involves the bank trading its own capital in various financial markets, such as equities, bonds, and derivatives, and holding investment portfolios. For instance, in 2023, the bank's net trading and investment income saw fluctuations, reflecting market conditions and strategic asset allocation.
This revenue stream is inherently more variable than interest income, as it's directly tied to market performance and the success of the bank's trading strategies. The returns generated can significantly impact the bank's overall profitability and contribute to its capital growth.
- Proprietary Trading: Direct engagement in buying and selling financial instruments using the bank's own funds.
- Investment Portfolios: Returns generated from holdings in securities, bonds, and other financial assets.
- Market Volatility: Income from this segment is sensitive to fluctuations in global financial markets.
- Capital Growth: Contributes to the bank's overall financial strength and expansion.
Asset Management and Trust Service Fees
Bank of China generates significant revenue from asset management and trust service fees. These fees are collected from the bank's activities in managing client assets across diverse funds, investment portfolios, and specialized trust services, providing a consistent and predictable income source.
As Bank of China expands its asset management arm, these fee-based revenues are becoming a more substantial component of its overall financial performance. This growth is directly tied to the increase in assets under management (AUM), with fees typically being a percentage of the total AUM, ensuring a recurring revenue stream that scales with the business.
- Asset Management Fees: Bank of China earns fees for managing mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and other pooled investment vehicles. These fees are often expressed as an annual percentage of the AUM.
- Trust Service Fees: Revenue is generated from administering trusts, including estate planning, wealth management, and corporate trusts. Fees can be based on the value of assets held in trust or on specific services rendered.
- Portfolio Management Fees: For customized investment portfolios managed on behalf of high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients, the bank charges fees for its investment expertise and ongoing management.
- Growth in AUM: The increasing global demand for wealth management services, particularly in Asia, supports the growth of Bank of China's AUM and, consequently, its fee income. In 2024, many major banks saw continued growth in their wealth management divisions, with AUM figures often reaching trillions of dollars, directly translating to substantial fee revenues for services like those offered by Bank of China.
Bank of China's revenue streams are diverse, extending beyond traditional net interest income. Fee and commission income, derived from services like wealth management and trade finance, provides a significant and more stable earnings base. Foreign exchange trading and proprietary investments also contribute, though these are more susceptible to market volatility.
The bank's asset management and trust services are increasingly important revenue generators, with fees directly linked to the growing volume of assets under management. This diversification strategy aims to create a more resilient and multifaceted income profile for the bank.
In 2024, the financial landscape continued to present opportunities and challenges across these revenue streams. For example, while net interest income remained a core driver, the bank's focus on expanding fee-based services like wealth management demonstrated a clear strategy for growth and stability.
| Revenue Stream | Description | 2024 Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Income | Profit from lending and deposit spreads | Core revenue driver, influenced by interest rate policies |
| Fees & Commissions | Income from wealth management, trade finance, advisory | Increasingly important for diversification and stability |
| Foreign Exchange Trading | Profits from currency conversion and trading | Capitalizes on market volatility and international trade |
| Proprietary Trading & Investments | Income from trading own capital and investment portfolios | Variable, dependent on market performance and strategy |
| Asset Management & Trust Fees | Fees for managing client assets and trust services | Growing segment driven by increasing Assets Under Management (AUM) |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The Bank of China Business Model Canvas is built using a combination of internal financial reports, extensive market research on global banking trends, and strategic analysis of regulatory environments. These diverse data sources ensure a comprehensive and accurate representation of the bank's operations and market position.
