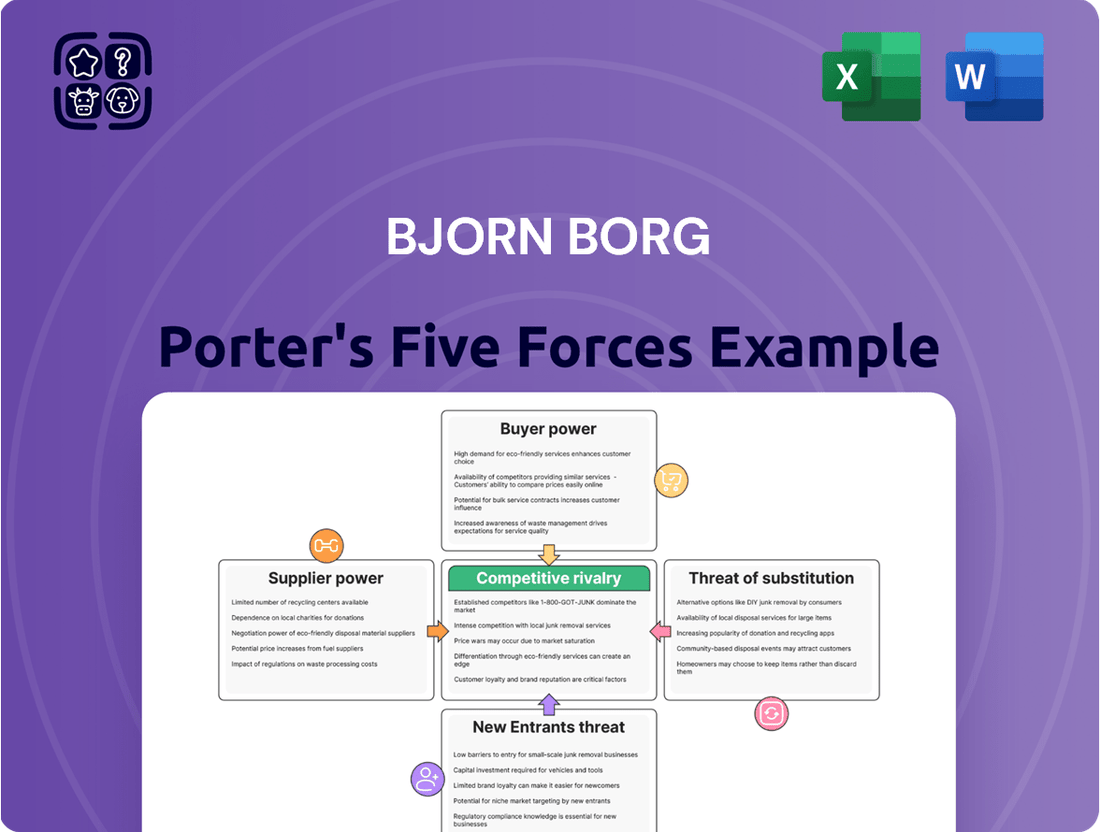
Bjorn Borg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bjorn Borg Bundle
Bjorn Borg, a brand synonymous with athletic performance and iconic style, faces a dynamic competitive landscape. Understanding the interplay of supplier power, buyer bargaining, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for its continued success.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Bjorn Borg’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
If Björn Borg depends on a limited number of suppliers for essential materials like high-performance fabrics or specific manufacturing techniques, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This bargaining power intensifies if it's costly to switch to other suppliers, perhaps due to specialized equipment, existing agreements, or unique intellectual property.
For instance, if a key fabric supplier to the sportswear industry, like those providing advanced moisture-wicking materials, has few competitors and Björn Borg has invested in machinery specific to that fabric, the supplier's power is amplified. In 2024, the global textile market saw significant price fluctuations, with some specialized synthetic fabric costs increasing by up to 15% due to supply chain disruptions, giving those producers more sway.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Björn Borg is influenced by the uniqueness of their inputs. If suppliers provide highly differentiated materials or specialized manufacturing processes critical to Björn Borg's athletic functionality and style, their leverage increases. For instance, exclusive fabric technologies or ethically sourced, unique materials could give suppliers more power.
Assessing the true uniqueness of these inputs is key. While Björn Borg emphasizes quality, the extent to which their suppliers' offerings are irreplaceable or difficult to substitute directly impacts supplier power. Without readily available alternatives, suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms, potentially affecting Björn Borg's profitability and operational flexibility.
Suppliers could increase their bargaining power if they credibly threaten to move into apparel manufacturing or retail, directly competing with Björn Borg. While this is uncommon for raw material providers, specialized component makers with strong brand awareness or existing distribution networks might consider it. However, the significant capital investment and brand development needed for apparel retail typically keep this threat at a low level.
Importance of Björn Borg to Suppliers
Björn Borg's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by how crucial its business is to them. If the company represents a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier's leverage diminishes because they rely heavily on Björn Borg's orders. Conversely, if Björn Borg is a minor customer to a large supplier, the supplier holds more power.
With annual revenues around SEK 989.7 million in 2024 (approximately €73.4 million), Björn Borg is a significant client. However, its true impact on the revenue streams of potentially massive global textile manufacturers needs careful evaluation to determine the extent of supplier dependence.
- Supplier Dependence: Björn Borg's revenue share is a key factor in assessing supplier bargaining power.
- Client Size: Björn Borg's 2024 revenue of ~SEK 990 million positions it as a considerable customer.
- Supplier Scale: The impact on large, diversified suppliers versus smaller, specialized ones will differ significantly.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for Björn Borg. If the company can readily source alternative fabrics, components, or manufacturing processes without incurring substantial costs or compromising product quality, the power of its current suppliers is naturally reduced.
For instance, consider the textile industry.
- In 2024, the global textile market saw a continued demand for recycled and bio-based materials, with some segments experiencing supply constraints for these specific inputs.
- Companies like Björn Borg that can efficiently pivot to more widely available conventional materials or develop in-house capabilities for alternative sourcing will lessen supplier leverage.
- Conversely, if Björn Borg relies heavily on specialized, high-performance, or sustainably certified materials where few suppliers exist, those suppliers gain considerable power.
Suppliers hold significant bargaining power when Björn Borg relies on a limited number of providers for unique or critical inputs, especially if switching costs are high. In 2024, the sportswear industry experienced increased costs for specialized synthetic fabrics, impacting brands that depend on these materials. This leverage is amplified when suppliers offer highly differentiated products or processes essential to Björn Borg's product performance and brand identity.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also shaped by Björn Borg's importance to them. If Björn Borg constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier's leverage is reduced. Conversely, if Björn Borg is a minor client, the supplier wields more power. Björn Borg's 2024 revenue of approximately SEK 990 million positions it as a notable customer, but its actual impact on large global textile manufacturers needs careful assessment.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example for Björn Borg |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers exist | Reliance on a single provider for patented fabric technology |
| Switching Costs | High if significant investment or disruption is involved | Need for new machinery to process alternative materials |
| Input Differentiation | High if inputs are unique and critical | Exclusive use of ethically sourced, high-performance yarns |
| Customer Dependence | Low if Björn Borg is a small customer | A large textile mill prioritizing orders from major global brands |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low if suppliers lack retail capabilities | Fabric manufacturers unlikely to enter the competitive sportswear market |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Bjorn Borg, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, revealing the strategic levers for sustained competitive advantage.
Instantly identify competitive threats and opportunities by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for Bjorn Borg.
Gain a clear, actionable understanding of market dynamics, allowing for swift strategic adjustments to mitigate competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Björn Borg operates in the competitive sports fashion sector, encompassing both performance gear and the increasingly popular athleisure segment. Customers in this market, especially when considering non-luxury items, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is particularly true in the current economic landscape of 2024, where consumers are actively seeking value and are more inclined to compare prices across brands.
The sheer volume of readily available alternatives in the sports fashion market directly fuels this customer price sensitivity. With numerous brands offering similar products, consumers can easily switch to a competitor if they perceive a better price point, further pressuring companies like Björn Borg to remain competitive on cost.
Customers wield considerable bargaining power when substitutes are readily available, a key factor in the apparel and footwear sector. The sheer volume of brands offering similar products means consumers can easily shift their allegiance if Bjorn Borg's pricing or product offerings aren't competitive. For instance, in 2024, the global sportswear market, which Bjorn Borg operates within, saw a significant influx of new entrants and expanded offerings from established players, further fragmenting consumer choice and amplifying this power.
The growth of e-commerce has dramatically shifted the balance of power towards consumers. In 2024, online retail sales are projected to reach over $6.5 trillion globally, a testament to how readily accessible product information and pricing comparisons have become. This digital landscape empowers shoppers to scrutinize features, read countless reviews, and identify the best value across numerous brands, significantly amplifying their ability to negotiate or switch to competitors.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For many of Björn Borg's product categories, such as underwear and basic sportswear, the cost and effort for a customer to switch to a competitor are minimal. This low switching cost significantly amplifies customer bargaining power.
Customers face no substantial contractual ties or technical hurdles that would make changing brands difficult. This ease of transition means consumers can readily explore and opt for alternative apparel and footwear providers, putting pressure on Björn Borg to maintain competitive pricing and product appeal.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily move between brands for apparel and footwear.
- No Significant Barriers: Lack of contractual obligations or technical complexities empowers customer choice.
- Market Impact: This low barrier encourages price sensitivity and brand loyalty challenges for Björn Borg.
Customer Concentration (Retailers)
Björn Borg's reliance on external retailers, alongside its direct-to-consumer channels, introduces a dynamic where customer concentration can significantly impact bargaining power. If a few major retail partners represent a substantial percentage of Björn Borg's overall revenue, these large retailers gain leverage.
This leverage can translate into demands for more favorable pricing, extended payment terms, or increased marketing and promotional assistance. Such demands, if met, could compress Björn Borg's profit margins and affect its overall financial flexibility. For instance, if a single large retailer accounts for over 10% of a brand's sales, their importance in negotiations escalates considerably.
Björn Borg's strategic push to expand its presence with larger retailers, particularly in key markets like Germany, highlights the potential for this factor to grow. As of 2024, the European apparel market, where Germany is a significant player, continues to see consolidation among major retail groups, potentially increasing the concentration of Björn Borg's customer base among fewer, larger entities.
- Customer Concentration Risk: A few large external retailers could wield significant bargaining power if they account for a disproportionate share of Björn Borg's sales.
- Negotiating Leverage: Powerful retailers may demand better pricing, payment terms, or marketing support, potentially impacting Björn Borg's profitability.
- Strategic Expansion: Björn Borg's focus on increasing its footprint with major retailers in markets like Germany could amplify this customer concentration.
- Market Trends: Ongoing consolidation within the European retail sector in 2024 suggests that the influence of large retail partners may continue to grow.
Customers in the sports fashion market, including Björn Borg's target demographic, possess substantial bargaining power. This is driven by the availability of numerous substitutes and the minimal costs associated with switching between brands, a trend amplified by the digital marketplace. In 2024, the ease of online price comparison and the vast array of choices available globally empower consumers to demand better value, directly impacting brands like Björn Borg.
The bargaining power of customers is further influenced by the concentration of Björn Borg's sales through large retail partners. In 2024, consolidation within the European retail sector means that a few major players could represent a significant portion of the brand's revenue, granting them considerable leverage in negotiations for pricing and promotional terms.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Björn Borg | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | Numerous competing sports fashion brands offer similar products. | Increases customer price sensitivity and reduces brand loyalty. | Global sportswear market fragmentation in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs for customers to change brands due to no contractual ties or technical barriers. | Empowers customers to easily shift to competitors offering better deals. | E-commerce facilitates easy comparison and switching. |
| Customer Concentration | Reliance on a few large retail partners for sales. | These partners gain leverage to negotiate favorable terms, impacting margins. | Consolidation in European retail in 2024. |
Same Document Delivered
Bjorn Borg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Bjorn Borg Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the sportswear industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The sports fashion and apparel market is incredibly crowded, featuring a vast array of competitors. This includes global powerhouses like Nike and Adidas, alongside numerous smaller, specialized brands and fast fashion giants. This diverse field of established players and emerging challengers significantly heightens the competitive intensity for Björn Borg.
The sportswear segment, a key area for Björn Borg, is experiencing robust growth, outperforming the broader apparel market. This expansion, however, doesn't eliminate competitive pressures. Even in expanding markets, a large number of determined competitors can lead to fierce rivalry as each seeks to capture a larger slice of the growing pie.
Björn Borg's own performance highlights this dynamic. The company reported a significant 13.5% sales increase in fiscal year 2024, followed by a commendable 9% rise in the first quarter of 2025. These figures confirm Björn Borg's operation within a thriving market, yet the need to consistently achieve such growth suggests a highly competitive landscape where standing out requires continuous effort and strategic maneuvering.
Björn Borg strives to stand out by blending athletic performance with modern fashion, a strategy also pursued by numerous competitors. Many brands in the sportswear and fashion industries are emphasizing sustainability, high-performance materials, and trend-conscious aesthetics, intensifying rivalry.
Building and sustaining strong customer loyalty is paramount for Björn Borg to effectively counter these competitive pressures. However, achieving this in a saturated market, where consumer tastes are varied and brand switching is common, presents a significant challenge. For instance, the global sportswear market, valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023, is highly competitive, with brands like Nike and Adidas demonstrating significant brand loyalty through extensive marketing and product innovation.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can trap companies in an industry, intensifying competitive rivalry. For Björn Borg, these barriers might include specialized manufacturing equipment for apparel or significant investments in retail store leases and branding, making it costly to simply walk away. This can lead to companies continuing operations even when profits are slim, simply to avoid the sunk costs of exiting.
The sporting apparel sector, where Björn Borg operates, often involves long-term commitments to suppliers and distribution networks. Dissolving these relationships can incur penalties or loss of future opportunities. Moreover, the social costs associated with closing facilities and laying off employees can also act as a deterrent to exiting, forcing continued participation in a potentially less profitable market.
While specific figures for Björn Borg's exit barriers aren't publicly detailed, the general industry landscape suggests potential challenges. For instance, in 2024, the global sportswear market saw continued investment in sustainable manufacturing processes, which could increase the specialization of assets. Companies might also be bound by multi-year contracts with athletes or sports leagues, further complicating an exit strategy.
- Specialized Assets: Investments in specific textile machinery or unique production lines for performance wear can be difficult to repurpose or sell.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers for materials or agreements with retailers for shelf space can create financial penalties for early termination.
- Brand Reputation: The significant investment in building and maintaining a brand like Björn Borg means that a sudden exit could damage its overall corporate value.
- Social Costs: The impact of layoffs on local communities and the company's public image can be a significant factor discouraging immediate closure of operations.
Product Differentiation and Innovation
The sports fashion sector thrives on constant innovation and unique product offerings. Björn Borg has demonstrated this by expanding its footwear and sports apparel lines, showing a commitment to product development. In 2024, the company reported continued growth in these key segments, reflecting successful product strategies.
However, this environment is intensely competitive. Rivals are also pouring resources into research and development, focusing on areas like eco-friendly materials and advanced smart fabrics. This means Björn Borg must maintain a relentless pace of innovation to avoid falling behind.
- Product Development Focus: Björn Borg's strategic growth in footwear and sports apparel highlights its dedication to innovation.
- Competitive Investment: Competitors are heavily investing in R&D, sustainable materials, and smart fabrics.
- Industry Trend: Continuous innovation is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the sports fashion market.
The competitive rivalry within the sports fashion and apparel market is exceptionally high, driven by a multitude of global brands and specialized niche players. Björn Borg faces intense pressure from established giants like Nike and Adidas, as well as emerging brands focusing on sustainability and fashion-forward designs. This crowded landscape necessitates continuous innovation and strategic differentiation to capture market share.
The sportswear segment, where Björn Borg operates, is experiencing significant growth, attracting numerous competitors vying for dominance. Björn Borg's own sales performance, with a 13.5% increase in fiscal year 2024 and a 9% rise in Q1 2025, underscores the dynamic nature of this market. However, achieving such growth in a fiercely competitive environment requires constant strategic adaptation and robust marketing efforts.
Many competitors are mirroring Björn Borg's strategy of blending athletic performance with fashion, intensifying the rivalry. Brands are increasingly emphasizing sustainable practices, advanced materials, and trend-driven aesthetics, making it challenging for any single player to maintain a unique selling proposition without significant investment in R&D and brand building.
The sportswear market, valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023, is characterized by high customer acquisition costs and the need for strong brand loyalty. Björn Borg must continually invest in marketing and product innovation to retain customers amidst the aggressive strategies of its competitors, who often leverage extensive global reach and significant marketing budgets.
| Competitor | Market Share (Est. 2024) | Key Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Nike | ~25-30% | Product innovation, athlete endorsements, digital engagement |
| Adidas | ~15-20% | Sustainability focus, collaborations, lifestyle integration |
| Puma | ~5-7% | Performance and lifestyle fusion, influencer marketing |
| Björn Borg | <1% (Global) | Fashion-forward sportswear, brand heritage, Scandinavian design |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Björn Borg's sportswear is significant, stemming from a broad range of product categories that can satisfy similar customer needs. These aren't just other sportswear brands; they extend to general casual wear and even formal attire that's increasingly designed with comfort in mind.
The burgeoning athleisure trend is a prime example, effectively blurring the lines between dedicated sportswear and everyday fashion. This growing acceptance of athletic-inspired clothing for non-sporting activities broadens the substitution possibilities considerably, as consumers may opt for comfortable, stylish casual wear instead of specialized sportswear for many occasions.
Customers weigh substitutes by comparing their price against the value they deliver, considering factors like performance, style, and comfort. If a substitute offers similar benefits for less money, or even better benefits at a slightly higher but reasonable cost, the threat to Bjorn Borg intensifies. For example, in 2024, the athleisure market saw continued growth, with many consumers opting for more budget-friendly activewear brands if the performance gap wasn't a critical differentiator for casual use.
Consumer trends, particularly the surge in health and wellness awareness, are reshaping how people view clothing. This heightened focus on well-being encourages a greater adoption of active lifestyles, blurring the lines between performance wear and everyday attire.
The integration of athleisure into daily wardrobes means that sports-inspired clothing is no longer confined to the gym or sports field. In 2024, the global athleisure market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating a significant expansion, making general apparel a more direct substitute for many consumers seeking comfort and style.
This shift means that for many occasions, consumers might opt for comfortable, stylish activewear over traditional casual wear. For instance, a consumer might choose a branded tracksuit or stylish leggings for running errands instead of jeans and a t-shirt, directly impacting the demand for conventional apparel brands.
Perceived Switching Costs for Buyers
Switching costs for buyers in the sportswear market, particularly for brands like Bjorn Borg, are generally quite low. While there might be some minor brand loyalty or habit in choosing a specific sportswear brand, the actual financial or functional cost of moving to a competitor’s product is minimal.
This low switching cost is amplified when considering substitutes beyond direct competitors. For instance, a consumer might easily switch from dedicated sportswear to general casual wear for everyday activities, or even opt for different types of athletic apparel from non-specialist brands. This flexibility in consumer choice significantly increases the threat of substitutes.
In 2024, the athleisure trend continued to blur the lines between performance sportswear and everyday casual wear. This means consumers can often fulfill their need for comfortable, sporty attire with items not traditionally classified as sportswear, further lowering the perceived switching cost away from specialized brands.
- Low Financial Switching Costs: Consumers face little to no penalty for changing sportswear brands, making them highly mobile.
- Ease of Transition to Casual Wear: The integration of athleisure means consumers can easily substitute specialized sportswear with general casual apparel for many daily uses.
- Impact of Athleisure Trend: In 2024, the continued popularity of athleisure provided readily available alternatives, diminishing the unique value proposition of dedicated sportswear brands.
- Consumer Choice Amplified: The abundance of comfortable and stylish casual wear options means consumers have many ways to meet their needs without relying solely on traditional sportswear.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are significantly increasing the threat of substitutes for Bjorn Borg's apparel. Innovations in fabric technology, like moisture-wicking and odor-control, are now standard in everyday clothing, not just sportswear. This means consumers can find comfort and performance in casual wear, making it a more appealing alternative to specialized athletic gear.
The availability of these advanced fabrics in a wider range of clothing blurs the lines between activewear and everyday fashion. For instance, by mid-2024, many athleisure brands reported double-digit growth in their casual lines, directly competing with traditional sportswear for consumer spending. This trend means consumers may opt for a versatile t-shirt that performs well in light activity and looks stylish for daily use, rather than purchasing a dedicated sports t-shirt.
- Fabric Innovation: Everyday apparel now frequently incorporates moisture-wicking and odor-control technologies.
- Blurred Lines: Non-sports apparel offers performance benefits, becoming a viable substitute.
- Consumer Preference Shift: Consumers increasingly seek comfort and functionality in casual wear, reducing reliance on specialized sportswear.
- Market Impact: Athleisure's growth indicates a strong consumer willingness to adopt versatile, performance-enhanced casual clothing.
The threat of substitutes for Björn Borg is substantial due to the broad appeal of athleisure and the increasing integration of comfort and performance features into everyday clothing. Consumers can easily opt for stylish casual wear that offers adequate comfort and functionality for many activities, diminishing the need for specialized sportswear.
The low switching costs, coupled with the widespread availability of versatile apparel, mean consumers can readily shift their spending. For example, in 2024, the global athleisure market's continued expansion provided a vast array of alternatives, making it simpler for consumers to choose general fashion items over dedicated sports brands for non-performance-oriented needs.
Technological advancements in fabrics have further leveled the playing field. Many casual wear items now boast moisture-wicking and odor-control properties, directly competing with the core benefits previously exclusive to sportswear.
This trend is reflected in market data, with consumers increasingly prioritizing comfort and style in their everyday wardrobe choices. The ease with which consumers can find suitable alternatives across different apparel categories significantly pressures specialized sportswear brands like Björn Borg.
| Category | 2024 Market Share (Approx.) | Key Substitute Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Athleisure Wear | 30% | Comfort, style, versatility for everyday use |
| General Casual Wear | 50% | Increasingly incorporates performance fabrics, broad accessibility |
| Specialized Sportswear (e.g., Björn Borg) | 20% | Performance, brand prestige, specific athletic function |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the competitive apparel and sports fashion sector, much like Björn Borg, demands significant upfront capital. This investment covers everything from initial design and product development to manufacturing, global marketing campaigns, and building robust distribution networks, encompassing both physical retail locations and sophisticated e-commerce operations. For instance, establishing a single flagship store can cost hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars in rent, fit-out, and inventory.
Björn Borg itself operates a considerable number of its own retail stores and a significant e-commerce presence. These direct-to-consumer channels necessitate substantial ongoing investment in inventory management, technology infrastructure, and customer service. The sheer scale of capital required to replicate such an established infrastructure presents a formidable obstacle for potential new players looking to enter the market.
Established brands like Björn Borg have cultivated significant brand loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to capture market share. This loyalty is often built on years of marketing, product quality, and emotional connection with consumers. For instance, in 2024, major sportswear brands continued to leverage their strong brand equity, with companies like Nike and Adidas consistently ranking among the most valuable brands globally, demonstrating the immense challenge new players face in establishing a similar level of customer trust and preference.
For new entrants in the apparel market, securing access to effective distribution channels presents a significant hurdle. This means either building their own retail and e-commerce infrastructure or negotiating shelf space with established retailers.
Incumbent brands like Bjorn Borg benefit from pre-existing relationships with retailers and a strong online presence, creating a barrier for newcomers. While e-commerce has somewhat leveled the playing field by allowing direct-to-consumer sales, gaining visibility and customer trust remains challenging.
Economies of Scale
Existing players in the sportswear and fashion industry, including Björn Borg, have established significant economies of scale. This means they can produce goods at a lower cost per unit due to high-volume operations in manufacturing, raw material sourcing, and widespread marketing campaigns. For instance, in 2024, major apparel brands often negotiate bulk discounts on fabrics and production runs, which smaller new entrants cannot replicate. This cost advantage is crucial in a market where price sensitivity can heavily influence consumer purchasing decisions.
New companies entering the market face a substantial hurdle in achieving similar cost efficiencies. They may have to absorb higher per-unit costs for materials, manufacturing, and marketing initially. This disparity in cost structure can place them at a distinct competitive disadvantage right from the start. For example, a new brand might pay 15-20% more for premium materials compared to an established brand sourcing at scale. This makes it challenging for them to compete on price and simultaneously invest in brand building and product development.
- Economies of Scale: Established brands like Björn Borg leverage bulk purchasing power for materials and manufacturing, leading to lower per-unit costs.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New companies struggle to match these cost efficiencies, potentially facing higher production expenses.
- Market Sensitivity: The sportswear market often reacts to price, making it difficult for new entrants with higher cost bases to compete effectively.
- 2024 Data Insight: Major apparel brands in 2024 often achieve production cost savings of 10-15% through large-scale operations compared to smaller competitors.
Regulatory Hurdles and Intellectual Property
New entrants in the apparel sector face significant regulatory challenges, particularly concerning labor laws and international trade agreements. For instance, in 2024, many brands are navigating evolving regulations around supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing, which can increase compliance costs.
Protecting intellectual property, such as unique fabric technologies or distinctive design elements, acts as a barrier. New companies must invest in legal frameworks to safeguard their innovations, a cost that can be substantial.
The growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical manufacturing practices adds another layer of complexity. By 2024, consumers and regulators alike are demanding greater accountability, pushing new entrants to adopt costly certifications and transparent production methods.
- Labor Law Compliance: Adherence to minimum wage, working hours, and safety standards across global manufacturing hubs.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Securing patents and trademarks for innovative designs and production techniques.
- Environmental Regulations: Meeting standards for water usage, chemical runoff, and carbon emissions in manufacturing processes.
- Trade Policies: Navigating tariffs, import/export restrictions, and country-specific trade agreements.
The threat of new entrants in the sportswear market, where Björn Borg operates, is generally moderate to high. Significant capital investment is required for design, manufacturing, and marketing, alongside the challenge of building brand loyalty against established players. For example, launching a new apparel line in 2024 often necessitates millions in upfront costs for inventory, marketing, and e-commerce infrastructure, making it a barrier for smaller startups.
Economies of scale achieved by incumbents like Björn Borg create a cost disadvantage for newcomers. Established brands benefit from bulk purchasing and efficient production, often resulting in 10-15% lower per-unit costs compared to new entrants in 2024. This cost disparity makes it difficult for new brands to compete on price while investing in brand development.
Brand loyalty is a critical factor, as consumers often stick with familiar names built on years of marketing and quality. In 2024, major sportswear brands continued to dominate market share, underscoring the difficulty new entrants face in capturing consumer preference and trust. Securing effective distribution channels, whether physical retail or online visibility, also presents a substantial hurdle.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Bjorn Borg Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the brand's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Euromonitor, and insights from financial news outlets such as Bloomberg.
