Big Lots Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Big Lots Bundle
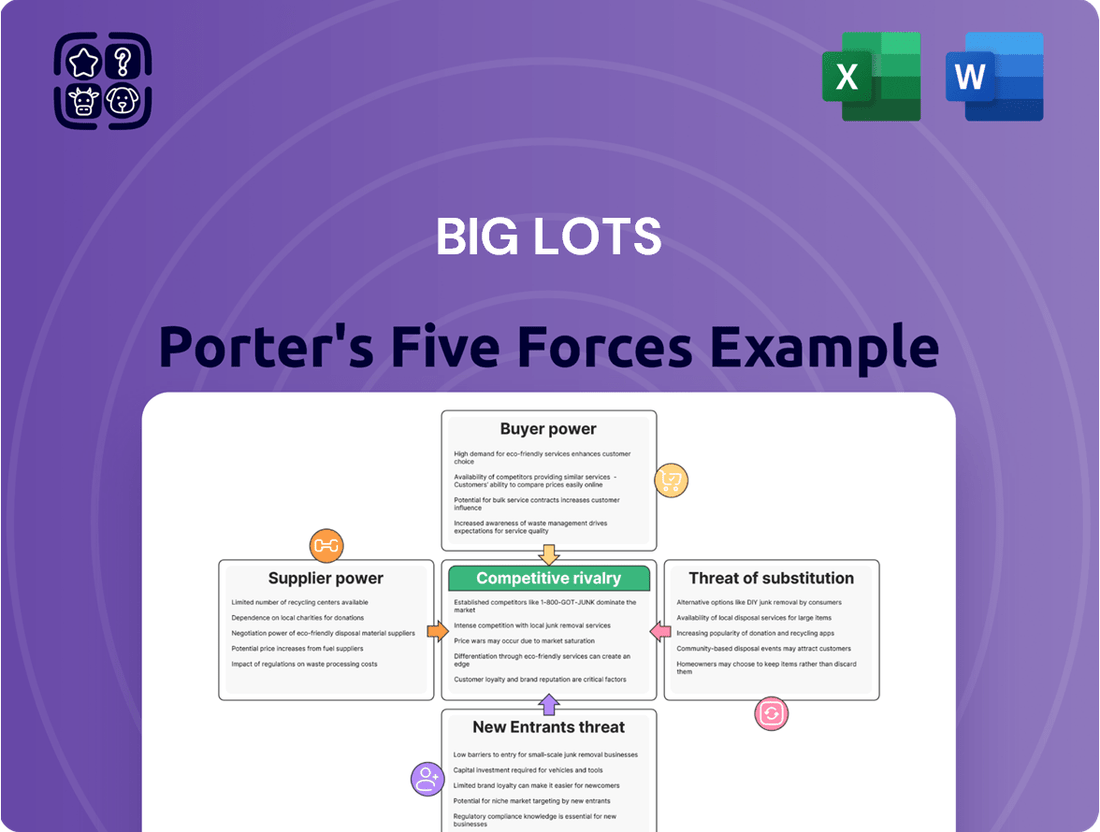
Big Lots navigates a retail landscape shaped by intense competition, with a moderate threat from new entrants due to established brands and supply chains. Buyer power is significant, as consumers easily switch between discount retailers based on price and promotions.
The threat of substitutes is also high, with online marketplaces and dollar stores offering similar value propositions. Supplier power is generally moderate, as Big Lots's purchasing volume gives it some leverage, but it relies on a diverse supplier base.
Rivalry among existing competitors is fierce, characterized by price wars and aggressive marketing. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Big Lots’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Big Lots benefits from a highly fragmented supplier base, primarily due to its opportunistic purchasing of closeouts and overstock merchandise from a vast array of vendors. This diverse sourcing strategy means no single supplier holds significant bargaining power over the company. By not depending on a few key manufacturers for its inventory, Big Lots maintains leverage, exemplified by its 2024 inventory management strategies focusing on flexible procurement. This diversification allows the company to secure favorable terms and pricing, supporting its value-driven retail model.
Big Lots employs an opportunistic sourcing model, primarily acquiring excess merchandise from manufacturers at significant discounts. This approach inherently diminishes the bargaining power of suppliers, as they often seek channels to offload surplus inventory that might otherwise incur storage costs or be liquidated at a greater loss. Big Lots provides a crucial avenue for these suppliers to recover capital, turning potential losses into revenue streams. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Big Lots continued to leverage its deep vendor relationships to secure favorable terms on closeout goods, which is vital as the company focuses on improving its merchandising and inventory turnover metrics.
Big Lots benefits from inherently low switching costs regarding its suppliers. The company's business model, focused on closeout and unbranded merchandise, allows it to easily pivot between different vendors without significant financial penalties. Unlike many traditional retailers, Big Lots is not typically bound by long-term contracts for specific branded goods, providing immense flexibility in sourcing. This strategic agility means that suppliers have limited leverage, as Big Lots can readily seek alternative sources, weakening their overall bargaining power in 2024.
Potential for Direct Sourcing
Big Lots is strategically reducing supplier bargaining power by expanding its direct sourcing initiatives. The company continues to invest in direct relationships with manufacturers, notably through establishing new sourcing offices in Asia. This move, a key focus for Big Lots in 2024, aims to bypass traditional middlemen, thereby cutting costs significantly. By building these direct channels, Big Lots enhances its control over product quality and supply chain resilience, lessening its dependence on a limited number of wholesale suppliers.
- Big Lots’ direct sourcing from Asia aims to reduce costs by eliminating intermediaries.
- In 2024, direct sourcing is a key strategy to improve profit margins.
- This approach strengthens Big Lots’ control over its supply chain and product flow.
- Reduced reliance on traditional wholesalers diminishes supplier bargaining power.
Supplier's Need for a Liquidation Channel
Suppliers, particularly manufacturers facing production overruns, discontinued items, or packaging changes, frequently seek liquidation channels like Big Lots to offload merchandise. This inherent need for an efficient outlet grants Big Lots significant leverage during negotiations. For many suppliers, accessing Big Lots' extensive retail network is crucial for inventory management, often outweighing the importance of any single supplier to Big Lots' overall purchasing strategy. This dynamic reduces the bargaining power of suppliers.
- Big Lots reported a net sales decline of 13.9% for fiscal year 2023, totaling $4.72 billion, indicating a continued reliance on opportunistic buys.
- The company's focus on closeout merchandise means suppliers are often competing for limited shelf space and purchase orders.
- Big Lots aims to maintain strong vendor relationships while capitalizing on distressed inventory opportunities, which were abundant in late 2023 and early 2024 due to retail overstocking.
- This model allows Big Lots to secure goods at favorable prices, reflecting their strong position in supplier negotiations.
Big Lots maintains low supplier bargaining power through its fragmented, opportunistic sourcing of closeout merchandise. Suppliers often rely on Big Lots to liquidate surplus inventory, granting the retailer significant negotiation leverage for favorable terms. The company's flexible sourcing and expanded direct import initiatives in 2024 further diminish supplier influence. This strategy, vital after FY2023’s $4.72 billion net sales, secures advantageous pricing.
| Metric | 2023 Data | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Net Sales | $4.72 Billion | Continued focus on opportunistic buys |
| Sales Decline (YoY) | 13.9% | Highlights need for cost-efficient sourcing |
| Supplier Leverage | Low | Strengthened by direct sourcing, overstock market |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Big Lots' market, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the discount retail sector.
Instantly visualize Big Lots' competitive landscape with a dynamic, interactive model that highlights key pressures and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Big Lots primarily targets budget-conscious consumers who exhibit high price sensitivity, making price a critical factor in their purchasing decisions. This forces the company to maintain competitive and often low pricing across its merchandise to attract and retain its customer base. For instance, Big Lots reported a comparable sales decrease of 9.9% in Q4 fiscal year 2023, reflecting consumer demand for value amidst economic pressures. This emphasis on affordability means customers wield significant power to demand competitive pricing, directly influencing Big Lots' profitability and merchandising strategies.
In the discount retail sector, customer brand loyalty is generally low, as purchasing decisions are primarily driven by price and perceived value. Shoppers are highly willing to switch between different discount stores, like Big Lots, Dollar General, or TJ Maxx, to find the best deals and maximize their savings. This lack of strong brand allegiance significantly increases the bargaining power of customers, compelling retailers to constantly compete on price and promotions. For instance, a Q1 2024 McKinsey report highlighted that value-seeking behaviors remain prevalent, with consumers readily shifting their purchasing to retailers offering more competitive pricing and perceived value.
Customers considering Big Lots have numerous alternatives, including other discount stores like Dollar General and Dollar Tree, mass-market retailers such as Walmart and Target, and a vast array of online marketplaces. The high number of competitors means consumers, empowered by easily accessible price comparisons, have a wide range of choices for home goods and essentials. This intense competition, especially with e-commerce growing by an estimated 9.9% in 2024, significantly empowers buyers to seek out the best possible prices and product assortments, impacting Big Lots' pricing strategies.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
Customers face virtually no costs when deciding to shop at a competitor instead of Big Lots. The products offered, ranging from home goods to consumables, are largely undifferentiated and readily available at numerous other discount retailers or grocery stores. This ease of switching, a key aspect of customer bargaining power, compels Big Lots to consistently offer compelling value, deep discounts, and unique closeout deals to retain its customer base.
- Big Lots reported a comparable sales decrease of 10.2% in Q4 2023, reflecting customer willingness to seek alternatives.
- The prevalence of similar general merchandise at retailers like Dollar General, TJX Companies, and Walmart increases customer options.
- Big Lots’ average basket size for Q4 2023 indicated a slight increase, but overall customer traffic remained a challenge.
- Promotional activity and loyalty programs are crucial for Big Lots to counteract the low switching barriers in 2024.
Access to Information
Modern consumers significantly influence Big Lots through their access to vast product and pricing information. In 2024, an estimated 76% of US consumers use their mobile devices to compare prices while shopping. This digital transparency allows them to readily find the best deals, increasing their ability to choose a competitor or negotiate. Big Lots must adapt to this informed customer base.
- Consumers leverage online platforms to compare Big Lots' prices against competitors.
- Mobile apps enable real-time price checks, enhancing customer negotiation power.
- Big Lots faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing due to this transparency.
Customers hold significant bargaining power over Big Lots due to high price sensitivity and readily available alternatives. Low brand loyalty and minimal switching costs, coupled with consumers' ability to compare prices using mobile devices, compel Big Lots to offer competitive pricing. For instance, e-commerce growth, estimated at 9.9% in 2024, empowers buyers with more choices and price transparency.
| Metric | 2024 Context | Impact on Big Lots | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparable Sales (Q4 2023) | -10.2% decrease | Reflects customer willingness to seek alternatives for value. | ||
| E-commerce Growth | +9.9% (estimated) | Increases customer options and price comparison capabilities. | ||
| Mobile Price Comparison | 76% US consumers use it | Enhances customer power to demand competitive pricing. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Big Lots Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Big Lots Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a detailed examination of competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products or services. You're looking at the actual document, ensuring transparency and accuracy in the competitive landscape assessment. Once your purchase is complete, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file. This means you receive the full, ready-to-use analysis without any discrepancies or missing information. The insights presented here will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of the strategic forces shaping Big Lots' market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The discount retail market is highly competitive, featuring numerous players vying for the same customer base. Big Lots faces intense rivalry from national chains like Walmart and Target, alongside dollar stores such as Dollar General and Dollar Tree, which reported over 20,000 combined U.S. stores in 2024. This market saturation drives aggressive competition on price, product selection, and store locations. For instance, Dollar General aims to open 800 new stores in 2024, intensifying the battle for budget-conscious consumers.
Price is a primary battleground in the discount retail sector, where competitors like Dollar General and TJX Companies aggressively vie for market share. These rivals frequently deploy promotions and deep discounts to attract budget-conscious consumers, intensifying pressure on Big Lots. This constant price competition, evident in promotional spending across the sector, consistently squeezes profit margins for all players. Such aggressive strategies force companies to maintain tight operational efficiencies to remain competitive in 2024.
Big Lots, despite aiming for a 'treasure hunt' experience, struggles with low product differentiation as many of its offerings overlap with competitors. Merchandise, particularly consumables and home goods, is often quite similar to what is found at other discount chains like Dollar General or TJ Maxx. This lack of strong, unique products intensifies competitive rivalry, pushing Big Lots into a price-centric battle. For instance, Walmart, a major competitor in many categories, reported net sales of $161.5 billion in Q1 2024, highlighting the vast, price-sensitive market where differentiation is key.
Strategic Moves by Competitors
Competitors are consistently evolving their strategies, expanding store footprints, and significantly enhancing e-commerce capabilities to capture market share. This relentless competitive pressure, exemplified by rivals like TJX Companies opening 1,600 new stores globally by early 2024, forces Big Lots to continuously adapt. The company's ongoing strategic initiatives, including its Project Springboard, are a direct response to these intense market shifts and the need to improve profitability amidst fierce rivalry.
- Competitors like Dollar General plan to open 800 new stores in 2024, increasing market saturation.
- E-commerce growth for discount retailers, such as Ollie's Bargain Outlet, continues to intensify the digital competitive landscape.
- Big Lots reported a net loss of $25.9 million in Q4 2023, reflecting ongoing competitive pressures.
- Big Lots is focusing on its back-to-basics strategy to improve core performance against rivals.
Slow Industry Growth
The discount department store sector, where Big Lots operates, has experienced notably sluggish growth, often bordering on negative trends in recent years. This mature market environment means companies like Big Lots are fighting for a slice of a pie that isn't significantly expanding. Achieving substantial growth becomes a zero-sum game, as any gains typically come at the expense of a competitor's market share, intensifying rivalry.
For instance, industry projections for discount retail often show low single-digit percentage growth, if any, for 2024. This limited expansion forces aggressive pricing and promotional activities among key players.
- The U.S. discount retail sector's overall growth has been constrained, with many segments seeing flat to declining sales volumes in 2024.
- Big Lots reported a net sales decline of 13% for fiscal year 2023, reflecting broader industry headwinds.
- Market saturation and evolving consumer spending habits contribute to the sector's limited growth prospects.
- Companies are increasingly reliant on customer retention and converting competitor's patrons rather than tapping into new market expansion.
Big Lots faces intense competitive rivalry from numerous discount retailers like Walmart, Target, and dollar stores, which collectively operate over 20,000 U.S. locations as of 2024. This market saturation drives aggressive price competition and rapid expansion, with Dollar General planning 800 new stores in 2024 alone. Low product differentiation for Big Lots, combined with a mature, low-growth sector, intensifies this battle, squeezing margins and necessitating continuous strategic adaptation.
| Competitor | 2024 Store Count/Expansion | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dollar General | >20,000 U.S. (combined with DLTR) | Aggressive expansion (800 new stores 2024) |
| TJX Companies | 1,600 new stores globally by early 2024 | Broad product range, treasure hunt |
| Walmart | $161.5B net sales Q1 2024 | Price leadership, vast selection |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Online retail giants such as Amazon and expansive e-commerce marketplaces present a substantial substitute for traditional brick-and-mortar discount stores like Big Lots. These platforms offer consumers a vast selection of products, often at highly competitive prices, combined with the convenience of direct home delivery. This threat is significantly amplified by the ongoing consumer shift towards online shopping; for instance, e-commerce sales in the US accounted for 16.6% of total retail sales in Q1 2024. The ease of comparing prices and accessing diverse inventories online directly impacts foot traffic and sales at physical discount retailers.
Large mass market retailers like Walmart and Target present a significant threat of substitution for Big Lots. These retail giants offer a comprehensive one-stop-shop experience, providing a vast array of products, including full-service grocery and pharmacy departments. In 2024, Walmart continued to dominate with its extensive product range and convenient services, attracting customers seeking a single shopping destination. Target also served as a strong substitute, combining value with a curated selection and accessible amenities. Their ability to deliver both competitive pricing and broad convenience makes them powerful alternatives, diverting potential Big Lots customers.
Membership-based warehouse clubs like Costco and BJ's Wholesale Club pose a significant threat to Big Lots by offering bulk products at highly competitive prices. For customers willing to purchase larger quantities, these clubs, with Costco reporting net sales of $58.52 billion for Q3 2024, present a compelling alternative to traditional discount stores. Their value proposition centers on low unit costs and a broad assortment, appealing to a segment of the market focused on value and bulk purchasing. This distinct model diverts a portion of Big Lots' potential customer base, particularly those seeking everyday essentials in larger sizes.
Second-hand and Thrift Stores
The rise of second-hand and thrift stores poses a significant substitute threat to Big Lots, especially with consumers increasingly prioritizing value and sustainability. These outlets, particularly popular with younger demographics, offer unique finds at extremely low price points, leveraging a similar treasure hunt appeal as discount retailers. This trend reflects a considerable shift in consumer spending habits towards more circular and budget-friendly options.
- The global second-hand apparel market is projected to reach $350 billion by 2027.
- ThredUp’s 2024 Resale Report noted 70% of consumers have shopped for secondhand items.
- Gen Z and Millennials are driving this growth, with 1 in 3 Gen Z consumers purchasing used apparel in 2023.
- Lower prices at thrift stores directly compete with Big Lots’ value proposition, especially for non-essential goods.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands
The rise of Direct-to-Consumer brands poses a growing threat as more companies sell online, bypassing traditional retailers. While individual DTC brands may not significantly impact Big Lots, their collective presence can gradually erode market share, especially in key categories like home decor and furniture. For instance, the US DTC e-commerce market is projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, reflecting a substantial shift in consumer purchasing habits. This trend forces Big Lots to innovate and offer unique value to retain its customer base.
- DTC e-commerce sales are projected to reach over $200 billion in the US by 2024.
- Big Lots' categories like furniture and home decor are particularly vulnerable to DTC substitutes.
- The collective impact of numerous smaller DTC brands erodes traditional retail's customer base.
- Consumers increasingly prefer the convenience and unique offerings of online direct purchases.
Big Lots faces a significant threat from diverse substitutes including online retailers like Amazon, mass market giants such as Walmart, and membership-based warehouse clubs like Costco. The rise of second-hand markets and direct-to-consumer brands further intensifies this pressure, offering consumers varied options for value and convenience. This broad competition necessitates Big Lots to continually differentiate its offerings and value proposition. The shift in consumer behavior towards online and budget-friendly alternatives impacts traditional retail foot traffic.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market Data | Impact on Big Lots |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce | US e-commerce sales 16.6% of retail Q1 2024 | Reduces physical store traffic |
| DTC Brands | US DTC e-commerce over $200 billion 2024 | Erodes share in key categories |
| Second-hand | 70% of consumers shopped secondhand 2024 | Competes on low price and value |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a national retail footprint in discount retail requires immense capital investment in real estate, inventory, and extensive distribution networks. Big Lots, operating over 1,400 stores as of early 2024, exemplifies a scale that is exceptionally difficult and costly for any new entrant to replicate. This substantial financial outlay creates a formidable barrier to entry, significantly deterring potential competitors. The sheer cost involved in building comparable infrastructure limits new market participation.
Established retailers like Big Lots leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in purchasing closeout inventory. Their extensive network and substantial buying power, reflected in fiscal year 2023 net sales of $4.72 billion, enable them to secure merchandise at exceptionally low per-unit costs. This scale extends to logistics and marketing, creating a formidable cost advantage. A new entrant, lacking such volume and established relationships, would face immense difficulty matching Big Lots' competitive pricing and operational efficiency.
Big Lots benefits from deep, long-standing relationships with a vast network of suppliers crucial for its closeout merchandise model. A new entrant would face significant hurdles establishing comparable connections, as these relationships are built on trust and consistent volume over many years. This makes it challenging for newcomers to secure the same quality or volume of opportunistic deals, which are vital for competitive pricing in 2024. Gaining access to the most lucrative closeout inventories, which typically require established trust and purchasing power, remains a substantial barrier for any potential competitor.
Brand Recognition and Customer Base
Big Lots possesses established brand recognition and a loyal customer base, making it challenging for new entrants to compete effectively. A new discount retailer would face substantial hurdles in building brand awareness and enticing customers away from Big Lots, who are accustomed to its value proposition. This requires significant marketing investment, potentially billions of dollars annually for national campaigns, and a truly compelling, differentiated offering to capture market share.
- Big Lots' value proposition and existing customer base deter new competitors.
- New entrants face high costs for brand awareness, requiring substantial marketing outlays.
- Big Lots continues to leverage its familiar presence in the discount retail sector.
- Differentiation is key for any new company aiming to disrupt the established market.
Intense Competition and Price Wars
The intense competition and aggressive pricing within the discount retail sector significantly deter potential new entrants. Any new player would face immediate pressure to engage in price wars, which inherently leads to very low initial profitability. Competing with established giants like Walmart and Dollar General, which commanded significant market shares in 2024, presents a formidable barrier. The sheer scale and existing price advantages of these incumbents make market penetration extremely challenging for newcomers.
- Walmart reported net sales of $611.2 billion for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2024, highlighting its dominant market position.
- Dollar General operated over 19,000 stores across the U.S. as of February 2024, showcasing its extensive reach.
- New entrants would struggle to match the economies of scale and supply chain efficiencies of these established players.
- The necessity of aggressive pricing strategies to attract customers would likely result in prolonged periods of unprofitability for new businesses.
The threat of new entrants for Big Lots remains low due to immense capital requirements for infrastructure, with Big Lots operating over 1,400 stores as of early 2024. Established economies of scale, including $4.72 billion in FY2023 net sales, provide significant cost advantages. Deep supplier relationships and strong brand recognition further deter new competitors. The fierce competition from dominant players like Walmart, with $611.2 billion in FY2024 net sales, makes market penetration exceptionally challenging for any newcomer.
| Barrier | Description | 2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High cost to establish national footprint. | Big Lots operates over 1,400 stores. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages in purchasing/logistics. | Big Lots FY2023 Net Sales: $4.72B. |
| Market Competition | Dominance of established giants. | Walmart FY2024 Net Sales: $611.2B. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Big Lots is informed by a comprehensive review of company annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld.
We also leverage data from retail industry publications, competitor news, and macroeconomic indicators to provide a thorough assessment of the competitive landscape impacting Big Lots.
