BE Semiconductor Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BE Semiconductor Industries Bundle
BE Semiconductor Industries operates in a dynamic semiconductor equipment market where intense rivalry and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its competitive landscape. Understanding the leverage of powerful suppliers and the bargaining power of its key customers is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview only scratches the surface of these critical market forces.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BE Semiconductor Industries’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) is significantly shaped by the concentration of specialized manufacturers. When there are only a handful of companies capable of producing critical, high-tech components essential for advanced semiconductor assembly equipment, their leverage naturally increases. This is especially true for specialized areas like the sophisticated components required for hybrid bonding solutions, where Besi relies on a limited pool of expert providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) is significantly influenced by the uniqueness of their inputs. When suppliers offer proprietary technologies or highly specialized components essential for Besi's advanced semiconductor assembly equipment, particularly for the burgeoning AI and high-performance computing sectors, their leverage increases substantially.
Besi's dependence on these unique inputs restricts its flexibility. Switching to alternative suppliers in such scenarios could lead to considerable costs, potential production delays, and a compromise in the quality or performance of Besi's cutting-edge machinery, thereby strengthening the supplier's position.
High switching costs for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. If Besi faces substantial expenses or disruptions in re-tooling, re-qualifying new suppliers, or redesigning its sophisticated semiconductor manufacturing equipment to integrate components from alternative sources, it becomes more difficult to change suppliers. This inertia effectively locks Besi into existing relationships, granting suppliers greater leverage in negotiating prices and contract terms. For instance, the specialized nature of semiconductor equipment components means that even minor changes can necessitate extensive validation processes, adding considerable cost and time to any supplier transition.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers of raw materials or components integrating forward into BE Semiconductor Industries' (BESI) semiconductor assembly equipment manufacturing is generally low. This is due to the significant capital investment, specialized technical expertise, and ongoing research and development needed to compete in this segment. For instance, the global semiconductor equipment market, including assembly and testing, was valued at approximately USD 25.5 billion in 2023, indicating substantial barriers to entry.
However, the risk can increase if a supplier offers highly integrated sub-assemblies or modules that can be readily incorporated into finished assembly equipment. In such cases, a supplier might possess the technical knowledge and existing customer relationships to transition into producing the final equipment, potentially disintermediating BESI. The high R&D expenditure in the semiconductor industry, with companies like BESI investing millions annually, further solidifies the need for deep technological capabilities, which are difficult for many suppliers to replicate.
- Low Threat: The specialized nature of semiconductor assembly equipment and the high capital outlay make forward integration by suppliers challenging.
- High Investment: Significant R&D and manufacturing infrastructure are required, creating a substantial barrier for potential entrants.
- Supplier Capability: Threat increases if suppliers provide easily integrated modules, possessing some relevant technical know-how.
- Industry Dynamics: The semiconductor equipment market, valued at tens of billions, demands advanced technological capabilities that are not easily acquired by component suppliers.
Importance of Besi to Supplier
The significance of BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If Besi accounts for a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier might be more inclined to offer favorable terms to maintain the relationship, thereby reducing their own bargaining power.
Conversely, if Besi represents a minor client for a large, diversified supplier, Besi's ability to negotiate terms would be considerably weaker. This dynamic is common across many industries where customer size dictates leverage.
- Besi's Revenue Contribution: For suppliers heavily reliant on Besi for a significant percentage of their sales, their bargaining power against Besi is diminished.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with a broad customer base are less vulnerable to Besi's demands, thus retaining greater bargaining power.
- Strategic Importance: If Besi is a key customer for a specialized supplier, the supplier's dependence on Besi's orders can reduce its leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) is moderate, influenced by the concentration of specialized component manufacturers and the unique nature of inputs. While Besi's significant revenue contribution can reduce supplier leverage, the high switching costs associated with re-qualifying specialized components for its advanced assembly equipment solidify supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact on Besi | Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High dependence on limited expert providers for critical components. | Increases power |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Reliance on proprietary technologies for AI and HPC sectors. | Increases power |
| Switching Costs | Substantial expenses and delays in re-tooling and validation. | Increases power |
| Besi's Revenue Contribution | Can reduce supplier leverage if Besi is a key client. | Decreases power |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for BE Semiconductor Industries by examining supplier power, buyer power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape of semiconductor manufacturing with a dynamic five forces analysis, highlighting key pressures on BE Semiconductor Industries.
Gain actionable insights into supplier power and threat of new entrants, enabling strategic adjustments for BE Semiconductor Industries.
Customers Bargaining Power
Besi's customer base is diverse, serving major players across the semiconductor manufacturing spectrum, including foundries and assembly subcontractors. This broad reach generally dilutes individual customer power.
However, if a few very large clients were to represent a disproportionately large share of Besi's revenue, their ability to negotiate better pricing or terms would increase significantly. For example, if the top 5 customers accounted for over 50% of sales, their collective bargaining power would be considerable.
Switching costs for customers in the semiconductor equipment industry, particularly for assembly solutions like those offered by BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi), are notably high. For semiconductor manufacturers, the process of changing their assembly equipment suppliers involves significant investment in re-qualifying new machinery, integrating it seamlessly with existing production lines, and managing the potential for costly downtime during the transition. This complexity and expense inherently limit the bargaining power of Besi's customers.
Customers in the semiconductor industry are often well-informed about prevailing market prices and the latest technological trends. This awareness can significantly amplify their negotiating leverage, particularly when dealing with more standardized assembly equipment where differentiation is less pronounced.
However, for sophisticated or cutting-edge packaging solutions, the distinct value offered by BE Semiconductor Industries' technology can diminish customer price sensitivity. For instance, in 2024, the demand for advanced packaging, crucial for AI chips and high-performance computing, saw significant growth, allowing suppliers of specialized equipment to command premium pricing due to the unique capabilities they offer.
Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of customers, such as semiconductor manufacturers, integrating backward and producing their own assembly equipment is generally low for BE Semiconductor Industries. This is largely because developing and manufacturing the highly specialized and technologically advanced machinery required for semiconductor assembly demands substantial R&D investment and deep technical expertise. For instance, the capital expenditure for a single advanced assembly line can run into tens of millions of dollars, making in-house production a financially prohibitive undertaking for most chipmakers.
The intricate nature of semiconductor assembly processes, which require precision engineering and continuous innovation to keep pace with Moore's Law and evolving chip architectures, further elevates the barrier to entry. Companies like BE Semiconductor Industries have built decades of experience and proprietary knowledge in areas like die bonding, wire bonding, and packaging technologies. This accumulated know-how is not easily replicated, especially considering the rapid pace of technological advancement in the semiconductor equipment sector.
- High R&D Costs: Semiconductor assembly equipment requires continuous innovation, with R&D spending often representing a significant portion of revenue for leading manufacturers.
- Substantial Capital Investment: The upfront cost for specialized manufacturing facilities and advanced machinery for producing semiconductor equipment is in the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Deep Technical Expertise: Mastery of complex processes like precision robotics, advanced optics, and material science is essential, representing a significant knowledge gap for potential new entrants.
- Economies of Scale: Established players benefit from economies of scale in production and supply chain management, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on cost.
Volume of Purchases
The sheer volume of purchases made by BE Semiconductor Industries' (Besi) key customers significantly influences their bargaining power. When major semiconductor manufacturers or large assembly operations place substantial orders, they gain leverage. This can lead Besi to offer preferential pricing or more accommodating contract terms to secure these high-volume deals, ensuring consistent revenue streams.
For instance, in 2023, Besi reported that its top ten customers accounted for a significant portion of its revenue, highlighting the concentration of purchasing power among a few large entities. This dependence on a limited number of large clients means these customers can negotiate more aggressively on price and delivery schedules.
- High-volume orders from major semiconductor fabs and assembly houses give these customers considerable sway.
- This can translate into Besi offering discounts or more favorable contract terms to secure these substantial deals.
- Besi's reliance on a few large clients, who represented a substantial revenue share in 2023, underscores this customer bargaining power.
While Besi's diverse customer base generally dilutes individual power, large clients with substantial order volumes wield significant influence. For example, Besi's top ten customers accounted for a significant portion of its revenue in 2023, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms.
The high switching costs associated with specialized semiconductor assembly equipment further limit customer bargaining power. The expense and complexity of re-qualifying machinery and integrating it into existing production lines create a strong incentive for customers to remain with their current suppliers.
Customers' awareness of market prices and technology trends can enhance their leverage, particularly for more standardized equipment. However, for cutting-edge solutions, Besi's technological differentiation in 2024, especially in advanced packaging for AI chips, allows for premium pricing, thereby diminishing customer price sensitivity.
The threat of backward integration, where customers produce their own assembly equipment, is minimal due to the immense R&D investment and deep technical expertise required, making it financially prohibitive for most chipmakers.
| Customer Segment | Influence Factor | Impact on Besi |
|---|---|---|
| Large Semiconductor Fabs | High-volume orders | Increased negotiation leverage for pricing and terms |
| Assembly Subcontractors | Standardized equipment needs | Price sensitivity and demand for competitive offers |
| AI Chip Manufacturers | Demand for advanced packaging | Reduced price sensitivity due to unique technological value |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
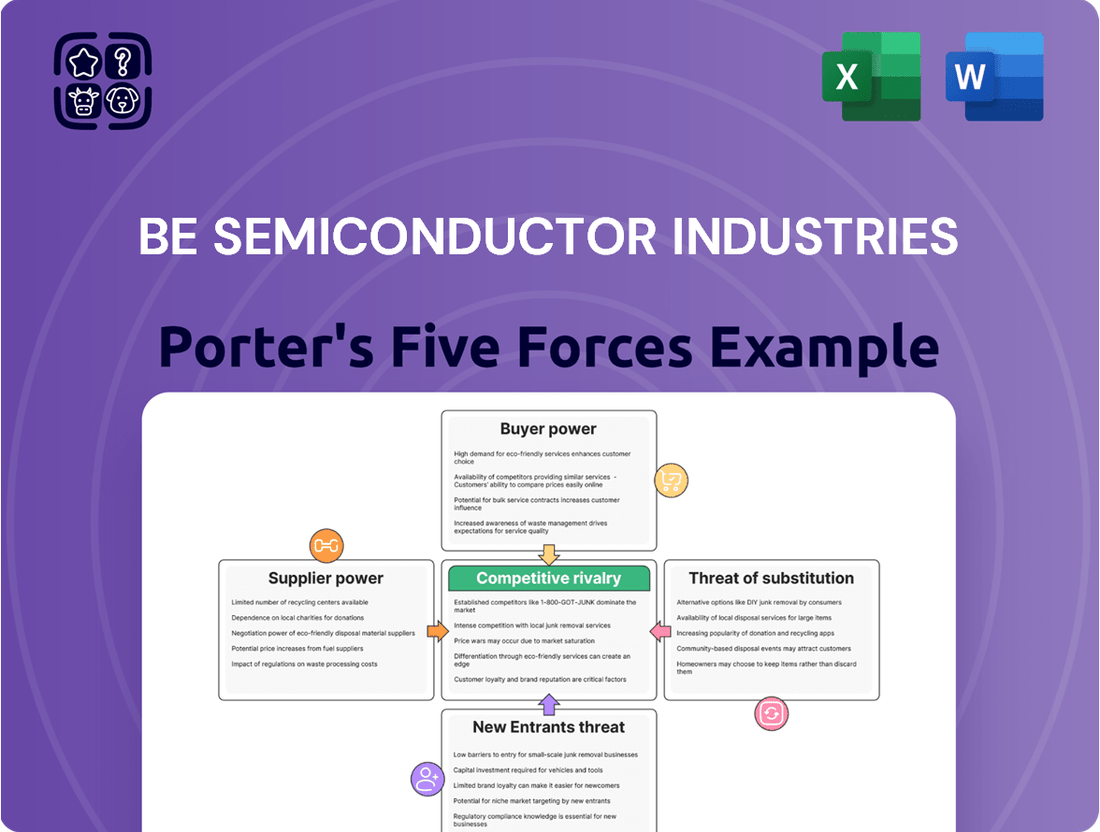
BE Semiconductor Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of BE Semiconductor Industries, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering an in-depth examination of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of substitutes, and new entrants. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights into BE Semiconductor Industries' market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The semiconductor assembly equipment market features a moderate number of significant global competitors. Key players like Lam Research, Applied Materials, Tokyo Electron, ASML, and KLA are well-established. Besi faces competition from these larger, more diversified suppliers as well as specialized companies focusing on specific market niches.
This competitive landscape intensifies rivalry, especially in rapidly expanding areas such as advanced packaging technologies. For instance, in 2023, the global semiconductor equipment market was valued at approximately $110 billion, with assembly and packaging equipment representing a substantial portion of this. Besi's direct competitors in this segment are numerous and often possess significant R&D budgets and market share.
The semiconductor equipment market is on a strong upward trajectory. Global sales are expected to hit record highs in both 2025 and 2026. This surge is largely fueled by the booming demand for AI technologies and the ongoing shift towards more advanced manufacturing processes.
While robust industry growth often tempers intense rivalry, the semiconductor sector presents a unique dynamic. The sheer speed of technological evolution, particularly in areas like advanced packaging for AI chips, means companies are fiercely competing for dominance. This rapid innovation cycle elevates the stakes and intensifies the battle for market share among key players.
Besi stands out by concentrating on sophisticated packaging solutions, such as hybrid bonding, essential for powering high-performance computing and AI. This focus allows them to offer specialized equipment that addresses the evolving needs of advanced semiconductor manufacturing.
In 2023, Besi reported a significant increase in their order intake, driven by demand for their advanced packaging technologies, demonstrating the market's appetite for innovation. Their commitment to research and development, with substantial investments allocated annually, is key to staying ahead.
This continuous innovation not only strengthens their market position but also helps mitigate direct competition. By offering unique, high-margin products, Besi cultivates strong customer loyalty and reduces the pressure from rivals offering more commoditized solutions.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the semiconductor equipment sector, like specialized machinery and substantial R&D commitments, mean companies may persist even in lean times. This can amplify competition as firms vie for sales to offset fixed expenses. For instance, BE Semiconductor Industries (BESI) operates in a capital-intensive environment where exiting the market involves significant write-downs on highly specific manufacturing equipment.
These barriers contribute to a more intense competitive landscape. Companies are often compelled to stay in the game, even when profitability is challenged, to avoid substantial losses on specialized assets. This dynamic can lead to price wars or aggressive market share grabs as competitors fight to maintain revenue streams and cover their high fixed costs.
- Specialized Assets: Semiconductor manufacturing equipment is highly specific and difficult to repurpose, leading to significant sunk costs for any player looking to exit.
- R&D Investment: Continuous and substantial investment in research and development is crucial for staying competitive, creating another barrier to exiting the market gracefully.
- Customer Relationships: Long-term contracts and deep integration with major semiconductor manufacturers make it challenging to disengage without impacting ongoing supply chains.
Market Share and Strategic Stakes
The drive to capture and hold market share, particularly in the burgeoning advanced packaging and AI sectors, intensifies competition among industry players. This strategic imperative is pushing companies to pour substantial resources into securing their standing in these vital markets, resulting in fierce competition for crucial customer contracts.
BE Semiconductor Industries (BESI) faces a highly competitive landscape. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor equipment market was projected to reach approximately $100 billion, with advanced packaging equipment being a significant growth driver. Companies like Applied Materials and ASML are major rivals, also vying for dominance in these high-growth segments.
- Market Share Focus: Companies are prioritizing market share gains in advanced packaging and AI, recognizing their future revenue potential.
- Investment in Growth: Significant capital is being deployed to enhance capabilities and secure positions in these critical, rapidly expanding areas.
- Aggressive Customer Acquisition: The competition for key semiconductor manufacturers' business is intense, leading to aggressive sales and technological strategies.
Competitive rivalry within the semiconductor equipment sector, particularly for BE Semiconductor Industries (BESI), is intense due to a limited number of major global players and the rapid pace of technological advancement. Companies like Lam Research, Applied Materials, and Tokyo Electron are significant competitors, often with broader product portfolios and substantial R&D budgets. This rivalry is amplified in high-growth areas such as advanced packaging, critical for AI technologies, where market share is fiercely contested.
The market's strong growth trajectory, with global sales expected to reach record highs in 2025 and 2026, fuels this competition. In 2024, the semiconductor equipment market was projected around $100 billion, with advanced packaging a key driver. BESI differentiates itself by focusing on specialized, high-margin solutions like hybrid bonding, essential for AI chips, which helps mitigate direct competition from more commoditized offerings.
High exit barriers, including specialized machinery and significant R&D commitments, mean companies remain active even during downturns, intensifying competition. For example, BESI's capital-intensive environment necessitates continued operation to avoid substantial losses on specific assets, leading to aggressive strategies to secure market share and revenue streams.
The drive for market share in advanced packaging and AI sectors is a primary catalyst for aggressive competition. Companies are investing heavily to enhance capabilities and secure crucial customer contracts, recognizing the future revenue potential in these vital, rapidly expanding areas.
| Competitor | Key Market Segments | 2023 Revenue (Approx. USD Billions) | 2024 Market Projection (Approx. USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lam Research | Wafer fabrication equipment, etching, deposition | 14.0 | 15.0 - 16.0 |
| Applied Materials | Semiconductor manufacturing equipment, display, and related services | 26.5 | 27.0 - 28.0 |
| Tokyo Electron | Semiconductor production equipment, flat panel display production equipment | 14.0 | 14.5 - 15.5 |
| ASML | Lithography systems | 31.4 | 32.0 - 33.0 |
| KLA Corporation | Process control and yield management solutions | 10.0 | 10.5 - 11.5 |
| BE Semiconductor Industries (BESI) | Assembly and packaging equipment | 3.0 | 3.2 - 3.5 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) primarily stems from alternative semiconductor assembly technologies that could reduce the demand for its current equipment. Emerging methods that achieve similar or better outcomes through different processes pose a significant risk. For instance, advancements in wafer-level packaging or advanced substrate technologies might bypass traditional assembly steps where Besi's solutions are critical.
Large semiconductor manufacturers, while not directly replacing specialized equipment, may bolster their in-house assembly capabilities for specific processes. This strategic move can lessen their dependence on external equipment suppliers like BE Semiconductor Industries, especially for simpler, standardized tasks. For instance, in 2024, major foundries continued to invest in advanced packaging technologies, potentially bringing some assembly steps in-house.
A significant shift in semiconductor chip architectures could present a considerable threat to BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi). If future chip designs fundamentally alter assembly processes, requiring entirely new equipment or rendering current packaging steps obsolete, Besi's existing product lines could see a decline in demand. For instance, the rise of advanced packaging techniques like chiplets, which integrate multiple smaller dies, might reduce the reliance on traditional monolithic chip assembly methods that Besi currently serves.
Software-based Solutions Reducing Hardware Needs
The growing power of software and design tools presents a threat by potentially reducing the reliance on new hardware. These advancements can optimize current equipment or even eliminate certain physical assembly tasks, acting as a substitute for outright equipment upgrades. For instance, sophisticated simulation software can reduce the need for physical prototyping, a cost that might otherwise necessitate new machinery.
However, for critical, high-precision physical assembly, especially in advanced semiconductor packaging, dedicated hardware remains essential and difficult to substitute. While software can enhance efficiency, it cannot replicate the fundamental physical processes required for certain intricate manufacturing steps. BE Semiconductor Industries' focus on advanced packaging solutions means that while software improvements are valuable, the core need for specialized assembly hardware is unlikely to disappear entirely.
- Software advancements can optimize existing hardware, potentially reducing the need for new equipment purchases by streamlining processes.
- Sophisticated design and simulation software can substitute for physical prototyping, lowering the capital expenditure on machinery.
- Despite software's growing capabilities, high-precision physical assembly in semiconductor manufacturing still fundamentally requires specialized hardware.
- BE Semiconductor Industries' core business in advanced packaging means hardware remains indispensable for critical physical assembly steps.
Outsourcing to OSATs with Different Equipment
The threat of substitutes for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) is amplified by the growing trend of semiconductor companies outsourcing assembly and test (OSAT) functions. If these OSAT providers begin utilizing equipment from Besi's rivals or adopt less capital-intensive alternative methods, it could directly reduce the demand for Besi's specialized tools from chip manufacturers. This shift represents a significant substitute, as manufacturers might opt for OSAT partners who have already integrated these alternative technologies, bypassing the need to invest in Besi's equipment themselves.
For instance, the global OSAT market was valued at approximately $35 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily. A substantial portion of this growth could be driven by OSATs investing in a wider array of equipment, potentially including those from Besi's competitors. This diversification by OSATs means chipmakers have more choices for their outsourced needs, weakening the exclusive reliance on Besi's offerings.
- OSAT Market Growth: The OSAT sector is a significant market, with projections indicating continued expansion, creating opportunities for alternative equipment suppliers.
- Technological Adoption: OSATs' willingness to adopt equipment from Besi's competitors or alternative, less capital-intensive technologies poses a direct substitution threat.
- Manufacturer Choices: Increased diversity in OSAT equipment offerings provides chip manufacturers with more options, potentially reducing their direct investment in Besi's solutions.
The threat of substitutes for BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) is primarily linked to alternative semiconductor assembly technologies and shifts in manufacturing strategies. Emerging methods in wafer-level packaging and advanced substrate technologies can bypass traditional assembly steps, potentially reducing demand for Besi's equipment. For example, advancements in chiplet architectures, which integrate multiple smaller dies, might lessen reliance on monolithic chip assembly methods that Besi currently serves.
Furthermore, the increasing capability of software and design tools can act as a substitute by optimizing existing hardware or even eliminating certain physical assembly tasks. While sophisticated simulation software can reduce the need for physical prototyping, thereby lowering capital expenditure on machinery, it's crucial to note that high-precision physical assembly in advanced semiconductor packaging still fundamentally requires specialized hardware, a core area for Besi.
The growing trend of semiconductor companies outsourcing assembly and test (OSAT) functions also presents a substitution risk. If OSAT providers adopt equipment from Besi's rivals or less capital-intensive alternative methods, it could directly reduce demand for Besi's specialized tools from chip manufacturers. The global OSAT market, valued at approximately $35 billion in 2023, is expected to grow, and OSATs' diversification in equipment choices could weaken direct investment in Besi's solutions.
| Threat Type | Description | Impact on Besi | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
| Alternative Assembly Technologies | Wafer-level packaging, advanced substrate technologies, chiplet integration | Reduces demand for traditional assembly equipment | Continued investment in advanced packaging by foundries |
| Software & Design Tools | Process optimization, virtual prototyping | Decreases need for new physical machinery, reduces capital expenditure | Increased use of simulation software for prototyping |
| OSAT Outsourcing | OSATs adopting competitor equipment or alternative methods | Weakens direct demand from chip manufacturers for Besi's solutions | OSAT market growth projected, increasing equipment diversity |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor assembly equipment sector, especially for cutting-edge solutions, necessitates significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in research and development to create advanced technologies, building state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and acquiring highly specialized machinery. For instance, developing next-generation packaging equipment can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
These elevated financial hurdles act as a formidable deterrent for potential new players. Establishing a competitive presence requires not only vast financial resources but also the ability to sustain prolonged periods of investment before achieving profitability. This makes it exceptionally challenging for smaller firms or those without deep pockets to enter the market and compete effectively against established giants.
Besi's commitment to advanced technologies, such as hybrid bonding and sophisticated packaging solutions for AI, creates a significant barrier for potential new entrants. This focus necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in research and development, demanding a deep well of technological expertise that is difficult and costly to replicate.
New companies entering this specialized semiconductor equipment market would face a considerable challenge in bridging the knowledge and innovation gap. For instance, Besi's reported R&D expenses for the full year 2023 reached €176.7 million, highlighting the scale of investment required to maintain a competitive edge in these cutting-edge fields.
Established players like BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi) possess a robust portfolio of intellectual property and patents covering their advanced assembly processes and specialized equipment. This strong IP protection acts as a significant barrier to entry.
Newcomers would struggle to innovate and develop competing technologies without potentially infringing on Besi's existing patents, which are crucial for their high-precision semiconductor packaging solutions.
Customer Relationships and Brand Loyalty
Besi Industries thrives on deeply entrenched customer relationships with the world's leading semiconductor manufacturers and foundries. These partnerships are built over years, requiring a demonstrated history of reliability, exceptional service, and consistent performance. For instance, Besi's ability to secure multi-year contracts with major players in the advanced packaging segment underscores the strength of these bonds.
The high switching costs associated with integrating new equipment and qualifying processes in semiconductor manufacturing act as a significant barrier. New entrants would face immense challenges in replicating Besi's established trust and proven track record. In 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see substantial investment in advanced packaging technologies, a core area for Besi, highlighting the critical nature of these long-term customer commitments.
- Long-standing partnerships with top-tier semiconductor firms.
- High switching costs for customers due to process integration.
- Proven track record and reliability are essential for gaining trust.
- Difficulty for new entrants to replicate Besi's established customer base.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players in the semiconductor equipment manufacturing industry, like BE Semiconductor Industries, benefit significantly from established economies of scale. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit production costs through bulk purchasing of raw materials and optimized manufacturing processes. For instance, in 2024, major players continued to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing facilities, further solidifying their cost advantages.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. They would need to make massive upfront investments to reach comparable production volumes, making it difficult to compete on price initially. This is particularly true for R&D, where significant ongoing expenditure is required to keep pace with technological advancements.
- Economies of Scale: BE Semiconductor Industries and its competitors leverage large-scale production to reduce costs per unit.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated knowledge and process improvements over time lead to greater efficiency and lower costs for established firms.
- High Initial Investment: New entrants require substantial capital to build manufacturing capacity and R&D capabilities, hindering their ability to achieve cost parity.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: The cost advantage of incumbents puts pressure on new companies to offer competitive pricing, impacting their profitability.
The threat of new entrants in the semiconductor assembly equipment market, particularly for advanced solutions like those offered by BE Semiconductor Industries (Besi), is relatively low. The significant capital required for R&D, state-of-the-art manufacturing, and specialized machinery, easily running into tens of millions for next-generation equipment, creates a substantial financial barrier. For example, Besi's 2023 R&D expenditure was €176.7 million, illustrating the scale of investment needed to compete.
Furthermore, established players benefit from strong intellectual property portfolios and deeply entrenched customer relationships, built on years of reliability and proven performance. Besi's multi-year contracts with leading semiconductor manufacturers highlight the difficulty for newcomers to replicate this trust and the high switching costs involved for customers integrating new equipment.
Economies of scale also play a crucial role, allowing incumbents to achieve lower per-unit production costs. New entrants would need massive upfront investments to match these efficiencies and competitive pricing, making it challenging to gain market share. The ongoing heavy investment in advanced manufacturing facilities by major players in 2024 further solidifies these cost advantages.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to Besi |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Very High (R&D, manufacturing, machinery) | Besi has established infrastructure and R&D capabilities. |
| Intellectual Property | Challenging to replicate/innovate without infringement | Besi holds strong patents for advanced processes. |
| Customer Relationships & Switching Costs | Difficult to build trust and overcome integration hurdles | Besi has long-standing partnerships and high customer loyalty. |
| Economies of Scale | Requires massive investment to achieve cost parity | Besi benefits from cost efficiencies due to scale. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our BE Semiconductor Industries Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of credible data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and Yole Développement. We also incorporate data from financial news outlets and competitor disclosures to provide a comprehensive view of the semiconductor equipment market.
